Zanaflex dosages: 4 mg, 2 mg
Zanaflex packs: 30 pills, 60 pills, 90 pills, 120 pills, 180 pills, 270 pills, 360 pills

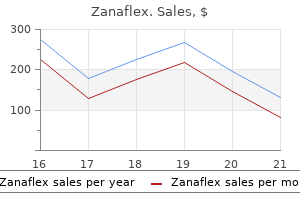
Zanaflex 4 mg discount with mastercard
Although these early data show profitable outcomes muscle relaxant half-life zanaflex 4 mg purchase on-line, you will want to muscle relaxant online zanaflex 4 mg effective observe that severe problems, some unique to these procedures, are being reported. These issues have prompted feedback concerning new procedures and materials for the remedy of incontinence and prolapse, warning that there are inadequate data supporting the routine use of those devices (Ostergard, 2007). Local problems similar to pelvic pain, defecatory pain, and dyspareunia have been reported after equipment procedures (Altman and Falconer, 2007; de Tayrac et al, 2007). When analyzing these sufferers, one must fastidiously look for areas of impaired healing, banding or tenting of the mesh, "set off factors" that elicit ache, and signs of focal irritation. If these irregular areas are identified, launch of the arms or the location of mesh rigidity might alleviate these areas of discomfort. When performing the mesh release, one should excise as a lot offending mesh material as possible before vaginal closure. In instances of an infection, granulomas, or persistent draining sinuses, all mesh involved within the contaminated areas must be eliminated. If no native incriminating components are discovered, a interval of conservative therapy consisting of physical remedy, trigger level injections, and other adjunctive techniques must be attempted first. The exposures seem to happen extra regularly on the anterior wall, and a concomitant hysterectomy considerably increases the danger (de Tayrac et al, 2007; Gauruder-Burmester et al, 2007). Measures to decrease the incidence of vaginal mesh exposure are minimizing excessive vaginal wall trimming and shutting without pressure. Some advocate closing with a vertical mattress approach to separate the graft from the wound (de Tayrac et al, 2006a). Examination by palpation as properly as visualization is important to detect this complication. Although some patients may be managed with both remark or native treatment, most would require excision with primary vaginal closure (de Tayrac et al, 2006a). Infected vaginal mesh can lead to sinus formation, abscess, and enterovaginal fistula formation. One case of necrotizing fasciitis with Staphylococcus aureus requiring extensive perineal debridement and colostomy has been reported after a kit process (Abdel-Fattah et al, 2008). Unfortunately, important lower urinary tract erosion into the bladder or urethra has additionally been reported, with vital consequences (Yamada et al, 2006). Including transvaginal kits systems, the incidences of visceral (including urethra) accidents have been reported from 2. The fate of bladder injury at the time of mesh prolapse repairs is way less certain. Extensive erosions into the bladder necessitating partial cystectomy have been reported (Abdel-Fattah et al, 2008). Rectal erosion of synthetic mesh may necessitate each rectal and vaginal excision (Hurtado et al, 2007). The trocars are passed through the pelvic muscular complex for both anterior and posterior package repairs. The trocars pass near the ischial spine, and vital intraoperative bleeding could happen. This would usually emanate from the pudendal neurovascular bundle, and embolization of the supply of bleeding has been reported (Mokrzycki and Hampton, 2007). Multiple authors have reported pelvic hematomas following transvaginal package procedures (Ignjatovic and Stosic, 2007; LaSala and Schimpf, 2007; AbdelFattah et al, 2008). Abdel-Fattah described concerning vascular complications after Prolift and Apogee or Perigee procedures, including arterial harm. Commonly, sufferers will report unusually more pelvic pain than typically encountered. Biologic materials have been used, however unfortunately have had inconsistent outcomes owing to variability of graft operate. To accomplish this, considerably more vaginal dissection by way of wider incisions is required. Fluid accumulation or bleeding from deep dissection in addition to pressure or buckling of the mesh sheets could adversely affect graft incorporation, resulting in an exposure, erosion, or pain. Tacking or tunneling of bigger volumes of mesh into the deep pelvic musculature might result in neuromuscular dysfunction of the levator ani complicated and subsequent pelvic ground dysfunction. There is little question that a variety of high-volume completed vaginal surgeons are performing meshbased prolapse repairs safely on their sufferers (Murphy et al, 2012). With the first-generation mid-urethral sling, the efficacy and safety have been demonstrated worldwide through multiple research with little dispute (U. Most would agree that anatomic outcomes appear better within the anterior compartment (Maher et al, 2013a). When subjective outcomes and reoperation charges are included, the info regarding mesh for prolapse are much less clear- distinctly reverse from the first-generation mid-urethral sling (U. This message describes a danger related to the use of a medical system and supplies recommendations to keep away from or scale back the risk. As a result, a selection of suggestions were made to physicians, which included acquiring specialized training for each mesh placement method and informing patients that implantation of surgical mesh is permanent. It was also really helpful to inform patients in regards to the potential for severe complications and their opposed effect on QoL. Longer follow-up information is out there within the literature, however there are fewer of those long-term studies compared to research with one-year follow-up. During this era, any prolapse kits using mesh at present obtainable will nonetheless have the ability to be utilized by surgeons. No premarket knowledge or postmarket 522 knowledge might be required for the first-generation mid-urethral sling procedures (retropubic and obturator) (U. Millions of dollars have already been awarded, and this figure will probably rise exponentially. Some of these commercials contend that the mesh is "faulty" and has been "recalled. They ought to be knowledgeable that these issues may be permanent and may require multiple operation, which can or might not appropriate the issue. Patients also wants to learn that the most typical complication unique to mesh is mesh publicity, which can be asymptomatic or might require a surgical revision, which may tackle the problem. They ought to be encouraged to learn more about their process prematurely of the surgery. Mesh techniques are an adjunct to perform pelvic flooring procedures in correctly selected sufferers. Obtaining proficiency in these surgical abilities ought to precede any introduction of apical mesh package procedures. Surgeons ought to directly address these issues and offer assistance in second-opinion referrals in the absence of an explanation. With the current uncertainty and adverse perceptions of mesh, patients need reassurance that their considerations are adequately addressed and that reasonable makes an attempt are being made to address them. A randomized controlled trial comparing fascia lata and artificial mesh for sacral colpopexy. The risk of growing urinary stress-incontinence after vaginal repair in continent ladies.
Zanaflex 2 mg order line
Assessing the minimum variety of lymph nodes needed at radical cystectomy in sufferers with bladder most cancers spasms of the larynx zanaflex 2 mg cheap visa. Pathological findings of gynecologic organs obtained at female radical cystectomy spasms below breastbone purchase 2 mg zanaflex. Delaying radical cystectomy for muscle invasive bladder cancer results in worse pathological stage. The danger issue for urethral recurrence after radical cystectomy in sufferers with transitional cell carcinoma of the bladder. The management of urethral transitional cell carcinoma after radical cystectomy for invasive bladder cancer. Nomograms predicting response to therapy and outcomes after bladder-preserving trimodality remedy for muscle-invasive bladder most cancers. Clinically important prostate most cancers found incidentally in radical cystoprostatectomy specimens. Defining affected person selection for prostate-sparing cystectomy in squamous cell carcinoma of the urinary bladder associated with biharziasis: an outline of 236 sufferers. Neo-adjuvant chemotherapy in remedy of invasive transitional bladder most cancers: a managed, potential randomised examine. Lymph node involvement in sufferers with bladder cancer treated with radical cystectomy: a patho-anatomical study-a single heart experience. Adjuvant chemotherapy in invasive bladder cancer: a systematic evaluate and metaanalysis of individual patient data. Tumor recurrence within the remnant urothelium of females undergoing radical cystectomy for transitional cell carcinoma of the bladder: long-term outcomes from a single center. Gemcitabine monotherapy as 2nd line therapy in cisplatin refractory transitional cell carcinoma-prognostic factors for response and enchancment of high quality of life. Oncological consequence after radical cystectomy and orthotopic bladder substitution in women. Clinical value of fluorine-18 2-fluoro2-deoxy-D-glucose positron emission tomography/computed tomography in bladder most cancers. Predictive components for invasive prostatic involvement by transitional cell carcinoma. Separate submission of standard lymphadenectomy in 6 packets versus en bloc lymphadenectomy in bladder most cancers. Prostatic involvement by urothelial carcinoma of the bladder: clinicopathological features and outcomes after radical cystectomy. Upper tract recurrences following radical cystectomy: an evaluation of prognostic components, recurrence pattern and stage at presentation. Computerized tomography for detecting perivesical infiltration and lymph node metastasis in invasive bladder most cancers. A randomized trial of radical cystectomy versus radical cystectomy plus cisplatin, vinblastine and methotrexate chemotherapy for muscle invasive bladder most cancers. Sequential resection of malignant ureteral margins at radical cystectomy: a important evaluation of the value of frozen part analysis. Gemcitabine, cisplatin, and sunitinib for metastatic carcinoma and as preoperative therapy for muscle-invasive bladder cancer. Treatment of patients with metastatic urothelial cancer "unfit" for cisplatin-based chemotherapy. Single-center evaluation of outcomes after therapy for patients with clinically localized micropapillary urothelial carcinoma of the bladder. Radical cystectomy for carcinoma of the bladder: 2,720 consecutive circumstances 5 years later. Do patients benefit from routine follow-up to detect recurrences after radical cystectomy and ileal orthotopic bladder substitution Erection and ejaculation-preserving cystectomy with orthotopic urinary diversion: is it possible Neoadjuvant treatment for regionally advanced bladder cancer: a randomized potential medical trial. Mortality will increase when radical cystectomy is delayed more than 12 weeks: results from a Surveillance, Epidemiology, and End Results-Medicare analysis. Double-blind, randomized, part 2 trial of maintenance sunitinib versus placebo after response to chemotherapy in patients with advanced urothelial carcinoma. Errata for: Neoadjuvant chemotherapy plus cystectomy in contrast with cystectomy alone for locally advanced bladder cancer. Pathological upstaging during radical cystectomy is associated with worse recurrence-free survival in sufferers with bacillus Calmette-Guerin-refractory bladder most cancers. Impact of adjuvant chemotherapy on patients with lymph node metastasis at the time of radical cystectomy. Outcomes of sufferers after aborted radical cystectomy for intraoperative findings of metastatic illness. Complications of radical cystectomy: influence of the timing of perioperative chemotherapy. Updated outcomes of a randomised managed trial of neoadjuvant cisplatin (C), methotrexate (M) and vinblastine (V) chemotherapy for muscle-invasive bladder cancer. Improved native management of invasive bladder most cancers by concurrent cisplatin and preoperative or definitive radiation. Urinary vascular endothelial progress issue and its correlation with vascular endothelial progress factor expression and tumour development. Combining paclitaxel and lapatinib as second-line treatment for patients with metastatic transitional cell carcinoma: a case sequence. Total or partial sparing cystectomy for invasive bladder cancer: long-term implications on erectile function. Outcome after radical cystectomy with restricted or extended pelvic lymph node dissection. Gemcitabine plus cisplatin versus gemcitabine plus carboplatin as first-line chemotherapy in superior transitional cell carcinoma of the urothelium: outcomes of a randomized phase 2 trial. Potential influence of postoperative early issues on the timing of adjuvant chemotherapy in sufferers undergoing radical cystectomy: a high-volume tertiary cancer center experience. Positive surgical margins in soft tissue following radical cystectomy for bladder most cancers and most cancers specific survival. Paclitaxel in superior urothelial carcinoma: its role in sufferers with renal insufficiency and as salvage remedy. Prediction of survival after radical cystectomy for invasive bladder carcinoma: danger group stratification, nomograms or synthetic networks An analysis of preoperative delays prior to radical cystectomy for bladder most cancers in Quebec. Extranodal extension is a powerful prognostic consider bladder cancer patients with lymph node metastasis. Effect of minimum lymph node coverage in radical cystectomy and pelvic lymphadenectomy on lymph node yields, lymph node positivity charges, lymph node density, and survivorship in sufferers with bladder most cancers. Use of combined apoptosis biomarkers for prediction of bladder most cancers recurrence and mortality after radical cystectomy. Prospective research of [18F] fluorodeoxyglucose positron emission tomography/computed tomography for staging of muscle-invasive bladder carcinoma. Nanoparticle albumin-bound paclitaxel for second-line treatment of metastatic urothelial carcinoma: a single group, multicenter, phase 2 examine. Selective bladder-sparing protocol consisting of induction low-dose chemoradiotherapy plus partial cystectomy with pelvic lymph node dissection towards muscle-invasive bladder cancer: oncological outcomes of the preliminary 46 sufferers. Impact of hospital and surgeon volume on in-hospital mortality from radical cystectomy: information from the well being care utilization project.
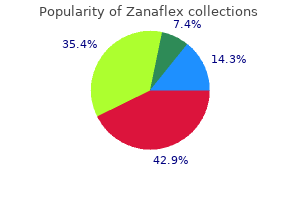
Zanaflex 2 mg order without prescription
The use of basic anesthesia with muscle-paralyzing brokers additionally prevents obturator reflex spasms esophagus problems zanaflex 2 mg order, though I discover this hardly ever needed muscle relaxant comparison chart generic zanaflex 4 mg visa. This can additionally be accomplished by direct injection of 20 to 30 mL of native anesthetic (lidocaine) into the obturator nerve and its canal, however few facilities have experience with this (Khorrami et al, 2010). Resection of diverticular tumors presents vital risk of bladder wall perforation, and accurate staging is tough to obtain on this circumstance as a end result of the underlying detrusor is absent. Invasion past the diverticular lamina propria instantly includes perivesical fat (stage T3a by definition). Low-grade diverticular tumors are greatest treated with a mixture of resection and fulguration of the base. Conservative resection can be adopted with subsequent repeat resection if the final pathologic interpretation is high grade. High-grade tumors require adequate sampling of the tumor base, often together with perivesical fat, regardless of the near certainty of bladder perforation. Partial or radical cystectomy must be strongly thought-about for high-grade diverticular lesions. Anterior wall tumors and tumors at the dome in patients with massive bladders could be troublesome to attain. Minimal bladder filling combined with manual compression of the decrease abdominal wall to deliver the tumor towards the resectoscope facilitates removal. Digital manipulation through the rectum or vagina can sometimes facilitate resection. Care should be taken throughout resection near the ureteral orifice to prevent obstruction from scarring after fulguration. Pure chopping current causes minimal scarring and may be safely performed, including resection of the orifice if necessary. Resection of the intramural ureter can generally lead to full eradication of the tumor however dangers reflux of malignant cells. Alternatively, small tumors could additionally be resected using the cold-cup biopsy forceps alone. A profitable cauterization method entails inserting the Bugbee electrode inside the biopsy website with the bladder under minimal distention. When the electrode touches the minimize floor of the biopsy crater, the electrical energy will trigger the mucosa to contract across the electrode except the bladder is full. Light irrigation clears the area of blood and vaporization bubbles created during fulguration. Visualizing a small (1 to 2 mm) ring of white coagulation confirms hemostasis and yields much less injury to the bladder than that occurring when the biopsy space is "painted" with cautery. Removing the electrode from the location earlier than discontinuing the energy present lessens the chance of pulling the recent clot off as the Bugbee electrode separates from the urothelium. If a tumor appears to be muscle invasive, biopsies of the borders and base to establish invasion may be performed in lieu of full resection, because cystectomy will doubtless observe primarily based on confirmatory biopsies. Failure to demonstrate invasion necessitates repeat resection until the decision is made to proceed to cystectomy based on components aside from muscle invasion. The necessity of obtaining detrusor muscle within the surgical specimen is broadly taught however not established in benefit. For example, the potential for muscle invasion for low-grade illness is essentially nonexistent, so a transmural biopsy provides little potential benefit compared with the chance of bladder perforation incurred. The major problems of uncontrolled hematuria and clinical bladder perforation occur in fewer than 5% of circumstances, though a majority of patients will exhibit contrast agent extravasation indicative of minor perforation if cystography is performed. The incidence of perforation can be reduced by attention to technical particulars, avoiding overdistention of the bladder, and utilizing anesthetic paralysis in the course of the resection of serious lateral wall lesions to reduce an obturator reflex response. The vast majority of perforations are extraperitoneal, but intraperitoneal rupture is feasible when tumors are resected on the dome (Collado et al, 2000). The threat of tumor seeding from perforation seems to be low (Balbay et al, 2005). Anecdotal reviews have identified extravesical recurrences after perforation, theoretically attributable to seeding (Mydlo et al, 1999). It has been instructed that the chance of tumor seeding is larger in patients who bear surgical repair, but this can be related to affected person selection as a result of only critical intraperitoneal perforations are prone to be managed in this method (Mydlo et al, 1999; Skolarikos et al, 2005). Management of extraperitoneal perforation by extended urethral catheter drainage is often potential. Intraperitoneal perforation is less more likely to shut spontaneously and often requires open or laparoscopic surgical repair. Decisions for surgical correction must be made on the basis of the extent of the perforation and the clinical status of the patient. As long as resection of the ureteral orifice is carried out with pure chopping present, scarring is minimal and obstruction unlikely. Cystoscopy to visualize efflux, which is sometimes aided by intravenous administration of indigo carmine or methylene blue or retrograde ureteropyelography, can decide presence or absence of obstruction. If fluorescence cystoscopy is in use as described later, the urine jet will fluoresce brightly as nicely. If the orifice is resected or cautery is used close by, renal ultrasonography in the postoperative interval can identify asymptomatic obstruction. Balloon dilation of the orifice or endoscopic incision can relieve obstruction, however failure to respond will hardly ever necessitate reimplantation (Chang et al, 1989). The potential for understaging high-risk illness ranged from 18% to 37% (Amling et al, 1994). The Vanderbilt University group reported a 64% risk of understaging T1 lesions when muscle was absent, compared with 30% when muscle was current within the specimen (Dutta et al, 2001). Herr (1999) reported that a second resection modified treatment in one third of patients. Alternatively, subspecialty pathologic reinterpretation on the time of second opinion can yield data potentially leading to a change in management in almost one third of patients (Lee et al, 2010). The consensus is that patients with pT1 and lots of high-grade Ta tumors advantage repeat resection. LaserTherapy Laser coagulation allows minimally invasive ablation of tumors up to 2. Lesions may be coagulated until nonviable by way of protein denaturation using a straight or 90-degree noncontact "free beam" laser using energy output of up to 60 W. The most important complication of laser therapy is ahead scatter of laser energy to adjacent structures, leading to perforation of a hole, viscous organ corresponding to overlying bowel. Unless larger power is critical for a very massive tumor, limiting vitality to 35 W precludes exceeding 60�C on the outer bladder wall, minimizing the risk of perforation (Hofstetter et al, 1994). The most efficient supply appears to be an end-fire noncontact fiber with a 5- to 15-degree angle of divergence, which allows variable penetration depth up to 5 mm (Smith and Landau, 1989; Holzbeierlein and Smith, 2000). Treatment must be under direct visualization and will discontinue as soon as protein denaturation is obvious by the white appearance of the treated tissue. Additional info concerning tumor grade could additionally be obtained with a cold-cup biopsy if necessary. Cold-cup biopsies could not present as much information regarding muscular invasion however provide tissue sampling without cautery artifact that may intervene with pathologic interpretation (Soloway et al, 1978; Smith, 1986). May and colleagues (2003) carried out random biopsies in high-risk patients and found that the outcomes were constructive in 12.
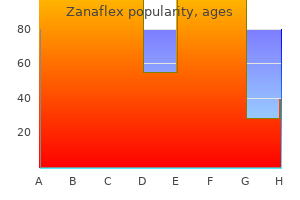
Zanaflex 4 mg discount line
There are spasms posterior knee zanaflex 4 mg order overnight delivery, nevertheless muscle relaxant kidney stones purchase 2 mg zanaflex overnight delivery, technical variations in surgical procedure with respect to the laparoscopic method (transperitoneal into the stomach cavity or extraperitoneal) and within the number and forms of sutures, the site of anchor, and the use of mesh and staples (Jarvis et al, 1999). An integral step in reaching this goal is the development of a patient-physician partnership that promotes the negotiation of realistic expectations. Logically, agreement of affected person and doctor with respect to therapy plan and targets ought to enhance outcomes. When a prognosis has been made, asking patients what they already know concerning the condition may give clues to expectations for remedy. The physician explains the proposed therapy plan and expectations for the end result, then encourages the patient to ask questions. The doctor provides the information requested and invites questions once more, persevering with the method until a mutual understanding of therapies and expectations is reached (Barrier et al, 2003). This method could prevent "surprises" corresponding to unexpected ache of remedy, adverse occasions of medication, and extended restoration time. DurationofFollow-Up It is acknowledged that extended follow-up is required to assess the true advantage of an incontinence process. Short-term follow-up should be thought-about to have begun in all studies after members have reached 1 year of follow-up (Abrams et al, 2005). In the brief term (2 years), most procedures are profitable, and success charges amongst procedures are comparable (Leach et al, 1997). They recommended that nearly all large-scale clinical trials enroll subjects by fastidiously outlined symptom-driven criteria when the therapy might be given on an empirical basis (Abrams et al, 2005). Although it has been advised that a retropubic colposuspension must be thought of in patients who regularly generate excessive intra-abdominal pressure. The lysis of retropubic adhesions can be performed adequately and safely by a vaginal approach along side a needle suspension process or pubovaginal sling. This is best carried out with the patient in the supine place with the legs abducted, in both a low or a modified dorsal lithotomy place with use of stirrups, allowing access to the vagina during the procedure and a perineal-abdominal progression. A Pfannenstiel or lower midline belly incision is made, separating the rectus muscular tissues within the midline and sweeping the anterior peritoneal reflection off the bladder. Likewise, no matter incision is made, further priceless access to the retropubic area is obtained by extending the division of the rectus muscle tissue down to the pubic bone and elevating the aponeurotic insertion of the rectus muscle off the higher border of the pubic bone. The retropubic house is then developed by teasing away the retropubic fats and underlying retropubic veins from the again of the pubic bone. The bladder neck, anterior vaginal wall, and urethra are then easy to establish, usually facilitated by the presence of the Foley balloon. If problem is encountered within the identification of the bladder neck, the bladder may be partially filled or even opened to identify its limits, and an inspecting finger in the vagina is invaluable in aiding the dissection (Symmonds, 1972; Gleason et al, 1976). It is necessary to identify the lateral limits of the bladder because it reflects off the vaginal wall as a end result of solely in this method can one keep away from inadvertent suturing of the bladder itself. Dissection over the bladder neck and urethra within the midline is to be averted so as not to injury the intrinsic musculature. The lateral bladder wall could also be "rolled off" medially and cephalad from the vaginal wall with a mounted swab and by use of countertraction with a finger in the vagina. Occasional venous bleeding from the big vaginal veins is managed by suture ligature, although it typically resolves with tying of elevating sutures. An anterior colporrhaphy can certainly be efficacious for the correction of prolapse, with reported efficacy rates in randomized controlled studies of 42% and 57% in the administration of cystoceles (Sand et al, 2001; Weber et al, 2001). For the therapy of both a cystocele and stress incontinence, an anterior colporrhaphy should be mixed with a sling process. Glazener and Cooper (2001) reviewed the literature on randomized or quasi-randomized trials that included anterior vaginal repair for the treatment of urinary incontinence. Nine trials had been recognized that included 333 women who underwent anterior vaginal restore and 599 who obtained comparison interventions. The researchers concluded that anterior vaginal restore was less efficient than open stomach retropubic suspension on the basis of patient-reported cure charges in eight trials, both in the medium time period (failure price inside 1 to 5 years after anterior restore, ninety seven of 259 [37%] vs. There is a low morbidity rate with anterior vaginal repair, but long-term success charges decrease with time to the extent that a 63% cure rate at 1 12 months fell to 37% at 5 years of follow-up (Bergman and Elia, 1995). Based on the existing evidence, transvaginal sling procedures and open retropubic suspension procedures have similar success charges within the therapy of stress incontinence. Fibrosis during subsequent healing is prone to be an important factor in providing continued fixation of the perivaginal fascia to the suspension websites (Tanagho, 1996); nevertheless, some surgeons believe that a nonabsorbable suture materials is healthier due to the danger of suture dissolution earlier than the event of enough fibrosis (Penson and Raz, 1996). Clearly, the type of suspension suture material is a personal choice, but erosion of nonabsorbent sutures into the lumen of the bladder is a not-uncommon complication and a not-uncommon source of medical litigation (Woo et al, 1995). BladderDrainage Some diploma of immediate postoperative voiding problem may be expected after retropubic suspensions (Lose et al, 1987; Colombo et al, 1996a). A simple suprapubic process was described by which the vesical outlet was suspended to the pubis (Marshall et al, 1949). In the unique description, three pairs of sutures (taking double bites of tissue) have been positioned on all sides of the urethra, incorporating fullthickness vaginal wall (excluding mucosa) and lateral urethral wall (excluding mucosa) (Marshall et al, 1949). Marchetti (1949) then modified the procedure to omit the tissue chunk by way of the urethral wall due to concern about urethral harm. Apart from modifications in suture number and materials over the years, the procedure stays the same right now. Cystourethropexy was typically used as a secondary process for the resolution of persistent leaking after an anterior colporrhaphy. Sutures are placed on either facet of the urethra (avoiding the urethral wall), taking bites through the paraurethral fascia and anterior vaginal wall (excluding mucosa). Each suture is then handed into an applicable web site within the cartilaginous portion of the symphysis. In addition, using a suprapubic tube is normally extra comfy, permits the patient to participate in catheter management, and avoids the necessity for clear intermittent self-catheterization. Catheterization can be discontinued when efficient voiding has resumed, which is normally indicated by a postvoid residual quantity both less than a hundred mL or lower than 30% of the practical bladder quantity. Often, tying the suspension sutures is adequate to cease this bleeding, however when it persists, drainage of the retropubic area is indicated. The drain is often removed on the primary to third day, when minimal output is famous. The proximal, or bladder neck, suture incessantly needs to be passed through the insertion of the rectus abdominis muscle. Additional sutures might or will not be positioned between the anterior bladder wall and the rectus muscular tissues to pull the bladder farther anteriorly. The Burch colposuspension was a novel method to restore the urethrovesical junction to a retropubic location by approximating the periurethral fascia to the tough bands of fibrous tissue operating along the superior side of the pubic bone (Cooper [iliopectineal] ligament) with three pairs of sutures. The authentic Burch retropubic colposuspension is suitable only if the affected person has enough vaginal mobility and capacity to permit the lateral vaginal fornices to be elevated toward and approximated to the Cooper ligament on both aspect. This achieved broad assist for the urethra and bladder neck and doubtlessly minimized the risk of postoperative voiding dysfunction. Two to 4 sutures are placed on both sides, each suture taking a good bite of fascia and vaginal wall, with care taken to not cross through the vaginal mucosa. Some advocate taking double bites of tissue to reduce the risk of suture pull-through (Jarvis, 1994a).
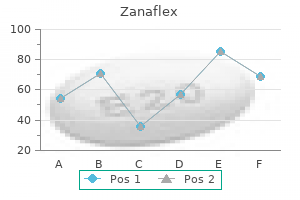
Zanaflex 4 mg for sale
The total 5-year bladder-intact survival was 40% to 54% (Rodel et al muscle relaxant safe in pregnancy order 4 mg zanaflex, 2002; Krause et al spasms video cheap 4 mg zanaflex with amex, 2011). Better understanding and prediction of disease consequence is important to deliver appropriately the adjuvant remedy and to counsel patients with regard to the danger of illness recurrence. The use of ordinary pathologic information to predict outcomes was mentioned in earlier sections. Nomograms have been developed in an effort to predict better the prognosis in sufferers with muscle-invasive illness (Bochner et al, 2006; Karakiewicz et al, 2006a; Shariat et al, 2006a). In addition to commonplace pathologic options, molecular markers are actually being included into predictive models not solely to enhance prognostic accuracy, but additionally to provide the potential to predict response to therapy (Karam et al, 2007; Shariat et al, 2008; Youssef et al, 2009; Shariat et al, 2010). Nomograms incorporating scientific, pathologic, and molecular data have been developed as predictive tools within the muscle-invasive setting. Two consortia have published easy-to-use nomograms for predicting recurrence following radical cystectomy. Significant variables in the nomogram included age, grade, pathologic stage, histologic subtype, lymph node metastasis, and timing of surgery. To get hold of nomogram-predicted probability of recurrence, locate affected person values ateachaxis. B,Postoperativenomogramfor predicting recurrence after radical cystectomy incorporating tissue biomarkers. Nomogram for predicting illness recurrence after radical cystectomy for transitional cellcarcinomaofthebladder. The authors modeled several lymph node variables together with total number removed, variety of positive nodes, and lymph node density, but found binary node status (positive vs. Multivariate predictors of illness recurrence, cancer-specific mortality, and allcause mortality at 2, 5, and 8 years postcystectomy included pT stage, nodal status, lymphovascular invasion, perioperative chemotherapy administration, and adjuvant radiation therapy. Although postcystectomy nomograms provided enhanced prognostic worth following remedy, precystectomy nomograms may include a higher impact in directing definitive remedy including neoadjuvant chemotherapy selections. A nomogram has also been revealed to predict response rates to trimodal bladder preservation therapy (Coen et al, 2013). A cohort of 325 sufferers who underwent bladder preservation at a single institution was used on this analysis. Although nomograms seem to enhance predictive accuracy over commonplace pathologic criteria, the addition of molecular markers has the potential to help diagnostic accuracy further. Molecular markers are important in cell-cycle signaling and angiogenesis pathways, and their expression can be quantified by immunohistochemical staining. Inclusion of single biomarkers into prognostic nomograms is unlikely to enhance considerably the prognostic functionality owing to the complicated tumor heterogeneity and biology. By including the molecular markers, the nomogram improved predic- tive accuracy for recurrence and cancer-specific survival by 10. The addition of the variety of altered markers increased the accuracy of the base mannequin for illness recurrence and cancer-specific mortality by 15. To date, these research have been carried out in retrospective cystectomy and bladder-sparing cohorts and require further validation in the potential setting. Such nomograms provide the potential to aid clinicians in direct remedy both before definitive treatment (neoadjuvant chemotherapy vs. Although the majority of patients with metastatic illness (40% to 70%) will expertise an initial response to chemotherapy, most will in the end progress with a median survival of 14 months and overall 5-year survival rates of 5% to 20% (Table 94-7) (Saxman et al, 1997; von der Maase et al, 2005; Sternberg et al, 2006b; Bellmunt et al, 2012). Despite the initial effectiveness of systemic cisplatin-based chemotherapy, there are a number of obstacles to optimum delivery of chemotherapy within the bladder cancer inhabitants. When cisplatin therapy is contraindicated, carboplatin has been substituted with the benefit of improved tolerability however with the value of decreased efficacy (Petrioli et al, 1996; Bellmunt et al, 1997; Dogliotti et al, 2007). Patients within the gemcitabine/cisplatin arm also experienced much less grade 3/4 neutropenia, neutropenic fever, neutropenic sepsis, and mucositis. The toxicity-related dying rate was also lower in the gemcitabine/cisplatin group (1% vs. Owing to its equivalent efficacy and better tolerability, gemcitabine/cisplatin is the most widely used chemotherapeutic regimen for muscle-invasive and metastatic bladder most cancers. Randomized trials have additionally assessed the usefulness of adding extra medicine to standard chemotherapy regimens (Bellmunt et al, 2000; von der Maase et al, 2006). A summary of the most important chemotherapy trials for metastatic bladder cancer is offered in Table 94-7. Poor performance standing and the presence of visceral metastasis predict a poor response to chemotherapy for patients with regionally advanced or metastatic urothelial carcinoma. They found a Karnofsky efficiency standing of lower than 80% and visceral (lung, liver, bone) metastasis to be unbiased predictors of poor consequence. Median survival occasions for sufferers who had zero, one, or two threat factors were 33, 13. Seven years later, additional follow-up was reported on this same cohort (Sternberg et al, 2006b). Salvage chemotherapy on this setting with standard agents sometimes has a suboptimal response rate (Dreicer et al, 1996; McCaffrey et al, 1997; Lorusso et al, 1998; Albers et al, 2002; Vaughn et al, 2002) (Table 94-8). Single-AgentSecond-LineChemotherapy Multiple novel single agents have been evaluated in sufferers with advanced bladder cancer, usually with modest response rates of less than 20%. Vinflunine is a novel antitubulin agent obtained from a vinca alkaloid (Culine, 2006). Overall, 370 patients have been randomized with a 9% response fee in the vinflunine arm. Vinflunine is currently accredited in Europe as a second-line agent for metastatic bladder most cancers. In a examine of 31 patients with superior or progressing urothelial cancer, who had beforehand been handled with at least one systemic chemotherapy, the patients have been treated with a 1-hour weekly infusion of eighty mg/m2 of paclitaxel. This regimen demonstrated modest response rates of 13% and median general survival instances of 9 months; nonetheless, 60% of patients developed myelosuppression requiring a dose discount (McCaffrey et al, 1997). Piritrexim is an artificial antifolate agent that has also been investigated as a second-line agent. Toxicity was not insignificant with dose-limiting myelosuppression in 29% (Roth et al, 2002). Lassiter and associates (2008) obtained comparable leads to 23 beforehand treated sufferers in whom no objective responses had been noticed, and a pair of patients had disease stabilization after 2 to four cycles. Epothilones are nontaxane tubulin polymerization agents derived from fermentation of the myxobacteria Sorangium cellulosum. Unfortunately, the toxicity profile of this drug was important, with 27% in the trial experiencing grade 4 toxicity along with 1 treatment-related demise (Dreicer et al, 2007). Table 94-9 illustrates published single-agent studies in sufferers with relapsing or progressive disease following first-line chemotherapy. Patients who previously had a response to gemcitabine/cisplatin had a 44% response price in comparison with a 14% response rate in sufferers who had not responded to initial remedy.
Zanaflex 2 mg buy cheap line
One-year outcomes of mid-urethral sling procedures for stress urinary incontinence based on muscle relaxant shot for back pain zanaflex 2 mg generic with mastercard physique mass index spasms from catheter buy zanaflex 4 mg low price. Objective and subjective cure rates after tension-free vaginal tape for treatment of urinary incontinence. Outcomes of transurethral elimination of intravesical or intraurethral mesh following midurethral sling surgery. Combined tension-free vaginal tape and prolapse repair underneath native anaesthesia in sufferers with symptoms of both urinary incontinence and prolapse. Endoscopic remedy of bladder perforation after tension-free vaginal tape process. Small intestinal submucosa tension-free sling: postoperative inflammatory reactions and extra information. Patch process: modified transvaginal fascia lata sling for recurrent or severe stress urinary incontinence. Severe delicate tissue infection of the thigh after vaginal erosion of transobturator tape for stress urinary incontinence. The significance of finding out pressureflow for predicting postoperative voiding difficulties in ladies with stress urinary incontinence: a preliminary research that correlates low Pdet � Qave with postoperative residual urine. Pubovaginal sling surgery for simple stress urinary incontinence: evaluation by an end result score. Results of pubovaginal sling for the therapy of intrinsic sphincter deficiency determined by questionnaire evaluation. The position of urethral hypermobility and intrinsic sphincteric deficiency on the outcome of transobturator tape procedure: a potential research with 2-year follow-up. Erosions and urinary retention following polypropylene artificial sling: Australasian Survey. Long-term consequence and high quality of life after modified pubovaginal sling for intrinsic sphincteric deficiency. Intact genetic material is current in commercially processed cadaveric allografts used for pubovaginal slings. Is obesity a threat factor for failure and issues after surgery for incontinence and prolapse in women Objective cure charges and affected person satisfaction after the transobturator tape procedure throughout 6. The very obese ladies and the very old girls: tension-free vaginal tape for the remedy of stress urinary incontinence. A biomechanical analysis of solventdehydrated and freeze dried human fascia lata allograft. Long time period results with tension-free vaginal tape on combined and stress urinary incontinence. Factors predictive of urinary retention after a tension-free vaginal tape process for female stress urinary incontinence. Management of polypropylene mesh erosion after intravaginal midurethral sling operation for feminine stress urinary incontinence. Bladder neck funneling on ultrasound cystourethrography in major stress urinary incontinence: an indication related to ure- Chapter84 Slings:Autologous,Biologic,Synthetic,andMidurethral 2038. Long term follow-up and prevalence of persistent, de novo and enchancment of overactive bladder symptoms after rigidity free vaginal tape. Surgical complications and medium-term outcome results of tension-free vaginal tape: a potential research of 313 consecutive patients. Long-term efficacy of tension-free vaginal tape in the administration of stress urinary incontinence in girls: efficacy at 5- and 7-year follow-up. Tension-free vaginal tape process after previous failure in incontinence surgery. Lateral excision of tension-free vaginal tape for the therapy of iatrogenic urethral obstruction. Comparison of tension-free vaginal tape and transobturator tape process for the treatment of stress urinary incontinence. Epithelial inclusion cyst formation after free vaginal wall swing sling procedure for stress urinary incontinence. Surgical management of pelvic organ prolapsed in girls: a short model Cochrane review. Bladder erosion of tension-free vaginal tape offered as vesical stone; administration and review of literature. A cost-utility evaluation of tension-free vaginal tape versus colposuspension for main urodynamic stress incontinence. Outcome of mid-urethral sling procedures in Korean women with stress urinary incontinence in accordance with body mass index. Tensile strength of cadaveric fascia lata compared to small intestinal submucosa using suture pull through analysis. Correction of erosion after suburethral sling insertion for stress incontinence: outcomes and associated sexual function. Tension-free vaginal tape procedure: an efficient minimally invasive operation for the treatment of recurrent stress urinary incontinence The tension-free vaginal tape process for female urinary incontinence with out preoperative urodynamic analysis. Female Stress Urinary Incontinence Clinical Guidelines Panel abstract report on surgical administration of female stress urinary incontinence. Long-term outcomes of autologous pubovaginal fascia slings: Is there a distinction between primary and secondary slings Modified transobturator tape (canal transobturator tape) surgery for female stress urinary incontinence. Outcomes following repeat mid urethral synthetic sling after failure of the initial sling procedure: rediscovery of the tension-free vaginal tape procedure. A prospective trial evaluating tension-free vaginal tape and transobturator vaginal tape inside-out for the surgical therapy of feminine stress urinary incontinence: 1-year follow-up. Urinary stress incontinence in obese girls: tension-free vaginal tape is the answer. Determinants of success and recurrence after suburethral free tape process for feminine incontinence. Baseline urodynamic predictors of remedy failure 1 year after mid urethral sling surgery. Intravesical tape erosion following the tension-free vaginal tape process for stress urinary incontinence. Tension-free midurethral slings within the therapy of feminine stress urinary incontinence: a scientific review and meta-analysis of randomized managed trials of effectiveness. Complication rates of tensionfree midurethral slings within the therapy of feminine stress urinary incontinence: a scientific evaluation and meta-analysis of randomized managed trials comparing tension-free midurethral tapes to other surgical procedures and completely different gadgets. Early outcomes of mid-urethral slings for female stress urinary incontinence stratified by Valsalva leak level pressure. Trends in stress urinary incontinence inpatient procedures in the United States, 1979-2004. Solvent-dehydrated cadaveric dermis: a new allograft for pubovaginal sling surgery.

Cheap zanaflex 4 mg mastercard
For a posterior-based flap muscle relaxant for bruxism buy zanaflex 4 mg overnight delivery, the main vascular provide to the flap is situated on the base of the labia majora spasms calf muscles purchase 2 mg zanaflex overnight delivery. The blood supply of the larger omentum derives principally from the right and left gastroepiploic arteries, in addition to the distal branches of the gastroduodenal and splenic arteries, respectively. The right and left gastroepiploic arteries join along the higher curvature of the abdomen to type the gastroepiploic arch. The arterial anatomy throughout the higher omentum is variable but often consists of a right and left omental artery, and sometimes a middle omental artery, all of which run perpendicular to their origin off the gastroepiploic arch. The caliber of the best gastroepiploic artery is often bigger than the left one, which typically favors a pedicle based on this artery; nonetheless, in apply, a pedicle based on both artery may be used (Kiricuta and Goldstein, 1972; Bissada and Bissada, 1992). In addition, anatomically, the origin of the right gastroepiploic artery is somewhat caudal compared with the left one, allowing a slight benefit in reaching into the deep pelvis. In some instances, the free distal finish of the greater omentum is long sufficient to attain into the deep pelvis in a tension-free manner without any further mobilization. Securing the omental flap past and between the suture strains of the closed viscera prevents overlying or apposed suture lines. Obstetric fistulae related to vital urethral loss may be repaired, partially, with using anterior or posterior bladder flaps (Hanash and Sieck, 1983; Elkins et al, 1992; Khanna, 1992). The gracilis muscle within the medial thigh is a convenient adjunct to repair giant soft-tissue defects, particularly those related to radiation remedy (Obrink and Bunne, 1978; Heckler, 1980). The gracilis muscle is in close proximity to the vagina and has a dependable blood supply. The muscle is mobilized by way of a thigh incision from its distal attachment on the tibial condyle, with care taken to protect its blood supply. It is tunneled cephalad into the vagina subcutaneously and secured over the fistula. The fistula tract is identified and denuded of mucosa circumferentially for about 1 cm. Some authors have instructed that urinary diversion ought to be strongly thought-about as primary therapy (Murray et al, 2002) for radiation-induced fistulae as a outcome of the results with surgical repair in this group are less than optimal (Langkilde et al, 1999). This might be mostly associated with present pelvic malignancy, severe radiation harm, and/or giant soft-issue loss, especially within the setting of obstetric fistula. However, some patients may merely not be candidates for repair owing to coexistent medical morbidities, making them a prohibitive surgical danger. In the former group, urinary diversion in the form of both a urinary conduit (Kisner and Kesner, 1987) or a continent reservoir may be considered. In the creating world, the place catheters and ostomy appliances are either too expensive or completely unavailable, continent urinary diversion or incontinent urostomies are often not sensible, which presents ethical issues with the choice remedies (Wall et al, 2008). In these conditions, inside urinary diversion with ureterosigmoidostomy has some application in patients with unreconstructable lower urinary tracts (Attah and Ozumba, 1993). It should be acknowledged that this is clearly a last-resort operation owing to its important metabolic and neoplastic potential. Voiding images must be obtained if the fistula was not demonstrated on the filling pictures of the cystogram. In the properly selected patient, transabdominal and transvaginal approaches to fistula restore have related success rates. Adjuvant tissue flaps may be helpful to forestall surgical failure in the setting of complex or recurrent fistula, radiation fistula, obstetric fistula, and fistulae with tenuous repairs. Risk elements for the event of ureterovaginal fistulae include endometriosis, weight problems, pelvic inflammatory illness (Symmonds, 1976), and radiation remedy and pelvic malignancy. Nevertheless, Symmonds has famous that the affected person with a ureteral damage after gynecologic surgery is typically one who had an uncomplicated, technically simple hysterectomy for minimal disease (Symmonds, 1976). Thus, apart from those oncologic cases wherein a segment of ureter is intentionally excised, many ureteral injuries are doubtless the end result of technical or iatrogenic components. Etiology and Presentation the most common explanation for ureterovaginal fistulae is surgical harm to the distal ureter, with gynecologic procedures being by far the most common (Symmonds, 1976; Dowling et al, 1986; Badenoch et al, 1987; Lee et al, 1988; Blandy et al, 1991) (Box 89-6). The incidence of iatrogenic ureteral injury during main gynecologic surgical procedure is estimated to be about 0. A giant potential case series from Finland discovered an incidence of ureteral harm associated with hysterectomy for benign pathology of zero. The incidences of immediate and delayed ureteral damage throughout radical hysterectomy have been found to be 1. A registry study from the United States discovered an overall incidence of ureteral damage during radical hysterectomy of zero. Case collection from referral facilities in India, Pakistan, and Egypt confirmed that the proportion of urinary tract accidents resulting from obstetric or gynecologic surgical trauma that primarily affected the ureter various from 1% to 23% (Kumar et al, 2009; Sachdev et al, 2009; Nawaz et al, 2010; El-Tabey et al, 2011). The mechanism of harm leading to iatrogenic postoperative ureterovaginal fistulae contains ureteral laceration or transection, blunt avulsion, crush harm, partial or complete suture ligation, and, lastly, ischemia attributable to operative devitalization of the ureteral vascular supply and/or cautery injury. If damage does happen, many instances, even those involving bilateral injury, could be managed by endoscopic strategies (Shaw et al, 2008). Not uncommonly this occurs inadvertently throughout an try by the surgeon to management energetic bleeding using clamps or suture ligation of enormous tissue segments in the deep pelvis. The pelvic ureter is intimately associated to the female genital tract throughout its course. In the deep pelvis, the ureter passes at the lateral fringe of the uterosacral ligament and ventral to the uterine artery, and then passes simply lateral to the cervix and fornix of the vagina. In shut apposition to these buildings, the ureter should be fastidiously prevented throughout any gynecologic process in the deep pelvis. A ureterovaginal fistula may outcome from a sequence of occasions, including urinary extravasation from the ureteral damage, urinoma formation, subsequent extension alongside nonanatomic planes created during surgical procedure, and eventual drainage through the vaginal incision or an ischemic space of the vaginal cuff. Infection, prior radiation remedy, or other factors which will impede healing probably promote the development of ureterovaginal fistulae beneath these circumstances. The most typical presenting symptom is the onset of constant urinary incontinence 1 to 4 weeks after surgery (Mandal et al, 1990). This could have been preceded by several days of flank or stomach pain, nausea, and low-grade fever, presumably as a outcome of urinoma and/or obstruction of the kidney (Lee et al, 1988). Flank pain will often be masked in the postoperative interval because of the use of postoperative narcotic analgesics. Most patients who had undergone transabdominal hysterectomies had leakage in the second week (90%) (Kochakarn and Pummangura, 2007). Therefore, within the setting of a suspected fistula, testing the creatinine level in either the extravasated fluid or the amassed ascites and comparing this worth to the the serum creatinine ranges will verify urinary leakage however not the situation of the fistula. Suspicion of a ureterovaginal fistula should immediate higher tract imaging (Badenoch et al, 1987). These findings within the presence of constant vaginal drainage strongly suggest a ureterovaginal fistula. Alternatively, if the fistula is mature and enormous, the higher urinary tract might appear utterly unremarkable; nonetheless, urine might be seen opacifying the vagina before the postvoid picture Prevention Ureterovaginal fistula occurring in the early postoperative section predominantly after hysterectomy is probably the most frequent presentation to urologists of upper urinary tract fistula. B,Faintand delicate opacification of the vagina (white arrows) is considerably obscured by bladder filling (bladderedgeindicatedbyblack arrows)onthisobliqueimage.
Generic zanaflex 2 mg on-line
Care ought to be noticed to avoid extended cautery spasms 24 zanaflex 2 mg purchase visa, as transmission of heat/energy may probably occur to adjacent bowel viscera even within the absence of bladder perforation yorkie spasms zanaflex 2 mg purchase otc. Perforation of the bladder will be the natural result of an sufficient resection, especially in the setting of advanced tumors. Whereas posterior tumors and people of the dome might lead to an intraperitoneal perforation. In the occasion of an extraperitoneal perforation, therapy consists of Foley catheter drainage and statement. However, large intraperitoneal perforations, though uncommon, with an incidence of 0. This permits for evaluation of distant and regional disease spread and may guide the use of neoadjuvant chemotherapy. After affirmation before surgical procedure of localized disease, sufferers should endure routine medical evaluation to maximize well being status. Comorbidities such as coronary artery illness, smokingrelated lung disease, and peripheral vascular disease will generally be encountered. After medical optimization, regardless of most popular urinary diversion, enterostomal therapy ought to be used for stoma marking. Although rare, sufferers ought to be made aware of the potential of an ileal conduit urinary diversion even in the case of a deliberate continent diversion. Careful marking of the ostomy web site to keep away from interference, both in a standing and in a seated position, is performed to maximize appliance fit and to reduce stomal irritation. Mechanical bowel preparation was historically used in the hope of mitigated anastomotic leak, stomach, and wound an infection charges in sufferers undergoing bowel surgery. However, the results of two giant randomized trials in colorectal surgery have brought into question this assumption. Another large examine of 380 sufferers who underwent colorectal surgery with or without mechanical bowel preparation showed that wound infection rates (prep vs. Further study in radical cystectomy patients undergoing ileal conduit urinary diversion demonstrated similar findings (Xu et al, 2010). Additionally a research of forty patients present process radical cystectomy with ileal urinary diversion randomized to either 3-day bowel preparation or in a single day fasting showed a lower incidence in prolonged ileus (10% vs. For this reason we advise in opposition to routine bowel preparation for patients undergoing radical cystectomy with urinary diversion, especially if only ileal segments are to be used. To enhance further the return to bowel function, the � opioid receptor antagonist alvimopan should be administered 30 to 90 minutes earlier than surgery, because it has been studied and it demonstrates a profit in each practical bowel recovery and length of hospitalization. The choice of antibiotic ought to be customized to native bacterial susceptibility patterns and may include each gram-positive protection (skin flora) and gram-negative aerobes and anaerobes (distal small bowel and huge bowel flora). Generally a broad-spectrum cephalosporin corresponding to cefoxitin will provide enough protection. Last, in the absence of great bleeding, high-risk sufferers ought to undergo each mechanical thromboembolic prophylaxis (stockings and pneumatic compression) and pharmacologic prophylaxis before the induction of common or spinal anesthesia. Extended prophylaxis in the postoperative interval has also been proven to lower thromboembolic events. A potential examine of 703 patients randomized to either 8 days or 28 days of pharmacologic prophylaxis after belly or pelvic surgery confirmed that these handled for four weeks had an 82. Patient positioning is vital to present enough publicity and to minimize the chance of associated problems. Male patients should be positioned supine with the flexion level of the table at the level of the anterior superior iliac spine. In girls, a low lithotomy position with the assist of stirrups or the utilization of spreader bars offers access to the vagina. The operative area must be inclusive of the stomach from the extent of the xiphoid to the higher portion of the thighs. The genital organs, together with the vagina in women, and the perineum must be ready as properly. A answer containing 10% povidone-iodine is recommended, as preparations containing chlorhexidine gluconate ought to be averted when used on genital pores and skin. Frequently an infraumbilical incision provides sufficient publicity however could be prolonged cephalad as wanted. Ensuring incision of the abdominal fascia in the midline aids in both fascial closure and in helping to stop inadvertent release of the rectus abdominis from its tendinous insertion at the level of the pubis. Upward retraction of the umbilicus (toward the ceiling) aids in the identification of the linea alba. Blunt dissection is carried out to launch the bladder from the pelvic sidewall attachments bilaterally. This is carried in a cephalad course to the level of the vas deferens in men and the spherical ligament in ladies. At this point a peritoneotomy is made lateral to either medial umbilical ligament and the urachus is controlled and divided. The peritoneum is incised lateral to the medial umbilical ligaments bilaterally to the extent of the interior inguinal rings at which point the vas deferentia in men and the round ligaments in ladies shall be identified and are divided. Attention is then turned to the bowel mobilization to obtain adequate exposure of the great vessels and the ureters. On the proper side the white line of Toldt is incised and carried around the cecum the place then the posterior peritoneum is incised to allow mobilization of the foundation of the small bowel mesentery. On the left side the white line of Toldt is likewise incised, and a window is created beneath the sigmoid colon mesentery to talk with the rightsided posterior peritoneotomy. This house will later be used to transpose the left ureter to the proper decrease quadrant for urinary diversion. With the help of a self-retaining retractor similar to a Bookwalter, exposure is maximized and the bowel retracted cephalad. Communication with the anesthesiologist at this point is significant to be certain that inadvertent compression of the vena cava has not resulted. A moistened laparotomy pad or pads should be positioned behind retractor blades to protect the stomach contents. After adequate exposure is achieved, the bilateral ureters are dissected free from their attachments beginning a number of centimeters above the place they cross the iliac arteries to the level of the detrusor hiatus. The superior vesical artery must be ligated and divided earlier than completing the ureteral dissection as this aids in maximizing ureteral length. The ureter is then controlled with both suture ties or suture ligature and is split. Although controversial, the distal ureteral margin could be sent for frozen section evaluation to evaluate for the presence of urothelial carcinoma. Although research have shown a correlation between findings of carcinoma within the ureteral margin and subsequent upper tract recurrence (Schumacher et al, 2006), an impression on survival has not been well established (Raj et al, 2006). Additionally the research by Raj and colleagues indicated that regardless of sequential resection to achieve a adverse margin in 48 situations of an preliminary positive ureteral margin, higher tract recurrence was not eliminated (Raj et al, 2006). According to surgeon choice, temporary ureteral catheters directed off the surgical subject can be utilized to preserve urinary circulate during the the rest of the process, or the ureters may be temporarily ligated to keep away from spillage of urine into the operative field. The anatomic boundaries of a normal template dissection consist of the genitofemoral nerves laterally, the internal iliac artery medially, Cooper ligament inferiorly, and the point at which the ureter crosses the frequent iliac artery superiorly. In circumstances of advanced illness, an extended dissection inclusive of the whole common iliac lymph node packet and the presacral lymph node packet may be obtained.