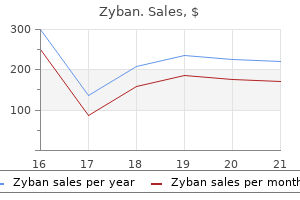
Zyban dosages: 150 mg
Zyban packs: 60 pills, 90 pills, 120 pills, 180 pills, 270 pills, 360 pills

150 mg zyban quality
Councill catheters are particularly helpful because they can be inserted or exchanged over a guidewire with out dropping entry to the kidney anxiety zone als zyban 150 mg discount on-line. Malecot and Pezzer nephrostomies have the benefit of a bigger lumen due to their lack of retention balloon tubing depression definition ww2 zyban 150 mg buy generic online. Re-entry catheters are designed to allow nephrostomy drainage while ensuring entry to the ureter, should this be essential. A tamponade (Kaye) catheter may be of particular use in instances of postoperative bleeding (Paul et al, 2003). The catheter with a symmetrical balloon had significantly higher flow with water and higher-viscosity fluid and better retention power in contrast with the other catheters (Canales et al, 2005). Anesthesia will not be an possibility in unwell patients with acute renal failure or sepsis with hemodynamic instability. Because stent placement under local anesthesia appears to be possible even in an workplace setting, this relative benefit might decline sooner or later (Sivalingam et al, 2013). Overall quality of life, nevertheless, has not been demonstrated to be statistically totally different between the 2 groups (Joshi et al, 2001; Monsky et al, 2013). Acute decompression of obstructed pyonephrosis is a urologic emergency, and failure to achieve immediate drainage is said to a better mortality threat (Borofsky et al, 2013). In addition, a tubeless procedure reduces hospital stay, analgesia requirement, and time to return to normal exercise (Yuan et al, 2011; Shen et al, 2012; Wang et al, 2012; Zhong et al, 2013). Nephrostomy tubes can also be used to administer therapeutic medicine to the higher urinary tract. If a nephrostomy tube is in place, it might be used to acquire a nephrostogram for diagnostic imaging. In the treatment of malignant ureteric obstruction, drainage failure is significantly more prevalent in sufferers with ureteral stents compared with patients with a nephrostomy tube (Ku et al, 2004). Quorum sensing is a bacterial communication course of depending on inhabitants density. Diffusible signaling molecules permit bacterial colonies to react to their surroundings in a synchronized method, regulating biofilm formation, virulence, and antibiotic resistance (Li and Nair, 2012; Bhardwaj et al, 2013). Bacteria contained in biofilm actively recruit different bacterial strains, resulting in biofilm consisting of as much as six completely different strains. Canales and colleagues demonstrated that parts of the conditioning film, 1-antitrypsin, Ig kappa, IgH G1, and histone H2B and H3A, were extremely related to stent encrustation (Canales et al, 2009). The issue in preventing and treating biofilm and biofilminduced infections is the consequence of the complexity of biofilm How to get hold of percutaneous entry to the kidney is described in Chapter eight. Transfusion rates of 2% to 4% have been reported as a end result of venous or arterial bleeding. Persistent arterial bleeding or arteriovenous fistula is an uncommon but extra extreme complication that requires enough imaging evaluation and, if essential, therapy with angioembolization. Thoracic complications (pneumothorax, hemothorax, hydrothorax, empyema) happen in zero. A self-retaining catheter or retainment suture fixation to the pores and skin can aid in stopping tube dislodgement (Lewis and Patel, 2004; Wah et al, 2004; Hausegger and Portugaller, 2006; Rana et al, 2007; Ali et al, 2013). Major complications are more frequent when procedures are carried out throughout on-call hours, with lack of skilled employees implicated as a contributing issue (Lewis and Patel, 2004). Biofilm Formation on Urinary Tract Biomaterials A biofilm is defined as a structured community of bacterial cells enclosed in a self-produced polymeric matrix and adherent to an inert or residing surface. Despite continuing developmental efforts to achieve more biocompatible materials and surface coatings, indwelling catheters, stents, and nephrostomy tubes utterly resistant to biofilm formation are as yet unavailable. Biofilm buildings include three layers: (1) the innermost layer, hooked up to the floor of the biomaterial, which features as a linking movie for subsequent layers; (2) the base film, composed of microorganisms connected to the linking movie; and (3) an outer layer or surface film, the place microorganisms could be released (Tenke et al, 2012). The thickness of a biofilm can vary from three to 490 �m and consists of some cell layers ranging to as a lot as 400 cells deep (Ganderton et al, 1992). The initial step in biofilm formation is the creation of a conditioning film on the surface of the biomaterial inside minutes of insertion (Reid et al, 1995). This conditioning film is composed of urinary components such as polysaccharides, Tamm-Horsfall proteins, electrolytes, and glycoproteins that adhere to the biomaterial surface. The conditioning film alters the floor traits of the biomaterial, facilitating bacterial adhesions (Reid and Busscher, 1992). The preliminary bacterial adhesion is influenced by hydrophobic and electrostatic interactions, ionic forces, osmolality, and urinary pH and remains to be reversible (Gristina, 1987). The bacteria produce a matrix of exopolysaccharides and glycocalyx, rendering their adhesion irreversible. The remainder is composed of interstitial areas crammed with fluid and water channels that enable transportation of nutrients and oxygen to the colonies (Tenke et al, 2012). Better understanding of basic processes and insights into biofilm formation and resistance mechanisms will guide the following generation of catheter and stent growth and design looking for the ideal biomaterial and coating. Relief of stent related signs: review of engineering and pharmacological solutions. Flexible cystoscopy in men: is topical anaesthesia with lignocaine gel worthwhile Current management of severely encrusted ureteral stents with a large related stone burden. Surgical decompression is related to decreased mortality in patients with sepsis and ureteral calculi. Biocompatibility, cell adhesion, and degradation of surface-modified biodegradable polymers designed for the higher urinary tract. Optimal prevention and administration of proximal ureteral stent migration and remigration. Crystalline bacterial biofilm formation on urinary catheters by urease-producing urinary tract pathogens: a simple method of management. Adult anterior urethral strictures: a national apply patterns survey of board certified urologists in the United States. Triclosan loaded ureteral stents decrease Proteus mirabilis 296 infection in a rabbit urinary tract an infection mannequin. Presence of 5 conditioning film proteins are extremely related to early stent encrustation. Intermittent catheterization with a hydrophilic-coated catheter delays urinary tract infections in acute spinal cord harm: a prospective, randomized, multicenter trial. Heparin coating on ureteral double J stents prevents encrustations: an in vivo case research. A randomized controlled examine to compare the 2% lignocaine and aqueous lubricating gels for feminine urethral catheterization. In vivo analysis of the third technology biodegradable stent: a novel strategy to avoiding the forgotten stent syndrome. Prospective randomized crossover trial of lubricant gel against an anaesthetic gel for outpatient cystoscopy.
Headsman (Buckhorn Plantain). Zyban.
- The common cold, cough, fevers, bleeding, inflammation of breathing passages such as bronchitis, sore mouth, sore throat, inflamed skin when applied directly to the irritated area, and other conditions.
- Dosing considerations for Buckhorn Plantain.
- What is Buckhorn Plantain?
- How does Buckhorn Plantain work?
- Are there safety concerns?
Source: http://www.rxlist.com/script/main/art.asp?articlekey=96720
Order zyban 150 mg free shipping
It is an intervention of significance anxiety guru cheap zyban 150 mg with visa, however depression vomiting 150 mg zyban purchase visa, that might be associated with short- and long-term complications. From 15% to 25% of hospitalized sufferers undergo a urethral catheter placement at some point throughout their stay (Glynn et al, 1997). Overuse of bladder catheterization has been reported to range from 15% to 40% of instances and is correlated with prolonged hospital keep (Apisarnthanarak et al, 2007; Tiwari et al, 2012). Catheters must be placed underneath antiseptic situations, placing the smallest potential catheter with adequate lubrication. Routine irrigation must be averted (Gould et al, 2010; Hooton et al, 2010; Tambyah and Oon, 2012). A latest Cochrane meta-analysis showed no distinction in urinary an infection rates in long-term catheterized sufferers when different catheter sorts had been compared (Jahn et al, 2012). There is inadequate evidence to reliably suggest the use of one catheter sort over one other. Use of prophylactic antibiotics on elimination of a bladder catheter, even after short-term catheterization, has been both recommended and discouraged (Wolf et al, 2008; Hooton et al, 2010). The authors proposed that extended catheterization results in urethral irritation and ischemia, and finally to urethral stricture (Fenton et al, 2005). Inflation of the balloon within the prostatic urethra or in a false passage can cause extreme hematuria, urethral rupture, and subsequent stricture (Lang et al, 2012). Taking into consideration that as much as 25% of hospitalized patients are catheterized at some point throughout their stay, recommending the routine use of antibiotics after catheter elimination would entail an unlimited utilization of antibiotics with the associated dangers of bacterial resistance and other drug-related unwanted effects. Complications include pericatheter urine leakage, unintentional removing, catheter blockage, hematuria, bladder stones, and bladder most cancers. The subgroup of patients with spinal twine injuries is at higher threat of problems (Hollingsworth et al, 2013). Inability to remove a transurethral bladder catheter could be a difficult complication. Entrapment of the catheter by anastomotic sutures after urethroplasty or radical prostatectomy poses a unique postoperative complication. When sutures are known to be degradable, one can retry catheter elimination 1 or 2 weeks after the initial attempt. If the sutures are nondegradable, the urethra can be accessed with a semirigid ureteroscope to visualize and divide the suture with laser energy (Nagarajan et al, 2005; Nagele et al, 2006). Cuffing of the balloon after deflation can cause the catheter to bind on the bladder neck. This phenomenon relies on the catheter used (material and manufacturer), indwelling time, urinary infection, and deflation method, with indwelling time being the most significant predictor. Resolution of this problem could also be achieved by instilling an additional 1 or 2 mL of fluid within the balloon and attempting to repeat aspiration. Overinflation of the balloon with the intention of getting it burst should be averted as a outcome of this may be painful and presumably lead to retained fragments of the catheter balloon within the bladder. If all else fails, ultrasound-guided needle puncture of the balloon is typically the ultimate approach. Inability to remove a catheter with a totally deflated balloon can also be brought on by catheter encrustation, especially if the catheter has been indwelling for an prolonged time. There is robust proof that the main causal issue of catheter encrustation is an infection with Proteus mirabilis. Especially in sufferers with long-term bladder catheterization, this circumstance may cause recurrent blockage of the catheter (Stickler and Feneley, 2010). Applying light traction to the catheter can cause the encrustation to dislodge, facilitating catheter removing. Increasing affected person fluid consumption and ingestion of citrate might delay or control this problem in recognized stone formers and continual catheter blockers (Stickler and Feneley, 2010). When website of stricture was taken into account, historical past of urethral catheterization was the most important causal factor of multifocal or panurethral strictures (Lumen et al, 2009). PreventionofIatrogenicTrauma the pressure in the catheter balloon when an incorrectly placed catheter is being inflated is much greater than when the catheter is in a correct place. Forces of extraction of a catheter are a lot decrease with 5 mL within the balloon than with 10 mL within the balloon (Wu et al, 2012). When high strain is perceived when inflating the balloon, one should reassess and make positive that the catheter is in the bladder. In sufferers at threat of inadvertent traumatic catheter extraction, the balloon is full of 5 mL as a substitute of 10 mL to lower the chance of significant urethral trauma. When extended catheterization is required, a smaller catheter, corresponding to 16 Fr, should be used. There ought to be a lower threshold for placing a suprapubic catheter when prolonged catheterization is anticipated (Fenton et al, 2005). With coaching and schooling, trauma from urethral catheterization may be lowered fivefold (Kashefi et al, 2008; Thomas et al, 2009). During transurethral resection of the prostate, suprapubic catheter placement is most well-liked by some urologists because a continuous move may be maintained at all times without influencing bladder stress (S�nchez Zalabardo et al, 2003). Short-term suprapubic catheter placement is usually helpful in postoperative conditions after urogenital surgical procedure to allow for bladder or urethral tissue therapeutic. Although a suprapubic catheter is more invasive than a transurethral catheter, proof means that the previous is extra acceptable than a transurethral catheter to surgical patients (McPhail et al, 2006). There is inadequate evidence supporting superiority of a suprapubic catheter over a transurethral catheter in short-term postoperative catheterization (Phipps et al, 2006). However, when considering the population of hospitalized sufferers in need of short-term catheterization (up to 14 days), a significant benefit has been found in favor of the suprapubic catheter when it comes to bacteriuria incidence and patient consolation (Ni�l-Weise and van den Broek, 2005). This reflects the lack of evidence-based data and limits the advice of a suprapubic catheter over a transurethral catheter for long-term catheterization. Whenever suprapubic catheter placement in kids is required, using ultrasound guidance in the course of the catheter placement is suggested. Contraindications to suprapubic catheter placement include previous lower stomach surgery resulting in unsafe percutaneous passage to the bladder, bladder most cancers, uncorrected coagulopathies or anticoagulation, belly wall an infection at the desired puncture web site, and the presence of vascular grafts near the popular tract (Harrison et al, 2011). In sufferers in whom one could suspect the presence of ascites, ultrasound is all the time used to affirm a large postvoid residual urine quantity as a end result of ascites can generally be mistaken for a large postmicturitional quantity on ultrasound bladder scan. Advantages of a suprapubic catheter embody elimination of danger of urethral stricture and penile erosion. A trial to void can be tried without the necessity for recatheterization if unsuccessful. Wound care for a suprapubic catheter is commonly simpler, especially in chair-bound sufferers. In sufferers requiring long-term catheter drainage, the location of a suprapubic catheter as a substitute for a transurethral catheter can be considered, and benefits and disadvantages must be discussed with the patient. In most patients the distended bladder displaces the intraperitoneal bowel loops out of the pelvis and away from the pubic symphysis. A minimal bladder quantity of 300 mL on bladder scan is advised earlier than suprapubic catheter placement is attempted (Albrecht et al, 2004). In performing blind puncture, the symphysis must be palpated and the access site must be chosen approximately one to two fingerbreadths above the symphysis. In overweight patients with an stomach pannus, placement of the tract in a skin fold is prevented to prevent dermatitis (Harrison et al, 2011).
Zyban 150 mg buy cheap on-line
Clinical trial comparing lomefloxacin and ofloxacin within the treatment of chronic bacterial prostatitis depression test extensive zyban 150 mg generic otc. Patterns of inflammation in prostatic hyperplasia: a histologic and bacteriologic examine bipolar depression for dummies cheap 150 mg zyban with amex. A examine on the role of Chlamydia trachomatis in chronic prostatitis-analysis of anti�Chlamydia trachomatis specific IgA in expressed prostate secretion by Western-blotting methodology. Comprehensive evaluation and therapy of seventy five males referred to chronic prostatitis clinic. Chronic pelvic ache represents probably the most prominent urogenital signs of "persistent prostatitis. Detecting urethral and prostatic irritation in sufferers with persistent prostatitis. Counting leukocytes in expressed prostatic secretions from sufferers with continual prostatitis/chronic pelvic pain syndrome. Inconsistent localization of grampositive bacteria to prostate-specific specimens from patients with chronic prostatitis. Influence of environmental elements on continual prostatitis-like symptoms in young males: outcomes of a community-based survey. Prevalence of prostatitis-like symptoms in Japanese males: a population-based study in a town in Hokkaido. Detection of Chlamydia trachomatis in urethra of sufferers with urogenital an infection. Cost effectiveness mannequin comparing trimethoprim sulfamethoxazole and ciprofloxacin for the treatment of persistent bacterial prostatitis. Pain, catastrophizing, and melancholy in chronic prostatitis/ continual pelvic ache syndrome. Terazosine and tamsulosin in non bacterial prostatitis: a randomized placebo-controlled study. Influence of environmental elements on prevalence, symptoms, and pathologic strategy of chronic prostatitis/chronic pelvic pain syndrome in northwest China. Retrograde transurethral balloon dilation of prostate: progressive administration of abacterial chronic prostatitis and prostatodynia. Eradication of surprising pathogens by mixture pharmacological remedy is paralleled by enchancment of indicators and symptoms of chronic prostatitis syndrome. Efficacy of repeated cycles of mixture remedy for the eradication of infecting organisms in persistent bacterial prostatitis. Semen analysis in chronic bacterial prostatitis: diagnostic and therapeutic implications. Search for uro-genital tract infections in patients with signs of prostatitis: research on cardio and strictly anaerobic micro organism, mycoplasmas, fungi, trichomonads and viruses. Symptoms suggestive of continual pelvic pain syndrome in an city inhabitants: prevalence and associations with lower urinary tract signs and erectile operate. Long-term effects of osteopathic treatment of continual prostatitis with continual pelvic pain syndrome: a 5-year follow-up of a randomized controlled trial and concerns on the pathophysiological context. Results of pudendal nerve neurolysis transposition in twelve sufferers affected by pudendal neuralgia. Few patients with "continual prostatitis" have important bladder outlet obstruction. Computed tomography�guided pudendal block for treatment of pelvic ache due to pudendal neuropathy. Diagnosing and treating chronic prostatitis: do urologists use the four-glass check. Quality of life is impaired in men with persistent prostatitis: the chronic prostatitis collaborative analysis network. Prostatitis: observations on the activity of trimethoprimsulfamethoxazole within the prostate. Long-term remedy of persistent bacterial prostatitis with trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole. Serum antibody titers in treatment with trimethoprimsulfamethoxazole for continual prostatitis. Alfuzosin remedy for chronic prostatitis/ persistent pelvic pain syndrome: a prospective, randomized, double-blind placebo managed, pilot examine. Epidemiology of prostatitis in Finnish males: a population-based cross-sectional examine. Chronic prostatitis/chronic pelvic pain syndrome can be characterised by prostatic tissue pressure measurements. Fears, sexual disturbances and character features in males with prostatitis: a population-based crosssectional study in Finland. Role of repeated prostatic therapeutic massage in persistent prostatitis: a systematic review of the literature. Chronic pelvic ache syndrome in males is related to reduction of relative grey matter quantity in the anterior cingulate cortex compared to healthy controls. Comparison of microscopic strategies for detecting irritation in expressed prostatic secretions. Lomefloxacin versus ciprofloxacin within the treatment of chronic bacterial prostatitis. Bacterial biofilms: affect on the pathogenesis, prognosis and therapy of urinary tract infections. Failure of a monotherapy strategy for tough chronic prostatitis/chronic pelvic pain syndrome. Repetitive prostatic therapeutic massage remedy for chronic refractory prostatitis: the Philippine expertise. The Canadian Prostatitis Research Group: Predictors of patient response to antibiotic remedy for chronic prostatitis/chronic pelvic pain syndrome: a potential multicenter medical trial. Development of an evidence-based cognitive behavioural therapy program for men with persistent prostatitis/ continual pelvic pain syndrome. Treatment of continual prostatitis/ persistent pelvic ache syndrome with tamsulosin: a randomized double blind trial. Research tips for persistent prostatitis: consensus report from the first National Institutes of Health International Prostatitis Collaborative Network. A randomized, placebo managed multi-center study to consider the security and efficacy of rofecoxib in the treatment of chronic non-bacterial prostatitis. Phenotypic approach to the administration of continual prostatitis/chronic pelvic ache syndrome. Ciprofloxacin in the treatment of persistent bacterial prostatitis: a potential, non-comparative multicentre medical trial with long-term follow-up. Oral levofloxacin 500 mg once daily within the therapy of continual bacterial prostatitis. Use of terazosin in prostatodynia and validation of a symptom rating questionnaire. The bacteriology of chronic prostatitis and seminal vesiculitis and elective localization of the micro organism as isolated. Clinical evaluation of the person with continual prostatitis/chronic pelvic pain syndrome.
Zyban 150 mg generic overnight delivery
The long-term efficacy of sacral neuromodulation within the administration of intractable cases of bladder ache syndrome: 14 years of experience in one centre anxiety quiz online generic zyban 150 mg otc. Maintenance of the response to dimethyl sulfoxide treatment utilizing hyperbaric oxygen in interstitial cystitis/painful bladder syndrome: a prospective anxiety icd 9 code zyban 150 mg buy, randomized, comparative study. Consensus statement for the administration of chronic pelvic ache and endometriosis: proceedings of an expert-panel consensus process. Bladder pain syndrome: do the totally different morphological and cystoscopic options correlate Efficacy of sacral neuromodulation in treatment of bladder ache syndrome: long-term follow-up. Botulinum A toxin intravesical injection in sufferers with painful bladder syndrome: 1-year followup. Combined intravesical sodium hyaluronate/chondroitin sulfate therapy for interstitial cystitis/bladder pain syndrome: a potential research. Summary of the National Institute of Arthritis, Diabetes, Digestive and Kidney Diseases Workshop on Interstitial Cystitis, National Institutes of Health, Bethesda, Maryland, August 28-29, 1987. Destruction of the vesicoureteric plexus for the therapy of hypersensitive bladder problems. Lumbar nerve root compression and interstitial cystitis-response to decompressive surgery. Prolonged hydrodistention of the bladder for symptomatic treatment of interstitial cystitis: efficacy at 6 months and 1 year. Psychometric evaluation of the University of Wisconsin Interstitial Cystitis Scale: implications to be used in randomized clinical trials. Reflex sympathetic dystrophy: model of a severe regional inflammatory response syndrome. Long-term use of opioids in chronic pain sufferers with nonterminal disease states. Expression of intercellular adhesion molecules within the bladder of patients with interstitial cystitis. Does the potassium stimulation take a look at predict cystometric, cystoscopic consequence in interstitial cystitis Bladder urothelial cells from patients with interstitial cystitis have an increased sensitivity to carbachol. The relationship of widespread medical circumstances and medication use with symptoms of painful bladder syndrome: results from the Boston Area Community Health Survey. Effects of mixture therapy of intravesical resiniferatoxin instillation and hydrodistention in patients with refractory painful bladder syndrome/interstitial cystitis: a pilot study. Sodium pentosanpolysulphate in the management of haemorrhagic cystitis: expertise with 14 sufferers. Paris: International Consultation on Urological Diseases/European Association of Urology; 2013. Status of worldwide consensus on interstitial cystitis/bladder pain syndrome/painful bladder syndrome: 2008 snapshot. Disintegrity of the vesical blood-urine barrier in interstitial cystitis: a vicious circle. Painful bladder disease: medical and pathoanatomical variations in one hundred fifteen patients. A prospective double-blind clinically controlled multicenter trial of sodium pentosanpolysulfate within the remedy of interstitial cystitis and associated painful bladder disease. Nonobstructive detrusor myopathy in a gaggle of patients with persistent abacterial cystitis. Urinary excretion of a metabolite of histamine (1,4-methyl-imidazole-acetic-acid) in painful bladder illness. Evaluation of transvaginal Theile therapeutic massage as a therapeutic intervention for ladies with interstitial cystitis. Clinical guidelines for interstitial cystitis and hypersensitive bladder syndrome. Nitric oxide as an goal marker for analysis of remedy response in sufferers with traditional interstitial cystitis. Hydrodistention plus bladder coaching versus hydrodistention for the remedy of interstitial cystitis. Risk elements that have an effect on the treatment of interstitial cystitis using intravesical therapy with a dimethyl sulfoxide cocktail. Urinary glycosaminoglycan excretion as a laboratory marker within the analysis of interstitial cystitis. The role of glycosaminoglycans in regular bladder physiology and the pathophysiology of interstitial cystitis. Hyaluronic acid: an efficient different therapy of interstitial cystitis, recurrent urinary tract infections, and hemorrhagic cystitis Mucosal muscarinic receptors improve bladder exercise in cats with feline interstitial cystitis. Dilemmas in diagnosing pelvic pain: a number of pelvic surgical procedures common in women with interstitial cystitis. Interstitial cystitis/painful bladder syndrome/bladder pain syndrome: the evolution of a model new paradigm. The diagnosis of interstitial cystitis revisited: classes realized from the National Institutes of Health Interstitial Cystitis Data Base examine. Immunologic and histologic analysis of the urinary bladder wall after group A streptococcal an infection. Interstitial cystitis: bladder mucosa lymphocyte immunophenotyping and peripheral blood flow cytometry analysis. Abnormal expression of differentiation associated proteins and proteoglycan core proteins in the urothelium of sufferers with interstitial cystitis. Is sensory urgency a part of the same spectrum of bladder dysfunction as detrusor overactivity Interstitial cystitis: elevated sympathetic innervation and associated neuropeptide synthesis. Topical heparin remedy normalizes urothelial permeability and vesical blood move in urgency/ frequency syndrome, urge incontinence and reversible interstitial cystitis. Impaired bladder perfusion in interstitial cystitis: a study of blood provide utilizing laser Doppler flowmetry. Elevated stress protein in transitional cells uncovered to urine from interstitial cystitis patients. Clinical symptoms scale for interstitial cystitis for diagnosis and for following the course of the disease. The distribution and function of chondroitin sulfate and other sulfated glycosaminoglycans within the human bladder and their contribution to the protecting bladder barrier. Clinical features and spectrum of sunshine microscopic changes in interstitial cystitis. Reflux esophagitis elevated the chance of bladder pain syndrome/interstitial cystitis: a 3-year follow-up research. Histamine content and mast cell count of detrusor muscle in sufferers with interstitial cystitis and other forms of persistent cystitis. Normalization of proliferation and tight junction formation in bladder epithelial cells from patients with interstitial cystitis/painful bladder syndrome by D-proline and D-pipecolic acid derivatives of antiproliferative factor. Bladder epithelial cells from patients with interstitial cystitis produce an inhibitor of heparin-binding epidermal growth factor-like growth issue manufacturing. Changes in human bladder epithelial cell gene expression associated with interstitial cystitis or antiproliferative factor remedy.
Zyban 150 mg buy cheap on-line
One group of investigators measured ureteroinfundibular angle (between the major axis of the ureter and the lower pole infundibulum) in 30 sufferers depression symptoms after quitting smoking discount 150 mg zyban mastercard. They decided an average angle of one hundred forty degrees with a most of one hundred seventy five degrees (Bagley and Rittenberg depression test form 150 mg zyban order otc, 1987). Active deflection of the ureteroscope of 180 degrees should enable visualization of the lower pole in most patients. However, reaching into the lower pole calyx with the tip of the ureteroscope in a fashion that enables endoscopic work to be accomplished can still be challenging. Active deflection occurs only at the distal tip of the ureteroscope, and the deflected segment may not be long sufficient to reach the decrease pole calyx. Most flexible ureteroscopes have a more flexible phase of the ureteroscope because of a weak spot in the durometer of the sheath, situated simply proximal to the point of lively deflection. This secondary, passive deflection mechanism addresses the issue of reaching the lower pole in some patients. By passive bending of the tip of the ureteroscope off the superior margin of Digital Ureteroscopes Digital flexible ureteroscopes have been developed and released by every of the three main endoscope manufacturers. Like digital flexible cystoscopes described earlier in this chapter, these ureteroscopes integrate the endoscope, the digital camera, and the light source. One group of investigators performed a potential comparison between digital and fiberoptic ureteroscopes to decide the affect of those larger-diameter digital scopes on affected person outcomes. Once perforated, sterilization of the flexible ureteroscope will result in fluid damage to the imaging system of the scope, making the scope unusable. The holmium laser may injury the working channel when the tip is very close to the tip of the working channel. To prevent this, the tip of the fiber should be seen in the central portion of the sphere of view. A latest growth in versatile ureteroscope design is the ability of the video system to stop laser activation when the laser fiber is too near the tip of the endoscope (Xavier et al, 2009). This "endoscope protection system" is activated in response to the video imaging system not "seeing" the blue colour of the outer cladding of the laser fiber. When this "proximity alert" is activated, the laser will automatically pause firing to forestall harm to the scope. Ureteroscopes, together with the working channel, should be cleansed with heat water and a nonabrasive detergent after every use. In another analysis of the efficacy of digital and flexible ureteroscopes, investigators determined a statistically equal stone-free rate but a considerably shorter operative time within the digital group (Somani et al, 2013). This is presumed to be a results of the improved visibility of the digital ureteroscopes. These digital ureteroscopes could advance future miniaturization, optimize digital resolution, and enhance sturdiness. The specs of currently obtainable versatile ureteroscopes are detailed in Table 7-4. Care and Sterilization Rigid and particularly flexible ureteroscopes are very delicate instruments and must be dealt with accordingly. Any damage to the working channel, deflecting mechanism, or fibers within the image bundle can render the ureteroscope ineffective. One series reported that repairs of flexible ureteroscopes were needed after solely three to thirteen hours of use (Afane et al, 2000). This can elevate a small irregular area of the channel that will be more vulnerable to harm. They are used for many parts of these procedures including institution of percutaneous and ureteroscopic entry, for straightening of the ureter, as a guide for dilation of the ureter or percutaneous tract, and for stent placement. There are many guidewires available differing in diameter, rigidity, tip design, supplies, and coating. The most common design is a strong stainless-steel core round which an outer wire is wrapped. Nitinol (nickel-titanium) can be used for inside core building, and this offers guidewires a kinkresistant, barely stiffer character. When the outer polyurethane layer is coated with a hydrophilic polymer, these wires turn into exceptionally slippery. These "glide wires" are useful for negotiating around impacted ureteral calculi, tortuous ureters, and ureteral strictures. Hydrophiliccoated wires are too slippery to be reliable security wires, due to their tendency to slide out of the patient. Bentson and Newton wire designs have flexible tips of as a lot as 15 cm and are seldom used right now. Fragmentation of calculi is produced by shock waves generated from an electric spark produced on the tip of the electrode (Denstedt and Clayman, 1990). Fragmentation of most calculi is good however could be less effective for more dense calculus compositions similar to cystine or calcium oxalate monohydrate. Pneumatic lithotripsy units fragment calculi using mechanical ("jackhammer") energy (Schulze et al, 1993). There are flexible probes out there that can be utilized with flexible ureteroscopes, however they significantly limit scope deflection (Zhu et al, 2000). The first laser successfully used for intraluminal lithotripsy was the pulsed dye laser. This laser vitality is essentially no longer used due to the inability to fragment sure compositions of calculi, and the excessive price of buy and maintenance. It has a wavelength of 2100 nm, which is absorbed in three mm of water, making it very secure to be used in urology (Blomley et al, 1995). Fragmentation is produced by a photothermal response with the crystalline matrix of calculi and produces stone mud rather than fragments, successfully removing a moderate quantity of the stone (Zagone et al, 2002). The flexible quartz fibers can be utilized with both inflexible and flexible ureteroscopes and are reusable. The holmium laser is effective for any composition of calculi (Bagley and Erhard, 1995; Denstedt et al, 1995; Erhard and Bagley, 1995; Grasso, 1996). It is also a diode-pumped laser (holmium is flashlamp pumped), permitting greater control over the pulse length and length (Hutchens et al, 2013). Other variable traits in guidewire building embody the distal tip design and the wire stiffness. The rigidity of the wires can be varied by altering the diameter and design of the inside core wire. Stiffer wires can be useful for straightening out tortuous ureters or displacing a large prostatic lobe. The selection of essentially the most appropriate guidewire for the endourologic task at hand can imply the difference between success and failure.
Zyban 150 mg discount overnight delivery
The most common indication for transurethral bladder catheterization is for drainage of an acute or persistent urinary retention or postvoid residual volume depression exercise routine zyban 150 mg buy generic on line. Drainage can be achieved by an indwelling catheter or by intermittent catheterization depression prevalence buy zyban 150 mg with amex, relying on the pathology, the recurring want for drainage, and the dexterity of the patient or caregivers. Although ultrasound-based bladder scanners are extensively used to estimate postvoid residual urine volume, essentially the most correct method of measurement is by emptying the bladder with transurethral catheterization. The second most common indication for bladder catheterization is to monitor urinary output. Patients with gross hematuria, regardless of its cause, will typically require a catheter for bladder irrigation and drainage of bloody urine and blood clots. Dilation with urethral catheters is essentially the most commonly used main treatment within the administration of urethral strictures (Bullock and Brandes, 2007). Simple urethral dilation could be carried out by blind insertion of a filiform chief followed by coaxial followers of increasing diameter or by passing Councill catheters of increasing diameter over a cystoscopically placed guidewire. A current Cochrane meta-analysis comparing easy dilation with endoscopic urethrotomy and open urethroplasty for urethral stricture was not definitive in providing recommendations surrounding preferred treatment of urethral stricture (Wong et al, 2012). The solely randomized trial comparing dilation with urethrotomy reported no vital difference in efficacy and stricture-free rates (Steenkamp et al, 1997; Heyns et al, 1998). In sufferers unable to present a clear urine pattern with repeated contamination of a midstream urine pattern, single catheterization may be used to get hold of an uncontaminated urine sample. Manometer-tipped catheters are utilized in urodynamic studies to measure the intravesical and urethral strain. Thermometer-tipped catheters are often used throughout extended surgeries offering both steady thermometry and enough drainage for urinary output measurement. In performing retrograde cystography, radiographic contrast materials is administered by bladder catheterization to opacify the urinary tract for diagnostic purposes. In urogenital trauma, which is roofed elsewhere on this textual content, insertion of a bladder catheter is, relying on the extent of the trauma, usually the first choice of remedy. This should be thought of solely after diagnostic workup of the potential urethral trauma has been accomplished so that the feasibility and appropriateness of transurethral catheter placement can be outlined. Differences in materials used in manufacture; variations in length, circumference, form of the catheter tip, and variety of channels; and varieties of coatings contribute to this vast array of such gadgets. The selection of catheter design and dimension is dependent upon the indication for use, expected fluid requiring drainage, anticipated indwelling time, age, gender, previous historical past, and patient anatomy. One ought to select the smallest size out there primarily based on these variables (Table 6-1). The use of feeding tubes as urethral catheters should be discouraged because their stiffness and size can be a source of problems (ischemic ulcers, urethral strictures, and knotting within the bladder) (Smith, 2003; Sarin, 2011). The optimum catheter for an preliminary attempt at transurethral bladder catheterization in grownup sufferers with no previous urologic historical past, no danger of urinary tract abnormality, and no recognized allergies, is a 16-Fr latex straight-tipped catheter. The most incessantly used retention mechanism is the retention balloon, which is inflated by way of a devoted channel. The three-way catheter allows for simultaneous instillation and drainage of fluids and is especially useful in patients with hematuria, clot retention, and pyuria. Continuous bladder irrigation is most commonly used postoperatively after urologic surgery, when hematuria and possible clot formation are to be expected. The three-way catheter is designed with a larger-thanaverage balloon to enable for instillation of 30 mL or extra, which can be helpful in achieving hemostasis after transurethral resection of the prostate by making use of traction on the catheter, thus compressing vessels on the bladder neck. The addition of channels to the preliminary single catheter design comes with probably unfavorable design requirements. The further lumens occupy space within the internal lumen of the catheter, lowering the inner diameter. The internal diameter of a 24-Fr single-lumen catheter is larger than the inside lumen of a 24-Fr two-way catheter, which in its turn is larger than the internal lumen of a 24-Fr three-way catheter. There are principally two available tip shapes, the Nelaton blindending straight tip and the coud� tip, or elbowed or Tiemann tip. Both versions exist in a Councill catheter model, which may be passed into the bladder over a guidewire if needed. Multiple variations similar to tapered tips or a number of aspect holes exist all through the big selection of accessible catheters. For short-term catheterization, latex or rubber catheters are most popular due to their availability and low value. Silicone catheters are stiffer and less prone to buckling when encountering resistance (Villanueva et al, 2011). The use of hydrophilic-coated catheters is of curiosity for intermittent catheterization. Antibiotic-impregnated catheters might delay bacteriuria in shortterm catheterization (<1 week). Such profit has not been substantiated in sufferers requiring longer-term catheterization (Schumm and Lam, 2008; Hooton et al, 2010). Bacterial-coated catheters have the theoretic advantage of colonizing the urine with a nonvirulent strain of Escherichia coli and have proven promising leads to small pilot trials. Studies on the feasibility and efficacy of medical use of such catheters are ongoing (Trautner et al, 2007; Prasad et al, 2009; Darouiche and Hull, 2012). A 2008 Cochrane meta-analysis demonstrated that using silver-alloy�coated catheters considerably lowered the incidence of asymptomatic bacteriuria in short- and long-term (>1 week) use of such catheters (Schumm and Lam, 2008). This information is important for optimum catheter choice and complication risk evaluation. All materials anticipated to be required ought to be available on the sterile drape. The affected person ought to be in supine position at a snug top for the individual performing the catheterization. Catheterization ought to be carried out in a sterile fashion and should begin with sterile draping of the affected person. When an indwelling catheter is being positioned, the balloon ought to be checked for integrity earlier than catheterization. The most recent American Heart Association tips now not advocate routine use of infective endocarditis prophylaxis for any genitourinary procedure, even in patients with the highestrisk cardiac conditions (Wilson et al, 2007). The whole catheter is introduced into the penis, as a lot as the bifurcation of the catheter and balloon valve. If no spontaneous urine drainage appears, gently pushing down on the suprapubic area or instilling a small quantity of clear sterile fluid and aspirating the catheter with a syringe ought to lead to drainage. If after such maneuvers no drainage occurs, the bladder is empty or the catheter is malpositioned. After verifying the proper place of the catheter in the bladder, inflate the balloon with sterile water, which has been demonstrated to be the optimal filling resolution, particularly if the catheter is to be in place for a quantity of days or longer (Sharpe et al, 2011). Although not conclusively confirmed, saline or glucose-based options can theoretically occlude the tubing by precipitation (Hui et al, 2004; Huang et al, 2009).
Syndromes
- Breathing problems
- Steroid therapy (usually prednisone)
- Use of blood-thinning drugs (anticoagulants)
- Infection (a slight risk any time the skin is broken)
- Nutcracker esophagus
- Nutrients and fluids
150 mg zyban purchase with visa
Predictive elements for sacral neuromodulation in persistent lower urinary tract dysfunction bipolar depression genetics purchase 150 mg zyban with amex. Urodynamic options of the pelvic pain patient and the impact of neurostimulation on these parameters anxiety neurosis zyban 150 mg low cost. Empirical evidence of bias; dimensions of methodological quality related to estimates of remedy results in controlled trials. Differences within the clinical presentation of interstitial cystitis/painful bladder syndrome in patients with or without sexual abuse historical past. Higher levels of cell apoptosis and irregular E-cadherin expression within the urothelium are related to inflammation in patients with interstitial cystitis/painful bladder syndrome. Immunohistochemical evidence suggests repeated intravesical utility of botulinum toxin A injections could 370. Hyperbaric oxygen remedy for painful bladder syndrome/interstitial cystitis immune to standard remedies: long-term outcomes of a case series in Japan. Bladder distention remedy for symptomatic aid of frequency and urgency: a ten year evaluation. Prevalence and correlates for interstitial cystitis symptoms in girls taking part in a well being screening project. Influence of smoking, coffee, and tea consumption on bladder ache syndrome in female twins. Mast cell involvement in interstitial cystitis: a evaluation of human and experimental proof. Activation of bladder mast cells in interstitial cystitis: a lightweight and electron microscopic research. Oral cimetidine offers effective symptom reduction in painful bladder illness: a potential, randomized, double-blind placebo-controlled trial. The "evil twin syndrome" in continual pelvic ache: a systematic review of prevalence research of bladder ache syndrome and endometriosis. Nerve stimulation for persistent pelvic ache and bladder pain syndrome: a systematic evaluation. Baseline associations amongst pathologic options and patient signs within the nationwide interstitial cystitis information base. Biopsy options are associated with main symptoms in interstitial cystitis: results from the Interstitial Cystitis Data Base study. Cyclophosphamide induced hemorrhagic cystitis successfully treated with pentosanpolysulfate. Long-term expertise with sodium chondroitin sulfate in patients with painful bladder syndrome. Mapping of pain phenotypes in female patients with bladder ache syndrome/interstitial cystitis and controls. Neurogenic inflammation and nerve progress factor: attainable roles in interstitial cystitis. Evaluation of urothelial TammHorsfall protein and serum antibody as a possible diagnostic marker for interstitial cystitis. Complement C3, eosinophil cationic protein and symptom evaluation in interstitial cystitis. A survey of putative anxietyassociated genes in panic disorder patients with and with out bladder signs. Admissions associated to interstitial cystitis in Japan: an estimation based mostly on the Japanese diagnosis procedure mixture database. Up-regulation of P2X3 receptor during stretch of bladder urothelial cells from sufferers with interstitial cystitis. Augmented stretch activated adenosine triphosphate release from bladder uroepithelial cells in sufferers with interstitial cystitis. Health-related quality of life in patients with interstitial cystitis/bladder pain syndrome and frequently associated comorbidities. Prospective, randomized, doubleblind, managed trial of laser laparoscopy within the treatment of pelvic pain associated with minimal, gentle, and average endometriosis. Followup report on a randomized controlled trial of laser laparoscopy in the remedy of pelvic ache associated with minimal to reasonable endometriosis. Panic dysfunction, social nervousness dysfunction, and a attainable medical syndrome beforehand linked to chromosome 13. Hyperbaric oxygen remedy for interstitial cystitis proof against typical remedies. Prevalence of chronic benign ache dysfunction amongst adults: a evaluate of the literature. The potential of non-adrenergic, non-cholinergic targets within the therapy of interstitial cystitis/painful bladder syndrome. Urinary tract infection and inflammation at onset of interstitial cystitis/painful bladder syndrome. Prognostic components for recent-onset interstitial cystitis/painful bladder syndrome. Sexuality and reproductive threat elements for interstitial cystitis/painful bladder syndrome in ladies. Interstitial cystitis/painful bladder syndrome: what do patients imply by "perceived" bladder pain Pilot research of sequential oral antibiotics for the remedy of interstitial cystitis. Antecedent nonbladder syndromes in case-control study of interstitial cystitis/painful bladder syndrome. Is there a excessive incidence of hysterectomy and other nonbladder surgeries earlier than and after onset of interstitial cystitis/bladder pain syndrome Prevalence of interstitial cystitis in first-degree relatives of sufferers with interstitial cystitis. Depressive disorders and panic assaults in girls with bladder pain syndrome/interstitial cystitis: a population-based pattern. Impact of urinary diversion procedures in the remedy of interstitial cystitis and continual bladder ache. Primary splenic marginal zone lymphoma with bladder metastases mimicking interstitial cystitis. Increased startle responses in interstitial cystitis: evidence for central hyperresponsiveness to visceral associated threat. Over expression of platelet-derived endothelial cell progress factor/thymidine phosphorylase in sufferers with interstitial cystitis and bladder carcinoma. Treatment of interstitial cystitis by intravesical instillation of hyaluronic acid: A prospective research on 31 patients]. Posterior tibial nerve stimulation as neuromodulative remedy of decrease urinary tract dysfunction. Systemic aspects of interstitial cystitis, immunology and linkage with autoimmune issues.
Zyban 150 mg buy cheap on line
Variations of this place embrace completely supine depression test free zyban 150 mg proven, supine with the ipsilateral aspect elevated anxiety symptoms in teens purchase 150 mg zyban, and supine combined with varying levels of ipsilateral flank elevation (in some with 90-degree rotation) and uneven lithotomy position (Falahatkar et al, 2008; Papatsoris et al, 2008; Scoffone et al, 2008; Zhou et al, 2008; Moraitis et al, 2012). In the ManagementofAnticoagulation With the rising use of antiplatelet and anticoagulant drugs within the basic population, the urologist is faced extra incessantly with planning percutaneous renal surgical procedure for sufferers taking such medicines (Riley and Averch, 2012). In addition, other medications-such as nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory agents and a few nutritional supplements-include anticoagulant or antiplatelet activity. Except as outlined in the following, these medications should typically be discontinued before percutaneous renal surgery. The preoperative cessation intervals vary: natural medicines, 1 week; aspirin, 1 week; warfarin, 5 days; clopidogrel, 5 days; nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory brokers, three to 7 days. Oral anticoagulant or antiplatelet activity medications should be discontinued before percutaneous renal surgery (except as noted in the following). Bridging with heparin derivatives may be required with resumption of oral anticoagulant or antiplatelet agents as soon as the chance of periprocedural hemorrhage has lessened. Expert multidisciplinary management may be required for those at high thromboembolic risk. For sufferers on clopidogrel or aspirin for secondary stroke prevention, especially after a latest stroke, cessation of the agent could additionally be sick suggested, and neurologic session is recommended if percutaneous renal surgery is being thought of. In the supine place, the skin entry site is lateral or anterolateral, so the most effective calyces to enter are often the anterior ones. For a procedure similar to percutaneous nephrolithotomy with the patient within the supine position, the access sheath is angled towards horizontal (compared with vertical during percutaneous nephrolithotomy in the inclined position), which reduces the pressure within the collecting system and facilitates stone fragments to wash out by way of the sheath. The supine position is a safer position with regard to neuromusculoskeletal complications, and the anesthesia team might choose this position (Atkinson et al, 2011). Finally, because the percutaneous entry is more lateral than throughout a inclined procedure, the devices are closer to the surgeon, which finally ends up in less physical strain on the surgeon and the chance for the surgeon to sit through the procedure. There are some disadvantages to the supine place for percutaneous renal surgery, however. Second, the lowered stress within the accumulating system ends in a decrease quantity and thus much less room for visualization and manipulation. Third, higher pole calyceal access is harder within the supine in contrast with inclined place, and percutaneous tract length is longer than within the prone position (Azhar et al, 2011; Duty et al, 2012). Finally, with optimum placement of pads and bolsters, the inclined place may provide better air flow than the supine position (Edgcombe et al, 2008, Atkinson et al, 2011). In a large, multi-institutional and retrospective examine of percutaneous nephrolithotomy, together with 4637 patients and 1138 sufferers with prone and supine positioning, respectively, operative time and stone-free rates favored the inclined position, however some patient security parameters favored the supine position (Valdivia et al, 2011). The flank (lateral decubitus) place, which first was described by Kerbl and colleagues (1994), is less commonly used for percutaneous renal surgical procedure. This position permits simultaneous access to the anterior and posterior features of the kidney and seems to be particularly helpful for morbidly obese patients or these with spinal deformities in whom both supine and prone positioning are troublesome (Gofrit et al, 2002; Basiri et al, 2008b; El-Husseiny et al, 2009). Randomized trials evaluating flank to prone place (Karami et al, 2010) and flank to supine to susceptible positions (Karami et al, 2013) confirmed no difference in outcomes. Although both the supine and flank positions offer some potential advantages over prone positioning in certain settings, significantly morbid weight problems and spinal deformities, the evidence suggests no overwhelming differences, so surgeon choice can decide the selection of place for percutaneous renal surgical procedure. As such, the rest of this chapter concerns entry right into a posterior calyx from a posterior or posterolateral course with the affected person in the inclined position, which remains the standard. The initial step in a percutaneous procedure is commonly cystoscopic retrograde placement of a ureteral catheter. This can be carried out with the patient in prone position (using a versatile cystoscope) or in lithotomy with subsequent prone repositioning. In the "upsidedown" bladder, the bubble of air from initial introduction of the cystoscope typically approximates the location of the ureteral orifices. Prone cystoscopy can be performed on a standard working or fluoroscopy desk however is simplified by the use of "spreader bars" on the foot of the table (also referred to as a "split-leg desk"). Support of the pinnacle with padding in a neutral position allows entry to the mouth. Place the ipsilateral arm above the pinnacle to transfer it from the operative field, with the shoulder and elbow at right angles, and pad generously. Position the contralateral arm in the identical way, or leave it straight and tucked on the facet. Rest the lateral features of the chest on rolled blankets or different cumbersome foam or gel bolsters to allow for chest and belly wall enlargement. Alternatively, purpose-made pads and helps present more assured affected person positioning (Papatsoris et al, 2009). Provide assist beneath the ankles to take pressure off the feet, and pad the knees and feet. Prepare the perineum and ipsilateral flank sterilely, and canopy unsterile areas with drapes. Cover the flank with an adherent drape that comes with a fluid collection pouch. In the prone place, the popular calyces are the posterior ones (or the posterior side of compound calyces), which allow better entry to the rest of the accumulating system. In cases that contain a calyceal diverticulum, slim infundibulum, or pathology in an eccentric anterior calyx, direct puncture into an anterior location might be required. Access above the tenth rib is related to a high incidence of pleural violation and lung damage and should be averted unless absolutely essential. Thorascopically guided entry superior to the 10th rib may be carried out to scale back the danger of lung damage (Finelli and Honey, 2001). Percutaneous access should by no means be instantly into an infundibulum or the renal pelvis, which significantly increases the risk of vascular injury (Sampaio et al, 1992). The state of the renal parenchyma overlying the meant calyx of entry additionally have to be thought of as a result of if it is thin, the tract into the amassing system could not close well after nephrostomy tube removing. An upper pole calyx is usually the most versatile web site via which to enter the higher urinary tract accumulating system. The renal pelvis, decrease pole calyces, and ureter often could be entered with a inflexible nephroscope from a well-placed upper pole access. Access to the middle calyces will often require a separate access or use of versatile instrumentation. Often a middle calyx will offer sufficient access to the ureteropelvic junction, as wanted in circumstances similar to endopyelotomy. In other instances, the calyx of entry ought to be selected primarily based on the distribution of the pathology to be treated. Efforts should be made to choose a calyx that can enable remedy through a single site with inflexible instrumentation. If this is inconceivable, then one should choose the site that may enable the largest portion of the pathology to be treated. The remaining pathology could be addressed with a second (and hardly ever a third or more) access or with versatile instrumentation via the initial access site. Subcostal access is the most secure path to the kidney because pleural accidents are rare with entry under the twelfth rib.
Buy zyban 150 mg with mastercard
Combination of pneumatic lithotripsy and transurethral prostatectomy in bladder stones with benign prostatic hyperplasia mood disorder exam questions generic zyban 150 mg with mastercard. Refinements in remedy of enormous bladder calculi: simultaneous percutaneous suprapubic and transurethral cystolithotripsy depression symptoms during pregnancy buy zyban 150 mg otc. Influence of ureteral stone elements on the outcomes of electrohydraulic lithotripsy. Comparative research of electrothermal bipolar vessel sealer and ultrasonic coagulating shears in laparoscopic colectomy. Laboratory and medical evaluation of pneumatically pushed intracorporeal lithotripsy. Holmium:yttrium-aluminum-garnet lithotripsy efficiency varies with stone composition. Masers and lasers; molecular amplification and oscillation by stimulated emission. Adjustable electrohydraulic lithotripsy for minimally invasive ureteroscopic stone remedy. Impact of voltage and capability on the electrical and acoustic output of intracorporeal electrohydraulic lithotripsy. Effect of stone composition on operative time during ureteroscopic holmium:yttrium-aluminum-garnet laser lithotripsy with active fragment retrieval. Morphological change within the urothelium after electrohydraulic versus pulsed dye laser lithotripsy. Thulium laser resection of prostate-tangerine technique in remedy of benign prostate hyperplasia. Thulium laser versus holmium laser transurethral enucleation of the prostate: 18 month follow-up knowledge of a single center. When bacterial virulence increases or host defense mechanisms lower, bacterial inoculation, colonization, and an infection of the urinary tract occur. Careful diagnosis and therapy result in successful decision of infections in most situations. Clinical manifestations can differ from asymptomatic bacterial colonization of the bladder to irritative symptoms similar to frequency and urgency associated with bacterial infection; higher tract infections related to fever, chills, and flank pain; and bacteremia related to extreme morbidity, including sepsis and demise. Shorter-course therapy and prophylactic antimicrobial agents have decreased the morbidity and value associated with recurrent cystitis in women. Although the overwhelming majority of sufferers respond promptly and are cured by remedy, early identification and treatment of patients with complicated infections that place them at vital threat stays a scientific problem to urologists. Bacteriuria is the presence of bacteria within the urine, which is normally free of bacteria. It has been assumed to be a legitimate indicator of either bacterial colonization or infection of the urinary tract. Although this is often true, studies in animals (Hultgren et al, 1985; Mulvey et al, 1998) and people (Elliott et al, 1985) have indicated that bacteria could also be within the urothelium in the absence of bacteriuria. Alternatively, bacteriuria might characterize bacterial contamination of an abacteriuric specimen during assortment. The risk of contamination will increase as the reliability of the gathering technique decreases from suprapubic aspiration to catheterization to voided specimens. The term significant bacteriuria has a clinical connotation and is used to describe the variety of micro organism in a suprapubically aspirated, catheterized, or voided specimen that exceeds the number usually caused by bacterial contamination of the skin, the urethra, or the prepuce or introitus, respectively. Bacteriuria without pyuria is usually indicative of bacterial colonization without an infection of the urinary tract. Pyuria without bacteriuria warrants analysis for tuberculosis, stones, or most cancers. Cystitis describes a medical syndrome of dysuria, frequency, urgency, and infrequently suprapubic pain. These symptoms, though generally indicative of bacterial cystitis, may also be associated with an infection of the urethra or vagina or noninfectious situations such as interstitial cystitis, bladder carcinoma, or calculi. Conversely, patients may be asymptomatic and have an infection of the bladder and presumably the upper urinary tract. The majority of these patients are ladies with isolated or recurrent bacterial cystitis or acute pyelonephritis, and the infecting pathogens are often vulnerable to and eradicated by a short course of inexpensive oral antimicrobial therapy. A sophisticated infection is related to components that enhance the possibility of buying micro organism and decrease the efficacy of remedy (Box 12-1). The urinary tract is structurally or functionally irregular, the host is compromised, and/or the micro organism have elevated virulence or antimicrobial resistance. Renal ailments that scale back the concentrating capability of the kidney or neurologic circumstances that alter bladder-emptying capabilities are commonly encountered useful abnormalities. Examples of anatomic abnormalities include obstruction associated with calculi or enlargement of the prostate or congenital or acquired sites of residual urine, corresponding to calyceal or bladder diverticula. A complicated infection is regularly brought on by bacteria which have publicity to many antimicrobial agents. An unresolved an infection is one which has not responded to antimicrobial therapy and is documented to be the same organism with an identical resistance profile. A recurrent an infection is one that occurs after documented, successful resolution of an antecedent an infection. Reinfection describes a new occasion associated with reintroduction of micro organism into the urinary tract from exterior. Antimicrobial prophylaxis is the prevention of reinfections of the urinary tract by the administration of antimicrobial medicine. If the time period is used correctly in reference to the urinary tract, it may be assumed that bacteria have been eradicated before prophylaxis is begun. Surgical antimicrobial prophylaxis entails administration of an antimicrobial agent earlier than and for a limited time after a process to forestall native or systemic postprocedural infections. A low, nightly dosage of an antimicrobial agent normally results in the urine displaying no development, as within the case of a stone colonized with bacteria. There may be serious difficulties in diagnosing spinal cord�injured and elderly sufferers who may be unable to localize the positioning of their discomfort. Bacterial an infection of the kidney could cause a focal, coarse scar within the renal cortex overlying a calyx, almost always accompanied by some calyceal distortion. Less generally, renal scarring from infection may find yourself in atrophic pyelonephritis or generalized thinning of the renal cortex, with a small kidney appearing radiographically just like one with postobstructive atrophy. Surveys screening for bacteriuria have shown that about 1% of schoolgirls (aged 5 to 14 years) (Kunin et al, 1962) have bacteriuria and that this determine will increase to about 4% by young adulthood after which by an extra 1% to 2% per decade of age. However, with rising age, the ratio of women to men with bacteriuria progressively decreases. At least 20% of ladies and 10% of men older than 65 years have bacteriuria (Boscia and Kaye, 1987; Juthani-Mehta, 2007).
Zyban 150 mg discount with visa
Nephroureteral Stent the Cope retention mechanism can also be used in nephroureteral stents depression the definition 150 mg zyban buy fast delivery. A nephroureteral stent has a renal coil like that of a Cope nephrostomy tube depression journal template zyban 150 mg order amex, but the tube continues on to a ureteral extension that travels down the ureter to end in a passive pigtail that rests within the bladder. The ureteral portion can be the same diameter as the nephrostomy portion, or it may be narrower. A nephroureteral stent is handed percutaneously over a wire that ends within the bladder. After the end is coiled generously in the bladder, careful inspection of the fluoroscopy image shows the location of the side holes in the renal coil. By moving the catheter out and in while pulling on the string and rotating the exterior portion of the tube clockwise, the Cope retention coil is formed in the renal pelvis. General Considerations some great benefits of a postoperative nephrostomy tube include good drainage and control of the upper urinary tract, and upkeep of percutaneous access for extra procedures. When hemorrhage does occur, nonetheless, the larger caliber of a nephrostomy tube provides better drainage of the higher urinary tract amassing system than does an internal ureteral stent. In addition, if a large perforation has occurred during the procedure, the additional diversion of urine away from the site might be advantageous. At least one group has attempted to scale back the discomfort associated with supracostal percutaneous renal surgical procedure by putting a smallcaliber postoperative nephrostomy tube in a model new subcostal site and leaving the dilated supracostal access site and not using a nephrostomy tube (although there was no control cohort for comparison) (Kim et al, 2006). Along with the nephrostomy, together with a tube that goes down the ureter supplies the greatest management and assurance of drainage. Because entry of a tube into the bladder is related to extra signs, however, such a tube should solely be used when wanted. Considerations include the scale of the affected person (which determines to a big extent the risk of tube dislodgement), the significance of maintaining drainage, and the will for ureteral intubation. Aside from the choice of retention mechanism, the primary remaining consideration is the diameter of the nephrostomy tube. A number of research have in contrast the impact of nephrostomy tube diameter after percutaneous renal surgical procedure, together with two nonrandomized prospective trials (Maheshwari et al, 2000; De Sio et al, 2011) and four randomized controlled trials comparing Circle Catheter A ultimate type of nephrostomy tube is the circle nephrostomy tube. The circle nephrostomy tube requires two percutaneous entry websites to the kidney, and this tube is most helpful when upkeep of two tracts is desired, such as for irrigation of the renal pelvis or if more than one entry is important for second-look nephroscopy (Kim et al, 2005). After acquiring access at two distant calyces, a versatile nephroscope or versatile ureteroscope passed over one wire is used to grasp the wire coming from the opposite website. When the endoscope is withdrawn, the wire is now in place to information placement of the circle nephrostomy tube. Among the six studies, comprising a total of 215 patients with nephrostomy tubes, five confirmed less pain and two reported less urinary leakage within the sufferers with smaller tubes. Small-caliber tubes may be removed safely on the bedside after a period of clamping to assess clinically for distal ureteral obstruction. This apply never met with widespread acceptance, especially after Winfield and colleagues (1986) reported disastrous outcomes with this method. The idea was revived in 1997 by Bellman and colleagues (1997), with the addition of an inside ureteral stent left in place for per week or two. Since then, many studies have evaluated the follow of omitting the nephrostomy tube after percutaneous renal surgical procedure. Although this system is called "tubeless," most collection employ a ureteral stent for a brief interval postoperatively. The potential advantages of omitting the nephrostomy tube after percutaneous renal surgery embody decreased ache and analgesic use, avoidance of an exterior drainage device, abbreviated hospital keep, and decreased well being care costs (secondary to shortening the period of hospitalization). Since the report of Bellman and colleagues (1997), many studies together with several randomized controlled trials have evaluated the omission of a nephrostomy tube postoperatively with the placement of an inside ureteral stent. It is necessary to notice that most of these studies excluded patients with vital bleeding or perforation or these for whom a second percutaneous procedure was anticipated. A meta-analysis of tubeless percutaneous nephrolithotomies published in 2012 included 9 randomized controlled trials involving 547 sufferers (Shen et al, 2012). The outcomes were stratified into four groups relative to the postprocedure drainage: tubeless with inner ureteral stent, small nephrostomy tube (8 to 9 Fr), medium nephrostomy tube (16 to 18 Fr), and huge nephrostomy tube (20 to 24 Fr). The meta-analysis demonstrated that hospital stay and postoperative pain have been reduced within the tubeless group in comparability with the medium and huge tube groups, however had been related in the tubeless and small tube teams. There were no vital differences between the tubeless group and any of the nephrostomy tube groups with regard to fever/infection, transfusion, or operative time. In two earlier meta-analyses that mixed the nephrostomy groups into two as a substitute of three teams, 4 to 10 Fr versus 14 to 24 Fr (Yuan et al, 2011) and 8 to 9 Fr versus 14 to 26 Fr (Ni et al, 2011), shorter hospital keep and reduced postoperative ache were noted in the tubeless groups even compared to the small nephrostomy group. Thus the preponderance of proof suggests that tubeless percutaneous nephrolithotomy leads to shorter hospital keep and decreased postoperative pain compared to use of enormous postprocedure nephrostomy tubes, but that these benefits are less sure compared to small nephrostomy tubes. Subsequent randomized controlled trials (Kara et al, 2010; Etemadian et al, 2011; Marchant et al, 2011; Shoma and Elshal, 2012; Lu et al, 2013) and one massive multi-institutional matched case-control examine involving 488 patients (Cormio et al, 2013) have yielded comparable outcomes with the exception of one research that indicated no benefit to the tubeless strategy when the nephrostomy tube within the comparison group was eliminated the morning after the procedure (Mishra et al, 2010). In one randomized managed trial, omission of the nephrostomy tube was associated with decreased price (Feng et al, 2001). The tubeless method seems to be protected even when supracostal access is used (Shah et al, 2006b; Jun-Ou and Lojanapiwat, 2010; Duty et al, 2013) and within the setting of bilateral simultaneous procedures (Gupta et al, 2003; Shah et al, 2005). There are some disadvantages to utilizing an inside ureteral stent as an alternative to a nephrostomy tube, however, including loss of the percutaneous tract for a secondary process and the fee, inconvenience, and discomfort associated with an inner ureteral stent that requires cystoscopic removal at a later date. To obviate the issues associated with the ureteral stent, several groups have offered options together with insertion of an externalized ureteral stent or insertion of an inside stent with an attached string that exits out the flank. In both circumstances the stent can then be eliminated before hospital discharge with out an additional process. Goh and Wolf (1999) first reported the use of an externalized ureteral stent (single pigtail) as a substitute for a postoperative nephrostomy tube. Shpall and colleagues (2007) described the modification of leaving the hooked up string on the stent and inserting the stent "the different means up" in order that the string can exit the flank. They described removing the stent as an outpatient three and 12 days postoperatively, but since then others have reported removing the stent on the bedside on the first postoperative day (Berkman et al, 2008). One nonrandomized comparison of percutaneous nephrolithotomy with and without electrode cauterization of the tract reported a lower blood transfusion fee within the first group (1. A nonrandomized comparability of tract cryotherapy without a nephrostomy tube in 30 patients versus a 24-Fr nephrostomy tube without tract cryotherapy in 30 patients advised that there was shorter hospitalization and fewer hemorrhage and urine leakage in the patients treated with cryotherapy. The high fee of postoperative hemorrhage requiring angioembolization within the management group (13%) confounds the analysis (Okeke et al, 2009). There have been four randomized controlled trials of hemostatic adjuncts for percutaneous renal surgical procedure without nephrostomy tubes, which compared patients managed without hemostatic adjuncts with those managed with gelatin sponge (Singh et al, 2008), oxidized cellulose (Aghamir et al, 2006), fibrin glue (Shah et al, 2006a), and collagen matrix coated with fibrin glue (Cormio et al, 2012). None of the three studies confirmed an impact of the adjunct on measures of hemostasis (postoperative hematocrit, hemorrhage, and/or blood transfusions). Narcotic use was less in the adjunct group in two of the three studies by which it was evaluated. Hospital stay and urinary leakage were each assessed in three studies, and each was improved in two research. Alternatives to native remedy of the tract embody systemic enhancements to hemostasis.