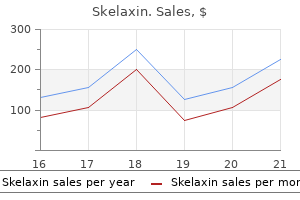
Skelaxin dosages: 400 mg
Skelaxin packs: 30 pills, 60 pills, 90 pills, 120 pills, 180 pills, 270 pills

Skelaxin 400 mg order amex
Right Eye Left Eye Demographics Hypoplastic nerves occur extra incessantly in males than females muscle relaxant amazon cheap skelaxin 400 mg fast delivery, and probably with out racial predilection spasms in lower abdomen skelaxin 400 mg order otc. Optical coherence tomography can usefully define the nerve fiber sample around the optic disc14 and enhance goal disc measurement. There is a spectrum between the normal, atrophic and hypoplastic disc that depends on how severe the causative event was and at which era or occasions it occurred. Timing and website of causative agents the timing of any "insult" is more probably to be after the retinal ganglion cell precursors appear and suggests that the defect, when severe, happens early in prenatal improvement. The development of the optic disc continues after start, albeit at a tremendously reduced price, and a few instances happen from an insult in late in pregnancy and even postnatally. Very hypoplastic discs could also be the results of an early insult, whereas refined levels of hypoplasia, where the optic disc dimension is general roughly normal, are due to a later insult. The baby can normally be saved quiet for a couple of moments by permitting feeding after the pupils have been dilated. The area of the optic disc (outer ring) consists of bare sclera or cribriform plate; this is variably larger than the circular area (inner ring), which contains any retinal nerve fibers (the optic disc "substance"). Histopathologically, retinal ganglion cell axons are lowered in quantity with normal mesodermal parts and glial supporting tissue. Many more circumstances are related to more widespread injury to other brain constructions. In humans these have been first described19 in a case in which trans-synaptic degeneration from a cerebral lesion gave rise to a pattern of optic disc hypoplasia and retinal nerve fiber defects that mirrored the sphere defect that the lesion caused. It could additionally be mixed with direct injury to the developing visual system occurring with trans-synaptic degeneration. Chiasmal hypoplasia and achiasmia When the optic nerves are hypoplastic, the chiasm is hypoplastic generally and the crossed and uncrossed fibers are lowered proportionally. The hypoplastic disc itself is atrophic and pale, suggesting persevering with injury to retinal ganglion cells and axons. Family historical past and genetics Familial circumstances are rare and not all necessarily genetic; in the absence of a recurrent environmental trigger (such as drugs or alcohol) or a family historical past or consanguinity, a very low recurrence threat could be given. Acuity may be normal regardless of quite massive cups, and area defects may trigger concern about glaucoma. Segmental optic disc hypoplasia subsequently results from an early injury at any website within the developing visible system. Superior segmental hypoplasia Babies of diabetic moms could have neurological anomalies, including optic disc hypoplasia. Female gender, brief gestation time, low delivery weight, and poor maternal diabetes control are additional threat components. EphB) are found in the superior (dorsal) retina; their absence in mice lets Septo-optic dysplasia Although the term septo-optic dysplasia implies absence of the septum pellucidum and optic nerve hypoplasia only, the syndrome encompasses a extensive variety of structural abnormalities of the cerebral hemispheres and commissures, hypothalamus, visual system, the pituitary physique and stalk. The upper halves of the optic discs are just about absent and the decrease halves are small. In holoprosencephaly, a variable midline facial defect is related to a single cerebral ventricle, and absence of the corpus callosum and septum pellucidum. A number of hormonal defects have been described starting from isolated growth hormone, adrenocorticotrophic, or antidiuretic hormone deficiency to panhypopituitarism. Growth hormone defects may current later in childhood, as progress can be stimulated by prolactin. Patients with any abnormalities will want professional monitoring and possibly therapy for all times. Although most are myopic and astigmatic, nearly half of the sufferers have non-refractive visual abnormalities associated with the defect, suggesting it could symbolize a form of segmental hypoplasia. Myopia and tilted optic discs commonly happen together in X-linked congenital stationary night time blindness. Although the anomaly was thought to be related to coloboma, in actuality the cause is unknown. When these occur bilaterally, superior bitemporal relative visible area defects could happen, which additionally cross the midline. When the kid has a fever or is in an unaccustomed sizzling local weather, a cascade happens which may end in dying. In many cases, the apparent area defect disappears with acceptable optical correction of the myopia brought on by the staphyloma. Fetal fissure-related optic disc abnormalities Coloboma Developmental aspects A coloboma is a defect that outcomes from an abnormality of the closure of the fetal fissure within the inferonasal quadrant of the creating optic cup. Incomplete closure creates a defect of any measurement from the margin of the pupil to the optic disc. Microphthalmos and scientific anophthalmos could symbolize excessive manifestations of the same disorder. Although this has no practical consequences, its diagnostic significance is as great as some other coloboma. Presentation Children with colobomas current both on account of the looks of microphthalmos, abnormally formed pupil, or, if bilateral, because of poor imaginative and prescient. If unilateral with poor imaginative and prescient, they may present with a squint or manifest latent nystagmus. If a fundus coloboma is intensive, the father or mother might discover an abnormal pink reflex on flash pictures or a mother may notice it when feeding the child with the light coming from behind her. Sometimes the systemic associations of colobomas are the presenting features, or the coloboma could solely be found on routine examination. Colobomas of the disc may be related to delicate manifestations of choroioretinal colobomas, iris or, not often, 570 inferonasal lens defects. Very rarely, neoplasms may happen along the line of closure of the fetal fissure: these embrace glioneuromas and medulloepitheliomas. Optic nerve colobomas cause various visual defects, relying on their size and the degree of macular involvement. Amblyopia is commonly a significant factor, associated to related myopic astigmatism. Heterotopic intraocular tissues, together with lacrimal, cartilage with or with out ossification, adipose, and easy muscle typically happen. Smooth muscle, when present, will be the foundation for periodic contraction of some colobomatous defects. Other eye malformations may be related, specifically to glaucoma resulting from an anterior chamber anomaly, which may additionally trigger disc excavation. Retinal detachment, subretinal neovascularization, and disciform degeneration may all happen as complications of colobomas of the choroid. An iris coloboma extended again to the optic disc but the optic disc itself was quite wholesome and there was a macula present.
Cranberry. Skelaxin.
- Treating type 2 diabetes.
- Dosing considerations for Cranberry.
- PREVENTING urinary tract infections (UTIs).
- What is Cranberry?
- Are there safety concerns?
- Skin healing, pleurisy, cancer, chronic fatigue syndrome (CFS), reducing urine odor, and other conditions.
- What other names is Cranberry known by?
- How does Cranberry work?
- Are there any interactions with medications?
Source: http://www.rxlist.com/script/main/art.asp?articlekey=96921
Cheap 400 mg skelaxin overnight delivery
There is a case report of in depth involvement of the orbit muscle relaxant tmj generic skelaxin 400 mg with mastercard, sinus muscle relaxant comparison chart skelaxin 400 mg buy with visa, infratemporal fossa, and brain in a newborn, which was managed expectantly. This is confirmed by excisional biopsy of essentially the most accessible lesions, which normally represents enough therapy. Biopsy is liable to precipitate bleeding, and therapy with topical steroids with frequent cautious follow-up is often efficacious on this context. These patients often present with a painless delicate tissue mass inflicting proptosis, or with ptosis or motility disturbances and diplopia. Surgical excision or debulking on the time of initial biopsy is suitable if this may be carried out with out significant risk to vital orbital buildings. Occasional orbital circumstances result in optic neuropathy that will warrant chemotherapy and even low-dose radiotherapy. Most instances resolve spontaneously or reply to treatment; nonetheless, a small variety of recalcitrant instances lead to disseminated persistent lymphadenopathy. The incidence of ophthalmic involvement varies extensively in several reports from 10�90%, which could mirror the totally different methodologies. Generally these patients demonstrate unilateral or bilateral proptosis, eyelid swelling or edema, or pain. The deposits might contain the intra- or extraconal areas, the extraocular muscular tissues, or the lacrimal gland. The presence of orbital or ocular lesions is adversely associated with prognosis for both acute myeloblastic and acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Once a tissue diagnosis has been established, systemic staging utilizing the American Joint Committee for Cancer, seventh version, is undertaken. Integration of eosinophilic granuloma of bone, "Letterer-Siwe illness and "Schuller-Christian disease" as associated manifestations of a single nosologic entity. Langerhans cell histiocytosis of the orbit: a need for interdisciplinary dialogue. Juvenile xanthogranuloma involving the eye and ocular adnexa tumor management, visual outcomes, and globe salvage in 30 sufferers. Extensive juvenile xanthogranuloma involving the orbit, sinuses, brain and subtemporal fossa in a newborn. Orbital and ocular manifestations of acute childhood leukemia: medical and statistical analysis of 180 sufferers. Orbital extra-medullary granulocytic sarcoma: clinicopathologic correlation with immunohistochemical options. Ophthalmologic manifestations of granulocytic sarcoma (myeloid sarcoma or chloroma). The third Pan American Lymphoma Ocular adnexal lymphoma is way less common in the pediatric population than in adults. Historically there has been an consciousness of the Epstein�Barr virus-mediated Burkitt lymphoma in the subSaharan African inhabitants, but this similar lesion can occur sporadically in non-endemic situations. References association of ophthalmology and American journal of ophthalmology lecture. Primary sporadic Burkitt lymphoma of the orbit, medical characteristics, management and outcomes, a case examine. Primary ocular adnexal lymphoma in pediatric patients: report of two instances and evaluate of the literature. The majority are concerned in the process of cell proliferation and ossification, and a lot of belong to a common molecular pathway. De novo mutations are of paternal origin and improve with paternal age, thought to be as a result of a co-location with mutations selling clonal expansion inside male germline progenitors (the "selfish spermatological selection" theory). Environmental elements have additionally been implicated within the etiology of craniosynostosis, together with maternal smoking and altitude, and intrauterine head constraint. Craniosynostoses, by which untimely closure of sutures causes an abnormally shaped skull. In addition, frontoethmoidal meningoencephaloceles, midline facial clefts, and amniotic bands are mentioned. Effects on the cranium Cranial sutures are fibrous joints offering a malleable quality to the head, permitting vaginal birth and progress of the brain throughout early development. The principal clinical manifestations have been given Greek or Latin descriptors; lately synostotic disorders have tended to simply be named according to the suture concerned. Trigonocephaly ("triangular head") is metopic suture synostosis; scaphocephaly ("boat-shaped head") is sagittal suture synostosis; plagiocephaly ("twisted head") is either unilateral coronal or unilateral lambdoid suture synostosis; and brachycephaly ("brief head") is bilateral coronal suture synostosis (Table 28. Multiple suture involvement leads to more complicated head morphologies, similar to tryphyllocephaly (Kleeblatschadel, clover leaf, or trilobed skull) or oxycephaly ("towering head"). Premature synostosis additionally happens in the Craniosynostosis Craniosynostosis is untimely fusion of one or more cranial vault sutures with resultant skull deformity. Thirty percent of circumstances are syndromic, usually with multiple suture involvement and associated primary malformations within the face, trunk, or extremities. Syndromic craniosynostosis sufferers present with significant cosmetic challenges and face advanced neurologic, ophthalmologic, and airway difficulties. Non-syndromic ("simple") craniosynostosis might have neurologic or ophthalmologic complications. Some cases of simple craniosynostosis represent the gentle finish of a spectrum of syndromic illness. Axial computed tomography of a patient with Saethre�Chotzen syndrome demonstrating shortened orbits and proptosis. Coronal suture nerve sheath and, when these are mutated, its failure to dilate may be as a result of abnormal fibrous tissue in the optic nerve sheath or lamina cribrosa. Lowering of the cribriform plate and anterior cranial fossa flooring with overgrowth of the ethmoid complex results in failure of anterior rotation of the orbital axes in fetal life (see Chapter 3), creating divergent orbital axes and hypertelorism (see Chapter 22). These adjustments in orbital axis and angulation enhance the likelihood of strabismus, which is seen in as a lot as 90% of sufferers. Cranial base underdevelopment compounds main midfacial hypoplasia by way of its oblique results on midfacial development. The ensuing abnormalities of palate, dentition, airway, and hearing could also be extreme. Effects on intracranial stress, the brain, and optic nerve Brain improvement is intimately tied to development of the skull; children with craniosynostosis may have developmental delay. Coronal computed tomography in a affected person with Crouzon syndrome demonstrating ex-cyclorotation of the orbits and their contents. A line drawn between the centers of the superior and inferior rectus muscle tissue emphasizes the angle. Deformational plagiocephaly is characterized by a history of improvement of the top shape within the first few months of life in affiliation with persistent positioning on one side, torticollis, or an inactive or developmentally delayed infant. The resultant occipitoparietal flattening could also be differentiated from unilateral lambdoid synostosis by a parallelogramshaped head seen from above and anterior displacement of the ipsilateral ear. The relatively giant head and poor neck muscle tone of the premature child leads to a laterally turned head, and will lead to a long slender head. The distinction from sagittal synostosis may be made by the cellular sagittal suture and correction of the pinnacle shape at three months of age as head control increases.
400 mg skelaxin discount free shipping
For this cause spasms vitamin deficiency skelaxin 400 mg buy mastercard, aphakic children wearing contact lenses should be prescribed a pair of glasses to be worn on a back-up basis muscle relaxant drugs z skelaxin 400 mg buy. Spectacles Aphakic spectacles are better tolerated than contact lenses by some children with bilateral aphakia, particularly between 18 months and 5 years of age. They even have the benefit of magnifying the apparent size of microphthalmic eyes. Immersion A-scan biometry in an anesthetized younger baby or optical biometry in an older baby are probably the most accurate technique of measuring axial length. An overcorrection with spectacles or contact lenses is normally necessary to totally focus the eye. Whatever optical correction is worn, frequent re-examinations are essential to ensure that the correction is up to date. Each examination ought to embody an assessment of fixation behavior or grating acuity in preverbal kids and optotype acuity in verbal children to detect or manage amblyopia. When amblyopia is present, occlusion remedy of the preferred eye should be initiated. Good visual outcomes may be achieved in children undergoing unilateral congenital cataract surgical procedure by patching the man eyes for 30�50% of waking hours. Patching therapy is most necessary during the important period of visible development throughout early childhood. Amblyopia could be treated in a baby wearing contact lenses to optically right bilateral aphakia by delaying insertion of the contact lens in the preferred eye for a specified time each day. Visual axis opacities Visual axis opacities may come up from fibrin forming a pupillary membrane, opacification of the residual posterior lens capsule, or lens re-proliferation extending into the visible axis. Because of the almost universal incidence of posterior capsular opacification in youngsters, a major posterior capsulotomy and anterior vitrectomy are recommended in children under 5 years of age. A topical cycloplegic agent must also be administered to stop the pupil from changing into miotic. Because of the increased risk of the attention being rubbed, spectacles or a shield ought to be worn over the eye in the course of the quick postoperative interval. Postoperativecomplications Amblyopia (see Chapter 73) Amblyopia is almost common in kids with dense congenital cataracts. It arises on account of the retina receiving a defocused image when the central visible pathways are forming. Uncorrected aphakia or induced anisometropia can exacerbate amblyopia even after the removal of a cataract. The posterior capsule was left intact on the time of cataract surgery and intraocular lens implantation. The capsulorrhexis has undergone progressive phimosis, which makes it troublesome to carry out retinoscopy. Intraocular pressure ought to be assessed at each outpatient examination after cataract surgery to screen for ocular hypertension. Rebound tonometry is best tolerated by young youngsters than applanation tonometry. Strabismus Strabismus is usually the presenting sign of a unilateral cataract in a baby. Esotropia is extra commonly observed in a baby with a congenital cataract, whereas exotropia is more incessantly noticed in a toddler with an acquired cataract. A delay within the elimination of an acquired cataract or optical correction in an older child can lead to diplopia after cataract surgery even after the eyes are surgically aligned because of a disturbance of central fusion. In most cases, the re-proliferating lens material is confined to the retro-iridial space, however it might lengthen into the pupil. In these situations, intraocular surgical procedure may be essential to clear the visible axis. In some instances, capsulotomies should be enlarged surgically so as to carry out refractions and to study the fundi. Irregular pupil An irregular pupil is a frequent complication of childish cataract surgical procedure and is most noticeable in kids with flippantly colored irides. Most generally it arises secondary to posterior synechaie between the iris and the residual lens capsule. Strands of vitreous extending to the surgical incision website might cause peaking of the pupil. This could additionally be averted by turning off the infusion line earlier than removing the vitrector from the eye, sustaining a low circulate of irrigating resolution, and minimizing the number of occasions the vitrector is inserted and removed from the attention. Even when the pupil is spherical after cataract surgical procedure, it frequently is much less reactive to gentle and pharmacological dilation. Glaucoma (see Chapter 38) Glaucoma could arise in the course of the early postoperative period or years later. Pupillary block glaucoma has the next incidence in neonates following lensectomy due to vitreous prolapse into the anterior chamber or pupillary membrane formation. This complication can largely be averted by performing an adequate anterior vitrectomy and atropinizing the pupil postoperatively. The danger of glaucoma increases twofold by performing cataract surgery at 1 month in comparability with 2 months of age. This 32-year-old lady underwent a lensectomy in her proper eye when 1 12 months of age. The iris usually becomes darker within the operated eye after cataract surgery during infancy. Retinal hemorrhages and detachments A hemorrhagic retinopathy develops in some infants after a lensectomy and anterior vitrectomy. In most circumstances, this consists of flame-shaped hemorrhages within the posterior pole that resolve with out sequelae in 1�2 weeks. In these cases, even after the hemorrhage has resolved, the visible acuity may remain reduced by amblyopia. Retinal detachments are infrequent and often occur a long time after the removing of a congenital cataract. They are notably widespread in developmentally delayed youngsters following cataract surgery as a end result of self-inflicted trauma. Retinal detachments are incessantly bilateral, and the visualization of the retinal breaks could additionally be hampered by miotic pupils and Soemmerring rings. The most typical organisms inflicting it in children are Staphylococcus aureus and Streptococcus pneumoniae. Even although most cases are diagnosed during the early postoperative interval, the visual prognosis is poor. In one collection, 65% of affected eyes ended up with no light perception regardless of aggressive treatment with intravitreal and systemic antibiotics. Intracameral antibiotics on the end of cataract surgical procedure have been shown to scale back the incidence of this complication. References Corneal edema Corneal edema might result from extreme corneal trauma after a protracted cataract surgical procedure or secondary to toxic anterior segment syndrome.
Cheap skelaxin 400 mg free shipping
The lesser trochanter is osteotomized and the distal insertion of the iliacus muscle on the linea aspera of the femur is freed with a periosteal elevator spasms in lower back skelaxin 400 mg line. H spasms from kidney stones skelaxin 400 mg buy lowest price, the iliacus and psoas muscle tissue are mirrored proximally by sharp and uninteresting dissection. It should be positioned as far posteriorly as potential to permit a more direct line of muscle motion. J, With the hip in extension and medial rotation, the larger trochanter is exposed by way of a longitudinal lateral incision. The vastus lateralis muscle is split and the lateral floor of the proximal 4 to 5 cm of femoral shaft is subperiosteally uncovered. K, It is necessary to avoid damaging the apophyseal growth plate of the higher trochanter. M and N, the iliopsoas muscle is then transferred laterally by this route with the Ober tendon passer. Next the hip is kidnapped a minimal of forty five to 60 degrees and internally rotated 10 to 15 levels. The web site of insertion of the iliopsoas tendon on the femoral shaft is determined and roughened with curved osteotomes. O, the lesser trochanter is anchored to the proximal end of the femur by one or two transversely positioned small staples. Mustard recommends making a trapdoor in the femur, into which the lesser trochanter is drawn and anchored by heavy wire sutures. P, the periosteum and vastus lateralis muscle are sutured to the edges and over the iliopsoas tendon. The tensor fasciae latae, gluteus medius and minimus, and abdominal muscle tissue are sutured to the iliac crest. A one-and-one-half hip spica forged is utilized with the hip in 60 levels of abduction, 10 to 15 degrees of medial rotation, and slight flexion. Postoperative Care Four to 6 weeks after surgical procedure, the affected person is readmitted to the hospital, the cast is removed, and a new bivalved hip spica solid is made. It must be minimize low on the lateral side in order that hip abduction workouts can be performed within the posterior half of the forged. Great care must be exercised to avoid inflicting a pathologic fracture of the femur when the child is lifted out of the solid. Training of the iliopsoas switch follows the same basic ideas as coaching of tendon transfers in poliomyelitis. In myelomeningocele, however, in depth paralysis of the decrease limb necessitates orthotic help, and the patient is way younger. Thus as soon because the transferred iliopsoas has honest motor energy and the lower limbs can be adducted to neutral place, weight bearing is permitted in bilateral above-knee orthoses. The butterfly pelvic band keeps the hips in 5 to 10 degrees of abduction during locomotion. At night time, the hips and the transfer are protected in the bivalved hip spica solid or in a plastic hip-knee-ankle-foot orthosis. A, A 3- to 4-cm-long incision (a) is revamped the lateral facet of the foot from the base of the fifth metatarsal to a degree 1 cm distal to the tip of the lateral malleolus. Subcutaneous tissue is divided, and the tendons of the peroneus longus and brevis are uncovered. A second incision (c) is then remodeled the fibular facet of the leg; it begins 3 cm above the lateral malleolus and extends proximally for a distance of 7 cm. Subcutaneous tissue and deep fascia are incised, and the peroneal tendons are uncovered by dividing their sheath. B, Next the peroneus brevis muscle is indifferent from the base of the fifth metatarsal and a whip suture is inserted into its distal finish. The peroneus brevis tendon is sutured to the distal stump of the peroneus longus tendon to protect the longitudinal arch and depression of the primary metatarsal. F E and F, the peroneus longus tendon is mobilized and, with a two-hand technique, gently pulled into the proximal wound within the leg. An sufficient opening is made in the intermuscular septum with care taken not to injure any neurovascular buildings. I G and H, A 2- to 3-cm-long longitudinal incision is revamped the dorsum of the foot (incision b partially A), centered over the bottom of the second metatarsal. The deep fascia is divided, and the extensor tendons are retracted to expose the proximal fourth of the second metatarsal. The periosteum is divided longitudinally and the cortex of the recipient bone is uncovered. With an Ober tendon passer, the peroneus longus tendon along with its sheath is passed into the anterior tibial compartment, deep to the cruciate crural and tarsal ligaments, and delivered into the incision on the dorsum of the foot. A direct line of pull of the peroneus longus tendon from its origin to its insertion must be ensured. A star-head hand drill is used to enlarge the opening to receive the tendon adequately. The peroneus longus tendon is handed via the recipient hole and sutured on itself under correct rigidity. The silk sutures on the finish of the tendon are passed from the big central gap to the lateral distal small holes and the tendon is securely sutured to the bone. A long-leg forged is utilized with the ankle in 5 levels of dorsiflexion and the knee in forty five levels of flexion. Postoperative care follows the guidelines outlined in the part on the rules of tendon transfer. The posterior tibial and peroneus longus and brevis tendons are divided distally at their insertion and delivered into the proximal wound. When the flexor hallucis longus tendon is to be transferred, its distal portion is sutured to the flexor hallucis brevis muscle. The anterior tibial tendon is delivered into the calf and heel through the interosseous route. A, A 5-cm-long posterior transverse incision is made across the heel along one of many skin creases in the part that neither presses the shoe nor touches the ground. B, the pores and skin and subcutaneous flaps are undercut and mirrored to expose the os calcis and the insertion of the Achilles tendon. An L-shaped reduce is made in the lateral two thirds of the insertion of the Achilles tendon. The divided portion is reflected proximally to expose the apophysis of the os calcis. C, Next, with a 9 sixty four -in drill, a gap is made through the calcaneus, beginning within the middle of the apophysis and popping out laterally at its plantar facet.
400 mg skelaxin cheap with visa
Characteristics that distinguish unintended from abusive harm in hospitalized younger children with head trauma zanaflex muscle relaxant buy generic skelaxin 400 mg line. Retinal haemorrhages in head trauma resulting from falls: differential analysis with non-accidental trauma in patients youthful than 2 years of age muscle relaxant 800 mg discount skelaxin 400 mg without prescription. Safeguarding youngsters and young people: roles and competences for health care employees. Centre for Disease Control and prevention: Injury Prevention and control: Violence prevention; Child maltreatment. Incidence and demography of nonaccidental head harm in southeast Scotland from a national database. Are there patterns of bruising in childhood that are diagnostic or suggestive of abuse Development and validation of a standardized software for reporting retinal findings in abusive head trauma. Use of digital camera imaging of eye fundus for telemedicine in children suspected of abusive head harm. An inter-observer and intra-observer examine of a classification of RetCam pictures of retinal haemorrhages in children. Grading system for retinal hemorrhages in abusive head trauma: Clinical description and reliability examine. Quantitative measurement of retinal hemorrhages in suspected victims of child abuse. Retinal haemorrhages and associated findings in abusive and non-abusive head trauma: a scientific evaluate. A Systematic Review of the Differential Diagnosis of Retinal Haemorrhages in Children with Clinical Features related to Child Abuse. Hand-held spectral area optical coherence tomography discovering in shaken-baby syndrome. Hemorrhagic Retinoschisis in Shaken Baby Syndrome Imaged with Spectral Domain Optical Coherence Tomography. Imaging the infant retina with a hand-held spectral-domain optical coherence tomography gadget. Update from the ophthalmology youngster abuse working get together: Royal College ophthalmologists. Bilateral rhegmatogenous retinal detachments with unilateral vitreous base avulsion because the presenting signs of kid abuse. Correlation between retinal abnormalities and intracranial abnormalities within the shaken child syndrome. Terson syndrome with ipsilateral severe hemorrhagic retinopathy in a 7-month-old baby. Dense vitreous hemorrhages predict poor visible and neurological prognosis in infants with shaken baby syndrome. Severe retinal hemorrhages in infants with aggressive, deadly Streptococcus pneumoniae meningitis. Diffuse unilateral hemorrhagic retinopathy associated with accidental perinatal strangulation. Bilateral retinal hemorrhages in a preterm infant with retinopathy of prematurity immediately following cardiopulmonary resuscitation. Retinal haemorrhages in an infant following RetCam screening for retinopathy of prematurity. Prevalence of retinal hemorrhages and baby abuse in kids who present with an apparent lifethreatening occasion. Prevalence of retinal hemorrhages in pediatric sufferers after in-hospital cardiopulmonary resuscitation: a prospective research. Prevalence of retinal hemorrhages in infants after extracorporeal membrane oxygenation. Incidence, distribution, and duration of birth-related retinal hemorrhages: a prospective study. Ocular histopathologic characteristics of cobalamin C kind vitamin B12 defect with methylmalonic aciduria and homocystinuria. Intraretinal hemorrhages and chronic subdural effusions: glutaric aciduria sort 1 can be mistaken for shaken child syndrome. An infant with methylmalonic aciduria and homocystinuria (cblC) presenting with retinal haemorrhages and subdural haematoma mimicking non-accidental damage. Shaken baby syndrome with out intracranial hemorrhage on preliminary computed tomography. A case of shaken child syndrome with unilateral retinal hemorrhage with no associated intracranial hemorrhage. Ocular findings in raised intracranial stress: a case of Terson syndrome in a 7-month-old toddler. A finite element toddler eye mannequin to investigate retinal forces in shaken baby syndrome. Vitreoretinal traction and perimacular retinal folds within the eyes of deliberately traumatized youngsters. Retinal hemorrhage and brain damage patterns on diffusion-weighted magnetic resonance imaging in kids with head trauma. Spectacles for the remedy of extreme myopia or hyperopia may cause prismatically induced optical aberrations, a narrow visual subject, and social ostracism as a outcome of unattractive thick lenses. Group 1, above, consists primarily of children with neurobehavioral abnormalities and cognitive incapacity. They have severe tactile aversion and thus refuse to put on glasses or contact lenses in spite of being functionally blind without the refractive correction. Their visible impairment might impede their attention and social interaction, exacerbating significant behavioral and social problems, and additional interfere with the development of normal communication abilities. This group is generally comprised of former untimely infants with severe retinopathy of prematurity and high myopia, kids with genetic mutations, or with autism spectrum dysfunction. In group 2, spectacle-induced aniseikonia and anisovergence impede stereopsis and binocular imaginative and prescient, and should cause asthenopia. Contact lenses, however, in children are often impractical due to difficulty with insertion, value, intolerance, non-compliance, and frequent loss. The outcome was variable ranges of visible impairment in the affected eye(s) relying on the severity of the refractive error. Refractive surgery, simply as in adults, reduces refractive error in these kids and thus reduces or eliminates these different related points. A new mindset is required after we take into consideration the management of severe refractive error in children. Untreated high refractive error in young kids can lead to severe levels of blur-induced amblyopia akin to that discovered with a dense congenital cataract or leukoma. Most recently, excimer laser refractive surgical procedure has been performed for accommodative esotropia with cheap outcomes.
400 mg skelaxin cheap overnight delivery
The minimum take a look at ought to evaluate responses in each quadrant along the major obliques (45� muscle relaxant pregnancy category cheap skelaxin 400 mg on-line, 135� muscle relaxant comparison chart 400 mg skelaxin buy otc, 225�, and 315�). The balance of consideration between central and peripheral stimuli influences measured subject extent in infants and young youngsters. Stimulus traits, together with spatial extent, rate of centrad motion, and rate of flicker all have demonstrable effect on field extent in infants and young youngsters. A substantial proportion of them might, nonetheless, have neurodevelopmental points that turn into obvious later in infancy or childhood. What underlies the delay in visible responsiveness in infants who clinically have regular eyes We believe that working towards an early, accurate prognosis is the path to the absolute best care of these patients. Finally, we caution that young infants with poor imaginative and prescient usually have delays in motor, social, and even language development. In the absence of visual enter (such as facial expressions), coordination of social cues and motor development might not occur. This scenario could worry and mislead family and physicians about world developmental delay. Optical, receptoral, and retinal constraints on foveal and peripheral imaginative and prescient within the human neonate. Development redistribution of photoreceptors throughout the Macaca nemestrina (pigtail macaque) retina. Monocular acuity norms for the Teller Acuity Cards between ages one month and four years. Large pattern inhabitants age norms for visual acuities obtained with Vistech-Teller Acuity Cards. Visual evoked potential primarily based acuity assessment in normal imaginative and prescient, artifically degraded imaginative and prescient, and in sufferers. Visual acuity in human infants: a evaluation and comparison of behavioral and electrophysiological research. Sensory Selectivity, Attentional Control, and Cross-Channel Integration in Early Visual Development. Exploring retinal improvement of strabismic infants using handheld optical coherence tomography. Development of the primate space of excessive acuity, three: temporal relationships between pit formation, retinal elongation and cone packing. Development of brain mechanisms for visible international processing and object segmentation. Validation of the acuity card process for evaluation of infants with ocular disorders. Acuity card assessment of visual function in the cryotherapy for retinopathy of prematurity trial. Preferential wanting acuity of pediatric patients with developmental disabilities. Grating visual acuity utilizing the preferential-looking method in elderly nursing home residents. Grating visual acuity with Teller playing cards in contrast with Snellen visual acuity in literate sufferers. Development of distinction sensitivity over the first 3 months of life within the human infant. Development of spatial contrast sensitivity from infancy to adulthood: psychophysical data. The role of distinction sensitivity charts and distinction letter charts in clinical practice. Contrast Sensitivity, Proceedings of the Retina Research Foundation Symposia, vol. Background adaptation in kids with a history of mild retinopathy of prematurity. Kinetic perimetry assessment of binocular visual field shape and size in young infants. Recognition acuity, grating acuity, distinction sensitivity, and visual fields in 6-year-old youngsters. Development of binoclar and monocular visual fields of human infants in the course of the first yr of life. Distance and near visual acuity, contrast sensitivity, and visual fields of 10-year-old children. Visual fields measured with double-arc perimetry in eyes with threshold retinopathy of prematurity from the cryotherapy for retinopathy of prematurity trial. Visual area defects in prematurely born sufferers with white matter injury of immaturity: a multiple-case study. Equivalent intrinsic noise, sampling effectivity, and distinction sensitivity in sufferers with retinitis pigmentosa. Hyperacuity thresholds of 1 sec: theoretical predictions and empirical validation. Outcome research of stereopsis in relation to period of misalignment in congenital esotropia. Retinal degeneration in youngsters: darkish adapted visible threshold and arteriolar diameter. The effect of sunshine adaptation on scotopic spatial summation in 10-week-old infants. Visual area extent at 6 years of age in children who had high-risk prethreshold retinopathy of prematurity. The affect of a central stimulus on visual field measurements in children from 3. Measured visible area extent varies with peripheral stimulus flicker price in very younger children. Does fee of stimulus presentation affect measured visual subject extent in infants and toddlers Visual acuity adjustments throughout maturity in normal, healthy eyes: seeing past 6/6. Contrast sensitivity in 10 year old preterm and full time period youngsters: a inhabitants primarily based research. The weight increases 40% by the middle of the second 12 months and 70% by the fifth year. The development of the attention parts is meticulously sequenced, and understanding the milestones of growth is essential to make sense of medical observations. However, every laboratory should establish normative knowledge for its personal tools and population.
Syndromes
- General anesthesia. You will be unconscious and unable to feel pain.
- Rheumatoid arthritis
- For a subcutaneous mastectomy, the surgeon removes the entire breast but leaves the nipple and areola (the colored circle around the nipple) in place.
- Very pale stools
- You suddenly have a harder time breathing or have more pain
- Tricyclic antidepressants (amitriptyline, nortriptyline, or carbamazepine)
- A bone graft
- Emitrip
- Abnormal heart rhythm
Skelaxin 400 mg buy generic on-line
Nonetheless muscle relaxant you mean whiskey skelaxin 400 mg lowest price, monitoring these sufferers for decreased imaginative and prescient within the fellow eye is prudent muscle relaxant hiccups order skelaxin 400 mg on-line. Reverseamblyopia Reverse amblyopia (occlusion amblyopia) is a form of deprivation amblyopia. It is a discount of vision in the fellow eye of more than one line because of a treatment prescribed for amblyopia within the fellow eye. It happens a lot much less usually with part-time occlusion and cycloplegic and optical methods of remedy. Reverse amblyopia generally recovers quickly, though there are reviews of permanent visible impairment or change in fixation. Examine the patient for indicators of optic neuropathy including the pupillary light reflex for evidence of an afferent pupil, shade imaginative and prescient, and appearance of the optic nerve and nerve fiber layer. If the acuity discount is confirmed, either stop the energetic amblyopia therapy and re-examine the patient in several weeks or proceed the therapy with cautious monitoring of the man eye. If the fellow eye is worse than the amblyopic eye, stop therapy and schedule a return go to. If the vision within the fellow eye is still reduced on the next visit, think about treating the previously fellow eye. Discontinuationoftreatment/ maintenancetherapy Most clinicians cease intensive therapy when the patient no longer shows enchancment. However, the period of therapy earlier than cessation of remedy is unclear, but 3 months with no improvement before stopping or reducing remedy is an affordable method. Once therapy is thought to have reached its most benefit, the author begins to "wean" the affected person over many months or perhaps a 12 months, reducing the remedy by 50% every 3 months. In any case, ongoing monitoring is required until 7 or 8 years of age with none energetic remedy apart from glasses to detect a recurrence, which is inconvenient but medically necessary. The likelihood of sustaining all, or a portion of, the development into maturity is no much less than 75% in retrospective studies. This is consistent with the demonstration of age-specific delicate durations in neurologic growth. For patients 7�12 years of age, 2�6 hours per day of patching with close to visible actions and atropine improved visual acuity even if the amblyopia had been beforehand handled. In a quantity of retrospective research and two medical trials for occlusion and pharmacologic therapy in patients lower than 7 years of age, no age impact might be demonstrated. However, compliance with occlusion remedy varies widely, from 30% to more than 90%. Pilot research of occlusion remedy with occlusion dose screens have proven the anticipated correlation of remedy compliance with outcomes. Treatment for children 7�12 years of age was optical only or optical plus prescribing patching 2�6 hours per day with near visual activities and atropine ophthalmic answer 1% every day. For teenagers 13�17 years of age, remedy was optical solely or optical plus prescribing patching 2�6 hours per day with close to visible activities. These data would help the earlier identification and initiation of amblyopia treatment. Prevalence of amblyopia and strabismus in White and African-American children aged 6 by way of seventy one months: the Baltimore Pediatric Eye Disease Study. Improvement in amblyopic eye function and contralateral eye disease: proof of residual plasticity. A randomized trial of prescribed patching regimens for remedy of severe amblyopia in kids. Treatment of extreme amblyopia with weekend atropine: outcomes from 2 randomized clinical trials. A randomized trial comparing Bangerter filters and patching for the remedy of reasonable amblyopia in youngsters. A randomized trial of near versus distance actions whereas patching for amblyopia in youngsters aged 3 to lower than 7 years. A randomized trial of levodopa as treatment for residual amblyopia in older kids. A preliminary report about the relation between visible acuity enhance and compliance in patching therapy for amblyopia. Prevalence of amblyopia and strabismus in African American and Hispanic kids ages 6 to seventy two months the multi-ethnic pediatric eye disease examine. Glasgow acuity cards: a brand new take a look at for the measurement of letter acuity in kids. Computerized method of visual acuity testing: adaptation of the amblyopia therapy study visible acuity testing protocol. Poor correlation between "fix� follow�maintain" monocular/binocular fixation sample evaluation and presence of functional amblyopia. A randomized trial to consider 2 hours of day by day patching for strabismic and anisometropic amblyopia in children. Randomised managed trial of remedy of unilateral visual impairment detected at preschool vision screening. The remedy of amblyopia: An analysis of the outcomes of amblyopia remedy using the pooled data of printed research. A comparability of atropine and patching therapies for moderate amblyopia by patient age, explanation for amblyopia, depth of amblyopia, and different components. A randomized trial of patching regimens for remedy of average amblyopia in children. The course of moderate amblyopia handled with atropine in kids: expertise of the amblyopia treatment examine. A randomized pilot research of near actions versus non-near actions during patching therapy for amblyopia. Impact of patching and atropine therapy on the kid and household in the amblyopia remedy study. Atropine occlusion within the treatment of strabismic amblyopia and its impact upon the non-amblyopic eye. Full-time atropine, intermittent atropine and optical penalization and binocular outcome in remedy of strabismic amblyopia. Anisometropic and stabismic amblyopia within the age group 2 years and above: A prospective research of the outcomes of remedy. Pharmacological plus optical penalization therapy for amblyopia: outcomes of a randomized trial. Cytidin-5-diphosphocholine enhances the impact of part-time occlusion in amblyopia. Efficacy of occlusion for strabismic amblyopia: can an optimum duration be identified Compliance and results of treatment for amblyopia in children greater than eight years old. Compliance with occlusion therapy for strabismic and anisometropic amblyopia: A pilot research.

Discount 400 mg skelaxin overnight delivery
Intravitreal chemotherapy for vitreous disease in retinoblastoma revisited: from prohibition to conditional indications back spasms 32 weeks pregnant 400 mg skelaxin cheap fast delivery. Profiling security of intravitreal injections for retinoblastoma utilizing an anti-reflux process and sterilisation of the needle track muscle relaxant medication prescription skelaxin 400 mg with mastercard. Colorimetric and longitudinal analysis of leukocoria in leisure photographs of kids with retinoblastoma. The International Classification of Retinoblastoma predicts chemoreduction success. A visible approach to offering prognostic data to mother and father of children with retinoblastoma. Socioeconomic and psychological influence of therapy for unilateral intraocular retinoblastoma. The epidemiological challenge of probably the most frequent eye most cancers: retinoblastoma, a problem of birth and death. National Retinoblastoma Strategy Canadian Guidelines for Care/Strat�gie th�rapeutique du r�tinoblastome guide clinique canadien. Second and subsequent tumours among 1927 retinoblastoma sufferers recognized in Britain 1951�2004. Retinoblastoma: the illness, gene and protein provide important leads to perceive cancer. Retinoma: spontaneous regression of retinoblastoma or benign manifestation of the mutation Risk of soppy tissue sarcomas by particular person subtype in survivors of hereditary retinoblastoma. Retinoblastoma with central retinal artery thrombosis that mimics extraocular illness. Hand-held high-resolution spectral domain optical coherence tomography in retinoblastoma: scientific and morphologic issues. Breaking down limitations to communicating complicated retinoblastoma data: can graphics be the solution Pre-enucleation chemotherapy for eyes severely affected by retinoblastoma masks risk of tumor extension and increases death from metastasis. Prosthetic conformers: a step in path of improved rehabilitation of enucleated children. Postenucleation adjuvant chemotherapy with vincristine, etoposide, and carboplatin for the treatment of high-risk retinoblastoma. Successful remedy of metastatic retinoblastoma with high-dose chemotherapy and autologous stem cell rescue in South America. Chemotherapy with focal therapy can treatment intraocular retinoblastoma without radiotherapy. Intra-arterial chemotherapy is simpler than sequential periocular and intravenous chemotherapy as salvage therapy for relapsed retinoblastoma. Intra-arterial chemotherapy for the administration of retinoblastoma: four-year experience. Efficacy and problems of super-selective intra-ophthalmic artery melphalan for the therapy of refractory retinoblastoma. The classification of vitreous seeds in retinoblastoma and response to intravitreal melphalan. Penetration of chemotherapy into vitreous is increased by cryotherapy and cyclosporine in rabbits. Outcome following preliminary external beam radiotherapy in sufferers with Reese-Ellsworth group Vb retinoblastoma. Secondary acute myelogenous leukemia in patients with retinoblastoma: is chemotherapy a factor Secondary leukemia or myelodysplastic syndrome after therapy with epipodophyllotoxins. Ocular motility adjustments after subtenon carboplatin chemotherapy for retinoblastoma. Plaque radiotherapy for retinoblastoma: long-term tumor management and treatment issues in 208 tumors. Second nonocular tumors in survivors of bilateral retinoblastoma: a possible age effect on radiation-related danger. These proliferate, and turn into aligned into vascular cords that develop lumina and differentiate into capillaries, a process often recognized as vasculogenesis. This is succeeded by angiogenesis in which vessels develop out from current vessels, transform, and type a mature retinal vascular network with capillary-free areas. This situation, then often recognized as retrolental fibroplasia, is a disorder of the immature retinal vasculature. Clinical and experimental proof supported a poisonous effect of oxygen on the immature retinal vasculature, which led to the restriction of oxygen use in preterm neonates. Phase I: decreased retinal vessel growth Premature start removes the fetus from a milieu uniquely suited to development, so not solely does it deprive the fetus of maternal vitamin, but in addition exposes the baby to a harsh environment requiring considerable physiological adaptation and likewise many potential pathological processes. The cardiopulmonary diversifications related to birth and switch from the fetal setting to room air embrace PaO2 rising from <25 mmHg (kPa <3. Stage 1 A flat gray-white demarcation line separates the vascularized from non-vascularized retina. The colour of the ridge may be white or pink, and small neovascular tufts could additionally be seen posterior to the ridge. Differentiating stage 1 and early stage 2 is difficult, however normally not prognostically essential. The new vessels could also be steady with, or disconnected from, the posterior border of the ridge, or lengthen into the vitreous. The extraretinal neovascularization could prolong from the area of the ridge into the vitreous or, usually in more Classification Table44. Stage 1 in its lower part, but the line becomes thicker (ridge) towards the highest of the picture. The shadow, just behind the lesion, indicates that the lesion is off the retinal surface. Stage 2 at top and backside of the picture with about 1 clock hour of gentle stage three disease that curls away from the ridge at its lower edge. Engorgement of the iris vessels and poor pupillary dilatation and vitreous haze are late signs and customarily indicate advanced disease. This scientific analysis is made by comparing with a reference photograph in the classification. This stage is additional defined based on the anterior and posterior characteristics of the funnel. Note the totally different look with different magnification and area of view between (A) and (B). Regression and backbone Resolution of acute phase retinopathy has been less nicely studied. The ridge thins and breaks up, and retinal vessels grow via the ridge into the peripheral avascular retina. The mean time of onset of signs of involution in youngsters with birth weights of less than 1251 g was 38.
400 mg skelaxin order with mastercard
During this period muscle relaxant cephalon buy cheap skelaxin 400 mg, the retina muscle relaxants kidney failure purchase skelaxin 400 mg without a prescription, optic nerve, vitreous, lens, and angle buildings develop (Table three. The process of invagination also entails the lens placode (plate), which leads to the formation of the lens pit. Further growth leads to the lens vesicle separating from the surface ectoderm. The anterior periocular mesenchyme within the mammal has contributions from cells of neural crest and mesodermal origins, in contrast to the chick the place there are only neural crest contributions. Thirdmonth Fourthmonth Eighth week Optic nerve growth predominates as more ganglion cells differentiate in the sensory retina, reaching 2. The axons begin to make contact with the brain and establish a rudimentary chiasm. M�ller cells seem and start to lengthen radial fibers inwards to form the interior limiting membrane and outward toward the potential exterior limiting membrane. The equatorial epithelial cells begin to divide and new cells are pushed posteriorly, then elongate to turn into the secondary lens fibers. The lens sutures develop the place the secondary lens fibers meet in a linear pattern at the anterior and posterior poles of the lens. The sutures initially are a line, however then evolve to be Y shaped anteriorly and an inverted Y posteriorly. Fifthmonth Sixthmonth Seventhmonth Eighthmonth ensuing lens vesicle is relatively giant and fills the optic cup. For the optic fissure to close, the perimeters of the optic cup should turn into closely apposed. The sensory retina thickens because of proliferation of cells in the germinative zone of the inside layer of the optic cup. The secondary vitreous, a cellular construction with related extracellular matrix, forms and begins to transform the first vitreous and fill the remaining retrolenticular house. The corneal epithelium develops from floor ectoderm and its maturation is expounded to eyelid improvement. It first turns into obvious round week sixteen and is well recognizable by the fifth month. This is marked by a change in stromal appearance on the periphery of the cornea, with cells acquiring a more polymorphic form and shedding common orientation. In place of the limbal folds identifiable in adult corneas, a ridgelike structure circumscribes and demarcates the developing cornea. These embrace dendritic cells and macrophages in the limbus and peripheral cornea. Mesenchymal stromal cells of neural crest and mesodermal origin migrate into the space between the corneal epithelium and corneal endothelium and turn into keratoblasts. Synchronized alignment of keratopodia and collagen contributes to lamella formation. This contains specification of the peripheral optic cup to a nonneuronal destiny (pigmented epithelial layer of iris). Periocular mesenchymal cells proliferate and migrate along the iris epithelial layers and differentiate into the iris stroma. Between the iris stroma and the (pigmented) iris epithelium, the sphincter and dilator smooth muscular tissues arise from neuroectoderm. These progenitors produce neurons which have the ability to regenerate the retina following damage. Differentiating lens fiber cells elongate and cover the old lens fiber core, leading to progress of the lens throughout development. All hyaloid vessels are arteries and the venous drainage is achieved by the choroidal veins. With the looks of the growing retinal vasculature at approximately the fifth month of gestation, the primary signs of hyaloid vessel regression may be detected. Regression of the structures derived from the primary vitreous is a crucial occasion, important for the formation of the crystalline (secondary) vitreous. Blood move in the hyaloid artery ceases across the seventh month, and the vessel is almost completely atrophied by start. Trabecular meshwork Trabecular meshwork formation begins around the fourth month of gestation. Primate retinal research establish the fovea as the initiation point for many developmental occasions within the retina, together with: cessation of mitosis, morphological maturation, apoptosis, opsin expression, and synaptogenesis. At week 34, cones and rods close to the pure cone space of the fovea have outer segments and are forming elongated axons, which terminate in distinct synaptic pedicles in the outer plexiform layer. The stimulus for vascular progress relies on the retinal neurons changing into metabolically active, resulting in native hypoxia. This is the converse of the rest of the retina and may provide a clue to the susceptibility of the macular to disease. Within the mind (as opposed to the spinal cord), motor neuron group is subservient to neuromeric organization. The cranial motor neurons are organized within individual rhombomeres (neuromeres of the rhombencephalon) or in adjoining neuromeric pairs. The midbrain and each hindbrain segment have their very own molecular "address" reflected by the expression of a singular mixture of transcription elements. Axon pathfinding is important for the establishment of proper neuronal connections during growth. The optic disc will type at the transition between the optic groove and retinal fissure. Emmetropization the human eye is programmed to obtain emmetropia in youth and to maintain emmetropia with advancing years. Eye growth is regulated in early postnatal life and optically driven mechanisms contribute to this course of. Understanding the function of progress factors in embryonic development: insights from the lens. Development of the corneal stroma, and the collagenproteoglycan associations that assist define its structure and performance. The lens: a classical mannequin of embryonic induction offering new insights into cell willpower in early improvement. Remodelling of the human vitreous and vitreoretinal interface � a dynamic course of. Changes in the variety of axons in the human embryonic nerve from eight to 10 weeks of gestation. Maintaining transparency: a evaluation of the developmental physiology and pathophysiology of two avascular tissues. Abnormal migration and distribution of neural crest cells in Pax6 heterozygous mutant eye, a mannequin for human eye ailments. Development, composition, and structural preparations of the ciliary zonule of the mouse. A quantitative research of the prenatal development of the aqueous outflow system in the human eye. Iris movement mediates vascular apoptosis throughout rat pupillary membrane regression.
Generic skelaxin 400 mg with visa
It happens primarily muscle relaxant that starts with the letter z skelaxin 400 mg buy discount online, but not completely muscle relaxant ibuprofen cheap skelaxin 400 mg line, in individuals of American Indian heritage. There is photophobia and blepharospasm with secondary corneal scarring and vascularization. Vitamin A deficiency should be excluded as a reason for conjunctival keratinization. Childhood blepharokeratoconjunctivitis: characterising a extreme phenotype in white adolescents. Chloramphenicol treatment for acute infective conjunctivitis in children in primary care: a randomised double-blind placebo-controlled trial. A randomised placebo-controlled trial of topical steroid in presumed viral conjunctivitis. Identification and control of nosocomial adenovirus keratoconjunctivitis in an ophthalmic division. Systematic review and metaanalysis of randomised clinical trials on topical remedies for vernal keratoconjunctivitis. Risk factors for the event of ocular problems of Stevens-Johnson syndrome and poisonous epidermal necrolysis. Ocular manifestations and complications of Stevens-Johnson syndrome and poisonous epidermal necrolysis: an Asian series. Technique of amniotic membrane transplant dressing in the management of acute Stevens-Johnson syndrome. A modified symblepharon ring for sutureless amniotic membrane patch to treat acute ocular surface burns. Onset of ocular graft-versushost illness symptoms after allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation. Cultivated limbal epithelial transplantation in youngsters with ocular floor burns. The influence of topical corticosteroid use earlier than diagnosis on the finish result of Acanthamoeba keratitis. Antiviral treatment and different therapeutic interventions for herpes simplex virus epithelial keratitis. The mycotic ulcer remedy trial: a randomized trial comparing natamycin vs voriconazole. They all had been male, antinuclear antibody negative, and 6 of the seven had polyarticular joint involvement. San Francisco: American Academy of Ophthalmology, 2002: Ophthalmology Monographs; Volume 15. Ocular manifestations in pediatric patients with acquired immunodeficiency syndrome. Ocular disease in youngsters with vertically acquired human immunodeficiency virus infection. Ocular manifestations of an infection with the human immunodeficiency virus in an African pediatric inhabitants. Human immunodeficiency virus infection in a toddler presenting as herpes zoster ophthalmicus. Prevalence and risk elements for developing ophthalmic manifestations in pediatric human immunodeficiency virus an infection. Immune reconstitution inflammatory syndrome in human immunodeficiency virus-infected kids in Peru. Correlation between severity of dysmorphism and age at analysis of immunodeficiency. Progressive outer retinal necrosis attributable to varicella-zoster virus in children with acquired immunodeficiency syndrome. In the absence of ocular signs or symptoms, we recommend that youngsters with severe immunosuppression obtain a dilated eye examination every 2�3 months, that those with advanced immunosuppression be examined every 6 months, and that these with mild or no immunosuppression be seen yearly. A exact prognosis allows good counseling of patients and households and an educated guess at visual outcomes and screening for possible future issues. Anophthalmos and microphthalmos Anophthalmos and microphthalmos are uncommon, with an incidence of between 6 and thirteen per a hundred,000 stay births. The imply axial length of the human full-term neonatal and adult eyes are roughly 17. This retardation of orbital development is halved when an orbital implant is used, and the severity of the general reduction in volume diminishes if the insult occurs at a later date. In consecutive or degenerative anophthalmos, an optic vesicle types, however subsequently degenerates. The presence of optic nerves, chiasm, or tract with anophthalmos might point out this pathogenesis. Many causes for anophthalmos have been proposed; these merge with the causes of microphthalmos (see below). Bilaterality and elevated severity indicate an early teratogenic or genetic developmental occasion. Microphthalmos It is important for the clinician to distinguish between isolated microphthalmos, colobomatous microphthalmos, and microphthalmos associated with systemic issues. Making the correct analysis will direct acceptable counseling of sufferers and their households. Although microphthalmos is often related to a small cornea, there could additionally be microphthalmos with a normal cornea, and microcornea without microphthalmos. Inadequate postnatal growth, secondary to decreased dimension of the optic cup, altered vitreous composition, and low intraocular strain, might play a role within the pathogenesis of simple micophthalmos. Idiopathic isolated microphthalmos Vision is variably affected, relying on the degree to which the eye is microphthalmic in addition to related excessive errors of refraction and consequent amblyopia. A Inherited isolated microphthalmos Although most circumstances had been previously thought to be sporadic,26 many have been found to be autosomal dominant or autosomal recessive. A excessive fee of consanguinity suggests an autosomal recessive inheritance in some instances. It is secondary to failure of optic fissure closure and the protrusion of a cyst from the coloboma. Because the cyst communicates with the attention, its removing could deflate the microphthalmic eye necessitating the removing of the latter. A three-generation household has been described with aniridia, anophthalmos, and microcephaly. An abortive form: the higher lid is partly fused with the upper cornea and conjunctiva and could additionally be colobomatous. A fourth autosomal dominant type exists during which the upper lid is very tall and fused with the lower one at the margins.