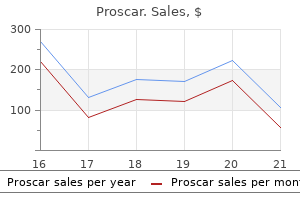
Proscar dosages: 5 mg
Proscar packs: 30 pills, 60 pills, 90 pills, 120 pills, 180 pills, 270 pills, 360 pills

Best 5 mg proscar
However prostate cancer ketoconazole proscar 5 mg generic free shipping, warning is required given recent observations that inhibition of power metabolism might have unintended consequences in some combinations (244) androgen hormone and pregnancy 5 mg proscar cheap mastercard. The molecular composition and association of the mycobacterial cell envelope, categorised as Gram positive however comprising an outer membrane and a periplasmic house, is kind of well understood and broadly includes three distinct layers (251, 253, 254). Exterior to the plasma membrane, a peptidoglycan layer links covalently to a mycolyl-arabinogalactan layer which is decorated with noncovalently linked lipids and lipoglycans such as the phosphatidylinositol mannosides, phthiocerol dimycocerosates, phenolic glycolipids, and lipoarabinomannan, which have been investigated for his or her roles in mycobacterial pathogenicity (255) and as diagnostic markers (256, 257). This outer membrane or "mycomembrane" is, in flip, surrounded by a loosely hooked up capsular layer predominantly comprising polysaccharides and proteins (95, 253). Less well understood is how the development, upkeep, and remodeling of the cell envelope are regulated and accomplished in concert with the mycobacterial cell cycle, 67. Mycobacterium tuberculosis Metabolism 1115 particularly in vivo in different host microenvironments (258, 259). Here, an rising theme is the application of superior, live-cell and time-lapse imaging in combination with elegant fluorescent bioreporters, in most cases fluorophore-linked analogs of pure cell wall precursors that are integrated into the cell wall without significant impairment of mycobacterial development (260�265). Moreover, advances in mass spectrometry have enabled the cataloguing of cell wall lipids, fatty acids, and proteins with ever greater decision (266), including beneath different growth circumstances (267), in response to drug therapy (268), and in drug resistance and drug tolerance (94, 269). Compound permeation (288), xenobiotic metabolism (289), and efflux (290�292) are three main innate mechanisms of drug resistance, all of which are poorly understood and correspondingly difficult to demonstrate or quantify. Though intuitively engaging, the evidence to support this conclusion remains scarce. Similarly, regardless of the frequency with which the inactivity of many compounds in opposition to M. The inability to decide rapidly and reliably whether a compound-and its analogs in a structure-activity relationship analysis-has misplaced activity owing to differential (lost) target engagement, inactivation by way of metabolic transformation, extrusion by efflux, or failure to penetrate severely undermines medicinal chemistry efforts. Without complete details about the fate of the utilized molecule, efforts to optimize physicochemical properties toward a drug-like lead are based mostly virtually completely on expertise, intuition, and empiricism. The scarcity of methods to enable rapid dedication of the intrabacillary accumulation and metabolism of compounds, even perhaps impartial of inhibitory activity, therefore presents a major obstacle to rational drug growth and means that strategies employed in different model systems (296, 297) might be usefully tailored to this end. This impression will, however, require confirmation via the use of superior metabolomics approaches to elucidate the Accessing Nutrients from the Host the number of M. Though deep sequencing suggests the chance for transmission of multiple genotypes (270), most historical estimates are that a single bacillus may be sufficient (271). Whatever the number, proliferation is determined by the ability of the invading pathogen to assimilate host nutrients for energy consumption and macromolecular synthesis. This obvious incongruity has pushed the seek for potential transport and porin proteins within the mycobacterial outer membrane (278, 279). In an intriguing twist, parallel work has suggested that, contrary to the connotations of its explosive moniker, the mycobacterial toxin might ship a "blast without power" (285), leading to necrotic cell death that may intentionally limit immunogenicity. That is, the availability of any nutrient should be distinguished from its accessibility to the infecting M. Harnessing Metabolism to Potentiate Drug Activity Earlier sections highlighted a few of the ways during which different intrinsic metabolic functions contribute to the innate resistance of M. Increasingly, nevertheless, information of metabolic perform is being exploited not solely to circumvent innate resistance mechanisms, but additionally to understand the metabolic features which might subvert antibiotic efficacy so as to determine novel countermeasures (64, 311, 312). Recent work highlighting the contribution of altered propionate metabolism to the emergence of drug resistance in M. Moreover, the rising variety of studies demonstrating altered metabolic operate in drug-resistant organisms, together with M. A corollary to the above is that metabolism might also be harnessed to improve drug action. For instance, the inferred mechanism of action of the repurposed agent, clofazimine, which triggers a redox cycling mechanism that generates toxic reactive oxygen species (315), reinforces the notion that bacilli could be trapped in a futile and in the end damaging metabolism. Notably, by combining clofazimine with other compounds targeting elements of the mycobacterial electron transport chain, Steyn and colleagues demonstrated the potential to enhance killing of M. In a similar example of this strategy, inactivation of the essential maltosyltransferase, GlgE, was shown to trigger an amplification loop which resulted in speedy mycobacterial demise owing to self-poisoning by maltose 1-phosphate accumulation (316). This strategy is distinct from both metabolic bypass (in which an alternate, perhaps less efficient or autonomous, mechanism exists to allow era of the identical important metabolite. A current report describing the identification of chemical inhibitors of the stringent response enzyme, RelMtb, a (p)ppGpp synthetase, offers a cogent demonstration of the potential of this therapeutic strategy (317). To some extent, this strategy overlaps with the thought, summarized in a latest evaluate, of creating "metabolismtargeted adjuvant therapies" to forestall antibiotic tolerance (311). In addition, they supply a number of illustrations of the potential to achieve or enhance antimycobacterial activity by interfering with bacillary metabolism. These embrace the direct inhibition of specific "tolerance/persistence" effectors such as isocitrate lyase (320) or nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide synthetase, NadE (321). Of explicit curiosity, although, is the proposition that stimulating bacillary respiration and vitality metabolism, for instance, by offering a glycolytic substrate along with another terminal electron acceptor corresponding to fumarate (322), can increase efficacy of recognized antibacterial brokers in opposition to apparently recalcitrant subpopulations. This idea not solely reinforces the influence of metabolic state on antibiotic efficacy (an apparent conclusion), however it also suggests the potential to manipulate bacillary metabolism artificially via the deliberate provision of nutrients which could drive a defined metabolic program that ensures susceptibility to the utilized agent. That is, it opens the door for a mix comprising an (inhibitory) antibiotic and a (stimulatory) metabolite. As noted above, figuring out the metabolic and physiological states adopted by the tubercle bacillus in the contaminated human host represents the ultimate word aim and, though nonetheless a significant challenge, seems increasingly attainable with the development of latest technologies. A recent techniques pharmacology examine (198) suggests another approach to this problem, namely, the potential to combine empirical knowledge derived from in vitro and in vivo experiments-ideally together with medical samples (197, 328)-to generate a complex mathematical model that simulates disease development inside a single locus. Their approach enabled a compelling demonstration of the capacity to incorporate both host and bacillary factors in constructing the model and, at the same time, raised the likelihood that this strategy could presumably be adapted to (or knowledgeable by) metabolomic, proteomic, and lipidomic information. Notably, the research also highlighted the emergent properties of a fancy system comprising infecting bacilli and various varieties of host immune cells (the variety was essentially restricted to a handful of T cell subsets and macrophage phenotypes owing to the demands of computational modeling). Again, this implies the potential to enable key insights into the dominant metabolic pathways active in several lesions, how these would possibly affect infection trajectories and pathological outcomes, and the way they may be exploited for improved chemotherapy. We apologize to those authors whose work was not cited here owing to area limitations. Large genomics datasets shed gentle on the evolution of the Mycobacterium tuberculosis complex. The world burden of tuberculosis: outcomes from the Global Burden of Disease Study 2015. The South African tuberculosis care cascade: estimated losses and methodological challenges. The epidemiological benefit of preferential targeting of tuberculosis management on the poor. Armed battle and inhabitants displacement as drivers of the evolution and dispersal of Mycobacterium tuberculosis. Reduced transmissibility of East African Indian strains of Mycobacterium tuberculosis. Mapping of genotype-phenotype variety among clinical isolates of Mycobacterium tuberculosis by sequence-based transcriptional profiling. Gene expression fashions based on a reference laboratory strain are poor predictors of Mycobacterium tuberculosis complex transcriptional variety. Functional and evolutionary genomics of Mycobacterium tuberculosis: insights from genomic deletions in 100 strains.
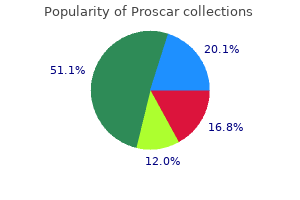
Effective 5 mg proscar
Roblin P androgen hormone vasopressin cheap proscar 5 mg line, Guillet V prostate cancer joint pain generic 5 mg proscar with amex, Joubert O, Keller D, Erard M, Maveyraud L, Pr�vost G, Mourey L. A covalent S-F heterodimer of leucotoxin reveals molecular plasticity of beta-barrel pore-forming toxins. The main websites of colonization are the skin and mucous membranes, and roughly 30% of the wholesome adult inhabitants are colonized by S. The commonest issues are pores and skin infections, and a few of the most severe are bloodstream infections, endocarditis, osteomyelitis, and necrotizing fasciitis (2). These accessory elements are used to set up dominance in the host and contribute to the pathogenicity of S. The functions of those molecules embody adherence to host cells, evasion of host defenses, nutrient degradation, and acquisition. These accessory genetic elements are encoded instantly on the chromosome and on mobile components that embrace phages, plasmids, and pathogenicity islands. Mobile genetic parts, similar to built-in bacteriophages (prophages), are some of the widespread contributors to S. Panton-Valentine leucocidin and the immune evasion cluster are two examples of virulence elements discovered on prophages (6, 7), with the latter being on a bacteriophage built-in into the hlb gene (8). Other important bacteriophage-encoded virulence components embody exfoliative toxin A (9, 10), cell wall-anchored virulence factor SasX (11), staphylococcal inhibitor of complement (scn) (12), staphylokinase (sak), chemotaxis inhibitory protein (chp) (13), and the enterotoxins encoded by sea (14), selk2, and selp (15). Staphylococcal pathogenicity islands are another cell genetic factor that may encode pyrogenic toxins called superantigens. The superantigen genes encoded on staphylococcal pathogenicity islands include poisonous shock toxin (tsst) (16), enterotoxin B (seb), and enterotoxin-like protein Q (selq) (15). The greatest studied of those regulatory techniques is the accessory gene regulator (agr), which was first described in 1986 and encodes a quorum-sensing system that acts as a master virulence regulator (27). Most important among them are the SarA protein family of transcriptional regulators (SarA, Rot, MgrA, etc. The goal of this article is to provide an outline of these regulatory methods (summarized in Table 1), and the interaction and significant features of every system might be covered. AgrB-mediated cleavage of AgrD ends in the formation of an enzyme-bound thiolactone intermediate (33� 35), and through an unclear mechanism this structure is transported across the membrane. This autocatalytic regulation is a hallmark of quorum-sensing techniques and enables S. AgrD is processed and transported into the surroundings by AgrB with the help of signal peptidase SpsB. Alpha-toxin is one of the most distinguished regulated toxins and is a crucial virulence determinant in pores and skin and gentle tissue infections (52, 53), pneumonia (54), and endovascular infections (55). Among these surface proteins, protein A stands out as a end result of its dominant role in pathogenicity in several kinds of S. Impact of Environmental and Host Stimuli on agr Function Because the agr system performs a central role in pathogenesis, S. The following sections outline some of these factors and the mechanisms via which they affect the agr quorum-sensing system. Oxidative stress attributable to reactive oxygen species also can induce disulfide bond formation in AgrA, leaving it incapable of binding its goal promoters (69). Host-derived elements Environmental cues One of the primary abiotic factors described to influence the agr system is pH. It was shown that acidic pH inhibits agr, which may be achieved both via the catabolism of glucose Host serum was one of many first recognized inhibitors of the S. In follow-up studies, it was found that apolipoprotein B inside serum is primarily responsible for this phenotype (73, 74). Initially, this was noticed utilizing the hemoglobin a and b chains, which inhibited exotoxin manufacturing and increased protein A ranges, suggesting that the agr system was repressed (76). Later studies demonstrated that, indeed, hemoglobin downregulates the agr P3 promoter activity and that this can happen during colonization or infection (77). Regulation of Staphylococcus aureus Virulence 673 Regulatory proteins Many studies have defined how S. CodY solely weakly binds to the P2 and P3 promoter areas, and as a substitute binds to a region inside agrC that incorporates the P1 promoter (79, 80). Although the P1 promoter is weak and solely drives agrA expression, the binding of CodY to this area could clarify the negative regulation of agr operate. In contrast to CodY, MgrA is a optimistic regulator of agr expression and belongs to the SarA-family of regulators. These studies used totally different strains, and due to this fact the regulation of agr by MgrA seems to be highly pressure specific. Finally, SarA is a optimistic regulator of agr exercise and one of the best-studied virulence regulators in S. Additionally, agr mutants display a decreased capacity to establish osteomyelitis in a rabbit model (93). Expression of saeR and saeS is driven by the constitutive P3 promoter, which is positioned within the coding region of saeQ (99, 100). Topological studies of the SaeS sensor kinase revealed a 9-amino acid extracellular loop that performs an important function in sign transduction. Three amino acids within the extracellular loop (M31, W32, and F33) had been found to be necessary for SaeS activity. Importance of agr During Infection Numerous research have shown that the agr system is required for various animal fashions of infection. Strains with agr mutations show smaller lesion sizes and decreased bacterial load in murine pores and skin infection models in comparison with wild-type strains (28, 87�90). Phosphorylated SaeR can then bind to the promoter area of goal genes and induce expression of numerous virulence factors (listed). The phosphorelay from SaeS to SaeR is inhibited by the mixed motion of SaeP and SaeQ. In addition, transcription of saeS and saeR is enhanced through the P3 promoter, which is situated within the coding region of saeQ. The inhibitory effect is relieved in an saeP mutant (110), suggesting that the SaeP lipoprotein contributes to this regulatory mechanism. Metals, particularly copper and zinc, intervene with the signal transduction from SaeS to SaeR by inhibiting the SaeS kinase exercise. Interestingly, zinc-bound calprotectin, a neutrophil intracellular protein, protects the Sae system from metal-mediated inhibition via an indirect mechanism (111). The noticed repression is a result of a direct interplay of SrrA with the respective promoters (117). This implies that glucose utilization results in the next demand for manganese in comparability with amino acid utilization. Depending on the strain, a deletion of SraP, SasG, or Ebh (in combination) inside an mgrA mutant background restores the clumping phenotype to wild-type ranges (84).
Generic proscar 5 mg with visa
In a single research utilizing a rat orthopedic implant infection model prostate cancer 1cd 10 cheap 5 mg proscar overnight delivery, native injection of phage significantly decreased S man health advice purchase proscar 5 mg mastercard. Nonconventional Therapeutics against Staphylococcus aureus 779 Pretreating the floor of such gadgets with a coating of phages may also prevent S. Studies analyzing phage-coated orthopedic implants in mice noticed a significant discount in bacterial adherence to the gadget (96) and bacterial load in adjoining tissues (97). Combined, these research counsel that phage remedy could be applicable to a number of S. A few attempts have been made to turn phages into drug delivery systems to enhance the efficacy of S. Additional reviews describe the utilization of phages to transfer the antibiotic chloramphenicol to S. Although the concept of manipulating phages into highly particular drug transfer techniques is appealing, further research is required to additional develop this technique and determine if it could be applicable to the extensive breadth of S. At this time, medical use of therapeutic phages is limited to European countries and the previous Soviet Union (71, 103�105). No formal laws or standards for phage remedy in these international locations exist, so well-documented clinical trials together with sturdy controls are lacking (104). Nevertheless, multiple stories have described constructive scientific outcomes related to phage remedy for a variety of S. These medical reviews, taken together with the growing physique of literature on in vitro and in vivo studies, reveal that phage remedy might be a possible technique for treating S. Due to the excessive specificity of phages, one important disadvantage can be a narrow spectrum of sensitive strains. Immune induction may also lead to the production of antibodies and subsequent clearance of phages, considerably decreasing the efficacy of the remedy (114). Moreover, as viruses are replicating organic agents, it would be extraordinarily difficult to standardize business manufacturing for medical use. Nonetheless, the potential of phage remedy may outweigh the drawbacks within the face of accelerating staphylococcal antibiotic resistance, and therefore it warrants continued consideration. Treatment with lysostaphin systemically or as a fabric coating has shown promise for eradication of S. This suggests that lysostaphin therapy may be an effective decolonization technique (124). Recombinant phage-derived lysins have also been demonstrated to be highly effective antimicrobials in vitro and in vivo (125). During the lytic phage cycle, viral peptidoglycan hydrolases (endolysins) are produced to facilitate the discharge of progeny virions by degrading the bacterial cell wall (126). Phage endolysins are significantly engaging as different antimicrobial candidates because of a high diploma of species and pressure specificity (127). Additionally, endolysins have advanced to bind and cleave extremely conserved buildings within the cell wall without necessitating intracellular transport of the enzyme, thus lowering the potential for resistance growth and avoiding mechanisms that play a role in standard antibiotic resistance. Staphylococcal endolysins can differ considerably at the amino acid sequence level, which is also reflected in their variety of enzymatic and antibacterial properties (129, 130). Combinations of endolysins have been proven to provide a synergistic therapy impact and would also assist decrease the prospect of resistance improvement (131�133). Moreover, recombinant endolysin proteins have the potential to be mass produced for clinical use. A number of endolysins and their antistaphylococcal activity have been characterized, with many identified as being highly efficient at clearing S. Since then, further endolysins with potent lytic actions towards drug-resistant strains of S. Numerous stories indicate that endolysins have the potential to be extremely effective towards pores and skin and soft tissue S. After 2 days, 100 percent of the endolysin-treated mice survived, whereas solely 25% of vehicle-treated mice survived (129). Moreover, intravitreal injection of the engineered endolysin Ply187 significantly reduced bacterial burdens within the eye and preserved retinal perform in a murine model of endophthalmitis (50). Recent attempts have been made to enhance the steadiness and supply of endolysins using nanoparticles. Moreover, complexing LysK in polycationic polymers enhanced enzyme stability and lytic exercise (143). Nanotechnology could prove to be an efficient method to enhance endolysin-based therapies and ensure stability at each storage and physiological temperatures. Notably, the primary technology of staphylococcal phage endolysin-based antimicrobial products is already available on the market, and scientific trials are underway for endolysin-based drugs. These skin merchandise are for the remedy of skin conditions with an infectious component, similar to pimples, rosacea, eczema, and pores and skin irritation, and include the energetic ingredient Staphefekt. It is the first to have undergone a great laboratory practice-compliant safety evaluation together with single and repeated dose toxicity and organ operate research in rats and dogs, in addition to additional pharmokinetics and security testing in monkeys (145, 146). No severe opposed effects were observed for any of the individuals, however there have been reports of gentle headache, fatigue, and myalgia (147). In gentle of those developments, endolysin-based therapies are more probably to be clinically utilized within the near future. Recent research have demonstrated that reprograming Cas9 to goal bacterial genomic sequences can lead to efficient cell killing (155, 156). Similar outcomes were observed when phagemids had been topically utilized in a murine skin colonization model. These results recommend that programming Cas9 nuclease to be a sequencespecific antimicrobial could be an effective remedy strategy, significantly against drug-resistant S. As talked about within the earlier part, bacteriophage supply methods are related to numerous drawbacks, not limited to lowered host range, poor penetration to areas of infection, and potential adverse well being results. Additional studies examining using nanoparticles and other alternative delivery techniques are warranted. Nonconventional Therapeutics towards Staphylococcus aureus 781 and upon illumination with gentle of a specific wavelength, turn into activated from a floor state to an excited state. Various biomolecules are affected throughout this process, specifically proteins, nucleic acids, and unsaturated lipids, resulting in irreversible injury and cell dying (163, 164). In some instances, the direct mechanism of cytotoxicity has been investigated, which depending on the photosensitizer and its subcellular location, may be attributed to inactivation of enzymes, damage to the cell membrane, or oblique injury to the chromosome (164�168). Most antimicrobial photosensitizers tested are natural, fragrant dyes, particularly porphyrins, chlorines, phthalocyanine, rose bengal, phenothiazines, and acridines (174). Although numerous photosensitizers have been approved to be used in humans, only a select few have been utilized clinically to treat microbial infections. For example, combining 50 g/ml toluidine blue O and a 15-minute publicity to an 632. Administration of the photosensitizer toluidine blue and a pink diode laser resulted in a direct bacterial reduction of 97% within the bone tissues of S. Continued analysis into the molecular markers that predict strain responses to photo-inactivation will assist in the improvement of more practical therapy modalities sooner or later. This novel method of focusing on the antimicrobial resistance mechanism itself resulted in little or no nonspecific photosensitizer uptake by host cells in vitro (205).
Generic 5 mg proscar amex
Correlation of cell membrane lipid profiles with daptomycin resistance in methicillinresistant Staphylococcus aureus prostate cancer 12 tumors proscar 5 mg buy low cost. Small-colony mutants of Staphylococcus aureus enable selection of gyrase-mediated resistance to dual-target fluoroquinolones prostate cancer hematuria buy proscar 5 mg low price. Bactericidal impact of tomatidine-tobramycin mixture towards methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus and Pseudomonas aeruginosa is enhanced by interspecific small-molecule interactions. Deferiprone and gallium-protoporphyrin have the capacity to potentiate the exercise of antibiotics in Staphylococcus aureus small colony variants. Distinguishing between resistance, tolerance and persistence to antibiotic therapy. Persistent and relapsing infections related to small-colony variants of Staphylococcus aureus. Selection for Staphylococcus aureus smallcolony variants as a end result of development in the presence of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Bacterial interactions and the microevolution of cytochrome bd: implications for pathogenesis. Small-colony variant selection as a survival strategy for Staphylococcus aureus within the presence of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Pseudomonas aeruginosa exoproducts determine antibiotic efficacy towards Staphylococcus aureus. Interspecific small molecule interactions between scientific isolates of Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Staphylococcus aureus from grownup cystic fibrosis patients. Staphylococcus aureus small-colony variants are independently associated with worse lung disease in youngsters with cystic fibrosis. Staphylococcus aureus serves as an iron supply for Pseudomonas aeruginosa throughout in vivo coculture. Role of lipid within the formation and function of the respiratory system of Staphylococcus aureus. Antibiotic exercise against small-colony variants of Staphylococcus aureus: review of in vitro, animal and medical information. Physiology and antibiotic susceptibility of Staphylococcus aureus small colony variants. Comparative in vitro exercise of finafloxacin in opposition to staphylococci displaying regular and small colony variant phenotypes. Oritavancin kills stationary-phase and biofilm Staphylococcus aureus cells in vitro. Staphylococcus aureus develops elevated resistance to antibiotics by forming dynamic small colony variants throughout continual osteomyelitis. Characterization of a vraG mutant in a genetically steady Staphylococcus aureus smallcolony variant and preliminary assessment to be used as a liveattenuated vaccine in opposition to intrammamary infections. Pharmacodynamic analysis of the activity of antibiotics in opposition to hemin- and menadione-dependent small-colony variants 561 142. Generation of persister cells of Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Staphylococcus aureus by chemical remedy and evaluation of their susceptibility to membrane-targeting brokers. Impact of Staphylococcus aureus on the pathogenesis of persistent cystic fibrosis lung illness. Phenotypic and genetic changes in the life cycle of small colony variants of Salmonella enterica serotype Typhimurium induced by streptomycin. Chronic prosthetic hip an infection attributable to a small-colony variant of Escherichia coli. In vitro serial passage of Staphylococcus aureus: adjustments in physiology, virulence issue production, and agr nucleotide sequence. Synthesis and deformylation of Staphylococcus aureus delta-toxin are linked to tricarboxylic acid cycle activity. Staphylococcus aureus dynamically adapts international regulators and virulence issue expression within the course from acute to chronic infection. Most of them are encoded primarily within the core genome, whereas a few of them are localized within cell components, pathogenic islands, or plasmids. Because these genes are sometimes essential for progress, they represent attention-grabbing targets for the event of other antimicrobial medicine in the battle towards multidrug-resistant S. This technique was used with the guanine and glucosamine-6phosphate (GlcN6P) riboswitches. Its product encodes an essential enzyme, which converts fructose-6-phosphate into GlcN6P, a building block of bacterial peptidoglycan. A current examine led to the design, synthesis, and characterization of a GlcN6P analogue, carba-GlcN6P, which constitutively prompts the glmS ribozyme of vancomycin-resistant S. Very lately, a brand new method referred to as "Term-seq" revealed that several antibiotic resistance genes are underneath the management of riboswitches responding to antibiotics generally used in opposition to Gram-positive pathogenic micro organism corresponding to Listeria spp. Not surprisingly, the presence of antibiotics can also modulate the regulatory exercise of T-boxes. Thereafter, the T-box senses the supply of glycine not just for its incorporation into nascent polypeptide chains during translation but additionally for the formation of pentaglycine bridges into the peptidoglycan molecule, linking two important pathways. Based on sequence and structure conservation, most of the T-boxes and riboswitches had been predicted in S. The consequence trusted the binding sites of the protein synthesis inhibitors (11). The best-studied instance in Gram-positive micro organism is the thermosensor regulating the expression of the transcriptional factor prfA, which activates the expression of a lot of the virulence genes in Listeria monocytogenes at high temperatures (13, 14). No such instance has but been demonstrated for other Gram-positive micro organism, together with S. Such components can doubtlessly be transferred horizontally to other bacterial species or be duplicated (20). Initially, pervasive transcription was thought-about a nonfunctional transcriptional noise. The state of affairs could be much more advanced, as a result of latest outcomes advised that the termination issue Rho performs a significant position in preventing pervasive transcription in Bacillus subtilis, but in addition in S. Three genes have been transcribed from the positive strand and two from the unfavorable strand. Moreover, one small open studying frame was detected within one of many genes from the minus strand and coded for a secreted peptide with similarity to the RelE toxin (32). Interestingly, this locus was expressed in a growthphase-dependent manner, in nutriment hunger, and in oxidative stress. In several cases, a second distinct website of interplay occurs in the coding area. However, whereas the SarA level remains comparatively fixed during bacterial progress, the expression of SprC fluctuates, which means that additional factors would possibly control its synthesis and that a mechanism of derepression should coexist beneath specific circumstances.
Generic 5 mg proscar
Molecular basis for control of conjugation by bacterial pheromone and inhibitor peptides prostate health essentials 5 mg proscar purchase amex. Mechanisms of peptide intercourse pheromone regulation of conjugation in Enterococcus faecalis prostate cancer gleason score 7 prognosis 5 mg proscar purchase with visa. Dominant-negative mutants of prgX: evidence for a role for PrgX dimerization in negative regulation of pheromone-inducible conjugation. Convergent transcription confers a bistable swap in Enterococcus faecalis conjugation. Enterococcus faecalis endocarditis severity in rabbits is reduced by IgG Fabs interfering with aggregation substance. Aggregation and binding substances enhance pathogenicity in rabbit models of Enterococcus faecalis endocarditis. A paracrine peptide intercourse pheromone additionally acts as an autocrine sign to induce plasmid transfer and virulence factor expression in vivo. Induction of surface exclusion (entry exclusion) by Streptococcus faecalis sex pheromones: use of monoclonal antibodies to establish an inducible surface antigen involved in the exclusion process. Identification of pheromone-induced floor proteins in Streptococcus faecalis and evidence of a role for lipoteichoic acid in formation of mating aggregates. Analysis of practical domains of the Enterococcus faecalis pheromone-induced floor protein aggregation substance. The range of conjugative relaxases and its application in plasmid classification. Toxins-antitoxins: plasmid upkeep, programmed cell demise, and cell cycle arrest. Cloning and characterization of a Bacteroides conjugal tetracyclineerythromycin resistance factor by using a shuttle cosmid vector. Integrative and conjugative elements: mosaic mobile genetic elements enabling dynamic lateral gene circulate. Tn916-like genetic parts: a various group of modular mobile parts conferring antibiotic resistance. An in silico evaluation of Tn916 as a software for generalized mutagenesis in Haemophilus influenzae Rd. Molecular characterization of two proteins involved within the excision of the conjugative transposon Tn1545: homologies with different site-specific recombinases. The integrase household of recombinase: group and function of the active site. Major groove recognition by threestranded b-sheets: affinity determinants and conserved structural features. Excision and insertion of the conjugative transposon Tn916 includes a novel recombination mechanism. Evidence that coupling sequences play a frequency-determining function in conjugative transposition of Tn916 in Enterococcus faecalis. Addiction toxin Fst has distinctive results on chromosome segregation and cell division in Enterococcus faecalis and Bacillus subtilis. Solution structure and membrane binding of the toxin fst of the par addiction module. Abundance of sort I toxin-antitoxin systems in bacteria: searches for model spanking new candidates and discovery of novel households. Examination of Enterococcus faecalis toxin-antitoxin system toxin Fst operate utilizing a pheromone-inducible expression vector with tight repression and broad dynamic range. Characterization of the results of an rpoC mutation that confers resistance to the Fst peptide toxin-antitoxin system toxin. A physical and practical analysis of Tn917, a Streptococcus transposon within the Tn3 family that features in Bacillus. Characterization of the gentamicin resistance transposon Tn5281 from Enterococcus faecalis and comparability to staphylococcal transposons Tn4001 and Tn4031. Transfer of Tn5385, a composite, multiresistance chromosomal factor from Enterococcus faecalis. Characterization of the left four kb of conjugative transposon Tn916: determinants concerned in excision. Excision of a conjugative transposon in vitro by the Int and Xis proteins of Tn916. Xis protein binding to the left arm stimulates excision of conjugative transposon Tn916. Xis protein of the conjugative transposon Tn916 plays dual opposing roles in transposon excision. The integrase of the conjugative transposon Tn916 directs strand- and sequence-specific cleavage of the origin of conjugal switch, oriT, by the endonuclease Orf20. Nucleotide sequence of the 18-kb conjugative transposon Tn916 from Enterococcus faecalis. Circularization of Tn916 is required for expression of the transposon-encoded switch features: characterization of long tetracycline-inducible transcripts studying via the attachment site. Inducibility of Tn916 conjugative transfer in Enterococcus faecalis by subinhibitory concentrations of ribosome-targeting antibiotics. Conjugative transposition of Tn916: the transposon int gene is required solely in the donor. Conjugative switch of Tn916 in Enterococcus faecalis: trans activation of homologous transposons. When phage, plasmids, and transposons collide: genomic islands, and conjugative- and 423 287. Investigating the mobilome in clinically necessary lineages of Enterococcus faecium and Enterococcus faecalis. Characterization of three plasmid deoxyribonucleic acid molecules in a pressure of Streptococcus faecalis: identification of a plasmid figuring out erythromycin resistance. Conjugation-independent, site-specific recombination on the oriT of the IncW plasmid R388 mediated by TrwC. Axe-Txe, a broad-spectrum proteic toxin-antitoxin system specified by a multidrugresistant, scientific isolate of Enterococcus faecium. Conjugative switch of the virulence gene, esp, amongst isolates of Enterococcus faecium and Enterococcus faecalis. Intra- and interspecies genomic switch of the Enterococcus faecalis pathogenicity island. Pyrosequencing-based comparative genome evaluation of the nosocomial pathogen Enterococcus faecium and identification of a giant transferable pathogenicity island. A composite bacteriophage alters colonization by an intestinal commensal bacterium. Lepage E, Brinster S, Caron C, Ducroix-Crepy C, Rigottier-Gois L, Dunny G, Hennequet-Antier C, Serror P.
Proscar 5 mg cheap mastercard
In vitro interplay of the housekeeping SecA1 with the accent SecA2 protein of Mycobacterium tuberculosis mens health lists 5 mg proscar purchase mastercard. Identification of two Mycobacterium smegmatis lipoproteins exported by a SecA2-dependent pathway cortical androgen stimulating hormone generic proscar 5 mg on-line. SecA2-dependent secretion of autolytic enzymes promotes Listeria monocytogenes pathogenesis. The SecA2 pathway of Mycobacterium tuberculosis exports effectors that work in concert to arrest phagosome and autophagosome maturation. A redox regulatory system crucial for mycobacterial survival in macrophages and biofilm development. PknG senses amino acid availability to management metabolism and virulence of Mycobacterium tuberculosis. Isolation of Mycobacterium tuberculosis mutants defective in the arrest of phagosome maturation. Genetic analysis of superoxide dismutase, the 23 kilodalton antigen of Mycobacterium tuberculosis. High-level heterologous expression and secretion in rapidly growing nonpathogenic mycobacteria of four major Mycobacterium tuberculosis extracellular proteins thought of to be main 1147 104. Site-directed mutagenesis of the katG gene of Mycobacterium tuberculosis: results on catalase-peroxidase actions and isoniazid resistance. Protein export by the mycobacterial SecA2 system is determined by the preprotein mature area. Mycobacterium tuberculosis SatS is a chaperone for the SecA2 protein export pathway. A protein secretion pathway important for Mycobacterium tuberculosis virulence is conserved and practical in Mycobacterium smegmatis. Purification and characterization of a lowmolecular-mass T-cell antigen secreted by Mycobacterium tuberculosis. Acute infection and macrophage subversion by Mycobacterium tuberculosis require a specialized secretion system. Phagosomal rupture by Mycobacterium tuberculosis results in toxicity and host cell death. The primary mechanism of attenuation of bacillus Calmette-Guerin is a loss of secreted lytic function required for invasion of lung interstitial tissue. C-terminal sign sequence promotes virulence factor secretion in Mycobacterium tuberculosis. Solution structure of the Mycobacterium tuberculosis EsxG�EsxH complex: practical implications and comparisons with 1149 163. Differential detergent extraction of Mycobacterium marinum cell envelope proteins identifies an extensively modified threonine-rich outer membrane protein with channel activity. A novel lipase belonging to the hormone-sensitive lipase household induced under hunger to utilize saved triacylglycerol in Mycobacterium tuberculosis. Correlation of phenotypic profiles using focused proteomics identifies mycobacterial esx-1 substrates. Di Luca M, Bottai D, Batoni G, Orgeur M, Aulicino A, Counoupas C, Campa M, Brosch R, Esin S. The mycosins of Mycobacterium tuberculosis H37Rv: a family of subtilisin-like serine proteases. Mycosin-1, a subtilisin-like serine protease of Mycobacterium tuberculosis, is cell wall-associated and expressed during an infection of macrophages. Folding mediated by an intramolecular chaperone: autoprocessing pathway of the precursor resolved through a substrate assisted catalysis mechanism. Pentapeptide boronic acid inhibitors of Mycobacterium tuberculosis MycP1 protease. Stephan J, Bender J, Wolschendorf F, Hoffmann C, Roth E, Mail�nder C, Engelhardt H, Niederweis M. The growth rate of Mycobacterium smegmatis depends on enough porin-mediated inflow of nutrients. An outer membrane channel protein of Mycobacterium tuberculosis with exotoxin exercise. Identification of an anionspecific channel in the cell wall of the Gram-positive bacterium Corynebacterium glutamicum. Biochemical and biophysical characterization of the cell wall porin of Corynebacterium glutamicum: the channel is fashioned by a low molecular mass polypeptide. Identification and characterization of PorH, a brand new cell wall channel of Corynebacterium glutamicum. Mycobacterium tuberculosis EspB binds phospholipids and mediates EsxA-independent virulence. Comparative proteome analysis of tradition supernatant proteins from virulent Mycobacterium tuberculosis H37Rv and attenuated M. Insights on the emergence of Mycobacterium tuberculosis from the evaluation of Mycobacterium kansasii. Structure of Staphylococcus aureus EsxA suggests a contribution to virulence by action as a transport chaperone and/or adaptor protein. Staphylococcal Esx proteins modulate apoptosis and release of intracellular Staphylococcus aureus throughout an infection in epithelial cells. High ranges of DegU-P activate an Esat-6-like secretion system in Bacillus subtilis. Mycobacterium tuberculosis makes use of host triacylglycerol to accumulate lipid droplets and acquires a dormancy-like phenotype in lipid-loaded macrophages. Protein Export across the Mycobacterial Cell Envelope complete characterization of trafficking modes, processing, mechanisms of action, immunity and ecology using comparative genomics. Protective immunity towards tuberculosis induced by vaccination with major extracellular proteins of Mycobacterium tuberculosis. Comprehensive evaluation of exported proteins from Mycobacterium tuberculosis H37Rv. Mycobacterium tuberculosis exploits asparagine to assimilate nitrogen and resist acid stress during infection. Indeed, the examine of diphtheria toxin established the structure-function paradigm for the examine of other toxins within the bacterial protein toxin area. Moreover, when coupled with the molecular genetic examine of the iron-activated regulatory component, DtxR, that controls the expression of diphtheria toxin, we now have an in depth understanding of the entire tox genetic system, from the regulation of expression to the molecular mechanism of diphtheria toxin motion. In this article, we review the development of our present understanding of diphtheria toxin, from its structure-function relationships to its mechanism of entry into the eukaryotic cell cytosol, the molecular mechanism of transition metal ion activation of DtxR and its regulation of tox expression, and finally, the protein engineering of diphtheria toxin for the event of highly potent and selective cellsurface receptor-targeted fusion protein toxins for the therapy of human diseases. It is well known that to cause scientific disease, the etiologic agent of diphtheria, Corynebacterium diphtheriae, must first be infected with one of a intently related family of bacteriophages that carry the structural gene for the toxin.
Proscar 5 mg buy discount online
The b-barrel pore is fashioned from a prepore by a conformational change in a toxin substructure often known as the amino latch (5) prostate 3 times normal size proscar 5 mg buy lowest price. Although lower than 40% of medical isolates from the United States carry a pvl-encoding prophage prostate cancer brachytherapy 5 mg proscar order otc, over 90% of strains associated with severe necrotizing pneumonia and community-acquired infections carry pvl (1, 52). Deletion of pvl ends in much less irritation, reduces tissue accidents and bacterial burden, and promotes host survival (57, 60). This locus includes three genes: the hlgA gene, transcribed by its personal promoter, followed by an operon containing hlgC and hlgB, transcribed by a different promoter (66). Intravitreal injection of g-hemolysins in rabbits is highly toxic, resulting in destruction of the eye and tissue harm in surrounding areas (69). The tissue injury could be the results of a mixture of toxin-mediated cell lysis and pyroptosis attributable to sublytic focus of the psma1 to psma four Phenol soluble modulins Exfoliative toxin A eta Exfoliative toxin B etb slow-eluting subunit, S-subunit, named on the idea of their liquid chromatography habits (28, 29). The current mannequin for leukocidin pore formation means that the S-subunit recognizes and binds to a surface receptor on the goal cell after which recruits the F-subunit for dimerization (30�32). This is followed by oligomerization with three additional dimers to type an octameric prepore on the target cell membrane (33). LukA has an 33-amino acid sequence on the N-terminus and a 10-amino acid C-terminal tail that are absent from different S-subunits, contributing to its divergence. The prestem domains of the prepore then extend to form a b-barrel pore that punctures the goal cell membrane. Upon receptor binding, the S-subunit dimerizes with the F-subunit, adopted by oligomerization of three further leukocidin dimers, leading to an octameric prepore. Similar to the a-toxin pore formation model, the prestem domains of the prepore extend to form a b-barrel pore, thus disrupting the goal cell membrane. The two genes within the locus, lukE and lukD, are cotranscribed during the late exponential phase (73). Retroorbital administration of microgram quantities of the toxin leads to acute lethality in mice (68). The amino latch is colored blue, the cap area red, the rim domain pink, and the prestem area green. The amino latch of HlgB is blue; the cap area for HlgA is cyan and HlgB is beige; the rim domains are yellow for HlgA and pink for HlgB; and the prestem domains are green. The HlgA protomers are cyan, the HlgB protomers are beige, and the b-barrel pore is green. The toxin is found in abundance within the secreted proteome in the course of the late exponential growth phase, which led to its discovery (78, 79). The C-terminal region of LukA is important for toxin exercise, because its deletion or mutation within this region. Since this can be a recently identified toxin, the regulation of e-toxin expression and the mode of action of the toxin are unknown. Lytic concentration of e-toxin in keratinocytes promotes the secretion proinflammatory cytokine, interleukin 8 (105). In distinction, sublytic concentration of e-toxin slows the speed of keratinocyte proliferation, suggesting a job for the toxin in impairing regular wound healing (105). A microgram amount of e-toxin can result in neutrophil recruitment to the injection web site when administered subcutaneously in rabbits (105). Moreover, the same dosage of e-toxin could cause rabbits to develop fever after intravenous administration of the toxin (105). Due to their extreme stability and excessive toxicity in people, some of them are classified as choose brokers for bioterrorism. However, the International Nomenclature Committee for Staphylococcal Superantigens renamed them in 2004 to mirror their lack of emetic and mitogenic properties (114). They were originally named for their capability to induce emesis, a key attribute of staphylococcal meals poisoning (114). Conventional antigens bind to B cell receptors on the complementarity-determining area (blue), a hypervariable region that confers antigen specificities. SpA binds at a continuing region of the receptor to activate B cells for supraclonal enlargement, which ends up in clonal deletion of SpA-activated B cells. B cell Superantigen Staphylococcal protein A (SpA) is the only recognized B cell superantigen produced by S. Mature SpA has 4 to 5 extremely conserved immunoglobulin (Ig) binding domains related by brief linkers at the N-terminus (131). These are followed by a hypervariable area called area X, which contains subregions Xr and Xc (132). The extremely variable and repetitive octapeptide in Xr is the idea of SpAtyping, a high-throughput method of grouping S. However, SpA proteins could be launched from the cell wall by the cell wall hydrolase, LytM (133). The Ig binding domains confer upon SpA the power to bind the Fcg portion of Igs to stop opsonization (134). During intravenous infection, SpA prevents opsonophagocytosis of the micro organism by sequestering Igs and impedes the event of particular anti-S. Cytotoxic Enzymes b-toxin (also often identified as b-hemolysin) the b-toxin encoding gene, hlb, is part of the core S. The prophage carries the immune evasion gene cluster encoding for immune evasion elements, such because the staphylococcal complement inhibitor proteins, chemotaxisinhibitory proteins, and staphylokinase (145). This toxin was first recognized in 1935 by Glenny and Stevens based mostly on a number of unique observations: hemolysis of erythrocytes within the presence of a-toxin neutralizing serum, lysis of sheep however not rabbit erythrocytes, and enhanced hemolysis caused by the temperature shifting from 37�C to a decrease temperature (152). This unique phenomenon is the results of ceramide hydrolysis products at 37�C being held collectively by cohesive forces within the membrane. Later, b-toxin was shown to enhance biofilm formation via catalyzing the formation of nucleoprotein matrix in biofilms; due to this fact, b-toxin can be a biofilm ligase (155). Intranasal administration of b-toxin induces the shedding of syndecan1, a serious heparan sulfate proteoglycan molecule on lung epithelial cells, and causes neutrophil infiltration into the lungs in mice (162). Desmogleins are cadherins which are required for desmosome cell-to-cell adhesion to preserve the integrity of the epidermis. Cleavage of Dsg1 disrupts the cell-to-cell adhesion of the dermis, resulting in blistering and desquamation of the superficial skin. The previous section mentioned the mechanisms of toxin-mediated host immune evasion and their roles in S. They could be broadly categorized into two teams: cofactors that activate host zymogens and enzymes for degradation of tissue components (Table 2). While these cofactors and secreted enzymes (exoenzymes) have totally different substrates and mechanisms of action, they perform to break down bacterial and host molecules for nutrient acquisition, bacterial survival, and dissemination. Cofactors for Host Enzyme Activation Coagulase (Coa), von Willebrand issue binding protein (vWbp), and staphylokinase (Sak) are cofactors produced by S. These three proteins hijack completely different features of the host coagulation system, thereby manipulating the host innate defenses to promote bacterial survival and dissemination. Staphylococcal coagulases: Coa and vWbp the ability to induce coagulation is doubtless one of the key criteria used in trendy medical microbiology for species classification within the genus Staphylococcus-separating coagulase-positive and coagulase-negative species. A majority of staphylococci are coagulase negative, but a few are coagulase optimistic species, including S. The causative brokers, Coa and vWbp, are highly energetic in coagulating human and rabbit plasma (183).