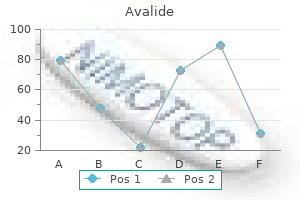
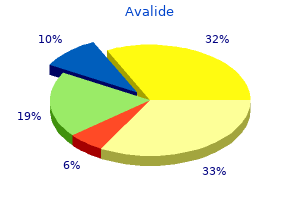
Avalide dosages: 162.5 mg
Avalide packs: 30 pills, 60 pills, 90 pills, 120 pills, 180 pills, 270 pills
Generic avalide 162.5 mg
D blood pressure chart dot proven avalide 162.5 mg, Model of sinoatrial node cell pacemaking as suggested by Maltsev and coworkers blood pressure meaning avalide 162.5 mg buy visa. The pacemaker locus can shift within or outdoors the sinoatrial node to cells discharging sooner or extra slowly. For example, if the slope of diastolic depolarization steepens and if the resting membrane potential becomes much less negative or the threshold potential extra adverse (within limits), the discharge rate increases. The identical mechanism reduces input resistance at diastolic potentials, which signifies that a greater depolarizing current can be required to achieve the "threshold" for firing an motion potential. Passive membrane properties, including membrane resistance, capacitance, and cable properties, play an important function in cardiac electrophysiology. Although the cardiac cell membrane is resistant to current circulate, it also has capacitive properties, which implies that it behaves like a battery and may retailer costs of reverse indicators on its two sides-an extra of adverse costs contained in the membrane balanced by equal constructive expenses outside the membrane. These resistive and capacitive properties cause the membrane to take a certain amount of time to respond to an utilized stimulus, rather than responding instantly, as a result of the costs across the capacitive membrane should be altered first. A subthreshold rectangular current pulse applied to the membrane produces a slowly rising and decaying change in membrane voltage somewhat than a rectangular voltage change. A, Isochronal map of atrial activation during sinus rhythm superimposed on a photograph of the endocardial surface of the sinoatrial node region. The number on every isochronal line indicates the time of activation in milliseconds. B, Vm (blue) and Cai (red) recordings from the superior (a), center (b), and inferior (c) sinoatrial node and proper atrium (d). Note the presence of slow diastolic depolarization in the Vm tracings a through c, but not in d. When aligned finish to finish, cardiac cells, particularly the His-Purkinje system, behave like a protracted cable by which present flows more easily inside the cell and to the adjoining cell across the hole junction than it does across the cell membrane to the surface. When present is injected at a point, most of it flows alongside contained in the cell, however some leaks out. Because of this loss of current, the change in voltage of a cell at a website distant from the point of utilized current is less than the change in membrane voltage at the point where the stimulus was utilized. A measure of this property of a cable known as the house or length constant lambda, which is the gap along the cable from the purpose of stimulation at which the voltage at steady state is 1/e (37%) of its worth at the level of introduction. Restated, describes how far current flows before leaking passively across the floor membrane to a worth a couple of third of its initial value. Because the current loop in any circuit must be closed, present must circulate again to its level of origin. Local circuit currents cross throughout hole junctions between cells and exit across the sarcolemmal membrane to shut the loop and complete the circuit. Inward excitation currents in one area (carried by Na+ in most regions) circulate intracellularly alongside the length of the tissue (carried largely by K+), escape across the membrane, and circulate extracellularly in a longitudinal course. The outside local circuit current is the present recorded on an electrocardiogram. Through these native circuit currents the transmembrane potential of every cell influences the transmembrane potential of its neighbor because of the passive circulate of present from one segment of the fiber to one other across the low-resistance hole junctions. As mentioned earlier, the speed of conduction depends on energetic membrane properties such as the magnitude of the Na+ current, a measure of which is Vmax. Passive membrane properties also contribute to conduction velocity and include the excitability threshold, which influences the potential of cells adjacent to the one which has been discharged to attain threshold; the intracellular resistance of the cell, determined by free ions in the cytoplasm; the resistance of the hole junction; and the cross-sectional area of the cell. The course of propagation is essential due to the influence of anisotropy, as talked about earlier. This change ought to be considered as a symptom of an underlying abnormality, analogous to fever or jaundice, rather than as a diagnostic category in and of itself as a end result of each the ionic modifications resulting in cellular depolarization and the extra fundamental biochemical or metabolic abnormalities liable for the ionic alterations in all probability have a number of causative components. For instance, acute myocardial ischemia results in decreased [K+]i and elevated [K+]o, release of norepinephrine, and acidosis, which may be associated to an increase in intracellular Ca2+ and Ca2+-induced transient inward currents and accumulation of amphipathic lipid metabolites and oxygen free radicals. All these changes can contribute to the development of an abnormal electrophysiologic setting and arrhythmias during ischemia and reperfusion. Knowledge of these modifications may provide insight into therapy that really reverses fundamental defects and restores membrane potential or different abnormalities to normal. The lowered resting membrane potential alters the depolarization and repolarization phases of the cardiac action potential. For instance, partial membrane depolarization causes a lower in the steady-state availability of fast sodium channels, thereby reducing the magnitude of peak I Na throughout section 0 of the motion potential. The subsequent reduction in Vmax and motion potential amplitude prolongs the conduction time of the propagated impulse, at instances to the purpose of block. These changes in motion potential are more doubtless to be heterogeneous, with unequal degrees of Na+ inactivation that create areas with minimally lowered velocity, extra severely depressed zones, and areas of complete block. Furthermore, if cardiacimpulse block occurs in a reasonably localized space without significant slowing of conduction proximal to the location of block, cells in this proximal zone exhibit brief action potentials and refractory intervals as a end result of unexcited cells distal to the block (still in a polarized state) electrotonically pace restoration in cells proximal to the positioning of block. If conduction slows progressively proximal to the location of block, the period of those action potentials and their refractory durations can be extended. It may be clinically tough to separate microanatomic reentry from automaticity, and often one is left with the consideration that a particular arrhythmia is "most according to" or "greatest explained by" one or the other electrophysiologic mechanism. Some tachyarrhythmias can be began by one mechanism and be perpetuated by another. An episode of tachycardia brought on by one mechanism can precipitate one other episode caused by a different mechanism. For example, an initiating tachycardia or untimely complex caused by abnormal automaticity can precipitate an episode of tachycardia sustained by reentry. However, by use of the features of entrainment (see later), arrhythmias attributable to macroreentry circuits can be recognized. DisordersofImpulseFormation Disorders in this category are characterised by an inappropriate discharge price of the traditional pacemaker, the sinoatrial node. Such problems of impulse formation may be brought on by dashing or slowing of a traditional pacemaker mechanism. A patient with persistent sinus tachycardia at relaxation or sinus bradycardia throughout exertion exhibits inappropriate sinus nodal discharge charges, however the ionic mechanisms liable for sinus nodal discharge can nonetheless be regular, although the kinetics or magnitude of the currents can be altered. Conversely, when a patient experiences ventricular tachycardia throughout acute myocardial infarction, ionic mechanisms ordinarily not involved within the formation of spontaneous impulses for this fiber kind may be operative and generate the tachycardia. In vitro research have demonstrated that myofibroblasts in infarct scars depolarize cardiomyocytes by heterocellular electrotonic interactions through hole junctions and also induce synchronized spontaneous exercise in neighboring cardiomyocytes. Automaticity at membrane potentials more adverse than -70 mV could additionally be attributable to If. Electrotonic effects from surrounding usually polarized or extra depolarized myocardium affect the development of automaticity. Abnormal automaticity could be produced in normal muscle or Purkinje fibers by applicable interventions, such as passage of current that reduces diastolic potential. An automatic discharge rate hastens with progressive depolarization, and hyperpolarizing pulses slow the spontaneous firing.
Generic 162.5 mg avalide otc
C blood pressure chart morning purchase avalide 162.5 mg with mastercard, They have been treated interventionally to restore broad patency in each pulse pressure mayo clinic avalide 162.5 mg buy cheap on line, as outlined in D. Development of azotemia or worsening renal function after treatment with an angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitor or angiotensin receptor blocker 5. Renal artery sympathetic denervation is a promising endovascular expertise for resistant hypertension55 however continues to be beneath investigation. A, Left stenosis and embolic (diameter 6 mm) having decrease restenosis safety device (long arrow). Markers proposed to indicate the chance of a medical response to renal artery stenting embody the clinical scenarios talked about earlier, excessive translesional gradient with vasodilators (analogous to coronary fractional move reserve), elevated brain natriuretic peptide, and a excessive resistive index (ratio of [peak systolic - end diastolic velocity]/peak systolic velocity) measured within the segmental arteries by duplex ultrasound. Although some sufferers with renal impairment and significant stenosis may even see an improvement in renal perform with stenting, roughly a 3rd of sufferers see no enchancment and in another 20% to 30% of sufferers renal operate worsens, possibly due to atheroembolization. Even although many operators use embolic safety devices throughout renal stenting, their value in preventing atheroemboli or worsening renal operate is unknown. Fibromuscular dysplasia is a rarer explanation for hypertension and infrequently occurs in youthful sufferers, with a better prevalence in girls. Such elements include hypercoagulable states, venous stasis, external obstruction, scarring or congenital abnormalities of veins, or injury to veins. An necessary clinical distinction is whether or not the deep venous thrombosis is related to an obvious reversible cause (provoked) or with out an obvious cause (unprovoked and requiring longer anticoagulation. Thrombosis at this web site occurs in a couple of third of all circumstances of lower extremity deep venous thrombosis26 and obstructs venous return from the decrease limb. Proximal deep venous thrombosis happens more regularly within the left leg on account of compression of the left iliac vein by the overlying proper iliac artery (May-Thurner syndrome). Acute severe proximal deep venous occlusion, characterized by a blue limb, pain, and limb ischemia (phlegmasia cerulea dolens) is commonly associated with malignancy. Chronic post-thrombotic syndrome occurs over a period of several years in about half the circumstances of iliofemoral deep venous thrombosis25 and is characterised by limb swelling, heaviness, and ache. Upper extremity deep venous thrombosis is expounded to effort-related proximal vein thrombosis in athletes (Paget-Schroetter syndrome), venous thoracic outlet syndrome, catheter-related thrombosis, or malignancy. Venous thoracic outlet syndrome is related to compression of the subclavian vein as it exits the thoracic cage between the clavicle, first rib, costoclavicular ligament, and subclavian and anterior scalene muscles. Catheter-related thrombosis is related to indwelling catheters, ports, and pacemaker or defibrillator leads. Malignancy with external obstruction is more generally associated with superior vena cava syndrome (see the subsequent section). Anticoagulation is the most common therapy of upper extremity deep venous thrombosis, however endovascular therapy can present aid from post-thrombotic syndrome. Endovascular therapy contains catheterdirected thrombolysis and remedy of any precipitating cause. A venogram of the left femoral vein was obtained after gaining access and venoplasty quickly after thrombolysis to the popliteal vein beneath ultrasound guidance. The affected person is mendacity face down on the table to allow entry to the popliteal vein. B, Multihole catheter across the venous occlubecause stents are topic to crushing sion; administration of lytic agents is started. C, Four hours after lysis following percutaneous transluminal angioplasty and fracture in this location. B, Venogram after 24 hours of catheter-directed thrombolysis with resolution of the thrombus however residual stenosis. Micari A, Cioppa A, Vadala G, et al: Clinical analysis of a paclitaxel-eluting balloon for therapy of femoropopliteal arterial illness: 12-month outcomes from a multicenter Italian registry. Schmidt A, Piorkowski M, Werner M, et al: First experience with drug-eluting balloons in infrapopliteal arteries: Restenosis fee and clinical end result. Tepe G, Zeller T, Albrecht T, et al: Local delivery of paclitaxel to inhibit restenosis during angioplasty of the leg. Werk M, Langner S, Reinkensmeier B, et al: Inhibition of restenosis in femoropopliteal arteries: Paclitaxel-coated versus uncoated balloon: Femoral paclitaxel randomized pilot trial. Typical causes embrace external compression, invasion from a tumor, or thrombosis associated to an indwelling central catheter. Angioplasty alone hardly ever relieves this situation efficiently because of vessel recoil, however stenting very successfully reduces signs. The stent normally must be oversized and extended well above and partly beneath the lesion so that it remains anchored and less more probably to embolize. Anticoagulation is usually prescribed, typically indefinitely for superior vena cava obstruction or thrombosis associated with malignancy. Ideally, indwelling catheters and pacemaker leads should be eliminated before stenting and reimplanted afterward if required. Long-term outcomes rely extra on the purpose for the superior vena cava obstruction, however in nonmalignant cases, excessive patency charges (>80%) over several years prevail. A report of the American College of Cardiology Foundation/American Heart Association Task Force on Practice Guidelines, and the American Stroke Association, American Association of Neuroscience Nurses, American Association of Neurological Surgeons, American College of Radiology, American Society of Neuroradiology, Congress of Neurological Surgeons, Society of Atherosclerosis Imaging and Prevention, Society for Cardiovascular Angiography and Interventions, Society of Interventional Radiology, Society of NeuroInterventional Surgery, Society for Vascular Medicine, and Society for Vascular Surgery. Zeller T: Current state of endovascular remedy of femoro-popliteal artery disease. Montero-Baker M, Schmidt A, Braunlich S, et al: Retrograde strategy for complex popliteal and tibioperoneal occlusions. Noory E, Rastan A, Schwarzwalder U, et al: Retrograde transpopliteal recanalization of continual superficial femoral artery occlusion after failed re-entry during antegrade subintimal angioplasty. Schillinger M, Sabeti S, Dick P, et al: Sustained benefit at 2 years of primary femoropopliteal stenting in contrast with balloon angioplasty with elective stenting. Lammer J, Bosiers M, Zeller T, et al: First medical trial of nitinol self-expanding everolimuseluting stent implantation for peripheral arterial occlusive illness. Amarenco P, Labreuche J, Mazighi M: Lessons from carotid endarterectomy and stenting trials. Zamani P, Kaufman J, Kinlay S: Ischemic steal syndrome following arm arteriovenous fistula for hemodialysis. Wheatley K, Ives N, Gray R, et al: Revascularization versus medical remedy for renal-artery stenosis. Savard S, Steichen O, Azarine A, et al: Association between 2 angiographic subtypes of renal fibromuscular dysplasia and scientific characteristics. Zartner P, Toussaint-Goetz N, Wiebe W, Schneider M: Vascular interventions in young sufferers present process transvenous pacemaker revision. In view of the surplus and growing prevalence of sort 2 diabetes and its incremental cardiovascular threat in contrast with type 1 diabetes, the main focus of this chapter is on sort 2 diabetes, except when specifically indicated in any other case. Diabetes is among the commonest continual ailments on the planet, affecting an estimated 285 million adults in 2010 (6. Although a lot attention traditionally has focused on the prevention and remedy of microvascular illness complications of diabetes.
162.5 mg avalide cheap free shipping
B blood pressure emergency 162.5 mg avalide purchase, Atrial pacing (cycle length of 500 msec) fails to alter the cycle size of the useful rhythm arrhythmia list purchase avalide 162.5 mg without prescription. C, After 30 seconds of ventricular pacing (cycle size of seven-hundred msec), suppression of the junctional focus results for nearly 7 seconds (overdrive suppression of automaticity). Surgery, electrolyte disturbances, myoendocarditis, tumors, Chagas disease, rheumatoid nodules, calcific aortic stenosis, myxedema, polymyositis, infiltrative processes. Ambulatory monitoring (Holter or external loop recorders) can be useful, however monitoring for longer periods may be essential, with extended (>3 weeks) Holter or external loop recorders being required. Longer durations of recording require an implantable loop recorder to establish the analysis. In sufferers with presyncope or syncope, one ought to suspect intermittent infra-His block in these with bundle branch block or an intraventricular conduction defect. Therefore, short-term or everlasting pacemaker insertion is indicated for sufferers with symptomatic bradyarrhythmias. Isoproterenol ought to be used with extreme warning or under no circumstances in patients with acute myocardial infarction. Basso C, Corrado D, Bauce B, Thiene G: Arrhythmogenic proper ventricular cardiomyopathy. Nademanee K, Veerakul G, Chandanamattha P, et al: Prevention of ventricular fibrillation episodes in Brugada syndrome by catheter ablation over the anterior right ventricular outflow tract epicardium. Belhassen B, Glick A, Viskin S: Excellent long-term reproducibility of the electrophysiologic efficacy of quinidine in patients with idiopathic ventricular fibrillation and Brugada syndrome. Knecht S, Sacher F, Wright M, et al: Long-term follow-up of idiopathic ventricular fibrillation ablation: A multicenter research. Lee P-C, Chen S-A, Hwang B: Atrioventricular node anatomy and physiology: Implications for ablation of atrioventricular nodal reentrant tachycardia. Bourke T, Vaseghi M, Michowitz Y, et al: Neuraxial modulation for refractory ventricular arrhythmias: Value of thoracic epidural anesthesia and surgical left cardiac sympathetic denervation. Slowing of the dominant pacemaker of the guts (usually the sinus node), which allows escape of a subsidiary or latent pacemaker. P wave morphology is determined by the rhythm controlling the atria-sinus, atrial tachycardia, junctional, flutter, or fibrillation. Intermittent giant (cannon) a waves could also be seen in the jugular venous pulse when atrial and ventricular contractions happen concurrently. The second coronary heart sound can break up normally or paradoxically, depending on the style of ventricular activation. A untimely beat representing ventricular capture can interrupt an everyday coronary heart rhythm. If a single pacemaker establishes control of each the atria and ventricles for one beat (capture) or a series of beats. Top, this tachycardia happens at a reasonably regular interval (W-shaped complexes) and is interrupted intermittently with sinus captures that produce functional proper and left bundle branch blocks. The junctional discharge rate is roughly 120 beats/min (cycle size = 500 msec) and the rhythm is irregular, generally shortened by sinus captures or delayed by hid conduction that resets and displaces the junctional focus. Bottom, Carotid sinus massage slows both the junctional and the sinus discharge charges. Atrial Fibrillation: Clinical Features, Mechanisms, and Management Fred Morady and Douglas P. The f waves have a rate of 300 to 600 beats/min and are variable in amplitude, form, and timing. The distinguishing characteristic from atrial flutter is the absence of uniform and regular atrial exercise in different leads of the electrocardiogram. In some sufferers, f waves are very small and never perceptible on the electrocardiogram. Note that f waves are variable in fee, form, and amplitude whereas flutter waves are constant in rate and all elements of morphology. On quick evaluation there may seem to be an everyday rate in maintaining with paroxysmal supraventricular tachycardia. In many research the left atrium contains the location of dominant frequency discharge, with a left-to-right gradient. The most typical temporary causes are extreme alcohol consumption (holiday heart), open coronary heart or thoracic surgery, myocardial infarction, pericarditis (see Chapter 71), myocarditis, and pulmonary embolism (see Chapter 73). If the signs occur each day, a 24-hour Holter recording is suitable. However, extended monitoring for two to four weeks with an occasion monitor or by mobile cardiac outpatient telemetry is acceptable for patients whose symptoms are sporadic (see Chapter 34). The historical past additionally ought to be directed at identification of potentially correctible causes. Laboratory testing ought to embody thyroid perform checks, liver perform exams, and renal perform tests. Echocardiography is always appropriate to consider atrial measurement and left ventricular function and to look for left ventricular hypertrophy, congenital heart illness (see Chapter 62), and valvular coronary heart disease. Chest radiography is suitable if the historical past or findings on bodily examination are suggestive of pulmonary illness (see Chapter 15). A stress test is appropriate for evaluation of ischemic heart disease in at-risk patients (see Chapter 13). It is well established that warfarin is more effective than aspirin for prevention of thromboembolic complications. The strongest predictors of ischemic stroke and systemic thromboembolism are a historical past of stroke or a transient ischemic episode and mitral stenosis. Each of the first 4 threat elements is worth 1 level, and a earlier stroke or transient ischemic occasion is value 2 factors. In a latest multicenter prospective examine, subclinical atrial tachyarrhythmias (atrial rate >190 beats/min for >6 minutes) were detected by system interrogation in 10. An necessary consideration in patients handled with an oral anticoagulant is the danger for bleeding. The web scientific benefit of warfarin was outlined because the number of strokes whereas not taking warfarin minus the variety of intracranial bleeding episodes while taking warfarin. The outcomes of these large cohort studies however, the choice to institute anticoagulation in a affected person in scientific follow should be individualized. In a meta-analysis of five 803 randomized scientific trials, aspirin reduced the chance for stroke by solely 18%. No information can be found to indicate superiority of a specific dose for prevention of thromboembolism. The primary consequence was a composite of stroke, myocardial infarction, systemic embolism, and vascular dying. When in contrast with placebo, clopidogrel decreased the risk for stroke by 28% and threat for the first outcome by 11% but elevated the chance for major hemorrhage. The study demonstrated that for each a thousand sufferers handled with the mix of aspirin plus clopidogrel instead of aspirin alone, 28 strokes (17 fatal or disabling) and 6 myocardial infarctions could be prevented, at a price of 20 major bleeding episodes (3 fatal).
Buy avalide 162.5 mg amex
For example blood pressure for children avalide 162.5 mg discount line, in those with hypoplastic left coronary heart syndrome and different duct-dependent lesions blood pressure cuff buy avalide 162.5 mg amex, prostaglandin E1 can be began instantly after birth, optimally in a hospital inside or hooked up to a pediatric cardiology facility. Note the smooth leftsided morphologic left ventricle versus the heavily trabeculated rightsided morphologic proper ventricle. In addition, the tricuspid valve is located extra inferiorly than its mitral counterpart. Note that the left-sided morphologic right ventricle is closely trabeculated with the tricuspid valve being inserted extra inferiorly than the right-sided mitral valve. Note that situs solitus and inversus are just the mirror image of (2) no moderator band, (3) no septal attachment of the mitral valve, and (4) larger (basal) insertion of the mitral valve. A morphologic right ventricle is a triangular-shaped construction with an inlet, trabecular, and outlet part. A morphologic left ventricle is an elliptical-shaped construction with a fantastic trabecular sample and absent septal attachments of the mitral valve in a normal coronary heart. Note the heavily trabeculated morphologic proper ventricle and the "compressed" low-pressure morphologic left ventricle. The image on the left reveals the superior vena cava connecting to the right-sided atrium. The proper image exhibits the pulmonary veins draining to the left-sided atrium in the identical case. Also notice the closely trabeculated right ventricle with evidence of the moderator band. Note on this picture that the left-sided tricuspid valve is inserted at a decrease level than its mitral counterpart. Also, the right-sided interventricular septum is easy, with no septal attachments from the right-sided mitral valve. These two pictures are from a coronary heart with dextrocardia and a double-inlet left ventricle. There has been recent consensus in the nomenclature such that these hearts are referred to as a "functionally single ventricle. This method has been the Rosetta stone of morphology in that it connects the European and North American classifications. Of note, in these hearts the apex may be left sided, midline, or on the proper, none of which has an influence on the classification of a functionally single ventricle. It is feasible to have normally related nice arteries, discordant arterial connections, or a single outlet with both aortic or pulmonary atresia. For instance, a smaller ventricle lying posterior to a larger one is kind of all the time a morphologic left ventricle. For example, in a double-inlet left ventricle, an L loop is more widespread with the morphologic left ventricle situated on the right of the hypoplastic morphologic proper ventricle. These are sometimes referred to as mitral or tricuspid atresia, Congenital Heart Disease > > > 1403. The superior vena cava can be seen connecting with the right-sided atrium and a few pulmonary veins to the leftsided atrium. Note that the nice vessels cross, with the aorta arising from the leftsided morphologic left ventricle and the pulmonary artery from the small right ventricle. In this case the aorta arises from the right-sided proper ventricle and the pulmonary artery from the left ventricle. The very location of the big ventricle in relation to the hypoplastic one helps in ascertaining the definition. That is, the morphologic proper ventricle is to the left and anterior to the morphologic left ventricle. The heart has a single outlet that might be seen arising from the morphologic right ventricle. There was no second chamber within the coronary heart and the designation of a morphologic left or proper ventricle is difficult. These two pictures show how the place of the ventricles may help in determining their morphology. On the left facet the larger chamber is posterior with the smaller one being anterior; thus the larger chamber is the morphologic left ventricle. Of notice, within the left panel the pulmonary artery arises from the right-sided proper ventricle, whereas it arises from the morphologic left ventricle in the best panel. Of significance, the ground of the absent connection consists of sulcus tissue, such that if a pin have been to be passed from the proper atrium via that tissue, it would end up outdoors the heart and never within the hypoplastic left or proper ventricle. All these hearts require a Fontan or single-ventricle palliation as a result of the smaller ventricle being incapable of supporting either the systemic or pulmonary venous circulation. It is feasible to have an aorta and pulmonary artery or a solitary outlet from either ventricle, with the other artery being atretic. Also, in some cases the solitary outlet can be a solitary trunk that gives rise to the pinnacle and neck vessels, the pulmonary and coronary arteries. The pulmonary artery may be distinguished by its early branching pattern into the left and proper pulmonary arteries; the pulmonary valve is all the time "hooked up" to the pulmonary artery. Similarly, the aorta could be distinguished by its "candy cane" form and the take-off of its three head and neck vessels (innominate, carotid, and subclavian arteries). Note the sulcus tissue where the tricuspid valve should be situated, the latter separating the proper atrium from the ventricular mass. This can be categorized as a practical single ventricle, and the affected person would need to undergo a Fontan operation. Once the place of the great arteries is deter- 62 mined, one can establish the ventriculoarterial relationship. When the morphologic proper ventricle ejects into the pulmonary artery and the morphologic left ventricle ejects into the aorta, ventriculoarterial concordance is current. When the morphologic proper ventricle ejects into the aorta and the morphologic left ventricle ejects into the pulmonary artery, ventriculoarterial discordance is current. Once segmental analysis has been completed, one can proceed to the standard echocardiographic windows to decide the nature of the particular lesions, as well as their hemodynamic relevance. These two pictures are from hearts with an absent right connection, the one on the left with related dextrocardia and the one on the proper with levocardia. Note the pulmonary veins draining into the left atrium and the wedge of sulcus tissue between within the flooring of the right atrium as seen on both photographs. Also notice the hypoplastic right ventricle on the right of the dominant left ventricle in the best panel. This is particularly essential in adult sufferers with a quantity of previous cardiac operations, in whom adequate transthoracic home windows are sometimes troublesome to obtain. Note that the tricuspid valve is perforate inasmuch as colour Doppler reveals some tricuspid valve regurgitation.
Order avalide 162.5 mg without a prescription
Imaging ought to be performed inside 2 hours of the resolution of symptoms blood pressure medication chronic cough purchase avalide 162.5 mg with visa, though information support its use for as a lot as blood pressure medication kinds avalide 162.5 mg generic visa four hours. Echocardiography can be used, with and without stress, to detect wall movement abnormalities in maintaining with myocardial ischemia. The presence of induced or baseline regional wall motion abnormalities correlates with a worse prognosis. The sensitivity of stress echocardiography appears to be similar to that of myocardial perfusion imaging (85% to 90%), and its specificity is somewhat better (80% to 95% versus 75% to 90%). The addition of T2-weighted imaging, which may detect myocardial edema and thus assist differentiate acute from persistent perfusion defects, improves the specificity to 96% without sacrificing sensitivity. The remaining 50% had proof of atherosclerosis, with 32% having minor plaque and 18% having a stenosis greater than 50%. Keller T, Zeller T, Peetz D, et al: Sensitive troponin I assay in early analysis of acute myocardial infarction. Reiter M, Twerenbold R, Reichlin T, et al: Early diagnosis of acute myocardial infarction in sufferers with pre-existing coronary artery illness utilizing more sensitive cardiac troponin assays. Reichlin T, Irfan A, Twerenbold R, et al: Utility of absolute and relative modifications in cardiac troponin concentrations in the early diagnosis of acute myocardial infarction. Lockie T, Nagel E, Redwood S, Plein S: Use of cardiovascular magnetic resonance imaging in acute coronary syndromes. Yang Q, Li K, Liu X, et al: Contrast-enhanced whole-heart coronary magnetic resonance angiography at 3. Characteristic findings include coagulation necrosis and contraction band necrosis, usually with patchy areas of myocytolysis at the periphery of the infarct. The "coronary care unit section" started in the mid-1960s and emphasised early detection and management of cardiac arrhythmias based mostly on the event of monitoring and cardioversion/defibrillation capabilities. The "high-technology phase," heralded by the introduction of the pulmonary artery balloon flotation catheter, set the stage for bedside hemodynamic monitoring and directed hemodynamic administration. All end in myocardial oxygen supply-demand mismatch and might precipitate ischemic signs, and all processes, when extreme or prolonged, will lead to myocardial necrosis or infarction. The reduction in flow may be caused by a very occlusive thrombus (bottom half, proper side) or by a subtotally occlusive thrombus (bottom half, middle). Models were adjusted for patient demographic traits, earlier heart problems, cardiovascular risk elements, continual lung illness, and systemic most cancers. The time period Q-wave infarcZone of perfusion tion was regularly thought-about to (area at risk) be just about synonymous with transCross section Completed infarction mural infarction, whereas non�Qof myocardium involving almost the wave infarctions had been usually referred entire area in danger to as subendocardial infarctions. Plaque rupture is present in virtually three quarters of circumstances and is more Plaque(SeealsoChapter41) prevalent in males. Plaque erosion is extra frequent in girls youthful Atherosclerotic plaque begins early in life and grows slowly over than 50 years, although the prevalence of rupture increases as decades. Other plaques may develop slowly and elicit stable or erosion is most likely plaque that has evolved to a morphology that symptoms. Lesions that had a larger plaque burden, signifying larger atherosclerotic content, and smaller lumen have been at best danger for subsequently triggering an acute coronary event. Red signifies necrotic core, darkish green indicates fibrous tissue, white indicates confluent dense calcium, and light-weight green indicates fibrofatty tissue. Myocardial relaxation-contraction is compromised, and irreversible cell injury begins within as early as 20 minutes. Nontransmural infarctions, however, incessantly occur within the presence of severely narrowed however still patent coronary arteries or when the infarcted region has adequate collateral circulation. At the top is a schematic diagram of the heart with the loca- tion of the most important epicardial coronary arteries. The center of the figure reveals the placement of the zones of necrosis following occlusion of a significant epicardial coronary artery. The myocardial hemorrhage at one edge of the infarct was associated with cardiac rupture, and the anterior scar (lower left) was indicative of an old infarct. Bottom, the early tissue response to the infarction process involves a combination of bland necrosis, inflammation, and hemorrhage. This form of myocardial necrosis, also termed contraction band necrosis or coagulative myocytolysis, outcomes primarily from extreme ischemia followed by reflow. Necrosis with contraction bands is caused by increased influx of Ca2+ into dying cells, which finally ends up in the arrest of cells within the contracted state within the periphery of huge infarcts and, to a larger extent, in nontransmural than in transmural infarcts. Ischemia without necrosis typically causes no acute adjustments visible on light microscopy, however extreme prolonged ischemia may end up in myocyte vacuolization, usually termed myocytolysis. Prolonged severe ischemia, which is doubtlessly reversible, causes cloudy swelling, as properly as hydropic, vascular, and fatty degeneration. An additional pathway of myocyte death involves apoptosis, or programmed cell death. After the first days, mononuclear phagocytes accumulated within the infarct in tissue. Finally, granulation tissue characterised by neovascularization and accumulation of extracellular matrix (fibrosis) adopted. Recent experimental work in mice has revealed a sequence of accumulation of subpopulations of mononuclear phagocytes. This highly orchestrated sequential recruitment of subpopulations of monocytes probably performs an essential position in myocardial therapeutic. The first wave of proinflammatory and phagocytically active mononuclear cells constitutes a "cleanup these early modifications are reversible. Changes after 60 minutes of occlusion include myocyte swelling, swelling and inside disruption of mitochondria, development of amorphous, flocculent aggregation and margination of nuclear chromatin, and leisure of myofibrils. After 20 minutes to 2 hours of ischemia, the adjustments in some cells turn into irreversible and progression of these alterations happens. Coagulation necrosis results from extreme, persistent ischemia and is normally present in the central region of infarcts; it causes arrest of muscle cells within the relaxed state and passive stretching of ischemic muscle cells. Mitochondrial damage with outstanding amorphous (flocculent) densities happens, but no calcification is evident. Top, Schematics of the time frames for early and late reperfusion of the myocardium provided by an occluded coronary artery. For roughly 30 minutes after the onset of even essentially the most extreme ischemia, myocardial damage is doubtlessly reversible; after this point, progressive lack of viability occurs and is complete by 6 to 12 hours. The sample of pathologic findings following reperfusion varies depending on the timing of reperfusion, earlier infarction, and collateral circulate. Modification of Pathologic Changes by Reperfusion When reperfusion of myocardium undergoing the evolutionary adjustments from ischemia to infarction occurs sufficiently early. A, One-day-old infarct displaying coagulative necrosis, wavy fibers with elongation, and narrowing as compared with adjacent normal fibers (lower right). Widened areas between the lifeless fibers include edema fluid and scattered neutrophils. D, Granulation tissue with a rich vascular network and early collagen deposition, roughly three weeks after infarction. E, Well-healed myocardial infarct with substitute of necrotic fibers by dense collagenous scar. This is the attribute appearance of markedly ischemic myocardium that has been reperfused.
Avalide 162.5 mg cheap amex
Bifascicular Block blood pressure 8860 buy 162.5 mg avalide visa, Including Left Bundle Branch Block the mix of proper bundle branch block with both left anterior or posterior divisional block or the mixture of left anterior and posterior divisional blocks blood pressure chart during exercise order 162.5 mg avalide otc. Mortality can also be high because of the occurrence of severe pump failure secondary to the in depth myocardial necrosis required to produce such an in depth intraventricular block. Complete bundle department block (either left or right), the mixture of right bundle department block and left anterior divisional (fascicular) block, and any of the various forms of trifascicular block are all more usually associated with anterior than with inferoposterior infarction. All these varieties are more frequent with massive infarcts and in older patients and have the next incidence of different accompanying arrhythmias than seen in sufferers with out bundle department block. This class consists of patients with new bilateral (bifascicular) bundle branch block. Intraventricular Block the proper bundle branch and the left posterior division have a twin blood supply from the left anterior descending and proper coronary arteries, whereas the left anterior division is provided by septal perforators originating from the left anterior descending coronary artery. The crucial task for clinicians is to distinguish recurrent angina or infarction from nonischemic causes of discomfort that may be caused by infarct enlargement, pericarditis, pulmonary embolism, and non�cardiac-related situations. Common causes are nervousness, persistent pain, left ventricular failure, fever, pericarditis, hypovolemia, pulmonary embolism, and the administration of medicine corresponding to atropine, epinephrine, or dopamine; hardly ever, it happens in patients with atrial infarction. Sinus tachycardia is especially frequent in sufferers with anterior infarction, especially in these with vital accompanying left ventricular dysfunction. Persistent sinus tachycardia can signify persistent heart failure and, in these circumstances, connotes a poor prognosis and extra mortality. An underlying trigger must be sought and acceptable treatment instituted, corresponding to analgesics for pain; diuretics for coronary heart failure; oxygen, beta blockers, and nitroglycerin for ischemia; and aspirin for fever or pericarditis. Diagnosis Extension of the original zone of necrosis or reinfarction right into a separate myocardial zone can be a difficult diagnosis, particularly throughout the first 24 hours after the index occasion. The presence of a rub and lack of responsiveness to nitroglycerin could additionally be useful in distinguishing pericardial discomfort, but doing so on clinical grounds is regularly difficult, and diagnostic coronary angiography may be essential to exclude acute native vessel or stent thrombosis. The elevated ventricular rate and loss of the atrial contribution to left ventricular filling can end result in a big reduction in cardiac output. If the arrhythmia is causing ongoing hypotension, ischemia, or coronary heart failure, cardioversion must be thought-about. Patients with recurrent episodes of atrial fibrillation should be handled Prognosis Regardless of whether or not postinfarction angina is persistent or limited, its presence is essential because of the associated larger short-term morbidity price. When hypotension, congestive coronary heart failure, or ventricular arrhythmias develop throughout recurrent ischemia, urgent catheterization and revascularization are indicated. Stent thrombosis can happen acutely (hours to days after deployment of a stent) or in a more subacute style (many months after deployment of a stent) (see Chapter 55). Late pericardial constriction brought on by anticoagulant-induced hemopericardium has been reported. Treatment of pericardial discomfort consists of aspirin, however usually in doses higher than prescribed routinely following infarction- doses of 650 mg orally as often as every 4 hours may be necessary. Clinically, sufferers with Dressler syndrome have malaise, fever, pericardial discomfort, leukocytosis, an elevated sedimentation fee, and a pericardial effusion. At autopsy, individuals with this syndrome usually demonstrate localized fibrinous pericarditis containing polymorphonuclear leukocytes. Treatment is with aspirin, 650 mg as usually as every four hours, and in large doses this is effective. The reabsorption price of a postinfarction pericardial effusion is gradual, with decision usually taking several months. The ache of pericarditis could additionally be confused with that resulting from postinfarction angina, recurrent infarction, or each. Additionally, the discomfort of pericarditis often turns into worse throughout a deep inspiration, but it can be relieved or diminished when the affected person sits up and leans forward. Although transient pericardial friction rubs are comparatively frequent within the first forty eight hours in sufferers with transmural infarction, ache or electrocardiographic adjustments occur a lot less often. The development of a pericardial rub, however, appears to correlate with a larger infarct and larger hemodynamic compromise. Nevertheless, detection of a pericardial effusion on echocardiography is often a sign for discontinuation of anticoagulation. The term left ventricular aneurysm (often termed true aneurysm) is generally reserved for a discrete, dyskinetic area of the left ventricular wall with a broad neck (to differentiate it from a pseudoaneurysm attributable to a contained myocardial rupture). LeftVentricularAneurysm Pathogenesis Aneurysm formation presumably happens when intraventricular pressure stretches the noncontracting infarcted coronary heart muscle and thus produces enlargement of the infarct, a relatively weak, skinny layer of necrotic muscle, and fibrous tissue that bulges with every cardiac contraction. With the passage of time, the wall of the aneurysm 1137 becomes more densely fibrotic, however it continues to bulge with systole and causes a few of the left ventricular stroke volume throughout each systole to be ineffective. An aneurysm rarely happens with multivessel illness when both intensive collaterals or a nonoccluded left anterior descending artery is current. They happen roughly four times extra usually at the apex and in the anterior wall than within the inferoposterior wall. The overlying pericardium usually adheres densely to the wall of the aneurysm, which may even turn into partially calcified after several years. True left ventricular aneurysms (in distinction to pseudoaneurysms) not often rupture quickly after growth. Late rupture, when the true aneurysm has turn out to be stabilized by the formation of dense fibrous tissue in its wall, virtually never happens. Although estimates range due to patient choice, roughly 10% of mural fifty two thrombi result in systemic embolization. Echocardiographically detectable features suggesting that a given thrombus is extra likely to embolize embrace increased mobility and protrusion into the ventricular chamber, visualization on multiple views, and contiguous zones of akinesis and hyperkinesis. Of observe, nevertheless, the info from fibrinolytic trials are tough to interpret because of the confounding effect of antithrombotic remedy with heparin. Recommendations for anticoagulation vary significantly, and fibrinolysis has precipitated deadly embolization. Nevertheless, anticoagulation for 3 to 6 months with warfarin is cheap for lots of patients with demonstrable mural thrombi. Prognosis and Treatment A left ventricular aneurysm will increase the chance for mortality, even in comparison with that in sufferers with a comparable left ventricular ejection fraction. Death in these patients is regularly sudden and presumably associated to the relatively excessive incidence of ventricular tachyarrhythmias that occur with aneurysms. Surgical aneurysmectomy typically succeeds provided that contractile performance in the nonaneurysmal portion of the left ventricle is comparatively preserved. In such circumstances, when the operation is performed for worsening heart failure or angina, operative mortality is comparatively low and scientific improvement may be expected. Several surgical methods for ventricular reconstruction have been developed to keep as normal a left ventricular shape as possible. Such sufferers appear to be appropriate candidates for discharge from the hospital in less than 5 days from the onset of symptoms. The determination relating to timing of discharge in LeftVentricularThrombus andArterialEmbolism Endocardial inflammation and the relative stasis of blood during the acute phase of infarction most likely present a thrombogenic floor for clots to kind in the left ventricle.
Discount 162.5 mg avalide with visa
Duckworth W blood pressure chart height 162.5 mg avalide buy with visa, Abraira C blood pressure medication itchy scalp avalide 162.5 mg proven, Moritz T, et al: Glucose management and vascular problems in veterans with kind 2 diabetes. Anand S, Yusuf S, Xie C, et al: Oral anticoagulant and antiplatelet therapy and peripheral arterial illness. Limbs International Medicinal Buflomedil Study Group, Leizorovicz A, Becker F: Oral buflomedil in the prevention of cardiovascular occasions in patients with peripheral arterial obstructive illness: A randomized, placebo-controlled, 4-year study. Rajagopalan S, Olin J, Deitcher S, et al: Use of a constitutively active hypoxia-inducible factor-1alpha transgene as a therapeutic technique in no-option crucial limb ischemia patients: Phase I dose-escalation expertise. Sandri M, Adams V, Gielen S, et al: Effects of exercise and ischemia on mobilization and useful activation of blood-derived progenitor cells in sufferers with ischemic syndromes: Results of three randomized research. Schillinger M, Minar E: Percutaneous treatment of peripheral artery disease: Novel techniques. Brown J, Lethaby A, Maxwell H, et al: Antiplatelet brokers for stopping thrombosis after peripheral arterial bypass surgical procedure. Atherosclerotic cArdiovAsculAr diseAse Acute Limb Ischemia and Atheroembolism a hundred twenty five. Noninvasive physiologic evaluation might embody the ankle-brachial and toebrachial indices, segmental stress measurements, Doppler waveform evaluation, pulse quantity recordings, and exercise testing (Table 58G-2; see Chapter 58). Supervised exercise coaching and cilostazol enhance walking distance in patients with claudication (Table 58G-3). Additional questions can decide whether the patient has pain even at rest or poorly healing or nonhealing wounds of the legs or ft. The tips advocate efficiency of a comprehensive pulse examination and cautious inspection of the feet. This includes measurement of blood pressure in both arms; auscultation of the carotid arteries, stomach, and femoral arteries for bruits; and palpation of the brachial, radial, ulnar, femoral, popliteal, dorsalis pedis, and posterior tibial artery pulses. The ft are inspected to assess pores and skin colour, temperature, integrity, and the presence of ulcerations (Table 58G-1). These procedures are broadly categorized as endovascular interventions and surgical reconstruction, although hybrid procedures consisting of each endovascular and surgical revascularization are additionally used. In figuring out the sort of revascularization procedure, one necessary consideration is the placement of the obstruction, which is broadly categorized as influx, involving the aorta and iliac arteries; outflow, including the femoral and popliteal arteries; or run-off, affecting the tibial and peroneal arteries. The determination to carry out endovascular or surgical procedures additionally is dependent upon the scientific context and the morphologic features and distribution of the stenotic and occlusive lesions. Surgical procedures embody aortobifemoral bypass; iliac endarterectomy; extra-anatomic bypass, corresponding to femoral-femoral and axillobifemoral bypass; and infrainguinal bypass procedures, corresponding to femoral-popliteal and femoral-tibial bypass. Patients who smoke cigarettes should be assisted by counseling and growing a plan for quitting that will embrace pharmacotherapy and/or referral to a smoking cessation program. In the absence of contraindications or different compelling clinical indications, a number of of the next pharmacologic therapies should be provided: varenicline, bupropion, and nicotine replacement remedy. A program of supervised exercise training is beneficial as an preliminary remedy modality for patients with intermittent claudication. Pentoxifylline (400 mg three times per day) may be thought-about as a second-line various remedy to cilostazol to enhance strolling distance in patients with intermittent claudication. Endovascular procedures are indicated for individuals with a vocational- or lifestyle-limiting incapacity due to intermittent claudication when the scientific features recommend an affordable chance of symptomatic enchancment with endovascular intervention and (1) the response to exercise or pharmacologic remedy has been inadequate and/or (2) the risk-to-benefit ratio may be very favorable. Stenting is efficient as main therapy for common iliac artery stenosis and occlusions. Stenting is effective as main remedy for exterior iliac artery stenosis and occlusions. Bypasses to the popliteal artery above the knee should be constructed with an autogenous vein when possible. Bypasses to the popliteal artery under the knee must be constructed with an autogenous vein when attainable. Stents (and other adjunctive methods similar to lasers, slicing balloons, atherectomy units, and thermal devices) could be useful within the femoral, popliteal, and tibial arteries as salvage remedy for a suboptimal or failed result from balloon dilation. The use of artificial grafts to the popliteal artery under the knee is cheap solely when no autogenous vein from the ipsilateral or contralateral leg or arms is out there. For sufferers with limb-threatening ischemia and an estimated life expectancy of >2 years, bypass surgical procedure, when potential and when an autogenous vein conduit is available, is reasonable to carry out because the preliminary treatment to improve distal blood flow. Because the presence of extra aggressive atherosclerotic occlusive illness is associated with much less durable ends in sufferers youthful than 50 years, the effectiveness of surgical intervention for intermittent claudication on this population is unclear. Patients with acute limb ischemia and a salvageable extremity should bear an emergency evaluation that defines the anatomic level of occlusion and leads to prompt endovascular or surgical revascularization. Mechanical thrombectomy units can be used as adjunctive remedy for acute limb ischemia secondary to peripheral arterial occlusion. Considerations for determining the kind of revascularization procedure used to deal with acute limb ischemia include the cause of acute arterial occlusion, the duration of time because the onset of symptoms, and the severity of limb ischemia (Table 58G-5). More than 60% of strokerelated deaths occur in women, and girls are less than half as doubtless as males to be able to stay independently after stroke. No evidence has shown that platelet antiaggregants cut back the risk for stroke in individuals at low threat. Thus aspirin may be thought of in women whose risk for stroke outweighs its associated bleeding risk. Depending on age and race or ethnicity, between roughly 6% and 25% of survivors may have a second stroke inside 5 years. There can additionally be concern that the total dose of aspirin (50 mg/day), although efficacious for secondary stroke prophylaxis, is under the dose proven to be effective for cardiac prophylaxis. To handle this potential limitation, a small extra dose of aspirin could be added. Cumulative hazard charges are shown for the first efficacy and security outcomes according to therapy group. A, Cumulative hazard rates for the first efficacy consequence (stroke or systemic embolism). B, Rates for the primary safety outcome (major bleeding) within the apixaban and aspirin groups. Kaplan-Meier analyses of the time to recurrent ischemic stroke or demise are proven according to treatment project. Of the sufferers who had a history of stroke before the research index stroke, these taking aspirin earlier than random assignment. The fee of recurrent stroke, however, was 29% in those that had failed aspirin and had been randomly assigned to warfarin. In addition, no data present that patients failing aspirin benefit from an alternate antiplatelet routine. The trial also discovered no evidence that warfarin is superior to aspirin or that clopidogrel is superior to aspirin for prevention in stroke in patients with low�ejection fraction congestive coronary heart failure. Kaplan-Meier curves for the cumulative chance of the primary endpoint based on remedy assignment are shown.