Ultracorten dosages: 40 mg, 20 mg, 10 mg, 5 mg
Ultracorten packs: 30 pills, 60 pills, 90 pills, 120 pills, 180 pills, 270 pills, 360 pills
Discount 5 mg ultracorten free shipping
Stems of origin of four branches specifically allergy associates ultracorten 20 mg order without a prescription, artery to the bulb of penis allergy forecast orlando buy 20 mg ultracorten fast delivery, urethral artery, deep and dorsal arteries of penis Bulbourethral glands Female Same Contents 1. Stems of origin of 4 branches specifically artery to bulb of vestibule, urethral artery, deep and dorsal arteries of clitoris 2 3. Deep transversus perinei It types an incomplete sheet of skeletal muscle extending across the urogenital triangle from the medial features of the ischiopubic rami. Posteriorly, the sheet is connected to perineal physique the place its fibres decussate with those of reverse aspect. Anteriorly, the muscles are poor and the visceral structures pass throughout the endopelvic fascia and the perineal membrane. Some fibres move to the deep part of exterior anal sphincter posteriorly and sphincter urethrae (contained within the urethra). Together with superficial transverse perinei, the muscle tissue act to tether (hold) the perineal body in median plane. Distal urethral sphincter mechanism It consists of intrinsic striated and clean muscular tissues of urethra and the pubourethralis part of levator ani which surrounds the urethra on the level of maximum concentration of those muscular tissues. Smooth muscle fibres additionally attain as much as the lowest a part of the neck of the bladder and between the 2, fibres lie on the surface of prostate. Some fibres are hooked up to inside floor of the ischiopubic ramus, forming compressor urethrae. Anteriorly Contents Same Same Same Same Open and continuous with the areas of the clitoris and the anterior abdominal wall Body of clitoris, made up only of two corpora cavernosa separated by an incomplete septum. Three sets of branches from perineal nerve- posterior scrotal nerve, branch to bulb and muscular branches b. Four branches from the artery of penis- artery to the bulb of penis, urethral artery, deep and dorsal arteries of penis a. Three sets of branches from perineal nerve- posterior labial nerve, department to bulb of vestibule and muscular branches b. Four branches from the artery of clitoris-artery to bulb of vestibule, urethral artery, deep and dorsal arteries of clitoris Greater vestibular glands and their ducts Nerves Vessels Glands and ducts Only the ducts of bulbourethral glands Table 28. Medial surface It covers the crus of ischial penis or crus ramus behind clitoridis; smaller the crus in females b. Posterior fibres, embrace the into the perineal of pudendal posterior finish membrane nerve of the bulb b. Middle fibres embrace the bulb embrace the and corpus corpus spongiosum, and spongiosum the raphe on their c. Anterior fibres are entire body of inserted into the penis raphe on the dorsal surface of the penis Fibres cross a. Body of clitoris and corpus spongiosum Inserted into the perineal body where it interlaces with other converging muscles 1. Middle fibres assist within the erection of the corpus spongiosum penis by compressing the bulb three. Anterior fibres additionally assist in the erection of penis by compressing the deep dorsal vein of penis In females, it acts as sphincter of vagina and assists in erection of clitoris Abdomen and Pelvis three. In superficial extravasation, the urine spreads downwards deep to the membranous layer of the superficial fascia. It first fills the superficial perineal house; and then the scrotum, the penis and the decrease part of the anterior abdominal wall. Their outer surfaces are coated with hair, and the inner surfaces are studded with massive sebaceous glands. The larger anterior ends are linked to each other beneath the mons pubis to form the anterior commissure. Labia Minora Labia minora are two thin folds of pores and skin, which lie inside the pudendal cleft. Anteriorly, each labium minus splits into two layers; the upper layer joins the corresponding layer of the other facet to kind the prepuce of the clitoris. Similarly, the decrease layers of the two sides be part of to form the frenulum of the clitoris. Clitoris three Vaginal orifice or introitus lies in the posterior a half of the vestibule, and is partly closed, in the virgin, by a skinny membrane known as the hymen. In married women, the hymen is represented by rounded tags of tissue known as the carunculae hymenales. Bulbs of the Vestibule the clitoris is an erectile organ, homologous with the penis. The physique of clitoris is made up of two corpora cavernosa enclosed in a fibrous sheath and partly separated by an incomplete pectiniform septum. The down-turned free end of clitoris is fashioned by a rounded tubercle, glans clitoridis, which caps the free ends of corpora. The glans is made up of erectile tissue steady posteriorly with the commissural venous plexus uniting proper and left bulbs of vestibule known as bulbar commissure. The floor of glans is extremely sensitive and plays an necessary function in sexual responses. The bulbs lie on both aspect of the vaginal and urethral orifices, superficial to the perineal membrane. The tapering anterior ends of the bulbs are united in front of the urethra by a venous plexus, referred to as the bulbar commissure. The expanded posterior ends of the bulbs partly overlap the higher vestibular glands. Greater Vestibular Glands of Bartholin Greater vestibular glands are homologous with the bulbourethral glands of Cowper within the male. Each gland has an extended duct about 2 cm lengthy which opens along side the hymen, between the hymen and the labium minus. The superficial fatty layer is continuous with the superficial fascia of the surrounding regions. Section the urogenital region is bounded by the interischial line which usually overlies the posterior border of the transverse perinei muscle tissue. On the deep side of perineal membrane lie deep transverse perenei; superficial to compressor urethrae and sphincter urethrovaginalis. Previous view was that sphincter urethrae prolonged between the 2 ischiopubic rami and was pierced by urethra and vagina however as of now the sphincter urethrae lies within urethra. In female, perineal membrane is less properly outlined and divided into two halves by urethra and vagina so that it varieties triangle on two sides. Compressor Urethrae Compressor urethrae arises from ischiopubic rami of every side by a small tendon. Fibres move anteriorly to meet their counterparts in a flat band which lies anterior to urethra. A variable variety of these fibres pass medially to reach the lower wall of vagina.
5 mg ultracorten order visa
The secondary centres appear at puberty allergy choices 10 mg ultracorten order with visa, two for the iliac crest allergy vs intolerance ultracorten 20 mg buy fast delivery, two for the Y-shaped cartilage of the acetabulum and one for the ischial tuberosity. Neck � Iliac crest is used for taking bone marrow biopsy in circumstances of anemia or leukemia. Femur has an higher rounded finish; a decrease bicondylar end and an extended shaft which is convex forwards. Side Determination Anatomical Position 1 the head is directed medially upwards and slightly forwards. Section the higher end of the femur contains the top, the neck, the larger trochanter (Greek runner) the lesser trochanter, the intertrochanteric line, and the intertrochanteric crest. Greater Trochanter 1 it is a giant quadrangular prominence positioned at the upper part of the junction of neck with the shaft. The apex is the inturned posterior part of the posterior 1 Lower Limb 1 the higher end bears a rounded head whereas the lower end is extensively expanded to kind two massive condyles. The higher border, concave and horizontal, meets the shaft on the larger trochanter. The lower border, straight and indirect, meets the shaft close to the lesser trochanter. The posterior floor is convex from above downwards and concave from aspect to facet. The posterior surface is crossed by a horizontal groove for the tendon of the obturator externus to be inserted into the trochanteric fossa. It is strengthened by a thickening of bone known as the calcar femorale current along its concavity. It is a vital radiological parameter which provides the thought of course of medullary canal and its alignment with the greater trochanter. The vessels produce longitudinal grooves and foramina directed in the direction of the pinnacle, primarily on the anterior and posterosuperior surfaces. The medial floor presents a rough impression above, and a deep trochanteric fossa under. Lesser Trochanter ridge which begins above, at the anterosuperior angle of the greater trochanter as a tubercle, and is steady beneath with the spiral line in front of the lesser trochanter. The spiral line winds around the shaft below the lesser trochanter to attain the posterior surface of the shaft. Intertrochanteric Crest Section It is a conical eminence directed medially and backwards from the junction of the posteroinferior a part of the neck with the shaft. Intertrochanteric Line 1 It marks the junction of the anterior floor of the neck with the shaft of the femur. It is a outstanding roughened It marks the junction of the posterior floor of the neck with the shaft of the femur. It is a smooth-rounded ridge, which begins above on the posterosuperior angle of the larger trochanter and ends at the lesser trochanter. It is convex forwards and is directed obliquely downwards and medially, as a end result of the higher ends of two femora are separated by the width of the pelvis, and their lower ends are shut collectively. In the center one-third, the shaft has three borders- medial, lateral and posterior and three surfaces- anterior, medial and lateral. The medial and lateral borders are rounded and ill-defined, but the posterior border is within the type of a broad roughened ridge, called the linea aspera (Latin tough line). The medial and lateral surfaces are directed more backwards than in course of the perimeters. In the upper one-third of the shaft, the two lips of the linea aspera diverge to enclose an extra posterior surface. The gluteal tuberosity is a broad roughened ridge on the lateral a part of the posterior surface. Thus, this part of the shaft has: Four borders-medial, lateral, medial supracondylar line and lateral supracondylar line. The medial border and medial supracondylar line meet inferiorly to obliterate the medial surface. Similarly the lateral border and lateral supracondylar line additionally meet inferiorly to obliterate the lateral floor. The tibial surfaces cover the inferior and posterior surfaces of the two condyles, and merge anteriorly with the patellar surface. The part of the floor over the lateral condyle is short and straight anteroposteriorly. Lateral Condyle the lateral condyle is flat laterally, and is extra consistent with the shaft. Intercondylar Fossa or Intercondylar Notch this notch separates the decrease and posterior components of the 2 condyles. It is limited anteriorly by the patellar articular floor, and posteriorly by the intercondylar line which separates the notch from the popliteal floor. Attachments on the Femur the lower end of the femur is broadly expanded to type two large condyles, one medial and one lateral. Anteriorly, the 2 condyles are united and are consistent with the entrance of the shaft. Articular Surface the two condyles are partially coated by a large articular surface which is divisible into patellar and tibial components. The easy posterior floor of the lesser trochanter is covered by a bursa that lies deep to the upper horizontal fibres of the adductor magnus. The medial and popliteal surfaces are naked, except for somewhat extension of the origin of the medial head of the gastrocnemius to the medial a part of popliteal floor. The deeper fibres of the lower half of the gluteus maximus are inserted into the gluteal tuberosity. The adductor longus is inserted along the medial lip of the linea aspera between the vastus medialis and the adductors brevis and magnus. The pectineus is inserted on a line extending from the lesser trochanter to the linea aspera. The medial and lateral intermuscular septa are attached to the lips of the linea aspera and to the supracondylar traces. The infrapatellar synovial fold is attached to the anterior border of the intercondylar fossa. The popliteal surface is covered with fats and varieties the ground of the popliteal fossa. When the knee is flexed the tendon of this muscle lies in the shallow posterior part of the groove. The anterior cruciate ligament is connected to the posterior a half of the medial floor of the lateral condyle, on a smooth impression. This is derived from the second perforating artery, branch of profunda femoris artery. Structure the angles and curvatures of the femur are strengthened on their concave sides by bony buttresses. The concavity of the neck-shaft angle is strengthened by a thickened buttress of compact bone, often recognized as the calcar femorale.
Ultracorten 5 mg otc
A variety of hypotheses and theories have been proposed in an attempt to allergy medicine poison ivy ultracorten 40 mg order line relate power enter to the diploma of measurement reduction produced allergy shots where to inject ultracorten 40 mg purchase. When designing a milling process for a given particle, probably the most appropriate energy relationship shall be required so as to calculate power consumptions. It has been thought of that the most appropriate values for n are 1 for particles bigger than 1 �m, where Kick-type behaviour happens, and a couple of for Rittingertype milling of smaller particles of lower than 1 �m. During a size discount process the particles of feed materials will be damaged down and particles in several dimension ranges undergo different amounts of breakage. This uneven milling leads to a change in the size distribution, which is superimposed on the final movement of the normal or log-normal curve in path of smaller particle diameters. With particle diameters smaller than roughly 5 �m, interactive cohesive forces between the particles typically predominate over comminution stresses as the comminution forces are distributed over increasing surface areas. This eventually leads to particle agglomeration as opposed to particle fracture, and size reduction ceases. In some instances, particle agglomeration occurs to such a degree that subsequent milling truly causes dimension enlargement. The shear charges current in cutter mills are useful in producing a coarse diploma of size discount of dried granulations previous to tableting. Size discount strategies There are many various kinds of size discount strategies, and the equipment out there for size reduction of pharmaceutical powders proceed to develop. This article illustrates the rules associated with methods which may be categorised based on the milling process employed to subdivide the powder particles. The approximate measurement discount vary achievable with every technique is illustrated, though it should be remembered that the extent of dimension discount is at all times related to milling time. Runner mills Size reduction by compression can be carried out on a small laboratory scale throughout growth utilizing a mortar and pestle. Roller mill A form of compression mill makes use of two cylindrical rollers mounted horizontally and rotated about their long axes. The dotted line on this, and in other subsequent size-range diagrams, refers to the size range the place the method is used much less usually. During milling, dimension reduction happens by fracture of particles between the 2 units of knives, which have a clearance of a few millimetres. Depending on the aim of the operation, the hammers could also be sq. faced, tapered to a leading edge or have a stepped form. Hammer mills consist of a collection of 4 or extra hammers, hinged on a central shaft which is enclosed inside a inflexible metal case. The angular velocity of the hammers produces a pressure rate as a lot as 80 s-1, which is so high that the majority particles bear brittle fracture. As measurement reduction continues, the inertia of particles hitting the hammers reduces markedly (as particle mass is reduced) and subsequent fracture is much less possible, so hammer mills are probably to produce powders with slim measurement distributions. Particles are retained within the mill by a display screen that allows only adequately comminuted particles to cross by way of. Vibration mills are crammed to roughly 80% whole quantity with porcelain or stainless-steel balls. During milling the entire body of the mill is vibrated and dimension reduction occurs by repeated impact. The effectivity of vibratory milling is larger than that of standard ball milling described later. Roller mill Roller mills use the principle of attrition to produce measurement reduction of solids in suspensions, pastes or ointments. Ball mill A ball mill is an example of a comminution methodology which produces measurement reduction by both influence and attrition of particles. The cylinder accommodates balls that occupy 30% to 50% of the whole volume, the ball dimension being depending on the feed and mill measurement. Mills may include balls with many various diameters as this helps to improve the method, as the large balls are inclined to break down the Fluid vitality mills Pin mills Ball mills 1 10 a hundred one thousand 10 000 Particle diameter (�m) one hundred 000 coarse feed supplies and the smaller balls assist to kind the fantastic product by reducing void spaces between balls. The quantity of material in a mill is of appreciable significance: too much feed produces a cushioning impact, and too little causes lack of efficiency and abrasive put on of the mill parts. The issue of best significance in the operation of the ball mill is the pace of rotation. This sequence is repeated, producing very little relative movement of the balls, so dimension reduction is minimal. Balls are lifted on the rising facet of the drum till their dynamic angle of repose is exceeded. At this point, they fall or roll back to the base of the drum in a cascade throughout the diameter of the mill. By this means, essentially the most environment friendly dimension reduction occurs by influence of the particles with the balls and by attrition. The optimum rate of rotation depends on the mill diameter but is usually of the order of 0. Fluid vitality mill Fluid energy milling is one other form of size discount method that acts by particle impaction and attrition. A fluid, often air, is injected as a high-pressure jet by way of nozzles at the backside of the loop. The high velocity of the air offers rise to zones of turbulence into which solid particles are fed. The excessive kinetic vitality of the air causes the particles to impact with other particles and with the sides of the mill with adequate momentum for fracture to happen. Turbulence ensures that the extent of particle�particle collisions is excessive sufficient to produce substantial dimension discount by impact and some attrition. A particle size classifier is included within the design in order that particles are retained in the toroid till sufficiently fantastic and are then entrained in the air stream that exhausts from the mill. Different mills can produce differing finish merchandise from the same starting materials. For instance, particle shape may vary according to whether dimension discount happens on account of impact or attrition. In addition, the proportion of nice particles in the product may range, so that other properties of the powder will be altered. Once the particle size required has been established, the selection of mills able to producing that size could additionally be modified from data of the particle properties, such as hardness and toughness. The influences of assorted process and material variables on the selection of a dimension discount technique are summarized in Table 10. Introduction to dimension separation Objectives of measurement separation the importance of particle dimension and the rules involved in differentiating a powder into fractions of identified particle size have been considered in Chapter 9. Methods for achieving the required size vary on a producing scale have been discussed in this chapter. An essential difference exists between the procedures known as size analysis and dimension separation.
Ultracorten 40 mg generic free shipping
Further Development of the Brain Prosencephalon allergy medicine makes me depressed quality ultracorten 20 mg, mesencephalon and rhombencephalon are first organized cephalocaudally allergy symptoms mouth sores ultracorten 5 mg order free shipping. Cephalic or mesencephalic flexure: this flexure is positioned within the area of midbrain. Pontine flexure: When the embryo is 5 weeks old, the prosencephalon consists of two lateral outpocketings-the primitive cerebral hemispheres. This is called pontine flexure, and it divides rhombencephalon into metencephalon and myelencephalon. The lumen of the spinal cord, the central canal is steady with that of primitive brain vesicles. The cavity of rhombencephalon is called fourth ventricle, those of cerebral hemisphere are lateral ventricles and cavity of diencephalon is third ventricle. Cavity of lateral ventricles communicates with that of third ventricle by way of interventricular foramen of Monro. Neural Crest Cells and their Derivatives During folding of the neural tube, a gaggle of cells are fashioned along each side of neural groove and after the formation of neural tube, lie between the surface ectoderm and neural tube. These cells (ectodermal in origin) migrate laterally, and are called neural crest cells. The choroid plexus of third ventricle is fashioned from ependymal cells of roof plate and the vascular mesenchyme. After the formation of the telencephalon, the lateral wall of diencephalon becomes thickened and gets divided into three areas, by appearance of two sulci. These are referred to as epithalamic and hyothalamic sulci, and the central half between the two sulci is identified as thalamus. The half above the epithalamic groove is a small area represented by habenular nuclei and pineal body. The pineal physique initially seems as an epithelial lining in the midline, however by the 7th week of intrauterine life, it begins to evaginate. It serves as a channel through which mild and darkness have an result on endocrine and behavioural rhythms, i. In the adult, calcium is incessantly deposited within the epiphysis and it even serves as a landmark on an X-ray skull. As a result of proliferative exercise; the assorted nuclei of thalamus are fashioned by multiplication of cells within the mantle layer of the wall of diencephalon. Hypothalamus forming decrease portion of the alar plate differentiates into a variety of nuclear areas which function regulation centre of the visceral features, i. The distinguished group of those nuclei is mammillary body, which varieties distinct protuberance on the ventral floor of the hypothalamus on each side of the midline. The cavities of hemispheres, the lateral ventricles, talk with the lumen of diencephalon, by way of the interventricular foramen of Monro. Lobes of Brain Cerebral hemispheres come up as bilateral (right and left) evaginations at the beginning of fifth week of development from the lateral wall of prosencephalon. As a result, this area bulges into the lumen of the lateral ventricle as well as into the foramen of Monro. In the area where the wall of hemisphere is hooked up to the roof of diencephalon, the neuroblasts fail to develop and it remains very thin. Here the hemispheric wall consists of a single layer of ependymal cells covered by vascular mesenchyme and collectively they type choroid plexus. Due to disproportionate growth of various parts of hemisphere, the choroid plexus protrudes into lateral ventricle along a line generally identified as choroid fissure. Above the choroid fissure, the wall of hemisphere is thickened, thus forming the hippocampus which primarily has an olfactory operate and this part bulges into lateral ventricle. With additional progress and enlargement, the hemispheres cowl the lateral aspect of diencephalon, mesencephalon and cranial portion of metencephalon. Corpus Striatum Continuous development of cerebral hemispheres in anterior, dorsal, posterior and inferior directions lead to formation of frontal, parietal, occipital and temporal lobes. As the growth in the area of corpus striatum slows down, the area between temporal and frontal lobes becomes depressed and varieties the insula. The area is later overgrown by adjacent lobes and at the time of delivery is kind of utterly covered. In later a part of fetal life because of growth in a restricted space, the sulci and gyri make their appearance. Cerebral Cortex Some of the cells of the mantle layer in thick basal a half of lateral wall of hemisphere form corpus striatum. It expands posteriorly and gets divided into two components: From growth viewpoint, the cerebral cortex consists of: a. The neocortex the creating telencephalon has a medial wall, apposed to the counterpart of the other facet, a superolateral wall and a basal wall. The hippocampal cortex develops in medial wall, pyriform cortex within the marginal layer-superficial to corpus striatum, and neocortex within the superolateral region. Motor areas of the cortex are rich in pyramidal cells, while the sensory areas have abundance of granular cells. It is a part of the wall of the neural tube that closes the cranial finish of the prosencephalon. After the appearance of telencephalic vesicles, lamina terminalis lies within the anterior wall of third ventricle. Neurons rising from one hemisphere pass to the opposite via the lamina terminalis. It consists of fibres connecting the olfactory bulb and associated mind areas of 1 hemisphere to those of reverse side. It appears in the 10th week of development and connects non-olfactory areas of the best and left facet. Development of Spinal Nerve Roots Positional Changes of Spinal Cord Motor nerve begins to seem in the course of the 4th week of improvement, arising from nerve cells located in the basal lamina (ventral horn) of spinal twine. Dorsal nerve roots kind the gathering of fibres arising from the cells During the third month of intrauterine life, the spinal wire extends the entire size of embryo. Due to fast growth of dura mater and vertebral column as relative to the neural tube, the terminal end of spinal cord is positioned, at delivery, at the stage of third lumbar vertebra. This means of recession continues after birth, on account of which, in the adult, spinal wire often ends on the higher border of 2nd lumbar or at lower border of 1st lumbar vertebra. Below this stage, a thread-like extension of pia mater forms filum terminale and is attached to the periosteum Brain�Neuroanatomy of the dorsal root ganglia (spinal ganglion). Central processes from these ganglia kind bundles that grow into spinal cord reverse the dorsal horns. Ventral primary rami provide limbs, ventral physique wall and kind main nerve plexuses, i.
Diseases
- Abdominal musculature absent microphthalmia joint laxity
- Petty Laxova Wiedemann syndrome
- Leipala Kaitila syndrome
- Silicosis
- Hepatic fibrosis
- Autonomic nervous system diseases
- Hemangioma
- Histidinuria renal tubular defect
- Epimetaphyseal skeletal dysplasia
- Osteoarthritis
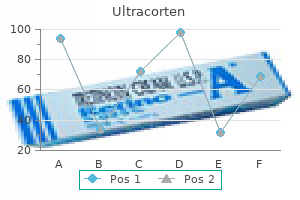
10 mg ultracorten order otc
Surface-active brokers are strongly adsorbed and have a pronounced affect on the floor cost allergy testing using hair ultracorten 10 mg buy line, imparting either a positive or a adverse cost relying on their ionic character allergy drugs 20 mg ultracorten. Here the cost is controlled by the the electrical double layer Consider a strong charged surface involved with an aqueous answer containing positive and adverse ions. The surface cost influences the distribution of ions within the aqueous medium: ions of charge opposite to that of the surface, termed counterions, are attracted in the course of the floor; ions of like charge, termed co-ions, are repelled from the floor. However, the distribution of the ions will also be affected by thermal agitation, which is able to are probably to redisperse the ions in solution. The principle of the electrical double layer deals with this distribution of ions and therefore with the magnitude of the electrical potentials which occur in the locality of the charged floor. A considerably simplified image of what pertains from the theories of Gouy, Chapman and Stern follows. The two parts of the double layer are separated by a airplane, the Stern airplane, at a couple of hydrated ion radius from the floor; thus counterions could also be held on the floor by electrostatic attraction, and the centre of these hydrated ions types the Stern aircraft. In addition to ions in the Stern layer, a specific amount of solvent will A protein is least soluble (the colloidal sol is least stable) at its isoelectric point and is quickly desolvated by very water-soluble salts corresponding to ammonium sulfate. This solvating layer is held to the surface, and the edge of the layer, termed the floor or aircraft of shear, represents the boundary of relative movement between the strong (and attached material) and the liquid. The potential at the plane of shear is termed the zeta potential, or electrokinetic potential, and its magnitude could also be measured utilizing microelectrophoresis or another of the electrokinetic phenomena. The thickness of the solvating layer is ill-defined, and the zeta potential therefore represents a possible at an unknown distance from the particle surface; its worth, however, is normally taken as being barely lower than that of the Stern potential. In the previous dialogue, it was said that the Stern plane existed at a hydrated ion radius from the particle floor; the hydrated ions are electrostatically interested in the particle surface. It is possible for ions/molecules to be extra strongly adsorbed at the floor, termed specific adsorption, than by easy electrostatic attraction. In truth, the particularly adsorbed ion/molecule may be uncharged as is the case with nonionic surface-active agents. The distance over which this occurs is 1/, referred to as the Debye�H�ckel size parameter or the thickness of the electrical double layer. The parameter depends on the electrolyte focus of the aqueous medium. As indicated earlier, the impact of specifically adsorbed ions could also be to lower the Stern potential and therefore the zeta potential without compressing the double layer. Thus the zeta potential could also be lowered by additives to the aqueous system in either (or both) of two different ways. Electrokinetic phenomena this is the final description applied to the phenomena that arise when makes an attempt are made to shear off the cell part of the electrical double layer from a charged surface. There are four such phenomena: particularly, electrophoresis, sedimentation potential, streaming potential and electroosmosis. All of those electrokinetic phenomena could additionally be used to measure the zeta potential but electrophoresis is the easiest to use and has the greatest pharmaceutical software. The motion of a charged particle (plus attached ions) relative to a stationary liquid under the affect of an applied electrical area is termed electrophoresis. A microscope outfitted with an eyepiece graticule is used, and the pace of movement of the particle underneath the affect of a recognized electric subject is measured. This is the electrophoretic velocity, v, and the electrophoretic mobility, u, is given by u=v E (5. Typically, a stable lyophobic colloidal particle could have an electrophoretic mobility of four � 10-8 m2 s-1 V-1. The equation used to convert the electrophoretic mobility, u, into the zeta potential depends on the value of a (is the Debye�H�ckel reciprocal length parameter described previously and a is the particle radius). For values of a > a hundred (as is the case for particles of radius 1 �m dispersed in 10-3 mol dm-3 sodium chloride solution), the Smoluchowski equation can be utilized: u = (5. The strategy of microelectrophoresis finds utility within the measurement of zeta potentials of model methods. The other electrokinetic phenomena are as follows: sedimentation potential, the reverse of electrophoresis, is the electrical field created when particles sediment; streaming potential, the electrical subject created when liquid is made to move alongside a stationary charged floor. Physical stability of colloidal systems In colloidal dispersions, frequent encounters between the particles happen due to Brownian motion. At a selected focus, the sol passes from the disperse to the aggregated state. For the electrolyte sorts in (a), the concentrations are about 10-4 mol dm-3, 10-3 mol dm-3, and 10-1 mol dm-3 respectively. These generalizations, (a) and (b), type what is known as the Schulze-Hardy rule Controlled by charge on particles Dispersions often of metals, inorganic crystals, etc. Sol particles remain dispersed due to electrical repulsion Sols of low viscosity, particles unsolvated and usually symmetric Lyophilic Dispersions are usually secure in the presence of electrolytes. The impact is due to desolvation of the lyophilic molecules and is determined by the tendency of the electrolyte ions to turn into hydrated. Lyophilic colloids when salted out may seem as amorphous droplets known as a coacervate Stability Formation of dispersion Controlled by cost and solvation of particles Generally proteins, macromolecules, etc. There is a big improve in entropy when rigidly held chains of a polymer within the dry state unfold in solution. The free power of formation is adverse, a secure thermodynamic system Usually high. Particles solvated and normally uneven Viscosity aggregates shaped sediment out, or momentary contact (flocculation), or whether or not the particles rebound and stay freely dispersed (a stable colloidal system) is decided by the forces of interaction between the particles. These forces can be divided into three groups: electrical forces of repulsion, forces of attraction and forces arising from solvation. An understanding of the first two explains the soundness of lyophobic techniques, and all three forces have to be thought-about in a discussion of the steadiness of lyophilic dispersions. In flocculation, the aggregates have an open structure by which the particles stay a small distance from each other. As a preliminary to dialogue on the steadiness of colloidal dispersions, a comparability of the final properties of lyophobic and lyophilic sols is given in Table 5. Repulsion between particles arises because of the osmotic impact produced by the rise within the number of charged species on overlap of the diffuse components of the electrical double layer. The attraction at giant interparticle distances, which produces the secondary minimal, arises as a outcome of the fall-off in repulsive energy with distance is extra speedy than that of attractive vitality. At intermediate distances, double layer repulsion might predominate, giving a primary maximum within the curve. Otherwise, the interacting particles will reach the power depth of the first minimum and irreversible aggregation, i. The depth of the secondary minimal is dependent upon the particle dimension, and particles may need to be of radius 1 �m or greater earlier than the attractive force is sufficiently nice for flocculation to happen.
Best 10 mg ultracorten
The incident gentle beam passes through a glass cell containing the dispersion allergy medicine link to alzheimer's purchase ultracorten 20 mg free shipping, and the scattered mild is detected by the photomultiplier tube mounted on a turntable which can be rotated to enable measurements at predetermined angles to the incident beam allergy medicine upset stomach 20 mg ultracorten cheap amex. Because the intensity of the scattered light is inversely proportional to the fourth energy of the wavelength of the sunshine used, blue mild (= 450 nm) is scattered far more than pink gentle (= 650 nm). Dynamic gentle scattering (photon correlation spectroscopy) Colloidal particles endure Brownian motion due to multiple collisions with neighbouring particles in solution. The intensity of the scattered gentle from these diffusing particles will fluctuate in time as a outcome of there will be constructive and destructive interference of the scattered gentle from the particles as the space between them is constantly changing with time. Analysis of those fluctuations can present details about their diffusion coefficient and therefore, from the Stokes�Einstein equation, their dimension and the distribution of sizes throughout the pattern. The timescale of the fluctuations in scattered light depth is extraordinarily fast (10-6 s to 10-3 s) and requires high-speed detection and recording systems to extract information from them. A highintensity laser is used as the sunshine supply, offering a slim beam of intense coherent mild which is directed via a really small aperture into the pattern cell. The gentle scattered by the particles contained inside this very small, well-defined, volume of the sample passes by way of a second small aperture and is measured using a high-speed detection system, the output of which is analysed utilizing the suitable software program and displayed on a pc monitor. Essentially, the instrument compares scattering intensity at very brief time intervals (time delays) and generates a correlation operate which, if the pattern is monodisperse, is in the type of an exponential decay curve. The numerical evaluation of the correlation operate to extract the particle dimension is Ultramicroscopy Colloidal particles are too small to be seen with an optical microscope. Light scattering is employed in the ultramicroscope first developed by Zsigmondy, by which a cell containing the colloid is considered against a darkish background at proper angles to an intense beam of incident mild. The particles, which exhibit Brownian motion, appear as spots of sunshine towards the darkish background. The ultramicroscope is used within the strategy of microelectrophoresis for measuring particle cost. Electron microscopy the electron microscope, capable of giving precise pictures of the particles, is used to observe the dimensions, shape and structure of colloidal particles. The success of the electron microscope is because of its high resolving power, outlined by method of d, the smallest distance by which two objects are separated yet stay distinguishable. The shorter the wavelength of the radiation used, the smaller is d and the greater the resolving energy. An optical microscope, using visible gentle as its radiation supply, gives d of about 0. The radiation source of the electron microscope is a beam of high-energy electrons having wavelengths in the area of zero. The electron beams are centered using electromagnets, and the entire system is underneath a excessive vacuum of about 10-3 Pa to10-5 Pa to give the electrons a free path. A major disadvantage of the electron microscope for viewing colloidal particles is that normally only dried samples can be examined. Consequently, it often provides no information on solvation or configuration in answer and, furthermore, the particles may be affected by pattern preparation. Electrical properties Electrical properties of interfaces Most surfaces purchase a surface electric cost when introduced into contact with an aqueous medium, the principal charging mechanisms being as follows. For example, the particles of silver iodide in a solution with excess I- will carry a negative charge, however the charge might be constructive if extra Ag+ is present. In a similar method, acidic medicine corresponding to ibuprofen and nalidixic acid also acquire a negative charge. The ionization of these teams, and so the net molecular cost, is decided by the pH of the system. At higher pH, the place the amino group is not ionized, the net charge on the molecule is unfavorable due to the ionization of the carboxyl group. At a sure particular pH, specific for every particular person protein, the whole variety of positive expenses will equal the total number of negative charges and the online charge will be zero. This pH is termed the isoelectric point of the protein, and the protein exists as its zwitterion. Surfaces in water are extra typically negatively charged than positively charged, because cations are typically more hydrated than anions. Consequently, the former have the larger tendency to reside in the bulk aqueous medium, whereas the smaller, less hydrated and extra polarizing anions have the larger tendency to reside on the particle floor. An estimation of the floor potential can be obtained from zeta potential measurements. As can be seen, the repulsion energy is an exponential function of the gap between the particles and has a variety of the order of the thickness of the double layer. For an assembly of molecules, dispersion forces are additive, summation resulting in long-range attraction between colloidal particles. This latter signifies that there might be an increased tendency for particles to flocculate within the secondary minimal, and that is the principle of the controlled flocculation approach to pharmaceutical suspension formulation described later. The primary maximum may also be lowered (and the secondary minimum deepened) by including substances, similar to ionic surface-active agents, which are particularly adsorbed inside the Stern layer. Here is decreased and therefore the zeta potential; the double layer is normally not compressed. The components of a combination of hydrophilic colloids can due to this fact be separated by a means of fractional precipitation, which entails the salting out of the varied parts at completely different concentrations of electrolyte. Lyophilic colloids can be thought of to turn out to be lyophobic by the addition of solvents such as acetone and alcohol. The particles turn out to be desolvated and are then very sensitive to precipitation by added electrolyte. Coacerva- Stability of lyophilic techniques Solutions of macromolecules, lyophilic colloidal sols, are stabilized by a combination of electrical double layer interplay and solvation, and each of these stabilizing factors should be sufficiently weakened before attraction predominates and the colloidal particles coagulate. Hydrophilic colloids are unaffected by the small amounts of added electrolyte which trigger hydrophobic sols to coagulate. However, when the focus of electrolyte is high, significantly with an electrolyte whose ions become strongly hydrated, the colloidal material loses its water of solvation to these ions and coagulates, i. Variation in the diploma of solvation of different hydrophilic colloids affects the focus of soluble electrolyte required to produce their tion is the separation of a colloid-rich layer from a lyophilic sol as the result of the addition of one other substance. This layer, which is present in the type of an amorphous liquid, constitutes the coacervate. Simple coacervation could also be caused by a salting-out impact on addition of electrolyte or addition of a nonsolvent. Complex coacervation happens when two oppositely charged lyophilic colloids are mixed. Gelatin at a pH under its isoelectric point is positively charged, and acacia above about pH three is negatively charged; a mix of solutions at about pH four ends in coacervation. If the coacervate is shaped in a stirred suspension of an insoluble solid, the macromolecular material will encompass the strong particles. The coated particles could be separated and dried, and this system types the basis of 1 technique of microencapsulation.
Ultracorten 5 mg buy
The inferior mesenteric plexus is fashioned chiefly by fibres from the aortic plexus allergy testing dust mites purchase 40 mg ultracorten mastercard. Sensory fibres from the diaphragm reach the coeliac plexus alongside the inferior phrenic arteries allergy shots lincoln ne trusted ultracorten 5 mg. The superior hypogastric plexus lies in front of the bifurcation of the stomach aorta, the left frequent iliac vein, the median sacral vessels, the physique of fifth lumbar vertebra, the promontory of the sacrum and between the two frequent iliac arteries. Parasympathetic Nerves and hindgut from the pelvic splanchnic nerves or nervi erigentes (S2�4). These fibres are distributed through the coeliac plexus and inferior hypogastric plexus, respectively. Functional Considerations Fibres from the pelvic splanchnic nerves attain it through the inferior hypogastric plexus. Usually, these fibres ascend by way of the left part of the superior hypogastric plexus, cross the sigmoid and left colic vessels, and are distributed alongside the vessels as nicely as independently to the derivatives of the hindgut. Branches In basic, the sympathetic nerves are vasomotor, motor to sphincters, inhibitory to peristalsis, and sensory to all of the viscera supplied. The parasympathetic nerves, then again, are motor and secretomotor to the gut and the glands related to it. Each inferior hypogastric or pelvic plexus lies in the extraperitoneal connective tissue of the pelvis. In the male, it lies on the aspect of the rectum, the seminal vesicle, the prostate and the posterior a half of the urinary bladder. In the female, it lies on the aspect of the rectum, the cervix, the vaginal fornix and the posterior a part of the urinary bladder; and likewise extends into the bottom of the broad ligament of the uterus. Sympathetic Nerves (T10�L2) 1 these are mainly derived from the hypogastric nerve which is represented either by a single nerve or by a plexus. Parasympathetic Nerves (S2�4) these are derived from the pelvic splanchnic nerves. Branches Parasympathetic System As already famous, the parasympathetic provide of the stomach correct comes from the vagi and of the pelvis Section Branches from the inferior hypogastric plexus are distributed to the pelvic viscera and a few abdominal viscera, both directly or along the branches of the interior iliac artery. Pain arising in viscera may also be felt within the pores and skin or other somatic tissues, provided by somatic nerves arising from the identical spinal section. Viscera usually have low amount of sensory output, whereas pores and skin is an space of high quantity of sensory output. Usually, the second, third and fourth lumbar ganglia are eliminated with the intervening chain, via an extraperitoneal approach. The first lumbar ganglion is preserved becuase it performs an necessary role in ejaculation. Normally, during ejaculation, it keeps the sphincter vesicae closed and thus prevents entry of semen into the urinary bladder. Presacral neurectomy: Division of the superior hypogastric plexus is called presacral neurectomy. However, the operation is successful in circumstances of intractable dysmenorrhoea as a end result of the pain fibres from the physique of uterus pass in the sympathetic nerves through the superior hypogastric plexus. In males, prescral neurectomy is adopted by lack of the ability of ejaculation because the sympathetic pathways to the seminal vesicle, vasa deferentia and prostate are interrupted. Developmental determinants of the independence and complexity of the enteric nervous system. This paper evaluations the molecular basis of normal an faulty enteric nervous system development. Later he developed a gentle swelling within the upper medial a half of thigh � What is this swelling more likely to be Ans: the delicate swelling in the thigh may be enlarged inguinal lymph nodes, a hernia, varicose vein or psoas abscess. Pus from tubercular lumbar vertebrae tracks down via the psoas sheath into the thigh, producing a gentle swelling in femoral triangle. In males, there are two openings-one of the gastrointestinal system and the opposite being the frequent opening of urinary and genital systems. In females, there are three separate openings-one every of the gastrointestinal, genital and urinary methods. Pudendal nerve supplies muscle tissue, skin, mucous membrane of both anal and urogenital triangles comprising the perineum. Deep Fascia It is fashioned by the inferior fascia of the pelvic diaphragm and the fascia masking the obturator internus below the attachment of the levator ani. Anococcygeal Ligament It is a fibrofatty mass permeated with muscle fibres derived from the levator ani and the exterior anal sphincter. On each side: � Conjoined ischiopubic rami � Ischial tuberosity � Sacrotuberous ligament. The anal area contains the termination of the anal canal within the median aircraft and an ischioanal fossa on each side. In males, the urethra enclosed within the root of penis, partly hidden anteriorly by the scrotum; and in females, the female exterior genital organs. In the urogenital region, there are the superficial perineal area or pouch and the deep perineal house or pouch. The chief neurovascular bundle of the perineum occupies a fascial tunnel, the pudendal canal, and contains the pudendal nerve and the inner pudendal vessels. Abdomen and Pelvis the perineal body, or the central level of the perineum, is a fibromuscular node located in the median plane, about 1. Two unpaired: � External anal sphincter � Fibres of longitudinal muscle coat of anal canal. Paired: � Bulbospongiosus � Superficial and deep transversus perinei � Levator ani. The perineal body is very important in the feminine for assist of the pelvic organs. This may result in prolapse of the urinary bladder, the uterus, the ovaries and even of the rectum. It is provided by the inferior rectal nerve and by the perineal branch of the fourth sacral nerve. The perineal branch of the fourth sacral nerve provides the pores and skin posterior to the anus. Section 2 Abdomen and Pelvis the ischioanal fossa is a wedge-shaped space situated one on both sides of the anal canal below the pelvic diaphragm. The apex is shaped by the line where the obturator fascia meets the inferior fascia of the pelvic diaphragm or anal fascia. The line corresponds to the origin of the levator ani from the lateral pelvic wall. Perianal Space Section the perianal fascia is within the form of a septum that passes laterally from the decrease end of the longitudinal coat of the anal canal. It extends medially from the white line of Hilton to the pudendal canal laterally.
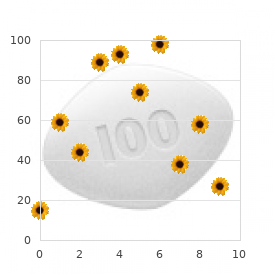
Ultracorten 10 mg generic online
Olivary nucleus the olivary nucleus is a large kirkland allergy medicine 600 generic ultracorten 40 mg visa, irregular cup-shaped structure forming the prominence on the anterolateral surface of the medulla allergy medicine makes me pee 5 mg ultracorten purchase otc. The superior olivary nucleus is situated within the pons and is composed of multiple nuclei involved within the central auditory pathways. The inferior olivary nucleus offers the only supply of climbing fibres to the cerebellum via the olivocerebellar pathway. White matter tracts Pyramidal tract the pyramids are large bundles of fibres forming prominences on each of side of the midline on the ventral medullary floor. Each is a convergence of the descending corticospinal tract fibres which have traversed the pons basis. Approximately 80 per cent of the fibres decussate into the contralateral lateral corticospinal tract. The uncrossed fibres continue within the ipsilateral anterior and lateral corticospinal tract. Nuclei Hypoglossal nucleus the hypoglossal nucleus lies near the midline on the dorsal tegmentum of the medulla. Dorsal motor nucleus of the vagus, nucleus tractus solitarius and nucleus ambiguous these three nuclei are thought-about together given their shut relation and interconnection with the glossopharyngeal, vagal and accent nerves: Internal arcuate fibres and medial lemniscus Many of the fibres that cross the midline within the open medulla are termed inner arcuate fibres. This incorporates the second-order neurons of the dorsal column medial lemniscal pathway and the olivocerebellar fibres operating from the inferior olivary nucleus into the cerebellum. The medial lemniscus is a continuation of the internal arcuate fibres that include the second-order neurons from the gracile and cuneate nuclei. It ascends via the pons and midbrain and its axons synapse in the ventral posterolateral nucleus of the thalamus. The dorsal motor nucleus of the vagus nerve lies lateral to the hypoglossal nucleus and forms the vagal trigone. This accommodates the preganglionic parasympathetic fibres of the vagus nerve that provide the thoracic and abdominal viscera. The nucleus tractus solitarius has connections with multiple constructions including the reticular formation and the dorsal motor nucleus. The nucleus ambiguus lies ventrolateral to the dorsal motor nucleus and the nucleus tractus solitarius. It con- Medial longitudinal fasciculus the medial longitudinal fasciculus is a white matter tract containing ascending and descending fibres that extend throughout the brainstem. The medial longitudinal fasciculus is close to the midline dorsally in the medulla and retains its midline position because it ascends however turns into more and more ventral. This permits coordination of eye movements with movement of the pinnacle, and performs a role in the vestibulo-ocular reflex. Spinocerebellar tract the spinocerebellar tracts are composed of a dorsal and a ventral element and are described in additional detail on p. The reticular formation the reticular formation is considered to be phylogenetically ancient given its function in controlling cardiovascular and respiratory function. It also has a spread of capabilities associated to awareness, consciousness, modulation of pain and motor function. Anatomically the reticular formation may be organized into three longitudinal columns: median, paramedian and lateral. Despite being an ill-defined community, numerous nuclei could be discerned within the reticular formation. Certain nuclei have specific neurotransmitters that project widely across the forebrain and have a extensive range of functions associated to consciousness, awareness, motion, studying and reward. For instance, the pedunculopontine nucleus accommodates cholinergic neurons, the locus coeruleus in the dorsal pons accommodates noradrenergic neurons, and serotinergic neurons are current within the raphe nuclei. Certain nuclei in the pons and medulla are thought of to be cardiovascular and respiratory centres. The reticular formation has a variety of afferent inputs from the spinal cord, cerebellum, cranial nerves and forebrain constructions. It has major ascending and descending outputs that are often identified as the reticular activating system and the reticulospinal tract, respectively. The ascending reticular activating system is important for reaching consciousness and connects the brainstem to the thalamus, through which it can affect various cortical constructions. Various nuclei within the pons and midbrain contribute to the ascending reticular activating system and harm to these buildings may find yourself in impaired consciousness. The descending medial and lateral reticulospinal tracts originate from the medulla and caudal pons. Their functions differ from the management of posture and limb motion to the modulation of ache. The spinal twine is roughly 40�50 cm in length and has variable anteroposterior and transverse diameters. It has cervical and lumbar enlargements to account for the increased number of sensory and motor neurons of the higher and lower limbs. The ventral median fissure and dorsal median sulcus split the spinal twine into left and right halves. The spinal twine is roofed by the three layers of meninges forming the thecal sac. The thecal sac extends beyond the extent of the conus medullaris and ends at the second sacral vertebral stage. From the apex of the conus, a fibrous extension, the filum terminale, continues caudally (see Chapter 25, p. The filum terminale internum passes through the lumbar cistern and penetrates the caudal aspect of the thecal sac, becoming the filum terminale externum. This continues by way of the sacral canal, exiting the sacral hiatus and inserting into the dorsal side of the first coccygeal phase. The grey matter is butterflyshaped and inside its centre lies the small central canal. The grey matter on each side consists of three columns, generally recognized as the ventral (anterior), lateral and dorsal (posterior) horns, that include a variety of neuronal cell bodies. There is additional subclassification of defined neurons into 10 layers (Rexed laminae). The ventral horn contains the massive motor neurons that supply voluntary striated muscular tissues. The dorsal horn incorporates the terminal axons of primary-order sensory neurons and the cell our bodies of the second-order sensory neurons that project cranially. Preganglionic sympathetic efferent neurons are current within the lateral horns from the L1 to T2 spinal cord segments. In the S2�S4 segments, the lateral horns are once more present and include the preganglionic parasympathetic efferent neurons.