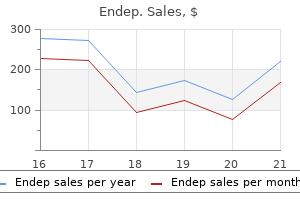
Endep dosages: 75 mg, 50 mg, 25 mg, 10 mg
Endep packs: 30 pills, 60 pills, 90 pills, 120 pills, 180 pills, 270 pills, 360 pills

Endep 25 mg low cost
The scientific and histopathologic features of all lacrimal sac tumors and pseudotumors are comparable and had been mentioned elsewhere medications and mothers milk 2014 25 mg endep. The management varies with the sort of lesion treatment xerosis endep 75 mg cheap without prescription, however is usually surgical removal by dacryocystectomy and subsequent reconstruction of the lacrimal drainage system. Oncocytic adenomatous hyperplasia of the lacrimal sac: a case report and evaluate of the literature. A uncommon solitary fibrous tumour of the lacrimal sac presenting as acquired nasolacrimal duct obstruction. Adenocarcinoma expleomorphic adenoma of the lacrimal sac and nasolacrimal duct: a case report. Granular cell tumor of the lacrimal sac and nasolacrimal duct: no invasive habits with incomplete resection. Primary lacrimal sac B-cell immunoblastic lymphoma simulating an acute dacryocystitis. Leiomyoma of the orbit and periocular area: a clinicopathologic research of four circumstances. Mucosa-associated lymphoid tissue lymphoma in lacrimal sac of 10-year-old boy with mass in left medial canthal space. Pyogenic granuloma of lacrimal sac presenting as an outgrowth through the superior canaliculus. Histopathology of a dacryolith in an aged patient with dacryocystitis secondary to actinomyces. It includes data of eyelid anatomy and experience with handling tumor tissue and beauty reconstruction. It is past the scope of this textbook and atlas to describe the nice details of surgical administration of eyelid tumors. In this chapter, we define some of the basic surgical approaches to eyelid tumors. A small trephine punch is ideal for such a biopsy, though an incisional biopsy with a scalpel can additionally be acceptable particularly for suspected basal cell carcinoma. An incisional diagnostic biopsy is generally acceptable for malignant tumors with low metastatic potential, corresponding to basal cell carcinoma and squamous cell carcinoma. Frozen sections or chemosurgery are usually advisable to insure that margins are freed from tumor before closure of the wound. A skin graft or flap may be necessary in some cases to shut the defect and decrease useful eyelid problems, similar to cicatricial ectropion. Donor skin can be obtained from the higher eyelid of the ipsilateral or contralateral eye, retroauricular skin, or other sites, relying on the preference of the surgeon and the scientific circumstances. Larger malignant tumors might require wide surgical removing and intensive eyelid reconstruction. Some malignant eyelid tumors that invade the orbital delicate tissues might require a subtotal or whole orbital exenteration. Technique of punch biopsy for diffuse lesion in higher eyelid suspected to be a large sebaceous gland carcinoma. If it seems on the time of surgery that primary closure would cause ectropion of eyelid, then a rotational flap or skin graft, often from the higher eyelid or retroauricular space, can be done. Lesion has been removed and marginal biopsy is being taken for frozen part readings. Nylon, silk or absorbable sutures can be utilized, relying on the surgeons choice. A simple choristoma contains one kind of tissue; a fancy choristoma has more than one kind. The primary choristomatous tissues that occur within the conjunctiva embrace skin, bone, lacrimal gland, and cartilage. Dermoid is the second most common epibulbar choristoma, following dermolipoma (1�17). A new syndrome of autosomal dominantly inherited, bilateral, annular limbal dermoids with corneal and conjunctival extension. Clinical Features Small dermoids are sometimes asymptomatic, however bigger lesions can cause irritation, astigmatism, and insufficient eyelid closure (6,12). It seems as a variably sized, yellow-white limbal mass inferotemporally however it can seem in different meridians (2�11). A conjunctival dermoid can present extensive corneal involvement with little involvement of the adjoining conjunctiva (13). An unusual variant (ring dermoid syndrome) is bilateral, straddles the corneoscleral limbus for 360 levels and has an autosomal-dominant mode of inheritance (15). Pathology Histopathologically, dermoid is lined by stratified squamous epithelium. Deep to the epithelium is dense collagenous tissue in which pilosebaceous items, sweat glands, and fat are often identifiable (2). In rare cases, bone could be current within the dermoid (complex choristoma) (16). It is feasible that dermoid develops secondary to faulty eyelid fold closure embryologically with secondary entrapment of skin and mesenchyme. Management Smaller asymptomatic dermoids could be noticed and bigger lesions could require excision (17). Reasons for surgical elimination embrace amblyopia, secondary astigmatism, encroachment on the visual axis, dellen formation, insufficient eyelid closure, and beauty concerns. Early elimination is advocated for symptomatic lesions to obtain a greater beauty end result. Removal could be achieved by superficial shaving or by deeper excision with lamellar keratoplasty for deeper lesions (12,17). Chapter 16 Conjunctival and Epibulbar Choristomas 251 Conjunctival Dermoid Conjunctival dermoid can happen as an isolated lesion or it can be a element of Goldenhar syndrome. Larger limbal dermoid with a dilated blood vessel in a 47-year-old woman with Goldenhar syndrome. Histopathology of limbal dermoid displaying a quantity of pilosebaceous units in dense collagenous tissue and foci of lipid. A lamellar keratoplasty was originally deliberate but it was found on the time of surgical procedure that the lesion prolonged for full thickness of the corneal stroma. Epibulbar dermoid is also known to lengthen via the limbus into the anterior chamber. The lesion was current at birth and the patient underwent surgical elimination at 15 years of age. The affected eye was enucleated elsewhere as a result of the child was having extreme psychosocial issues. Both eyes of a baby at time of examination beneath anesthesia, exhibiting atypical dermoid on the corneoscleral limbus inferiorly. The nodules within the anterior chamber have been aspirated and they partially collapsed, a finding compatible with a cyst related to the presumed stable dermoid.
Endep 75 mg otc
It can occur anyplace on the physique medications in checked baggage endep 25 mg generic, however has a predilection for the face and eyelids medicine hat alberta canada 25 mg endep. Trichoepithelioma accounts for about 1% to 2% of biopsied sweat gland or hair follicle tumors (10). Benign hair-follicle derived tumours within the differential prognosis of basal cell carcinoma of the eyelids: A clinicopathological comparability. Clinical Features Solitary trichoepithelioma usually has its onset in early adulthood as a skin-colored, dome-shaped papule that may remain stable or steadily enlarge and turn into crusty (1,2). Larger trichoepithelioma could have telangiectatic blood vessels and resemble basal cell carcinoma. It begins as multiple, skin-colored, agency papules usually between 2 and 8 mm in diameter, located mainly within the nasolabial folds, facial skin, and sometimes the eyelids (7). The medical appearance could also be much like nevoid basal cell carcinoma syndrome, facial angiofibromas of tuberous sclerosis, sarcoidosis, or syringoma. Multiple trichoepitheliomas have also been noticed in affiliation with a quantity of cylindromas, a situation that also has autosomaldominant inheritance (7,12,13). Pathology Histopathologically, trichoepithelioma is characterised by irregular lobules of proliferating basal cells with distinct keratin cysts (horn cysts), that characterize immature hair structures. The keratin cysts might resemble those seen with seborrheic keratosis or keratotic basal cell carcinoma and the tumor may be difficult to differentiate from basal cell carcinoma or squamous cell carcinoma in many situations. Electron microscopy and immunohistochemical research suggest that the tumor arises from hair matrix cells and the horn cysts represent makes an attempt at hair shaft formation (7,8). If an incisional biopsy confirms trichoepithelioma, definitive surgical removal can be done with much less beneficiant margins than for basal cell carcinoma, thus facilitating surgical reconstruction (15). Multiple trichoepitheliomas are managed similarly; administration varies with the scientific findings. Chapter 5 Eyelid Hair Follicle Tumors 81 Eyelid and Facial Trichoepithelioma Trichoepithelioma may be solitary or a quantity of. Histopathology of trichoepithelioma, exhibiting deep tumor nodules with keratin cysts. This was excised and proved to be basal cell carcinoma arising in a patient with familial multiple trichoepithelioma. Histopathology of another case of trichoepithelioma, exhibiting the well-defined keratin cysts. Trichofolliculoma, a extra frequent lesion than trichoadenoma, is a benign, slow-growing tumor of hair follicle origin that happens most often in the head and neck area and can involve the eyelid (1�9). It accounts for about 1% to 2% of biopsied sweat gland or hair follicle tumors (3,4). Benign hair-follicle derived tumours in the differential prognosis of basal cell carcinoma of the eyelids: a clinicopathological comparison. Clinical Features Trichofolliculoma presents as a dome-shaped, skin-colored nodule with a characteristic central pore via which typical cotton-like nice hairs, generally white lanugo hairs, protrude. Clinically, it could be confused with sebaceous cysts, nevus, or basal cell carcinoma. Pathology Microscopically, trichofolliculoma consists of a dilated hair follicle orifice that incorporates hair and keratin. It is a extremely differentiated lesion with branching strands of basaloid cells extending from the dilated follicle into the adjacent connective tissue. Some authorities think about it to be a hamartomatous lesion, representing essentially the most differentiated form of pilar tumor (3). Management Trichofolliculoma is usually best managed by complete surgical excision, just like different benign adnexal tumors. Trichoadenoma Trichoadenoma is a rare, benign cutaneous tumor of hair follicle differentiation. It usually occurs on the face and has a solitary, nodular configuration, typically with superficial, telangiectatic vessels (10). It usually resembles a basal cell carcinoma, but can have a verrucous configuration and resemble seborrheic keratosis. Histopathology of trichofolliculoma exhibiting craterlike opening by way of which keratin and hair are protruding. Note that the lesion is deep to the epidermis, in distinction to basal cell carcinoma and seborrheic keratosis. It is considered one of the adnexal tumors that may arise from nevus sebaceous of Jadassohn (4). In a sequence of 31 trichilemmomas involving the ocular area, affected person ages ranged from 22 to 88 years, with a mean of fifty six years. Affected sufferers should be evaluated for different tumors associated with this illness, notably breast and thyroid cancers. The trichilemmomas may precede breast cancer analysis, enabling earlier prognosis of breast most cancers in such cases (6,7). Pathology Histopathologically, trichilemmoma is characterised by lobular acanthosis composed mainly of glycogen-rich cells. The periphery of each lobule reveals palisading of columnar cells with a definite basement membrane (1,3,7). It could resemble basal cell carcinoma, squamous cell carcinoma, or seborrheic keratosis (7). A variant is the desmoplastic trichilemmoma, which exhibits irregular extensions of cells of the outer root sheath that project into sclerotic collagen bundles, mimicking invasive basal cell carcinoma (7,12,13). Management Like many other tumors in this part, the management of trichilemmoma is full surgical excision (2). Complete surgical excision is the preferred remedy; there are uncommon reviews of trichilemmal carcinoma of the eyelid (14,15). On occasion, a trichilemmoma can have malignant adjustments histopathologically (trichilemmal carcinoma). Histopathology of trichilemma exhibiting well-defined, glycogen-rich cells steady with dermis. Pilomatrixoma is often solitary, tends to affect young individuals, and includes the periorbital area in 17% of cases. About 40% develop within the first decade of life and an additional 20% within the second decade (6,9). Pilomatrixoma has a predisposition to occur within the higher eyelid and eyebrow (1�17). Pilomatrixoma of the top and neck in children: a examine of 38 instances and a evaluate of the literature. Its characteristic location close to the lateral side of the eyebrow incessantly suggests the medical prognosis of dermoid cyst (12). In rare instances, it has presented on the back of the eyelid from the tarsal conjunctiva.
Order endep 75 mg on line
Influence of age on secretion of cholesterol and synthesis of bile acids by the liver treatment croup endep 50 mg buy generic line. Effect of aging on biliary lipid composition and bile acid metabolism in normal Chilean girls symptoms after miscarriage buy 10 mg endep free shipping. Aging per se is an unbiased risk issue for ldl cholesterol gallstone formation in gallstone susceptible mice. Relation to adjustments in serum and biliary lipids during hormonal therapy of prostatic carcinoma. Estrogen receptor alpha, but not beta, performs a major position in 17beta-estradiol-induced murine ldl cholesterol gallstones. Overexpression of estrogen receptor alpha increases hepatic cholesterogenesis, resulting in biliary hypersecretion in mice. Genetic evaluation of ldl cholesterol gallstone formation: trying to find Lith (gallstone) genes. Pregnancy and cholelithiasis: pathogenesis and natural course of gallstones identified in early puerperium. Gallstone formation after fast weight reduction: a potential study in patients undergoing gastric bypass surgery for therapy of morbid obesity. A prospective research of symptomatic gallstones in girls: relation with oral contraceptives and different threat components. Menopausal hormone remedy and danger of cholecystectomy: a prospective examine based on the French E3N cohort. Influence of bezafibrate on hepatic cholesterol metabolism in gallstone patients: reduced activity of ldl cholesterol 7 alpha-hydroxylase. Association of a historical past of gallbladder illness with a decreased concentration of high-density-lipoprotein cholesterol. Complete mapping of crystallization pathways throughout cholesterol precipitation from mannequin bile: affect of physical-chemical variables of pathophysiologic relevance and identification of a stable liquid crystalline state in cold, dilute and hydrophilic bile salt-containing systems. No pathophysiologic relationship of soluble biliary proteins to ldl cholesterol crystallization in human bile. Bile salt hydrophobicity controls vesicle secretion charges and transformations in native bile. Imaging biliary lipid secretion in the rat: ultrastructural evidence for vesiculation of the hepatocyte canalicular membrane. Quantifying anomalous intestinal sterol uptake, lymphatic transport, and biliary secretion in Abcg8(-/-) mice. Hepatic Niemann-Pick C1-like 1 regulates biliary ldl cholesterol concentration and is a goal of ezetimibe. Homozygous disruption of the murine mdr2 P-glycoprotein gene leads to an entire absence of phospholipid from bile and to liver disease. Genotype-phenotype relationships in the low-phospholipid-associated cholelithiasis syndrome: a research of 156 consecutive sufferers. Severe cholestasis induced by cholic acid feeding in knockout mice of sister of P-glycoprotein. Nucleation time: a key factor within the pathogenesis of cholesterol gallstone disease. Central adiposity, regional fat distribution, and the danger of cholecystectomy in girls. Gallbladder disease is related to insulin resistance in a high threat Hispanic inhabitants. Gallstone disease is associated with more extreme liver harm in patients with non-alcoholic fatty liver illness. Cholelithiasis and markers of nonalcoholic fatty liver illness in patients with metabolic risk factors. Fatty liver illness: predictors of nonalcoholic steatohepatitis and gallbladder disease in morbid weight problems. Abnormalities of serum cholecystokinin and gallbladder emptying in celiac disease. Gallbladder emptying and somatostatin and cholecystokinin plasma levels in celiac disease. Impaired intestinal cholecystokinin secretion, a captivating however ignored link between coeliac disease and cholesterol gallstone disease. Long-term statin use and the risk of gallstone disease: a population-based case-control research. A prospective study of coffee consumption and the risk of symptomatic gallstone illness in males. Coffee intake is related to decrease threat of symptomatic gallstone illness in ladies. Ternary and quaternary aqueous techniques containing bile salt, lecithin, and cholesterol. Characterization of crystallization pathways during ldl cholesterol precipitation from human gallbladder biles: identical pathways to corresponding mannequin biles with three predominating sequences. Phenotypic characterization of Lith genes that determine susceptibility to cholesterol cholelithiasis in inbred mice: physical-chemistry of gallbladder bile. Filamentous, helical, and tubular microstructures throughout ldl cholesterol crystallization from bile. Phospholipid molecular species affect crystal habits and transition sequences of metastable intermediates during cholesterol crystallization from bile salt-rich mannequin bile. Newer pathogenetic concepts in ldl cholesterol gallstone formation: a unitary hypothesis. Role of gallbladder mucus hypersecretion in the evolution of ldl cholesterol gallstones. Mucus hypersecretion within the gallbladder epithelium of ground squirrels fed a lithogenic diet for the induction of ldl cholesterol gallstones. Targeted disruption of the murine mucin gene 1 decreases susceptibility to cholesterol gallstone formation. Isolation of a potent cholesterol nucleation-promoting activity from human gallbladder bile: function within the pathogenesis of gallstone disease. Inhibition of ldl cholesterol crystal formation by apolipoproteins in supersaturated mannequin bile. Apolipoprotein A-I in bile inhibits ldl cholesterol crystallization and modifies transcellular lipid switch by way of cultured human gallbladder epithelial cells. The impact of bile acid hydrophobicity on nucleation of several types of cholesterol crystals from model bile vesicles. Effects of bile salt and phospholipid hydrophobicity on lithogenicity of human gallbladder bile. Gallbladder motility and cholesterol crystallization in bile from patients with pigment and ldl cholesterol gallstones.
Quality endep 25 mg
Spindle cell tumors symptoms 24 hours before death endep 10 mg discount line, like nodular fasciitis treatment plan for anxiety purchase endep 50 mg online, fibromatosis, fibrous histiocytoma, and fibrosarcoma, may require information of the medical history and the help of a wonderful pathologist to make the definitive diagnosis. Some of these lesions are extra likely to happen in the orbit and are mentioned in additional element within the part on orbital tumors. Juvenile Fibromatosis Juvenile fibromatosis is a benign, fibrous tissue proliferation that may often affect the eyelid area of young children as a diffuse, nonencapsulated subcutaneous progress. The differential analysis consists of leiomyoma, neurofibroma, and well-differentiated fibrosarcoma. Multicentric Reticulohistiocytosis Multicentric reticulohistiocytosis is a uncommon systemic disorder characterized by an idiopathic proliferation of histiocytes. Fibrous Histiocytoma Fibrous histiocytoma is a delicate tissue tumor composed of a proliferation of fibroblasts and histiocytes. Although fibrous histiocytoma of the eyelid is a benign tumor, some orbital fibrous histiocytomas are malignant. Fibrosarcoma Fibrosarcoma is a malignant neoplasm that may develop spontaneously or can occur in the eyelid and orbital area following irradiation for the hereditary type of retinoblastoma. The main kind happens in younger kids with a mean age at diagnosis of four years (4). It consists histopathologically of immature spindle-shaped fibroblastic cells in a classic herringbone pattern or in interlacing fascicles. The finest management is broad surgical excision when essential, which may necessitate orbital exenteration in some instances, notably if the tumor is incompletely eliminated or recurs (4). Supplemental chemotherapy or irradiation may be needed depending on the scientific circumstances. Although the tumor can recur regionally after incomplete excision, metastasis is uncommon and the systemic prognosis for the first type is favorable. The prognosis for a patient with radiation-induced fibrosarcoma is less favorable due to danger for added new cancers related to the hereditary form of retinoblastoma. Chapter 10 Eyelid Histiocytic, Myxoid, and Fibrous Lesions 189 Selected References 1. Juvenile fibromatosis of the periorbital area and eyelid: a clinicopathologic examine of 6 circumstances. Juvenile fibromatosis in a 5-month-old child with massive involvement of upper eyelid and involvement of the orbit. The mass is composed of fibroblasts, histiocytes, and huge atypical hyperchromatic giant cells. The patient additionally had spotty pores and skin pigmentation and similar cutaneous lesions on ear and in groin. Facial and eyelid lesions in a 25-year-old woman with multicentric reticulohistiocytosis. In this part we focus on a few of the more necessary ones that may have an result on the eyelids, beginning with eccrine hidrocystoma (1�8). It usually occurs on the cheeks and eyelids of adult girls and may be comparable clinically to other cutaneous cysts. In distinction to apocrine hidrocystoma, which is almost at all times solitary, eccrine hidrocystoma is extra likely to be a number of. Heat, humidity, and perspiration could cause them to turn out to be larger, extra quite a few, and more symptomatic (3). Clinical Features Clinically, eccrine hidrocystoma characteristically seems as a transparent cystic translucent lesion, often close to the eyelid margin. Ultrasound biomicroscopy has been used to detect the cystic nature of the lesion and to differentiate it from melanoma and other solid tumors (8). Pathology Histopathologically, eccrine hidrocystoma is a clear cystic lesion lined by 2 layers of cuboidal epithelial cells. This lesion seems pigmented, simulating a melanoma, a finding additionally widespread in apocrine hidrocystoma. It generally occurs in adults, with a mean age of fifty five years, but is often seen in kids (2,5,6). Syndrome of cystic eyelids, palmo-plantar keratosis, hypodontia, and hypotrichosis as a possible autosomal recessive trait. Apocrine hidrocystomas of the lids, hypodontia, palmar-plantar hyperkeratosis and onychodystrophy. Photo essay: bilateral multiple eyelid apocrine hidrocystomas and ectodermal dysplasia. Excision of a number of eyelid apocrine hidrocystomas by way of an en-bloc lower eyelid blepharoplasty incision. Multiple apocrine hidrocystomas: treatment with carbon dioxide laser vaporization. Clinical Features Apocrine hidrocystoma is a easy or multiloculated cystic lesion that can develop on the eyelid, eyebrow, or near the medial or lateral canthus (1�7). Schopf-Schulz-Passarge Syndrome There is a variant of hereditary ectodermal dysplasia in which some cases have multiple apocrine hidrocystomas affecting both the higher and decrease eyelids bilaterally. These patients also can reveal hypodontia, palmar�plantar hyperkeratosis, and onychodystrophy (8�12,16). This constellation of findings known as the Schopf-Schulz-Passarge syndrome (8�12,16). Some circumstances appear isolated; others have an autosomal-dominant or -recessive sample (12). Pathology Microscopically, apocrine hidrocystoma is a cystic lesion with a clear lumen lined by a double layer of cells (1�7). The innermost layer has apical snouts that project into the lumen, a attribute function of apocrine cells. Multiple lesions have been eliminated by an eyelid blepharoplasty method to prevent rupture of the cysts (13). Other strategies, together with carbon dioxide laser vaporization, have been profitable (14). A latest report described successful treatment of multiple periocular apocrine hidrocystomas by chemical ablation of the cyst epithelium with trichloroacetic acid (15). Chapter 11 Eyelid Cystic Lesions Simulating Neoplasms 197 Eyelid Apocrine Hidrocystoma Depicted is a clinicopathologic correlation in an 18-year-old lady with a slightly larger bluish subcutaneous lesion within the nasal side of the best upper eyelid. A sebaceous cyst is usually secondary to occlusion of the duct of a sebaceous gland and can happen on the eyelid and adjacent tissue. Perhaps the commonest sebaceous cyst of the eyelid develops within the meibomian glands of the higher tarsus, from retention of meibomian gland material. Larger sebaceous cysts (pilar cysts) are most likely to arise in areas the place there are quite a few massive hair follicles. Hence, it generally develops on the scalp (90%), occasionally in the eyebrow area, and less typically within the medial canthus and eyelid (3,5). Clinical Features Sebaceous cyst of meibomian gland seems as a focal, subcutaneous nodule with minimal or no inflammation.
50 mg endep generic fast delivery
In the liver medications 122 endep 50 mg otc, arteries medications pictures 10 mg endep generic overnight delivery, portal veins, and bile ducts are surrounded by a fibrous sheath, the Glissonian sheath, whereas hepatic veins lack this construction. The right and left hepatic ducts drain the right and left lobes of the liver, respectively. The fusion of the right and left hepatic ducts provides rise to the frequent hepatic duct. The caudate lobe normally drains to the origin of the left hepatic duct or to the best hepatic duct. The cystic duct normally drains into the lateral facet of the common hepatic duct under its origin to type the bile duct (or common bile duct). They cross the diaphragm to enter precardiac, superior phrenic, and juxtaesophageal lymph nodes or travel alongside the right or left inferior phrenic artery to the celiac nodes. Deep lymphatic vessels leave the liver on the porta hepatis to drain into the foraminal node on the epiploic foramen and the superior pancreatic nodes. Lymphatic vessels that go away the liver with the hepatic veins continue in the wall of the inferior vena cava. Hepatocytes seem as polygonal cells with spherical nuclei of various sizes with frequent binucleate cells. Portal tracts inside the parenchyma contain a branch of the hepatic arteriole, portal vein, and bile duct working collectively as a triad and accompanied by nerve fibers and lymphatic vessels. Terminal hepatic arterioles and terminal portal venules originate from portal tracts and provide blood to the sinusoids. The sinusoids lead blended portal and arterial blood from the portal tract to the terminal hepatic venules (also generally recognized as central veins). These terminal hepatic venules drain into sublobular veins, then into hepatic veins, and ultimately to the vena cava. They are fenestrated and lack a basement membrane, constituting a comparatively "leaky" barrier. Endothelial cells additionally regulate sinusoidal vascular tone through paracrine regulation of stellate cell contractility. Lining the sinusoids are Kupffer cells, that are extra quite a few, bigger, and more phagocytically active within the periportal area. When hepatic stellate cells are activated within the setting of liver inflammation and damage, they transform into myofibroblasts that specific desmin and easy muscle actin and synthesize extracellular matrix. A perisinusoidal space, the space of Disse, remains between the sinusoidal lining and the vascular pole of hepatocytes and communicates with the sinusoidal house via multiple fenestrations. Lymphatic fluid accumulates within the space of Disse and then passes into the area of Mall earlier than draining into lymphatic vessels. Canaliculi direct bile to the terminal canals of Hering, that are lined partly by hepatocytes and partly by cholangiocytes. The canals of Hering cross into bile ductules, which are lined totally by cholangiocytes. Interlobular bile ducts connect to septal bile ducts and then into hepatic bile ducts. Histologically, the smaller ducts are lined by cuboidal cells, whereas the bigger ducts are lined by columnar epithelial cells. Organization of Liver Parenchyma the basic lobule of the liver was described in 1833 by Kiernan as a hexagon with a central vein at its heart and portal tracts at three corners. Because many glands have a duct as the middle of their functional unit, Mall envisioned the fundamental unit of the liver to be the portal unit, outlined at its center by a portal tract and at its periphery by central veins. At the left is the basic hepatic lobule, with the central vein as its center and portal tracts at three corners. Near the middle is the portal unit, with the portal tract at its center and central veins and nodal factors at its periphery. At the right is the liver acinus, the center of which is the terminal afferent vessel (in the portal tract) and the periphery of which is drained by the terminal hepatic venule, or central vein. At the periphery of the acinus lies the terminal hepatic venule (the "central vein") which drains a number of acini. The parenchymal portion of the portal and hepatic venous techniques consists of minute facet branches that originate as orderly rows along the terminal branches of the conducting portion. The portal venous branches divide a number of instances more often than the hepatic venous branches, thereby creating a larger number of portal venous channels for each hepatic venous channel. The "central vein," in the meantime, is definitely 6 to eight draining venules that individually face a corresponding inflow unit. The conical cluster of hepatocytes fed by a septal branch and drained by a hepatic vein department forms a "main lobule. Matsumoto and Kawakami also famous that the sinusoids that arise from the septal branches have a transverse course near the portal tract earlier than turning radially to the central vein, and this mattress of transverse sinusoids forms a sickle-shaped "influx front" for perfusion of the lobule that differs from the linear provide proposed by the acinus mannequin. This association defines 2 zones: the peripheral part of the classic lobule composed of adjoining sickle-shaped areas and the centrilobular portion bound by these sickle-shaped areas. Immunohistochemical research of hepatic enzymes spotlight the presence of a steady periportal community round portal tracts and terminal afferent vessels and a distinct concentric perivenous area around the central vein, supporting the concept liver structure resembles the traditional lobule more than the acinus. For instance, gluconeogenesis happens largely in the periportal region (zone 1), whereas glycolysis happens predominantly in the centrilobular region (zone 3). Zonation may be more complicated than historically envisioned, with nonmonotonic distribution of some enzymes. In a kind 1 shunt, portal blood is diverted utterly into the inferior vena cava, with absence of the portal vein. This kind of shunt occurs more often in girls than in boys; is related to different congenital abnormalities similar to cardiac defects, biliary atresia, and polysplenia; might manifest with hypergalactosemia, hyperbilirubinemia, hyperammonemia, or variceal bleeding; and could also be difficult by the formation of hepatic tumors similar to focal nodular hyperplasia (see Chapter 96). Liver improvement update: new embryo models, cell lineage control, and morphogenesis. Jagged1 within the portal vein mesenchyme regulates intrahepatic bile duct development: insights into Alagille syndrome. Tissue-resident macrophages originate from yolk-sac-derived erythro-myeloid progenitors. The stem cell niche of human livers: symmetry between growth and regeneration. In vitro expansion of single Lgr5+ liver stem cells induced by Wnt-driven regeneration. The fate of the vitelline and umbilical veins in the course of the growth of the human liver. Epithelial expression of angiogenic growth components modulate arterial vasculogenesis in human liver development. Clinical and anatomical basis for the classification of the structural components of liver.
Purchase 10 mg endep with amex
It usually occurs within the coronary heart medications on airplanes buy endep 10 mg fast delivery, but can arise within the orbit medicine over the counter endep 50 mg order fast delivery, eyelid, and conjunctiva (1�6). Pathology Lipoma reveals unfastened myxoid connective with pleomorphic lipocytes, usually with a spindle cell configuration. Clinical Features Conjunctival myxoma appears as a delicate, freely movable, pinkwhite lesion usually discovered within the temporal bulbar conjunctiva. Clinical Features Although a number of lesions can happen on the eyelid in association with multicentric reticulohistiocytosis (12), cases reported in the conjunctiva have been in adults and appeared as localized lots at the corneoscleral limbus without systemic evidence of multicentric reticulohistiocytosis (13). Carney Complex Conjunctival and eyelid myxoma can happen in association with an autosomal-dominant condition referred to as Carney complicated, characterised by myxomas, spotty pigmentation of pores and skin and mucous membranes, endocrine overactivity, and schwannomas (8,9). Most conjunctival myxomas have been solitary, with out systemic evidence of Carney advanced (1�6). However, any myxoma of the eyelid or conjunctiva should immediate analysis for cardiac myxoma, a life-threatening situation. Eyelid and conjunctival myxomas can turn out to be apparent long earlier than cardiac myxoma is acknowledged. Pathology Reticulohistiocytoma is composed of huge mononuclear or multinucleated cells with fine granular cytoplasm. It differs from juvenile xanthogranuloma in that it happens in adults and lacks Touton giant cells histopathologically (13). Pathology Myxoma is a hypocellular lesion consisting of sparse stellate and spindle-shaped cells interspersed in a myxoid stroma. Special stains and electron microscopy could assist to differentiate myxoma from related lesions like myxoid liposarcoma, spindle cell lipoma, myxoid neurofibroma, and rhabdomyosarcoma (6). If the prognosis is suspected and the lesion is small and asymptomatic, observation solely may be appropriate. Conjunctival Lipoma General Considerations Although lipoma is often seen in the orbit, conjunctival lipoma is uncommon and has usually been of the pleomorphic kind (10,11). Clinical Features Clinically, pleomorphic lipoma occurs in adults and has an analogous look to the myxoma described. Chapter 21 Conjunctival Neural, Xanthomatous, Fibrous, Myxomatous, and Lipomatous Tumors 377 Conjunctival Myxoma, Lipoma, and Reticulohistiocytoma 1. Hematoxylin and eosin stain on the left reveals spindle-shaped cells in unfastened myxoid stroma. The details of classification, medical options, histopathologic characteristics, and prognosis are discussed elsewhere (1,2) and are past the scope of this chapter. The gastric lesion appears to have an affiliation with Helicobacter pylori an infection. If such a relationship is established, antibiotics may show to be the best initial administration. Plasmacytoma and carefully related lymphoplasmacytoid tumors can hardly ever arise in the conjunctiva (1�10). Tumors composed of malignant plasma cells are often associated with multiple myeloma, during which instances the illness is manifested primarily in bone. However, soft tissue plasmacytoma can even happen as a part of a quantity of myeloma or as a solitary lesion. If the lymphoid infiltrate was unilateral, the possibility of systemic lymphoma was 17% and if the lymphoid infiltrate was bilateral the probabilities for systemic lymphoma were 47%. The authors use these figures in counseling the patient with a conjunctival lymphoid infiltrate. The medical options of conjunctival plasmacytoma are probably equivalent to these previously described for lymphoma. The lesion can current as a localized or diffuse salmon-colored infiltration (21�29). Immunohistochemistry may be helpful in determining whether or not the lesions are monoclonal or polyclonal. However, it seems that evidently immunohistochemistry has limitations in determining prognosis; many monoclonal lesions might observe a benign scientific course. Most conjunctival lymphomas are non-Hodgkin B-cell lymphomas; Hodgkin lymphoma and T-cell lymphoma have an result on the conjunctiva much less frequently (9). Plasmacytoma is composed of somewhat uniform massive spherical to ovoid cells with ample cytoplasm, displaced nucleus, clumping of nuclear chromatin, outstanding nucleoli, and variable mitotic activity (21�29). Clinical Features Clinically, a lymphoid tumor is often a diffuse, slightly elevated fleshy pink mass that has been likened to smoked salmon. It is mostly located within the forniceal or bulbar conjunctiva, but occasionally occurs on the limbus. It normally has a gentle vascular provide, but giant dilated conjunctival nutrient vessels could be obvious in larger tumors. Although conjunctival lymphoma often has a smooth surface, it can have a multinodular appearance and resemble follicular conjunctivitis. Therefore, biopsy is important to assist set up the analysis and a systemic analysis must be accomplished in all affected sufferers to exclude the presence of systemic lymphoma. It can be essential to counsel the affected person with a conjunctival lymphoid infiltrate as to the probabilities of developing systemic lymphoma. A evaluate of 117 Management If the conjunctival lesion is small and circumscribed, an excisional biopsy and supplemental cryotherapy can sometimes be carried out and no further remedy may be needed. However, we biopsy sufficient tissue for diagnosis, but not so much as to require grafting. This seems logical since conjunctival lymphoma is sensitive to radiotherapy and broad excision appears pointless. Others have instructed that larger lesions ought to be excised, even if amniotic membrane transplant is critical to shut the defect (8). When the lesion has been biopsied and confirmed histopathologically, more treatment should often be given. If the affected person has systemic lymphoma, then remedy ought to initially be chemotherapy. If the lesion is solitary, with no systemic lymphoma, external beam irradiation is Chapter 22 Conjunctival Lymphoid, Leukemic, and Metastatic Tumors 381 usually the therapy of alternative. The dose of exterior beam irradiation ranges from 2,000 cGy for benign lesions to four,000 cGy for extra malignant lesions. A current report described some sufferers who actually had regression of the lesion after biopsy only (14). Although it stays controversial, we currently consider that periodic observation could additionally be the preferred treatment in some cases. In patients with intensive residual tumor or with progression after biopsy, however, radiotherapy is usually advisable. The patient must be evaluated initially and periodically for multiple myeloma and monoclonal gammopathy. Fornix and conjunctiva reconstruction by amniotic membrane in a patient with conjunctival mucosa-associated lymphoid tissue lymphoma. Bilateral conjunctival mucosa-associated lymphoid tissue lymphoma misdiagnosed as allergic conjunctivitis.
Diseases
- Acanthocytosis chorea
- Adenoma of the adrenal gland
- Schizophrenia
- Dk phocomelia syndrome
- Micro syndrome
- Zellweger syndrome
- Loffredo Cennamo Cecio syndrome
- Activated protein C resistance
- Nail patella syndrome
- Heart aneurysm
Endep 10 mg discount on line
All other patients ought to be encouraged to undergo laparoscopic cholecystectomy for symptomatic gallbladder pain symptoms rheumatic fever 50 mg endep cheap amex. Biliary Pain and Chronic Cholecystitis Patient Selection Most operations for biliary tract disorders are carried out to relieve signs related to intermittent obstruction of the cystic duct by gallstones medications 7 rights purchase endep 75 mg on-line. Histologically, gallbladders from sufferers experiencing repeated assaults of biliary ache normally, but not always, show fibrosis and mononuclear cell infiltration that are attribute of chronic cholecystitis. Furthermore, sufferers with biliary pain are more probably than sufferers with asymptomatic stones to experience complications of gallstones. As with any operation, the potential benefits by way of relief of signs and prevention of future issues must be weighed in opposition to the danger of surgical procedure. Fortunately, the physiologic stress of cholecystectomy is minimal, and the operation could also be undertaken safely even in older adults and the infirm. In the poorly compensated cirrhotic patient, the danger of cholecystectomy is considerably greater. When cholecystectomy is carried out for uncomplicated biliary ache, routine perioperative antibiotics are seldom indicated. In general, sufferers with asymptomatic gallstones should be reassured that life-threatening complications are uncommon and that symptoms related to the stones develop in only a minority of patients. In truth, most sufferers in whom issues of gallstones develop have antecedent biliary ache. Nevertheless, the strategy of prophylactic cholecystectomy in all asymptomatic patients most likely has no major advantage over the recommendation that cholecystectomy be limited to symptomatic sufferers. Native Americans, for example, seem to have a fee of gallstoneassociated gallbladder most cancers excessive sufficient to justify prophylactic cholecystectomy. Morbidity and mortality charges for diabetic sufferers who undergo emergency operations for issues of gallstone illness have also been thought to be excessive. Evaluation the diagnosis of biliary ache is usually suspected from the scientific history (see Chapters 11 and 65). Few preoperative laboratory checks are routinely needed, though liver biochemical exams should be carried out to screen for unsuspected choledocholithiasis if the surgeon does cholangiography on selected patients somewhat than routine cholangiography on every affected person. If gangrenous or emphysematous cholecystitis is suspected, an agent effective against anaerobic organisms ought to be included. If cholecystitis is severe and issues similar to perforation seem imminent, cholecystectomy ought to be undertaken urgently. If the nature of the symptoms is uncertain, surgical procedure may be indicated to establish the prognosis. Conversely, the older grownup affected person with concurrent diseases such as coronary heart failure could profit from an initial nonoperative approach. In the previous, the timing of cholecystectomy for the typical affected person with acute cholecystitis was controversial. Multiple potential randomized managed scientific trials have in contrast the strategies of early (within three days of presentation) and delayed (after 6 to eight weeks) surgery for acute cholecystitis (Table 66. Despite preliminary issues as to its safety in acute cholecystitis, laparoscopic cholecystectomy is possible generally. Technical problems are encountered often in sufferers with severe irritation that obscures identification of the structures of the hepatocystic triangle or with coagulopathy. In these settings, an alternate method to whole cholecystectomy, such as laparoscopic subtotal fenestrating or reconstituting cholecystectomy or use of an open approach, could also be essential. The advantages of laparoscopic cholecystectomy in sufferers with biliary ache, including decreased incisional ache, shortened hospital stay, and extra rapid return to work, also apply to patients with acute cholecystitis. For the high-risk patient with extreme concurrent diseases, similar to liver, pulmonary, or coronary heart failure, cholecystostomy (gallbladder drainage) is preferable to cholecystectomy. Operative cholecystostomy has been outdated by a percutaneous strategy in most sufferers. Alternatively, residual stones may be removed via the cholecystostomy tube, and the affected person could additionally be managed expectantly. Recurrent biliary signs develop in approximately half of all patients treated with a cholecystostomy. More just lately, endoscopic transmural gallbladder drainage has proven to be as effective as percutaneous drainage in decompressing the gallbladder in patients deemed to be unfit for surgery. Acute cholecystitis in diabetic patients is related to a considerably higher frequency of infectious complications, corresponding to sepsis, compared with nondiabetic sufferers. Similarly, acute cholecystitis in older adults may have a deceptively benign clinical presentation but is associated with high rates of occult severe acute cholecystitis including empyema and gangrene. As with diabetic patients, early cholecystectomy is warranted in older grownup patients to guarantee immediate management of an infection. Most commonly, acalculous cholecystitis happens in a patient hospitalized for other severe diseases, such as trauma, burns, or main surgical procedure. It could develop in outpatients, among whom older grownup male sufferers with peripheral vascular illness appear to be at highest threat. Gangrene, empyema, and perforation of the gallbladder complicate the course of acalculous cholecystitis more generally than they complicate the course of acute cholecystitis caused by gallstones. Prompt elimination of the gallbladder is particularly necessary when gangrene or empyema is suspected and when perforation is imminent. In some patients, however, the chance of surgical procedure is high because of the severity of their underlying sickness. These patients may be managed initially with placement of a percutaneous tube cholecystostomy underneath ultrasound steerage. Those in whom evidence of intra-abdominal sepsis develops or persistent obstruction of the cystic duct is seen on cholangiography require cholecystectomy. B, Cholangiogram through a percutaneous cholecystostomy (small arrow) displaying a gallstone impacted on the neck of the gallbladder (large arrow). Emphysematous Cholecystitis Emphysematous cholecystitis is an unusual situation characterised by infection of the gallbladder wall by gas-forming micro organism, notably anaerobes (see Chapter 65). Gangrene and perforation commonly complicate the course of emphysematous cholecystitis. The therapy of emphysematous cholecystitis is immediate laparoscopic cholecystectomy after restoration of fluid and electrolyte balance. Antibiotics are indicated, with protection directed towards Gramnegative rods and anaerobic bacteria. Special Problems Gallstone Disease During Pregnancy Occasionally, gallbladder illness is first noted or turns into more troublesome throughout pregnancy. The most typical medical displays on this setting are worsening biliary pain and acute cholecystitis. The potential teratogenic results of conventional radiography and radionuclide scanning make these techniques unjustified within the pregnant patient.
Buy endep 50 mg line
Outline of surgical approach designed to acquire surgical margins as broad as possible symptoms just before giving birth endep 50 mg generic mastercard. Frozen sections indicated that there was no residual tumor and this was later confirmed with everlasting sections medications vertigo generic 50 mg endep fast delivery. Appearance at time of surgical closure by reconstruction with sliding anterior lamellar flap. It can develop as a solitary lesion unassociated with systemic illness or as multifocal or diffuse lesions related to kind 1 neurofibromatosis. The eyelid and orbit may be involved by neurofibroma in three alternative ways: solitary neurofibroma, a number of localized neurofibromas, and plexiform neurofibroma (1�11). Plexiform neurofibroma of the eyelid characteristically extends for far into the orbit. If the overlying pores and skin is spared, it might be preserved, facilitating a main closure. The multiple small cutaneous neurofibromas related to neurofibromatosis are normally asymptomatic and could be adopted with out energetic remedy. The lesion is often ill-defined and bleeds profusely at the time of surgical resection (9�11). When such a lesion turns into cosmetically unacceptable, surgical debulking could also be tried (8). The carbon dioxide laser is reported to be of great help in such cases (9,10). Because of the extent of many plexiform neurofibromas, a multidisciplinary approach with ophthalmologists, otolaryngologists, and neurosurgeons is commonly needed. Clinical Features Solitary neurofibroma, additionally referred to as fibroma molluscum, is a circumscribed subcutaneous nodular lesion of variable dimension. Multiple neurofibromas that affect the pores and skin in sufferers with kind 1 neurofibromatosis can even concurrently happen on the eyelids (1�3,5,6). They seem as a quantity of, discrete, subcutaneous nodules on the eyelid and adjoining pores and skin. Like the same neurofibromas on the extraocular pores and skin, they in all probability have a low potential to endure malignant transformation; malignant peripheral nerve sheath tumors in the eyelid are quite rare. Eyelid involvement is often related to contiguous involvement of the deeper tissues in the orbit (1�4). It develops in younger children as a thickening of the entire eyelid that originally causes an S-shaped curve to the margin of the higher eyelid (1�4). This lesion can present gradual progressive enlargement and prolong into the malar space of the eyebrow and conjunctiva. Pathology In contrast to schwannoma (discussed in the next section), which is a tumor composed nearly completely of Schwann cells, neurofibroma is composed of a mixture of Schwann cells, peripheral nerve axons, endoneural fibroblasts, and perineural cells. Bodian stain helps to delineate the axons and extra particular stains can help in the diagnosis and in identification of components of the tumor (7). Management A small, asymptomatic solitary neurofibroma of the eyelid may be adopted conservatively. If surgery turns into necessary, the lesion can normally be eliminated utterly by method of an eyelid crease incision; broad margins are Chapter 7 Neural Tumors of the Eyelid 119 Selected References 1. Orbital and eyelid manifestations of neurofibromatosis: a scientific study and literature evaluate. Surgical debulking of eyelid and anterior orbital plexiform neurofibromas by the use of the carbon dioxide laser. Solitary neurofibroma (fibroma molluscum) of the higher eyelid in a affected person without neurofibromatosis. The most distinguished ones are just under the eyebrow superotemporally, immediately above the cilia superonasally, and on the decrease eyelid near the lateral canthus. Massive plexiform neurofibroma of higher and lower eyelids in a affected person with kind 1 neurofibromatosis. Massive plexiform neurofibroma of left facet of face, with eyebrow and eyelid involvement. Massive plexiform neurofibroma of upper eyelid in a affected person with neurofibromatosis. Low-power photomicrograph displaying intertwining enlarged nerves typical of plexiform neurofibroma. Photomicrograph of cutaneous neurofibroma displaying randomly organized spindle cells with mucinous cytoplasm. Multiple schwannomas can happen in patients with neurofibromatosis, however solitary schwannoma is normally unassociated with that entity. Schwannoma is known to arise within the orbit (1�8); often, it occurs in the uveal tract, conjunctiva, caruncle, or eyelid. Clinical Features Clinically, schwannoma of the eyelid appears as a firm subcutaneous mass that may simulate a chalazion. Management Management is full excision; incomplete removal is associated with eventual recurrence and extra aggressive behavior (3�5). Superficial epithelioid schwannoma presenting as a subcutaneous higher eyelid mass. This lesion was beforehand managed elsewhere by curettage with the presumed diagnosis of chalazion, however it subsequently recurred. This lesion was additionally beforehand managed elsewhere by curettage with the presumed analysis of chalazion; nonetheless it recurred in the identical location. It arises from specialised neuroendocrine receptor cells of the skin and mucous membranes, often recognized as Merkel cells. These cells seem to mediate touch sensation and are thought to be derived from the neural crest. It is an aggressive malignant tumor that can exhibit native recurrence and distant metastasis. Although figures range, about 50% of sufferers are believed to develop regional or distant metastasis (4). There are several latest stories and critiques of eyelid and eyebrow involvement (1�33). Management Management is wide surgical excision with frozen section or Mohs chemosurgery management, just like that for basal cell carcinoma (2). Regional lymph noted dissection, irradiation, and chemotherapy are believed to improve the prognosis (2,sixteen,33). Radiotherapy (50 Gy) has been reported to obtain complete tumor control after 24 months (20). Concerning prognosis, Merkel cell carcinoma usually reveals early regional lymph node metastasis and distant metastasis.
Buy endep 25 mg otc
If the osteoid content is low and the fibrovascular content high medications with acetaminophen 10 mg endep cheap free shipping, then the lesion appears much less dense than bone treatment 2011 endep 25 mg generic on line. In some cases, linear shadows radiate from the main mass as a end result of tumor cells grow in fingerlike projections from the primary mass. Pathology and Pathogenesis Orbital osteosarcoma is composed of malignant spindle cells with hyperchromatic nuclei and numerous mitotic figures. In many instances, the matrix of the tumor incorporates chondroid and fibromatoid components and numerous blood vessels. Thin-walled sinusoidal areas could comprise neoplastic cells, maybe accounting for the bloodborne metastasis. Axial computed tomography of a 19-year-old girl with no prior history of retinoblastoma who offered with proptosis of the left eye. Note the diffuse mass within the medial facet of orbit with involvement of the ethmoid sinus. Facial appearance of a 5-year-old child who at age 1 year underwent enucleation of the best eye and irradiation of the left eye for retinoblastoma. Note the orbital implant in the best orbit and the intensive bony mass superotemporally in the left orbit. Histopathology of one other case of osteosarcoma exhibiting bone and malignant spindle cells. Fibrous dysplasia, a fibro-osseous malformation that presumably outcomes from an idiopathic arrest in the maturation of bone at the woven bone stage, can typically contain the orbital bones (1�22). The monostotic type accounts for 80% of instances, of which 20% affect the craniofacial bones. The frontal bone is most often concerned, adopted by the sphenoid and ethmoid bones. Orbital fibrous dysplasia is generally of the monostotic kind, although it often includes contiguous bones (3). The polyostotic type often is discovered as a part of Albright syndrome, characterized by precocious puberty in ladies and mottled pores and skin pigmentation ipsilateral to the osseous involvement. It was also found to be the most typical fibro-osseous lesion among the many giant sequence of major bone tumors of the orbit reported by Selva and associates (10). Fibrous dysplasia has been identified to hardly ever bear malignant transformation into osteosarcoma, fibrosarcoma, and other neoplasms, notably after irradiation (4). Pathology Histopathologically, fibrous dysplasia is composed of benign spindle cells in a fibrous tissue stroma and trabeculae of immature woven bone without osteoblasts. This function helps to differentiate fibrous dysplasia from ossifying fibroma, by which osteoblasts are normally evident. Management Management of fibrous dysplasia of the orbital bones has typically been conservative because the lesion could remain relatively stable for many years. However, in current years, there has been an inclination by some clinicians to treat this condition earlier (4). If the method encroaches on the optic canal or becomes cosmetically unacceptable, then surgical resection and craniofacial reconstruction could be undertaken, usually along side a neurosurgeon or otolaryngologist. It has been recommended that all dysplastic bone should be eliminated as a end result of progression can continue after incomplete resection (16). Some authors have postulated that visual loss is more probably owing to secondary mucocele or hemorrhage in the lesion. Clinical Features Orbital fibrous dysplasia usually has its onset within the first decade (1,2). The disease is slowly progressive, although it may slow down or stop in center life. Diagnostic Approaches On computed tomography and magnetic resonance imaging, changes in the concerned bones vary from small translucent zones to large diffuse areas of sclerosis. The lesion can have a "floor glass" look and tends to expand the bone with thinning of the overlying cortex (4). In the case of sphenoid bone involvement, lateral views finest depict the lesion and particular optic canal views can detect early compression of the optic foramen. Fibrous dysplasia could have imaging features just like meningioma, however the latter tends to occur among middleaged women and may have a homogeneous thickening of bone with out the discernable cortical rim (3). Chapter 33 Orbital Osseous, Fibro-osseous, and Cartilaginous Tumors 645 Selected References 1. Non-epithelial tumors of the nasal cavity, paranasal sinuses, and nasopharynx: a clinicopathologic examine. Osseous and fibroosseous lesions, together with osteoma, fibrous dysplasia, ossifying fibroma, osteoblastoma, giant cell tumor, and osteosarcoma. Fibro-osseous, osseous, and cartilaginous lesions of the orbit and paraorbital region. Massive proptosis and swelling of the temporal fossa in a 38-year-old girl with fibrous dysplasia. Proptosis and downward displacement of the proper eye in a 13-year-old boy with fibrous dysplasia. Young adult lady with slight upward displacement of left eye and delicate left proptosis. The medical diagnosis was sphenoid wing meningioma, however biopsy confirmed fibrous dysplasia. The lesion has a predilection for the mandible, however, when the orbit is affected, the frontal, ethmoid, and maxillary bones are primarily concerned (1�15). In a sequence of 21 cases, the imply age at analysis is 18 years (range, 4 months to fifty two years) (3). Clinical Features Ossifying fibroma that entails the orbit produces gradual proptosis and displacement of the globe, the course relying on which orbital bones are affected. It begins as a monostotic lesion, however can gradually prolong to contain adjacent bones and even lengthen to the opposite orbit (3). Diagnostic Approaches Computed tomography of ossifying fibroma demonstrates a round to ovoid expansion of the involved bone that may have a nonhomogeneous matrix and a skinny rim of sclerotic bone across the margins of the lesion. Pathology On low magnification histopathology, ossifying fibroma is characteristically composed of benign spindle cells in a vascular fibrous stroma, with scattered bony ossicles that closely resemble psammoma our bodies seen in meningioma. A thin rim of osteoblasts may help to differentiate ossifying fibroma from fibrous dysplasia. Management Because of its extra aggressive behavior, the popular management of orbital ossifying fibroma is early surgical removing. Most affected sufferers have developed progressive symptoms that justify surgical elimination combined with craniofacial reconstruction (1�4). In intensive cases, a multidisciplinary method to management is advisable, including orbital specialists, radiologists, neurosurgeons, otolaryngologists, craniofacial surgeons, and pathologists (11). Chapter 33 Orbital Osseous, Fibro-osseous, and Cartilaginous Tumors 649 Selected References 1. Ossifying fibroma involving the paranasal sinuses, orbit, and anterior cranial fossa: case report. Clinical, computed tomographic, and histopathologic characteristics of juvenile ossifying fibroma with orbital involvement.
Order endep 75 mg on line
During follow up medicine 66 296 white round pill discount 10 mg endep overnight delivery, abdominal ache developed in 44% shakira medicine cheap 25 mg endep mastercard, and 29% had what had been deemed to be functional abdominal complaints. This study illustrates again each the frequent resolution and relatively benign nature of asymptomatic gallstone illness. Special Patient Populations the clinical manifestations of gallstones are shown schematically in. Although the usual strategy to asymptomatic gallstones is observation, some patients with asymptomatic gallstones could also be at elevated risk of issues and will require consideration of prophylactic cholecystectomy. An increased danger of cholangiocarcinoma and gallbladder carcinoma has been related to sure issues of the biliary tract and in some ethnic groups Risk factors embrace choledochal cysts, Caroli illness, pancreaticobiliary malunion (also referred to as anomalous union of the pancreatic and biliary ducts, in which the pancreatic duct drains into the bile duct), massive gallbladder adenomas, and porcelain gallbladder (see Chapters fifty five, sixty two, and 67). Patients at increased threat of biliary most cancers may benefit from prophylactic cholecystectomy. If stomach surgery is deliberate for an additional indication, an incidental cholecystectomy ought to be performed. Pigment gallstones are widespread and infrequently asymptomatic in sufferers with sickle cell disease. Some authorities recommend combined prophylactic splenectomy and cholecystectomy in young asymptomatic patients with hereditary spherocytosis if gallstones are present. Morbidly overweight individuals who undergo bariatric surgical procedure are at high threat of problems of gallstones (see Chapters 7 and 8). A prospective research of patients with insulinresistant diabetes mellitus showed that after 5 years of follow-up, signs had developed in 15% of the asymptomatic patients. Percentages indicate approximate frequencies of problems that occur in persons with gallstones, based mostly on pure history data. The most frequent end result is for the affected person with a stone to remain asymptomatic throughout life (1). Biliary pain (2), acute cholecystitis (3), cholangitis (5), and pancreatitis (5) are the most common complications. Mirizzi syndrome (4), cholecystoenteric fistula (6), Bouveret syndrome (6), and gallbladder most cancers (7) are uncommon. Notably absent from the record of imaging research of the biliary tract is the plain stomach movie. Although useful on occasion for evaluating patients with stomach ache, plain abdominal films are restricted by a lack of sensitivity and specificity. Only 50% of pigment stones and 20% of ldl cholesterol stones comprise enough calcium to be visible on a plain abdominal movie. Because 80% of gallstones in the Western world are of the ldl cholesterol type, solely 25% of stones can be detected by easy radiographs. Plain stomach films have their greatest usefulness in evaluating patients with a few of the unusual problems of gallstones It has the extra benefit of being moveable and thus out there at the bedside of a critically ill patient. The stones are mobile and customarily congregate in the dependent portion of the gallbladder. Rarely, superior scarring and contraction of the gallbladder around gallstones make locating the gallbladder or the stones impossible, raising the potential of gallbladder most cancers. The contracted gallbladder filled with stones could give a "doublearc shadow" or "wall-echo shadow" signal, with the gallbladder wall, echogenic stones, and acoustic shadowing seen in quick proximity. Unfortunately, within the crucial care setting, these nonspecific findings are seen frequently in patients with no different proof of gallbladder disease. Subsequent cholecystectomy Treatment (see Chapters sixty six and 70) aSee Chapter fifty eight for a discussion of biliary pancreatitis. With repositioning of the affected person, stones will transfer, thereby excluding the possibility of a gallbladder polyp. Multiple gallstones may be seen inside the gallbladder lumen, with related acoustic shadowing. Presence of the signal has a positive predictive value of larger than 90% for detecting acute cholecystitis if gallstones are current. False-positive results happen primarily in fasting or critically unwell sufferers, in whom gallbladder motility is decreased. The discount in gallbladder motility results in greater water resorption, which finally ends up in a gelatinous bile. In critically sick patients, cholestasis and hepatocyte dysfunction lead to lowered clearance of radionuclide imaging brokers. Although nonvisualization of the gallbladder because of cystic duct obstruction is the hallmark of acute cholecystitis, pericholecystic hepatic uptake of radionuclide is a useful secondary sign. Another scan is obtained 30 minutes after injection of morphine, and if the gallbladder is 35 min 45 min 60 min. The gamma-emitting radioisotope diisopropyl iminodiacetic acid is injected intravenously, quickly taken up by the liver (at 5 minutes), and excreted into bile (at 20 minutes). Sequential pictures show the isotope quickly getting into the duodenum (at forty five minutes) and passing distally within the small gut with out ever being concentrated within the gallbladder. Failure of the gallbladder to be visualized as a sizzling spot within 30 to 60 minutes constitutes a optimistic outcome and implies obstruction of the cystic duct. The gallbladder is probably not visualized in roughly half of critically sick sufferers even after injection of morphine, thereby resulting in false-positive cholescintigraphy outcomes. An additional necessary position for cholescintigraphy is the noninvasive detection of bile leakage from the cystic duct as a complication of cholecystectomy (see Chapter 66). Stones throughout the bile duct appear as filling defects and can be detected with a sensitivity of around 95%. In sufferers who present with a complication of gallstones, corresponding to acute cholecystitis, a historical past of recurrent episodes of stomach pain within the months preceding the complication is commonly elicited. The term "chronic cholecystitis" to describe biliary pain ought to be prevented as a outcome of it implies the presence of a chronic inflammatory infiltrate that will or is in all probability not present in a given affected person. Recurrent episodes of biliary pain can also be associated with a scarred, shrunken gallbladder and Rokitansky-Aschoff sinuses (intramural diverticula). Ingestion of a meal usually precipitates ache, but more commonly no inciting occasion is apparent. The onset of biliary pain is extra more doubtless to happen in periods of weight discount and marked bodily inactivity such as extended mattress relaxation than at other times. The time period "biliary colic," used up to now, is a misnomer as a outcome of the ache is steady somewhat than intermittent, as would be instructed by the word colic. The pain increases gradually over a period of 15 minutes to an hour after which remains at a plateau for an hour or extra before slowly resolving. In one third of patients, the onset of ache may be more sudden, and on rare events, the ache might cease abruptly. Pain lasting greater than 6 hours suggests acute cholecystitis rather than easy biliary pain (see Chapter 11). Radiation of the pain to the scapula, right shoulder, or decrease stomach happens in half of sufferers.