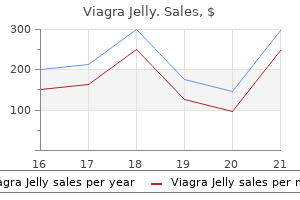
Viagra Jelly dosages: 100 mg
Viagra Jelly packs: 10 pills, 30 pills, 60 pills, 90 pills, 120 pills

Buy viagra jelly 100 mg
Treatment with pharmacologic doses of glucocorticoids is the commonest reason for Cushing syndrome in kids erectile dysfunction doctor las vegas viagra jelly 100 mg generic mastercard. Adrenal tumors are the commonest cause of endogenous Cushing syndrome in children youthful than 7 years old impotence and smoking safe 100 mg viagra jelly, whereas Cushing illness is more frequent in older youngsters and adolescents. The differential findings in the particular etiology of Cushing syndrome are listed in. The first step in the prognosis of Cushing syndrome is affirmation of elevated cortisol concentrations. Measurement of midnight salivary cortisol concentrations is useful, as a end result of people with Cushing syndrome typically manifest lack of regular cortisol diurnal variation. Some obese people have elevated cortisol secretion rates; correction for body surface area generally normalizes the results. Overnight, low-dose, and high-dose dexamethasone suppression tests could assist verify the analysis and discriminate among the many potential etiologies. Most obese individuals present suppression of the morning cortisol focus after an overnight dexamethasone stimulation check (1. Once endogenous extreme glucocorticoid secretion is confirmed, further studies are wanted to establish the precise etiology. Because pituitary adenomas could also be small, bilateral inferior petrosal sinus sampling could also be necessary to localize the adenoma before surgery. These images show how dramatic the adjustments related to Cushing syndrome are and the way quickly they happen. Note the centripetal weight problems of the trunk compared with the extremities after the onset of Cushing syndrome. C, Moon facies, clearly demonstrated, should elevate the diagnostic index of Cushing syndrome. Excessive adipose tissue over the lower cervical and upper thoracic spine is characteristic of Cushing syndrome. Primary adrenal insufficiency is characterised by glucocorticoid and mineralocorticoid deficiencies. If untreated, sufferers with Addison disease progressively weaken and vascular collapse ensues. The decreased circulating plasma volume is reflected by the thinned, slender heart shadow seen on a chest radiograph. Many of these disorders have been found to be associated with monogenic disorders. Autoimmune destruction of the adrenal gland has now changed tuberculosis as the most common reason for the illness particularly among adults. The kind 2 type (Schmidt syndrome) is characterized by diabetes, hypothyroidism, and adrenal insufficiency. Neonatal adrenal hemorrhages and meningitis (Waterhouse-Friderichsen syndrome) can destroy the adrenal cortex leading to acute adrenal insufficiency. Genetic issues related to adrenal destruction embody adrenoleukodystrophy, Zellweger Syndrome, and Wolman Syndrome. A, this affected person reveals the thin habitus and ill look attribute of Addison disease. The Zellweger syndrome represents a spectrum of autosomal recessive problems with three overlapping phenotypes that differ in severity and age at presentation. These problems embrace Zellweger syndrome, childish Refsum disease, and neonatal adrenoleukodystrophy. Ocular abnormalities, hepatic dysfunction, and developmental delay could also be present. The diagnosis may be verified by useful assays in cultured pores and skin fibroblasts and followed by mutation evaluation. Congenital adrenal hypoplasia in males may occur as a contiguous gene defect in affiliation with Duchenne muscular dystrophy and glycerol kinase deficiency. Symptoms of acute adrenal insufficiency typically develop around 6 to 8 weeks after start when the fetal zone of the adrenal cortex involutes. This disorder presents in younger kids with failure to thrive, hyperpigmentation, and hypoglycemia. Defects in adrenal steroidogenesis are related to major adrenal insufficiency. The specific symptoms and laboratory findings of those autosomal recessive disorders replicate the precise defect in steroidogenesis. Pathways for the synthesis of mineralocorticoids (aldosterone), glucocorticoids (cortisol), and androgens (testosterone) are proven. Androstenedione is secreted by the adrenal cortex and transformed to testosterone or estradiol in the periphery. In probably the most extreme forms, mineralocorticoid biosynthesis is also inadequate, resulting in continual salt loss, hyponatremia, hyperkalemia, and elevated plasma renin activity. Excessive prenatal androgen biosynthesis is related to masculinization of the exterior genitalia of affected female infants. Affected females usually have ambiguous symmetrical external genitalia with nonpalpable gonads at birth. Affected male infants have normal male exterior genitalia with hyperpigmentation of the scrotum. Hyperkalemia, hyponatremia, failure to thrive, and hypoglycemia, ultimately culminating in shock, ensue inside 10 to 14 days of delivery in the untreated toddler as penalties of the severe mineralocorticoid and glucocorticoid deficiencies. Affected males usually current with pubic hair, phallic enlargement, prepubertal testes, tall stature, and advanced skeletal maturation. Affected adolescent women often present with hirsutism, oligomenorrhea, and acne. Affected females show normal female external genital development and delayed puberty, whereas affected males are undervirilized at birth; elevated mineralocorticoid concentrations can be associated with hypertension. Congenital lipoid adrenal hyperplasia is characterized by inadequate virilization of affected male features, adrenal insufficiency presenting within the late neonatal interval, and lipoid hyperplasia of the adrenal glands. Both issues cause early defects in adrenal, testicular, and ovarian steroidogenesis. The clinical manifestations include defective steroidogenesis and skeletal anomalies. This syndrome is associated with craniosynostosis, midface hypoplasia, and choanal stenosis. Extraadrenal tumors arising from both sympathetic and parasympathetic paraganglia are paragangliomas. Symptoms might embody headache, diaphoresis, palpitations, tremor, nausea, weakness, nervousness, and weight loss. Altered mental status, orthostatic hypotension, syncope, or cardiac arrhythmias could happen. Both pheochromocytoma and/or paraganglioma could occur in certain familial syndromes. It is important to differentiate among these inherited problems as a end result of the pure history and scientific administration might differ depending on the precise genetic disorder.
100 mg viagra jelly
Hoppenfeld S: Physical examination of the spine and extremities erectile dysfunction treatment auckland viagra jelly 100 mg purchase without a prescription, New York erectile dysfunction treatment protocol 100 mg viagra jelly purchase mastercard, 1976, Appleton-Century-Crofts. Return to Play After Concussion the difficulty of timing of return to play of the athlete who has incurred a concussion is considered one of specific importance, the reason being that struggling a second concussion whereas the athlete remains to be symptomatic from a first can lead to the catastrophic phenomenon known as second influence syndrome. This is characterised by relentless cerebrovascular congestion and edema with lack of autoregulation of cerebral blood move, often culminating in herniation and dying. Concussion is defined as a condition characterized by momentary impairment of neurologic function after a head harm. Other acute signs may embody dizziness, headache, drowsiness, confusion, disorientation, delayed response times, problem concentrating, emotional lability or inappropriateness, visual modifications, and impaired coordination. In the acute state of affairs, obviously any athlete with extended lack of consciousness, irregular neurologic findings, persistently altered mental status, or development of acute symptoms deserves prompt transfer to the hospital for further analysis and imaging. In milder instances of head harm, a sideline assessment of psychological status (orientation, capability to focus, and short-term memory) and of neurologic status (strength, sensation, coordination) is indicated to determine whether any indicators and symptoms of concussion are current. If a participant has a suspected concussion, he or she must be faraway from play and never returned to play that day. Appropriate medical evaluation with a concussion protocol can be used to decide fitness for return to play sooner or later. Recent evidence does recommend extended rest may be deleterious to the athlete postconcussion in phrases of restoration. Return to Play After Exacerbation of Underlying Disorder For recommendations concerning return to play of athletes who incur different injuries or exacerbation of symptoms of persistent ailments, see Sports and Exercise for Children with Chronic Health Conditions: Guidelines for Participation from Leading Pediatric Authorities (Goldberg, 1995), Care of the Young Athlete (Sullivan and Anderson, 2000), and Principles and Practice of Primary Care Sports Medicine (Garrett et al, 2001). Form is commonly related to appearance, which is why aesthetics often plays an important position in cosmetic surgery. Although all surgeons restore perform to some extent, cosmetic surgery emphasizes features that improve high quality of life, corresponding to eating, talking, self-confidence, and social interactions. Patients with craniofacial anomalies, for example, might find a way to eat and breathe, however because one of the primary capabilities of the face is to appear to be a face, such individuals often suffer some vital isolation and social nervousness. Because many deformities impression both function and look, issues encountered in pediatric cosmetic surgery may be distressing to the affected person and household alike. The face is so central to human identification and recognition that craniofacial abnormalities can have an result on bonding, integration and socialization from infancy onward. As children learn to recognize self and non-self, obvious differences can result in teasing and struggling that can affect normal psychological improvement. Many of pediatric anomalies are associated with more intensive problems or syndromes, making identification crucial for prognosis and prognosis. Additionally, children are particularly prone to trauma and different acquired abnormalities that require the surgeon to apply principles of reconstruction each for type and function, but in addition for progress. This chapter familiarizes the pediatrician or neonatologist with the more frequent pathologies of kind and performance that the pediatric plastic surgeon treats. It is necessary to educate parents that although improvements are the rule quite than the exception, the severity of the defect, variability in wound therapeutic, and the growth of the patient make the ultimate end result difficult to predict. Craniofacial Embryology Congenital anomalies are best understood from an embryologic perspective. At 4 weeks, the fetus has a transparent cephalic/caudal axis and differentiated endoderm, mesoderm, and ectoderm. On both facet of the neural tube, the paraxial mesoderm divides into segmented tissue blocks referred to as somitomeres cephalically and somites from the occiput caudally, which ultimately type the bones of the neurocranium, or protective vault of the mind. Simultaneously, mesenchymal differentiation of neural crest cells participates within the formation of the viscerocranium, or the facial skeleton. The neurocranium consists of plates that ultimately turn into the grownup frontal, occipital, sphenoid, ethmoid, paired temporal, and paired parietal bones. They are separated by sutures and fontanelles that serve two primary functions: (1) to permit molding of the top as it passes through the start canal in parturition, and (2) to enable speedy enhance of brain quantity, which doubles in the first 6 months of life and once more by 2 years old. Anteriorly, the sagittal suture becomes anterior fontanelle where it intersects the paired coronal sutures that separate the frontal bones from the parietal bones. Posteriorly, the sagittal suture turns into the posterior fontanelle the place it meets the indirect L-shaped lambdoid sutures. Finally, the metopic suture runs longitudinally between the 2 paired frontal bones. Closure of the posterior fontanelle occurs inside the first 6 months of life, whereas the anterior fontanelle closes between 12 and 18 months old. The metopic suture closes at about 7 months old, and it completely fuses such that the grownup frontal bone has no proof of a former metopic suture. The sagittal and coronal sutures are subsequent to fuse, in a posterior-to-anterolateral course. Prenatal or postnatal untimely fusion is called craniosynostosis, which causes irregular cranium form by proscribing development within the direction of the fusion, and can lead to irregular intracranial strain because the brain grows towards a fixed restriction. The facial skeleton, or viscerocranium, is supported on a scaffold of 14 bones: the vomer; the mandible; and the paired nasal, maxilla, lacrimal, zygoma, palatal, and inferior nasal concha. By the tip of the fourth gestational week, the neural crest�derived mesenchyme differentiates to type three facial prominences: the maxillary, mandibular, and frontonasal. Over the course of the next 2 weeks, migration and fusion end result within the sculpture of the facial options supported by the underlying bony face. The frontal/nasal prominence gives rise to the brow, bridge of the nostril, and medial and lateral nasal prominences that additional outline the decrease nose. Likewise, human speech is complicated and shared by no different creature, and thus palate and speech surgery are also inside the identical subject. On the other hand, all animals share the frequent inside structures and capabilities concerned with hearing and ear drainage, nasal drainage, airway, sight, and mastication. The exterior shapes of the ear, nostril, or lips are clearly the realm of the plastic surgeon. This section divides the craniofacial area into higher third, middle third, and decrease third. The upper third offers with abnormalities of the skull and forehead, including deformational plagiocephaly, and each nonsyndromic and syndromic craniosynostosis. A aspect of the higher lip, and the mandibular prominence develops into the decrease lip. Abnormal migration, fusion, or disruption of established events during this cascade ends in anomalies. Cleft Lip, Nose, and Palate Cleft lip, nostril, and palate are the most frequent presentations of orofacial clefts, which are the most common congenital anomalies in the United States, estimated to be 1 in 590 reside births annually (Basseri et al, 2011; Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, 2006; Parker et al, 2010) (Table 23. Approximately 1 in 700 people within the United States is affected, or about 15,000 reside births per 12 months. Although the cleft could also be a part of an identifiable syndrome, it extra commonly happens as a solitary nonsyndromic defect. Facial clefting is incessantly categorized into cleft lip with or without cleft palate and the isolated cleft palate. Epidemiologically, a distinction is notable between the two with respect to incidence, race, and sex.
Buy generic viagra jelly 100 mg
Loperamide erectile dysfunction drugs kamagra viagra jelly 100 mg cheap overnight delivery, opiates (tincture of opium impotence quoad hoc meaning buy 100 mg viagra jelly with visa, belladonna, and opium capsules), and anticholinergic agents (diphenoxylate and atropine [Lomotil]) are the best nonspecific antidiarrheal agents. Pectin and kaolin preparations (bind toxins) and bismuth subsalicylate (antibacterial properties) are also helpful in symptomatic remedy of acute diarrhea. Octreotide is helpful in hormone-mediated secretory diarrhea but can be of profit in refractory diarrhea. Medications Empiric antibiotic remedy is just really helpful in patients with moderate-to-severe disease and associated systemic symptoms while awaiting stool cultures. Antibiotics can enhance the chance of hemolytic-uremic syndrome associated with Shiga toxin-producing E. Oral metronidazole is the remedy of alternative for gentle to moderate pseudomembranous colitis, whereas oral vancomycin can be utilized for resistant cases or intolerance to metronidazole (Am J Gastroenterol 2013;108:478). Fidaxomicin and fecal microbiota transplant symbolize newer therapy options (Am J Gastroenterol 2014;109:1065; see Chapter 14, Treatment of Infectious Diseases). Symptomatic amebiasis is treated with metronidazole, followed by paromomycin or iodoquinol to remove cysts. Therapy for giardiasis consists of metronidazole or tinidazole, with quinacrine representing an alternate agent. Stool studies (ova and parasites, culture), endoscopic biopsies, and serologic testing may help in diagnosis. Management consists of particular therapy if pathogens are identified; symptomatic measures could also be of benefit in idiopathic instances (Gastroenterol Clin North Am 2012;41:677). Etiology Recent modifications in bowel habits may suggest an natural trigger, whereas long-standing constipation is more prone to be functional. Female gender, older age, lack of exercise, low caloric consumption, low-fiber diet, and disorders that trigger ache on defecation. Colonic transit studies, anorectal manometry, and defecography are reserved for resistant cases and not utilizing a structural explanation after preliminary workup. However, fecal impactions ought to be resolved earlier than fiber supplementation is initiated. Osmotic cathartics include nonabsorbable salts or carbohydrates that cause water retention within the lumen of the colon. Sodium biphosphate (Fleet) enemas can be utilized for mild-to-moderate constipation and for bowel cleaning earlier than sigmoidoscopy; these ought to be averted in renal failure. Oil-based enemas (cottonseed, Colace, hypaque) can be utilized in refractory constipation. Subcutaneous methylnaltrexone, a selective peripherally performing -opioid receptor antagonist, is efficient for speedy relief of opioid-induced constipation (Am J Gastroenterol 2013;108:1566; N Engl J Med 2008;358:2332). Prucalopride is approved in Europe for persistent constipation (Aliment Pharmacol Ther 2010;32:1113). Patients might experience gentle belly discomfort, nausea, and vomiting with the bowel preparation. Nonabsorbable phosphate (Fleet phosphosoda, 20-45 mL with 10-24 oz liquid, taken the day before and morning of the procedure), a hyperosmotic solution, draws fluid into the intestine lumen and produces bowel actions in 0. It is also out there in pill form (Visicol or OsmoPrep, 32-40 tablets, taken at the fee of 3-4 tablets each 15 min with eight oz fluid). Phosphosoda can lead to severe dehydration, hyperphosphatemia, hypocalcemia, hypokalemia, hypernatremia, and acidosis. A dreaded rare complication is acute phosphate nephropathy, the place calcium phosphate deposits cause irreversible dysfunction of renal tubules leading to renal failure. Proximity of bowel preparation to procedure time improves effectiveness of cleansing and visualization through the procedure. Therefore, splitting bowel preparation into two doses may be useful, with one dose administered the evening prior and the second dose administered the morning of the procedure (Am J Gastroenterol 2012;107:1036; Am J Gastroenterol 2010;105:1319). Two-day bowel preparation is usually indicated in aged or debilitated people when conventional bowel preparation is contraindicated, not tolerated, or ineffective. Tap water enemas (1-L volume) can cleanse the distal colon when colonoscopy is indicated in sufferers with proximal bowel obstruction. Other options: Biofeedback remedy and sacral nerve stimulation could be effective for idiopathic constipation proof against medical remedy (Gut 2010;59:333). Extraesophageal manifestations can include cough, laryngitis, bronchial asthma, and dental erosions. Differential Diagnosis Other disorders that can lead to esophagitis embody: Eosinophilic esophagitis (EoE), characterized by eosinophilic infiltration of esophageal mucosa, is increasingly recognized as an etiology for foregut signs. Atopy (allergic rhinitis, eczema, asthma) is frequent, and food allergens may set off the method. First-line remedy for EoE contains topical steroids (swallowed fluticasone, 880-1760 g/d in two to four divided doses, or swallowed budesonide, 2 mg/d in two to four divided doses); prednisone is an alternate possibility if topical steroids are ineffective (Gastroenterology 2014;147:324). The presence of typical oral lesions (thrush, herpetic vesicles) could suggest an etiologic agent. Candida esophagitis is the most common esophageal an infection and typically happens within the setting of esophageal stasis, impaired cell-mediated immunity from immunosuppressive remedy. Endoscopic visualization of typical whitish plaques has close to 100% sensitivity for analysis. Empiric antifungal brokers are appropriate when concurrent oropharyngeal thrush is current, reserving endoscopy for nonresponse to therapy. Fluconazole 100-200 mg/d or itraconazole 200 mg/d for 14-21 days is really helpful as initial remedy for Candida esophagitis; nystatin (100,000 units/mL, 5 mL tid for 3 weeks) and clotrimazole troches (10 mg 4 to 5 occasions a day for 2 weeks) are alternatives for oropharyngeal candidiasis. For infections refractory to azoles, a short course of parenteral amphotericin B (0. The situation is usually self-limited in immunocompetent hosts (Curr Opin Gastroenterol 2008;24:496). Diagnostic Testing Endoscopy with biopsies is primarily indicated for avoiding misdiagnosis of alternate causes of esophageal symptoms. Alarm signs of dysphagia, odynophagia, early satiety, weight loss, or bleeding should immediate endoscopy (N Engl J Med 2008;359:1700). Ambulatory pH or pH impedance monitoring can be used to quantify esophageal acid publicity and reflux events and/or to assess symptom-reflux correlation in sufferers with ongoing symptoms despite acid suppression (especially if endoscopy is negative) or these with atypical symptoms. Baclofen, the prototype agent, reduces reflux occasions, however central unwanted effects could be limiting (Aliment Pharmacol Ther 2012;35:1036). Although fundoplication may provide better symptom control and quality of life within the quick time period, new postoperative symptoms and surgical failure can also happen (Surg Endosc 2011;25:2547). Elevated esophageal acid exposure and correlation of signs to reflux occasions on ambulatory pH monitoring predict a higher likelihood of a successful surgical outcome. Patients with medical treatment failures need careful analysis to decide whether signs are certainly associated to acid reflux earlier than surgical options are considered; these sufferers typically have other diagnoses including EoE, esophageal motor problems, visceral hypersensitivity, and useful heartburn. Potential issues of surgical procedure embody dysphagia, incapability to belch, gas-bloat syndrome, and bowel symptoms including flatulence, diarrhea, and stomach pain. Diffuse esophageal spasm is a spastic disorder characterized by premature, nonperistaltic contractions in the esophageal body (Gastroenterology 2011;141:469).
Buy cheap viagra jelly 100 mg online
This could produce a compression fracture of a lumbar vertebra or impotence pronunciation 100 mg viagra jelly order fast delivery, more doubtless erectile dysfunction doctors boise idaho order 100 mg viagra jelly mastercard, a shear fracture through the physique of the vertebra, in addition to the pedicle and spinous course of. An anteroposterior view of the backbone could present lateral displacement of a portion of the concerned vertebral body. Because the fulcrum of the damage is anterior the place the lap belt contacts the anterior abdominal wall, this injury produces a characteristic rectangular bruise and abrasion over the decrease abdomen. Associated intraabdominal injury, particularly a ruptured viscus, is widespread, and the resultant abdominal pain might overshadow that of the vertebral injury. B and C, Anteroposterior and lateral radiographs present a transverse fracture of the proximal fifth metatarsal. D, this boy caught his left foot on steps and fell along with his forefoot in plantar flexion, thereby incurring a transverse fracture of the distal portion of his second metatarsal. Adolescents involved in long-distance working or strolling could incur stress fractures of the shafts of the second and third metatarsals, which are the site of maximal stress and weight application during the push-off section of walking and working. These are often microfractures and may be radiographically invisible till healing turns into detectable 3 to four weeks after onset. Fortunately, increased use of three-point belts in again seats is lowering the frequency of this damage. Pelvic Avulsion Fractures Pelvic avulsion fractures are a phenomenon unique to adolescents, with a peak occurrence between 13 and 14 years old in ladies and 15 and 17 years old in boys. The incidence of those fractures is increasing with the rising participation of adolescents in competitive sports activities. Most end result from a sudden, violent muscular contraction whereas the ipsilateral extremity is held in a static position or when a muscle is abruptly lengthened throughout isometric contraction. They are probably to occur throughout sprinting and are because of the sudden, highly effective contraction of the hamstring muscular tissues when the hip is flexed and the knee prolonged. These, too, are inclined to happen during working, usually during an abrupt directional change. Some instances of anterior inferior/ superior iliac spine avulsions happen with kicking. At the time of injury, the patient experiences sudden pain at the website and issue strolling. On examination, level tenderness and swelling are famous over the concerned apophysis and weak point on active hip motion is seen secondary to pain. In viewing radiographs, it is necessary to compare the involved aspect with the conventional facet to detect displacement of the avulsed fragment and to keep away from mistaking a normal apophysis for a fracture. Treatment is conservative and consists of some days of mattress relaxation till the ache subsides, adopted by 2 to 6 weeks of crutch-walking, with a gradual improve in weight bearing as pain permits. Thereafter, cautious reconditioning facilitates a secure return to full activity, normally within 6 to 10 weeks. Pathologic Fractures Children with extreme osteopenia or osteoporosis, whether or not stemming from an inherited disorder or disuse secondary to neurologic or neuromuscular disease, are at considerably increased risk of incurring fractures as the outcomes of minor falls and even during routine bodily therapy exercises. Localized bone lesions, including these caused by osteomyelitis, tumors, or cysts, could cause localized cortical thinning as they expand. Examples of some of these circumstances and representative fractures are introduced in Chapter 6. This 14-year-old football participant sprinting for a landing fell on his abdomen and skilled sharp left hip pain. While running in gym class, this 15-year-old boy experienced the sudden onset of left hip ache and problem strolling. He had point tenderness over the anterior inferior iliac backbone and full range of hip movement but experienced pain on flexion and inside rotation. C, Another 15-year-old boy, who developed sudden onset of right hip ache and lack of ability to bear weight whereas kicking a soccer ball, has a big avulsion fracture of the anterior superior iliac spine (arrows). In scientific practice, the interstitial stress elevation should reach roughly 35 to forty five mm Hg for this to occur. Because the enclosed fascial boundary of the concerned muscle compartment is unyielding, hemorrhage or edema inside it might possibly cause interstitial stress to rise to such ranges, leading to muscle ischemia and neurovascular compromise. A displaced fracture of the proximal tibial metaphysis is the fracture most probably to be difficult by a compartment syndrome. Other fractures which are nicely documented to predispose to the event of this drawback include supracondylar humerus fractures and displaced forearm fractures. Passive movement of the terminal digits (fingers or toes) exacerbates the ache, and lively motion is avoided. In view of the reality that pulses might never be diminished or absent despite a full-blown, florid compartment syndrome, the diagnosis or determination to deal with should by no means be based mostly solely on the presence or absence of the peripheral pulses. Because scientific analysis may be difficult, especially in the uncooperative or comatose child, intracompartmental needle strain readings are beneficial. Emergency surgical decompression of the fascial covering of all concerned compartments is important to prevent irreversible muscle and nerve injury. After fascial decompression, reduction of pain and return of energetic muscle power are quick. This younger infant presented after a serious vehicle accident with what appeared to be a traumatic hip dislocation without an related fracture. B, the follow-up movie taken 2 weeks later reveals vigorous callus formation around the proximal femur and periosteal new bone formation both proximally and distally, thus, confirming the existence of related femoral fractures. Because of the elasticity and relatively greater power of the ligaments, forces that may have resulted in dislocation in an older adolescent have as a substitute triggered epiphyseal separation and displacement of the proximal humeral epiphysis on this prepubescent child. Hence, the emphasis in pediatric orthopedics is on examining the whole extremity and on including the joints proximal and distal to a suspected fracture website in the radiographic examination. It should also be remembered that in infants epiphyseal separations earlier than ossification can simulate dislocations. For example, separation of the distal humeral epiphysis in infancy presents a radiographic image suggestive of posterior displacement of the olecranon. The most frequent sites of dislocation in children are the hip, patellofemoral joint, and interphalangeal joints. In youngsters youthful than 5 years old, the softness of the acetabulum and relative ligamentous laxity enable dislocation with out the application of extreme force, and thus there could also be no related fractures. In older youngsters, violent pressure is required and dislocation is often accompanied by fractures of the femur and acetabulum. The youngster presents in extreme pain with the involved leg held in adduction, internally rotated and flexed. A place of extension, external rotation, and abduction is adopted by sufferers with the much less widespread anterior dislocation. A, In the anteroposterior view, the right femoral head appears to be displaced laterally and superiorly. Even in patients without an apparent related fracture, epiphyseal separation or avulsion of an acetabular fragment may have occurred. Prompt reduction is necessary, each to relieve ache and to scale back the danger of secondary avascular necrosis of the femoral head. Postreduction films are essential, because these usually tend to disclose the fact that an epiphyseal separation has occurred and tend to present incomplete discount if a radiolucent intraarticular fragment is present.
Diseases
- Scleroderma
- Epiphyseal dysplasia dysmorphism camptodactyly
- Say Meyer syndrome
- Vitamin D resistant rickets
- Brain cavernous angioma
- Phenobarbital embryopathy
- Catecholamine hypertension
- Hirschsprung disease
- Triple A syndrome
- Myoneurogastrointestinal encephalopathy syndrome

Purchase 100 mg viagra jelly visa
In truth diabetes and erectile dysfunction relationship viagra jelly 100 mg amex, compliance charges with the "Safe to Sleep" campaign correlate with the incidence of deformational plagiocephaly erectile dysfunction kidney viagra jelly 100 mg buy mastercard, with the white inhabitants affected essentially the most, followed by African Americans and Hispanics. Other associated components are male gender, multiparity, and torticollis, of which the latter is associated with up to 20% of infants with deformational plagiocephaly. Right-sided deformational plagiocephaly is more widespread, probably because of right-handed mothers holding infants in a Positional molding right-side-down position to nurse, causing stress and flattening of the right occiput. Regardless of the aspect, as quickly as a preferential supine place develops, it turns into recurring and tough to appropriate. History normally confirms a traditional head at delivery and bought asymmetry that worsens with time. As the occiput becomes flatter, up to 80% of infants will have anterior displacement of the ipsilateral forehead, with concomitant improve within the peak of the ipsilateral palpebral fissure, anterior displacement of the ipsilateral ear, and anterior displacement of the ipsilateral cheek, which could be seen from the anterior view. Posteriorly, the mastoid skull bases should be symmetric; in any other case, there can be suspicion for a true unilateral lambdoid synostosis, described later. Whenever not sleeping, infants should be positioned prone ("tummy time") to decrease preferential supine positioning and to enhance shoulder girdle energy. Changing the place of stimuli within the crib can also affect the toddler to turn to a different side. Although a rolled-up towel or foam pinned to the clothes on one aspect will stop the toddler from sleeping on that facet, care should be exercised to avoid materials in cribs that pose risks to the sleeping toddler. Before 10 months old, an orthotic helmet worn 23 or extra hours per day permits the malleable infant cranium to develop into the shape of the symmetric helmet. Infants are usually monitored each 2 to three months for contour and neurologic development. In cases of syndromic craniosynostosis and midface hypoplasia, sufferers also needs to be routinely evaluated for midface retrusion causing airway obstruction, obstructive sleep apnea and exposure keratopathy. Treatment normally occurs earlier than 12 months old, whereas the cranium is comparatively malleable and the dura can stimulate osteogenesis. Surgery consists of a bicoronal scalp incision to expose the calvarium; the plastic surgeon then draws the outlines of the bony items to make, and the neurosurgeon then elevates the pieces off the brain. When the deformity extends to the supraorbital rim, the elevation of the fronto-orbital bar for reconstruction adds appreciable length to the operation as a outcome of each the mind and globes have to be protected. The plastic surgeon then reassembles the cranium items with absorbable plates, screws, and sutures to reshape the pinnacle. Regardless of remedy, patients need to be monitored postoperatively at least yearly, for neurologic, ophthalmologic, and developmental modifications, and for recurrence of craniofacial deformities. Nonsyndromic, Simple Craniosynostoses Up to 70% of straightforward, isolated craniosynostoses occur sporadically. Autosomal dominant and recessive familial patterns have been identified in 8% of cases. If one mother or father and child are affected, subsequent pregnancies are quoted to have a 50% incidence risk. Simple sagittal synostosis is probably the most generally encountered easy craniosynostosis, representing 57% of circumstances. Sagittal Synostosis Sagittal synostosis, the premature fusion of the sagittal suture, leads to elevated anteroposterior length and biparietal narrowing, which is named scaphocephaly. Isolated nonsyndromic sagittal synostosis is the commonest type of craniosynostosis. Sagittal suture synostosis can vary from predominantly anterior fusion, to predominantly posterior fusion, to complete fusion, inflicting barely different cranium shapes. Isolated anterior sagittal suture fusion will manifest frontal bossing, whereas posterior sagittal suture fusion will exhibit occipital bossing. Bossing of both the frontal and occipital domains with related biparietal narrowing outcomes from full fusion of the suture. A ridged sagittal suture may be palpable as discussed previously, but intracranial and ophthalmic dangers are low. The objectives of restore are therefore appearance-related, to scale back the anterior and posterior prominences whereas widening the biparietal dimension. Metopic Synostosis the metopic suture is the primary cranial suture to fuse, sometimes at about 7 months old. Significantly untimely fusion leads the Skull Craniosynostosis is outlined as premature closing of the sutures between the cranial bones throughout growth, resulting in deformities of the skull. Primary craniosynostosis originates from pathology of the concerned suture, whereas secondary craniosynostosis outcomes from dysgenesis of the underlying brain that then misdirects cranial enlargement. The development abnormality brought on by untimely fusion of a particular suture results in a characteristic head form sample. So a sagittal craniosynostosis ends in irregular development parallel to the fused sagittal suture leading to anteroposterior elongation and temporal narrowing, leading to a scaphocephaly, or "boat-shaped head. The incidence of craniosynostosis is approximately 1 in 2500 stay births throughout ethnic populations however varies between genders depending on the sutures involved. In simple craniosynostosis, genetics and fetal environment could each play roles, as a result of twins and infants delivered from breech position have the next incidence. The genes concerned in lots of the syndromic craniosynostoses are recognized and are described later. Anterior (C), lateral (D), and vertex (E) views of the craniofacial skeleton of a child with sagittal synostosis. Metopic synostosis has an incidence of between 1: 2500 and 1: 15,000 births, accounting for 10% to 20% of isolated craniosynostoses. Physical examination exhibits the keel-shaped brow with hypotelorism, upward slanting of the eyelids laterally, and a triangular shape to the forehead and supraorbital ridge, each of that are retrusive. Although usually isolated, 8% to 15% of children affected with trigonocephaly will have related anomalies involving the extremities or the central nervous, cardiac, or genitourinary system. Anterior (C) and vertex (D) views of the craniofacial skeleton of a child with metopic synostosis. Severe form changes may be corrected by anterior cranial vault remodeling with reshaping of the triangular fronto-orbital rim. Families should be endorsed that a metopic ridge is nonpathologic and should be anticipated to turn into less distinguished with time. Nonsyndromic unilateral coronal synostosis has an estimated incidence of 1 in 2500 stay births and accounts for 15% to 30% of cases of craniosynostosis. Its etiology is unknown, but proposed causes embrace fetal head constraint, thyrotoxicosis, and certain vitamin deficiencies. Synostosis of a single coronal suture results in a widened ipsilateral palpebral fissure, an elevated and anteriorly positioned ipsilateral ear, nasal root deviation towards the affected suture, chin deviation away from the affected suture, and a superiorly and posteriorly displaced supraorbital rim and eyebrow known as the harlequin eye deformity. Posterior view of the craniofacial skeleton of a kid with left-sided lambdoid synostosis. Treatment of coronal synostosis contains anterior cranial enlargement with vault remodeling and fronto-orbital development. Some centers carry out suture craniectomy with helmet remedy, especially for the unicoronal coronal synostosis, where symmetry is tough to obtain. Lambdoid Synostosis Lambdoid synostosis may contain one or each of the lambdoid sutures and is the least frequent of the craniosynostoses.
Generic viagra jelly 100 mg with mastercard
A basic cutaneous discovering of Proteus syndrome is a particularly thick erectile dysfunction caused by hydrochlorothiazide viagra jelly 100 mg generic without a prescription, raised impotence in men over 60 best 100 mg viagra jelly, and deeply grooved lesion often recognized as a cerebriform connective tissue nevus. This pelvic x-ray of a young girl with Gorham-Stout syndrome demonstrates osteolysis of the best pelvic constructions. The dysfunction targets the neurologic, pulmonary, gastrointestinal, nasopharyngeal, and cutaneous methods. Telangiectasias are the cutaneous manifestations that have a propensity for the nostril, lips, oral cavity, and fingers and appear to improve with growing older. These lesions appear as pink spots with a spider leg look that blanch with palpation, then rapidly return when launched. Gene testing has allowed for genetic diagnosis and screening prior to medical illness presentation. It emphasizes that the systematic analysis of the kid with a vascular lesion serves as the primary mode of prognosis. Imaging is used often solely to clarify between overlapping classes of disease and preparation for possible intervention. Part 2: vascular tumours of intermediate malignancy and malignant tumours, Br J Dermatol 171:474�484, 2014. Part 1: benign vascular tumours aside from infantile hemangiomas, Br J Dermatol 171:466�473, 2014. Wassef M, Blei F, Adams D, et al: Vascular anomalies classification: recommendations from the International Society for the Study of Vascular Anomalies, Pediatrics 136(1):e203�e214, 2015. Classic locations of telangiectasia affecting the lips (A), tongue (B), and fingertips (C). There are often few of those lesions within the first twenty years of life, however they improve with age. Careful nutritional assessment, including dietary monitoring and simple anthropometric monitoring, continues to be important as a marker of basic health to acknowledge tendencies in undernutrition, overnutrition, and the recognition of both acute and persistent disease. Monitoring of nutrition continues to be important all through childhood and adolescence as dietary habits are established, to promote general wholesome habits that stay nicely past childhood and into adult life. From a world perspective, undernutrition and diarrheal illness trigger untold morbidity and mortality. In the developed world, dietary evaluation is at the forefront in each well-child care and the administration of continual illness. Gastrointestinal complaints are commonplace in each acute illness in addition to the presenting manifestations of major gastrointestinal ailments. Because a major function of the gastrointestinal system is to provide fluid, vitamins/ minerals, and the power requirements to sustain viability and growth, the interaction between gastroenterology and nutrition is readily apparent. However, for the needs of this chapter, diet and gastroenterology are divided into two sections, with a give consideration to the entities generally seen by pediatric major care physicians. Within the first 6 months, delivery weight usually doubles and by 1 12 months it triples, with size near doubling. As such, the traditional caloric and protein requirements for development are accordingly greater (Table eleven. The gasoline for this development is human breast milk or formulation which have been derived to simulate the main components of breast milk. Although generally thought of nutritionally replete, breast milk lacks substantial amounts of vitamin D and fluoride, requiring supplementation from a multivitamin. Low quantities of vitamin K stores at delivery and in breast milk have led to a regular apply of intramuscular vitamin K injection at delivery. Breast milk also incorporates a decrease quantity of iron, albeit in a bioavailable form, requiring extra supplementation by way of a multivitamin or strong meals as an toddler makes use of the iron shops obtained in utero and reaches a physiologic nadir in the second half of the first 12 months of life. Standard infant formulas do contain enough iron, vitamin K, and vitamin D and are nutritionally replete when diluted in fluoridated water. There has been a virtual explosion of the sorts of formulas out there for infant feeding. Basic Monitoring of Growth and Nutrition Growth evaluation continues to be commonplace in pediatric apply as each a surrogate for nutritional adequacy and basic well being status. Growth charts are the means by which to monitor simple anthropometric knowledge to achieve this goal. Nationally standardized progress charts, in use since 1977, have been up to date over time. These charts present development requirements that describe healthy progress beneath optimal circumstances, embrace longitudinal knowledge from zero to 24 months old, and are based mostly on the breast-fed infant. The up to date version uses weight for age, length/height for age, and occipital/frontal circumference for age. Despite this, the characteristics of development of a child over time could be a useful comparative measure of what could be thought of regular progress to precise growth. Growth charts are also obtainable for specialised populations, corresponding to infants with trisomy 21 and premature infants. Care should be taken when utilizing these progress charts, as a result of the numbers of patients in the pattern section are less than in the usual growth charts. Examples of this would include infants with end-stage liver disease and marked ascites or vascular malformations/ hypertrophy of an organ or appendage, which falsely elevates true body weight. For the great majority of infants and children, development charts are often adequate to assess general development. Normal Childhood/Adolescent Nutrition and Growth As an toddler reaches 12 months old, the caloric requirements essential for progress continue to diminish as the rate of development decreases 394 11 NutritionandGastroenterology 395 Table11. Obesity is the results of overnutrition and has grown to epidemic proportions within the United States and other developed nations. Undernutrition outcomes from insufficient consumption, absorption, or digestion of nutrients, or insufficient consumption for elevated metabolic needs. The Waterlow standards assess undernutrition by plotting weight for height, as a measure of current nutritional standing, and top for age, which reflects the chronicity of the malnutrition. A traditional classification of utmost protein energy malnutrition includes marasmus, kwashiorkor, and marasmic kwashiorkor. Marasmus, defined as predominantly caloric/energy deficiency, is characterized by marked emaciation; lack of subcutaneous fats and muscle; brittle, sparse hair; and poor nail growth. Diarrhea is common as intestinal cell turnover slows, leading to blunted intestinal villi and a secondary malabsorptive state. Secondary results of marasmus, corresponding to hypothermia and bradycardia, happen late in the scientific course. Kwashiorkor, then again, outcomes from a food plan rich in energy but missing protein. The youngster is often edematous, which turns into strikingly obvious after nutritional repletion.
Cheap viagra jelly 100 mg otc
The metaphyseal parts of long bones and the sub-epiphyseal portions of flat and irregular bones are the usual sites erectile dysfunction medication for high blood pressure cheap viagra jelly 100 mg line. Blunt trauma may be a predisposing factor constipation causes erectile dysfunction order viagra jelly 100 mg online, by manufacturing of small-vessel occlusion with secondary stasis, anoxia, and necrosis. Children with sickle hemoglobinopathies are particularly susceptible to hematogenous osteomyelitis as a end result of underlying vascular bone disease and asplenia. Spread from a contiguous focus of infection accounts for most remaining cases of osteomyelitis, similar to infections of fracture sites, surgical wounds and hardware, and puncture wounds, as well as extension of an infection from an adjoining web site of cellulitis or an abscess. Osteomyelitis may be additional subdivided into acute, subacute, and persistent varieties, according to duration of symptoms; the acute form is by far the commonest. The major clinical discovering in every form is localized bone pain, which is usually fixed, progressively extra extreme, and exacerbated by movement. The overlying delicate tissues might seem regular or may be warm, mildly swollen, and infrequently erythematous, however in contrast to cellulitis, surface findings are sometimes subtle and induration is uncommon. A, this 1-month-old introduced decreased movement of the left arm and distinguished swelling of the higher arm and shoulder. B, Swelling of the entire leg and foot with overlying erythremia is evident in this 2 12 -month-old toddler, who had fast extension of osteomyelitis of the tibia. Acute Osteomyelitis Acute Hematogenous Osteomyelitis Most sufferers with acute hematogenous osteomyelitis present inside 1 week of onset of signs. Infants younger than 6 months old typically current with out systemic indicators of infection but could have fever or a septic presentation. Initially, irritability and anorexia are distinguished, adopted by evidence of pain on movement or of decreased use of a limb (pseudoparalysis). Localized delicate tissue swelling and diffuse tenderness could develop, which might extend quickly to involve the complete extremity, reflecting speedy spread of infection within the bone. Careful attention must be given to joint examination because of the high risk of joint extension and secondary septic arthritis. A historical past of antecedent upper respiratory tract or skin an infection is current in over 50% of cases. Systemic symptoms consist primarily of fever and irritability in association with refusal to stroll, limp, or decreased use of an extremity. A small proportion current with extra severe systemic symptoms, together with chills, lethargy, irritability, anorexia, vomiting, and dehydration. At this age, children are sometimes unable to localize ache, however by statement they may be discovered to keep away from transferring the concerned extremity or to hold a particular joint in flexion persistently. Soft tissue swelling and warmth could also be noted overlying a metaphysis, but it could be delicate or absent in early instances or undetectable if the proximal femur is involved. Even with careful examination, focal tenderness could also be difficult to detect early in the course. Children older than 2 years old with acute osteomyelitis are generally febrile but hardly ever toxic. They usually tend to localize ache, and level tenderness is mostly easy to elicit. Unless sympathetic effusion has developed, the adjacent joint may be passively moved via its full vary of movement, although this exacerbates the ache. Osteomyelitis in websites apart from the lengthy bones of the extremities could be difficult. Although fever and an irregular gait are the most common presenting complaints, lower stomach and groin ache, hip or buttock pain, sciatica, and thigh pain (with swelling) can be prominent early complaints. Often, the preliminary medical image suggests appendicitis, pelvic abscess, or femoral osteomyelitis. A high degree of suspicion and cautious examination are essential to set up the prognosis. The onset of pain within the lower stomach somewhat than the periumbilical area, absence of gastrointestinal signs or rebound tenderness, and regular findings on rectal examination assist distinguish pelvic osteomyelitis from acute appendicitis. Furthermore, although most sufferers have ache on hip movement in a number of planes, range of movement is both regular or solely barely restricted, and with careful examination, point tenderness can usually be detected. Acute Osteomyelitis Due to Contiguous Spread Acute osteomyelitis ensuing from the contiguous spread of an infection must be suspected in sufferers with prior puncture wounds, deep lacerations, surgical incisions or hardware, open fractures, abscesses, or cellulitis who experience a sudden onset of increased pain on the website. This ache is perceived as deep, extreme, and constant and is aggravated by motion. Osteomyelitis due to extension of main delicate tissue an infection could current as worsening after a interval of preliminary enchancment or failure to response to antimicrobials. Diagnostic Methods in Acute Osteomyelitis Standard laboratory and radiographic research are of restricted use within the prognosis of acute osteomyelitis. These markers are useful in identifying an inflammatory process and for serial measurement to doc response to therapy. Plain radiographic changes lag behind the clinical manifestations and could be refined. The first noticeable radiographic change, often seen about 3 days after the onset of symptoms, is the presence of deep soft-tissue swelling. Subsequently, the swelling will increase, obliterating fascial planes, and extends to contain subcutaneous tissues. These gentle tissue modifications may be difficult to respect every time osteomyelitis entails vertebrae or pelvis; however, in instances of pelvic osteomyelitis, clouding of the obturator foramen, distortion of the fascial planes across the adjoining hip, and even displacement of the bladder may be detectable. If a sympathetic joint effusion is current or if rupture into the joint has occurred, joint space widening or bony displacement could additionally be evident. These modifications include periosteal elevation followed by focal proof of bone lysis and, subsequently, by sclerosis or new bone formation on the margins of the lytic lesion. Technetium scan supplies improved identification and localization of acute osteomyelitis, displaying abnormalities as early as 24 to 48 hours after symptom onset and revealing discrete areas of elevated uptake. The process is particularly useful as a diagnostic adjunct in instances of pelvic and vertebral osteomyelitis. Technetium scans are additionally helpful in delineating extra foci in the rare sufferers with a quantity of sites. Standard radiographs stay important in figuring out fractures and malignancies, which may simulate the looks of osteomyelitis on bone scans. Importantly, 5% to 20% of kids with acute osteomyelitis can have a false-negative bone scan in the course of the first few days. Fever, hip and thigh pain, and refusal to stroll have been the chief complaints on this 5-year-old baby with osteomyelitis of the proximal femur. On inspection, she lay nonetheless, holding the left leg externally rotated and flexed at the hip and knee. A, the primary noticeable change, occurring about three days after onset, is deep gentle tissue swelling, seen here adjoining to the metaphysis of the distal tibia on the left. B, In this neonate, a radiolucency is obvious in the proximal metaphysis of the best femur, which can be displaced upward and laterally.
Viagra jelly 100 mg purchase on line
C erectile dysfunction over 65 discount viagra jelly 100 mg overnight delivery, Thick-walled vesicles on an erythematous base were famous in this youngster venogenic erectile dysfunction treatment purchase 100 mg viagra jelly visa, who confirmed early findings of intraoral involvement. Grouped, thick-walled vesicles on an erythematous base which may be painful and tend to coalesce, ulcerate, and then crust are the typical traits of a herpetic whitlow. Lesions seem in crops and primarily contain areas of pores and skin presently or lately affected by eczema. Typically, they evolve to kind pustules, which rupture and kind crusts over the course of some days. However, the slower evolution of lesions, the tendency of such lesions to turn into hemorrhagic, their concentration in eczematous areas, and the persistence of fever and systemic symptoms for as lengthy as 1 week help to distinguish this disorder from varicella. Severity ranges from mild to fulminant and depends partly on the extent of the preceding dermatitis. When the world of involvement is large, fluid losses can be extreme and potentially fatal. A significant threat of secondary bacterial infection additionally exists, in contrast to uncomplicated herpetic infections. Fever, daylight, local trauma, menses, and emotional stress are recognized triggers, and since the mouth is the most important site of main infection, labial and perioral lesions (cold sores) are seen mostly. Many sufferers report a prodrome of localized burning together with stinging or itching earlier than the eruption of grouped vesicles. These vesicles comprise yellow, serous fluid and infrequently appear smaller and less thick-walled than primary lesions. Although fever and systemic symptoms are absent, regional nodes may be enlarged and tender. The localization of the lesions to a small space helps to distinguish them from these of herpes zoster. In its most typical type, infectious mononucleosis is characterised by fever, fatigue, pharyngitis, lymphadenopathy, splenomegaly, atypical lymphocytosis, and a positive heterophil antibody response. Primary herpes simplex infection in a toddler with underlying eczema produces crops of hemorrhagic vesiculopustular lesions restricted to areas of preexisting dermatitis, which then rupture and crust. Photophobia and edema of the eyelids and periorbital tissues may be famous in some sufferers. The acute part is usually heralded by a fever, which may show extensive day by day fluctuations. The sore throat tends to improve in severity over several days before abating and may be associated with significant dysphagia. Tonsillar and adenoidal enlargement can vary from delicate to marked, and the tonsillar surface may vary in appearance from certainly one of mild erythema to certainly one of extreme exudative irritation with palatal and uvular edema. The anterior cervical lymph nodes are routinely enlarged, and posterior cervical adenopathy is attribute. In traditional cases, the adenopathy becomes generalized toward the tip of the primary week. Splenomegaly develops in roughly 50% of sufferers in the second to third week of sickness; 10% have related hepatic enlargement. B, Severe pharyngotonsillitis is seen on this youngster, whose tonsils are markedly enlarged and covered with exudate. Lesions on his face are hemorrhagic and confluent as a outcome of prior irritation. Usually an erythematous maculopapular rubelliform rash, the exanthem can be morbilliform, scarlatiniform, urticarial, hemorrhagic, or even nodular. Rare manifestations or complications of mononucleosis embody pneumonitis with a pattern of a diffuse, atypical pneumonia; hematologic abnormalities, such as direct Coombs test�positive hemolytic anemia and thrombocytopenia; icteric hepatitis; neurologic disorders, similar to acute cerebellar ataxia, encephalitis, aseptic meningitis, myelitis, or Guillain-Barr� syndrome; and, not often, myocarditis and pericarditis. Neurologic and hepatic involvement or widely disseminated disease occasionally may be fulminant, resulting in demise, significantly for immunocompromised patients with lymphocyte dysfunction. Other uncommon issues embrace acute higher airway obstruction, ensuing from tonsillar and adenoidal hypertrophy and splenic rupture. The latter may occur spontaneously or as a result of minor trauma, repeated palpation, or the elevated intraabdominal pressure related to defecation. This is manifested by mouth respiratory, retractions with recumbency, and stertorous loud night time breathing and apnea during sleep. On occasion, headache, nausea, myalgias, and peripheral polyarthralgias (particularly in adolescent and younger grownup women) are reported. The rash begins on the face, with massive, bright red, erythematous patches appearing over both cheeks. These patches are warm and nontender and have circumscribed borders which are usually macular but could additionally be barely raised. The facial lesions start to fade on the next day, and a symmetrical, macular or barely raised, lacy, erythematous rash appears on the extensor surfaces of the extremities. Over the next day or so, the rash could unfold to the flexor surfaces, buttocks, and trunk. Studies have proven that the virus is transmitted primarily by respiratory secretions and that, after transmission, it replicates in purple blood cell precursors within the bone marrow. It then might cause a biphasic sickness, with fever and nonspecific signs accompanied by red blood cell suppression occurring approximately 1 week later, adopted by the appearance of the basic fifth disease exanthem 1 to 2 weeks thereafter. Measles (Rubeola) Measles is a extremely contagious, often extreme acute illness with a typical prodrome and mode of evolution. Prodromal symptoms include fever, malaise, dry (occasionally croupy) cough, coryza, and conjunctivitis with clear discharge and marked photophobia. From 1 to 2 days after onset of prodromal signs, a pathognomonic enanthem (Koplik spots) appears on the buccal mucosa. The lesions consist of tiny bluish-white dots surrounded by pink halos, which increase in number after which fade over a 2- to 3-day interval. The exanthem is seen first on day 3 or four, because the prodromal symptoms and fever peak in severity. It is a blotchy, erythematous, blanching, maculopapular eruption that appears on the hairline and spreads cephalocaudally over 3 days, in the end involving the palms and soles. Once generalized, the rash becomes confluent over proximal areas but remains discrete distally. The incubation interval for measles is 7�21 days, and patients are contagious from approximately four days before the looks of rash till about four days after. Morbidity is excessive and mortality not uncommon, particularly in children of creating international locations. Potential complications (resulting both from extension of the first an infection or from secondary invasion by bacterial pathogens) include otitis media (most frequently), pneumonia, obstructive laryngotracheitis, and acute encephalitis. Roseola Infantum (Human Herpesvirus 6, Exanthem Subitum) Roseola infantum is a febrile illness that primarily affects youngsters between 6 and 36 months old. The medical course begins abruptly with speedy temperature elevation, which sometimes precipitates a febrile seizure. Fever and irritability persist for about 72 hours, whereupon the fever abruptly subsides.