Crestor dosages: 20 mg, 10 mg, 5 mg
Crestor packs: 30 pills, 60 pills, 90 pills, 120 pills, 180 pills, 270 pills, 360 pills

10 mg crestor purchase
Recent immune standing determines the source of antigens that drive homesotatic T cell enlargement cholesterol levels good or bad crestor 10 mg cheap with amex. B cell-intrinsic MyD88 signaling prevents the lethal dissemination of commensal micro organism during colonic harm quick cholesterol test discount crestor 5 mg amex. Naturally transmitted segmented filamentous bacteria segregate with diabetes safety in nonobese diabetic mice. Has the microbiota performed a crucial role in the evolution of the adaptive immune system Genetic and spontaneous fashions of inflammatory bowel disease in rodents: proof for abnormalities in mucosal immune regulation. The Toll-like receptor 2 pathway establishes colonization by a commensal of the human microbiota. Th17 cells are the dominant T cell subtype primed by Shigella flexneri mediating protective immunity. Outer membrane vesicles of a human commensal mediate immune regulation and illness protection. The microbial metabolites, short-chain fatty acids, regulate colonic treg cell homeostasis. Neuropilin 1 is expressed on thymusderived pure regulatory T cells, however not mucosa-generated induced Foxp3+ T reg cells. Mucosal immune responses are involved in several immune and inflammatory ailments, affecting organs with or without mucosal surfaces. We now acknowledge that basophils are additionally an necessary part of mucosal defenses and pathogenic mechanisms of immune illnesses. This chapter discusses the ontogeny and plasticity of both cells, their ability to provoke or influence immune processes, and their involvement in mucosal immunology. Given limitations in house in this chapter and the wealth of excellent, recent reviews on mast cells and basophils, we refer the reader to many of those (Moon et al. Mast Cell Progenitors the nature of mast cell progenitors has been studied in mice and in humans. More details of mast cell ontogeny in mice are offered in the glorious evaluate by Gurish and Austen (Gurish and Austen, 2012), together with proof for a splenic mast cell/basophil widespread progenitor. Recruitment of progenitors into tissues involves factors that promote their mobilization from bone marrow, assist their chemotaxis in the direction of particular tissues, and allow them to migrate into the tissue and be retained; these precursors then differentiate domestically. Lipid mediators may be necessary for recruitment of mast cell progenitors to tissues during inflammation. Finally, varied immune and inflammatory cells are important in mast cell progenitor recruitment (Alcaide et al. Progenitor Differentiation into Mast Cell Subsets the maturation phases of mast cell development occur after the dedicated progenitor enters peripheral tissues, where the microenvironment determines gene expression and the phenotypic plasticity of the mast cells generated. Evidence signifies that these mast cell subsets come from the same progenitor (Kitamura et al. In distinction, in humans there are a minimum of three subpopulations of mast cells (Weidner and Austen, 1993; Gurish and Austen, 2012) Progenitor Recruitment to Peripheral Tissues As early as 1983, it was proven that mast cell precursors can be present in varied peripheral organs and in significantly excessive numbers in the gut (Crapper and Schrader, 1983). Mast cell precursor numbers increase following antigenic stimulation within the gut and lymph nodes (Crapper and Schrader, 1983) and in the lung (Abonia et al. Mast Cell Survival and Turnover Mast cell numbers in peripheral tissues are regulated by a balance between cell proliferation, differentiation, and death. The numbers of mast cells in tissues could be decided by progenitor recruitment and apoptosis. Apoptosis of mast cells could be initiated by diverse stimuli, including Fas�Fas ligand interactions, presence or absence of progress and survival components, and expression of genes that regulate responsiveness to such components (Ekoff and Nilsson, 2011). Sphingosine 1-phosphate receptors can even improve mast cell survival throughout hypoxia (Zhang et al. More details on mast cell phenotypes are mentioned below in the part on "mast cell characteristics. The effects of specific cytokines and microenvironmental components range in different phases of mast cell improvement (Moon et al. Cytokines can even have an result on the phenotype of the cells and the expression of proteinases as will be mentioned elsewhere. A variety of cytokines that suppress mast cell apoptosis affect the expression of members of the family of the antiapoptotic gene Bcl2 (Ekoff and Nilsson, 2011). Mast cell survival may also be promoted by ligation of FcR1 with monomeric IgE within the absence of antigen to cross-link the receptor (Kalesnikoff et al. This might be a mechanism that will increase mast cells in allergic disease and parasitic infections the place there are excessive levels of circulating IgE. Therefore, much of our information about basophilopoiesis comes from human studies (Befus et al. There can be proof of lineage sharing between basophils and mast cells and/or megakaryocytes (Arock et al. Basophil Recruitment to Peripheral Tissues In distinction to mast cells, basophils can enter the peripheral blood from bone marrow as mature cells. However, there are also circulating basophil progenitors, and whether or when extramedullary basophilopoiesis is distinguished requires further research. Mice inhalation of Aspergillus fumigatus leads to fast increase in basophil numbers in the spleen and blood, but also in the lung (Poddighe et al. Activation of the Fas�Fas ligand pathway induces basophil apoptosis (Matsumoto et al. Expression of IgG receptors on mast cells is each species and phenotype dependent. A valuable method to distinguish mast cell phenotypes in rats, mice, and humans is predicated on their particular content of proteinases (Trivedi and Caughey, 2010; Caughey, 2011). Presumably, the microenvironment dictates outstanding plasticity in gene expression amongst mast cells in mucosal and different websites, a phenomenon that has been largely unexplored to date in mast cells (Andersson et al. In blood, basophils are round, however the form modifications as they migrate into tissues. Basophils also have an abundance of condensed chromatin across the periphery of the nucleus. They typically include fewer granules which are electron dense and extra homogeneous showing than mast cell granules. One of the differences between mast cells and basophils is that proteinases are plentiful in mast cells however not in basophils. Human basophils express each tryptase and tryptase, although at two orders of magnitude lower than mast cells (Jogie-Brahim et al. There is also a major difference in expression of Fc receptors between the basophils and mast cells.
Dambrose (Inositol). Crestor.
- How does Inositol work?
- Autism.
- Diabetic nerve problems.
- What is Inositol?
- Panic disorder.
- Are there safety concerns?
- Obsessive-compulsive disorder (OCD).
- Schizophrenia.
Source: http://www.rxlist.com/script/main/art.asp?articlekey=96321
Quality 5 mg crestor
Commensal micro organism in the intestine show cholesterol chart generic crestor 20 mg otc, mouth ldl cholesterol level definition crestor 20 mg generic with visa, and doubtless genital tract are coated with IgA antibodies that react with the micro organism on the premise of specific reactivity, polyreactivity, and likewise via interactions dependent on glycan chains of the antibody molecules (Mestecky and Russell, 2009). In sharp distinction to the function of mucosal antibodies, that are effectively involved in the elimination of pathogens of mucosal surfaces, the interaction of secretory antibodies with commensals results in their stability, and therefore the selective and attribute colonization of individual mucosal areas (see Chapter 50). A important comparability of these findings highlights the general rules involved in mucosal tolerance, i. Dysfunctional innate and adaptive immunity in the mucosa might end in dysregulated immune responses, irritation, and tissue harm. The position of the microbiota in adaptive immunity has been very extensively investigated using gnotobiological fashions. B cell improvement and the function of gastrointestinal lymphoid tissue in mucosal responses have been described in pioneering research (Cebra et al. Commensal micro organism might influence the event of the T cell repertoire of murine intestinal lymphocytes. There is a recent and increasing interest within the potential role of the microbiota in etiopathogenesis of inflammatory and neoplastic diseases. Today, based mostly on the enormously rising curiosity within the well being results of the microbiota, gnotobiotic services have proliferated in Europe, Japan, and North America. The methods for producing and rearing animals under germ-free conditions have been additional developed, and the embryo switch technique, along with cesarean section, is today the preferred methodology in lots of facilities. Gnotobiotic technology and sterilization protocols have improved, and long-term housing of wild-type and transgenic mouse colonies is possible. Gnotobiotic technology will continue to render perception into host�bacterial interactions as well as the contribution of the microbiome in well being and disease. Thus, disturbance of the intestinal microbiota in quantity or quality (dysbiosis) due to enhanced hygienic situations and/or antibiotic use has been linked to weight problems (Backhed et al. It is assumed that dysbiosis in the intestine lumen might have an result on distant anatomical sites by dysregulation of host immune responses. The concept that an imbalanced commensal microbial ecosystem performs a causal role in these illnesses is supported by primary research in gnotobiotic animal fashions. Infections are the most plausible modulators of inflammation, and a few microbes are now implicated as triggers of inflammatory and autoimmune illnesses (Bach, 2002; Kivity et al. Infection can induce and perpetuate autoimmunity by a quantity of antigen-specific and antigen-nonspecific mechanisms. The former consists of molecular mimicry, expression of modified, cryptic, or new antigenic determinants, and the second consists of polyclonal lymphocyte activation and Gnotobiology and the Study of Complex Interactions Chapter eight 115 bystander activation. Only few infectious triggers and their mechanisms of motion have been identified, similar to streptococci in rheumatic coronary heart illness (Fae et al. A vital decrease of Bifidobacteria and Lactobacilli has additionally been reported (Giaffer et al. Finally, it has been suggested that disease phenotype and genotype are associated with specific compositional modifications in intestinalassociated microbiota (Frank et al. Overall, lowered diversity, increased temporal instability, and elevated proportion of pathobionts (Bacteroides fragilis, E. More lately, research have proven that beneath particular pathogen-free situations, mice with faulty bacterial signaling (Nod1-/-; Nod2-/-) have increased colitis severity after administration of dextran sodium sulfate, if the management mice are also colonized with the identical microbiota as the knockout mice. The outcomes support the speculation that intestinal microbiota influences colitis severity, and this impact is extra pronounced in a genetically vulnerable host. Furthermore, modulation of the microbiota with an outlined ecosystem or specific probiotic that targets the phenotype related to the genetic risk decreases irritation and improves colitis end result (Natividad et al. Some beneficial effects of probiotics should still be current with filtered preparations or heat-killed micro organism (Verdu et al. It has been suggested that restoration of a balanced microbiota by probiotic bacteria supplementation might end in host resistance to irritation. These modifications could be mediated immediately, by competitors with other microbes for vitamins or biofilm modes of progress and by manufacturing of bacteriocins with specific antimicrobial spectra (Lievin et al. Competition may also be indirect, for example, by stimulation of a bunch immune response that preferentially affects totally different microbes (Kaila et al. Interestingly, probiotic bacteria can stimulate different host mechanisms of immune response with important influence on gut microbiota, as just lately shown for E. This effect may be defined by current findings showing that Lactobacillus acidophilus secretes molecule(s) able to downregulating expression of genes involved within the attachment of enterohemorrhagic E. Taken together the results counsel that some probiotics may prevent pathobionts from inflicting hurt to the host. Local immunomodulation also can affect the resident gut microbiota, since both antimicrobial peptides and cytokines produced by the host mucosa have immunomodulatory in addition to selective antibiotic properties (Yang et al. Large quantities of cytokines produced by intestine mucosa during inflammation can induce adjustments within the gene expression of intestine microbes, rising their pathogenicity. Lower counts in anti-inflammatory commensal bacteria believed to play homeostatic roles, such as Bifidobacteria and F. Also, rodshaped bacteria, identified within the small intestines of children born through the Swedish celiac epidemic, have been proposed as a danger issue contributing to the fourfold increase in illness incidence in children during that time (Forsberg et al. A recent examine has discovered increased abundance of Staphylococcus epidermidis coding for methillicin resistance in celiac sufferers compared to healthy topics (Sanchez et al. Collectively these studies suggest an association of a dysbiotic microbiota in celiac illness. However, a research in an animal model of gluten sensitivity indicated that a dysbiotic flora could be a danger factor in gluten sensitization and proposed that during experimental conditions that disrupt the intestinal barrier, immune activation to intestinal microbiota could predispose individuals to an increased susceptibility to gluten (Natividad et al. Animal studies recommend that perturbation of the microbiota by the above-described triggers ends in low-grade irritation and altered visceral perception, which could be reversed by particular probiotic bacteria (Verdu et al. Certain microbial stimuli, or rather lack of them, can disturb well-balanced postnatal development of T cell subpopulations. The Th2 kind of response, which is dominant at start, is balanced in favor of the Th1 type and regulatory type soon after supply, as a result of the stimulation of the immune system by early colonization by microbes. The presence of intestine microbiota at this crucial stage of life is essential for growth of oral tolerance, as demonstrated in gnotobiotic animals (Sudo et al. The enhance within the prevalence of allergies in developed international locations could be traced back to the economic revolution in the nineteenth century (Emanuel, 1988). This pattern is now spreading outdoors Western Europe and North America, to quickly creating international locations in Latin America, Africa, and Asia (Pearce et al. The hygiene speculation was formulated to explain this pattern by decreased microbial stimulation caused by diminishing household measurement, improved living standards, and higher personal hygiene (Strachan, 1989). This speculation should be interpreted in a broader sense, as the absence of infectious stimuli in adolescence and the poor Gnotobiology and the Study of Complex Interactions Chapter eight 117 improvement of the intestine microbiota group (Bjorksten et al. There is a big distinction in the neonatal gut microbiota composition between allergic and nonallergic topics (Kalliomaki et al. The significance of each intestine microbiota and youth period for long-time allergy prevention was shown when colonization with probiotic E. The causal function for a dysbiotic microbiota within the genesis of food allergic reactions remains unclear, though some animal studies have suggested that oral tolerance development in germfree mice may be altered. Despite some controversy in this area, overall the research recommend that the presence of a balanced commensal ecosystem promotes regulatory mechanisms that might decrease the incidence of meals allergies (Tsuda et al.
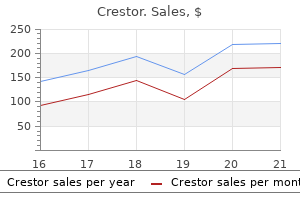
Crestor 5 mg quality
Primary prevention � Use of oral medication when attainable is likely to zinc cholesterol levels crestor 20 mg buy low cost produce fewer drug reactions than using topical or parenteral drugs cholesterol foods good and bad buy crestor 5 mg. Secondary prevention � Withdrawal of the offending drug is the first step in stopping future reactions. Differential diagnosis � the differential analysis is dependent on the scientific presentation of the individual affected person as drug allergy represents a spectrum of hypersensitivity reactions with heterogeneous mechanisms and medical presentations. Label affected person as allergic and advocate avoidance of the suspected offending drug No Clinical history: Did reaction happen inside 1 hour of drug administration Yes Skin prick testing + Allergic + Allergic + Allergic � Immediate reading intradermal test � Graded drug challenge* � Non-allergic Allergic Non-allergic No Patch test and/or delayed reading intradermal test + Allergic + � Graded drug challenge* � *Graded challenge is used to exclude an allergy to the drug in question, and is often solely carried out in patients thought of unlikely to be allergic to that drug 304 Part 1: Allergy typical presentation � there are a extensive variety of scientific presentations of drug allergy, as this dysfunction represents a spectrum of hypersensitivity reactions. Immediate drug reactions often current with urticaria, angioedema, rhinitis, wheezing, vomiting, diarrhea, or anaphylaxis. Nonimmediate reactions often current with a variety of cutaneous symptoms, although other organ signs are regularly also involved. Physical examination � As cutaneous manifestations are the most common presentation for drug allergic reactions, the bodily examination should involve a meticulous skin examination. On bodily examination, one also needs to assess for symptoms of anaphylaxis, lymphadenopathy, organomegaly, and all systems that could account for the clinical presentation. Useful clinical determination guidelines and calculators � Severe exfoliative dermatitides, such as Stevens�Johnson syndrome and toxic epidermal necrolysis, are doubtlessly lifethreatening reactions characterised by fever and mucocutaneous lesions leading to necrosis and sloughing of the dermis. While pores and skin testing may be helpful to affirm a direct hypersensitivity response to medication, it has only been totally validated for penicillin. Allergy to NonAntibiotic Drugs 305 Potential pitfalls/common errors made regarding diagnosis of disease � Maculopapular exanthems and delayed pores and skin eruptions are widespread in kids and are primarily related to viral infections. Section 4: therapy remedy rationale � Once a drug allergy is confirmed, there are three options for continuing treatment in a affected person: 1. Providing a similar, but not equivalent medication to the offending drug is an possibility, though there are crossreactive reactions which might be attainable depending on the drug and type of allergic reaction in question. When to hospitalize � Patients suspected to have Stevens�Johnson syndrome or poisonous epidermal necrolysis must be admitted to the hospital, presumably to the intensive care unit or a burn unit depending on the extent of pores and skin involvement and presence of comorbidities. Allergy 2014;sixty nine:420�37 Joint task Force on Practice Parameters; American Academy of Allergy, Asthma and Immunology; American College of Allergy, Asthma and Immunology; Joint Council of Allergy, Asthma and Immunology. J Allergy Clin Immunol 2012;130:1225 Allergy to NonAntibiotic Drugs 307 Liu A, Fanning L, Chong h, Fernandez J, Sloane D, SanchoSerra M, et al. Multiple drug intolerance syndrome: prevalence, medical traits, and management. Ann Allergy Asthma Immunol 2012;108:88�93 Suggested web sites American Academy of Allergy Asthma and Immunology. It is contraindicated for many who have had more severe reactions such as Stevens�Johnson syndrome, toxic epidermal necrolysis, and serum illness. Section 1: Background Definition of disease � Drug desensitization is a process that induces a brief state of unresponsiveness to allow the safe administration of a drug. Desensitization is contraindicated for extreme, nonIge mediated reactions corresponding to Stevens�Johnson syndrome, toxic epidermal necrolysis, and serum illness. Physical examination � Prior to starting the desensitization procedure, an entire physical evaluation of the affected person ought to be carried out to doc the baseline standing, including important signs. Frequent assessments are performed throughout the procedure to assess for any changes from baseline that would counsel an allergic response. Lists of imaging techniques No imaging studies are indicated for drug desensitization. Potential pitfalls/common errors made regarding prognosis of disease � reactions in the course of the desensitization procedure can happen so applicable treatments should be immediately obtainable. Section 4: therapy therapy rationale � Desensitization entails administering incremental doses of the drug administered via the oral, intravenous, or subcutaneous routes. Drug Desensitization 311 � Specific protocols have been published for penicillin, cephalosporins, insulin, and different medicines. If future treatment courses are needed, the desensitization process will want to be repeated. When to hospitalize � Drug desensitization procedures should be performed in a monitored setting with personnel, drugs, and tools necessary to deal with anaphylaxis available. Approximately onethird of penicillin desensitization procedures are related to allergic reactions, and 11 % of sufferers undergoing desensitization to chemotherapeutic brokers expertise allergic reactions. Section 7: studying list Joint task Force on Practice Parameters; American Academy of Allergy, Asthma and Immunology; American College of Allergy, Asthma and Immunology; Joint Council of Allergy, Asthma and Immunology. J Allergy Clin Immunol 2010;125:S126�37 Liu A, Fanning L, Chong h, Fernandez J, Sloane D, SanchoSerra M, et al. Clin exp Allergy 2011;41:1679�89 Scherer K, Brockow K, Aberer W, Gooi Jh, Demoly P, romano A, et al. It can be indicated for hymenoptera stings leading to systemic reactions attributable to honeybees, yellow jackets, white faced hornets, and fire ants. Section 1: Background � the primary documented use of allergy immunotherapy was to grass pollen for the therapy of hay fever in the early 1900s. For immunotherapy, the actual allergens are extracted from source materials such as animal pelt, mold cultures, and pollens. Combinations of those proteins and glycoproteins are blended in a selected method to formulate a therapeutic immunotherapy answer. Conventionally, the buildup part involves giving an incrementally rising weekly injection over 6 months to achieve upkeep therapy. An various approach is cluster immunotherapy, which involves administering a number of incrementally growing doses in Mount Sinai Expert Guides: Allergy and Clinical Immunology, First Edition. Of sufferers who obtain upkeep dose, 85% obtain some level of symptom aid. Section 2: Prevention � Allergen immunotherapy is used to forestall the development of signs or the event of bronchial asthma in allergic patients and to stop sufferers with allergy to one antigen from creating a quantity of allergic reactions. Section 3: Diagnosis � the preliminary steps involve analyzing and acquiring an in depth historical past from patients presenting with signs of rhinitis/conjunctivitis including rhinorrhea, congestion, postnasal drip, allergic conjunctivitis, asthma, or systemic reactions to stinging bugs. While each strategies of testing reveal circulating Ige, the pores and skin take a look at provides instant evidence of hypersensitivity to a particular allergen. Candidates for allergen immunotherapy are those patients with demonstrable Ige via skin or blood exams and scientific symptoms of allergy. Section 5: Special populations � Candidates for allergy immunotherapy embrace those sufferers with allergic symptomatology as nicely as goal measures of hypersensitivity demonstrated by a optimistic skin check or allergen particular serum Ige, no matter age. Section 6: Prognosis � Allergen immunotherapy could be very effective at controlling and reducing the signs of allergic rhinitis. In a big retrospective study of each kids and adults with allergic rhinitis, a major cost saving was demonstrated in these treated with allergen immunotherapy. No three Not a candidate for immunotherapy Yes 4 Assess risks, bene ts and prices of applicable management choices Immunotherapy Allergen publicity discount Medications Patient preferences Response to prior therapy Severity of illness 5 Is immunotherapy really helpful for this affected person No 6 Immunotherapy not given Yes 7 Obtain knowledgeable consent Counsel and educate patient in regards to the bene ts and dangers of immunotherapy including anticipated period and onset of ef cacy 8 Identify Speci c allergenic extracts Starting dose and immunotherapy schedule Maintenance dose Immunotherapy (Procedure) 317 9 Administer immunotherapy Safety equipment and procedures in place Medical personnel appropriately educated to establish and treat immunotherapy reactions At least 30 minutes wait in of ce after injection 10 Reactions to immunotherapy injections Yes eleven Manage response: Reassess risk�bene t of immunotherapy Consider dose/schedule adjustment Consider discontinuing immunotherapy No 12 Follow-up each 6�12 months while on immunotherapy or extra frequently for evaluation/management of immunotherapy reactions and/or underlying allergic illness or co-morbid circumstances Assess at follow up Clinical response to immunotherapy. Section 7: reading record DiBona D, plaia A, LetoBarone M, La piana S, Di Lorenzo G.
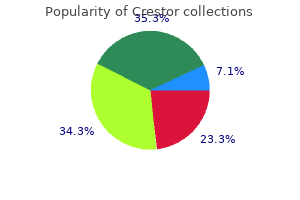
Generic crestor 5 mg without prescription
The ensuing enlargement of commensal anaerobic micro organism similar to segmented filamentous micro organism causes hyperactivation of B cells within the small Function of Mucosal IgD the operate of IgD has puzzled immunologists over the previous several many years cholesterol levels in meats buy 20 mg crestor overnight delivery. Originally thought to be a lately developed isotype cholesterol equation 20 mg crestor with mastercard, IgD is now recognized to be an evolutionarily historical molecule that has been conserved throughout evolution to complement the capabilities of IgM (Ohta and Flajnik, 2006). IgD would afford safety to the respiratory mucosa by binding to pathogenic bacteria such as Moraxella catarrhalis and Haemophilus influenzae and their virulence factors (Forsgren et al. Furthermore, IgD cross-linking triggers basophil release of antimicrobial peptides that kill pathogenic respiratory micro organism and cytokines that enhance irritation (Chen et al. Therefore, IgD could contribute to higher respiratory immunity not solely by neutralizing pathogens and excluding commensals, but also by recruiting circulating innate immune cells with antimicrobial and immunostimulating functions (Cerutti et al. Some of these people have fewer mucosal infections than patients with regular or decreased IgD responses (Brandtzaeg et al. The resulting primary I-S-C transcript undergoes splicing to generate a germline I-C transcript that lacks an open reading body and thus fails to encode a protein. Molecular Basis of IgD Production Although IgM is first expressed by pre-B cells, IgD emerges later during B-cell ontogeny, being principally expressed by transitional and mature B cells (Chen and Cerutti, 2010b). Nonetheless, most of these hyper-IgM sufferers present regular or elevated serum IgD, which may derive from uncommon IgD+IgM+ plasma cells that secrete both IgM and IgD via various splicing (Chen et al. In people, IgD+IgM- B cells inhabit the circulation, tonsils, nasal cavities, lachrymal glands, and salivary glands however are only hardly ever detected within the intestine (Chen and Cerutti, 2011; Chen et al. Here, a brief Regulation and Function of Mucosal IgA and IgD Chapter 32 689 overview of systemic IgG responses is followed by a dialogue of the peculiarities of IgA production in the intestine. The extrafollicular pathway generates short-lived plasmablasts that secrete IgM, whereas the follicular pathway generates Bcl-6�expressing germinal middle B cells often identified as centroblasts and centrocytes (Victora and Nussenzweig, 2012; Vinuesa et al. Eventually, high-affinity centrocytes differentiate into memory B cells and plasmablasts that specific IgG or IgM (Crotty, 2011; Victora and Nussenzweig, 2012; Vinuesa et al. In addition to coming into the circulation, reminiscence B cells type IgG+ extrafollicular aggregates and IgM+ follicular constructions in lymphoid organs (Dogan et al. In the presence of a recall antigen, IgG+ reminiscence B cells quickly generate IgG-secreting plasmablasts, whereas IgM+ reminiscence B cells initiate a secondary germinal center response (Dogan et al. Unlike IgM+ plasmablasts, IgG+ plasmablasts residence to the bone marrow, the place they turn out to be long-lived plasma cells that launch high-affinity IgG into the circulation for months or years (Shlomchik and Weisel, 2012). The chemokines required for the homing of IgG-expressing plasmablasts to the respiratory and urogenital tracts remain poorly understood. In this aggressive situation, a excessive price of plasma cell generation may be anticipated to limit plasma cell survival. On the contrary, the composition of the human microbiota is surprisingly secure, and mucosal vaccination can confer safety through IgA (Pabst, 2012; Faith et al. This finding implies that the intestinal IgA system might recall previously selected specificities expressed by dominant B-cell clones. But how can we reconcile the presence of dominant clones with the lack of classical prime-boost options in bacteria-specific IgA responses (Hapfelmeier et al. One chance is that IgA responses to vaccines and pathogens involve dominant B-cell clones beforehand chosen by steady elements of the microbiota (Pabst, 2012). Thus, the technology of IgA likely occurs partly through the activation of naive B cells and partly through the re-activation of beforehand selected memory B cells. Accordingly, the pool of gut plasma cells consists of an oligoclonal element, by which a couple of clones are extremely expanded, and a polyclonal element, during which many different clones are current at low frequency (Lindner et al. Dominant B-cell clones might respond to new antigens if these antigens have sufficient structural similarity with the ones beforehand encountered. This strategy might present the IgA system with the necessary flexibility to respond to pathogens whereas offering sufficient stability to accommodate minor modifications within the resident microbiota. This primitive pathway involves antibodysecreting cells much like B-1 cells (Zhang et al. Of notice, this induction requires neither T cells nor a germinal middle reaction (Tsuji et al. In addition to harboring chromosomal S- or I- rearrangements and showing biased L chain gene utilization, most upper respiratory IgD+IgM- B cells categorical clonally related and extremely hypermutated V(D)J genes (Chen and Cerutti, 2010b; Arpin et al. These molecular footprints counsel that IgD+IgM- B cells endure oligoclonal expansion after repeatedly entering the germinal middle in response to persistent publicity to respiratory antigens (Koelsch et al. Despite their high mutation fee, human IgD+IgM- B cells are highly polyreactive (Koelsch et al. Gut-associated lymphoid tissue contains the molecular machinery to assist T-celldependent and T-cell-independent class swap recombination. Common variable immunodeficiency syndrome and nodular lymphoid hyperplasia within the small gut. Cell floor recycling of internalized antigen permits dendritic cell priming of B cells. Human reminiscence B cells originate from three distinct germinal center-dependent and -independent maturation pathways. Human intestinal IgA response is generated within the organized gutassociated lymphoid tissue but not in the lamina propria. Presence of J chain in human immunocytes containing numerous immunoglobulin classes. Although higher identified for its ability to neutralize toxins and some pathogens, IgA also plays an important position within the selection and maintenance of a various and spatially diversified neighborhood of commensal micro organism. Yet, the exact mobile and signaling components of these pathways and their relative contribution to mucosal immunity and homeostasis remain to be totally elucidated. Further studies are also needed to characterize how intestinal IgA discriminates commensals from pathogens and whether or not specific commensals are wanted to optimize homeostatic IgA responses. Moreover, more analysis is required to higher characterize the reactivity and protecting function of IgD within the higher respiratory tract, in addition to the mechanisms by which IgD prompts innate immune cells and translocates throughout epithelial cells. Such information could not only facilitate the event of novel vaccine strategies, but also contribute to a better understanding of intestinal and respiratory immunopathologies, together with inflammatory bowel disease and meals allergy symptoms. Mucosal B cells: phenotypic characteristics, transcriptional regulation, and homing properties. Common variable immune deficiency: critiques, continued puzzles, and a model new registry. Immunoglobulin D enhances the release of tumor necrosis factor-alpha, and interleukin-1 beta in addition to interleukin-1 receptor antagonist from human mononuclear cells. Anti-inflammatory function for intracellular dimeric immunoglobulin a by neutralization of lipopolysaccharide in epithelial cells. Mechanisms of divergence and convergence of the human immunoglobulin alpha1 and alpha2 constant region gene sequences. Reversible microbial colonization of germ-free mice reveals the dynamics of IgA immune responses.
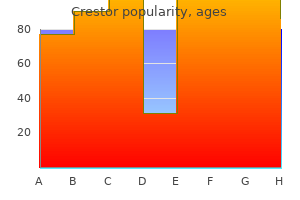
Order 5 mg crestor fast delivery
Nevertheless cholesterol levels very low order crestor 5 mg without prescription, some genetic knockouts have been useful tools in exploring the connection between intestinal barrier function and colitis pathogenesis cholesterol medication effects crestor 5 mg discount on-line. These embrace studies of knockout mice missing tight junction-associated proteins (Vetrano et al. However, the function of claudins-10 and -15 as paracellular ion channels (Van Itallie et al. However, delicate mucosal immune activation and T helper 1 cell polarization was noticed (Su et al. This suggests that intestinal epithelial tight junction barrier loss can enhance the speed of disease pathogenesis in a vulnerable particular person. Taken together, these knowledge implicate the leak pathway in the course of the early levels of disease pathogenesis. The ensuing tight junction-independent barrier loss then permits disease development in the absence of elevated pore or leak pathway permeability (Su et al. In a manner that additionally recapitulates human disease, the presentation of colitis in these mice is variable in terms of severity and age at onset. Conversely, disease penetrance can be enhanced by Helicobacter hepaticus infection (Matharu et al. This had led many to investigate why intestinal barrier loss is inadequate to trigger illness (Boirivant et al. This question is addressed most directly in a study that assessed disease susceptibility after intrarectal ethanol administration, which causes transient epithelial cell damage, mucosal erosion, and barrier loss (Boirivant et al. Although irritation can result in barrier dysfunction, barrier dysfunction may also precede disease development. Further, increased intestinal permeability activates regulatory immune processes that could be tolerogenic and limit responses to transient luminal antigen publicity. Occludin regulates macromolecule flux across the intestinal epithelial tight junction barrier. Claudin-2 expression induces cation-selective channels in tight junctions of epithelial cells. Protein kinase C regulates the phosphorylation and cellular localization of occludin. Structure-function studies of claudin extracellular domains by cysteine-scanning mutagenesis. Effects of phlorizin and sodium on glucose-elicited alterations of cell junctions in intestinal epithelia. Multiple domains of occludin are involved in the regulation of paracellular permeability. Absorption of 51chromium-labeled ethylenediaminetetraacetate in inflammatory bowel disease. Epithelial Cells: Structure, Transport, and Barrier Function Chapter 12 205 Boirivant, M. Genome-wide affiliation study of 14,000 instances of seven frequent diseases and 3,000 shared controls. The confluence of increased permeability, inflammation, and pain in irritable bowel syndrome. Next era exome sequencing of paediatric inflammatory bowel illness patients identifies rare and novel variants in candidate genes. Morphological components influencing transepithelial permeability: a mannequin for the resistance of the zonula occludens. Epithelial myosin mild chain kinase-dependent barrier dysfunction mediates T cell activation-induced diarrhea in vivo. Claudin extracellular domains determine paracellular cost selectivity and resistance but not tight junction fibril structure. Claudins create charge-selective channels within the paracellular pathway between epithelial cells. Zonula occludens-1 and -2 are cytosolic scaffolds that regulate the assembly of cellular junctions. Zonula occludens-1 and -2 regulate apical cell structure and the zonula adherens cytoskeleton in polarized epithelia. Permeability of the rat small intestinal epithelium alongside the villus- crypt axis: effects of glucose transport. Claudin-1 and -2: novel integral membrane proteins localizing at tight junctions with no sequence similarity to occludin. Claudin-based tight junctions are essential for the mammalian epidermal barrier: a lesson from claudin-1-deficient mice. A single gene product, claudin-1 or -2, reconstitutes tight junction strands and recruits occludin in fibroblasts. In vivo analysis of cadherin operate in the mouse intestinal epithelium: essential roles in adhesion, upkeep of differentiation, and regulation of programmed cell dying. Inflammatory bowel disease and adenomas in mice expressing a dominant adverse N-cadherin. Claudin profiling within the mouse throughout postnatal intestinal development and alongside the gastrointestinal tract reveals advanced expression patterns. Tricellulin constitutes a novel barrier at tricellular contacts of epithelial cells. Intestinal permeability assessed with polyethylene glycols in youngsters with diarrhea as a outcome of rotavirus and customary bacterial pathogens in a creating community. Cooperativity among secretory IgA, the polymeric immunoglobin receptor, and the intestine microbiota promotes host� microbial mutualism. Epithelial Cells: Structure, Transport, and Barrier Function Chapter 12 207 Katsuno, T. Deficiency of zonula occludens-1 causes embryonic deadly phenotype related to defected yolk sac angiogenesis and apoptosis of embryonic cells. Compartmentalization established by claudin-11-based tight junctions in stria vascularis is required for listening to via generation of endocochlear potential. Expression patterns of claudins, tight junction adhesion molecules, within the internal ear. Clonality, founder mutations, and subject cancerization in human ulcerative colitis-associated neoplasia. Structural foundation for physiological regulation of paracellular pathways in intestinal epithelia. Interleukin-10 gene-deficient mice develop a main intestinal permeability defect in response to enteric microflora. Partitioning of paracellular conductance alongside the ileal crypt-villus axis: a hypothesis based on structural analysis with detailed consideration of tight junction structure-function relationships. Junctional adhesion molecule, a novel member of the immunoglobulin superfamily that distributes at intercellular junctions and modulates monocyte transmigration. Discrimination of site-specific alterations in gastrointestinal permeability within the rat. Environmental stress-induced gastrointestinal permeability is mediated by endogenous glucocorticoids in the rat.
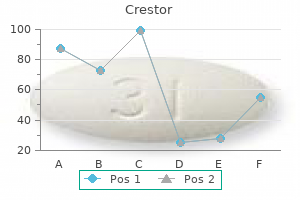
Crestor 5 mg order with mastercard
Apart from creating this bodily barrier cholesterol test over the counter buy 10 mg crestor mastercard, epithelial cells (1) secrete protective effector molecules cholesterol ratio mercola 10 mg crestor discount overnight delivery, (2) pattern bacterial antigens, and (3) recruit each innate and adaptive immune effectors to the positioning of an infection. Mucin, produced by goblet cells, is a fancy combination of very numerous, high molecular weight, glycosylated macromolecules that, by advantage of carbohydrate variety, is capable of binding almost any particle that lands on the mucosal floor (Klein et al. Mucus harbors numerous further protecting molecules including surfactants, digestive enzymes, antimicrobial peptides. Mucus move, driven partially by the motile cilia on epithelial cell surfaces, will constitutively shuttle free bacteria and exfoliated, contaminated cells away from the epithelial cell floor. The Microbiomes the wholesome mucosal immune system is dependent on commensal bacteria that benefit the host by (1) metabolizing sure carbohydrates and producing dietary shortchain fatty acids, (2) blocking pathogenic micro organism within the mucosa, (3) regulating epithelial cell turnover and mucin synthesis, (4) triggering bacterial sensors on epithelial cells and hematopoietic cells, and (5) driving growth of immune effectors (Ashida et al. Thus, in the wholesome state, finely balanced relations exist among micro organism, epithelial cells, dietary parts, and the immune response (Iweala and Nagler, 2006). The human respiratory and gastrointestinal tracts have vastly completely different microbiota. The respiratory tract could be divided into two regions: the nasopharynx and the lung. The nasopharynx harbors a rich commensal microbiome and respiratory pathogens commonly enter the host by colonizing this region and interacting with resident flora inducing a transient inflammatory response. The presence of these micro organism is most likely helpful, if simply to occupy a niche and forestall colonization by more pathogenic strains. Most respiratory pathogens initially colonize the nasopharynx and have to be aspirated into the lungs to initiate pneumonia. As pathogens pass to the decrease airways and lung parenchyma, the endogenous flora turns into sparse in density and species, together with some Pseudomonas, Streptococcus, Prevotella, Fusobacterium, Haemophilus, Veillonella, and Porphyromonas (Mandell, 1995; Erb-Downward et al. The human gastrointestinal tract is the site of probably the most intensive interactions between the human host and the microbial world. The intestinal epithelium covers roughly 200 square meters, and is colonized by bacteria that can attain densities of 1011 bacteria per milliliter in regions of the large intestine (Savage, 1977). It is estimated that approximately a thousand species can colonize the intestine and each individual harbors a pool of on common one hundred sixty species in certainly one of three completely different mixtures known as enterotypes (Balter, 2012). The immune system interacts with this endogenous flora to preserve homeostasis (Hooper et al. Mucin serves to reduce bacterial-epithelial contact and distinctive anatomic adaptations compartmentalize the sampling of the gut flora by dendritic cells. The commensals are required for clearance of invading pathogens by outcompeting their capacity to grow on similar carbohydrates (Kamada et al. Innate Bacterial Sensors Epithelial cells, related mucosal dendritic cells, and other hematopoietic cells sense micro organism by a wide selection of mechanisms. Cytokine/chemokine secretion might subsequently recruit a variety of innate and adaptive immune effectors to the site of an infection. The full management of bacteria relies on sample recognition and downstream indicators as evidenced by increased susceptibility to Clostridium difficile in MyD88 knockout mice (Ryan et al. Motifs may be detected directly within the case of cytoinvasive pathogens or shuttled into the cell cytosol in the case of pathogens inhabiting the phagosome. These complexes operate predominantly in hematopoietic cells, particularly macrophage and dendritic cells, although there are stories of restricted inflammasome exercise in epithelial cells (Tang et al. One extra end result of autophagy is enhanced antigen presentation to immune effectors. Innate and Adaptive Immune Effectors Innate and adaptive immunity towards bacteria at the mucosal epithelial cell surface is central to the management of pathogens and mammalian survival. Classically, the innate effector cells (described in higher detail in different chapters) include pure killer cells, macrophages, dendritic cells, neutrophils, eosinophils, basophils, and mast cells. These serve in part to engulf bacteria and current bacterial antigens to the adaptive immune system. They can even reside within the epithelial lining of mucosal surfaces (intraepithelial lymphocytes) or within the lumen. Particularly relevant to the epithelial cell surface is the secretion of immunoglobulin (Ig)A by mature B cells. Pathogen-specific IgA is constitutively produced for months or years following an infection (Rudraraju et al. IgA capabilities by blocking bacterial access to epithelial cell membranes, blocking virulence elements, and selling transport of antigens across epithelial cells for dendritic cell sampling (Mantis et al. Infection limited to the airways is exemplified by the interaction of Bordetella pertussis, the trigger of whooping cough, with ciliated cells of the bronchi (Locht, 1999; Coote, 2001). Nasopharyngeal Colonization All wholesome youngsters and adults are colonized repetitively and normally asymptomatically with decision over a period of a quantity of weeks. Colonization entails interactions between the pathogen and the resident flora in addition to initiation of an inflammatory course of by interacting with host cells (see evaluate by Weiser, 2010). For example, the competitive interactions the pneumococcus directs at commensal bacteria include the manufacturing of bacteriocins and hydrogen peroxide with a variety of bactericidal results. This causes the epithelial barrier to turn into extra permeable and neutrophils and inflammatory mediators are recruited. Over time, the inflammatory response is attenuated and the pneumococcus varieties a biofilm utilizing the interplay of the serine wealthy protein PsrP with keratin-10 (Sanchez et al. Respiratory tract pathogens regulate gene expression in response to indicators attribute of each anatomical location (Stock et al. This part switching is beneath genetic control and serves to fine-tune the bacterial side of the bacterial/host cell interface. In all circumstances, the micro organism use two-component sign transduction methods to allow the change. This mechanism of phase switching within the respiratory tract was first understood intimately for the Bvg system in B. For pneumococcus, efficient colonization of the mucosa is regulated by a part change in colony morphology from opaque (suited to the bloodstream) to clear (adapted to nasopharynx), which has less capsule and more floor adhesins (Weiser, 1998). Colonization can additionally be controlled by the Cia system, which regulates expression of the serine protease, HtrA, and other unknown genes (Sebert et al. Loss of CiaR/H ends in a 1000-fold lower within the amount of bacteria colonizing the nasopharynx and a 25-fold lower in expression of HtrA versus wildtype. Prolonged colonization of the nasopharynx affords a possibility for bacteria to enter the bloodstream with out passing via the lung. The pIgR-IgA dimer complex strikes by way of a collection of endosomal compartments to be secreted on the apex. Exported pIgR is cleaved releasing secretory part (the extracellular domain of pIgR) certain to the IgA dimer (sIgA). Bacterial Interactions with Mucosal Epithelial Cells Chapter 49 959 Progression into the Lower Respiratory Tract Mucus is the primary innate defense defending respiratory epithelial cells from microorganisms and serves as a physical barrier to infection (Knowles and Boucher, 2002). Bacteria evade mucin entrapment by decreasing the variety of receptors on their surfaces or by enzymatic digestion of mucin by glycohydrolases (Gottschalk, 1960). Digestion of mucin reduces the viscosity of the mucus enabling bacteria to penetrate to the epithelial floor. For instance, removal of sialic acid from glycans on host cells by neuraminidases is a strategy utilized by all respiratory pathogens, even viruses.
Syndromes
- Endoscopic treatments for enlarged veins in the throat (bleeding varicies)
- Men - 40 inches or more
- Coronary bypass
- Shoulder dislocation
- Raw fish or oysters
- Excessive bleeding
- Infection
- Laparoscopy
Buy crestor 20 mg with mastercard
This is compounded by the many gaps in our understanding of the factors governing the biophysical properties of mucus and its constituents and their molecular and practical relationships cholesterol test results explained australia 10 mg crestor purchase with visa. Mucus is a viscoelastic materials cholesterol ratio 2.0 crestor 10 mg buy generic line, the viscosity of which varies between mucosal tissues and within particular person tissues beneath completely different environmental and pathophysiological conditions. Mucus is typically >95% water and appropriate hydration of mucus is vital for it to assume the correct rheological and biophysical properties and functions. However, there are a quantity of subfamilies of mucins with quite distinct buildings and capabilities together with the secreted polymeric gel-forming mucins, secreted non-gel-forming mucins, and the cell floor mucins (the identified human mucins are listed in Table 1). In fact, despite their functional and structural similarities these mucin subfamilies appear to have evolved individually, with glycoproteins sharing the features of the secreted gel-forming mucins present in primitive metazoans, while the cell floor mucins appear to have emerged in vertebrates (Lang et al. Individual mucins are expressed by a number of tissues and neoexpression of mucins not usually current can occur throughout disease. The composition and functional properties of particular person mucins can also range between particular person tissues, inside tissues between totally different individuals, and within tissues between different illness states, because of differing repertoires of Golgi-resident glycosyltransferases, which construct the advanced O-linked glycans on the mucin domains that are rich in serine and threonine, that are the amino acids that can be O-glycosylated. Adding additional complexity the mucin genes are extremely polymorphic, which is prone to contribute to differing susceptibilities to mucosal illness between individuals. The biosynthesis and construction of every of the mucin subfamilies are described intimately within the following section. These members of the family are synthesized mainly in specialised secretory cells recognized both as goblet cells or mucous cells depending on the tissue. The functional consequences of differential glycosylation remain to be absolutely elucidated; nonetheless, mucin glycans can act as particular binding sites for microbes and the in depth glycosylation of the central region of the mucin polypeptide renders the mucin proof against protease degradation. Furthermore, as discussed later, experimental alterations in mucin glycosylation can predispose to mucosal infection and irritation, underlining the significance of those domains. Mucins and Mucus Chapter 14 235 Mucins are difficult to assess biochemically particularly of their polymerized forms and subsequently there are substantial gaps in our data of their biosynthesis. Some of this knowledge has been gleaned by analyzing small fragments of the mucins expressed in cultured cells, which may present misleading insights. The Golgi equipment of mucin producing cells incorporates an array of transmembrane enzymes, the glycosyltransferases, which progressively build the complicated O-linked glycans found on mucins. Expression levels of the enzymes and their particular person sequence motif preferences on the mucin polypeptide seem to decide the glycosylation websites utilized (Gerken et al. The sugar chains are then prolonged by the action of different glycosyltransferases that sequentially add the sugars including N-acetylglucosamine, galactose, N-acetylgalactosamine, fucose, and sialic acid. These chains could be linear or branched ensuing in a heterogeneous array of glycan structures present on particular person mucins in every tissue. The glycans can be negatively charged because of terminal sialic acids or sulfated sugar residues or may be impartial. Further polymerization through disulfide bond formation of the N-termini occurs and the mucin polymers (that can range from 2 to greater than 20 monomers) are tightly packed into secretory granules with large quantities of Ca2+ to offset the negatively charged glycans, although different "packaging" elements are likely additionally to be concerned. The nature of N-terminal polymerization is controversial and should differ between mucins (Ridley et al. Insight on mucin assembly has been gained from the extensive literature on von Willebrand issue, which shares the homologous N-terminal domains important for polymerization. N-terminal dimerization of von Willebrand issue ends in lengthy thread-like polymers, which is in keeping with electron microscopy pictures of mucins isolated from mucus, and with a long-held biophysicists view of mucus consisting of tangled threads. Whether this form of polymerization is the same for all mucins stays to be seen. Mucins are launched from granules constitutively or following stimuli by fusion with the apical cell membrane. For a comprehensive evaluation of the regulation of mucin granule exocytosis see Davis and Dickey (2008). When mucins are released, they turn out to be rapidly hydrated and exchange calcium for sodium ions and as this occurs the mucus gel is fashioned with a 100- to 1000-fold increase in volume (Tam and Verdugo, 1981; Verdugo, 1990). Images of mucus in the intestine present striated layers of mucus and it could be that every "layer" is the mucus fashioned from the discharge of mucins from granules by a person cell. However, reliance on these morphological features could be deceptive in goblet cells where mucin manufacturing is slowed or secretion is enhanced, resulting in depletion of the theca. Mucin producing cells can be discovered throughout the mucosal layer itself as is the case in the intestine and lung, and/or could be present in submucosal glands, which extrude mucus fluids onto the mucosa as can be discovered, for instance, within the mouth (salivary glands), esophagus, and lung. The life span of these mucin producing cells additionally varies considerably between different mucosal tissues from only 4 to 5 days within the human intestine to many months within the lung (Rock and Hogan, 2011). While the main position of goblet cells is to produce mucin, a latest research means that in the gut these cells also take up antigenic materials from the luminal floor, transport it to the basal membrane, after which exchange this material into underlying dendritic cells (McDole et al. Dendritic cells are key antigen presenting cells that regulate immune responses and due to this fact goblet cells appear to be involved within the initiation of immunity in addition to barrier operate. Cell Surface Mucins the shared feature of secreted and cell surface mucins is a typically massive heavily O-glycosylated mucin area often consisting of repeat sequences. All of the cell floor mucins have fairly advanced cytoplasmic domains that appear to be involved in intracellular signaling, although they lack any endogenous kinase activity. Many mucosal cells have large amounts of subapical stores of cell floor mucins in membranous vacuoles as a reservoir to replace mucins misplaced from the cell surface. A parallel biosynthetic pathway results in inclusion of cell floor mucins in exosomes (small membranous extrusions) secreted apically by mucosal epithelial cells (Kesimer et al. Alternative splice isoforms have been described for a few of the cell floor mucins, including isoforms lacking a transmembrane area which might be prone to be instantly secreted from the cell. However, these variants have mainly been described in the context of adenocarcinomas during which mucin expression may be very excessive and which may present aberrant splicing, and it stays to be seen whether or not any of these alternative isoforms have a substantial role in normal mucosal biology. Transcriptional Regulation of Mucin Gene Expression As noted above, mucins are produced by a quantity of cell types, particular epithelial mucins various widely among organs and influenced by developmental, cell-specific, and environmental elements. The photomicrographs of hematoxylin and eosin-stained mouse colon (top left) and small gut (bottom left) show the localization of the goblet cells identified by their nonstaining thecae. The transmission electron micrograph on the proper exhibits a murine intestinal goblet cell highlighting the distinctive morphological appearance dominated by the stored mucin granules in the theca, and figuring out the important thing organelles concerned in mucin biosynthesis. Although mucin gene expression is tightly linked to tissue-specific cellular differentiation, the mucin genes themselves are regulated by a myriad of extracellular and intracellular indicators. The activity of transcriptional regulators is influenced by numerous extracellular and intracellular alerts together with reactive oxygen species, proteases, interleukins, polypeptide hormones, microbial pathogens, and their merchandise. Toxicants, including H2O2, tobacco smoke, and lipid mediators, also induce expression of mucins in various tissues. Thus, consistent with the critical position of mucus and innate immunity, the regulation of each goblet cell differentiation and the expression of particular mucin genes are tightly linked to mobile responses to nonpathogenic and pathogenic microbes and to toxicant exposures which have advanced to protect epithelial surfaces in diverse organs. Goblet Cell Differentiation within the Respiratory Tract the respiratory tract, including nasal passages, sinuses, and conducting airways are lined by a posh epithelium composed of numerous epithelial cell sorts, together with goblet cells, whose abundance varies alongside its proximal�peripheral axis. In regular airways, goblet cells are current in relatively low numbers, airways being lined primarily by pseudostratified epithelium consisting of basal, ciliated, and nongoblet secretory cells. In the human lung, numerous submucosal glands that comprise mucin producing goblet cells are present in cartilaginous airways.

Crestor 5 mg purchase mastercard
Reply to "Gut-associated lymphoid tissue incorporates the molecular equipment to assist T-cell-dependent and T-cell-independent class swap recombination" cholesterol medication causing kidney disease 20 mg crestor proven. Telling aside pal from foe: discriminating between commensals and pathogens at mucosal websites cholesterol test eating night before cheap crestor 20 mg fast delivery. Effector-triggered versus pattern-triggered immunity: how animals sense pathogens. Segmented filamentous micro organism are potent stimuli of a physiologically normal state of the murine intestine mucosal immune system. Ontogenesis of the secretory immune system and innate defence elements in human parotid glands. Low-level hypermutation in T cell-independent germinal centers compared with high mutation charges associated with T cell-dependent germinal facilities. Requirement for lymphoid tissue-inducer cells in isolated follicle formation and T cellindependent immunoglobulin A technology in the intestine. The quantity of secreted IgA might not determine the secretory IgA coating ratio of gastrointestinal micro organism. Distinct function of floor lymphotoxin expressed by B cells within the group of secondary lymphoid tissues. Distribution of immunoglobulin-containing cells in human bone marrow and lymphoid tissues. Quantitative distribution of immunoglobulin-producing cells in gastric mucosa: relation to continual gastritis and glandular atrophy. Contribution of immunoglobulin-secreting cells within the murine small gut to the "background" immunoglobulin manufacturing. Integrin-mediated interactions between B cells and follicular dendritic cells influence germinal heart B cell health. Microbial colonization influences early B-lineage development in the intestine lamina propria. The presence of IgA on the surface of rat thoractic duct lymphocytes which include internal IgA. How B cells seize, process and present antigens: an important position for cell polarity. Human immunoglobulin choice associated with class switch and attainable tolerogenic origins for C class-switched B cells. Longitudinal analysis of the prevalence, upkeep, and IgA response to species of the order Bacteroidales within the human gut. Given their persistent exposure to exterior assaults, mucosal organs have advanced a quantity of layers of defensive mechanisms characterised by elevated specificity. Besides physical, mechanical, and chemical defensive strategies, mucosal surfaces use sophisticated immunological mechanisms to repel toxins and microbes. In addition to forming chemical and mechanical limitations, delivering antimicrobial compounds and transporting secretory antibodies, epithelial cells regulate the signaling networks that connect the mucosal immune system with the external setting, including bacteria. Mammals have co-evolved with microbes for more than one hundred fifty million years and thus have developed symbiotic and Mucosal Immunology. Despite exceeding the number of eukaryotic cells forming our body by a minimal of an order of magnitude, bacteria peacefully live as commensals in the intestinal mucosa (Macpherson and Harris, 2004). These commensals course of indigestible polysaccharides, synthesize essential vitamins, stimulate the maturation of the intestine immune system, and form an ecological area of interest that stops the expansion of pathogens. Conversely, the lumen of the gut provides commensals with a steady habitat wealthy in power derived from the ingested meals. The confinement of commensals within the intestinal lumen includes the release of immunoglobulin A (IgA) into mucosal secretions (Brandtzaeg et al. Due to the vast area coated by the intestinal mucosa, IgA can be essentially the most plentiful antibody in our body. Of note, IgA establishes a state of "armed peace" in the homeostatic interaction between commensal micro organism and their host. When commensals or pathogens trespass the epithelial barrier, a state of "open struggle" breaks out and IgA receives help from IgG to repel the microbial intruders. In this life-threatening state of affairs, IgG provides a second line of defense that controls microbial dissemination by eliciting a strong inflammatory response. Under homeostatic situations, totally different mucosal districts are characterized by distinct antibody "signatures. In people, the intestinal and urogenital tracts produce an IgA subclass termed IgA2, whereas the respiratory tract incorporates IgD, the least understood part of our antibody repertoire (Brandtzaeg et al. This chapter discusses the elemental principles underlying the regulation and performance of IgA and IgD responses on the mucosal interface. Antigen recognition range is generated by bone marrow pro-B cells by the use of V(D)J recombination (Schlissel, 2003). In mice, liver and bone marrow B-cell precursors give rise to B-1 cells, which are phenotypically and functionally distinct from B-2 cells (Hayakawa and Hardy, 1988; Baumgarth, 2011). Mucosal IgA and IgM antibodies also engage the polymeric Ig receptor (pIgR) on epithelial cells (Brandtzaeg et al. The presence of this novel B cell developmental pathway remains to be ascertained in people. Thus, the intestine microenvironment may be essential to present checkpoint alerts that take away autoreactivity from the peripheral B-cell repertoire. Mucosal Antibody Composition Mucosal secretions comprise all antibody lessons, however the relative abundance of every antibody class markedly differs in distinct anatomic locations. The antibody class composition of a given mucosal website is in all probability going decided by the composition of the native microbiota, by the standard of native class switch-inducing alerts, and by differences in epithelial cell expression of specific antibody transporters and plasma cell�recruiting chemokines. Topography of IgA IgA is the most ample antibody isotype in mucosal secretions, whereas IgG is extra abundant than IgA in urogenital secretions, bronchoalveolar fluid, and hepatic bile (Brandtzaeg et al. IgD may be detected in nasal, salivary, lacrimal, and bronchoalveolar secretions (Chen and Cerutti, 2010b), whereas some IgE is current in nasal, bronchoalveolar, and intestinal secretions, particularly in allergic people (Gould and Sutton, 2008). Although circulating IgA is largely monomeric in humans, mucosal IgA forms dimers and oligomers in both mice and people (Mestecky and McGhee, 1987). In mucosal secretions, polymeric IgA (pIgA) originates from the interaction of two to four monomeric IgA (mIgA) molecules with a small polypeptide termed becoming a member of (J) chain, which is synthesized by mucosal antibody�secreting plasma cells (Brandtzaeg, 1974b). This J chain stabilizes pIgA and is recognized by the pIgR, an antibody-transporting protein expressed on the basolateral surface of mucosal epithelial cells (Mostov and Deitcher, 1986; Mestecky et al. Once the J chain of pIgA binds to the pIgR, the ensuing advanced is translocated across epithelial cells onto the mucosal floor via a course of generally identified as transcytosis (Mostov and Deitcher, 1986). Human IgA contains IgA1 and IgA2 subclasses encoded by distinct C1 and C2 genes (Cerutti, 2008b). These IgA proteins possess a seemingly identical receptorbinding profile however have a different distribution within the body (Mestecky et al. Whereas IgA1 is present in both circulating and mucosal compartments, IgA2 is mostly present in the mucosal compartment (Mestecky et al. Upper respiratory and small intestinal secretions include more IgA1 than IgA2, whereas large intestinal and feminine urogenital secretions contain more IgA2 than IgA1 (Mestecky et al. In general, IgA2 is extra plentiful at sites closely colonized by micro organism (Kett et al. This distribution may reflect the truth that IgA2 has a shorter hinge area, which makes IgA2 extra resistant than IgA1 to degradation by bacterial proteases (Flanagan et al.
Crestor 10 mg buy low price
Lymphoid Structures the speaking network of lymphatic vessels essential to achieve dissemination of lymphomyeloid cells develops within the early stage of fetal development cholesterol and lecithin in eggs buy 20 mg crestor mastercard. Lymphatic vessels in humans start to differentiate at 35�42 days of gestation (Yoffey and Courtice normal cholesterol levels chart australia crestor 5 mg order with mastercard, 1970). Discrete major B cell follicles, T cell zones with high endothelial venules, a dome area, and a follicle-associated epithelium are noticed within the human fetal intestine around 130�140 days of gestation (Spencer et al. Lymphocyte aggregations seem in the vermiform appendix about 120 days of gestation (Malas et al. The high endothelial venules categorical intercellular adhesion molecules and vascular cell adhesion molecules (Dohan et al. The Fc receptor for immunoglobulin G (IgG) has been detected along the human fetal intestine and is believed to play a role within the uptake and transport of IgG from amniotic fluid (Shah et al. In normal fetuses, illdefined lymphoid aggregates are seen at 110 days of gestation, with well-defined aggregates at a hundred and forty days of gestation (Gould and Isaacson, 1993). The early stages of growth of intestinal villi with columnar epithelium in people and the graduation of tight junctions have been observed from nine weeks (270 days) of gestation (Polak-Charcon et al. The adjustments in patterns of glycosylation of the oligosaccharides at the intestinal epithelial surface after birth might affect colonization patterns within the intestine. Although many of the analysis has been undertaken in rodents, the modifications from sialylation in the fetus to fucosylation within the neonatal interval mixed with galactosylation in the grownup (Dai et al. B Lymphocytes and the IgA Secretory Mechanism the ontogeny of the mucosal B cell and secretory IgA (S-IgA) equipment is unclear because of variations in methods and mucosal websites examined in addition to inherent difficulties in determining the precise age of the fetus. In mice, the B-1 cells play an necessary role in the production of IgA plasma cells within the intestinal mucosa (Kroese et al. In the bronchi and major salivary glands, IgM+ cells have been reported from a hundred and forty days of gestation, and in the minor salivary glands and bronchioles, a quantity of IgM+ cells have been observed from one hundred seventy five days of gestation. IgA+ cells have been reported in association with the bronchi and salivary glands at 180 days of gestation (Iwase et al. However, sensitive polymerase chain reaction methods have shown that IgA and IgM synthesis may happen within the lung and intestine at as early as 110 days of gestation (Moro et al. In the human fetal parotid salivary gland, occasional IgM- and IgA-producing cells occur from a hundred and seventy days of gestation (Iwase et al. IgA-producing cells are predominantly of the IgA1 subclass and are additionally becoming a member of (J)-chain optimistic (Thrane et al. Crypts develop within the neonatal palatine tonsils at about one hundred twenty days of gestation, and the crypt epithelium is rapidly populated by dendritic cells and lymphocytes (Von Gaudecker and Muller-Hermelink, 1982). The consensus of most studies suggests that pIgR expression seems within the respiratory tract sooner than within the intestinal epithelium, however by 200 days of gestation, expression quickly increases at both sites. In the lung, pIgR has been reported within the bronchial floor epithelium and between the epithelium and the epithelial cells at as early as 56 days of gestation (Ogra et al. A marked improve in pIgR expression happens within the columnar epithelium of the large bronchi at about a hundred and forty days of gestation (Iwase et al. The pIgR could be detected in the apical cytoplasm of some epithelial cells of duct-like buildings in salivary glands by 143 days of gestation (Iwase et al. Two investigations confirmed that pIgR expression in salivary gland ducts elevated from one hundred seventy five days of gestation to approximately 200 days of gestation, after which no additional modifications had been seen in either the depth or the distribution of expression (Iwase et al. Synthesis of pIgR within the intestine could happen at as early as 40 days of gestation (Moro et al. However, pIgR expression in the small intestine is normally current by about 90�120 days of gestation (Crago et al. Immunofluorescence studies present that pIgR expression by intestinal epithelial cells occurs in comparatively small amounts by 200 days of gestation and thereafter increases quickly to show an grownup distribution pattern by one week postpartum (Rognum et al. The third of the element proteins of secretory immunoglobulins is the J chain, which participates in the intracellular polymerization of IgA and IgM. J-chain expression within the human fetus is an early event in B cell ontogeny and precedes the expression of the chain (Moro et al. T Lymphocytes T cells are noticed in the human terminal ilium at as early as one hundred days of gestation. By 140 days, these cells are organized round distinct B cell follicular areas (Spencer et al. There is uncertainty regarding the exact phenotype of the creating T cell repertoire. A massive inhabitants of T lymphocytes proliferating within the human fetal gut seem to achieve this within the absence of antigenic stimulation. However, it has been advised that mobile stores of those proteins are depleted because of suckling (Thrane et al. In a earlier part, the event of the intestinal epithelium was mentioned. As the growing human strikes from fetal to unbiased life, a major change in intestinal epithelium perform is required to present each absorptive and barrier capability. A great deal more analysis is required to perceive these changes and the way they interact with the developing innate and acquired immune defenses. Specific Immunity the mucosal immune equipment is anatomically in place prior to birth, with all elements recognized by 200 days of gestation. Immune stimulation in these instances arises from intrauterine an infection and presumably as an anti-idiotypic response to maternal antibody. However, antigen-independent B cell differentiation is a further possibility Table 1). In addition, in untimely infants who develop pulmonary an infection, IgA- or IgMcontaining plasma cells seem in association with the bronchial glands on the equal of the thirty ninth gestational week. IgG-containing cells appear one to two weeks later in affiliation with the submucosal layer of the bronchi (Takemura and Eishi, 1985; Mellander et al. It is quite probable that these secretory antibodies are of fetal origin, as fetal exposure to poliovirus in Sweden is highly unlikely (Mellander et al. In one case, antibodies had been detected in the infant of a hypogammaglobulinemic mom who was being administered intravenous immunoglobulin that contained only IgG antibodies in opposition to E. Other Key Cellular Components Other mobile elements necessary for effective mucosal immunity appear in the gastrointestinal tract in a timeframe much like that of lymphoid cell strains. Mucosal dendritic cells play a key function within the homing of activated T lymphocytes to the mucosal sites by way of the expression of homing receptors and the induction of both tolerance or active immunity in response to antigens offered at mucosal surfaces (Johansson-Lindbom and Agace, 2007; Cutler and Jotwani, 2006). Dendritic cells and macrophages seem in the lamina propria from about 12 weeks (80�90 days) however have impaired responses to lipopolysaccharide, suggesting an immature state (Smith et al. The mucosal immune system is established early in the first trimester of pregnancy. There is the potential for abnormalities growing in utero if the pregnancy is uncovered to adverse circumstances, similar to infection or chemical toxicity; having an effective immune system is important during this critical section. The prenatal growth of mucosal lymphoid constructions and cell populations is proven in Table 1. Prenatal Immunocompetence Innate Defenses Innate protection elements afford nonspecific protection in fetal life and at the time of start in the absence of adaptive specific immunity.
Cheap 20 mg crestor free shipping
The functional Physical Properties of IgA Early revelations about the form and dimensions of mIgA lowering cholesterol by diet alone crestor 10 mg cheap visa, dimeric (d) IgA cholesterol ratio target discount 5 mg crestor with mastercard, and S-IgA emerged from electron microscopy of varied IgA preparations. Taken together, these experiments are according to dIgA having a double Y-shaped appearance, with the 2 monomers interacting by way of the information of their Fc regions (Bloth and Svehag, 1971; Munn et al. These studies give an approximate worth for IgA Fc length of 63�70 � (Feinstein et al. The Fc size estimates are compatible with an end-to-end association of the Fc regions because overlap of the Fc regions may be anticipated to result in a much shorter Fc�Fc size than that observed in dIgA. Moreover, hydrodynamic knowledge from sedimentation and viscosity experiments are suitable with this similar extended arrangement of the two Fc regions (Bj�rk and Lindh, 1974). Mucosal Immunoglobulins Chapter 17 291 Electron microscopy experiments have additionally proven IgA molecules to be versatile and capable of adopting a extensive range of Fab arm angles (Feinstein et al. Although early work had questioned the level of flexibility in IgA (Weltman and Davis, 1970), fluorescence polarization and spin-label techniques later showed segmental flexibility in IgA to be comparable to that of IgG (Zagyansky and Gavrilova, 1974; Dudich et al. More recently, low-resolution methods corresponding to X-ray and neutron scattering have supplied information on the structure of human mIgA1 and mIgA2 in resolution (Boehm et al. IgA Fab and Fc regions have been modeled using the recognized crystal constructions for the corresponding IgG fragments, and a molecular dynamics curve fit search technique generated random hinge structures to connect them. Scattering curves have been calculated for these models and tested in opposition to experimental scattering information for human IgA samples. Given the apparent flexibility of IgA, the T shapes presumably mirror averages of the many conformations presumed to be available, during which the Fab arms flex in relation to the Fc. Possibly crucial revelation from these studies was the anticipated prolonged attain of the Fab arms of human IgA1 compared with that of human IgA2 and human IgG1. Hence, IgA1, to a larger extent than IgG1 or IgA2, could additionally be able to bivalent interactions when antigen molecules are extensively spaced. The resolution structural studies have been prolonged to human dIgA1, S-IgA1, and S-IgA2 (Bonner et al. Using dIgA1 isolated from myeloma serum, a near-planar construction was predicted during which the two Fc areas type a barely bent association with end-to-end contacts, with the J chain situated at their interface (Bonner et al. However, it ought to be careworn that the J chain construction and orientation used on this mannequin is bigoted; therefore, further experimentation might be essential to present a definitive understanding of how the Fc areas and J chain are literally organized. The predicted near-planar structure of dIgA1 appears to be conserved in S-IgA1 (Bonner et al. However, it ought to be kept in thoughts that these models fail to account for the interaction websites on IgA Fc which were outlined by mutagenesis research in several laboratories (see -Chains). In both instances, the light chains are shown in light grey and the heavy chains in darkish gray. The figure provides a face view of the Fc area of IgA1, whereas a aspect view of the Fc region of IgA2 is proven. Although in IgA1 and L chains are linked by disulfides, in IgA2 molecules inter-L chains could also be absent relying on the 2 chain allotype (see -Chains). Although controversial, most stoichiometric studies point out that every molecule of pIg, whether or not dimer, tetramer, or pentamer, contains only one molecule of J chain (Halpern and Koshland, 1973; Zikan et al. However, it seems that different pIgA myeloma proteins display a extremely variable content of J chain (Brandtzaeg and Prydz, 1984; Vaerman et al. In native pIgA, some antigenic determinants of J chain are poorly uncovered, suggesting that this polypeptide may be a minimal of partially obscured by the Fc area of pIgA. Cleavage of interchain disulfide bonds is usually enough to release J chain from pIgA and S-IgA, suggesting that only weak noncovalent interactions exist between J chain and the Fc area of pIgA and S-IgA (Mestecky et al. Mucosal Immunoglobulins Chapter 17 293 with J chain attaching or bonding both mIgA subunits at cysteine 471 of one -chain belonging to every monomer subunit (Bastian et al. In the absence of relevant crystallographic analyses, the exact nature of and J chain interactions remains enigmatic. Models primarily based on solution constructions (mentioned above in Physical properties of IgA) and accompanying glycan analysis (Royle et al. Moreover, in these fashions, the orientation of J chain has been arbitrarily assigned. Thus, the cleavage of disulfide bonds beneath mildly reducing conditions and within the absence of dissociating brokers. Presumably, this increased resistance to proteolysis confers on S-IgA molecules a significant useful benefit in the gastrointestinal milieu. Nevertheless, tryptic fragments of S-IgA may be generated by cleavage at increased (50�60�C) temperatures (Zikan et al. Furthermore, particulars of pIgA-pIgR interactions that happen on the surfaces and in the course of the epithelial cell transcytosis are described in Chapter 19. However, IgA shows several essential structural variations from IgG and IgD, notably the presence of a unique hinge region between the C1 and C2 domains, and the extension of the chain C terminus by 18 amino acid residues not present within the, and chains Table 3). The numbers embrace advanced and high-mannose sort N-linked chains inside the entire (V and C region) chains. However, there are notable differences within the arrangement of interchain disulfides and the place of N-linked glycans. The two chains are anchored to one another at the high of the C2 domains by disulfide bridges. Three (or four) cysteines on every heavy chain (Cys 242, Cys 299, Cys 301, and presumably Cys 241) are implicated in these linkages. The exact disulfide bond arrangements differ in the crystals of IgA1 Fc complexed with the 2 completely different ligands, according to a degree of disulfide interchange (Ramsland et al. The N-linked sugar moieties connected to Asn 263 are externally positioned, mendacity on the outer floor of the C2 domains with considerable further contacts with the C3 domains. Mucosal Immunoglobulins Chapter 17 295 Comparative research of H chains of all isotypes have indicated a substantial degree of basic structural homology between individual domains; nonetheless, the number of domains within the C region and the presence and structure of the hinge region are typical of each isotype Table 3). To maximize alignment, at positions the place further residues occur in some sequences dashes are used within the remaining sequences. Numbering is based on the generally adopted scheme used for IgA1 Bur (Putnam et al. Because the hinge and C2 domains are encoded in a single exon, the beginning of the C2 was taken as the first Cys residue encoded by this exon in human IgA1. Fc area of assorted isotypes display a putting homology when aligned in accordance with the invariant Cys and Trp residues (Putnam, 1989). In particular, the highly homologous place of Cys residues that take part in the formation of intradomain disulfide bridges is critical in sustaining the widespread structural options of all domains, no matter their Ig isotypes. IgA and IgM show the very best diploma of sequence homologies in their Fc areas that, respectively, comprise the C2 and C3 domains and the tailpiece of IgA and the C3 and C4 domains and the tailpiece of IgM (Low et al. This excessive degree of main structure homologies between IgA and IgM seems to mirror their shut evolutionary origin. Furthermore, IgA and IgM molecules share important structure�function similarities corresponding to the flexibility to kind polymers, bind J chain via their penultimate Cys residues in structurally analogous tailpieces (Mestecky et al. Moreover, S-IgM functionally replaces S-IgA in most IgAdeficient individuals (Plebani et al. However, structural homologies of IgA subclasses inside one species are very excessive.