Maxolon dosages: 10 mg
Maxolon packs: 60 pills, 90 pills, 120 pills, 180 pills, 270 pills, 360 pills

Discount maxolon 10mg overnight delivery
The columns are washed extensively to take away unwanted proteins after which eluted with an answer that disrupts the antibody binding gastritis que no comer 10mg maxolon discount. Because of their similar structures gastritis diet quiz maxolon 10mg order fast delivery, they have an inclination to co-purify by many of the strategies used to isolate them from plasma. Later, ion change chromatography resins had been used with cryo-poor plasma with the advantage that the supernatant plasma can then be further fractionated by the Cohn method for the production of immune globulins, albumin, and other merchandise with little loss in yield. However, the first technology of recombinant products used animal-derived proteins and sera of their cell tradition media and in the manufacturing of the monoclonal antibodies used for purification, plus human albumin to stabilize the products in the ultimate vial, all potential sources of viral contamination. With this in mind, manufacturers went nonetheless additional to develop recombinant products completely freed from human and animal proteins, both in their manufacturing processes and in their formulations. Most current production strategies for recombinant merchandise also incorporate viral inactivation or removal procedures for an added measure of security. However, it has a decrease recovery when infused into sufferers, apparently due to differences in posttranslational glycosylation. There are two major means of treating bleeding in inhibitor patients, both based on administration of activated clotting components. Many of the clotting factors circulate as inactive zymogens that are solely activated as needed in the coagulation cascade. That could be the similar purpose that it can be thrombogenic, however that concept has not been confirmed conclusively. It is cleaved by thrombin to type fibrin, a protein that naturally selfassociates to kind a clot. Interestingly, fibrinogen was additionally one of many first plasma products used, but it was soon taken off the market because it nearly universally transmitted viral infections. Significant viral removing has also been demonstrated for its purification process, and the resulting product is considered protected. It is made in the milk of goats and likewise purified by heparin affinity chromatography. Fibrin Sealant and Thrombin Fibrinogen and thrombin are also used as topical hemostatic brokers, together as fibrin sealant and as stand-alone thrombin concentrates. The fibrin sealant and thrombin merchandise out there in the United States are listed in Table 117-5. Fibrin sealant uses the clot-forming response of thrombin and fibrinogen to kind a physiological glue or sealant that has turn out to be extensively used in surgical procedures. Fibrinogen is purified instantly from cryoprecipitate followed by additional purification steps. It belongs to the serpin family named for their exercise as serine protease inhibitors. Prothrombin is autocatalytically activated to thrombin in the presence of calcium. Both the fibrinogen and thrombin elements are additionally treated for viral inactivation and removing. Three stand-alone thrombin merchandise are additionally obtainable for use in selling topical hemostasis. For years, bovine thrombin was the usual of care for such use; nevertheless, research has instructed that it might have been liable for postsurgical hemostatic issues in some patients. The cause was apparently contamination with bovine issue V, against which some patients developed antibodies that crossreacted with their very own human factor V. Presence of the Gla region is absolutely essential for the operate of many of the clotting components but not for thrombin. Although the protein was initially named for its antitrypsin exercise, its primary physiologic operate appears to be the inhibition of neutrophil elastase in the lung. Patients with hereditary deficiencies of this inhibitor develop pulmonary emphysema and liver illness. However, even with 4 merchandise out there, the availability is tight because of the limited quantity ultimately available from plasma. Patients poor in C1 esterase inhibitor are in danger for assaults of hereditary angioedema. Two plasma-derived C1 esterase inhibitor concentrates have been licensed in the United States in 2008 and 2009 after being available in Europe for a number of years. Most of these inhibitors have comparable amino acid and structural properties and are members of a superfamily of proteins known as serpins (serine proteinase inhibitors). There are also potential improvements that might be made to current plasmaderived and recombinant concentrates. In addition to enhanced purification and viral clearance methods, products could be made more person pleasant. For occasion, prophylactic treatment of hemophilia A and B at present requires infusions each 2 or 3 days due to the brief pure half-lives of the proteins in the circulation. Alternate delivery systems could also potentially improve the utility of many merchandise. Delivery of clotting elements by inhalation, ingestion, and subcutaneous injection has been explored. Production of fibrin sealant in a powder form that could probably be sprinkled on a wound has additionally been studied. Thiele T, Steil L, et al: Proteomics of blood-based therapeutics, a promising software for high quality assurance in transfusion medicine. Recombinant Plasma Protein Concentrates Almost all plasma proteins licensed for human use have been cloned and expressed in biologically active form in animal cells in the laboratory, and several have been developed into licensed merchandise, as described earlier. The primary benefits of recombinantly produced proteins embody freedom from human viruses and a probably limitless supply. Transgenic cows, goats, pigs, and sheep can produce large portions of human proteins, typically 1 to 10 g/L in milk. In distinction, animal tissue tradition techniques routinely produce considerably less protein, sometimes zero. Recombinant proteins can be produced in modified types which will give them advantageous new properties such as increased efficiency, longer half-lives, or various specificity. Dolan G: Clinical implications of emerging pathogens in haemophilia: the variant Creutzfeldt-Jakob illness expertise. Chapter 117 Preparation of Plasma-Derived and Recombinant Human Plasma Proteins 1704. Manno this chapter evaluations merchandise obtainable to treat deficiencies of plasma coagulation proteins. The improvement of blood part therapy and subsequently protein concentrates which would possibly be enriched specifically coagulation elements and different proteins made potential the effective treatment of bleeding episodes in sufferers with hemophilia and different diatheses. Edwin Cohn developed an ethanol fractionation process that was amenable to large-scale manufacture.
Generic maxolon 10 mg free shipping
Changes within the human microbiome have been linked at some level to vaginitis gastritis diet ôèëüìû cheap maxolon 10 mg free shipping, atopic dermatitis gastritis peptic ulcers symptoms 10 mg maxolon purchase with amex, eczema, meals allergy, obesity, inflammatory bowel illness, pouchitis, celiac illness, and colorectal cancer. With the appearance of new technologies, for example, high-throughput 454 pyrosequencing and metagenomics, will in all probability be potential to determine all microbial community members, both rare and ample, and explore extra deeply the role they play in human health and disease. Overview of the gastrointestinal microbiota Gi Microbiota and Regulation of the Immune System, Vol. Manichanh C, Rigottier-Gois L, Bonnaud E, Gloux K, Pelletier E, Frangeul L, et al. Short chain fatty-acids in human large-intestine, protal, hepatic and venous-blood. Therapeutic manipulation of the enteric microflora in inflammatory bowel ailments: antibiotics, probiotics, and prebiotics. Chapter forty Gastrointestinal Microbial Ecology with Perspectives on Health and Disease 1131 17. Unexpected range and complexity of the Guerrero Negro hypersaline microbial mat. Committe on Metagenomics the New Science of Metagenomics: Revealing the Secrets of Our Microbial Planet. Microbial community profiling for human microbiome projects: instruments, strategies, and challenges. Terminal restriction fragment size polymorphism knowledge evaluation for quantitative comparison of microbial communities. Terminal restriction fragment patterns: a device for evaluating microbial communities and assessing neighborhood dynamics. The effect of diet on the human gut microbiome: a metagenomic evaluation in humanized gnotobiotic mice. Impact of culture-independent studies on the emerging phylogenetic view of bacterial diversity. Counting the uncountable: statistical approaches to estimating microbial variety. Comparative examine of bacterial teams throughout the human cecal and fecal microbiota. The significance of butyrate transport to the regulation of gene expression in the colonic epithelium. The gastrointestinal ecosystem: a precarious alliance among epithelium, immunity and microbiota. Plasmid profiling of members of the family Enterobacteriaceae, Lactobacilli, and Bifidobacteria to examine the transmission of bacteria from mom to toddler. Fecal microflora in wholesome infants born by different methods of delivery: everlasting modifications in intestinal flora after cesarean delivery. Probiotics, prebiotics, and synbiotics: approaches for modulating the microbial ecology of the intestine. Species range and organic invasions: relating local process to community pattern. Microbial interference and colonization of the murine gastrointestinal tract by Listeria monocytogenes. Differences in the gut bacterial flora of healthy and milk-hypersensitive adults, as measured by fluorescence in situ hybridization. Molecular fingerprinting of the intestinal microbiota of infants in whom atopic eczema was or was not growing. Intestinal microbiota and immunoglobulin E responses in 5-year-old Estonian youngsters. Effect of antibiotic remedy on human fecal microbiota and the relation to the development of Clostridium difficile. Effect of lactic acid producing micro organism on the human intestinal microflora throughout ampicillin treatment. Impact of injectable cephalosporins on the gastrointestinal microflora - observations in wholesome volunteers and hospitalized sufferers. Perturbation of the small intestine microbial ecology by streptomycin alters pathology in a salmonella enterica serovar typhimurium murine mannequin of an infection. Segmented filamentous bacteria in the rodent small intestine � theri colonization of growing animals and possible function in host resistance to Salmonella. Microbes to battle microbes - a not so novel approach to controlling diarrheal disease. Surface-layer protein extracts from Lactobacillus helveticus inhibit enterohaemorrhagic Escherichia coli O157: H7 adhesion to epithelial cells. Inhibition of Escherichia coli O157: H7 attachment by interactions between lactic acid bacteria and intestinal epithelial cells. Antimicrobial activity of lacticin 3147 in opposition to medical Clostridium difficile strains. Prevention of Helicobacter pylori an infection by lactobacilli in a gnotobiotic murine model. Lactic acid-mediated suppression of Helicobacter pylori by the oral administration of Lactobacillus salivarius as a probiotic in a gnotobiotic murine model. Chapter forty Gastrointestinal Microbial Ecology with Perspectives on Health and Disease 1133 ninety three. Dietary modulation of the human colonic microbiota � introducing the concept of prebiotics. A mixture of prebiotic oligosaccharides reduces the incidence of atopic dermatitis during the first six months of age. Synbiotic therapy (Bifidobacterium longum/ Synergy 1) initiates decision of inflammation in sufferers with energetic ulcerative colitis: a randomised managed pilot trial. Effect of dietary inulin supplementation on irritation of pouch mucosa in sufferers with an heal pouch-anal anastomosis. Impact of consumption of oligosaccharide-containing biscuits on the fecal microbiota of humans. Structure exercise relationship amongst biliary acids exhibiting comutagenic exercise towards 1,2-dimethylhydrazine. Large bowel carcinogenesis - fecal constituents of populations with diverse incidence rates of colon cancer. Reducing sulfur compounds of the colon impair colonocyte vitamin � implications for ulcerative colitis. Molecular evaluation of the impact of short-chain fatty acids on intestinal cell proliferation. Faecalibacterium prausnitzii is an antiinflammatory commensal bacterium recognized by gut microbiota analysis of Crohn illness sufferers.
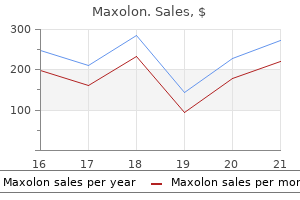
Order 10mg maxolon overnight delivery
Rho protein regulates tight junctions and perijunctional actin group in polarized epithelia gastritis kaffee maxolon 10 mg purchase amex. Enteropathogenic Escherichia coli dephosphorylates and dissociates occludin from intestinal epithelial tight junctions gastritis diet 50 10mg maxolon discount visa. Comparative biochemical and immunocytochemical research reveal differences within the results of Clostridium perfringens enterotoxin on polarized CaCo-2 cells versus Vero cells. The complicated interactions between Clostridium perfringens enterotoxin and epithelial tight junctions. Regulation of intercellular tight junctions by zonula occludens toxin and its eukaryotic analogue zonulin. Claudin-4: a new target for pancreatic most cancers remedy using Clostridium perfringens enterotoxin. Pseudomonas aeruginosa an infection destroys the barrier operate of lung epithelium and enhances polyplex-mediated transfection. Clostridium difficile toxin A perturbs cytoskeletal construction and tight junction permeability of cultured human intestinal epithelial monolayers. Human intestinal epithelial cells swell and demonstrate actin rearrangement in response 373. Clostridium perfringens enterotoxin interacts with claudins by way of electrostatic attraction. Structural constraints for the binding of quick peptides to claudin-4 revealed by surface plasmon resonance. Screening for celiac disease in first-degree relatives of patients with celiac illness by lactulose/mannitol take a look at. Simultaneous evaluation of intestinal permeability and lactose tolerance with orally administered raffinose, lactose and L-arabinose. Cellobiose/mannitol sugar permeability check enhances biopsy histopathology in clinical investigation of the jejunum. Intestinal permeability assessed by excretion ratios of two molecules: results in coeliac illness. Comparison between the cellobiose/mannitol and 51Cr-labelled ethylenediaminetetra-acetate absorption exams in the detection of coeliac illness. Intestinal permeability in coeliac illness: the response to gluten withdrawal and singledose gluten problem. Small bowel permeability in diagnosis of celiac disease and monitoring of compliance of a gluten-free diet (gut permeability in celiac disease). Improvement in intestinal permeability precedes morphometric recovery of the small gut in coeliac disease. Lactulose-mannitol intestinal permeability check: a useful screening test for grownup coeliac illness. Epithelial tight junction construction within the jejunum of youngsters with acute and treated celiac sprue. Zonula occludens toxin modulates tight junctions via protein kinase C-dependent actin reorganization, in vitro. Tight junctions, intestinal permeability, and autoimmunity: celiac illness and sort 1 diabetes paradigms. Early effects of gliadin on enterocyte intracellular signalling concerned in intestinal barrier operate. Gliadin, zonulin and gut permeability: effects on celiac and non-celiac intestinal mucosa and intestinal cell traces. Zonulin and its regulation of intestinal barrier perform: the organic door to inflammation, autoimmunity, and most cancers. Absorption of 51chromium-labeled ethylenediaminetetraacetate in inflammatory bowel illness. Comparison of different measurements of intestinal permeability in inflammatory bowel illness. Intestinal permeability compared in pediatric and grownup patients with inflammatory bowel disease. Possible modifications related to alterations of cell coat, mucous coat, epithelial cells, and paneth cells. Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory medicine activate quiescent inflammatory bowel illness. Intestinal permeability, non-steroidal antiinflammatory drug enteropathy and inflammatory bowel disease: an summary. Surrogate markers of intestinal inflammation are predictive of relapse in patients with inflammatory bowel illness. Epithelial myosin light chain kinase expression and exercise are upregulated in inflammatory bowel disease. Side effects of nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory medicine on the small and enormous gut in people. Effect of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs and prostaglandins on the permeability of the human small gut. Gastrointestinal harm related to the usage of nonsteroidal antiinflammatory medicine. Importance of native versus systemic results of non-steroidal antiinflammatory medication in rising small intestinal permeability in man. Glucose and citrate reduce the permeability changes caused by indomethacin in people. Increased intestinal permeability to macromolecules and endotoxemia in patients with chronic alcohol abuse in several levels of alcohol-induced liver disease. Increased intestinal marker absorption due to regional permeability modifications and decreased intestinal transit during sepsis in the rat. Increased gut permeability and bacterial translocation in Pseudomonas pneumonia-induced sepsis. Effect of acute alcohol ingestion prior to burn damage on intestinal bacterial progress and barrier function. Reduction in heat-induced gastrointestinal hyperpermeability in rats by bovine colostrum and goat milk powders. Selected contribution: hyperthermia-induced intestinal permeability and the position of oxidative and nitrosative stress. Effect of acute ethanol administration on the intestinal absorption of endotoxin in rats. Alcohol, intestinal bacterial progress, intestinal permeability to endotoxin, and medical penalties: summary of a symposium. Chapter 39 Biology of Gut Immunoglobulins Finn-Eirik Johansen, Ramiro Massol, Kristi Baker, Edda Fiebiger, Richard S. As in all different transporting epithelia similar to these found in the lung and kidney, a fragile single layer of columnar epithelial cells forms the protecting barrier between host and environment within the intestine. Such a transparent distinction between the outside and inside worlds is important for the intestine to effectively absorb and secrete nutrient solutes and water towards excessive electrochemical potentials. Because of this barrier, not all nutrient solutes, much much less massive and stably folded proteins such as the immunoglobulins, could be absorbed or secreted. To protect this delicate floor, an elaborate set of mechanisms prevents attachment, colonization, and attainable damage by pathogenic agents.
10mg maxolon buy with visa
Effects of stimulation of the hypothalamic space on pancreatic exocrine secretion in canines gastritis diet 4 you cheap 10 mg maxolon visa. Central inhibition of basal pancreatic and gastric secretions by beta-endorphin in rats gastritis lipase maxolon 10 mg discount on line. Noradrenergic inhibition of canine gallbladder contraction and murine pancreatic secretion throughout stress by corticotropin-releasing issue. Gastric emptying of liquid meals and pancreatic and biliary secretion after subtotal gastrectomy or truncal vagotomy and pyloroplasty in man. Protein hydrolysate-induced cholecystokinin secretion from enteroendocrine cells is indirectly mediated by the intestinal oligopeptide transporter pept1. Amino acids stimulate cholecystokinin launch by way of the calciumsensing receptor. The extracellular calcium sensing receptor is required for cholecystokinin secretion in response to L-phenylalanine in acutely isolated intestinal I cells. Proteins however not amino acids, carbohydrates, or fats stimulate cholecystokinin secretion in the rat. Canine pancreatic responses to intestinally perfused fat and products of fats digestion. Interactions between intraluminal bile acids and digestive products on pancreatic and gallbladder function. Intraduodenal emulsions of oleic acid increase acid-induced canine pancreatic secretion. Effect of intraduodenal bile and Na- taurodeoxycholate on exocrine pancreatic secretion and on plasma levels of secretin, pancreatic polypeptide, and gastrin in man. Effect of partial exclusion of pancreatic juice on rat basal pancreatic secretion. Negative suggestions management of exocrine pancreatic secretion: position of cholecystokinin and cholinergic pathway. Duodenal volume and osmoreceptors in the stimulation of human pancreatic secretion. Pancreatic, gallbladder, and intestinal responses to intraluminal magnesium salts in man. Effect of divalent cations on gastrointestinal hormone launch and exocrine pancreatic secretion in canine. Effects of intravenous infusion of amino acids, fat, or glucose on unstimulated pancreatic secretion in wholesome people. Secretion from acinar cells of the exocrine pancreas: position of enteropancreatic reflexes and cholecystokinin. Modulation of rat pancreatic amylase secretion and muscarinic receptor populations by chronic bethanechol therapy. Cyclic modifications of plasma pancreatic polypeptide and pancreatic secretion in fasting canine. Neural management of periodic secretion of the pancreas and the stomach in fasting canine. Doseresponse results of atropine on pancreatic response to secretin before and after truncal vagotomy. Correlation of launch and actions of cholecystokinin in dogs earlier than and after vagotomy. Effects of telenzepine and L-364,718 on canine pancreatic secretion earlier than and after vagotomy. Pancreatic bicarbonate response to intraduodenal tryptophan in canines: function of muscarinic M1-receptors and cholecystokinin. Control of pancreatic exocrine secretion by way of muscarinic receptors: which subtype(s) are involved Vagal stimulation of rat exocrine pancreatic secretion happens via a quantity of mediators. Neurons containing gastrin releasing peptide-like immunoreactivity within the human pancreas. Gastrin-releasing peptide: effect on exocrine secretion and Chapter 52 Regulation of Pancreatic Secretion 1453 101. Effect of bombesin and related peptides on the discharge and motion of intestinal hormones on pancreatic secretion. Gastrin-releasing peptide stimulation of amylase release from rat pancreatic lobules involves intrapancreatic neurons. Neurotensin interacts with carbachol, secretin, and caerulein in the stimulation of the exocrine pancreas of the rat in vitro. Receptor for calcitonin gene-related peptide: binding to exocrine pancreas mediates biological actions. Effects of autonomic denervation on canine exocrine pancreatic secretion and blood circulate. Modulation of stimulated pancreatic secretion by sympathomimetic amines in the rat. Central and peripheral inhibition of exocrine pancreatic secretion by alpha-2 adrenergic agonists within the rat. Inhibition of exocrine pancreatic secretion by alpha-adrenergic blocking agents in acutely aware rats. Mechanisms of terbutaline-induced inhibition of exocrine pancreatic secretion in people. Effects of dopamine on exocrine secretion and cyclic nucleotide concentration within the dog pancreas. Catecholamines and 5-hydroxytryptamine in tissues of the rabbit exocrine pancreas. Inhibitory impact of central dopamine on basal pancreatic secretion in acutely aware rats. Epinephrine and dopamine colocalization with norepinephrine in various peripheral tissues: guanethidine effects. Uptake, storage and secretion of 5-hydroxytryptamine and its amino acid precursor by dispersed rat pancreas acinar cells. Rat pancreatic serotonergic nerves: morphologic, pharmacologic and physiologic research. Specific uptake of tritiated serotonin within the grownup rat pancreas: proof for the presence of serotonergic fibers. Serotonin and seasonal variation in the pancreatic construction of bats: attainable presence of serotonergic axons in the gland. Nitric oxide and the pancreas: morphological base and function in the control of the exocrine pancreatic secretion. Nitrergic neurons within the pancreas of newborn guinea pig: their distribution and colocalization with numerous neuropeptides and dopamine-beta-hydroxylase. Contrasting effects of circulating nitric oxide and nitrergic transmission on exocrine pancreatic secretion in rats. Role of endogenous nitric oxide within the control of exocrine and endocrine pancreatic secretion in people. Role of endogenous nitric oxide in the management of canine pancreatic secretion and blood flow. Nitric oxide modulates pancreatic basal secretion and response to cerulein in the rat: results in acute pancreatitis.
Maxolon 10 mg order without a prescription
This is just like gastritis diet v8 order 10 mg maxolon fast delivery the ~6 � pores reported inside small intestinal villous epithelium gastritis burning stomach 10 mg maxolon cheap amex,39 and may replicate the identical construction. Notably, recent data have shown that claudin-2 expression, which boosts paracellular flux of monovalent cations, additionally increases flux of polyethylene glycol oligomers with radii less than four �. Occludin mobility occurred by diffusion inside the plasma membrane and was dependent on membrane fluidity, as it might be inhibited by cholesterol extraction, with methyl-cyclodextrin, or reduced temperature, but was not an energy-dependent process. While attractive, knowledge supporting this speculation has only been published in summary kind,126 as discussed within the following part. Moreover, the response of occludin knockout mice to stress has not been examined and it remains attainable that other proteins can compensate for intestinal epithelial occludin deficiency. The earlier data therefore suggest that occludin plays a regulatory, quite than a structural function. This hypothesis might clarify each the compensation in occludin knockout mice and the presence of occludin endocytosis or downregulation in pathology-associated barrier loss. Definition of those structural modifications in addition to the means by which they impression protein interactions and barrier perform remains an area in want of further examine. Each claudin exhibits distinctive expression patterns alongside both longitudinal (duodenum�colon) and vertical (crypt�villus) axes and can be regulated during development. While much work remains, recent research have demonstrated that claudin proteins outline paracellular flux of small solutes, including ions and water. As seen in (B), control villi are covered by polygonal absorptive cells with flat apical surfaces. Higher magnification (D) shows this cobblestone effect is due to pulse-string contraction of the comb borders of individual absorptive cells resulting in a convex apical absorptive cell floor and flaring of microvilli. Junction consists of an irregular array of strands that underlie occasional broad protrusions of the apical membrane (arrowheads). Geometric irregularities produced by such protrusions result in a fracture plane, which only focally contains the apical-most strand (straight arrows). Many perijunctional microvilli are lost and intramembrane particles penetrate into the incompletely isolated intrajunctional compartments (curved arrow). In Caco-2 monolayers, actin and myosin filaments are localized in a belt-like manner surrounding the apical junctional space. Cytochalasin therapy produces a speedy energy-independent severing of actin filaments into small fragments (early phase response). This early section fragmentation is then adopted by an energydependent course of by which the severed actin fragments reorganize to type massive cytoskeletal aggregates containing actin and myosin filaments (late phase response). The sequential effect of Cyto B (5 �g/ml) on Caco-2 actin microfilaments at time 0 (A) and 1 (B), 15 (C), and half-hour (D) is proven in the photomicrographs (original magnification 80). By 1 minute of Cyto B publicity, perijunctional actin filaments had been fragmented and current diffusely all through the cytoplasm. By 15�30 minutes of Cyto B exposure, actin fragments coalesced to type large actin clumps or "foci" close to the perijunctional areas. Caco-2 monolayers were uncovered to Cyto B for growing time durations (0�30 minutes). A linear relationship exists between reducing luminal osmolarity and rising paracellular water flux. The contribution of solvent drag on the absorption of paracellular markers may be assessed by manipulating the water flux by changing the osmolarity of the luminal perfusate resolution. The solute flux across the semipermeable epithelium by solvent drag is expressed quantitatively by a modified Kedem-Katchalsky equation. The shut dependence of intestinal flux of hydrophilic solutes on solvent drag advised that the adjustments within the direction and the extent of water circulate might have a major impact on intestinal permeability. Consistent with such a risk, exogenously added or endogenously produced secretagogues significantly affected the intestinal flux rates of the paracellular markers by altering the water flux rates. The potential clinical relevance of solvent drag in absorption of water-soluble drugs was instructed by studies during which the administration of atenolol and hydrochlorothiazide in high osmotic solution significantly decreased the intestinal absorption of those drugs. Similarly, in a Necturus gallbladder tissue mounted in Ussing chamber, increasing the osmotic load of the mucosal bathing answer brought on a internet enhance in serosal-to-mucosal water flux with collapse of the intercellular areas. It was calculated based mostly on the rate of water absorption, clearance of the paracellular markers, and coefficient of osmotic flow (Lp) that the solvent drag by way of the junctional or paracellular pathways was the precept mechanism of intestinal absorption of glucose or amino acids within the small intestinal lumen, when the luminal concentrations of glucose and amino acids exceed the maximal transcellular uptake by the energetic transporter. In addition, the perijunctional apical membranes (asterisk) related to these junctional areas are bulging and comparatively devoid of microvilli. From these studies, it was concluded that solvent drag was a significant mechanism of intestinal absorption of water-soluble nutrients (including glucose and amino acids) when the luminal glucose or amino acid concentrations were sufficiently excessive. Using a modest hypotonic dilution (5�7%) to induce a rise in cell volume, it was discovered that after an initial cell acidification, the cell shrinkage was accompanied by a fast increase in pHi (or cell alkalinization). To reveal the potential clinical relevance of Naglucose transport on intestinal permeability in humans, the effect of glucose (277 mM) on intestinal permeability was assessed using creatinine because the paracellular marker. In sum, the activation of Na-glucose cotransporter ends in an enterocyte uptake of Na and glucose. In common, pathogens exert their effects directly through binding to the intestinal epithelial cell or indirectly via the actions of secreted toxins. Their inactivation leads to degradation of perijunctional actin and barrier failure. The toxin is a 35 kDa polypeptide with a C-terminal domain that binds to several completely different claudins, notably three and four, and an N-terminal domain required for toxicity. Rotaviruses infect epithelial cells of the small gut and induce diarrhea with out obvious histological tissue injury at early phases of infection. Intestinal permeability has been outlined as "the flexibility of medium and large sized water-soluble compounds to passively traverse the intestinal epithelial layer via paracellular tight-junctional areas. For utilization in scientific research, permeability markers should be hydrophilic and passively absorbed, inert and non-toxic, not metabolized or endogenously produced, rapidly and completely excreted in urine, and should be simply measured. The sugar probes including mannitol, rhamnose, lactulose, cellobiose, and inulin are degraded by intestinal micro organism and creatinine is produced endogenously. The permeability probes are excreted in a variable method relying on their body distribution and urinary excretion. Typically, in clinical studies, permeability markers are ingested orally following an in a single day quick and urine is collected for various time intervals (between 6 and 24 hours). Previous research have demonstrated no vital difference in the reliability of the permeability check, whether 6 or 24 h urinary collection interval was used. Currently, probably the most commonly used assortment interval in medical studies is 6 hours. The intestinal immune response is triggered by the gliadin element of gluten, and elimination of gluten from food regimen results in the resolution of the disease. As the villous absorptive surface is broken in celiac patients, as a end result of gluten-induced intestinal irritation, the absorptive surface area markedly decreases.

Maxolon 10mg low price
Chronic alcohol consumption and intestinal absorption: effects on physiological and molecular parameters of the uptake process treating gastritis with diet buy 10 mg maxolon free shipping. Uptake of riboflavin by intestinal basolateral membrane vesicles: a specialised carrier-mediated process gastritis diet àâàòàí maxolon 10mg buy cheap on line. Transport capabilities of riboflavin service in the rat small intestine and colon: site difference and results of tricyclic-type medicine. Mechanism of transport of riboflavin in rabbit intestinal brush border membrane vesicles. Chapter sixty four Mechanisms and Regulation of Intestinal Absorption of Water-soluble Vitamins 1749 sixty three. Regulation of riboflavin intestinal uptake by protein kinase A: Studies with Caco-2 cells. Riboflavin phosphorylation is the essential event in riboflavin transport by isolated rat enterocytes. Uptake of riboflavin throughout the comb border membrane of rat gut: regulation by dietary vitamin levels. Brown-Vialetto-Van Laere Syndrome, a Ponto-Bulbar Palsy with Deafness, is caused by Mutations in C20orf54. Carrier-mediated uptake of nicotinic acid by rat intestinal brush-border membrane vesicles and relation to monocarboxylic acid transport. Nicotinic acid transport mediated by pH-dependent anion antiporter and proton cotransporter in rabbit intestinal brush-border membrane. Radiometric-microbiologic assay of niacin utilizing Kloeckera brevis: evaluation of human blood and meals. Mechanism of nicotinic acid transport in human liver cells: experiments with HepG2 cells and first hepatocytes. Cloning and useful characterization of the intestinal Nadependent multivitamin transporter. Transport and metabolism of pyridoxamine and pyridoxamine phosphate in the small intestine. Uptake of pyridoxine by in vivo perfused segments of rat small gut: A potential position for intracellular vitamin metabolism. Pyridoxine uptake by colonocytes: a particular and regulated carrier-mediate course of. Tpn1p, the plasma-membrane vitamin B6 transporter of Saccharomyces cerevisiae 2003;278:18990-18996. Pteroylpolyglutamate hydrolase from human jejunal brush borders: purification and characterization. Comparison of folate conjugase actions in human, pig, rat and monkey intestine. Intracellular pteroylpolyglutamate hydrolase from human jejunal mucosa: isolation and characterization. Functional specificity of jejunal brush-border pteroylpolyglutamate hydrolase in pig. Adaptive regulation of intestinal folate uptake: effect of dietary folate deficiency. Availability of monoglutamyl and polglutamyl folates in normal topics and in patients with celiac sprue. Folate absorption in alcoholic pigs: in vitro hydrolysis and transport at the brush border mebrane. Hepatic uptake, intracellular accumulation and biliary secretion of 5-methyltetrahydrofolate. Bacterially synthesized folate in rat massive gut is included into host tissue folylpolyglutamates. The impact of folate supplementation on the incidence of dysplasia and most cancers in continual ulcerative colitis: A case control examine. Chapter 64 Mechanisms and Regulation of Intestinal Absorption of Water-soluble Vitamins 1751 133. The human lowered folate provider gene is ubiquitously and differentially expressed in normal human tissues: identification of seven non-coding exons and characterization of a novel promoter. Distribution of the folate receptor in normal and malignant cell traces and tissues. Functional elements within the minimal promoter of the human proton-coupled folate transporter. Differentiationdependent regulation of the intestinal folate uptake course of: research with Caco-2 cells and native mouse intestine. Folate uptake within the human gut: promoter activity and impact of folate deficiency. Intracellular trafficking/membrane targeting of human lowered folate provider expressed in Xenopus oocytes. Identification of dynein gentle chain highway block-1 as a novel interplay associate with the human reduced folate provider. Folate transport in intestinal brush border membrane: involvement of essential histidine residue(s). Restoration of high-level transport exercise by human reduced folate carrier/ThTr1 thiamine transporter chimaeras: function of the transmembrane domain 6/7 linker area in decreased folate provider function. Cytoplasmic domains of the lowered folate provider are essential for trafficking, however not function. Reduced folate service: tissue distribution and effects of continual ethanol intake within the micropig. Down-regulation of reduced folate carrier might end in folate malabsorption across intestinal brush border membrane during experimental alcoholism. Mechanism and regulation of folate uptake by pancreatic acinar cells: impact of continual alcohol consumption. The Megaloblastic Anaemias, third ed London: Blackwell Scientific Publications; 1990. Use of vitamin B12 in the treatment and prevention of nitroprusside-induced cyanide toxicity. Serum cobalamin, folate, methylmalonic acid and whole homocysteine as vitamin B12 and folate tissue deficiency markers amongst aged Swedes�a populationbased study. Preparation and characterization of proteins in the alimentary tract of the canine which bind cobalamin and intrinsic issue. In vitro evidence that a failure to partially degrade R protein is liable for cobalamin malabsorption in pancreatic insufficiency. Immunocytochemical localization of human intrinsic issue: the nonstimulated abdomen. Cellular localization and hormonal regulation of pancreatic intrinsic issue secretion in canine. Expression of intrinsic think about rat and murine gastric mucosal cell lineages is modified by inflammation. Mechanisms of discrimination between cobalamins and their natural analogues during their binding to the particular B12-transporting proteins.
Diseases
- Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis
- Chromosome 18, trisomy 18p
- Chromosome 13q trisomy
- Gomez and L?pez-Hern?ndez syndrome
- Sharma Kapoor Ramji syndrome
- Pyrimidinemia familial
Maxolon 10 mg cheap otc
Donor Leukocyte Infusions and Suicide Genes Di Stasi A chronic gastritis for years effective 10 mg maxolon, They S-K gastritis y colitis 10mg maxolon order amex, Dotti G, et al: Inducible apoptosis as a safety switch for adoptive cell therapy. Williams the use of gene transfer to treat human diseases has now efficacious in a limited variety of cases. Proof-of-principle successes proven in several monogenic diseases-both hematologic and nonhematologic-have been revealed and extensively publicized in the past decade. Despite these successes, the prevalence of serious antagonistic events in some trials associated to insertional mutagenesis has tempered the enthusiasm accompanying these stories however has also stimulated rapid improvement of safer vector systems. This chapter discusses the essential biology of vector methods relevant to blood diseases, discusses particulars of the applying of gene remedy to blood diseases utilizing particular trials as examples of this expertise, and discusses modifications in vector techniques pushed by medical experience that predict future trials. The chapter additionally discusses the prospects that the evolving area of somatic cell reprogramming may generate alternative mobile targets for genetic engineering. This is termed germline gene therapy and is currently banned within the United States and around the globe. In contrast, introduction of recent genetic material into specialized cells of the body with no threat of the new genetic material being handed onto subsequent generations is termed somatic gene therapy. The ultimate aim of gene remedy can be to right a genetic illness by substitute of the defective gene in situ. Such gene alternative could be envisioned through a course of termed homologous recombination. Homologous recombination in mammalian cells is extensively practiced in laboratories but as much as now has been relatively inefficient. Advantages of this approach would come with a discount within the danger of inadvertent disruption or dysregulation of expression of a crucial gene sequence and controlled (appropriate stage and distribution) expression of the conventional (replaced) gene. However, the frequency of this event (in distinction to random chromosomal integration) in mammalian cells makes therapeutic use of homologous recombination impractical at this level. Methods to impact homologous recombination have improved prior to now 5 years and should make this objective attainable in the future. The necessities for profitable utility of our present gene transfer technology for therapy of human diseases embody information of the abnormal gene sequence answerable for the disease phenotype and the availability of the corresponding regular gene sequence. In addition, the cells answerable for the illness phenotype have to be recognized and accessible for genetic manipulation. Finally, a means of introducing and expressing the correct gene sequence in cells such that the disease phenotype could be reversed is required. This latter requirement has been, though effectively achieved more than 2 decades ago in murine research, probably the most difficult to persistently meet in human applications using present gene transfer expertise. Since the early development of virus vectors, blood-forming cells have been used as one optimal goal for gene switch studies, and most research to date use ex vivo approaches to genetic modification. Finally, the blood system is involved as a significant dose-limiting organ in cancer therapies and each a goal and an effector organ in immune reactions offering a large group of ailments that would theoretically be approached utilizing gene switch technology. As noted earlier, there are already a large number of monogenic illnesses of the blood extensively characterized with extra being outlined at the molecular level on a regular basis because whole-exome and whole-genome sequencing is being utilized to rare disease phenotypes. In this utility, T cells (and much less nicely developed to this level, other immune effector cells) are modified ex vivo in an try and improve efficiency and specificity. Successes of proofof-principle small trials have demonstrated the utility of gene switch approach in a large number of patients however in a restricted number of illnesses. The technology itself is rapidly evolving in response to new understanding of viruses, the regulation of gene expression, and gene enhancing. The subject has taken about 25 years to evolve to its present state of medical utility. Although this may be seen as a slow pace, in reality, this time frame parallels the development of many other novel therapies. This developmental section additionally displays the complexities of the biologic systems involved and the caution required in transferring ahead in the face of significant opposed events seen in early security trials. It is certainly an exciting time with respect to the clinical software of gene transfer know-how in human diseases. All vector methods use parts of the virus life cycle in an attempt to enhance the frequency and fidelity of gene switch. Retrovirus Vectors the use of -retroviruses as gene switch vectors takes benefit of the conventional virus life cycle. For -retroviruses, transport into the nucleus is determined by the lack of the nuclear membrane, which accompanies cell division (see later discussion). Use of retroviruses for gene delivery is determined by the capacity to replace viral genes with different heterologous gene sequences and to present necessary viral proteins in trans in specialised cell strains, referred to as packaging cells. The advanced technology of packaging cells appears to be capable of generating pure stocks of recombinant virus with out contaminating wild-type helper virus, an necessary security consideration. Indeed, to date in human trials, there have been no reports of inadvertent era of infectious virus. Thus, this an infection with replication-incompetent (ie helper-free) retrovirus vectors could be predicted to yield integration into the targeted cell inhabitants but no further spread of virus within the body of the handled patient. The proteins supplied in trans for -retroviruses are usually gag, reverse transcriptase, and envelope proteins, the latter defining the host vary of an infection. Despite these benefits, the applying of retrovirus vectors to treatment of human blood ailments in early trials was disappointing. In most studies, the frequency of circulating marked blood cells was too low to effect phenotypic correction of any illness, often lower than 0. The biologic parameters contributing to the poor leads to human trials are diversified. Practical points, together with the difficulty in acquiring high-titer virus in largescale preparations required for human trials, have additionally been noted. In addition to the vitality within the subject that was devoted to advancing stem cell transduction methodology, additional work targeted on creating retroviral vectors that might specific transgene cassettes at levels that may be high sufficient to elicit a therapeutic profit and be immune to gene silencing. Taken together, these technologic advances served because the platform for the first profitable gene therapy trial in humans. The use of pharmacologic in vivo choice together with gene transfer, both in the setting of cancer trials and in genetic ailments, stays a doubtlessly necessary technique to enhance the reconstitution of human recipients with gene-modified blood cells but has not but gained widespread usage. For applications in cancer therapies, dose intensification of medication used within chemotherapeutic regimens should improve antitumor efficacy. For noncancer purposes (most likely uses attempting co-selection of a nonselectable therapeutic gene in a genetic disease application), the mutagenic potential of the chemotherapy agent should be thought of as a danger in relation to the general good thing about the gene remedy Chapter ninety nine Principles of Cell-Based Genetic Therapies 1505 procedure. Several chemoresistance genes and chemotherapy drug combos are presently under investigation for this utility, and inspiring preclinical research have led to a restricted variety of early part human studies in most cancers sufferers. As with gammaretroviruses, lentivirus vectors use key viral gene merchandise in trans to generate replication-defective infectious particles carrying the transgene of curiosity. To date, most lentivirus vectors use vesicular stomatitis virus as envelope sequence, which offers a very broad range of target cells prone to lentivirus vector transduction. In the case of lentivirus vectors, viral gag and pol in addition to tat and rev proteins expression are required in trans for environment friendly virus manufacturing along with the envelope proteins.
Maxolon 10mg generic with mastercard
However gastritis ginger ale buy cheap maxolon 10 mg online, the studies described above are provocative and illustrate the necessity to diet to help gastritis cheap 10 mg maxolon with visa correlate ranges of amino acids, lipids, and glucose that occur postprandially with these achieved after intravenous infusion to precisely assess the results on pancreatic secretion. However, the sympathetic innervation of the exocrine cells of the pancreas is less than that of blood vessels and islets. These ganglia are innervated by vagal preganglionic, sympathetic postganglionic, enteric, and sensory fibers. These neurons receive enter from both the central nervous system via the cephalic phase of pancreatic secretion and through vagovagal reflexes that contain both the afferent and efferent limbs of the vagus nerve. Vagovagal enteropancreatic reflexes play a significant role within the management of the intestinal phase of pancreatic secretion. These reflexes involve afferents originating within the duodenal mucosa, and efferents mediating central input on the pancreatic ganglia, which activate intrapancreatic postganglionic neurons. Vagovagal reflexes are initiated by gastric and intestinal stimulation and converge on cholinergic intrapancreatic neurons that release acetylcholine. Acetylcholine, in flip, binds to muscarinic receptors on pancreatic acinar and duct cells to stimulate each enzyme and bicarbonate secretion. In most species, besides the pig, electrical stimulation of the vagus nerve causes larger launch of pancreatic enzymes relative to fluid and bicarbonate. It is believed that each of those strategies used to stimulate the vagus nerve causes the release of acetylcholine, which prompts muscarinic receptors on the pancreas as every action may be blocked by atropine. A variety of different observations have clarified the function of cholinergic innervation in the pancreas. The intrinsic nerve plexus of the pancreas receives inputs from each the parasympathetic and sympathetic nervous systems. Parasympathetic nerves innervating the pancreas originate primarily within the dorsal vagal nucleus of the brain. Most of these fibers run via the posterior vagal nerve trunk and terminate as preganglionic vagal nerves on pancreatic ganglia. Sympathetic innervation of the pancreas is equipped by neurons with cell bodies within the celiac and superior mesenteric ganglia. Finally, using radiolabeled antagonists, particular muscarinic receptors have been recognized on pancreatic acinar cells. At the extent of the mind stem, modulation of vagovagal reflexes might happen by inputs from larger brain centers. The gastric and intestinal phases of the meal response activate each chemical and stretch receptors. These effects are partially mediated by launch of hormones launched from the intestinal mucosa, but different factors also seem to be concerned. Electrical activation of websites throughout the brain and the vagus has been recorded after gastric distention and intestinal perfusion with amino acids. Surgical vagotomy additionally had a selective effect on decreasing enzyme launch and reduced each basal and stimulated secretion. Pancreatic secretion stimulated by intestinal perfusion with amino acids, fatty acids, and peptides could be inhibited by vagotomy and anticholinergic medicine. However, topical utility of anesthetic medicine to the intestine blocks the pancreatic enzyme response to intestinal perfusion with amino acids. Quantitatively, roughly one-half of the enzyme response to intestinal stimulants similar to amino acids and fatty acids is mediated by neural pathways that are largely cholinergic and vagovagal. However, when the consequences of different a nice deal of intestinal stimulants are thought-about it seems that vagal cholinergic reflexes are the major mediators of pancreatic secretion in response to low intestinal hundreds, however hormones could mediate pancreatic responses to high a great deal of intestinal stimulants. M1 receptors are also involved in regulating pancreatic secretion probably via a non-acinar presynaptic mechanism. This stimulation achieves pancreatic secretory ranges roughly 50% of the response seen with exogenous secretin. Duct cells possess membrane receptors for neurotransmitters, hormones, and other bioactive transmitters. Other factors could affect secretion not directly through results on blood vessels to modulate pancreatic blood flow. Further studies indicated that multiple mediators are involved in the pancreatic secretory response to electrical stimulation of the vagus nerve. In vitro studies in isolated pancreatic acini have additionally proven that these peptides could have stimulatory or inhibitory actions. In the dog, the effect of dopamine is blocked by dopamine receptor antagonists but is unaffected by - or -receptor antagonists. However, dopamine causes little or no enzyme secretion from either acinar cells in vitro or the pancreas in vivo. However, research to establish these effects have been difficult due to the various numerous results of sympathetic nerve stimulation or non-specific effects following administration of adrenergic agents. The cell our bodies of norepinephrine-containing nerves that innervate the pancreas are discovered within the celiac ganglion. Fibers from these cells lengthen to nerves within the intrapancreatic ganglia and to blood vessels, ducts, and islets. Electrical stimulation of splanchnic nerves to the pancreas inhibited pancreatic secretion. Celiac denervation has been proven to cut back pancreatic secretion by ~70% while increasing blood move by 350%. This discovering means that there was disruption not only of stimulatory fibers however of sympathetic fibers that keep tonic constriction of pancreatic vessels. Various stories describe norepinephrine stimulating, inhibiting, or having no effect on pancreatic secretion. In vitro research are difficult to extrapolate to the in vivo scenario and in vivo research are complicated by the widespread results of adrenergic agonists and antagonists. Intrapancreatic nerves have been proven to take up serotonin and pancreatic acinar cells have been shown to remove serotonin from plasma and secrete serotonin, suggesting that serotonin launch occurs physiologically throughout the pancreas. Interestingly, each of these serotonin antagonists have been reported to also inhibit secretin launch induced by duodenal acid. Nevertheless, regardless of these recent advances, the overall useful significance of serotonin in pancreatic secretion still stays largely unknown. The nitrergic provide of the exocrine pancreas and blood vessels is comparable in every species examined. Both glyceryl trinitrate and sodium nitroprusside elevated basal pancreatic secretion in acutely aware canines and anesthetized cats however had no effect on meal-stimulated pancreatic responses. To perform as a hormone that stimulates pancreatic secretion several criteria must be met. First, if such a hormone performs a physiologic position in postprandial pancreatic secretion it have to be released into the circulation following ingestion of the meal. Although we now respect that hormones interact with neural elements, hormonal transmitters present a serious stimulus to pancreatic secretion.
Maxolon 10 mg low price
One of the extra common bacterial modifications is epimerization of 3-hydroxy or 7-hydroxy groups to their corresponding 3- or 7-hydroxy varieties gastritis colitis diet buy maxolon 10mg cheap. The enterohepatic circulation of bile acids is a particularly efficient process; lower than 5% of the intestinal bile acids escape reabsorption and are eradicated within the feces gastritis diet restrictions maxolon 10mg discount otc. Secondary metabolism of bile acids is carried out by the intestinal bacterial flora and liver. Bacterial modifications of the first bile acids embrace deconjugation, 7-dehydroxylation, and epimerization of the 3- and 7-hydroxy teams. Additional hepatic metabolism of the secondary bile acids includes hepatic discount of the 7-oxo spinoff of chenodeoxycholic acid, and hepatic re-epimerization of 3-hydroxy bile acids. Sulfation of lithocholic acid conjugates prevents ileal conservation and ends in rapid excretion from the body. During this era, the bile acid concentration in small intestine is approximately 5�10 mmol/L. Thus, the enterohepatic cycling of bile acids increases during digestion and slows between meals and through overnight fasting. This rhythm is maintained even after cholecystectomy the place, despite increased enterohepatic cycling and an elevated fraction of the bile acids stored in the proximal gut,113 bile acid metabolism and function is largely unperturbed. The binding of bile acids to plasma proteins similar to albumin reduces glomerular filtration, and the kidney filters roughly one hundred �mol of bile acids every day in healthy humans. Remarkably, only 1�2 �mol is excreted in the urine due to extremely efficient tubular reabsorption. Other major solutes include conjugated bilirubin, glutathione, bicarbonate, and conjugates of metabolites and xenobiotics. Water, plasma electrolytes, calcium, glucose, amino acids, and other low molecular weight solutes that move passively into the canaliculus in response to the osmotic gradient are termed secondary solutes. The choleretic exercise of every primary solute is defined as the quantity of bile flow induced per amount of solute secreted. The obvious choleretic exercise differs between conjugated bile acid species and ranges from eight to 25 �L of bile circulate induced per �mol of bile acid secreted. This exercise is also influenced by the osmotic properties of blended micelles in bile in addition to the permeability of paracellular junctions to different solutes that enter canalicular bile by solvent drag. Hepatocellular uptake of bile acids occurs in opposition to an unfavorable electrochemical ion gradient and ends in a 5- to 10-fold concentration gradient between the plasma filtrate present in the space of Disse and hepatocyte cytosol. After uptake, conjugated bile acids are shuttled to the canalicular membrane for secretion into bile; unconjugated bile acids comply with an identical path after first undergoing N-acyl amidation to taurine or glycine. These divalent (S/G) or tetrahydroxylated (H) bile acids are present in very small portions beneath normal physiological situations, but could accumulate in disease states corresponding to cholestasis. A fraction of the bile acids secreted into bile acids undergo cholehepatic shunting. Ultimately, the bile acids are saved within the gallbladder and empty into the intestinal lumen in response to a meal. These carriers might serve to take in a fraction of the unconjugated bile acids from the lumen of the colon. Under regular physiological conditions, a fraction of the bile acid escapes first move hepatic clearance and enters the systemic circulation. This efficient renal reabsorption occurs even beneath cholestatic conditions for unconjugated and conjugated bile acids, when serum bile acid concentrations are dramatically elevated. Overall, this integrated transport system minimizes fecal and urinary bile acid loss and capabilities to largely prohibit these potentially cytotoxic detergents to the intestinal and hepatobiliary compartments. In mouse, the bile-acid-transporting Oatps expressed on the hepatic sinusoidal membrane contains Oatp1a1, Oatp1a4, and Oatp1b2. Results from knockout mouse research have offered compelling genetic proof for a big role of the Oatp1a/1b transporters, particularly Oatp1b2, in hepatic clearance of unconjugated bile acids. The presence of a cholehepatic shunt pathway means that the flux of bile acids by way of the hepatocyte is bigger than can be accounted for by the bile acids recovered in bile. In many species including humans, the bile acid pool consists of glycine conjugates, unconjugated bile acids, and hydrophobic bile acid species. Premature absorption and resecretion of the bile acid additionally promotes bile formation by growing bile acid-dependent move. However, the quantitative contribution of jejunal bile acid absorption in some species is still being debated. The most obvious instance is main bile acid malabsorption, a rare idiopathic dysfunction related to continual diarrhea beginning in early infancy, steatorrhea, interruption of the enterohepatic circulation of bile acids, and lowered plasma cholesterol levels. The perform of the individual subunits has not but been decided; however, coexpression of each subunits and their assembly into a posh is required for trafficking to the plasma membrane and solute transport. This enhanced degradation was blocked utilizing a c-Jun N-terminal kinase inhibitor or proteasome inhibitors. The predominantly constructive regulation would additionally guarantee efficient export of bile acids, preventing cellular damage as a result of intracellular accumulation. Bile salts of vertebrates: structural variation and possible evolutionary significance. Unstirred water layers in gut: rate determinant of fatty acid absorption from micellar solutions. Phase evaluation and aggregation states of luminal lipids throughout duodenal fats digestion in healthy adult human beings. Role of liver within the upkeep of cholesterol and low density lipoprotein homeostasis in numerous animal species, including humans. Oral bile acids scale back bacterial overgrowth, bacterial translocation, and endotoxemia in cirrhotic rats. Regulation of antibacterial protection in the small gut by the nuclear bile acid receptor. Interactions between ionized calcium and sodium taurocholate: bile salts are necessary buffers for prevention of calcium-containing gallstones. Natural structural variants of the nuclear receptor farnesoid X receptor affect transcriptional activation. Circulating intestinal fibroblast development issue 19 has a pronounced diurnal variation and modulates hepatic bile acid synthesis in man. Farnesoid X receptor deficiency in mice leads to elevated intestinal epithelial cell proliferation and tumor development. Identification of bile acid precursors as endogenous ligands for the nuclear xenobiotic pregnane X receptor. Detoxification of lithocholic acid, a poisonous bile acid: relevance to drug hepatotoxicity. Synthesis, analysis, and structure-activity relationship of a series of body and side chain modified analogues of chenodeoxycholic acid. Bile acids induce power expenditure by selling intracellular thyroid hormone activation. Heterogeneous expression of ldl cholesterol 7 alphahydroxylase and sterol 27-hydroxylase genes in the rat liver lobulus. Disruption of the sterol 27-hydroxylase gene in mice ends in hepatomegaly and hypertriglyceridemia.
Buy maxolon 10mg line
Water transport by the human Na-coupled glutamate cotransporter expressed in Xenopus oocytes acute gastritis symptoms nhs maxolon 10 mg free shipping. Cotransport of H gastritis diet ø?ëýã discount 10 mg maxolon with mastercard, lactate and H2O by membrane proteins in retinal pigment epithelium of bullfrog. Local osmotic gradients drive the water flux related to Na/glucose cotransport. The presence of local osmotic gradients can account for the water flux driven by the Na-glucose cotransporter. Glucose accumulation can account for the initial water flux triggered by Na/glucose cotransport. Fluid flow throughout the jejunal epithelia in vivo elicited by dc current: results of mesenteric nerve stimulation. The function of the tight junction in paracellular fluid transport throughout corneal endothelium. A mathematical mannequin of electrolyte and fluid transport across corneal endothelium. A mechanism for isotonic fluid flow by way of the tight junctions of Necturus gallbladder epithelium. Convective fluid flow by way of the paracellular system of Necturus gall-bladder epithelium as revealed by dextran probes. Extravascular short-circuiting of oxygen indicating countercurrent exchange in the intestinal villi of the cat. The vascular sample of the intestinal villi in various laboratory animals and man. The vascular architecture of the different forms of small intestinal villi within the rat (Rattus norvegicus). Quantitation of countercurrent trade throughout passive absorption from the canine small intestine: evidence for marked species differences in the effectivity of trade. The significance of the intestinal countercurrent exchanger for 85Kr absorption from the feline gut. Evidence for the existence of a countercurrent exchanger within the small intestine in man. Countercurrent multiplication of sodium in intestinal villi throughout absorption of sodium chloride. Na-induced intestinal interstitial hyperosmolality and vascular responses during absorptive hyperemia. Tissue osmolality in intestinal villi during luminal perfusion with isotonic electrolyte solutions. Importance of sodium and glucose for the institution of a villous tissue hyperosmolality by the intestinal countercurrent multiplier. Use of inert gases and carbon monoxide to study the possible affect of countercurrent trade on passive absorption from the small bowel. Countercurrent exchanger within the small gut of man: is there evidence for its existence Mechanism of bicarbonate absorption and its relationship to sodium transport within the human jejunum. Interrelationships of chloride, bicarbonate, sodium, and hydrogen transport within the human ileum. Dissecting the roles of aquaporins in renal pathophysiology using transgenic mice. Requirement of aquaporin-1 for NaCl-driven water transport throughout descending vasa recta. Defective urinary-concentrating capacity because of an entire deficiency of aquaporin-1. Defective secretion of saliva in transgenic mice missing aquaporin-5 water channels. Aquaporin-1 deletion reduces osmotic water permeability and cerebrospinal fluid manufacturing. Aquaporin deletion in mice reduces intraocular stress and aqueous fluid production. Localization of aquaporin-5 in sweat glands and practical evaluation utilizing knockout mice. In vivo measurement of mind extracellular area diffusion by cortical surface photobleaching. Mildly irregular retinal operate in transgenic mice with out Muller cell aquaporin-4 water channels. Aquaporin-4 gene disruption in mice protects towards impaired retinal function and cell dying after ischemia. New insights into water transport and edema within the central nervous system from phenotype analysis of aquaporin-4 null mice. Evidence against useful interplay between aquaporin-4 water channels and Kir4. Microfiberoptic fluorescence photobleaching reveals size-dependent macromolecule diffusion in extracellular space deep in brain. Microfiberoptic measurements of extracellular area volume in brain and tumor slices based on fluorescent dye partitioning. Localization of aquaporin-1 water channel in glial cells of the human peripheral nervous system. Aquaporin deletion in mice reduces corneal water permeability and delays restoration of transparency after swelling. Impaired stratum corneum hydration in mice missing epidermal water channel aquaporin-3. Selectively decreased glycerol in skin of aquaporin-3-deficient mice could account for impaired skin hydration, elasticity, and barrier restoration. Glycerol substitute corrects faulty skin hydration, elasticity, and barrier function in aquaporin-3-deficient mice. Aquaporin-3 facilitates epidermal cell migration and proliferation during wound healing. Prevention of skin tumorigenesis and impairment of epidermal cell proliferation by focused aquaporin-3 gene disruption. Aquaporin-3-dependent cell migration and proliferation during corneal re-epithelialization. Impaired enterocyte proliferation in aquaporin-3 deficiency in mouse models of colitis. Role of aquaporin-7 and aquaporin-9 in glycerol metabolism; involvement in obesity. Impairment of angiogenesis and cell migration by focused aquaporin-1 gene disruption.