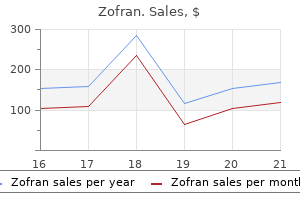
Zofran dosages: 8 mg, 4 mg
Zofran packs: 30 pills, 60 pills, 90 pills, 120 pills, 180 pills, 270 pills, 360 pills

4 mg zofran proven
Plain chest radiographs are nonetheless normally the primary imaging studies obtained postnatally in infants with suspected or known congenital heart illness symptoms checklist zofran 4 mg cheap otc, albeit followed shortly by cardiac echocardiography symptoms low potassium 8 mg zofran discount fast delivery. While chest radiographs could be totally regular in infants with significant congenital heart illness or depict only non-specific abnormality, there are some radiographic findings that counsel the presence and nature of the underlying cardiac anomaly. They may come up from the higher extremity arteries, aorta beneath the diaphragm, ductus arteriosus, or coronary artery. When systemic collaterals provide blood provide to the lungs, the appearance of the pulmonary vasculature tends to be atypical on imaging studies. Because of comparatively poor renal operate within the first week of postnatal life, contrast administration is generally avoided unless absolutely essential. As with all different imaging research in kids, attention should be paid to acquiring a diagnostically useful research on the lowest attainable dose. Prostaglandin therapy to keep patency of the ductus arteriosus had been initiated in the supply room because of the prenatal echo findings. This was the only systemic arterial provide to the lungs, no additional aorticopulmonary or other collaterals had been recognized. Additional related anomalies might embody atrial septal defect and common atrioventricular canal (especially in Down syndrome). Tetralogy of Fallot with pulmonary atresia may also be asymptomatic when pulmonary and systemic blood flows are well balanced. Patients generally do nicely postoperatively with the major problems being residual central or peripheral pulmonary stenoses and pulmonary regurgitation that will lead to subsequent proper ventricular dysfunction. Reoperation at a later age to place a homograft or different pulmonary valve is regularly required. The timing and sort of surgical intervention is dependent upon the character and supply of pulmonary blood supply. When the ductus arteriosus is the most important or sole collateral supply to the lungs (duct dependent) the infant might turn into critically unwell when the ductus begins to close and prostaglandin infusion is required to maintain the duct open. This tends to be a precarious scenario and early surgical intervention (a central shunt or complete repair) is usually necessary to guarantee a reliable pulmonary blood supply. A large collateral from the coronary circulation could also be one other indication for early surgical procedure to stop coronary steal and ischemia. If there are adequate collateral vessels, surgical intervention could also be postponed until after the quick neonatal period. A common pitfall is the false appearance resembling an uplifted cardiac apex in a standard but lordotically positioned chest radiograph. There is marked overinflation of the right lung with leftward cardiomediastinal shift and the suggestion of a right perihilar mediastinal mass. Imaging description A six-month-old lady was evaluated by her primary care doctor for noisy respiratory whereas feeding and failure to thrive. The trachea is normally regular in kind 1 although a right tracheal bronchus could also be current (subtype 1B). Appropriate administration addressing each the airway and vascular anomalies is essential for an excellent outcome. Differential analysis Recognition of narrowing, compression, displacement, or poor definition of the airway with or without air trapping on plain chest radiographs raises the question of an underlying lesion. Relatively latest improvement of tracheoplasty techniques has markedly modified the beforehand poor prognosis for long phase airway stenosis. Rings, slings, and different issues: vascular compression of the toddler trachea up to date from the midcentury to the millennium the legacy of Robert E. The evolution of the pulmonary arterial sling syndrome, with particular reference to the need for reoperations because of untreated tracheal stenosis. The configuration suggests congenital tracheal stenosis with complete cartilagenous rings this was confirmed at bronchoscopy. The presence and severity of symptoms differ with the degree of tracheal compression and a free ring could also be asymptomatic. These vascular anomalies encircle the trachea and esophagus and should occasionally produce dysphagia rather than respiratory symptoms, especially in older kids. The most symptomatic vascular ring in infancy is a double aortic arch (persistence of early fetal anatomy) the place the ascending and descending aorta and bilateral arches that give rise to ipsilateral separate carotid and subclavian arteries tightly encircle the airway and esophagus. Right aortic arch with aberrant left subclavian artery is the most generally occurring type of vascular ring but tends to be a comparatively unfastened ring and may be asymptomatic. There are different rings that occur uncommonly including left arch with aberrant proper subclavian and proper Kommerell diverticulum and ductal ligament in addition to occasional vascular rings associated with a mirror image right arch, left Kommerell diverticulum, and ductal ligament. Much more commonly a mirror image proper arch is associated with congenital heart ailments similar to tetralogy of Fallot and truncus arteriosus with no ring. The surgical approach to vascular rings varies with the exact anatomy and is mostly intended to break the encircling ring of vessels and relieve tracheoesophageal compression. This most often entails a left thoracotomy with division of the smaller left arch and ligamentum arteriosum (double aortic arch) or simply the ligamentum (right arch with aberrant left subclavian). Her mom offered a history of noisy respiratory since birth and repeated episodes of wheezing and respiratory an infection. The chest radiographs were interpreted as normal in the emergency room; the toddler was admitted to the hospital for possible viral upper respiratory infection. The vascular ring encircled the trachea and esophagus with marked compression of the decrease trachea on the site of the vascular abnormality. Importance It is crucial to embrace cautious analysis of the airway in the overall assessment of plain chest radiographs. The presence of a right-side aortic arch (often finest appreciated by leftward deviation of the airway at the level of the arch) and anterior bowing and narrowing of the decrease trachea on the lateral view are the most frequent radiographic clues suggesting the presence of a vascular ring. Teaching level An underlying vascular abnormality such as a vascular ring could also be liable for acute or recurrent respiratory signs. Careful scrutiny of plain chest radiographs might counsel a attainable underlying abnormality that can be further outlined by detailed cross-sectional angiographic research. The main plain radiographic findings that suggest a possible vascular ring are leftward deviation of the trachea by a right-sided aortic arch on the frontal radiograph and anterior tracheal bowing on the lateral radiograph. Rings, slings, and other issues: Vascular compression of the infant trachea updated from the mid century to the millennium the legacy of Robert E. Ultra quick computed tomography and magnetic resonance angiography in pediatric cardiology. Differential prognosis Differential considerations include other vascular abnormalities that can compress the airway together with pulmonary sling and innominate artery syndrome in addition to abnormally positioned or enlarged vessels (such as a malpositioned aortic arch in meso- or dextrocardia and right pulmonary hypoplasia or agenesis in addition to an enlarged aorta in congenital anomalies similar to tetralogy of Fallot or truncus arteriosus). Middle mediastinal plenty similar to benign or malignant adenopathy, foregut duplication cyst, and esophageal lesions can even produce continual airway compressive signs. Large anterior or posterior mediastinal masses corresponding to lymphoma or neuroblastoma can even displace and compress the airway.
Zofran 8 mg buy with visa
They may current as ascites however extra frequently appear as an infiltrative hypoechoic mass with skinny septations within the retroperitoneum that will extend into the limbs 4 medications list at walmart zofran 4 mg safe. On colour Doppler medications hypertension 8 mg zofran cheap with visa, the lesions show minimal or sluggish circulate in the septa of the lesions. Lymphangiomas are part of a spectrum of vascular malformations, with variable levels of lymphatic and venous components. Differential diagnosis · Neuroblastoma: the commonest retroperitoneal tumor in fetuses. The cystic neuroblastoma usually has extra well-defined borders than a lymphangioma. It is often nicely circum scribed, displacing the adjoining structures, and should include fats and calcifications. These lesions contain enlarged branching vascular components rather than the fluidfilled septated cysts typical of a lymphatic malformation. There is however overlap with lymphatic and venous lesions, quite often coexisting. Infantile hemangiomas are strong vascular lesions in the gentle tissues or viscera which might be often small at birth but could rapidly enlarge in the first few months of life and have a tendency to spontaneously involute subsequently. Klippel-Trenaunay-Weber syndrome presenting as massive lymphangiohemangioma of the thigh: prenatal analysis. Teaching point Lymphatic malformations are the most typical cystic delicate tissue mass in babies. They might develop rapidly both in utero and after start and compress and displace important organs, creating a comparatively poor prognosis for a benign lesion. Accurate analysis and assessment of the extent of the lesion is important for acceptable parental counseling, as well as pre- and postnatal administration. Doppler research demonstrated some venous and arterial circulate in the septa of the lesion (not shown). It is essential to pay special consideration to the rectum in the fetus to assess regular echogenicity of meconium and rule out any urorectal malformation. The fluid-sensitive sequences demonstrated distended fluid-filled colon, including the rectum, and within the fluid a quantity of low sign depth pellets have been noted. The diagnosis of imperforate anus with urorectal fistula was made based on these findings. A newborn belly radiograph demonstrated discrete oval to rounded calcifications along the course of the colon, consistent with intraluminal calcified meconium. Importance In the fetus, meconium is shaped primarily by the buildup of dehydrated amniotic fluid swallowed by the fetus, bile salts, and desquamation of enteric cells. Anal atresia is typically differentiated into two sorts: low atresia (below the levator ani muscle) and high atresia (above the levator ani muscle). An urorectal fistula is typically related to excessive anal atresia, mainly in boys (ratio boys:women ј 6:1). In girls, imperforate anus is most incessantly associated with urogenital sinus or a cloaca. Cloaca usually presents with a fluid-filled bladder and vagina and with a rudimentary sigmoid colon. In anal atresia with urorectal fistula, the mixing of urine with meconium could result within the precipitation and calcification of intraluminal meconium. Precipitated and calcified meconium appears on imaging as small pellets known as enteroliths that are floating in the urine-filled bowel. This discovering is strongly suggestive of anal atresia with urorectal fistula, but can also happen in other kinds of urorectal malformation the place urine is involved with meconium. Meconium ileus often manifests with dilated loops of distal small bowel filled with very echogenic meconium. Meconium peritonitis: When an in utero bowel perforation has occurred (most commonly related to meconium ileus), calcifications might be seen within the peritoneal cavity or a fluid, and meconium-filled cyst. The calcifications related to meconium peritonitis are most likely to be clustered alongside peritoneal surfaces and the sting of intraperitoneal organs such as the liver. Distal ileal atresia: Dilated loops of distal small bowel and microcolon may be seen. The rectum is usually small and difficult to establish with out normal meconium signal or fluid. Congenital chloride diarrhea: Is a uncommon anomaly of transmembrane chloride transport within the fetal bowel and pre sents with diffuse distention of the bowel by fluid, including the colon and the rectum. High T1 signal meconium should be identified within the rectum by the third trimester. Presence of fluid-filled sigmoid and rectum-containing enteroliths is strongly suggestive of high anal atresia with urorectal fistula or other urorectal malformation with fecal/urine mixing. Note excessive sign content in additional proximal dilated loops of bowel, a reversal of the normal appearance on a T1-weighted image. This is pathognomonic for intraluminal meconium that calcifies in contact with urine. It is crucial to study the kidneys rigorously utilizing a high-resolution linear transducer to be able to recognize refined abnormalities similar to tiny subcortical cysts. However, the amount of amniotic fluid remained normal throughout the pregnancy and the affected person carried the child to term. Typical scientific presentation the diagnosis of cystic dysplasia is often advised on the prenatal anatomic screening ultrasound around 20 weeks of gestational age. It is important to pay special consideration to elevated renal echogenicity, lack of corticomedullary differentiation, and presence of small subcortical cysts. Hydronephrosis (pelvis measuring in transverse diameter more than four mm earlier than 32 weeks and more than 7mm after 32 weeks) might or will not be present. Importance Renal cystic dysplasia is normally unilateral and should have an effect on a whole kidney, a segment of a kidney, or a pole of a duplex kidney. They are sometimes diagnosed on the routine anatomic scan around 20 weeks of gestational age. During being pregnant, a single functioning kidney is often adequate to produce a normal quantity of amniotic fluid. When each kidneys are affected there could also be poor renal operate in utero manifesting as oligo- or anhydramnios. When bilateral renal dysplasia is current, parental counseling and fetal administration will be considerably completely different than in a fetus with a contralateral normal kidney. Hydronephrosis: Renal pelvis and the renal calyces interconnect as opposed to discrete separate cysts. Common causes of obstruction in utero include ureteropelvic junction obstruction, ureterovesical junction obstruction, posterior urethral valves, and obstructed ectopic higher pole of a duplicated amassing system. Cystic neuroblastoma: A congenital tumor arising from the adrenal gland and appears as a cystic lesion that displaces the kidney inferiorly. Mesoblastic nephroma: A heterogeneous lesion of the kidney; is usually predominantly stable however might have some cystic or hemorrhagic components. Autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease: Hereditary disease affecting each kidneys. Although the cysts often appear in adulthood, it could be detected in some situations prenatally.
Zofran 4 mg generic amex
Pathology & Pathogenesis Corrosive brokers (acid and pepsin) secreted by the abdomen play a key role in gastric ulcer treatment hypothyroidism order zofran 8 mg fast delivery, duodenal ulcer symptoms liver disease zofran 4 mg discount visa, and acute erosive gastritis. Each of these ailments has a particular but overlapping pathogenesis with the widespread themes of either excessive acid secretion or diminished mucosal protection. Exactly why one but not another form of acid-peptic disease ought to develop in a given individual remains unclear. H pylori an infection can cause acid-peptic disease by multiple mechanisms, including direct alteration of sign transduction in mucosal and immune cells, which in flip can improve acid secretion and diminish mucosal defenses. As many as 90% of infected individuals show indicators of inflammation (gastritis or duodenitis) on endoscopy, although many of those individuals are clinically asymptomatic. Despite this high price of association of irritation with H pylori infection, the necessary position of different factors is indicated by the reality that only about 15% of contaminated people ever develop a clinically important ulcer. Nevertheless, the role of H pylori is of explicit scientific significance because, of sufferers who do develop acid-peptic illness, especially among these with duodenal ulcers, the overwhelming majority have H pylori an infection. The latter presentation reflects the reality that in some instances acidpeptic disease can be painless within the early levels and could be detected solely when it results in an intra-abdominal catastrophe. Classically, duodenal ulcer presents as gnawing or burning epigastric pain occurring 1ͳ hours after meals, usually waking the affected person at evening, with antacids or meals producing aid. Elderly sufferers specifically often current with a complication of duodenal ulcer but no history of pain. The figure shows that almost all patients with gastroduodenal ulcers or gastric lymphoma or adenocarcinoma have additionally been contaminated with H pylori. Note, however, that the circles are to not scale, because gastric most cancers occurs in less than 1% of these contaminated with H pylori. Note, too, that relationships among the different conditions are more advanced than depicted. There are quite a few strains of H pylori that vary of their production of poisons similar to CagA and VacA that directly alter mobile signaling pathways. Gastric Ulcer Gastric ulcer is distinguished from erosive gastritis by the depth of the lesion, with gastric ulcers penetrating via the mucosa. The precise ulcer crater is usually surrounded by an area of intact however infected mucosa, suggesting that gastritis is a predisposing lesion to improvement of gastric ulcer. It is likely that gastric ulcer represents the finish result of a number of different abnormalities summarized next. Some gastric ulcers are believed to be associated to impaired mucosal defenses, because the acid and pepsin secretory capacity of some affected patients is normal or even below normal. Motility defects have been proposed to contribute to growth of gastric ulcer in at least 3 ways. First, they contribute due to a tendency of duodenal contents to reflux back through an incompetent pyloric sphincter. Bile acids within the duodenal reflux materials act as an irritant and could additionally be an necessary contributor to a diminished mucosal barrier towards acid and pepsin. Second, they could contribute as a end result of delayed emptying of gastric contents, together with reflux materials, into the duodenum. Third, they could contribute on account of delayed gastric emptying and therefore food retention, causing increased gastrin secretion and gastric acid manufacturing. Prostaglandins are known to enhance mucosal blood flow as properly as bicarbonate and mucus secretion and to stimulate mucosal cell repair and renewal. H pylori an infection of the abdomen physique causes suppression of parietal cells, low acid secretion, atrophic gastritis, intestinal metaplasia, and predisposition to gastric cancer. H pylori infection primarily of the stomach antrum causes decreased somatostatin and elevated gastrin secretion, increasing acid secretion and predisposition to duodenal ulceration. Acid hypersecretion, gastric anoxia (eg, in shock), altered pure defenses (especially diminished mucus secretion), altered epithelial renewal, adjustments in tissue mediators (eg, prostaglandins), reduced intramucosal pH, and intramucosal vitality deficits have been instructed as components within the improvement of superficial gastric mucosal injury. Chronic Atrophic Gastritis Chronic atrophic gastritis is a heterogeneous group of situations characterized by inflammatory cell infiltration with gastric mucosal atrophy that results in dying of parietal cells and ultimate dropout of gastric glands. The capacity to secrete gastric acid is progressively decreased, and the serum levels of gastrin are elevated in an try and restore parietal cell activity. Atrophic gastritis can be a purely autoimmune disease related to production of autoantibodies to parietal cells, intrinsic issue, and gastrin, however it can also be the outcome of H pylori infection. Autoimmune gastritis can progress to pernicious anemia, whereas atrophic gastritis in the setting of H pylori infection significantly increases the danger of development to gastric adenocarcinoma. In which acid-peptic dysfunction are diminished mucosal defenses extra essential than acid hypersecretion? What evidence signifies the significance of H pylori infection in acid-peptic disease? What evidence suggests that other factors apart from H pylori infection contribute to acid-peptic disease? Duodenal Ulcer Even extra commonly than gastric ulcers, duodenal ulcers are sequelae of H pylori an infection, caused by altered mucosal inflammatory responses and excessive acid secretion. Genetic elements also play a job; research support the existence of a heritable part in duodenal ulcers distinct from that concerned in gastric ulcer. The condition can also occur silently, producing metabolic derangements (eg, of blood glucose in sufferers with diabetes mellitus) in the absence of somatic symptoms. Etiology Gastroparesis is a typical complication of poorly controlled diabetes mellitus, with consequent autonomic neuropathy. Acute huge hemorrhage (>10% of blood quantity over minutes to hours) is manifested by hypotension, tachycardia, and orthostatic blood pressure and heart price modifications on standing, often with dizziness. Pathology & Pathogenesis Disorders of gastric motility result from alterations in a quantity of regular gastric functions. These embody (1) serving as a reservoir for ingested solids and liquids (eg, alteration attributable to resection of the stomach); (2) mixing and homogenizing ingested food; and (3) functioning as a barrier that enables solely small spurts of well-mixed chyme beyond the pyloric sphincter. The ensuing disorders span the vary from partial or full gastric outlet obstruction to excessively fast emptying and sometimes outcome from interference with the conventional mechanisms by which these functions are controlled. Acute Conditions Abdominal pain, trauma, irritation Postoperative state Acute infections, gastroenteritis Acute metabolic disorders: Acidosis, hypokalemia, hypercalcemia or hypocalcemia, hepatic coma, myxedema Immobilization Hyperglycemia (glucose >200 mg/dL) Pharmaceutical brokers and hormones Opioids, including endorphins and pharmacologic brokers (eg, morphine) Anticholinergics Tricyclic antidepressants Beta-adrenergic agonists Levodopa Aluminum hydroxide antacids Gastrin Cholecystokinin Somatostatin Chronic Conditions Mechanical Gastric ulcer Duodenal ulcer Idiopathic hypertrophic pyloric stenosis Superior mesenteric artery syndrome Acid-peptic illness Gastroesophageal reflux Gastric ulcer disease, nonulcer dyspepsia Gastritis Atrophic gastritis with or without pernicious anemia Viral gastroenteritis (acute or chronic gastritis) Metabolic and endocrine Diabetic ketoacidosis (acute) Diabetic gastroparesis (chronic) Addison disease Hypothyroidism Pregnancy? Collagen-vascular illnesses Scleroderma Dermatomyositis Polymyositis Systemic lupus erythematosus? Pseudo-obstruction Idiopathic, hollow visceral myopathy Secondary (eg, amyloidosis, Chagas disease, muscular dystrophies, paraneoplastic syndrome) Postgastric surgery Postvagotomy or postgastric resections Medications Anticholinergics, opioid analgesics, levodopa, tricyclic antidepressants Hormones (pharmacologic studies) Gastrin, cholecystokinin, somatostatin Anorexia nervosa: bulimia Idiopathic Gastric dysrhythmias: tachygastria Gastroduodenal dyssynchrony Central nervous system: tabes dorsalis, despair vagal control results in excessive tonic contraction and symptoms of assorted degrees of gastric outlet obstruction. Disorders that have an effect on the enteric nervous system such as the neuropathy of diabetes mellitus and surgical slicing of the stomach wall or vagal trunk usually trigger delayed emptying. However, it is essential to do not overlook that, in some instances, delayed emptying may end up in signs anticipated from excessively fast emptying. For instance, an excessively contracted pylorus that may open utterly but does so sometimes can lead to entry into the duodenum of too massive a bolus of chyme from the excessively distended abdomen. Such a bolus may not be effectively handled by the small intestine, leading to poor absorption and diarrheal symptoms characteristic of the dumping syndrome.
Discount zofran 8 mg amex
However medications given for bipolar disorder generic zofran 4 mg with amex, persistent fever beyond the fourth or fifth day of sickness - or spiking temperatures to 40у or extra - could signify improvement of infectious complications similar to contaminated peripancreatic fluid collections symptoms low blood sugar discount 4 mg zofran with visa, infected pancreatic necrosis, or ascending cholangitis. The cardinal laboratory discovering in acute pancreatitis is elevation of the serum amylase, typically as a lot as 10- to 20-fold. The serum amylase elevation occurs virtually instantly (within hours), but it usually returns to normal inside 48ͷ2 hours even if symptoms continue. The sensitivity of the serum amylase in acute pancreatitis is estimated to be 705%, meaning B. Early Complications of Acute Pancreatitis Shock might happen in extreme acute pancreatitis on account of several interrelated factors. Hypovolemia outcomes from huge exudation of plasma and hemorrhage into the retroperitoneal house and from accumulation of fluid in the gut as a outcome of ileus. Hypotension and shock can also result from release of kinins into the overall circulation. For example, activation during acute irritation of the proteolytic enzyme kallikrein results in peripheral vasodilation through liberation of the vasoactive peptides, bradykinin and kallidin. The contracted intravascular volume combined with the hypotension may lead to myocardial and cerebral ischemia, respiratory failure, metabolic acidosis, and decreased urinary output or renal failure as a result of acute tubular necrosis. Clinically affected sufferers may current with hemorrhagic discoloration (purpura) in the subcutaneous tissues across the umbilicus (Cullen sign) or within the flanks (Grey Turner sign). The splenic and portal veins are in shut proximity to the pancreas and thus can turn into involved within the inflammatory process. Splenic vein thrombosis happens in approximately 11% and portal vein thrombosis in approximately 2% of patients. Most thrombi are asymptomatic, however they may be associated with the development of venous hypertension and formation of varices over time. Pulmonary issues are a dreaded manifestation of severe acute pancreatitis and occur in 15͵0% of sufferers. It is estimated that 50% of early deaths in sufferers with extreme acute pancreatitis are associated with respiratory failure because of profound acute lung harm. The pathophysiology of this acute lung harm appears to involve a rise in permeability of the alveolar-capillary membrane. The endothelial cell destruction within the alveolar capillaries may be mediated by circulating activated pancreatic enzymes together with elastase and phospholipase A2. Pulmonary surfactant, another important alveolar barrier, appears to be destroyed by phospholipase A2. Additional pulmonary injury seems to be mediated by inflammatory leukocytes that are sequestered in the alveoli and interstitial tissues, with subsequent launch of proinflammatory cytokines and chemokines that result in additional tissue destruction. Acute pancreatitis could additionally be accompanied by a small (usually left-sided) pleural effusion. The effusion could additionally be reactive and therefore secondary to a direct impact of the infected, swollen pancreas on the pleura abutting the diaphragm (typically transudative). Alternatively, in circumstances of severe acute pancreatitis, an effusion may be as a end result of the tracking of exudative fluid from the pancreatic mattress retroperitoneally into the pleural cavity via defects in the diaphragm. Characteristically, the pleural fluid on this latter circumstance is an exudate with high ranges of protein, lactate dehydrogenase, and amylase. The effusion might contribute to segmental atelectasis of the lower lobes, leading to ventilation-perfusion mismatch and hypoxia. Given the protean displays of acute pancreatitis, there was confusion concerning the classification of acute pancreatitis and any associated problems. Recent consensus tips have supplied accurate standards to aid in its analysis, remedy, and prognosis. The 2012 revision of the Atlanta 437 classification represents the most recent standardized definitions for characterization of acute pancreatitis. Acute pancreatitis is acknowledged to exist in two main types: interstitial edematous pancreatitis and necrotizing pancreatitis. This form of the disease sometimes is clinically much less severe, with symptoms routinely resolving within every week of presentation. Necrotizing pancreatitis (necrosis of the pancreatic and peripancreatic tissues) happens in approximately 5ͱ0% of sufferers. The pure history of sufferers with necrotizing pancreatitis varies relying on whether pancreatic/peripancreatic necrosis stays stable or liquefies, turns into infected, persists, or resolves. However, you will need to document infected pancreatic necrosis by image-guided fantastic needle aspiration (percutaneous or endoscopic) and subsequent optimistic aspirate cultures as a end result of most pancreatic necrosis is in reality sterile. Infected pancreatic necrosis is a very severe complication of severe acute pancreatitis with a mortality fee of 25͵0%. Early issues of acute pancreatitis embrace both systemic and local problems. Systemic issues embrace the presence of organ failure, which defines extreme acute pancreatitis. Organ failure may be transient (resolves inside 48 hours) or persistent (affects prognosis). Early local complications of acute pancreatitis are defined by their presence throughout the first four weeks of disease onset. Acute peripancreatic fluid collections develop within the early part of acute pancreatitis and may occur within the absence of pancreatic necrosis. Sequential imaging studies may be essential to outline the evolution of these lesions. They may variably communicate with the pancreatic duct when necrosis is related to ductal disruption, and they may become secondarily infected. Percutaneous drainage is the mainstay of remedy, with surgical or endoscopic drainage reserved for refractory cases. Walled-off necrosis is a mature, encapsulated collection of debris with a well-defined inflammatory rind that occurs beyond 4 weeks from onset of necrotizing pancreatitis. In sufferers with persistent signs, with failure to improve clinically, or with secondary an infection, intervention for walled-off necrosis may be necessary. Surgical necrosectomy, which may be accomplished by open or minimally invasive strategies, or endoscopic transgastric necrosectomy may be considered. Pancreatic ascites happens when a direct connection develops between the pancreatic duct and the peritoneal cavity. Left untreated, massive pancreatic ascites could result in pleural effusions, subcutaneous fat necrosis, or abdominal compartment syndrome. Treatment usually entails drainage of the ascites and management of the pancreatic ductal disruption, both by endoscopic pancreatic duct stent placement or by surgical therapy. Late Complications of Acute Pancreatitis Late issues of acute pancreatitis might similarly be divided into systemic and native effects. Systemic issues embrace persistent organ failure and want for prolonged intensive care, components that portend a poor prognosis. Local problems are defined by their presence beyond four weeks from the onset of illness and are sometimes characterised by serial imaging that documents their evolution. Pancreatic pseudocysts are nonepithelium-lined cavities that contain plasma, blood, pus, and pancreatic juice.

8 mg zofran buy free shipping
Complications of Restorative Proctocolectomy with Ileal Pouch-Anal Anastomosis 393 Clinical diagnosis History Medical and surgical historical past symptoms 4dp5dt zofran 4 mg purchase with mastercard medicine x 2016 8 mg zofran visa. Laboratory prognosis List of diagnostic exams Laboratory indicators of inflammatory response and dehydration could additionally be useful. Section 4: Treatment Treatment rationale Antibiotics are the mainstay of therapy for pouchitis. Patients treated with ciprofloxacin had significantly higher discount in illness exercise and also fewer unwanted side effects than these treated with metronidazole. The most common indication for pouch excision is ongoing anastomotic-related pelvic sepsis. Pelvic pouch excision could be accompanied by commonplace ileostomy or a continent (Kock pouch) ileostomy. A proximal, permanent ileostomy leaving the pelvic pouch in situ may be carried out. Cystoscopic placement of ureteral catheters is important to keep away from damage to the ureters. The ileoanal anastomosis is released circumferentially and the pouch eliminated and the influx ileum is transected as distally as possible. In some circumstances the pelvic pouch may be used to construct the Kock pouch, thereby avoiding extra loss of small bowel. The most typical indication for pouch excision is ongoing, anastomotic related pelvic sepsis Surgical: Pouch excision is performed utilizing a combined abdomino-pelvic approach. The pure history of surgical procedure for ulcerative colitis in a populationbased cohort from Olmsted County, Minnesota. Restorative proctocolectomy for ulcerative colitis difficult by colorectal cancer. Occasionally, biopsies obtained by endoscopy could also be necessary if the diagnosis is in question. Disease classification Radiation enteritis may be classified as acute or persistent relying on the timing of the onset of symptoms from the radiation publicity, which may result in distinct clinical, endoscopic, and histologic presentations. The severity is dependent upon a number of elements including the dose and duration of radiation publicity. The preliminary histologic injury could be seen within hours of radiation administration. As a outcome, the mucosa develops inflammatory modifications with infiltration of the lamina propria with polymorphic nuclear and plasma cells, progressing to flattening of the villi, denudation, and a decreased absorptive floor space. Radiation-exposed cells are directly affected, resulting in a change in cellular perform. Ischemia causes fibrosis within the lamina propria and submucosa, which further causes vascular insult and ischemia, resulting in a vicious cycle. Comorbidities (inflammatory bowel illness, collagen vascular disorders, diabetes, hypertension, atherosclerosis). The diploma of injury varies among people and is influenced by genomic susceptibility to ionizing radiation. Other patientrelated risk components include reduced physique mass index, smoking, belly adhesions ensuing from prior surgery, and sure comorbidities corresponding to diabetes, hypertension or atherosclerosis, collagen vascular illnesses, and inflammatory bowel illness. Treatment-related danger components include volume of bowel within the radiation subject, radiation dose and method, and concomitant chemotherapy use. Generally, investigation occurs in patients with the appropriate threat components and signs. Primary prevention Conventional non-invasive strategies embody extreme inclined or Trendelenburg positioning, bladder distention, abdominal wall compression, or the use of a stomach board. However, the true efficacy and reproducibility of these techniques have been questioned. Native tissue such as omentum, posterior rectus sheath, peritoneum, bladder, or uterine broad ligament has been used but its adequacy is unproven in prospective research. Prosthetic materials such as non-absorbable mesh can perform as a sling, however can be difficult by an infection and fistula formation. Pelvic area occupying methods utilizing saline-filled silicon implants have been associated with their own set of problems including bladder, ureteric and iliac vessel compression, deep vein thrombosis, pulmonary embolism, an infection, fistula formation, and constipation. More lately, a method was developed that permits for the laparoscopic placement of a short lived tissue expander, which appears promising. If the prognosis continues to be unclear, biopsy of the affected bowel could be useful in establishing the diagnosis. Other commonly presenting signs are abdominal pain, nausea, vomiting, anorexia, malaise, and, much less usually, gastrointestinal hemorrhage or obstruction. Also, the timing and high quality of symptoms should be according to radiation enteritis. Physical examination the following findings could recommend radiation enteritis: Dehydration (poor pores and skin tone, dry mucous membranes). Significant inflammation can lead to ulceration, hemorrhage, obstruction, and perforation. Radiation Enterocolitis 403 Iron panel with ferritin Iron deficiency indicates gastrointestinal bleeding and probably duodenal enteritis. Lists of imaging techniques Imaging research are helpful to decide the extent and nature of bowel harm. The study is relatively invasive, requiring nasogastric tube placement and may be troublesome for sufferers to tolerate. There is a scarcity of data relating to the utilization of capsule endoscopy in radiation enteritis, however some medical expertise helps its use. In severe cases, diarrhea could be managed with medications like sulfasalazine and loperamide. Treatment options can be divided into nutritional, medical remedy, and surgical remedy. Dietary adjustment together with drugs that minimize diarrhea (antidiarrheals, bile acid binders, antibiotics) is the mainstay of conservative remedy. One should additionally be careful of the unwanted facet effects of antibiotics in and of themselves, together with the increased danger of subsequent infections similar to Clostridium difficile colitis. However, there are restricted potential research supporting the role of dietary adjustment to enhance medical outcomes. Despite this, some authors advocate avoidance of meals high in fiber as this will likely lower diarrhea. In order to management bleeding, endoscopy permits the direct utility of cautery utilizing a quantity of units. It usually requires a couple of session with sufficient time in between sessions to allow the tissue to heal. Bipolar and heater probes are readily available in most endoscopic facilities, and can be utilized fairly safely and successfully. Use of this method can be quite tedious, nevertheless, when a big area of mucosa is concerned.
Discount 4 mg zofran
Yeom Typical medical scenario the period of signs is often quick previous to medications online zofran 4 mg discount with mastercard prognosis (<3 months) treatment 6th february purchase zofran 8 mg otc, together with nausea, vomiting, and complications. In children less than one year of age, increasing head dimension and lethargy could be the presenting signs whereas in older youngsters and adults, ataxia might predominate. Spinal tumor seeding is present in approximately 30% of preliminary diagnoses and symptoms referable to spinal involvement may be current. Imaging description A three-year-old girl offered with again pain, vomiting, lethargy, and ataxia over a 1-month interval. Differential analysis Ependymoma, atypical teratoid/rhabdoid tumor, and astrocytoma are differential concerns for a posterior fossa neoplasm in childhood. Importance Medulloblastomas are the most typical posterior fossa tumors in kids (3040%) and comprise 1520% of intracranial neoplasms in children. Medulloblastomas are highly malignant tumors and could additionally be composed of traditional undifferentiated primitive small round cells, though histologic variants similar to desmoplastic, intensive nodular, and large cell histologies could additionally be seen, the latter of which imparts a worse prognosis. The case introduced here is of the massive cell histology with extensive spread and rapid growth. Cysts and calcifications are possible inside the tumor and enhancement is variable. Teaching level the most typical malignant posterior fossa tumor in children is medulloblastoma, an aggressive neoplasm which frequently disseminates alongside the subarachnoid spaces without proper remedy. Yeom of thymus is unique, with hypoechoic cortex and echogenic medulla containing linear and echogenic septae. A small clinically inapparent superior extension of thymic tissue into the neck is often seen in pediatric neck and chest cross-sectional imaging. The imaging look, homogeneity, and contiguity with mediastinal thymic tissues are sometimes helpful in defining this tissue as regular thymus. Imaging description A five-month-old boy offered with a palpable left neck mass. Importance the primordial thymus arises from the third and fourth pharyngeal pouches during the sixth week of gestational life. During the seventh week, thymic primordia migrate medially and caudally, forming the thymopharyngeal duct, to their last anatomic location in the anterior mediastinum. Ectopic and accessory thymic tissue could occur anywhere along the descending pathway of the thymopharyngeal duct (from the angle of the mandible to the superior mediastinum) due to arrest in migration, sequestration, or failure of involution. Ectopic thymic tissue and remnants are congenital lesions that may be stable and/or cystic in nature. Most ectopic cervical thymic tissue is unilateral and normally on the left for causes that are unclear. Manifestation of ectopic thymic tissue as a neck mass may be mistaken for a pathologic process. Differential analysis the differential diagnosis of ectopic cervical thymus includes branchial cleft cyst, cystic hygroma, cystic teratoma, thyroglossal duct cyst, esophageal duplication cyst, reactive adenopathy, lymphoproliferative disorders, neoplasms, and lipoblastoma. Teaching level Ectopic cervical thymus might current as a neck mass or cyst, most frequently left sided, and may be simply mistaken for pathology. As in many different situations, data of the variations in location and look of regular tissues is important to recommend likely or attainable differential considerations and direct or curtail additional investigation. Clinical and radiologic evaluation of the traditional and abnormal thymus: pearls and pitfalls. Typical clinical scenario Clinically apparent ectopic cervical thymus is a uncommon situation and normally presents as an asymptomatic mass or neck swelling on routine bodily examination. In 50% of circumstances, this situation happens in children between two and 13 years of age and is extra frequent in males. These lesions could also be large in dimension and might trigger compression and displacement of neighboring constructions resulting in symptoms of stridor, hoarseness, or dysphagia. Coronal contrastenhanced T1-weighted image (c) exhibits gentle homogeneous enhancement inside this mass, similar to mediastinal thymic tissue however without particular contiguity. A one-month-old woman with an acutely enlarging left neck mass and respiratory distress. Transverse shade Doppler ultrasound of the left neck demonstrates a large cyst with a thickened hyperemic wall containing dependent echogenic particles (a). Turbid fluid, which was thought to be associated to acute an infection, was discovered in the cyst on the time of surgical elimination. Yeom patient eligibility for bone marrow transplant and evaluating therapy response. Most significantly, distinction enhancement has essential predictive value; an absence of enhancement predicts secure disease in 85% of patients. Imaging description A six-year-old male introduced with hyponatremia and hyperpigmentation. Typical scientific situation the childhood cerebral type accounts for one-third of cases, normally creating between 5 and nine years of age. Symptoms related to adrenal insufficiency could precede neurologic impairment, with many such instances receiving the preliminary analysis of Addison disease. Behavioral adjustments embody hyperactivity, aggressive behavior, and worsening faculty efficiency, often initiating diagnostic analysis for attentiondeficit/hyperactivity disorder. Nonetheless, these early options finally give way to a relentless progressive neurocognitive impairment, blindness, and spastic quadriplegia. The most typical scientific symptoms are sensorineural hearing loss (90%), pyramidal tract signs (50%), visible deficits (40%), behavioral abnormalities (33%), and seizures (6%). The pathologic abnormalities within the mind encompass widespread demyelination of the white matter. In most cases, the process begins in the splenium of the corpus callosum and spreads bilaterally to the occipital and parietal periventricular regions. Histopathologic examination reveals different zones of demyelination within the affected mind, with anterior zones demonstrating energetic inflammatory demyelination, while posterior zones seem destroyed and burnt out. In truth, in 80% of cases, imaging shows abnormalities in the occipital white matter. After administration of distinction, a zone of enhancement could be seen where the energetic demyelinating entrance advances into unaffected areas. In basic, the end-stage demonstrates vital atrophy of enormous parts of affected white matter in a typical symmetrical sample. Nevertheless, only bone marrow transplant has been discovered to alter the medical disease course. In adults, gliomas and lymphomas may be included as well however are much less generally as symmetrical. Children underneath two years of age with very important organ dysfunction are most likely to have a really poor prognosis. The lesions usually are lytic with ill-defined margins, which later turn into more demarcated with rising sclerosis. In the early phases, these lytic lesions can seem aggressive with ill-defined borders and a moth-eaten look.
Buy 8 mg zofran fast delivery
Physical examination Specific findings on bodily examination are uncommon in patients with esophageal motility problems treatment modalities 8 mg zofran otc medicine daughter lyrics zofran 4 mg discount amex. Weight loss, cachexia, and supraclavicular lymph nodes could characterize an underlying neoplasic dysfunction manifesting as pseudo-achalasia. List of imaging techniques A barium swallow or cine-esophagram should be the primary take a look at of alternative if an esophageal motility dysfunction is suspected. Not solely are strictures, webs, rings, or neoplasia dominated out (or in), but the peristaltic perform (or lack of) may be considered fluoroscopically. The presence of a hiatus hernia could additionally be seen in sufferers with chronic reflux or a "corkscrew" esophagus could also be observed in spastic issues. Biopsies of esophageal or gastric mucosa could also be carried out if a lesion is suspected. Radio-telemetry transmits knowledge on the degree of acidification inside the esophagus for as much as 48 hours. Fluid acts as a conductor of electrical current while air ends in high resistance (impedance) to the move of current inside the esophageal probe. Barium swallow or endoscopy to exclude obstructive pathology of the esophagus is necessary previous to motility research. However, repeat injections (25 models in each quadrant) are often essential, and long-term efficacy is restricted. Intraoperative endoscopy is usually carried out to verify anatomic positioning of the myotomy. Once a myotomy is performed, then a procedure to forestall reflux (fundoplication) is usually carried out on the identical time. Care must be taken to not make the fundoplication too tight, in any other case dysphagia will happen. Children Although achalasia and other motility esophageal motility disorders are uncommon within the pediatric population, the therapies of these conditions are much like that of adults. Elderly Treatment of the elderly is similar to that of younger sufferers, though the dosages of some medicines might must be lowered to keep away from unwanted facet effects corresponding to hypotension and tachycardia. Natural historical past of untreated illness There is an increased incidence of esophageal neoplasia in sufferers with long-standing achalasia. In addition, if untreated, the esophagus will continue to dilate, which may lead to stasis of meals with subsequent aspiration. Prognosis for treated sufferers the prognosis for patients with main motility issues is usually good, though symptoms may persists regardless of pharmacologic remedy. Follow-up checks and monitoring Because of the increased incidence of esophageal most cancers in sufferers with achalasia compared with the final population, endoscopic surveillance must be considered in long-standing illness, although the particular frequency of endoscopy is unclear as a outcome of a lot of the lesions are detected as superior neoplasia. Esophageal motility disorders by means of strain topography: the Chicago Classification. Long-term esophageal cancer threat in patients with primary achalasia: a potential examine. A new period in esophageal diagnostics: the image-based paradigm of high-resolution manometry. Clarification of esophageal defects in sufferers with manometric ineffective esophageal motility: research utilizing mixed impedance-manometry. Section 1: Background Medication-induced esophageal harm may occur with many commonly used medicines, and at any age. Symptoms embody chest ache, often pleuritic, which may be confused with pulmonary embolism, acute coronary syndromes, or gastroesophageal reflux. Because of this medical overlap, and because many causative drugs are taken over-the-counter, and may have been used by the affected person for years, medication-induced esophageal damage is probably not thought of by patients or acknowledged by physicians. Economic influence Likely under-estimated, if not totally unknown, as a end result of under-reporting. Etiology Risk elements that predispose to medication-induced esophageal injury: Reduced saliva production: growing older, sicca syndrome, anticholinergic medications. Because signs of medication-induced esophageal harm can overlap with different conditions, cardiac and pulmonary causes must be ruled out, but the potential for drug-induced injury must nonetheless be thought of, especially in patients taking one or more of the drugs generally related to such harm. Endoscopic findings include discrete solitary ulcers, multiple ulcers of various sizes, diffuse severe esophagitis, and changes mimicking esophageal candidiasis. Esophageal Disorders Related to Medication, Trauma, and Infection one hundred forty five Chronic harm could cause hemorrhage, stricture formation, septations, fistulas, and perforations. Severe odynophagia may also be reported, and may immediately suggest an underlying esophageal trigger. Clinical analysis History A full, present medication history have to be obtained. The nature of the presenting chest ache must be evaluated and assessed for the likelihood of coronary or embolic phenomena, and acceptable consultations obtained if clinically warranted. Laboratory diagnosis List of diagnostic exams Routine laboratory studies are of little diagnostic worth. Odynophagia could additionally be relieved by the use of topical viscous lidocaine, or, if required, narcotics. Minimizing the usage of probably harmful medications is beneficial, if clinically potential. Section 5: Special Populations Elderly Many aged patients are taking bisphosphonates for osteoporosis, and have to be reminded often to observe the usual caveats for these medication, including remaining in an upright position for a minimum of half-hour after taking the drug and taking with a full glass of water. Section 6: Prognosis Prognosis is great if the offending medicine is identified and discontinued before stricture formation or perforation. Such accidents can happen in a standard esophagus, as well as in these with underlying illnesses or anatomical situations affecting the patency of the lumen. The cervical esophagus, particularly across the pyriform sinus, is the most common website of such perforations. Injury because of longterm indwelling nasogastric tubes also can happen, because of gastroesophageal reflux, and chronic injury from extended acid publicity. This might result in formation of strictures, which are typically lengthy, slender, and tough to dilate. Tracheoesophageal fistula has been reported after extended use of a cuffed endotracheal tube. Injuries have additionally occurred from transesophageal echocardiography probes and thoracostomy tubes. Most cases of blunt esophageal perforations occur from steering wheel impacts or seat belts throughout motorized vehicle accidents. Most penetrating wounds resulting in esophageal perforations are attributable to knife or gunshot wounds. Section 2: Prevention Quality measures in endoscopy and endotracheal intubation are presently being investigated. Routine use of nasogastric tubes for decompression following abdominal surgical procedure is discouraged. Distal esophageal injuries may lengthen into the mediastinum and pleura, and will cause injury to the aorta. Clinical diagnosis History A historical past of recent motor vehicle accident, gunshot, or knife wound will be obvious.
Cheap zofran 8 mg
Postnatally medicine wheel teachings discount 8 mg zofran fast delivery, lifelong hormonal replacement with hydrocortisone (glucocorticoid) and fludrocortisone (mineralocorticoid) can ensure regular puberty and fertility medicine 029 purchase zofran 8 mg online. Antiandrogen therapy (with flutamide) permits reduction within the dose of hydrocortisone typically required to suppress androgen ranges. In ladies, the androgenic steroids (adrenal and ovarian) are thought to be required for the maintenance of libido and the capacity to achieve orgasm. In congenital adrenal hyperplasia, excessive secretion of adrenal androgens outcomes from considered one of a number of enzymatic defects in steroid metabolism. Congenital adrenal hyperplasia is actually a group of autosomal recessive disorders, in every of which, because of an enzyme defect, the bulk of steroid hormone production by the adrenal cortex shifts from corticosteroids to androgens. More than 90% of circumstances are because of deficiency of the enzyme steroid 21-hydroxylase. Other instances of congenital adrenal hyperplasia are related to steroid 11-hydroxylase (cytochrome P450c11) deficiency. What is the effect of extra or deficiency of adrenal androgens on in any other case normal grownup women and men (ie, people with normal gonads)? Review of techniques reveals several months of weight achieve and menstrual irregularity. There are prominent purplish striae over the abdomen and a quantity of bruises over each decrease legs. List four causes of Cushing syndrome and discuss the relationships among the many hypothalamus, pituitary, and adrenal in each case. The scan is unremarkable except for the discovering of a 3-cm mass in the best adrenal gland. She stories a gradual onset of weakness, lethargy, and simple fatigability during the last 3 months. Review of methods reveals only recent menstrual irregularity, with no menses in 2. Blood strain is 90/50 mm Hg (compared with previous readings of 110/75 and 120/80 mm Hg), and her weight is down 13 pounds since her final visit eleven months in the past. The physician seeing her wonders whether or not she has now developed adrenal insufficiency (Addison disease). If Addison illness has developed, what ought to the serum electrolytes present, and why? What is the pathogenesis of the hypotension, weight loss, and pores and skin hyperpigmentation? A cautious evaluate of systems reveals signs of fatigue, lack of stamina, and frequent urination, significantly at night. What is the mechanism by which primary aldosteronism causes the historical past, bodily examination, and laboratory findings in this patient? He is brought back for a repeat examination at 2 weeks, and repeat blood exams show a nonetheless elevated 17-hydroxyprogesterone level, a sodium of 125 mEq/L, a potassium of 5. He is suspected of having the salt wasting type of congenital adrenal hyperplasia. X-linked adrenoleukodystrophy: clinical, metabolic, genetic and pathophysiological features. Primary aldosteronism in 2011: in the course of a greater understanding of causation and penalties. During the reproductive years, these disorders typically present as altered menstruation, pelvic pain, or infertility. Cancers arising in these tissues happen more usually in the late reproductive or menopausal years. Some organs are positioned deep and are comparatively inaccessible to palpation (ovaries). Others have few sensory nerves (ovary, fallopian tubes) and hence stay asymptomatic. Additionally, the breasts have massive quantities of adipose tissue, which might make early detection of breast most cancers tough. Disorders of the female reproductive system can even occur on account of illness in different organs whose function affects reproductive organs (eg, the mind, hypothalamus, pituitary, thyroid, adrenals, kidney, and liver). Conversely, disorders of the reproductive system may cause disorders in other tissues. Ovarian hormones are needed for the maintenance and health of most tissues in women. Alterations in these hormones can result in osteoporosis (loss of bone mass), atrophy and irritation of estrogen-deprived tissues (eg, atrophic vaginitis), atherogenesis and alterations in cardiovascular compliance, and an increased risk of some forms of most cancers (eg, endometrial carcinoma as a consequence of estrogen excess and progesterone deficiency). Dysfunction of the reproductive system can also contribute to unique variants of systemic problems, such as gestational diabetes and the hypertensive syndrome of preeclampsia-eclampsia. How do feminine reproductive system disorders current through the reproductive years? To what may you ascribe the dearth of discount in mortality fee from ovarian cancer in distinction to cervical cancer? These supporting cells produce steroids and paracrine products necessary in follicular maturation and coordination of occasions in copy. The fallopian tubes, that are open to the peritoneal house, connect the ovaries to the uterus. The uterus accommodates an inner hormone-sensitive mucosal lining, the endometrium. Surrounding the endometrium is the graceful muscle layer of the uterus, the myometrium. Contractions of the myometrium lead to menstrual cramps or expel the fetus at parturition. The cervix is contiguous with the uterus and is the conduit for passage of menses or the fetus into the vagina, the muscular tube opening into the vulva. Once at the genital ridge, they multiply and induce male or feminine gonads relying on the id of the sex chromosomes. After this time, differentiation of the interior and exterior genitalia occurs, figuring out the phenotypic intercourse of the person, which becomes totally developed after puberty. During embryogenesis, the inner genitalia are fashioned from a twin genital duct system inside the urogenital ridge. The first to type is the wolffian duct, adopted by the m𬬥rian duct, which is dependent on prior wolffian duct growth. After 8 weeks of gestation, manufacturing of anti-m𬬥rian hormone by Sertoli cells within the fetal testes leads to regression of the m𬬥rian ducts, whereas production of testosterone by the Leydig cells results in persistence of the wolffian duct and subsequent growth of the prostate, epididymis, and seminal vesicles. In the absence of those secretions, feminine inner reproductive organs are fashioned from the m𬬥rian ducts, and the wolffian structures degenerate. Similarly, the exterior genitalia of males develop in the presence of dihydrotestosterone; within the absence of this hormone, the common embryologic constructions give rise to female external genitalia. During feminine development, the female ovaries comprise about 7 million oogonia by 24 weeks of gestation. The majority of these cells die throughout intrauterine life, leaving solely about 1 million major oocytes at delivery.