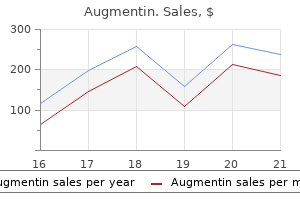
Augmentin dosages: 1000 mg, 625 mg, 375 mg
Augmentin packs: 10 pills, 20 pills, 30 pills, 60 pills, 90 pills, 120 pills, 180 pills, 270 pills, 360 pills

625 mg augmentin buy otc
C antibiotic injection for strep 1000 mg augmentin generic with visa, She is shown after undergoing ear cartilage spacer insertion with canthal anchoring virus 42 states cheap 625 mg augmentin with mastercard. The disadvantage of ear cartilage is its long-term visibility, which often necessitates local excision of the visible edges. C, She is proven after decrease lid repositioning with a vertical vector midface carry and lateral canthal anchoring. In some patients with very distinguished eyes and extra extreme decrease lid retraction, a wider vertical width of spacer (up to 1 cm in vertical width) may be needed. For these patients, a particular method is needed to secure the spacer in place; this entails putting transcutaneous quilting sutures to stabilize the higher edge of the spacer. We commonly undermine the fornix conjunctiva to cover exposed spacer material when wider spacers are used. D, Lid eversion shows misalignment of the superior fringe of the spacer, ensuing from rigidity; trimming was required. Placement of quilting sutures on the superior fringe of the spacer would have prevented this drawback. B, She is shown after correction with a spacer graft consisting of Medpor, a lateral canthoplasty, and lower blepharoplasty. B, the affected person is proven after medial canthoplasty to correct the medial ectropion and reducing the lateral canthus again to the traditional place. Straight iris scissors are used to perform the blepharotomy, with care taken to be sure that the eye protector is in its proper position. The desired amount of spacer material, 6 mm on average, is first contoured after which sutured to the minimize edges of the blepharotomy incision with a 6-0 absorbable suture in an end-to-end style. Upward movement of the cheek strikes pores and skin right into a poor lid, but the canthus and cheek have to be anchored securely. Even in a reoperative patient, with proper launch of the cheek and upward motion, surprisingly large amounts of skin can be recruited upward into the lower lid with vertical repositioning of the cheek. Similar to a main midface carry, in a secondary vertical cheek carry, areas of launch have to be mobilized in the midface. Cheek attachments on the lateral orbital rim are launched within the preperiosteal aircraft, whereas attachments at the inferior orbital rim and zygomatic space are launched in the subperiosteal plane, as performed in a primary cheek lift. B, Because of operative adhesions, a most subperiosteal dissection is critical for cheek release in some sufferers undergoing revision surgery. B, She is shown after present process a conservative vertical-vector cheek lift with canthal anchoring. B, She is proven after undergoing lower lid repositioning with a vertical-vector cheek raise with canthal anchoring. No skin grafts were needed, however two sequential vertical-vector cheek lifts had been required for full correction. B, She underwent recruitment of cheek tissue and excision of scars with canthal anchoring. Multiple procedures were needed; nonetheless, no skin grafts were required for this end result. In these instances, a safe attachment of the canthus to the lateral orbital rim could be obtained utilizing drill-hole fixation of the canthal tendons. The positioning of the canthal drillhole is set based on the quantity of eye prominence. In some sufferers with very prominent eyes or center lamellar scarring, spacer grafts may be needed. For anchoring, we use a everlasting suture-double-armed 4-0 Mersilene with a half-circle needle. Both arms of the suture are introduced via the opening and secured to the periosteum or the temporal fascia. This is done intraoperatively by snugging the canthus against the lateral orbital rim and checking the effect on the decrease lid position. The subsequent step is to decide whether or not a canthoplasty (lid shortening) or canthopexy (length preserving) procedure should be carried out. The identical criteria apply to performing a canthoplasty versus a canthopexy as with a patient undergoing primary surgical procedure. If a canthopexy is performed, you will need to take a secure chunk with the suture within the widespread and decrease lateral canthal ligament. Improved eyelid closure with traction from the anchoring suture should be instantly evident. After the specified canthal repositioning has been obtained by way of the drill-hole, the 2 arms of the double-armed 4-0 Mersilene are sutured to the periosteum or temporal fascia for fixation. A, the drill-hole is aligned at the desired vertical level, relying on eye prominence. B, A double-armed suture is used to thread the canthal tendon into the drill-hole, and the sutures are anchored to the temporal fascia. B, Corrective drill-hole fixation of the decrease lids and canthi was carried out to produce the desired positive canthal tilt. Reinforcement With a Graft or Flap to Correct Deficient or Scarred Lateral Eyelid Tissue In some cases, the lateral edge of the decrease lid has become friable from scar tissue ensuing from previous surgery. Even if a drill-hole is used for refixation, the edge of the lid might pull through or cheesewire by way of over time. In these circumstances, extra help have to be provided to the lateral fringe of the decrease lid. If the orbital rim periosteum is substantial and intact, a lateral periosteal flap, as utilized in eyelid reconstruction, can be utilized to improve support to the lateral eyelid tissue. Unfortunately, most sufferers present process reconstruction after aesthetic surgery have poor periosteum. In this situation, greater support of the lateral lower lid tissue could be obtained with the usage of free grafts of temporalis fascia or tensor fascia lata to reinforce the anchoring. In most circumstances, the canthus is first realigned with sutures in a conventional method, and the supporting fascia can be sutured to it as an onlay graft to additional strengthen the lid-canthal attachment. B, this affected person presented after undergoing two decrease lid blepharoplasty procedures that resulted in decrease lid retraction. C, A vertical-vector cheek raise and a lateral canthoplasty, which was reinforced with a 0. An autologous fascia strip was connected to repair poor lateral eyelid tissue. D, the fascia strip was in place before the lower lid was reattached on the canthus. After attachment of the lower lid, the fascia strip was sutured to the lateral rim and temporal fascia. Combined Drill-Hole Fixation and Lateral Lid Reinforcement to Correct a Deficiency in Orbital Rim Periosteum and Lateral Eyelid Tissue Some sufferers who undergo revision surgery, notably those that have had multiple procedures, could have deficiencies in each the orbital rim periosteum and the lateral eyelid correct, making lateral canthal anchoring more difficult. In these circumstances, assist in both areas is required by combining drill-hole fixation with eyelid spacer bolster. The most safe technique of fixation is to convey the drill-hole sutures through the spacer bolster after it has been hooked up to the eyelid and orbital rim.
Wood-Rose (Hawaiian Baby Woodrose). Augmentin.
- How does Hawaiian Baby Woodrose work?
- Pain relief and promoting sweating.
- What is Hawaiian Baby Woodrose?
- Dosing considerations for Hawaiian Baby Woodrose.
- Are there safety concerns?
- Are there any interactions with medications?
Source: http://www.rxlist.com/script/main/art.asp?articlekey=96344
Augmentin 375 mg line
The orbitomalar ligament contributes to the help of the midface for the formation of a youthful lid-cheek junction virus ntl generic augmentin 1000 mg overnight delivery. With growing older antibiotics for sinus infection penicillin 375 mg augmentin amex, the area inferior to the orbitomalar ligament and superior to the zygomaticofacial ligament can turn out to be engorged with fluid from poor or scarred lymphatic drainage. The tear trough could be seen as a normal variation in youthful individuals, however it typically deepens with age. The indentation is shaped by contributions from bone, muscle, and overlying soft tissue. It is formed by the arcus marginalis, the orbitomalar ligament, the origin of the orbicularis oculi muscle superolateral to the origins of the levator labii superioris, and the levator alaeque nasi muscular tissues. A complicated vascular community of blood circulate throughout the eyelids is formed by anastomoses from the interior carotid by way of branches of the ophthalmic artery, which connects with the terminal branches of vessels derived from the exterior carotid system. B, Clinical application: retrograde move from an intraarterial injection into the supraorbital artery, which can lead to blindness. Care have to be taken to avoid intraarterial injections of fillers and other substances, significantly with the use of syringes that produce sturdy hydrostatic pressure. Ophthalmic Artery the ophthalmic artery first sends branches to the eye after which anastomoses with the ethmoidal arteries. It travels forward to the anterior orbital rim to form the supratrochlear and supraorbital arteries. This pathway turns into clinically essential when injections within the glabellar area are planned. Injury may end result in the cannulation of a department, which may cause an embolus of fat or filler to enter the ophthalmic artery; this can result in impaired vision or blindness. Blindness can happen with inadvertent injections into the supraorbital or supratrochlear vessels that result in retrograde move into the ophthalmic artery, which then moves forward by way of the central retinal artery. Although periorbital arterial collateral circulation is great external to the globe, collateral blood flow within the orbit and retina is poor with many end arterioles. The lacrimal artery arises from the ophthalmic artery laterally, close to the optic foramen; it provides off a branch that passes via the superior orbital fissure and that anastomoses with the middle meningeal artery via the meningeal foramen anterior to the frontosphenoid suture. The lacrimal artery then proceeds anteriorly along the superior border of the lateral rectus to supply the lacrimal gland and some of the lateral eyelid. External Carotid Supply the branches of the external carotid artery that offer the eyelid are the facial artery, the inner maxillary artery, and the superficial temporal artery. The facial artery crosses the mandible anterior to the masseter muscle, courses diagonally to the nasolabial fold, and passes beneath the 2 paired lip elevators. It turns into more superficial and lies between the levator labii superioris and the levator alaeque nasi muscular tissues. At that point, the facial artery becomes the angular artery, which turns into superficial on the medial canthus and lies beneath the orbicularis muscle 6 to 8 mm medial to the canthus and 5 mm anterior to the lacrimal sac. The angular artery then perforates the orbital septum above the medial canthal ligament to anastomose with branches of the ophthalmic artery. The use of blunt cannulas must be thought-about for filler injections on this area. The superficial temporal artery is a terminal branch of the external carotid that anastomoses with the arteries of the scalp. After it surfaces in entrance of the ear, it lies superficially in the superficial muscle aircraft above the muscle tissue, separated from the pores and skin by various quantities of subcutaneous tissue. Branches that come up from the superficial temporal artery provide blood to the lateral orbit and the eyelids. The zygomaticofacial artery provides collateral blood move between the internal maxillary artery and the lacrimal department of the ophthalmic artery. Another department of the superficial temporal artery is the transverse facial artery, which provides blood to the lateral eyelids. The inner maxillary artery becomes the infraorbital artery because it traverses the inferior orbital fissure, the pterygopalatine fossa, and the infraorbital groove or the bony canal in the flooring of the orbit. This artery could be concerned with blowout fractures of the orbital ground and often needs to be released from the canal throughout surgical restore. The infraorbital artery exits through the infraorbital foramen to supply blood to the decrease eyelid and the cheek area. The infraorbital artery anastomoses with terminal branches of the dorsal nasal artery. There are three arcades in the higher lid and orbit and two arcades within the lower lid and orbit. Branches of the supraorbital, supratrochlear, Chapter 1 � Periorbital and Eyelid Anatomy 35 and dorsal nasal arteries also contribute to the vascular arcades to provide the eyelids with a wonderful blood supply. Posterior to the septum, the medial palpebral artery arises from the ophthalmic artery temporal to the trochlea and then divides into inferior and superior branches simply earlier than traversing the orbital septum. The higher and decrease eyelid arcades connect medially with the superior and inferior medial palpebral arteries. Laterally, they join with the 2 lateral palpebral arteries which would possibly be terminal branches of the lacrimal artery. The marginal arcade lies on the anterior tarsal surface 2 to 3 mm from the eyelid margin. The branches hyperlink the (4) facial and frontal branches of the superficial temporal arteries. The infraorbital arteries (arrows) come up from the maxillary artery of the external carotid artery. B, the supraorbital, supratrochlear, and infraorbital branches that supply the eyelids. B Inferior medial palpebral artery Supraorbital artery Superior and inferior palpebral arterial arches Supratrochlear artery Infraorbital artery Dorsal nasal artery Angular artery 36 Part I � Fundamentals ciliary arteries near the corneoscleral limbus. A much less developed arcade system arises within the lower eyelid medially from the inferior palpebral artery; laterally, it anastomoses with the lacrimal and zygomaticofacial branch of the superficial temporal artery. The inferior palpebral artery travels along the inferior border of the tarsus in the subtarsal space three. The medial aspect of the lower eyelid can be provided by branches of the infraorbital artery. Additional anastomoses of the exterior carotid supply the inferior marginal arcade, along with branches of the infraorbital artery and the anterior deep temporal artery. The vascular arcades of the eyelid are provided with blood flow from the nasal and temporal sides. It is clinically essential to perceive that the majority of blood flow comes from the nasal anastomoses to the carotid system. Most of the excessive bleeding that happens with blepharoplasty and that ends in postoperative hematomas comes from the small arterioles situated inside the nasal fat pads. Most surgeons notice more bleeding medially than laterally in the eyelid throughout surgery. A better understanding of eyelid vascularity should end result in the modification of surgical techniques and reduce postoperative issues after eyelid surgical procedure. Another necessary clinical facet of the arcade in the decrease lid is its location beneath the eyelid margin.
1000 mg augmentin cheap mastercard
Although nasal chondromucosa is used with the traditional Mustard� flap antibiotics for acne treatment discount augmentin 1000 mg without a prescription, other posterior lining grafts may be used (Box 26-2) antibiotic resistance fda 625 mg augmentin discount fast delivery. C, A Mustard� cheek flap was developed and undermined within the suborbicularis plane, exposing the suborbicularis oculi fats. F, the chondromucosal graft was mounted on the interior floor of the Mustard� flap. It is essential that the flap be secured with canthal fixation to avoid postoperative retraction of the decrease lid. A transposition brow flap (Fricke flap) can be used however requires a posterior lamellar backing. The Imre flap is a vertical myocutaneous flap (or in some cases, a skin flap) with an angle of rotation toward the inside canthus. The nasolabial transposition flap is mostly based in the inside canthus and requires undermining of the flap and adjoining cheek tissue for successful transposition. C, Because of pores and skin rigidity, the donor site was covered with a full-thickness pores and skin graft. Transposition Cheek Flap A transposition flap may be hinged at either the medial or lateral canthus however is extra generally hinged medially. The thicker tissue is rotated upward to type the external assist of the lid and is secured with fixation to the medial and lateral canthi. Rotation Cheek Flap the rotation cheek flap is an upward-rotated cheek flap facilitated by inferior incisions above the mouth and cheek area, with undermining and upward advancement. It must also be fixated medially and laterally, as previously described, and be provided with posterior lamellar mucous membrane. Temporal Forehead Transposition Flap (Fricke Flap) the Fricke transposition flap has been used in the higher lid, as described in Chapter sixteen, however it also could be transposed farther downward right into a decrease lid defect to kind the idea for support within the lower lid. However, in 40% to 50% of circumstances, composite grafts lose eyelashes regardless of good take of the gentle tissue. The posterior lamellar graft may be lined with a blepharoplasty-type myocutaneous flap. C, Before the tissue is placed for posterior lamellar replacement, the skin-muscle layer must be removed inferior to the lash follicles. B, the probes are excised and the tubing is secured under the inferior turbinate with multiple knots. C, Lacrimal intubation and reapproximation of the lower lid edge behind the lacrimal sac area. D, Final closure of the defect, with residual canaliculus as a new ostia to the floor. Chapter 26 � Lower Eyelid Reconstruction 783 If residual lower lid canaliculus is current, an try to intubate the canaliculus while performing a reconstructive procedure might prevent later problems of epiphora. A Crawford silicone intubation set was used to create an ostium with the residual lower canaliculus. C, Two months postoperatively, the flaps are healed and the silicone tubing is in place. B, Closeup showing the reconstructed right lower lid with Crawford tubes in place. Larger defects may require a calming incision with a lateral canthotomy to facilitate the development of lateral tissue. A Tenzel flap is probably the most generally used flap for partial lower lid reconstruction. Larger or complete defects of the lower lid require transposition flaps or rotation flaps with mucosal lining to reduce corneal irritation. Lateral canthal help is an integral part of decrease lid reconstruction to avoid ectropion. Simultaneous cheek and decrease eyelid reconstruction with mixtures of native flaps. Die Bildung neuer Augenlider (Blepharoplastik) nach Zerst�rungen and Dadurch Hervorgebrachten Ausw�rts-Wendungen Derselben. Oculoplastic surgery for lower eyelid reconstruction after periocular cutaneous carcinoma. Total lower eyelid reconstruction with a prefabricated flap using auricular cartilage. Secondary intention healing in lower eyelid reconstruction-a useful therapy choice. Total decrease eyelid reconstruction with free posterior auricular chondrocutaneous flap. Upper eyelid reconstruction with a horizontal V-Y myotarsocutaneous development flap. Total decrease eyelid reconstruction with superficial temporal fascia flap and porous polyethylene implant: a case report. The reconstructive strategies which would possibly be emphasized for the periorbital space are sometimes people who describe eyelid reconstruction and overlook the medial and lateral canthi. Although the eyelids could be reconstructed, they need a medial and lateral fulcrum point to permit the periorbital muscular tissues to operate. In addition to soft tissue protection, the canthal anchoring strategies are an important part of eyelid reconstruction. Eyelid defects following harm or cancer resection usually extend into the canthal area. Isolated canthal defects can include parts of the eyelid, eyelid attachments to the orbit, and gentle tissue extending beyond these areas. Many of the techniques described in this chapter are extensions of eyelid reconstruction procedures described in earlier chapters. Medial Canthal Reconstruction Defects of the medial canthus most commonly happen following excision of pores and skin tumors or trauma. Techniques for anterior lamella replacement embody pure granulation, full-thickness skin grafts, and flaps from the glabellar area and cheek to restore eyelid and internal canthal soft tissue. A preliminary step in canthal restore is widespread to all posterior lamella reconstruction previous to protection with anterior lamella tissue. If the tarsoligamentous sling is indifferent from the nasal wall with the defect, the preliminary step in repair must be reattachment of the tarsoligamentous sling to the nasal orbit to create a normal contour for the canthus. Attachment to the posterior reflection of the medial canthal tendon is necessary not solely to create a traditional appearance but in addition to accommodate secondary lacrimal procedures corresponding to placement of a Jones tube, which requires a standard medial canthal angle to function correctly. A strong permanent suture corresponding to 4-0 Prolene is placed through the tarsal remnants of each higher and lower lid and then attached to the posterior reflection of the medial canthal tendon. A small P-2 half-circle needle facilitates the position of this suture posterior to the lacrimal sac to ensure that the lid to abut the medial globe, allowing the canaliculi to perform correctly. The remaining skin and anterior lamella defect can be closed by grafts or flaps depending on the vascularity of the tissue bed.
Purchase augmentin 1000 mg amex
Lateral view of cranium exhibits destruction of sella turcica region of base produced by sphenooccipital chordoma (arrow) antimicrobial 2008 augmentin 625 mg cheap on-line. T2-weighted magnetic resonance image of chordoma at base of cranium reveals excessive signal depth mass in region of sphenoid bone (arrows) antibiotics jaundice purchase augmentin 1000 mg overnight delivery. Vertebral chordomas produce lytic lesions that will involve two or more adjoining vertebral our bodies. Computed tomography and magnetic resonance imaging are indispensable in evaluating each the extent of the lesion and the involvement of adjacent constructions. They are regularly myxoid or gelatinous in look and might mimic chondrosarcoma or mucinous adenocarcinoma. Despite good demarcation, the tumor often extends past its grossly recognizable borders. Chordomas often involve the medullary canal, compressing the spinal wire and its nerves. The level of cellularity can vary considerably amongst circumstances and in several areas of the identical tumor. In basic, most chordomas exhibit clearly recognizable nuclear pleomorphism with occasional large atypical cells. Occasionally, the vacuoles encircle the nucleus, which stays centered in the cytoplasm and produces the so-called physaliphorous appearance. The basic giant physaliphorous cell has a centrally located nucleus surrounded by a slender rim of cytoplasm that in flip, is encircled by a ring of more peripherally located cytoplasmic vacuoles. Such lesions are descriptively referred to as lipoma-like chordomas and could additionally be confused with benign or malignant lipomatous tumors. On the opposite hand, highly mobile lesions with minimal vacuolization and dense eosinophilic cytoplasm may mimic epithelial neoplasms. Areas of cartilage can vary from small microscopic foci to giant prominent areas. Therefore chordomas can be occasionally tough to distinguish from chondrosarcoma. The term chondroid chordoma has been proposed to designate hybrid lesions that exhibit options of each lesions-chordoma and chondrosarcoma. The controversy over this entity and its potential for medical significance are mentioned separately. The presence of abnormal multivacuolated cytoplasm with centrally placed, scalloped nucleus (that is, physaliphorous cells) is the hallmark of chordoma. Such classical cells are, nonetheless, uncommon; within the overwhelming majority, the cells present dense eosinophilic cytoplasm or are lipoblast-like with single or a number of larger cytoplasmic vacuoles displacing the nucleus peripherally. Cytologic options combined with radiologic and medical presentation permit appropriate cytologic prognosis in most cases of chordoma. The immunohistochemical options similar to coexpression of epithelial markers and S-100 protein may be also examined in cytologic preparations. Chordoma cells comprise intermediate filaments and are linked by desmosome-like junctions. The extracellular matrix consists of a nice, granular substance of low electron density. A, Computed tomography shows lobulated mass protruding posteriorly and anteriorly from origin in sacrococcygeal junction. B, T1-weighted sagittal magnetic resonance image of chordoma shown in A with bigger posterior and anterior low signal mass (arrows). Lateral radiograph of cervical backbone shows damaging lesion of body of C2 (arrows). In basic chordoma recapitulate a gene expression signature of notochordal cells. Among all of the markers, brachyury seems to be the most particular for chordoma and notochordal tissue and is useful in the differential diagnosis. The most common cytogenetic abnormality is hypodiploidy with lack of the quick arm of chromosome 3, and lack of proximal 1p in addition to monosomy of chromosome 10. Chordomas are additionally characterized by frequent gains of genetic materials on 5q, 7q, 12q, and 20q. The cytogenetic information means that tumor suppressor genes on 1p and 3q in addition to oncogenes mapping to 5q, 7q, 12q, and 20q might play a task within the improvement of those tumors. The presence of physaliphorous cells and a trabecular or cordlike arrangement along with a myxoid matrix are typical for chordoma. However, standard chondrosarcoma sometimes could present a cordlike arrangement of cells and myxoid stroma. In such situations, positivity for S-100 protein and unfavorable staining for epithelial markers favor chondrosarcoma. Other myxoid bone tumors, similar to chondromyxoid fibroma, which not often happens within the axial skeleton, are most unlikely to be confused with chordoma. Highly mobile areas with cohesive solid cellular sheets and prominent nuclear atypia may be confused, especially in a limited biopsy specimen, with an epithelial neoplasm. Extensive clear-cell change and the signet-ring look of chordoma cells can lead to a misdiagnosis of metastatic adenocarcinoma or less frequently lipomatous tumor. Among varied epithelial tumors metastatic to the skeleton a chromophobe variant of renal cell carcinoma may superficially resemble a chordoma. Strict adherence to medical and radiographic knowledge often helps to keep away from this error. A, Axial computed tomography reveals damaging mass protruding posteriorly and anteriorly from the sacrum (arrows). B, T1-weighted sagittal magnetic resonance image of chordoma proven in A with predominantly anterior low sign mass (arrows). C, Sagitally reduce resection specimen of the tumor shown in A and B demonstrates a lobulated, fleshy tumor mass destroying the sacrum and increasing to the gentle tissue anteriorly and posteriorly. D, Histologic part of identical tumor reveals cords of chordoma cells with multivesicular cytoplasm growing in a myxoid stroma. A, Resection specimen of sacral chordoma showing a gelatinous tumor growing anteriorly from the coccyx. C, Gross photograph of a bisected lumbar (L5) vertebral resection specimen showing a gelatinous tumor mass replacing almost the complete vertebral body. D, Specimen radiograph of tumor shown in C exhibiting harmful lesion changing the vertebral body. A, Bisected tumor from sacral region reveals tan-gray soft tissue with myxoid appearance. B, Bisected tumor mass from sacral region reveals multilobulated myxoid tumor tissue with hemorrhagic areas. C, Autopsy specimen reveals recurrent chordoma of cervical backbone invading medullary canal and compressing spinal wire (arrows). D, Sagittally minimize resection specimen of recurrent sacrococcygeal chordoma reveals multiple grey, fleshy nodules inside coccyx and adjoining delicate tissue (arrows).
Discount 375 mg augmentin with mastercard
Furthermore antibiotic kill curve augmentin 625 mg online buy cheap, a high hairline requires placement of the endoscopic incisions more posteriorly throughout the hair infection quality control staff in a sterilization unit of a hospital purchase 375 mg augmentin free shipping, which regularly makes the surgical procedure tougher. The introduction of a straight fiberoptic endoscope is harder in patients with marked forehead convexity. They embody a pretrichial biplanar process, which elevates the forehead and lowers the hairline concurrently. In some patients the brow skin could be tightened more by stress-free incisions in the periosteum and possibly in the galea on the midforehead level. In some men with deep transverse furrows within the midforehead pores and skin, elevating the forehead and smoothing the brow are achieved. GlabEllar rHytids Paired vertical strains and a transverse wrinkle in the glabellar area outcome from contraction of the paired corrugator supercilii and procerus muscles. This area can be improved by partial excision of the muscular tissues, combined with superior elevation and redraping performed with an endoscopic forehead carry. The endoscopic view provides clear visualization of the procerus and corrugator muscular tissues and the supraorbital and supratrochlear neurovascular bundles. This facilitates partial myectomy of the muscles across the midbelly of the muscle, while preserving the nerves and preventing bleeding. Once the brow is elevated with fixation vertically and laterally, improvement of the glabellar rhytids is evident. The temporal line of fusion is released deep to the temporal parietal fascia on the superficial layer of the deep temporal fascia, under direct imaginative and prescient from lateral to medial to prevent dissection under the temporalis muscle. The subperiosteal or preperiosteal airplane is related to the lateral temporal dissection to launch the retaining ligaments of the temporal forehead. The sentinel vein is visualized and preserved by avoiding the situation of the temporal department of the facial nerve. If a subperiosteal dissection is carried out, the periosteum is divided lateral to the supraorbital nerve. This facilitates release and elevation of the tail of the brow and excision and fixation of the scalp to the deep temporal fascia. In patients with a receding hairline or a outstanding forehead, endoscopic visualization could also be challenging due to the gap and angle that the endoscope needs to traverse. Traction on the forehead and scalp tissues turns into a lot much less efficient the farther posterior the incisions are made. The lower the forehead hairline and the less the curvature of the forehead, the better the endoscopic approach. It is extensively carried out because of surgeon preference and/or lack of expertise or equipment required for an endoscopic brow raise. Because the coronal incision usually extends laterally, it additionally features a temporal brow raise in most cases. Shortcomings of a coronal forehead raise include an inclination for overcorrection, more hair loss, numbness posterior to the scar, a extra invasive surgical procedure with an extended scar throughout the whole scalp, and fewer affected person acceptance. For these reasons, endoscopically assisted forehead lifts are most well-liked in most patients. This procedure also elevates the brows and improves the glabellar frown traces with a partial myectomy of the procerus and corrugator muscle tissue. In these cases, a pretrichial coronal incision with elevation at the subcutaneous stage supplies higher entry for endoscopic visualization whereas preserving the sensory branches to the brow and scalp. A biplanar carry prevents additional hairline elevation and can be utilized to decrease the hairline whereas elevating the brow. This process is primarily of historical curiosity, as a end result of the scar is placed in the center of the forehead. It could be reserved for aged male patients with vital forehead ptosis that decreases the superior visual subject. It is performed via an incision posterior to the hairline, with dissection in the subgaleal airplane deep to the temporoparietal fascia. The process can elevate the tail of the forehead and proper lateral orbital rhytids or smile lines. It is beneficial for revising insufficient temporal elevation after an endoscopic brow raise or face lift. A temporal carry can be useful as an adjunct to right residual lateral rhytids and laxity after an higher blepharoplasty or a midface lift. A direct brow carry requires a short incision just above the central forehead hairs; it produces minor scar visibility, though often no worse than present brow wrinkles. Those with a lower, unstable brow require some forehead elevation to stop downward pulling on the forehead by an upper blepharoplasty. The advantage of an inner browpexy over a direct brow raise is that the procedure is carried out through the lateral side of the higher blepharoplasty incision. Preperiosteal dissection is performed 10 to 15 mm above the superior orbital rim lateral to the supraorbital nerve. A everlasting suture is positioned 10 mm above the supraorbital rim in the periosteum and to the deep subcutaneous and dermal tissue at the inferior aspect of the peak of the brow. The suture is placed in a horizontal mattress method, and when completed, stabilization of the lateral forehead may be palpated. In patients with an unstable forehead, the technique is more effective for stabilizing the lateral brow to prevent lateral brow pull down by an upper blepharoplasty through the healing phase. Significant long-term elevation of the lateral forehead is tough to obtain with an inner brow lift and requires a temporal raise or a browpexy. B, A 12 months after an higher and decrease blepharoplasty and an internal browpexy, his brows are elevated, and the proper eyebrow has a peak. The procedure may additionally be carried out in isolation throughout higher blepharoplasty to enhance the glabellar area, without altering the appearance of the relaxation of the forehead. Furthermore, the supraorbital and supratrochlear neurovascular bundles are readily visualized and preserved, adding a degree of threat to the procedure. Although the procerus could be divided or partially removed, some authors have really helpful performing this procedure with out direct visualization. In our expertise, the most important drawback of this approach is the shortage of vertical elevation wanted to clean the glabellar rhytids with transpalpebral resection. Although the corrugator may be successfully weakened, the lack of vertical tightening limits this procedure in contrast with brow lifts, which additionally elevate and tighten the forehead. Its benefit is direct visualization of the procerus and corrugator muscular tissues for resection. It also offers a protected and effective strategy to the forehead, with a very low danger of frontal branch paresis, whereas elevating the forehead and enhancing forehead and glabellar rhytids. The limited scalp incisions make the method less invasive, thereby significantly rising affected person acceptance.
Augmentin 375 mg purchase amex
A spacer may be inserted within the posterior lamella of the lid both transconjunctivally or transcutaneously antibiotic drug classes 625 mg augmentin purchase otc. Technique With the external strategy antibiotics classes generic augmentin 375 mg without a prescription, a subciliary incision is made to elevate a skin-muscle septal flap. The midface lift is performed (see Chapter 8) and combined with fats switch and canthal anchoring. With significant lid retraction, scleral present should be current after canthal anchoring. In some instances, recession of the capsulopalpebral fascia may adequately restore the lower lid position. B, Lower lid retractors (capsulopalpebral fascia and inferior tarsal muscle) have been peeled away from the underlying conjunctiva. C, A spacer is then inserted between the inferior tarsal edge and recessed retractors (ear cartilage on this case). D, the exterior skin-muscle flap is sutured again into position after blepharoplasty. B, the affected person is seen after spacers have been inserted into both decrease lids and the right higher lid. B, the affected person is seen after lower lid blepharoplasty and a midface raise with transcutaneous insertion of spacers into the decrease lids. In these instances, wider spacer inserts (up to 1 cm in vertical width) may be needed. B, Results after decrease lid surgery with a spacer implant and fats grafting to the malar space are illustrated. Augmentation with alloplastic implant material or with fat injections has been reported and provides some improvement. We presently use large-volume dermal fats grafts positioned subperiosteally in the malar space, which has produced vastly superior leads to our arms. Technique the subperiosteal midface lift and fat switch are carried out in the usual means (see Chapter 8). Care is taken on this dissection to keep away from traumatizing the levator labia muscle and the buccal branch of the facial nerve. Dermis and fat may be taken from any space by which the dermis is thick and adequate subdermal fats is available. We normally take an ellipse-shaped dermal fats graft from the iliac crest area, as described in Chapter four. The graft is positioned by manipulating the dermis, which is placed in the subperiosteal and suborbicularis house with the dermis oriented toward the skin. A massive cutting closure needle is used to convey one arm of three 4-0 Vicryl sutures from the exterior cheek surface to the dissected area, which is then inserted into the inferior, nasal, and temporal edges of the dermis. The second arm of the sutures is then brought externally and tied, anchoring the dermis in position. D, Patient with exophthalmos and a recessed malar area who had prior orbital decompression. E, the affected person is seen immediately postoperatively; dermal fats grafting to malar area with spacers inserted into the decrease lid. B and D, the patient is seen four months after eyelid surgical procedure by which spacer implants were positioned and dermal fats grafting was accomplished to the malar area. B and D, Six months after eyelid surgical procedure during which spacers had been implanted within the lower lid and dermal fats grafting was carried out to the malar space. Important considerations earlier than surgical procedure embrace figuring out the standing of the lively inflammatory course of, evaluating the patient for another rehabilitative procedures that may be needed (orbital decompression, strabismus surgery), and planning the corrective procedures accordingly (Box 32-1). Consider ancillary strategies for the forehead: endoscopic brow carry with corrugator removal due to continual frowning. Consider malar augmentation in sufferers with significant exophthalmos and malar recession. Periorbital aesthetic and useful repositioning of the globe with orbital expansion for globe recession and elimination of fat volume from the orbit together with eyelid surgery often is compromised by the swelling that follows strabismus surgical procedure. After strabismus surgery, the subsequent surgical procedure may be orbital decompression and defatting of orbital fat to retroplace the globe by several millimeters. Once this has stabilized, higher and decrease lid surgery can be considered to assist correct lagophthalmos and restore a more aesthetic appearance to the eyelids. Polytetrafluoroethylene as an interpositional graft material for the correction of decrease eyelid retraction. A review of surgical techniques to appropriate upper eyelid retraction related to thyroid eye illness. Transconjunctival fats elimination mixed with conservative medial wall/floor orbital decompression for Graves orbitopathy. A new approach for the therapy of lagophthalmos in sufferers with stabilized exophthalmos in Graves-Basedow disease. Correction of exophthalmos and eyelid deformities in sufferers with extreme thyroid ophthalmopathy. Certain childhood eyelid anomalies may initially seem to require quick consideration due to potential harm to the eye or impairment of visual improvement. Other anomalies create an appearance that may be unacceptable to the father or mother or baby, but they are often treated extra electively. Although the most typical structural eyelid anomaly within the pediatric age group that requires surgical procedure is ptosis of the upper lid, a number of different genetic and congenital eyelid abnormalities first seen at delivery or during childhood require ophthalmologic and oculoplastic remedy. Hamartomas are common orbital tumors that are outside of the scope of eyelid deformities. The pediatric eyelid defects that require surgical intervention include colobomas; clefts involving the face and periorbital region; lash rotation defects, together with epiblepharon, entropion, symblepharon, and euryblepharon; and syndromic defects, such as ptosis, telecanthus, epicanthal folds, and orbital and canthal dystopia. Eyelid colobomas, congenital entropion, ectropion, epiblepharon, and epicanthal folds may require surgical consideration. Commonly accepted techniques for surgical restore of those situations are presented, along with their implications relating to visual development. They are normally positioned within the upper eyelid but might happen laterally in the decrease eyelid. They can occur unilaterally or bilaterally, in the absence of different anomalies, or in affiliation with different cleft and dysplasia syndromes. Chapter 33 � Pediatric Eyelid Anomalies 973 Colobomas can also happen as a part of one of many first arch syndromes, similar to Goldenhar and Treacher Collins syndromes, and could also be associated with a facial cleft. Associated ocular anomalies embrace dermoid, lipodermoid, keratoconus, coloboma of the iris, and microphthalmia. Eyelid colobomas are related to a excessive incidence of strabismus, refractive error or opacities in the ocular media, and fibrous bands that restrict ocular motion. B, the same child has a preauricular appendage; eyelid cleft deformities are widespread in these sufferers. An eyelid coloboma is an almost fixed characteristic of Treacher Collins syndrome, which is autosomal dominant with variable penetrance and expressivity.
Syndromes
- Is there a headache?
- Fluids through a vein (IV)
- Medicines to control symptoms such as muscle spasms, urinary problems, fatigue or mood problems
- Breathing support
- The loss of smell continues or is getting worse
- Fever
- Paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria (PNH)
Augmentin 625 mg visa
With agency anchoring antibiotics in pregnancy augmentin 1000 mg effective, contracture of the inner canthal orbicularis produces a counterpull and a vertical vector of eyelid closure throughout blinking infection after sex augmentin 625 mg buy without a prescription. This counterpull is absent with canthal dehiscence or a free-floating lateral canthus, and the eyelids pull towards the nostril, impairing the vertical vector of closure. Chapter 14 � Correction of Lower Lid Malposition 431 Looking at a affected person in repose, minor levels of canthal dehiscence is in all probability not apparent to the surgeon. Nevertheless, many sufferers are symptomatic, with eye exposure and discomfort; some even tape their eyes closed at evening. Restoring canthal integrity by canthal refixation restores regular eyelid closure mechanics. Her eyelid closure was impaired, and she or he was forced to tape her eyelids closed at evening. It has turn out to be clear to us over the earlier few years that anchoring the canthus above the midpupil degree causes weakening because of the improper fulcrum vector in the mechanics of higher lid closure in sufferers with very distinguished eyes. B, Possible mechanisms of higher lid closure impairment: weakened mechanical leverage of closure of the higher lid with blinking and upward clotheslining. B, She is proven after higher and decrease lid blepharoplasty and secondary lower lid retinacular supraplacement to correct postoperative scleral present. C, Upper lid closure is impaired as the results of extreme supraplacement of the lower lid. The methods used to elevate the decrease lid on this situation are (1) lower lid release procedures and (2) crisscross canthal anchoring. Lower Lid Release Procedures With lower lid launch procedures, the lower lid edge must be pushed upward or be allowed to move upward by launch of rigidity under the lid margin. This is best carried out by release of the capsulopalpebral fascia in mild circumstances of lower lid retraction and by release of the decrease lid posterior lamella with insertion of a spacer, which is usually reserved for extra extreme cases. Crisscross Canthal Anchoring We developed the crisscross canthal anchoring approach as an different alternative to mitigate the impact of decrease lid canthal supraplacement. Chapter 14 � Correction of Lower Lid Malposition 435 Following lysis, the lower lid could additionally be elevated and fixated, with or with out utilizing a spacer. The higher lid canthal tendon is reinserted at a stage beneath the lower lid insertion to type a crisscross fixation. Crisscross fixation may be carried out without drill-hole fixation if the periosteum is adequate. We regularly use drill-holes in revision instances, because of the shortage of periosteum. Alignment of the sides of the upper and decrease lid on the lateral canthus turns into more difficult as the fixation points become farther aside. After crisscross anchoring, a marginal adhesion tarsorrhaphy is often needed to obtain precise alignment of the lateral fringe of the higher and lower lid. C, In main gaze after crisscross canthal anchoring (periosteal attachment), her eye fissure shape is improved. Chapter 14 � Correction of Lower Lid Malposition 437 reanchorinG the cheek flaP: anchorinG of the orbicUlaris-sMas flaP the inferior arc In addition to lateral canthal anchoring, the opposite reanchoring process wanted for patients present process revision surgical procedure entails repositioning midface tissue upward, thereby recruiting pores and skin into the decrease lid, reanchoring the orbicularis in the cheek flap upward with vertical motion. In aesthetic surgery, this method is preferable to pores and skin grafting and, in most cases, has allowed us to keep away from the use of skin grafts in these patients. In some sufferers a extra localized exterior skin-muscle incision may be made temporally, and the lower lid within the subciliary area may be extended previous the canthal angle. A subcutaneous dissection exposes a portion of the inferior arc of the orbicularis muscle laterally. Immediately postoperatively, good cheek position could also be evident, but with time, decrease lid retraction could recur. Additional sutures are used to fixate the fascia and orbicularis to the temporal fascia. No subcutaneous dissection is required over the orbicularis, because the fixating sutures might be placed in the undersurface of the flap. D, the fascia strip was hooked up to the superior orbital rim, elevating the cheek and decrease lid. Spacer grafts to the decrease lid had been reviewed, since a comprehensive dialogue of this broad matter is important. Surgeons have to know when to use a spacer, as a end result of the pure tendency could additionally be to avoid planning a spacer, since this implies a larger operation. The best consequence for success after one revision is the best for the affected person despite the operation. Overall, restoration of both aesthetic and eyelid function may be achieved with important enchancment. Lateral orbicularis oculi muscle plasty in conjunction with face lifting for periorbital rejuvenation. Secondary correction of unsatisfactory blepharoplasty: removing multilaminated septal constructions and grafting of preaponeurotic fat. Full-thickness lower eyelid reconstruction with a conchal chondroperichondral graft and local coverage with mio-cutaneous flaps-our divisional expertise. Management of postblepharoplasty decrease eyelid retraction with hard palate grafts and lateral tarsal strip. The safety and functions of acellular human dermal allograft in ophthalmic plastic and reconstructive surgery: a preliminary report. Efficacy of "thick" acellular human dermis (AlloDerm) for lower eyelid reconstruction. The use of porous polyethylene (Medpor) lower eyelid spacers in lid heightening and stabilisation. Comparison of biomechanical properties of AlloDerm and Enduragen as static facial sling biomaterials. Correction of lower eyelid retraction with high density porous polyethylene: the Medpor lower eyelid spacer. Lateral canthal dysfunction or fishmouth syndrome can be seen as a complication caused by lateral canthal dehiscence after eyelid surgical procedure and commonly produces signs in the patient which are described as the inability to close the upper and lower eyelids tightly together like "the mouth of a fish gasping for air. As previously mentioned, poor eyelid closure can result from pores and skin deficiency or intrinsic eyelid stiffness ensuing from scarring throughout the subcutaneous tissue in the higher or decrease lid. More refined causes of poor eyelid closure embody the dehiscence of lateral canthal fixation and a lower within the strength and tone of the lateral canthal attachments to the lateral orbital rim, which generally end in abnormal eyelid blinking and weak closure. Lateral canthal dysfunction is probably not recognized by static pictures and subsequently requires videos or shut examination of eyelid opening and closure. Critical evaluation of the patient regarding eyelid closure while blinking, nasal eyelid motion during a blink, inward lateral canthal motion from instability, and rotation of lash position with a blink should be famous on the physical examination. Dehiscence or stretching of both the higher and lower lid elements of the lateral canthal tendon may cause an irregular medially oriented motion of the eyelid on blinking, resembling a concentric fishmouth motion as an alternative of the more vertically oriented movement, which happens with normal blinking. B, Lateral canthal ligaments create resistance for vertical closure of the eyelids during contraction of the inside canthal orbicularis muscle. D, A weak lateral canthal fixation level is a standard underlying explanation for a weak blink and fishmouth blink motion caused by reduced countertension to contraction of the internal canthal orbicularis muscle, leading to incompetent closure and nasal motion of the eyelids quite than downward motion. Some of those sufferers had "regular" look on photographs and static examination however an irregular and disproportionate severity of signs.
Augmentin 625 mg line
It may be associated with different eyelid anomalies viruswin32pariteb purchase augmentin 625 mg amex, together with ptosis and telecanthus antibiotics for acne oxytetracycline cheap augmentin 625 mg with amex. For maximal improvement in youngsters with a severe vertical pores and skin shortage, skin grafting also is performed. D, After the resection, canthal anchoring sutures had been connected to the lateral rim. C, She was capable of wait till she was older to come to us for a one-stage resection and full-thickness skin graft and lateral canthoplasty to the upper lid. Surgeons ought to concentrate on the periorbtal area to reserve the visual axis and preserve depth perception. Facial debulking can additionally be performed; nonetheless, the facial nerve is at excessive danger of harm. The visible entry must be restored as quickly as potential whereas making certain protective masking of the cornea to stop exposure and dryness. Temporary and adjustable frontalis suspension is the workhorse procedure for establishing visual input to the affected eyelid. Syndromes with associated congenital ptosis require surgery to stop amblyopia, whereas defects causing lash irritation of the cornea or publicity of the cornea require surgical safety of the cornea and globe. Pediatric oculoplastic reconstruction is a continuum of treatment as these kids develop, to provide them with a steady, functional eyelid with an appropriate aesthetic appearance. Blepharophimosis: a suggestion for early surgery in patients with severe ptosis. The elements influencing visual improvement in blepharophimosis-ptosisepicanthus inversus syndrome. Lower eyelid orbicularis oculi musculocutaneous flap for recon struction of nasal tip and supratip defects. Unilateral congenital blepharoptosis repair by anterior levator advancement and resection: an educational evaluate. Statistical analysis of issues of the frontalis aponeurosis flap for correction of complete blepharoptosis. Surgical repair of the syndrome of epicanthus inversus, blepharophimosis and ptosis. Congenital entropion, epiblepharon, and antimongoloid obliquity of the palpebral fissure. Ocular findings in the facioauriculovertebral sequence (Goldenhar-Gorlin syndrome). Treatment of congenital types of telecanthus with custom-designed titanium medial canthal tendon screws. Nasopalpebral lipoma-coloboma syndrome: a brand new autosomal dominant dysplasia-malformation syndrome with congenital nasopalpebral lipomas, eyelid colobomas, telecanthus, and maxillary hypoplasia. Large pedunculated congenital corneal dermoid in affiliation with eyelid coloboma. Clinical characteristics and surgical therapy of congenital blepharophimosis syndrome. Gore-Tex soft-tissue patch frontalis suspension technique in congenital ptosis and in blepharophimosis-ptosis syndrome. Surgical treatment of congenital blepharophimosis syndrome and longterm follow-up. Early reconstruction surgery resolving visible occlusion and ocular malformation: a case report. Modification of Mustard� approach for correction of epicanthus in Asian sufferers. A compelled duction check ought to be carried out with topical anesthetic to affirm entrapment. Trapdoor fractures with proof of orbital contents under the trapdoor and a optimistic pressured duction test will require surgery after a 5- to 7-day period to permit the swelling to start to resolve, if potential. Byron Smith and William Regan to describe a hydraulic fracture of the orbit ensuing from an object barely larger than the circumference of the orbit. It was demonstrated in research through the use of a hurling ball in cadavers to simulate a blowout fracture. The findings confirmed that putting the orbital rim will increase orbital pressure, which can lead to a fracture of the orbital flooring and medial orbital wall without an orbital rim fracture. The unique web site of the produced orbital fracture was within the orbital plate of the maxilla, encompassing the infraorbital canal. The hydraulic pressure opens the fracture and propels orbital gentle 1005 1006 Part V � Orbital and Lacrimal Surgery tissues into the fracture, which narrows because the drive subsides, usually inflicting tissue entrapment with the ground acting as a trapdoor. Limitation of eye movement in upgaze and downgaze is the result of mechanical restriction of movement, mostly of the inferior rectus muscle and typically the inferior oblique muscle. Decreased sensation in the distribution of the infraorbital nerve is widespread in patients who maintain fractures of the orbital ground. This numbness may contain the decrease eyelid, cheek, palate, and upper lip, however often improves over months. Experimental posterior displacement of the inferior orbital rim also produces buckling and fracture of the orbital floor that extends to the inferior medial wall. Several fracture patterns are recognized, together with linear, minimally displaced breaks that develop parallel and medial to the inferior orbital groove. Nondisplaced linear and trapdoor fractures are more likely to produce diplopia, whereas enophthalmos is more widespread following punched-out and comminuted fractures. Fractures of the lower medial wall happen commonly with fractures of the orbital flooring. The trapdoor is hinged nasally and opens and traps the orbital fat and septum, not often the muscle itself, thereby tethering the globe. Chapter 34 � Blowout Fracture of the Orbital Floor 1007 Orbital tissue swells, further growing the entrapment of the globe rotation, with restriction in upgaze and downgaze. Patients normally have eyelid swelling and in many cases subconjunctival hemorrhage. In children, the fracture can be poorly detected due to the white eye blowout fracture. Children are tough to examine and often have extreme squinting, nausea, and vomiting, which is brought on by the oculovagal reflex; in over 50% of kids that is misdiagnosed as a concussion. A high index of suspicion is required, because kids require surgical procedure inside forty eight hours to keep away from permanent muscle ischemia, scarring, and diplopia, not like adults, who can wait 3 to four days for the swelling to scale back. Passive rotation of the globe with compelled rotation reveals tethering of the globe. It should be remembered that mechanical restriction with a positive pressured duction test can happen with a hematoma of the extraocular muscle sheath, or marked orbital edema, in addition to frank entrapment of orbital tissues.
Discount augmentin 1000 mg free shipping
Nozue M antibiotics long term effects 1000 mg augmentin discount with mastercard, Oshiro Y antibiotics mechanism of action augmentin 1000 mg cheap on-line, Kurata M, et al: Treatment and prognosis in colorectal most cancers patients with bone metastasis. Pauzner R, Istomin V, Segal-Lieberman G, et al: Bilateral patellar metastases as the medical presentation of bronchogenic adenocarcinoma. Santini D, Tampellini M, Vincenzi B, et al: Natural historical past of bone metastasis in colorectal cancer: ultimate results of a big Italian bone metastases examine. Urvoy P, Mestdagh H, Butin E, et al: Patellar metastasis from a large bowel adenocarcinoma. Nakajima T, Suzuki M, Ando S, et al: Spontaneous regression of bone metastasis from renal cell carcinoma: a case report. Ozaki O, Kitagawa W, Koshiishi H, et al: Thyroid carcinoma metastasized to the sternum: resection of the sternum and reconstruction with acrylic resin. Schlumberger M, Challeton C, De Vathaire F, et al: Radioactive iodine remedy and exterior radiotherapy for lung and bone metastases from thyroid carcinoma. Sesenna E, Tullio A, Piazza P: Treatment of craniofacial metastasis of a renal adenocarcinoma: report of case and evaluation of literature. Szendroi A, Dinya E, Kardos M, et al: Prognostic elements and survival of renal clear cell carcinoma sufferers with bone metastases. Takashi M, Takagi Y, Sakata T, et al: Surgical therapy of renal cell carcinoma metastases: prognostic significance. Van Poppel H, Baert L: Nephrectomy for metastatic renal cell carcinoma and surgery for distant metastases. Woodward E, Jagdev S, McParland L, et al: Skeletal issues and survival in renal cell carcinoma sufferers with bone metastases. Yamasoba T, Kikuchi S, Sugasawa M, et al: Occult follicular carcinoma metastasizing to the sinonasal tract. Zohar Y, Strauss M: Occult distant metastases of well-differentiated thyroid carcinoma. Benard J: Genetic alterations related to metastatic dissemination and chemoresistance in neuroblastoma. Nishida Y, Tsukushi S, Urakawa H, et al: High incidence of regional and in-transit lymph node metastasis in patients with alveolar rhabdomyosarcoma. Seidal T, Mark J, Hagmar B, et al: Alveolar rhabdomyosarcoma: a cytogenetic and correlated cytological and histological research. Sotelo-Avila C, Gonzalez-Crussi F, Sadowinski S, et al: Clear cell sarcoma of the kidney: a clinicopathologic study of 21 patients with long-term follow-up evaluation. Sridhar S, Al-Moallem B, Kamal H, et al: New insights into the genetics of neuroblastoma. Tonelli R, McIntyre A, Camerin C, et al: Antitumor activity of sustained N-myc discount in rhabdomyosarcomas and transcriptional block by antigene remedy. Turc-Carel C, Lizard-Nacol S, Justrabo E, et al: Consistent chromosomal translocation in alveolar rhabdomyosarcoma. Wang-Wuu S, Soukup S, Ballard E, et al: Chromosomal analysis of sixteen human rhabdomyosarcomas. Whang-Peng J, Knutsen T, Theil K, et al: Cytogenetic research in subgroups of rhabdomyosarcoma. Hayashi Y, Kanda N, Inaba T, et al: Cytogenetic findings and prognosis in neuroblastoma with emphasis on marker chromosome 1. Kaneko Y, Kanda N, Maseki N, et al: Different karyotypic patterns in early and advanced stage neuroblastomas. Many of the nodules subsequently turn out to be indifferent from the synovial membrane and float within the joint. The course of sometimes includes the synovium diffusely, has a high propensity for recurrences, and will severely compromise the function of a joint. The peak incidence is in the fifth decade of life, but the age range varies widely from the primary to seventh a long time. Male patients are predominantly affected, and the male-tofemale ratio is approximately 2: 1. Synovial chondromatosis preferentially includes the main weight-bearing joints, however any joint could also be concerned. A few cases involve joints of the shoulder and acral skeleton, the intervertebral facet joint, and the temporomandibular joint. Clinical Symptoms the scientific presentation consists of pain, swelling, and limitation of motion. The patient might have a history of signs lasting several months to several decades, but normally symptoms have continued for several years, with the common being 5 years. Superimposition of enchondral ossification is related to the development of linear calcifications. These constructions correspond to well-developed ossified nodules which might be composed of a shell of bone with a central space mimicking a medullary cavity. A and B, Lateral (A) and anteroposterior (B) radiographs of foot and ankle show long-standing synovial chondromatosis involving tendon sheaths. Note extensive involvement of extraarticular synovium of tendons and eggshell pattern of mineralization with central lucency in a variety of the nodules. B, Computed tomogram documents multifocal calcification in periarticular delicate tissue. C, Specimen radiograph of resected synovial pad with multifocal calcified nodules representing areas of cartilaginous metaplasia. A, Sagittal magnetic resonance picture shows high sign in loose our bodies with areas of signal void representing mineralization of cartilage and bone matrix. B, Lateral radiograph of knee shows cartilaginous and bony loose our bodies in knee joint below patella; joint area is preserved. Each cartilage nodule ranges in measurement from a small focus (<1 mm) that requires a magnifying glass to be seen to a larger lesion measuring more than 1 cm in diameter. In addition to individual nodules focally, larger cartilaginous areas represent coalescent smaller nodules of cartilage. These larger cartilaginous plenty have multinodular (granular) surfaces, and their multifocal origin can still be seen on cut surface. Occasionally in long-standing cases, the adjoining bursae or tendons may be concerned. On the idea of gross options, synovial chondromatosis may be divided into two types: diffuse and localized. The diffuse kind is characterized by a number of nodules that involve virtually the entire synovium of the joint. In rare circumstances a nodular type of synovial chondromatosis can have a configuration of a polypoid pedunculated mass protruding into the joint space. In typical cases the cartilage cells form unfastened clusters, but a uniform distribution of cartilage cells can additionally be seen.
Buy discount augmentin 625 mg on line
Midface fractures: advantages of instant extended open reduction and bone grafting 00g infection augmentin 1000 mg amex. Single eyelid incision for exposure of the zygomatic bone and orbital reconstruction antibiotics for sinus infection not helping discount augmentin 1000 mg overnight delivery. The use of Teflon in orbital flooring reconstruction following blunt facial trauma: a 20-year experience. High-dose corticosteroids for remedy of imaginative and prescient loss as a outcome of indirect damage to the optic nerve. The benefit is retention of the extraocular muscles for improved postoperative motion of a prosthetic eye. Well-vascularized tissue protection is required for both evisceration and enucleation. This risk, though low, ought to be discussed with sufferers earlier than surgery if attainable. Evisceration Evisceration involves removal of the contents of the attention whereas leaving the scleral shell and muscle attachments intact. The scleral shell is typically filled with a spherical implant, usually of mounted dimension, and is sutured together. Evisceration is especially helpful in patients with a scarcity of conjunctiva, whereas enucleation can additional shorten the conjunctival fornix size. Historically, evisceration has been used in circumstances of severe 1047 1048 Part V � Orbital and Lacrimal Surgery an infection to forestall possible dissemination of a pathogen. The procedure is simpler and shorter than enucleation and, in lots of circumstances, has produced greater movement of the prosthetic eye. Evisceration could be carried out with the patient underneath regional anesthesia; however, some sufferers require common anesthesia. Evisceration may be contraindicated when no pathologic specimen is recognized and in circumstances of attainable sympathetic ophthalmia. The rate of implant extrusion may be higher with this process, as a result of the size of the enucleation implant is proscribed. A 365-degree conjunctival periotomy is carried out, with undermining carried uveally in the sub-Tenon house again to the equator of the globe. An incision through the corneal limbus is made with corneal scleral scissors and extended across the limbus, leaving the cornea connected to the globe with a 20-degree strand. A cyclodialysis spatula is introduced to separate the iris root and ciliary body utterly from the cornea. Alternatively, the sharp fringe of a Freer elevator with a suction tip can be utilized to remove all uveal tissues. Cotton-tipped applicators, moistened with absolute alcohol (100% ethanol), could also be used to denature residual uveal pigment. Relaxing cuts by way of the residual sclera of the globe could additionally be made, whereas the emissary veins and their exit sites are famous. The dimension of the spherical implant is somewhat restricted; a maximal implant measurement of 6 mm can be used except these expansive sclerotic maneuvers are performed in a radial trend through the scleral shell. An 18 to 20 mm sphere (silicone or acrylic) can be positioned in the expanded scleral shell. Placement of a hydroxyapatite implant at the time of evisceration requires excision of the posterior part of the sclera to present a large window for fibrovascular ingrowth. An 18 to 20 mm hydroxyapatite implant that has been predrilled with 6 to 8 holes with a 20-gauge needle can be inserted into the scleral pocket. Hydroxyapatite implants after evisceration can be associated with more postoperative pain than silicone and acrylic implants. The scleral edges anteriorly are overlapped and secured with a double-armed nonabsorbable suture in a mattress method. B, Removal of the attention contents with sharp dissection, without penetrating the globe and leaving a clear scleral wall. The placement of bigger implants producing extra postoperative socket volume is possible after enucleation. After the pathology involving the attention itself is managed, and after enucleation (or evisceration), the goal in every patient is to put together the socket to retain volume and to guarantee the model new prosthetic eye will have a more normal appearance. Corrective procedures for these issues are needed and are described in Chapter 37. The hydroxyapatite implant (Perry) works properly in lots of sufferers but requires multiple procedures and revisions and in some cases causes persistent socket irritation. This requires modification of the surface of the socket to a extra rigid, flattened floor to tilt the implant with movement. In the past, the mechanics of motion in a nonex- Chapter 36 � Evisceration and Enucleation 1051 posed implant would require anterior socket friction to be transmitted to the prosthetic eye. If the inserted orbital implant has a rigid, flat floor, or if additional flat tissue (ear cartilage or dermal fat) is grafted on prime of the implant, extra prosthetic eye movement might be potential. With a nonexposed implant, socket rotation is transmitted to the prosthetic eye primarily by way of tilting of the socket, with rotational forces transmitted at the edges of the socket. This facilitates placement of a smaller prosthetic eye that might be more easily rotated. Box 36-1 Volumes of Components Involved in Enucleation and Most Commonly Used Orbital Implants Volume Information Enucleated eye (average size): 7. C, Measurements of the varying distances of the rectus muscle from the corneal limbus (spiral of Tillaux). The sutures ought to be placed distal enough from the insertion of the extraocular muscle tissue on the globe to guarantee a residual stump for traction when the muscle is severed. The inferior oblique muscle is olated with a muscle hook pointed inward and then rotated outward in the inferior nasal portion of the orbit. The tendons are severed between the 6-0 Vicryl traction sutures and the insertion, leaving sufficient stump to grasp with a hemostat or to place a silk traction suture. The globe can be rotated freely and a single silk traction suture positioned, often within the stump of the medial rectus tendon, permitting the globe to be retracted ahead when the nerve is severed. The globe is introduced ahead before the snare is compressed posteriorly across the nerve. B, the enucleated eye with traction sutures and the desired margin of the optic nerve, significantly for a malignancy of the attention. Relaxing incisions in the capsule could also be needed, relying on the dimensions of the implant. C, the final closure of the capsule over the implant, with the rectus muscular tissues isolated. The conjunctiva is carefully closed to ensure an enough blood provide from the fornices. This will vascularize the dermal fat graft over a smaller ear cartilage graft, which can forestall blood provide. VarIatIons on BasIc EnuclEatIon tEchnIquE Abdominal Dermal Fat Graft An autologous fats graft may be positioned as an implant.