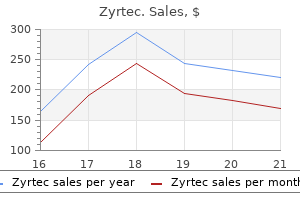
Zyrtec dosages: 10 mg, 5 mg
Zyrtec packs: 30 pills, 60 pills, 90 pills, 120 pills, 180 pills, 270 pills, 360 pills

Zyrtec 5 mg discount online
A neuropathy can produce denervation atrophy with small angular fibers allergy testing san francisco 10 mg zyrtec buy with mastercard, teams of atrophic fibers allergy hacks trusted zyrtec 5 mg, and, on account of reinnervation, teams of fibers of the identical histochemical sort and goal fibers. Typical myopathic abnormalities embody central nuclei, each small and enormous hypertrophic round fibers, cut up fibers, and degenerating and regenerating fibers. Inflammatory myopathies produce mononuclear inflammatory cells within the endomysial and perimysial connective tissue between fibers and infrequently round blood vessels. The atrophy of fibers situated on the periphery of a muscle fascicle, perifascicular atrophy, is a typical discovering in a specific inflammatory myopathy, dermatomyositis. Any long-standing continual myopathy can produce a rise in connective tissue and fat. The enzymatic stains can reveal a nonspecific type 1 fiber predominance in a selection of myopathies. Western blot determinations from muscle tissue could be performed for sure muscle proteins. Currently, this evaluation is often limited to the dystrophin assays in potential dystrophinopathies when the light microscopic immune stains and the molecular genetic studies are inconclusive in establishing Duchenne or Becker dystrophy. More recently, Western blot can measure the quantity of protein in dysferlinopathies and calpain-3 defects. Molecular Genetic Studies Specific molecular genetic defects are identified for an increasing variety of myopathies. These can be found, for instance, in Duchenne and Becker dystrophy, dysferlinopathies, sarcoglycanopathies, caveolin-3, and glycosylation defects, etc. Other blood checks which are important particularly in muscle cramps embrace electrolyte determinations for potassium (particularly for periodic paralysis), sodium, calcium, phosphate, and, hardly ever, magnesium. Endocrine myopathies are normally evaluated by way of blood assays for establishing thyroid illness and in rare instances parathyroid, or adrenal gland dysfunction. Forearm testing is normal in all issues of fat metabolism and mitochondrial and likewise in some glycolytic problems with fastened muscle weak spot similar to acid maltase deficiency. Muscle imaging has been of curiosity as a analysis method in unusual myopathies to present information relating to the extent of distribution and progression of the illness. In addition, magnetic resonance spectroscopy is a helpful analysis tool in the examine of varied metabolic myopathies. Ptosis Further Reading Carpenter S and Karpati G (2001) Pathology of Skeletal Muscle, 2nd edn. This must be suspected if the urine checks are constructive for blood, however no red blood cells are seen. Imaging and spectroscopy research Techniques to picture muscle embody computed tomography, magnetic resonance imaging, and ultrasound. A variety of drugs and abused substances trigger myopathy, a disturbance in muscle structure, function, or each. Therefore, all sufferers with myopathy symptoms ought to have their drug listing rigorously scrutinized, and they need to be requested about potential exposures to illicit medicine and alcohol. Myopathies sometimes produce shoulder and hip girdle weakness in conjunction with preserved deep tendon reflexes (at least early in the course) and normal sensation. Peripheral neuropathies tend to involve distal muscular tissues predominantly and usually lead to loss of tendon reflexes early at the aspect of sensory disturbance or loss. Toxic myopathies can develop acutely over hours or days, subacutely over weeks, or chronically over months or years. Acute myopathies tend to produce symmetrical and proximal predominant or generalized limb weakness. If enough muscle cell (myocyte) breakdown happens, muscle products, including the oxygen-carrying myoglobin, spill into the urine, producing myoglobinuria. Also, if severe, myoglobin and other products injury the kidneys and will precipitate renal failure. Electrolyte imbalances including low phosphate (hypophosphatemia), excessive potassium (hyperkalemia), and low calcium (hypocalcemia) may occur. The subacute to chronic myopathies tend to produce more insidious proximal limb and neck weakness with or without related pain. Acute Myopathies Rhabdomyolysis Rhabdomyolysis might occur from the toxic illicit medication and pharmacological agents listed in Table 1. Significant hypokalemia (low potassium) from numerous medical conditions and drugs, such as diuretics, laxatives, the antifungal agent amphotericin, and natural substances, similar to continual licorice ingestion (glycyrrhizic acid), and ingestion of uncooked cottonseed oil (gossypol) can cause rhabdomyolysis. Ingestion of the edible mushroom Tricholoma equestre is related to rhabdomyolysis and cardiomyopathy. Usually, the mechanism of rhabdomyolysis is unsure, however finally myocyte damage seems to happen from an increase in free sarcoplasmic or mitochondrial calcium and activation of proteolytic enzymes. Treatment contains intravenous fluids and urine alkalinization so as to prevent renal failure. The complication tends to happen after months of remedy but sometimes after just a few weeks of therapy. The mitosis blockers can also have an result on cardiac muscle, and amiodarone can have an effect on the optic nerve. Colchicine neuromyopathy tends to affect patients with kidney insufficiency and patients receiving cyclosporine and lipid-lowering brokers. This agent is intended for intermittent use in gout assaults and toxicity may arise if used frequently for an extended interval. Statin and Cholesterol-Lowering Agent Myopathies Most cholesterol-lowering agents may cause a subacute to continual, typically painful, myopathy and generally overt rhabdomyolysis. Simple muscle aches (myalgia) is comparatively widespread but the exact incidence is unknown. More severe toxicity such as extreme rhabdomyolysis is very uncommon however properly described and doubtlessly fatal. More generally used brokers, corresponding to simvastatin, lovastatin, and pravastatin had been intermediate and of comparable threat. Patients have issue weaning from mechanical air flow (diaphragm weakness), generalized limb weakness, or each. Electrophysiological research normally show regular sensory responses and sometimes low-amplitude motor responses and evidence of lowered muscle fiber excitability. Histological findings vary from atrophy of kind 2 greater than type 1 muscle fibers to muscle necrosis, but the commonest feature is the lack of myosin thick filaments. Even the supplement purple yeast rice, generally used in lipid disorders to avoid prescription medicines, is related to muscle toxicity, myalgia, and infrequently rhabdomyolysis. This unregulated meals, as properly as some others, contains the fungus Monascus purpureus (Monacolin K, the same lively ingredient as lovastatin). Statins can unmask or probably set off another beforehand asymptomatic neuromuscular illness, such as autoimmune myositis, including polymyositis and dermatomyositis. Statins have additionally been linked to an entity termed necrotizing autoimmune myopathy. Patients with this situation produce antibodies directed against the same enzyme targeted by statins, 3-hydroxy3-methylglutaryl coenzyme A reductase.
Buy 10 mg zyrtec with amex
Tumors could show a spectrum of differentiation from (A) primitive small round cells and polyhedral tumor cells with enlarged allergy dog food discount zyrtec 10 mg on line, hyperchromatic nuclei and deeply eosinophilic cytoplasm to (B) differentiated strap cells with clearly seen cross-striations allergy medicine you can take while breastfeeding zyrtec 10 mg buy with amex. Tumors are composed of primitive small round cells, that are arranged in discohesive nests inside a fibrous stroma. Macroscopically, leiomyosarcomas are probably to be properly circumscribed however are larger and softer than leiomyomas and often exhibit necrosis, hemorrhage and cystic degeneration. Well-differentiated tumor cells have elongated nuclei and eosinophilic cytoplasm; poorly differentiated ones present marked elevated cellularity and extreme cytologic atypia. Leiomyosarcoma is differentiated from leiomyoma mainly by cellularity, atypia, mitotic activity and necrosis, which also indicates the prognosis. Most leiomyosarcomas ultimately metastasize, though dissemination might happen as late as 15 or extra years after resection of the primary tumor. Leiomyosarcomas have advanced chromosomal rearrangements and numerous somatic mutations, but no attribute alterations have been documented. Their histologic look is variable and all show a degree of mitotic exercise and numerous intralesional T lymphocytes. By contrast, angiosarcomas account for less than 1% of all sarcomas and are more frequent in older adults. The tumor consists of spindle cells with elongated, hyperchromatic nuclei; a variable diploma of pleomorphism; and frequent mitoses. Synovial sarcomas could also be monophasic (B), composed of swirling fascicles of plump spindle cells with monomorphic, hyperchromatic nuclei, or biphasic (C), displaying each spindle cell mesenchymal differentiation and epithelial differentiation within the type of irregular glands containing eosinophilic proteinaceous materials. The tumors tend to be surrounded by a glistening pseudocapsule and in lots of instances are cystic. They vary from small nodules to masses of 15 cm or more in diameter, the common being 3�5 cm. Microscopically, synovial sarcoma is classically described as having a biphasic pattern. Fluid-filled glandular areas lined by epithelium-like tumor cells are embedded in a sarcomatous, spindle cell background. These components differ in proportion, distribution and cellular differentiation, with the spindle cells often significantly more quite a few than the glandular parts. If the epithelial component is missing, the tumor is referred to as monophasic synovial sarcoma. Although monophasic synovial sarcoma resembles fibrosarcoma, its atypical spindle cells are plumper and swirled with a "college of fish" look, somewhat than being arranged in a herringbone pattern. Synovial sarcoma normally expresses cytokeratin or epithelial membrane antigen, additional evidence of epithelial differentiation. The recurrence fee of synovial sarcoma is excessive, and metastases happen in over 60% of cases. The 5-year survival rate is 50%, and individuals who die normally have in depth lung metastases. They might arise anywhere within the physique however are commonly located in deep delicate tissues close to joints, tendon sheaths or joint capsules. Synovial sarcomas happen principally in young adults and usually current as a painful mass in the extremity. Despite the name, synovial sarcomas neither arise from synovial tissues nor show synoviocyte differentiation. The periphery of the myotube quickly accumulates myofibrils, containing myosin and actin, which turn into arrayed within the cross-banded pattern attribute of striated muscle. Before innervation, the sarcolemma of the myotube contains diffusely distributed nicotinic receptors for acetylcholine on its surface membrane. Upon innervation, these receptors turn out to be highly concentrated at the motor endplate. An individual muscle fiber is innervated by solely a single nerve ending, but each motor neuron innervates many muscle fibers. After innervation, the myofiber nuclei transfer from the center to arrange themselves in a regular sample beneath the sarcolemma. Mature skeletal muscle cells are syncytia (multiple nuclei inside a single cytoplasm) and may be several centimeters in length. Muscle fibers answerable for motion are extrafusal fibers, while these in stretch receptors (muscle spindle organs. In most main myopathies, the damage affects extrafusal fibers but not intrafusal fibers. Cross-striations of striated muscle are created by the arrangement of the myofilaments of the myofibril (compare to . The darkish A band outcomes from the thick myosin filaments and the thinner, partially overlapping actin filaments. In the center of the H band, the center of each myosin filament thickens, forming intermolecular bridging with the adjacent myosin filament and giving rise to the M line. With contraction, the myosin filaments pull the actin filaments, inflicting the H zone to disappear, the I band to shrink and the A band to stay the identical. The endoplasmic reticulum (sarcoplasmic reticulum) types an extensive, complex tubular community with periodic dilations (cisternae) around every myofibril. The cisternae are intently apposed to the transverse tubules, that are derived from the cell membrane (sarcolemma) and form a transverse community, which resembles rooster wire, round each myofibril, giving extensive communication between the inner and external environments. Thus, muscle spindle organs, that are usually inconspicuous in routine histologic preparations, turn into comparatively extra outstanding as extrafusal fibers disappear. Actin filaments overlap myosin filaments to a variable extent, depending on the diploma of muscle contraction. The skinny filaments kind a hexagonal array round each thick filament (best seen in cross-section). M line: Zone of intermolecular bridging and thickening of myosin filaments on the midline of the A band, which forms a skinny, slightly darker electron-dense band. The sliding actin filaments advance farther into the A band, decreasing sarcomere length. As a outcome, the I band and H zone shorten, whereas the A band remains almost constant. There are many filamentous proteins that make up the sarcomeres, and multiple proteins that anchor sarcomeres to the sarcolemma. These proteins may be mutated or abnormally regulated in muscular dystrophies (see below). The sarcoplasmic reticulum surrounds each myofibril and varieties an elaborate membranous network with irregular dilations (cisternae) juxtaposed to a transverse tubular community derived from the sarcolemma. The transverse tubular system (T-tubule system) is arranged across the fiber like rooster wire, each ring wrapping around a person myofibril. This association permits an electrical stimulus to proceed alongside the muscle fiber floor and turn out to be diffusely and quickly internalized through the transverse tubular system. The electrical signal is translated into a chemical signal between the transverse tubule and the cisternae of the sarcoplasmic reticulum. This process releases calcium from the sarcoplasmic reticulum into the neighborhood of myofibrils, triggering muscle contraction.
Buy zyrtec 10 mg low price
These agents result in allergy testing queens ny purchase 5 mg zyrtec with amex hyperplasia of foveolar cells quinolone allergy symptoms buy 5 mg zyrtec with mastercard, leading to loss of the normal almost flat surface. Additional changes could embody reactive hyperplasia of foveolar cells and proliferation of lamina propria clean muscle. Inflammation is infrequent except there has been an ulcer or erosion with a subsequent localized inflammatory response. There is a dense infiltrate of T lymphocytes (arrows) in the surface, and here extending into the rest of the gland. The corkscrew contour of the antral glands deviates from normal architecture in this patient with bile reflux. Gastric ulcers normally afflict the middle-aged and aged and affect both sexes equally. Racial variations have been postulated, but most information recommend that each one ethnic teams are vulnerable in an urban Western setting. Surveys within the United States and Great Britain present a pattern toward an inverse relation between duodenal ulcers and socioeconomic standing and training. Since acid production is blocked, antral G cells visibly multiply in compensation and produce excess gastrin. Iron sulfate tablets might trigger surface encrustation by the mineral and its congeners. Cytokines produced by inflammatory cells in response to the an infection stimulate gastrin release and suppress somatostatin secretion. These effects, plus launch of histamine metabolites from the organism itself, may stimulate basal gastric acid secretion. In addition, luminal cytokines from the stomach might enter and injure duodenal epithelium. Such an effect may improve acid load within the duodenum, contributing to duodenal ulceration. Acidification of the duodenal bulb leads to islands of metaplastic gastric mucosa within the duodenum in many sufferers with peptic ulcers. Peptic ulceration might occur as far proximally as the esophagus and as far distally as the Meckel diverticulum with gastric heterotopia, however the illness principally affects the distal abdomen and proximal duodenum. Many clinical and epidemiologic options distinguish gastric from duodenal ulcers; the common factors that unite them are gastric hydrochloric acid secretion and H. Duodenal ulcers occur 30% extra typically in folks with sort O blood than in those with different types. Pepsinogen I is secreted by gastric chief and mucous neck cells and appears in gastric juice, blood and urine. Serum levels of this proenzyme correlate with the capability for gastric acid secretion and replicate parietal cell mass. Someone with high blood pepsinogen I ranges has 5 instances the normal risk of growing a duodenal ulcer. Hyperpepsinogenemia has been attributed to autosomal dominant inheritance and may mirror an inherited tendency to increased parietal cell mass. Half of children of ulcer patients with hyperpepsinogenemia have hyperpepsinogenemia themselves. Many such sufferers have regular pepsinogen I ranges and still present familial aggregation. Family clustering of duodenal ulcers and speedy gastric emptying have been noted, as has familial hyperfunction of antral G cells. Possible mechanisms in the pathogenesis of duodenal ulcer disease associated with Helicobacter pylori infection. The gastric and duodenal factors which were implicated as possible mechanisms within the pathogenesis of duodenal ulcers are summarized in. Gastric secretion of pepsin, which may also play a task in peptic ulceration, parallels that of hydrochloric acid. Other nonsteroidal antiinflammatory brokers and analgesics have been incriminated in peptic ulcerogenesis. Prolonged therapy with high doses of corticosteroids may also enhance the risk of peptic ulceration barely. Patients with duodenal ulcers may have up to double the normal parietal cell mass and maximal acid secretion. Increased chief cell mass often accompanies elevated parietal cells, reflecting the prevalence of hyperpepsinogenemia in patients with ulcers. Acid secretion in individuals with duodenal ulcers may be more sensitive than normal to gastric secretagogues such as gastrin, possibly owing to increased vagal tone or increased affinity of parietal cells for gastrin. Duodenal bulb acidification usually inhibits further gastric emptying, however not in most people with duodenal ulcers. In them, duodenal acidification results in continued, somewhat than delayed, gastric emptying. In ulcer patients, duodenal pH after a meal decreases to a decrease degree and stays depressed longer than in normal folks. Such duodenal hyperacidity actually displays the gastric elements mentioned above. The function of neutralizing components, particularly bicarbonate secretion by the duodenal mucosa or by the pancreas in response to secretin, is uncertain. Factors corresponding to prostaglandins could or could not shield the duodenum as they do the gastric mucosa (see above). Most patients with gastric ulcers secrete much less acid than do those with duodenal ulcers and even less than regular individuals. Factors implicated include (1) back-diffusion of acid into the mucosa, (2) decreased parietal cell mass and (3) abnormalities of parietal cells themselves. Their ulcers are often near the pylorus and are considered variants of duodenal ulcers. Interestingly, intense gastric hypersecretion such as happens in the Zollinger-Ellison syndrome (see below) is associated with severe ulceration of the duodenum and even the jejunum, but not often of the stomach. The concurrence of gastric ulcers and gastric hyposecretion implies that (1) the gastric mucosa might in some way be significantly sensitive to low concentrations of acid; (2) something other than acid could harm the mucosa. Bile reflux (particularly deoxycholic acid and lysolecithin) and pancreatic secretions may contribute to the development of gastric ulcers. End-stage renal illness with hemodialysis increases the risk of peptic ulceration. Patients with kidney transplants have a much higher incidence of peptic ulceration and its problems, similar to bleeding and perforation. There is an elevated frequency of peptic ulcers in folks with multiple endocrine neoplasia kind 1 (see Chapter 27).
Buy cheap zyrtec 10 mg online
Large confluent sheets of paraimmunoblasts or different large lymphoid cells might symbolize transformation to diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (see below) allergy testing for dogs zyrtec 10 mg discount amex. Bone marrow involvement ranges from full effacement of the marrow space to patchy interstitial or nonparatrabecular infiltrate of various degree allergy testing for bees order zyrtec 10 mg with visa. A smear of peripheral blood reveals numerous small to medium-sized lymphocytes with clumped nuclear chromatin. On microscopic examination, the nodal structure is changed by a diffuse proliferation of small lymphocytes admixed with a low number of bigger cells generally known as paraimmunoblasts (arrows) present in scattered proliferation facilities. Often the primary hint of the illness is an irregular complete blood rely displaying absolute lymphocytosis. Flow cytometry of the peripheral blood is enough to establish the diagnosis generally. The different peripheral counts may be normal or abnormal, and findings such as platelet rely and hemoglobin stage are used to stage the illness. Erythrocyte and platelet counts are initially normal, however because the disease advances, extreme anemia, thrombocytopenia and even neutropenia can develop. A optimistic Coombs check occurs in the course of the course of illness in up to 20% of sufferers and may be associated with immune-mediated hemolytic anemia. A small monoclonal paraprotein could additionally be current in some sufferers, most of which are of the IgM heavy-chain sort (in distinction to sufferers with multiple myeloma, who most often have IgG paraproteinemias). Hypogammaglobulinemia happens in 50%�75% of circumstances in some unspecified time within the future during the disease; the degree of hypogammaglobulinemia generally correlates with illness stage and is responsible for infectious problems. The T cells, although elevated in number, usually show impaired delayedtype hypersensitivity reactivity, which may contribute to the increased threat of an infection. For instance, sufferers with low illness burden can survive over 10 years, while others with extensive illness or poor prognostic features show fast development and may not survive more than 2 or 3 years. Transformation to prolymphocytic leukemia happens in 15%�30% of cases and is the most common form of progression. This sort of transformation is heralded by worsening cytopenias, increasing splenomegaly and progressive increases in prolymphocytes in the blood or paraimmunoblasts in lymph nodes or other tissues. Transformation to diffuse large B-cell lymphoma, Richter syndrome, occurs in 10% of circumstances. This form of progression is marked by the looks of a quickly enlarging mass, worsening of systemic symptoms and a high lactate dehydrogenase level in the serum. Other uncommon types of transformation also occur, including a Hodgkin lymphoma or Hodgkin-like transformation, the latter occurring more regularly in patients handled with certain chemotherapeutic medication. Most patients who endure prolymphocytic or Richter transformation survive lower than 1 12 months. The neoplastic cells are heterogeneous, with a combination of small and huge cleaved cells and centroblasts. This largely displays the histologic grade, which is dependent upon the number of centroblasts in the neoplastic follicles. It solely not often happens in individuals underneath age 20, and is extra common in girls than men. It places expression of the antiapoptotic protein, Bcl-2, beneath control of the IgH promoter, and results in Bcl-2 overexpression. Bcl-2 protein is an inhibitor of apoptosis and provides a survival advantage to the lymphoma cells. The neoplastic follicles are current in high density, and are often in a back-to-back association with little intervening paracortex. The neoplastic follicle facilities (germinal centers) include a mixture of small and enormous cells with irregular nuclear contours (centrocytes/cleaved cells) and scattered centroblasts, which have spherical nuclear contours and multiple nucleoli connected to the nuclear membrane. Malignant lymphoid follicle germinal centers could be distinguished from normal/reactive germinal facilities utilizing immunohistochemistry for Bcl-2. Circulating follicular lymphoma cells are current within the blood in 10% of cases; they show distinguished nuclear irregularity and deep nuclear clefts. Extranodal displays are comparatively uncommon, compared to other B-cell lymphomas. The lymphadenopathy is painless and may have followed a waxing and waning course before the patient seeks medical attention. As discussed above, the scientific course is linked to histologic grade, and progression/transformation to more aggressive illness might happen in 50% of cases. The neoplastic follicles are composed of predominantly small cleaved cells (centrocytes) and only some scattered centroblasts are present. The neoplastic follicle reveals a mix of small and enormous cleaved cells and centroblasts characterised by multiple nucleoli (arrows). The neoplastic follicle reveals a predominance of centroblasts with solely uncommon admixed centrocytes. The persistence of a follicular pattern helps distinguish this entity from diffuse massive B-cell lymphoma. Cyclin D1 drives cell cycle development on the G1-to-S-phase transition, by binding to Cdk4/6. This event results in phosphorylation of retinoblastoma (Rb) and subsequent activation of transcription factors promoting cell cycle progression from the G1 to S section (see Chapter 5). Unlike many different small B-cell lymphomas, giant reworked cells and/or centroblasts are absent or uncommon. The presence of scattered epithelioid histiocytes and hyalinized small blood vessels completes the image of typical circumstances. There are 2 major variants: one with a extra nodularappearing pattern the place the lymphoma cells encompass the germinal facilities (mantle zone pattern) and one other the place the cells are larger and resemble lymphoblasts (blastic/blastoid variant). The mantle zone pattern is thought to behave much less aggressively than the standard sort, whereas the blastic/blastoid variant is more aggressive. Multifocal mucosal involvement of the intestine (mostly small gut and colon) might produce a pattern often known as lymphomatous polyposis. At nearer examination, the population of lymphocytes consists of monotonous, small cells with irregular nuclei. Marginal Zone Lymphomas the marginal zone lymphomas are a heterogeneous group of mature B-cell tumors that arise in lymph nodes, spleen and extranodal tissues. The lymphoma cells are thought to arise from the marginal zone of the lymphoid follicle, which incorporates memory B cells which have gone via the germinal center response (postgerminal center). Regardless of the first site of involvement, all marginal zone lymphomas share similar morphologic and immunophenotypic features. The malignant B cells are heterogeneous and embrace various proportions of small angulated lymphocytes, mediumsized monocytoid lymphocytes with ample cytoplasm, plasmacytoid lymphocytes and even admixed clonal plasma cells. The tumor cells invade glandular epithelium or epithelia of mucosal surfaces, resulting in lymphoepithelial lesions. Common cytogenetic abnormalities are listed in Table 26-19 and, together with clonal IgH gene rearrangements, might assist to set up the diagnosis if gastric infiltrates are subtle. There is a slight female predominance partially because they may happen at sites of autoimmune diseases.
Discount zyrtec 5 mg free shipping
Lymphocytes in tonsils and Peyer patches arrive in those sites by migration via the tall endothelial cells of vessels allergy treatment for foods zyrtec 10 mg generic on-line, that are corresponding to jalapeno allergy treatment zyrtec 10 mg visa the postcapillary venules in lymph nodes. B cells bear activation, transformation and choice in the lymph nodes and spleen. All lymphocyte growth entails a tightly controlled sequence of gene expression and silencing that leads to sequential gain and loss of nuclear material and modifications cytoplasmic and/or surface antigen expression. Patterns of antigenic expression identify the lineage and maturation stage of normal and neoplastic lymphoid cells (see beneath and Chapter 4). Larger nodes are thought of clinically enlarged and may be abnormal microscopically. Sometimes many nodes inside a series or group may be enlarged and/or matted together, usually a characteristic of malignancy. Individual lymph nodes are surrounded by a skinny fibrous capsule with internally radiating trabeculae, which offers structural help. There, they turn out to be Ig-secreting plasma cells, or they exit the lymph nodes as memory B cells. Plasma cells have eccentric nuclei with clumped chromatin marginated on the nuclear membrane, historically described as "clock-face chromatin. Recombination of T-cell receptor genes generates a diverse inhabitants of T cells, every of which may acknowledge a single antigen. Once mature and educated, T cells leave the thymus to lymph nodes, spleen and peripheral blood to become postthymic T cells. The antigens presented to T-helper cells are peptide fragments derived from partial digestion of foreign proteins by macrophages and/or different antigen-presenting cells. The T-helper cells in turn work together with B lymphocytes that express the identical antigenic specificity and induce the latter to proliferate and differentiate into plasma cells. Lymphocytes have numerous morphologies in stained peripheral blood and bone marrow smears, in addition to in tissue sections. Like other blast cells, immature lymphoid cells have excessive nuclear-to-cytoplasmic ratios, fine chromatin and visual nucleoli. Following the lymphoid stem cell and precursor stage in the bone marrow, B cells mature into naive B lymphocytes and home to the secondary lymphoid organs (primarily lymph nodes). The germinal-center response represents an important turntable for immunoglobulin variable-region gene mutations, Ig heavy-chain change and differentiation into plasma cells and reminiscence B cells. B-cell immunoblasts and plasmacytoid immunoblasts reside within the T-cell�rich paracortex and medulla, respectively. While a selection of cell sizes (including many massive reworked or activated cells) are normally present in the secondary lymphoid organs, the lymphocytes that circulate within the blood and those within the bone marrow are mainly small and heterogeneous. In peripheral blood smears, transformed cytotoxic T cells are variant lymphocytes (sometimes called "atypical lymphocytes"). Variant lymphocytes are probably to have plentiful blue-gray cytoplasm and a number of nucleoli in Wright-Giemsa�stained smears. The similar cells in tissue sections stained with hematoxylin and eosin have round to oval nuclei, one to several eosinophilic nucleoli apposed to their nuclear membranes and ample clear to purple cytoplasm. Precise identification and characterization of lymphoid cells requires flow cytometric or immunohistochemical evaluation. The term "variant lymphocytes" covers atypical lymphocytes and huge granular lymphocytes. Bone marrow plasmacytosis greater than 10% is typically related to a plasma cell neoplasm. In each reactive and neoplastic plasma cell proliferations, immunoglobulin may accumulate in the cytoplasm to form outstanding eosinophilic globules, generally identified as Russell bodies. Similarly, benign and neoplastic plasma cells might comprise nuclear pseudoinclusions (Dutcher bodies), which characterize immunoglobulin invaginated into the nucleus and seen in cross-section. Lymphocytopenia Usually Reflects a Decrease in T-Helper Lymphocytes Peripheral blood lymphocytopenia is outlined as a blood lymphocyte rely less than 1500/L in adults or lower than 3000/L in children. An absolute lymphocytosis attributable to a heterogeneous inhabitants of small and bigger lymphoid cells, including atypical lymphocytes, is characteristic of this Ebstein-Barr virus� pushed dysfunction. Lymphocytes in benign lymphocytoses are normally reactive showing and morphologically heterogeneous, however atypical lymphocytes may also be seen. Other much less frequent causes of reactive lymphocytosis include pertussis, persistent bacterial infections such as tuberculosis and brucellosis, stress and cigarette smoking. Persistent absolute lymphocytosis, greater than 4000/L, particularly in adults, raises suspicion for a lymphoproliferative dysfunction and deserves additional analysis. Decreased lymphocyte manufacturing: Several congenital and purchased immunodeficiency syndromes entail lowered era of lymphocytes. Impaired T-cell production additionally occurs with some lymphomas, such as classical Hodgkin lymphoma, notably in advanced levels. Loss of lymphocytes: Disorders associated with damage to intestinal lymphatics can lead to lack of lymph fluid and lymphocytes into the intestine lumen. Such illnesses embody protein-losing enteropathies, Whipple disease and circumstances of increased central venous strain. Immunologic injury to lymphocytes could happen in collagen vascular ailments, similar to systemic lupus erythematosus. Bone Marrow Plasmacytosis May Signify a Plasma Cell Disorder Reactive Lymphoid Hyperplasia Is a Response to Diverse Stimuli, Including Infections, Inflammation and Tumors Lymph nodes might bear hyperplasia of all cellular parts, or any mixture of B cells, T cells and mononuclear phagocytes, in response to a variety of infectious, inflammatory and neoplastic issues. The histology and magnitude of lymph node enlargement in reactive hyperplasia are features of the age of the affected person (children are inclined to show larger immunoreactivity than do adults), the immunologic competence of the host and the inciting stimulus. Acute suppurative and necrotizing lymphadenitis happens in lymph nodes that drain websites of acute bacterial or fungal infections. Such nodes enlarge rapidly due to edema and hyperemia, and are usually tender because the capsule becomes distended. Lymph node sinuses and stroma are infiltrated by neutrophils and variable numbers of bland macrophages. Well- or poorly defined granulomas are common, and necrosis can be focal and Plasma cells in peripheral blood: It is unusual to find plasma cells within the blood. The presence of circulating plasma cells within the blood of an grownup raises suspicion for a plasma cell neoplasm, corresponding to plasma cell myeloma (see below). Reactive bone marrow plasmacytosis: Plasma cells usually account for lower than 3% of hematopoietic cells within the bone marrow. If they make up larger than 3% of bone marrow cells, plasmacytosis is diagnosed, and it might be polyclonal or monoclonal. In youngsters and younger adults, most plasmacytoses are brought on by reactive conditions similar to continual infections or systemic inflammatory problems. The main patterns of reactive hyperplasia are contrasted with the architecture of a standard lymph node. Follicular hyperplasia, with an elevated number of enlarged and irregularly formed follicles, is characteristic of B-cell immunoreactivity. This patten is seen in reactive proliferations of the mononuclear�phagocyte system.
Dipsacus fullonum (Teazle). Zyrtec.
- What is Teazle?
- Arthritis, psoriasis, and small wounds.
- How does Teazle work?
- Are there safety concerns?
- Dosing considerations for Teazle.
Source: http://www.rxlist.com/script/main/art.asp?articlekey=96223
Generic 5 mg zyrtec
Pigment Stones May Be Black or Brown Black Pigment Stones Black pigment stones measure less than 1 cm and are irregular and glassy allergy medicine baby order zyrtec 5 mg without a prescription. Chronic hemolysis allergy medicine generic name zyrtec 5 mg generic overnight delivery, as in hemoglobionopathies, predisposes to growth of black pigment stones. Either as a outcome of it increases hemolysis or because of harm to liver cells, cirrhosis is also associated with a excessive incidence of black stones. Unconjugated bilirubin is insoluble in bile and is normally current in only trace amounts. If increased unconjugated bilirubin is secreted by hepatocytes, it precipitates as calcium bilirubinate, in all probability round a nidus of mucinous glycoproteins. Patients with out identified predisposing elements who develop black pigment stones have elevated concentrations of unconjugated bilirubin within the bile for unknown causes. The rare cases in Western international locations are seen in patients with continual mechanical obstruction to bile flow, as in sclerosing cholangitis, or the presence of a catheter in the widespread bile duct after frequent bile duct surgical procedure. Bacterial -glucuronidase or other hydrolytic enzymes hydrolyze conjugated bilirubin to its unconjugated kind, which favors formation of brown stones. The 15-year cumulative chance that asymptomatic stones will result in biliary ache or different issues is lower than 20%. Most complications of cholelithiasis relate to gallstones obstructing the cystic or common bile ducts. Passage of a stone into the cystic duct typically, however not at all times, causes severe biliary colic and will lead to acute cholecystitis. Repeated bouts of acute cholecystitis give rise to persistent cholecystitis, which can also result from the presence of stones alone. Gallstones entering the common duct (choledocholithiasis) could trigger obstructive jaundice, cholangitis and pancreatitis. Passage of a big gallstone into the small gut may even cause intestinal obstruction, known as gallstone ileus. Gallbladder faraway from a patient with acute cholecystitis demonstrates ulceration of the mucosa (left) and acute and chronic inflammation. The lumen of the dilated gallbladder is crammed with clear mucus and contains cholesterol stones. Rarely, in empyema of the gallbladder, the cystic duct is completely obstructed, allowing micro organism to invade the gallbladder and distending the organ with cloudy, purulent fluid. In the gallbladder wall, edema and hemorrhage are putting, with accompanying acute and persistent inflammation. The mucosa shows focal ulcers or, in severe cases, widespread necrosis (gangrenous cholecystitis). More often, inflammatory adhesions type a pericholecystic abscess and restrict unfold of gallbladder contents after perforation. Erosion of gallbladder contents into a viscus could create a cholecystenteric fistula. It is almost always related to gallstones but may also outcome from repeated attacks of acute cholecystitis. The remaining instances (acalculous cholecystitis) are linked to sepsis, extreme trauma, infection of the gallbladder with Salmonella typhosa and polyarteritis nodosa. Bacterial an infection is often a consequence of biliary obstruction somewhat than a major occasion. Obstruction of the cystic duct by a gallstone might lead to launch of phospholipase by the gallbladder epithelium. The mucous coat of the epithelium is disrupted, exposing mucosal cells to the detergent motion of concentrated bile salts. Mild jaundice, brought on by stones in, or edema of, the frequent bile duct, is seen in 20% of patients. The acute sickness typically subsides inside every week, however persistent pain, fever, leukocytosis and shaking chills herald development of the illness and the necessity for cholecystectomy. As irritation resolves, the gallbladder wall becomes fibrotic and the mucosa heals. The same specimen as in A reveals continual inflammation of the gallbladder and a sinus of Rokitansky-Aschoff extending into the muscularis. The fibrotic wall is chronically inflamed all through and penetrated by Rokitansky-Aschoff sinuses. Long-standing irritation may lead to calcification of the gallbladder wall (porcelain gallbladder). A combined proliferation of smooth muscle and Rokitansky-Aschoff sinuses is an adenomyoma and is adenomyomatus hyperplasia when it diffusely involves the gallbladder. Similar benign tumors may occur within the bile ducts, the place they may obstruct biliary move and cause jaundice and thus come to scientific consideration. The prognosis is best made by ultrasound examination, which exhibits gallstones in a thick, contracted gallbladder. Calcified (porcelain) gallbladders (see above) are particularly susceptible to creating gallbladder cancer. The mucosa exhibits scattered, yellow flecks (strawberry gallbladder), and mucosal folds are swollen with giant, foamy macrophages, in which a small nucleus is displaced to the periphery. It is often desmoplastic, and thus the gallbladder wall turns into thickened and leathery. Anaplastic, big cell and spindle cell varieties, in addition to adenosquamous carcinoma of the gallbladder, have been reported. Metastases happen by way of both lymphatic unfold and direct extension into the liver, contiguous constructions and peritoneum. For sensible purposes, only these patients whose tumors are discovered by the way throughout cholecystectomy are cured. A surgically resected gallbladder has been opened to reveal a thickened wall infiltrated by adenocarcinoma, which also demonstrates exophytic development into the lumen. In Asia, bile duct carcinoma is related to biliary infestation by the fluke C. As in carcinoma of the gallbladder, progress may be endophytic (into the lumen) or diffusely infiltrative. The prognosis is poor, however as symptoms arise early in the disease, the finish result is somewhat higher than for gallbladder carcinoma. Surgical treatment of cancer of the ampulla of Vater provides a 5-year survival fee of about 35%. Carcinomas of the Bile Duct and Ampulla of Vater Present as Obstructive Jaundice Cancer of the extrahepatic bile ducts (extrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma; see above) is almost always adenocarcinoma. It may happen wherever along the duct, together with the purpose the place the proper and left hepatic ducts be a part of to form the widespread hepatic duct (hilar cholangiocarcinoma). These tumors are less widespread than gallbladder most cancers and affect both sexes comparably. The ventral pancreas and the common bile duct migrate posteriorly around the duodenum. The ductal methods of the 2 embryonic pancreatic anlagen merge at 7 weeks, to form a main pancreatic duct (duct of Wirsung).
Zyrtec 5 mg order mastercard
Other threat factors embody benzene publicity allergy forecast brooklyn ny zyrtec 5 mg cheap fast delivery, cigarette smoking and congenital disorders such as Fanconi anemia or Kostmann syndrome allergy migraine zyrtec 5 mg without prescription. Dysplasia is most frequently seen in erythroid precursors, which present megaloblastoid changes, multinucleation, nuclear budding, bridging between nuclei and karyorrhexis. A part of lymph node shows effacement of the traditional structure by sheets of mast cells. Increased numbers of blasts, complex cytogenetic abnormalities, sure specific mutations and elevated cytopenia confer a worse prognosis. Dysplastic megakaryocytes could also be mononuclear or hypolobated or present nuclear separation. If a affected person has isolated deletion of the lengthy arm of chromosome 5 (5q�), macrocytic anemia, megaloblastoid erythropoiesis with or with out ringed sideroblasts and normal or elevated platelets with monolobated megakaryocytes, that affected person is likely to be an aged woman and to have a extra favorable prognosis. By contrast, deletion of chromosome 7 (7q�) has an unfavorable prognosis (Table 26-14). Some cases are attributed to prior radiation, cytotoxic chemotherapy or benzene exposure. Typically, the malignant cells pack the bone marrow and displace normal hematopoietic cells. Myeloblasts are medium-sized to giant cells with spherical or slightly irregular nuclei and immature nuclear chromatin. Some cases present eosinophilic, slender cytoplasmic inclusions, Auer rods, which are coalesced main granules. Auer rods are specific for the myeloid lineage and preclude a prognosis of lymphoblastic leukemia. Smear of a bone marrow aspirate stained with Prussian blue shows an erythroid precursor cell containing iron-laden mitochondria that encircle the nuclei (ringed sideroblast). A bone marrow section is hypercellular, ensuing from effacement of the traditional structure by myeloblasts. Although leukemic myeloblasts divide more slowly than do normal hematopoietic precursor cells, they also endure spontaneous cell demise less usually than regular cells. The expanded pool of irregular leukemic blasts overwhelms the marrow and suppresses normal hematopoiesis. Immunophenotyping by move cytometry establishes the myeloid nature of the tumor cells. Acute erythroid leukemia: Acute erythroid leukemias function prominent erythroid proliferation. Erythroleukemia is outlined by erythroid precursors making up larger than 50% of all nucleated cells within the bone marrow, and at least 20% of the remaining nonerythroid inhabitants are myeloblasts. The second kind, pure erythroid leukemia, is characterised by neoplastic immature cells committed to erythroid lineage making up higher than 80% of the bone marrow nucleated cells. A rare, extra chronic form of this illness (erythremic myelosis or di Guglielmo syndrome) has pure erythroblasts. The bone marrow is packed with tumor cells with promyelocytic morphologic features. The skin from a patient with acute monoblastic leukemia (leukemia cutis) reveals neoplastic myeloid cells. The subcapsular sinus extends alongside the penetrating fibrous trabeculae, forming trabecular sinuses, which in the end connect to the efferent lymphatic vessels. The sinuses are lined by macrophages, which are involved in antigen presentation (see Chapter 4). The arrangement of the sinuses maximizes publicity to international antigens present in the lymph to macrophages and immunoreactive lymphocytes in the lymph nodes. The cortex is subdivided into a follicular space (which accommodates principally B cells) and a paracortical area (predominantly T cells, plus many postcapillary venules). Lymphocytes from the circulation enter the lymph node cortex by migrating through the tall endothelial cells of the postcapillary venules within the paracortex. T cells tend to remain in the paracortex, while B lymphocytes home to the follicle germinal facilities. The B-cell�rich cortex contains two kinds of follicles: (1) immunologically inactive follicles, known as primary follicles; and (2) immunologically active follicles, called secondary follicles. Primary follicles are cohesive aggregates of small lymphocytes without well-defined germinal centers or mantle zones. Secondary follicles include germinal facilities by which massive noncleaved lymphocytes (centroblasts) mingle with small and bigger lymphocytes with cleaved nuclei (centrocytes). Macrophages, and to a lesser extent dendritic cells, provide progress elements for activated B cells. The T-cell�rich paracortex, also referred to as the deep cortex or parafollicular area, is both between the B-cell follicles and deep to them. Hematogones improve in number throughout viral infections and in bone marrow recovery after chemotherapy or stem cell transplantation. A fraction of the bone marrow-derived progenitor B cells go away the marrow and home to lymph node germinal centers, the place additional development and selection occurs. Specifically, B cells with adequate affinity for antigen survive the germinal middle reaction and ultimately go away the follicle compartment. As B lymphocytes mature, the genes for Ig heavy (H) chains are rearranged, resulting in the synthesis of IgM antibodies. After activation and clonal growth on this entity is typically referred to as a chloroma because of its greenish color, granulocytic sarcoma or monoblastic sarcoma. Cohesive clusters of macrophages and occasional multinucleated large cells are attribute of the granulomatous inflammation sample. Although the exact cause is commonly unknown, the condition normally resolves promptly. A part of a hyperplastic lymph node exhibits distinguished follicles (germinal centers) containing numerous macrophages with pale cytoplasm. The location of the nodes involved in reactive lymphadenopathy typically provides a clue to its trigger. For example, posterior auricular lymph nodes are generally enlarged in rubella an infection; occipital lymph nodes in scalp infections; posterior cervical lymph nodes in toxoplasmosis; axillary lymph nodes in infections of the arms or chest wall; and inguinal lymph nodes in venereal infections and infections of the legs. Generalized lymphadenopathy might occur in systemic infections, hyperthyroidism, drug hypersensitivity reactions and autoimmune diseases. Mixed Patterns of Reactive Lymph Node Hyperplasia Some infectious illnesses are associated with mixed patterns of lymphoid hyperplasia, by which several totally different features are distinguished. For instance, in toxoplasmosis, one sees prominent follicular hyperplasia and small collections of epithelioid macrophages in interfollicular regions and around the hyperplastic follicles. Cat-scratch illness elicits follicular hyperplasia and suppurative granulomas with a stellate appearance. Lymphadenitis caused by lymphogranuloma venereum and tularemia (see Chapter 9) resembles that seen in cat-scratch illness. Follicular Hyperplasia Hyperplasia of secondary follicles (germinal centers) and plasmacytosis of medullary cords indicate B-cell immunoreactivity. In nonspecific reactive follicular hyperplasia, distinguished hyperplastic follicles happen mainly in the cortices of the lymph node. The activated B cells in these follicles vary from small cells with irregular, cleaved nuclei to massive immunoblasts.
Purchase 5 mg zyrtec otc
The most common mutations cause defects in bone acidification allergy treatment for 6 month old 10 mg zyrtec cheap with amex, which is necessary for osteoclastic bone resorption allergy forecast houston 5 mg zyrtec purchase with mastercard. Other mutations that trigger osteopetrosis contain transcription elements or cytokines needed for the osteoclast differentiation. These bones are extremely radiopaque and weigh two to 3 times more than regular bone. The mineralized cartilage can be weak and friable, in order that the bones in osteopetrosis fracture simply. Grossly, bones in osteopetrosis are widened within the metaphysis and diaphysis, causing the attribute "Erlenmeyer flask" deformity. Depending on the mutation, osteoclasts may be absent, present in normal numbers or even plentiful. In the case of osteopetrosis characterized by normal or elevated numbers of osteoclasts, the molecular defect lies in a gene involved in the operate of osteoclasts, rather than in their formation. A radiograph of a child shows markedly misshapen and dense bones of the lower extremities, attribute of "marble bone illness. A gross specimen of the femur exhibits obliteration of the marrow space by dense bone. A photomicrograph of the bone of a child with autosomal recessive osteopetrosis demonstrates disorganization of bony trabeculae by retention of primary spongiosa (mixed spicules) and additional obliteration of the marrow space by secondary spongiosa. Marrow suppression in patients with the malignant form of osteopetrosis may be sufficiently severe to lead to severe anemia or pancytopenia. To compensate for loss of marrow hematopoiesis, extramedullary hematopoiesis happens within the liver, spleen and lymph nodes, and these structures are enlarged. Narrowing of neural foramina causes cranial nerve involvement, and subsequent strangulation of nerves leads to blindness and deafness. Osteopetrosis could be handled by bone marrow transplantation, which provides rise to a model new clone of practical osteoclasts. Patients have ache over the affected areas, fatigue, muscle losing, atrophy and gait abnormalities. When a fracture happens, the fracture callus could additionally be extensive sufficient to resemble a tumor. As the child grows, fractures are inclined to decrease in severity and frequency, and stature is generally unaffected. The sclerae are very skinny, with a blue color attributable to the underlying choroid. Progressive listening to loss, which develops to complete deafness in adulthood, outcomes from fusion of the auditory ossicles. The joint laxity associated with the situation ultimately leads to kyphoscoliosis and flat feet. Because of hypoplasia of the dentine and pulp, the teeth are misshapen and bluish yellow. The resulting phenotype will range from delicate to deadly depending on which gene is affected, the placement within the collagen triple helix at which the substitution happens and which amino acid is substituted for glycine. Affected infants are stillborn or die inside a few days after birth, in a way being crushed to death. Almost all bones sustain fractures throughout delivery or during uterine contractions in labor. In some patients, abnormalities of the tooth are additionally conspicuous (dentinogenesis imperfecta). Inheritance is often autosomal dominant, though (rarely) autosomal recessive varieties are reported. These sufferers eventually develop severe shortening of their stature because of progressive bone fractures and extreme kyphoscoliosis. On radiologic examination, bones are extremely thin, delicate and abnormally curved. A radiograph illustrates the markedly thin and attenuated humerus and bones of the forearm. The situation is heterogeneous in presentation, and there may or will not be dental illness. In this dysfunction, abnormal cross-linkages of collagen lead to thin, delicate and weak collagen fibrils. Over a period of years, the cortex matures, however this will not happen till adolescence or even later. These patients are vigorously treated with orthopedic units, together with rods inserted into the medullary cavities to prevent the dwarfing impact of a quantity of fractures. Osteoprogenitor cells for bone marrow transplantation, development components, bisphosphonates and gene remedy to enhance collagen synthesis have been present process scientific trials in an try to modify the course and severity of the disease. In 2�5 days, the hemorrhage types a large clot, which have to be resorbed so that the fracture can heal. By the tip of the primary week, a lot of the clot is organized by invasion of blood vessels and early fibrosis. Since bone formation requires an excellent blood provide, woven bone spicules start to seem on the periphery of the clot. Pluripotential mesenchymal cells from the delicate tissue and inside the bone marrow give rise to the osteoblasts that synthesize woven bone. In most fractures, cartilage also is shaped and is ultimately resorbed by endochondral ossification. Woven bone also forms contained in the marrow cavity at the fringe of the blood clot as a outcome of vascular tissue is also current in that location. The Reparative Phase the reparative part follows the first week after a fracture and should final for months, relying on the degree of movement and the fixation of the fracture. Repair proceeds from the periphery towards the middle of the fracture website and accomplishes two aims: (1) to manage and resorb the blood clot and, extra importantly, (2) to neovascularize building of the callus, which is ready to eventually bridge the fracture website. Armies of osteoclasts inside the Haversian canals form chopping cones that bore into the cortex towards the fracture website. A new vessel accompanies the chopping cone, supplying vitamins to these cells and providing more pluripotential cells for cell renewal. At the identical time, the external callus, which is found on the surface of the bone and is fashioned from the periosteum and the soft tissue mesenchymal cells, continues to grow toward the fracture website. Simultaneously, an endosteal or internal callus types inside the medullary cavity and grows outward toward the fracture site. The cortical chopping cones attain the fracture site and the ends of the fractured bone begin to appear beveled and smooth, as the positioning is reworked by osteoclasts. The same is true of the endosteal surface of the cortex, as the interior callus works its approach to the fracture website. Where there are massive areas of cartilage, new blood vessels invade the calcified cartilage, after which the endochondral sequence duplicates the normal formation of bone on the development plate. A pressure perpendicular to the long axis of the bone ends in a transverse fracture. Fracture Healing Is Divided into Inflammatory, Reparative and Remodeling Phases the duration of every part.