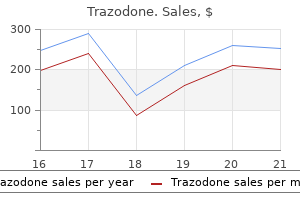
Trazodone dosages: 100 mg
Trazodone packs: 30 pills, 60 pills, 90 pills, 120 pills, 180 pills, 270 pills, 360 pills

Purchase trazodone 100 mg online
Thus medications quizlet discount trazodone 100 mg with mastercard, the spinal cord is the most important conduit of information from the skin treatment hyponatremia trazodone 100 mg buy on line, joints, and muscles to the mind, and vice versa. The neurons of the spinal gray matter begin the analysis of sensory info, play a important position in coordinating movements, and orchestrate easy reflexes (such as jerking away your foot from a thumbtack). Note that the telencephalon consists of two hemispheres, though only one is illustrated. The lateral ventricles are continuous with the third ventricle of the diencephalon. The aqueduct connects with the fourth ventricle that lies at the core of the hindbrain. You should see by now that discovering your way around the brain is easy if you can establish which elements of the ventricular system are in the neighborhood (Table 7. Even in the sophisticated human brain, the ventricular system holds the vital thing to understanding mind construction. You can see immediately that there are certainly many similarities but in addition some apparent differences. The diencephalon surrounds the third ventricle, the midbrain surrounds the cerebral aqueduct, and the cerebellum, pons, and medulla encompass the fourth ventricle. Notice how the pons swells beneath the cerebellum, and the way structurally elaborate the cerebellum is. The grooves in the floor of the cerebrum are known as sulci (singular: sulcus), and the bumps are called gyri (singular: gyrus). Remember, the thin sheet of neurons that lies slightly below the floor of the cerebrum is the cerebral cortex. Sulci and gyri result from the large growth of the surface area of the cerebral cortex throughout human fetal improvement. The adult human cortex, measuring about 1100 cm2, must fold and wrinkle to fit throughout the confines of the cranium. This increase in cortical surface space is among the "distortions" of the human brain. Clinical and experimental evidence indicates that the cortex is the seat of uniquely human reasoning and cognition. Without cerebral cortex, an individual would be blind, deaf, dumb, and unable to provoke voluntary movement. On the other hand, notice once more the expansion of the cerebral hemisphere within the human. Three different lobes (named after skull bones) also describe the elements of human cerebrum. The portion of the cerebrum lying just under the frontal bone of the forehead is identified as the frontal lobe. The deep central sulcus marks the posterior border of the frontal lobe, caudal to which lies the parietal lobe, beneath the parietal bone. Caudal to that, at the again of the cerebrum under the occipital bone, lies the occipital lobe. It is necessary to realize that, regardless of the disproportionate progress of the cerebrum, the human brain nonetheless follows the essential mammalian mind plan laid out during embryonic growth. First, the cell bodies of cortical neurons are always arranged in layers, or sheets, that usually lie parallel to the surface of the brain. In both species, the cortex lies slightly below the pia mater of the cerebral hemisphere, contains a molecular layer, and has pyramidal cells organized in layers. Third, a minimum of one cell layer accommodates pyramidal cells that emit giant dendrites, called apical dendrites, that extend up to layer I, where they kind multiple branches. Thus, we can say that the cerebral cortex has a attribute cytoarchitecture that distinguishes it, for example, from the nuclei of the basal telencephalon or the thalamus. This construction is called the hippocampus, which, despite its bends, has only a single cell layer. The olfactory cortex is separated by a sulcus, called the rhinal fissure, from another more elaborate kind of cortex that has many cell layers. In this section of a rat mind, the lateral ventricles lie between the neocortex and the hippocampus on each side. What area of mind stem is this, primarily based on the appearance of the fluid-filled space at its core Most neuroscientists are such neocortical chauvinists (ourselves included) that the time period cortex, if left unqualified, is usually supposed to discuss with the cerebral neocortex. Further dialogue of the hippocampus is reserved until later in this e-book, after we explore its position in the limbic system (Chapter 18) and in memory and studying (Chapters 24 and 25). Areas of Neocortex Just as cytoarchitecture can be used to distinguish the cerebral cortex from the basal telencephalon, and the neocortex from the olfactory cortex, it can be used to divide the neocortex up into totally different zones. This is precisely what the famous German neuroanatomist Korbinian Brodmann did firstly of the twentieth century. In this map, each space of cortex having a standard cytoarchitecture is given a number. Similarly, we can say that area 4 is motor cortex because neurons in this space project axons directly to the motor neurons of the ventral horn that command muscle tissue to contract. Notice that the different capabilities of these two areas are specified by their totally different connections. A downside that has fascinated neuroscientists since the time of Brodmann is how the neocortex has changed over the course of mammalian evolution. The floor area of the cortex varies tremendously among species; for example, a comparison of mouse, monkey, and human cortex reveals variations in measurement on the order of 1:one hundred:a thousand. Thus, we can conclude that the quantity of cortex has changed over the course of evolution, but not its primary structure. This cylinder, normally described as a neocortical column, accommodates on the order of 10,000 neurons and 100 million synapses (approximately 10,000 synapses per neuron). We want to understand the detailed wiring diagram of how these neurons connect with each other: the connectome of the neocortex. This is a tall order because synapses can be recognized with confidence solely utilizing electron microscopy, which requires very skinny (50 nm) sections of tissue. To give an thought of the magnitude of the challenge, think about the project that South African Nobel laureate Sidney Brenner and his collaborators conducted in the Laboratory of Molecular Biology at the National Institute for Medical Research at Mill Hill, in North London, England. Brenner was convinced that understanding the neural foundation of conduct required a circuit diagram, and to tackle this, he chose a easy organism, the 1 mm lengthy flatworm, Caenorhabditis elegans (usually abbreviated C. Despite this relative simplicity, the "mind of the worm," as they called their project, took over a dozen years to complete. Since the publication of this work in 1986, lots of the obstacles to reconstructing a synaptic wiring diagram have begun to yield to advances in know-how, together with automated sectioning of brain tissue for electron microscopy and computer-aided reconstruction of volumes of tissue from very skinny sections (Box 7. Detailed comparisons of cortical structure and function in living species with diverse evolutionary histories recommend that the primordial neocortex of our frequent mammalian ancestor consisted mainly of three kinds of cortex.
100 mg trazodone with visa
Garcia fed rats a sweet liquid medications bladder infections trazodone 100 mg buy generic line, and chapter 7 medications and older adults trazodone 100 mg order line, in some circumstances, he then gave them a drug that made them briefly really feel unwell. After even one such trial, rats that had obtained the drug avoided the candy stimulus forever. W Extensive research has proven that flavor aversion studying leads to a particularly sturdy form of associative reminiscence. It is best for food stimuli (taste and scent both contribute); it requires remarkably little expertise (as little as one trial); and it can final a really long time-more than 50 years in some people! For fashionable humans, this memory mechanism can backfire; many perfectly good fried clams have remained uneaten. Food aversion could be a more major problem for patients undergoing radiation or chemotherapy for most cancers, when the nausea induced by their treatments makes many meals unpalatable. On the other hand, taste aversion studying has additionally been used to forestall coyotes from stealing domestic sheep and to assist individuals cut back their dependence on alcohol and cigarettes. Then you might connect every receptor kind, by separate sets of axons, to neurons within the brain that additionally reply to only one particular taste. This concept is the labeled line hypothesis, and at first it appears simple and rational. At the beginning of the gustatory system-the taste receptor cells-something like labeled strains are used. Primary style axons are even much less specific than receptor cells, and most central taste neurons continue to be broadly responsive all the way into the cortex. In different words, the response of a single style cell is usually ambiguous in regards to the meals being tasted; the labels on the taste traces are unsure somewhat than distinct. Each receptor cell synapses onto a primary taste axon that additionally receives input from several different receptor cells in that papilla in addition to its neighbors. This signifies that one axon may mix the taste information from quite a few style cells. If one of those cells is usually delicate to bitter stimuli and one other to salt stimuli, then the axon will reply to salt and bitter. This sample continues into the mind: Neurons of the gustatory nucleus receive synapses from many axons of various style specificities, they usually could turn out to be much less selective for tastes than the primary taste axons. All of this mixing of style info would possibly seem like an inefficient method to design a coding system. The likely reply is a scheme that features options of roughly labeled lines and inhabitants coding, during which the responses of a lot of broadly tuned neurons, somewhat than a small number of exactly tuned neurons, are used to specify the properties of a particular stimulus, such as a taste. Population coding schemes seem to be used throughout the sensory and motor systems of the mind, as we will see in later chapters. Only with a big inhabitants of style cells, with different response patterns, can the mind distinguish between particular various tastes. The relevant population could even embody neurons activated by the olfactory, temperature, and textural features of a food; definitely, the coldness and creaminess of chocolate ice cream contribute to our ability to distinguish it from chocolate cake. It combines with taste to help us identify foods, and it increases our enjoyment of many of them. But it could also warn of doubtless dangerous substances (spoiled meat) or places (smoke-filled rooms). In olfaction, the warnings from dangerous smells could outweigh the advantages of fine smells; by some estimates, we will odor a number of hundred thousand substances, but only about 20% of them smell nice. Chemicals released by the physique, called pheromones, are important alerts for reproductive behaviors, and they can also be used to mark territories, establish individuals, and point out aggression or submission. The olfactory epithelium consists of a layer of olfactory receptor cells, supporting cells, and basal cells. Odorants dissolve within the mucus layer and make contact with the cilia of the olfactory cells. These dramatic outcomes are one of the best evidence yet that humans can talk with pheromones. Many animals use the accessory olfactory system to detect pheromones and mediate quite a lot of social behaviors involving mother, mating, territory, and food. It consists of separate chemically delicate areas in the nasal cavity, in particular the vomeronasal organ, which projects to the accessory olfactory bulb and from there provides enter to the hypothalamus. The scent of a lady may indeed be a supply of arousal for sexually experienced males, presumably due to realized associations. Considering the industrial implications of such a substance, we may be certain the search will continue. Each of dors can certainly emotions and arouse reminiscences, but are us has a particular set of odors that marks our identity as surely as our fingerprints or genes do. Bloodhounds have nice problem distinguishing between the smells of equivalent twins, but not between those of fraternal siblings. For some animals, odor id is important: When her lamb is born, the ewe establishes a long-term reminiscence of its particular odor and develops an enduring bond based mostly largely on olfactory cues. In a newly inseminated female mouse, the scent of a wierd male (but not the odor of her latest mate, which she remembers) will trigger an abortion of the being pregnant. The moms, in turn, can usually identify the odor of their own toddler from amongst several choices. About 30 years ago, researcher Martha McClintock reported that women who spend lots of time together. In 1998, McClintock and Kathleen Stern, working at the University of Chicago, found that odorless compounds from one group of ladies (the "donors") could affect the timing of the menstrual cycles of different women (the "recipients"). Body chemicals were collected by inserting cotton pads beneath the arms of the donors for no much less than 8 hours. Unlike taste receptor cells, olfactory receptors are real neurons, with axons of their very own that penetrate into the central nervous system. Supporting cells are just like glia; among other things, they help produce mucus. Olfactory receptors (similar to taste receptors) regularly grow, die, and regenerate, in a cycle that lasts about 4�8 weeks. In fact, olfactory receptor cells are one of the only a few forms of neurons within the nervous system which would possibly be frequently replaced throughout life. Sniffing brings air through the convoluted nasal passages, however only a small share of that air passes over the olfactory epithelium. The epithelium exudes a thin coating of mucus, which flows continuously and is changed about each 10 minutes. Chemical stimuli in the air, referred to as odorants, dissolve in the mucus layer earlier than they attain receptor cells. Mucus consists of a water base with dissolved mucopolysaccharides (long chains of sugars); quite lots of proteins, including antibodies, enzymes, and odorant binding proteins; and salts.
Trazodone 100 mg with visa
Cannon instructed this was prone to alternative medicine trazodone 100 mg quality characterize a homeostatic response of excitable cells to the lack of enter medicine 627 trazodone 100 mg cheap with mastercard. An analogous phenomenon happens in cortical neurons after manipulations of overall synaptic enter. But what does this gross adjustment of general synaptic strength do to the rigorously tuned patterns of synaptic weights that have stored reminiscences This adjustment of absolute synaptic effectiveness that preserves the relative distribution of synaptic weights is identified as synaptic scaling. With metaplasticity and scaling, the neuron keeps a lid on the roiling boil of ongoing synaptic plasticity. Proper neuronal function, experience-dependent shifts in selectivity, and studying and reminiscence all require the appropriate stability of synaptic change and stability. In most examples of synaptic plasticity, transmission is initially modified as a result of changing the number of phosphate teams which are attached to proteins within the synaptic membrane. Adding phosphate groups to a protein can change synaptic effectiveness and type a memory, however solely as lengthy as the phosphate teams stay attached to that protein. Phosphorylation as a long-term reminiscence consolidation mechanism is problematic for 2 reasons: 1. Most proteins in the mind have a lifespan of less than 2 weeks and are present process a continual means of substitute. Thus, we want to think about mechanisms that might convert what initially is a change in synaptic protein phosphorylation to a form that may final a lifetime. Regulatory Catalytic (a) Second messenger (Ca2+- calmodulin) Persistently Active Protein Kinases Phosphorylation of synaptic proteins, and reminiscence, could be maintained if the kinases, the enzymes that connect phosphate groups to proteins, had been made to stay "on" on a daily basis. Normally the kinases are tightly regulated and are "on" only in the presence of a second messenger. But what if learning changed these kinases so that they no longer required the second messenger Recent evidence means that some kinases can turn into impartial of their second messengers. Each subunit catalyzes the phosphorylation of substrate proteins in response to a rise in Ca2 -calmodulin. Normally, in the absence of the suitable second messenger, the knife is closed and the catalytic area is covered by the regulatory area. When the messenger is eliminated, the molecule usually snaps shut, and the kinase turns off again. The general idea that an autophosphorylating kinase may store information on the synapse, initially proposed by John Lisman at Brandeis University, known as the molecular change hypothesis. Excitement concerning the function of this protein kinase originates with the work of Todd Sacktor on the State University of New York Downstate Medical Center. These research reveal that if brain protein synthesis is inhibited at the time of coaching, the animals study usually but fail to bear in mind when tested days later. A deficit in long-term memory is also usually noticed if the inhibitors are injected shortly after coaching. However, the recollections turn out to be increasingly immune to the inhibition of protein synthesis as the interval between the coaching and the injection of inhibitor is increased. These findings point out a requirement for model new protein synthesis through the interval of memory consolidation, when short-term recollections are converted into long-term ones. As we discussed, the reminiscence is created in a single trial and may be measured by how a lot a rat avoids the placement the place it received a foot shock (usually the dark side of a field with two rooms separated by a door). These modifications, perhaps with the help of persistently lively kinases, work against the elements that might erase a memory (such as molecular turnover). But how do the proteins required for consolidating synaptic modifications and recollections find the modified synapses An answer is suggested by a intelligent series of experiments carried out collaboratively within the late Nineteen Nineties by Julietta Frey in Magdeburg, Germany, and Richard Morris in Edinburgh, Scotland. Frey and Morris asked if the newly synthesized proteins acted solely on the synapses whose activity triggered their synthesis. By varying the interval between the weak and powerful stimulation of the two inputs, Frey and Morris have been capable of determine that the tag lasts about 2 hours. This means of gene expression is regulated by transcription elements within the nucleus. Now, tasks that may take regular flies many trials to study might be remembered after a single coaching trial. A failure of memories to consolidate is a function of numerous mind issues in addition to the getting older process. The current understanding of how consolidation is regulated has spawned a new business centered on growing memory-enhancing medication. By analogy, think about the widespread use of such medication as Viagra launched to treat male erectile dysfunction. Although compounds have been found that increase reminiscence consolidation, their unwanted effects have up to now prevented their improvement into medication. As was the case for medicine that enhance athletic performance, the ethics of utilizing memory boosters within the absence of a transparent medical justification are certain to be hotly debated. How does the synapse make use of the well timed incidence of gene expression and the arrival of a new protein This illustration summarizes some of the structural modifications which were observed within the neocortex when mice are uncovered to new sensory environments which may be encoded as memory. Work on the invertebrate Aplysia has shown that some types of long-term (but not short-term) reminiscence can cause a doubling of the number of synapses made by some neurons! Do related structural adjustments occur within the mammalian nervous system after studying This is a difficult downside to solve experimentally because of the complexity of the mammalian brain and the distributed nature of reminiscence. One approach has been to compare mind structure in animals that have had ample opportunity to be taught with that of animals which have had little probability to be taught. For example, placing a laboratory rat in a "advanced" setting full of toys and playmates (other rats) has been shown to improve the variety of synapses per neuron within the occipital cortex by about 25%. It is necessary to acknowledge that there are limits to structural plasticity in the grownup mind. As we discussed in Chapter 23, massive adjustments in mind circuitry are typically confined to crucial durations of early life. Regardless of the species, brain location, and memory type, many of the underlying mechanisms seem to be universal. These momentary adjustments are converted to everlasting ones, and long-term recollections, by altering the construction of the synapse. In many types of memory, this entails new protein synthesis and the meeting of latest microcircuits. In both case, learning requires many of the similar mechanisms that have been used to refine mind circuitry throughout improvement. What is the most common cellular correlate of reminiscence formation within the cerebral cortex
Buy trazodone 100 mg
The chilly homogenization method was developed to overcome the challenges of the new homogenization methodology symptoms miscarriage 100 mg trazodone generic mastercard. This mixture is then cooled underneath dry ice or liquid nitrogen to ensure crystallization medicine in the middle ages order trazodone 100 mg overnight delivery, after which ground with an acceptable mill (eg, ball mill, jet mill, or mortar mill) to kind microparticles [104,105]. After milling, the microparticles shaped are dispersed in a cold surfactant resolution and homogenized at or below room temperature to yield nanoparticles. Lyophilization could be carried out to improve the steadiness of the shaped nanoparticles. For an efficient lyophilization course of, cryoprotectants (eg, mannitol, sucrose, and sorbitol) are added to shield the integrity of the nanoparticles through the freezedrying course of. Morphology and Particle Size Determination Here, microscopy is most frequently used to determine this. These microscopic strategies all give three-dimensional photographs of the nanoparticles. Dynamic gentle scattering can additionally be used to determine particle measurement and size distribution (polydispersity index) of nanoparticles. The outcomes are often Homogenization Method this contains two methods: the hot-melt homogenization approach for heat-stable medication, and the coldmelt homogenization method for heat-labile medicine. Particle size of drugs is decreased by impact, shear, cavitation, and turbulence [102]. Loading Capacity that is normally determined when preparing stable lipid nanoparticles. It is usually expressed as a share of the entrapped drug relative to the lipid phase (lipid and drug) [108]. Solubility of the drug within the lipid soften as well as polymorphic type of the lipid or chemical and bodily construction of the solid lipid matrix are a few of the elements affecting the loading capacity of a lipid matrix [109]. Swelling and subsequent diffusion of drug molecules out of the nanoparticle matrix. This mechanism or phenomenon is usually responsible for the "burst impact" experienced with some formulations. Thorough washing of the nanoparticles after preparation may prevent this in circumstances the place there are surface-bound drug molecules. Ex Vivo Evaluation and Use of Bioengineered Cornea In ex vivo studies, viable excised cornea from rabbit, pig, goat, or different mammals is used as the permeability barrier. Alternatively, a assemble of the cornea is bioengineered in the laboratory and used as the permeability barrier to assess ocular formulations [6,111]. Bioengineering of cornea is finished using stroma and epithelial cells obtained from donor cornea. Surface Charge or Zeta Potential the flexibility of nanoparticles to exist singly or in aggregates is a operate of their floor charge or zeta potential. Some zetasizers can measure both the floor cost and measurement of particles, thus performing a twin purpose [110]. In Vivo Evaluation the modified release properties of nanoparticles in addition to their small particle size make them helpful for delivering an enormous array of drugs, both oral and parenteral. The meant use of the drug and administration route will determine the animal species and mannequin to be used for in vivo analysis. Typical assays carried out embody pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic evaluations of administered medication, in addition to toxicity profiling of the administered nanoparticles normally because of the scale of those particles. Nanoparticles may be taken up by cells or move throughout biological membranes via completely different mechanisms (eg, passive diffusion, motion throughout tight junctions, or endocytosis). Nanoparticle characteristics corresponding to lipophilicity and floor charge affect passive diffusion throughout biological membranes [112e114]. These could possibly be helpful in figuring out the compatibility of excipients with drug and other substances as properly as figuring out the presence of polymorphs. Information on the ability of the formulated nanomedicines to retain the integrated drug might be obtained from these measurements. This raises the expectations of the pharmaceutical industries in drug growth for ophthalmology. Ocular nanomedicines might obtain noninvasive sustained drug release for eye problems in both anterior and posterior segments of the attention. While designing nanomedicines for the attention, a clear understanding of the complexities of the pathological conditions and physiological barriers in normal and diseased eyes In Vitro Determination this involves figuring out drug launch in simulated body fluids and utilizing synthetic membranes of various molecular weight cutoffs to mimic the barrier provided by the cornea. Usually, drug release from nanoparticles can happen through any of these three mechanisms: 1. An best nanomedicine should obtain an effective drug concentration on the goal tissue for an extended period of time whereas minimizing systemic publicity, and it must be each comfy and easy to use. One of the strategies to overcome the drawbacks of present nanoparticle supply techniques is to mix technologies as obtained in lipogelosomes, bioadhesives, and hybrid nanoparticles. This would enhance significantly ocular bioavailability of topically administered medicine. Many novel products are anticipated to appear within the field of ophthalmology within the near future. Lipid nanoparticulate drug supply techniques: A revolution in dosage type design and improvement. Skin (integument) is the biggest organ by each weight (10e20%) and floor space (approximately 1. The outermost layer is an dermis layer containing keratinocytes, melanocytes, Langerhans, and Merkel cells. The outermost layer is linked to the dermis layer (connective tissue) by way of the basement membrane. However, a dermis layer (sweat glands, hair follicles, nervous cells, lymph, and blood vessels) has been connected to the loose connective tissue and is rich in fat. It is a stratified squamous epithelium; its major cells are keratinocytes, that are concerned in keratin synthesis; and it includes five layers: stratum corneum, lucidum, granulosum, spinosum, and basale. Each of these layers, based on their particular cell distribution, has its own task. In truth, mature keratinocytes within the type of hexagonal and nonviable cornfield cells (corneocytes) are found in stratum corneum. Keratin contained in the corneocytes (10e30 layers) ends in the corneocyte absorbing three times its weight in water [2,4]. He found that each epithelial cells and connective tissue are essential for skin regeneration. During recent years, nanoscience approaches have been acknowledged as promising strategies to develop pores and skin substitutes to overcome obstacles in wound therapeutic, skin regeneration, and aging issues. In the "Skin Wound Regeneration" part, the wound-healing course of is mentioned in more detail.
Generic trazodone 100 mg amex
Perhaps the drug administration at the time of memory reactivation led to a reconsolidated memory with weakened emotional influence symptoms in spanish cheap trazodone 100 mg line. Note that on this case symptoms 5 days before your missed period trazodone 100 mg order overnight delivery, the propranolol therapy affected the emotional weight of the memory however not the declarative reminiscence itself. This extinction therapy within the mice is discovered to cut back or eliminate concern related to the chamber if the therapy is started in the future after the traumatic experience but not 30 days later. This enzyme, which switches neuroplasticity genes off within the nucleus of neurons (discussed in Chapter 25), was found to be inactive the day after the electrical shock however lively a month later. With the genes energetic and the traumatic memories revived by the loud sound, it was attainable to reconsolidate the memory in a much less fearful form. Effect of post-retrieval propranolol on psychophysiologic responding throughout subsequent script-driven traumatic imagery in post-traumatic stress dysfunction. Epigenetic priming of memory updating during reconsolidation to attenuate remote worry reminiscences. The first was the standard model described earlier, during which the rat learned to move as effectively as attainable when retrieving the food from every of the baited arms of the maze. In the second version, small lights had been illuminated above a quantity of arms containing food, and the unlit arms had no food. In this case, optimal efficiency meant that the animal stored returning to retrieve food from lit arms as lengthy as they have been lit, and averted arms that have been by no means lit. The "gentle" model of the duty was supposed to draw on procedural reminiscence because of the constant affiliation between the presence of meals and the illuminated lights. Performance on the 2 variations of the radial arm maze task have been affected in markedly alternative ways by two types of brain lesions. If the hippocampal system was broken (in this case, with a lesion to the fornix that sends hippocampal output), efficiency was degraded on the usual maze task but was relatively unaffected on the light version. Conversely, a lesion within the striatum impaired performance of the light task however had little impact on the usual task. Recordings produced from the rat striatum in other experiments showed that neural responses modified because the animals discovered a procedure related to a food reward. Over the levels of learning and mastering the maze, more cells responded to the beginning and the goal and fewer to the flip. When the rats first performed the duty (stage 1), the best percentage of neurons responded when the animals was the reward arm. However, in later phases of the experiment, as training and testing progressed, this percentage decreased considerably. As the rats mastered the process, increasingly extra neurons turned responsive firstly and completion of the task. Also, increasing numbers of neurons responded throughout more than one stage of the task. One attainable interpretation of those changes in response patterns is that they replicate the formation of a behavior for which the striatum codes a sequence of behaviors initiated within the T-maze state of affairs. However, think about one other task in which the animal repeatedly sees two visible stimuli, corresponding to a square and a cross, and should learn to associate a meals reward with only the cross. In monkeys, lesions that involve the striatum or connections to it have quite different effects from medial temporal lesions. But when the striatum is damaged, the animal is unable to type the habit of all the time retrieving food associated with one visual stimulus somewhat than another. Thus, there seem to be somewhat distinct anatomical systems for declarative memory and procedural memory, and behaviors corresponding to realized habits utilize the striatum. Based on repeated exposure to the combinations, patients needed to study to predict sun or rain by inferring the associations. In the primary task, patients saw one, two, or three out of four attainable cues in considered one of 14 possible combinations. For each affected person, the experimenter assigned different probabilities that varied cues had been related to solar or rain. By being informed when they guessed accurately or incorrectly concerning the predicted climate, the sufferers slowly built up an affiliation between the cues and the climate. The concept behind this task was that it draws on the formation of a stimulus�response habit. In the second task, declarative memory was tested by having sufferers reply multiple-choice questions about the appearance of the cues and the pc display. These results counsel that the striatum in humans could play a role in procedural reminiscence as part of a system distinct from the medial temporal system used for declarative reminiscence. We use working reminiscence to briefly maintain onto info, and the patterns of sensory input from a few of our experiences are assembled into permanent engrams. You realized the structure of the brain and are able to impress Aunt Tilly by making a sketch displaying the location of the medulla oblongata. Structures within the medial temporal lobe and diencephalon are important for reminiscence consolidation, and engrams are saved within the neocortex through interactions with the hippocampus and other constructions. Specifying exactly what every brain structure contributes to learning and reminiscence continues to problem researchers. We have seen that reminiscences may be classified based on length, the type of info saved, and the mind structures concerned. Early brain research relied on deciphering the results of mind lesions on amnesia. The distinct forms of reminiscence, and the truth that one kind can be disrupted without affecting others in amnesia, point out that a number of brain systems are used for reminiscence storage. More recent research makes use of human mind imaging and molecular genetic strategies to examine reminiscence formation and type out the temporal processes and a number of methods. There is even hope that one day there shall be a therapy to considerably cut back the deleterious consequences of traumatic memories. When we attempt to remember a telephone number, an interruption could make us forget, suggesting that reminiscences are initially held in a very fragile form. Long-term memory is much more strong; it can survive interruption, anesthesia, and the conventional bumps and traumas of life. If you attempt to recall how many windows there are in your own home by mentally strolling from room to room, are you using declarative memory, procedural memory, or each What sort of experiment would possibly you conduct to find the place within the brain that people use to hold a telephone quantity in mind Why did Lashley conclude that every one cortical areas contribute equally to learning and memory What proof is there that declarative and nondeclarative memory use distinctly different circuits The a number of trace model of reminiscence consolidation was proposed to cope with what concern(s) about the standard mannequin of reminiscence consolidation Hippocampalneocortical interactions in reminiscence formation, consolidation, and reconsolidation. As we noticed in Chapter 24, primary neuroscientific analysis is beginning to reply this question. As Hebb identified, reminiscences can result from subtle alterations in synapses, and these alterations can be extensively distributed within the mind. This insight helps narrow the search for a bodily foundation of reminiscence, synaptic modifications, however it also raises a dilemma.
Trazodone 100 mg without a prescription
From this point onward medications listed alphabetically trazodone 100 mg discount line, the somatic sensory system of 1 aspect of the brain is anxious with sensations originating from the opposite side of the body 20 medications that cause memory loss cheap trazodone 100 mg with visa. The axons of the dorsal column nuclei ascend inside a conspicuous white matter tract referred to as the medial lemniscus. Remember that nearly no sensory data goes directly into the neocortex without first synapsing in the thalamus (olfaction is the exception). It is tempting to assume that sensory data is simply transferred, unchanged, via nuclei within the brain stem and thalamus on its approach to the cortex, with the actual processing going down only in the cortex. In each dorsal column and thalamic nuclei, appreciable transformation of knowledge takes place. As a common rule, data is altered each time it passes by way of a set of synapses in the mind. In specific, inhibitory interactions between adjacent units of inputs in the dorsal column�medial lemniscal pathway improve the responses to tactile stimuli (Box 12. Neurons of each the thalamus and the dorsal column nuclei are additionally managed by input from the cerebral cortex. Somatic sensation of the face is supplied mostly by the big trigeminal nerves (cranial nerve V), which enter the mind at the pons (see Chapter 7). The sensory connections of the trigeminal nerve are analogous to those of the dorsal roots. The large-diameter sensory axons of the trigeminal nerve carry tactile info from pores and skin mechanoreceptors. One widespread transformation is the amplification of differences within the exercise of neighboring neurons, also identified as distinction enhancement. If all of the photoreceptors providing input to a ganglion cell are evenly illuminated, the cell hardly notices. Contrast enhancement is a general function of knowledge processing in sensory pathways, together with the somatic sensory system. One common mechanism underlying contrast enhancement is lateral inhibition, whereby neighboring cells inhibit one another. Dorsal root ganglion neurons lettered a by way of g relay data by way of excitatory synapses to dorsal column nucleus neurons A through G. All of the neurons fireplace with baseline rates of 5 spikes/sec, even within the absence of stimulation. This simple relay does nothing to improve the distinction between the more lively neuron, d, and the opposite neurons. The contrast in exercise between neuron D and its neighbors C and E, for instance, is 10 versus 5 spikes/sec. Calculate the exercise of each cell by multiplying the enter to every synapse by its synaptic gain, and then summing the impact of all of the synapses on the cell. The distinction in exercise between neuron D and its neighbors C and E is now 20 versus 0 spikes/sec. Somatosensory Cortex As with all other sensory methods, probably the most advanced ranges of somatosensory processing happen in the cerebral cortex. Rapidly adapting neurons D3 D2 a dense input from the thalamus; nonetheless, this area is concerned with the sense of physique place quite than touch. The projection from 3b to area 1 sends primarily texture information, whereas the projection to space 2 emphasizes size and shape. Small lesions in space 1 or 2 produce predictable deficiencies in discrimination of texture, size, and shape. In fact, the concept of the cortical column, so superbly elaborated by Hubel and Wiesel in visual cortex, was actually first described in somatic sensory cortex by Johns Hopkins University scientist Vernon Mountcastle. Electrical stimulation of the S1 surface can cause somatic sensations localized to a selected part of the body. Systematically, moving the stimulator around S1 will trigger the feeling to move throughout the body. American-Canadian neurosurgeon Wilder Penfield, working at McGill University from the Nineteen Thirties via the Nineteen Fifties, truly used this methodology to map the cortex of neurosurgical sufferers. The receptive fields of many S1 neurons produce an orderly map of the body on the cortex. Within the world of each finger representation are alternating columns of cells with rapidly adapting (green) and slowly adapting (red) sensory responses. Neurons in each area are most conscious of the elements of the body illustrated above them. We have seen previously that the mind has maps of different sensory surfaces, such as the light-sensitive retina within the eye (retinotopy) and the sound frequency-sensitive cochlea within the inner ear (tonotopy). Somatotopic maps generated by electrical stimulation and neuronal recording methods are similar. A somatotopic map is sometimes referred to as a homunculus (from the Latin diminutive of "man"; the little man in the brain). However, a recent study utilizing practical magnetic resonance imaging demonstrated that the penis is definitely represented in a less stunning place on the map: in an area between the stomach and the legs. Unfortunately, neither Penfield nor contemporary researchers have spent much time mapping the somatosensory maps of the female physique and its distinctive options (what some have referred to as the "hermunculus"). The relative size of cortex devoted to each body half is correlated with the density of sensory input obtained from that part. The inset shows the sample of barrels, laid out in five rows; examine with the five rows of vibrissae in the photograph in part a. The importance of contact information from our palms and fingers is apparent, but why throw so much cortical computing power on the mouth Two doubtless causes are that tactile sensations are necessary within the production of speech and that your lips and tongue (feeling, in addition to tasting) are the last line of protection when deciding if a morsel is delicious, nutritious meals, or something that could choke you, break your tooth, or chunk again. Remarkably, the sensory alerts from each vibrissa follicle go to one clearly defined cluster of S1 neurons; such clusters are referred to as barrels. The somatotopic map of rodent vibrissae is well seen in skinny sections of S1; the five rows of cortical barrels precisely match the 5 rows of facial vibrissae (Box 12. Studies of the "barrel cortex" in rats and mice have revealed much about the capabilities of sensory cortex. Just as the visual system builds a number of retinotopic maps, the somatic sensory system has a quantity of maps of the physique. Carefully compare the maps in areas 3b and 1; they map the identical elements of the body, actually in parallel alongside adjacent strips of cortex. Several completely different authors, in practically forgotten papers written over 50 years earlier, confirmed this sample of neurons; however that was earlier than recording was possible, so nobody knew the operate of the cortex. Van der Loos, I who taught neuroanatomy, gave me a place to work at Johns Hopkins throughout an elective interval. I ready specimens in a method so that I may precisely place them for slicing (I knew the place I usually received responses to stimulating the face) and reduce thicker sections than customary. About 10:00 on a shiny late spring morning, after struggling to mount the first sections on slides, I took them down a corridor to the darkish scholar histology lab, the place I had a microscope. There was no doubt about what I had seen; I instantly confirmed the slides to Van der Loos, who was the second person on the planet to know that whiskers are stamped in the mouse mind.
Diseases
- Staphylococcal infection
- Autonomic nervous system diseases
- Treponema infection
- Pulmonary branches stenosis
- Hunter Carpenter Mcdonald syndrome
- Epilepsia partialis continua
- Macleod Fraser syndrome
Purchase trazodone 100 mg mastercard
Based on my six-month stay in his laboratory treatment molluscum contagiosum trazodone 100 mg purchase online, Grundfest nominated me for a research place at the National Institutes of Health symptoms 28 weeks pregnant generic trazodone 100 mg mastercard. I realized that the problems of memory storage, as soon as the exclusive province of psychologists and psychoanalysts, were now approachable with the strategies of cell biology. I thought perhaps the nerve cells that participate in memory storage would have novel properties that would communicate to me of memory! Our work confirmed, surprisingly, that these cells from the area of the brain that encodes our dearest reminiscences perform pretty much the same means as other nerve cells in the brain. I further realized that to discover memory I would want to research not nerve cells per se, however nerve cells during a learning experience that leads to the formation of a memory. I became satisfied that to achieve bringing the ability of cell biology to bear on the study of studying and memory, I would first should take a really completely different approach, a reductionist approach. My first step needed to be to research not the most complex case however the easiest case of reminiscence storage-and to examine it in the simplest, most tractable experimental animal out there. While a reductionist strategy was within the realm of conventional biology, most investigators have been reluctant to apply it to psychological processes corresponding to learning and memory. From the outset it seemed to me that the mechanisms of reminiscence storage are so necessary for survival that they should have been conserved via evolution. Moreover, a molecular evaluation of learning, regardless of how simple the animal or the duty, was more likely to reveal those mechanisms. I needed to develop an experimental system in which a simple reflex conduct, controlled by a small variety of giant, accessible nerve cells, could possibly be modified by a easy type of learning like classical conditioning. After taking a look at crayfish, lobsters, worms, and flies, I settled on the marine snail Aplysia, which has extremely large nerve cells which may be conducive to recording. One of the two people in the world working on Aplysia at the moment was Ladislav Tauc, so I spent 1962�1963 in Paris with him, and I really have labored on Aplysia ever since. In the early Nineteen Sixties we had no frame of reference for finding out the biological foundation of reminiscence formation and storage. One was the combination subject approach, which assumed that info is stored within the bioelectric subject generated by the aggregate exercise of many neurons. This reflex undergoes sensitization (a simple form of learning) when a noxious stimulus is applied to the tail of the animal. I discovered that short-term memory outcomes from a transient strengthening of preexisting synaptic connections, because of the modification of preexisting proteins, whereas long-term memory results from a persistent strengthening of synaptic connections brought about by alterations in gene expression, the synthesis of new proteins, and the expansion of recent synaptic connections. A noxious stimulus to the tail activates serotonergic modulatory neurons that influence synaptic transmission on the sensory�motor synapse. Beginning in 1980, the insights and strategies of molecular biology enabled us to identify widespread mechanisms of short-term reminiscence in numerous animals and to explore how short-term reminiscence is converted to long-term reminiscence. Moreover, the dendrites of the motor neurons, which obtain the alerts from the sensory neurons, develop and remodel to accommodate the extra sensory enter. In the gill-withdrawal reflex of Aplysia, modifications in synaptic energy happen not only within the connections between sensory and motor neurons but also in the connections between sensory neurons and interneurons. Thus, even in a simple reflex, reminiscence appears to be distributed amongst a quantity of sites. Studies showed additional that a single synaptic connection is able to being modified in reverse ways by totally different types of learning and for various intervals of time, paralleling the different phases of memory. By 1980 my progress on Aplysia had been so heartening that I summoned up the braveness to return to the hippocampus. There I discovered, much as Charles Darwin may need predicted, that when nature finds a solution that works, it tends to maintain on to it. In different phrases, the identical common principles that govern short- and long-term reminiscence storage in easy animals additionally apply to complex ones. Recall from Chapter 24 that a major input to the hippocampus is the entorhinal cortex. The entorhinal cortex sends information to the hippocampus by method of a bundle of axons known as the perforant path. Information flows from the entorhinal cortex via the perforant path to the dentate gyrus. In such a brain slice preparation, fiber tracts could be stimulated electrically and synaptic responses recorded. Because cells in the slice may be noticed, stimulating and recording electrodes could be positioned with the precision previously obtainable only in invertebrate preparations. In 1973, an essential discovery was made within the hippocampus by Timothy Bliss and Terje L�mo, working collectively in Norway. Usually such a check stimulation is given each minute or so for 15�30 minutes to make sure that the baseline response is secure. The tetanus to input 1 (arrow) yields a potentiated response to stimulation of this input. This property, that only the lively inputs show the synaptic plasticity, is identified as input specificity. One exceptional feature of this plasticity is that it could be induced by a brief tetanus, lasting lower than a second, consisting of stimulation at frequencies nicely within the range of normal axon firing. No surprise this form of synaptic plasticity has attracted curiosity as a candidate mechanism for declarative memory. Initially, no single input is powerful sufficient to evoke an action potential in the postsynaptic neuron. In this manner, the sight of a duck could be associated with the quack of a duck (they usually happen on the same time), however by no means with the bark of a canine. Speaking of associations, remember the concept of a Hebb synapse, launched in Chapter 23, to account for features of visual improvement Excitatory synaptic transmission within the hippocampus is mediated by glutamate receptors. Donald Hebb proposed that every particular person synapse grows somewhat stronger when it efficiently participates within the firing of the postsynaptic neuron. Is there a role for postsynaptic action potentials in this "robust" depolarization However, action potentials are generated within the soma in response to depolarization of the membrane beyond threshold. Because this occurs far-off from the synapses located out on the dendritic tree, it was assumed for a time that the actual occurrence of the spike was not essential for the mechanism of synaptic potentiation. The important thing was the sturdy depolarization in the dendrite, because of summed synaptic currents, which, coincidentally, was additionally often sufficient to evoke a postsynaptic motion potential. This new attention resulted from the invention that action potentials generated in the soma can truly "back-propagate" into the dendrites of some cells. The well timed prevalence of the action potential is adequate to awaken these dormant channels by ejecting the Mg2. Recall from Chapters 5 and 6 that protein kinases regulate other proteins by phosphorylating (attaching phosphate teams to) them. Following the rise in postsynaptic [Ca2]i and the activation of the kinases, the molecular path that results in a potentiated synapse gets harder to follow. In specific, postsynaptic dendritic spines seem to bud and type new synaptic contacts with axons.

Trazodone 100 mg cheap with amex
These tiny blood vessels run down the stalk of the pituitary and department within the anterior lobe symptoms diabetes 100 mg trazodone cheap free shipping. This community of blood vessels is called the hypothalamo-pituitary portal circulation medicine x protein powder 100 mg trazodone order. Hypophysiotropic hormones secreted by hypothalamic neurons into the portal circulation journey downstream until they bind to particular receptors on the floor of pituitary cells. Activation of these receptors causes the pituitary cells to both secrete or cease secreting hormones into the overall circulation. Located just above the kidneys, the adrenal glands encompass two components, a shell referred to as the adrenal cortex and a center referred to as the adrenal medulla. In truth, a good stimulus for cortisol launch is stress, starting from physiological stress, such as a loss of blood; to optimistic emotional stimulation, such as falling in love; to psychological stress, corresponding to anxiousness over an upcoming exam. Parvocellular neurosecretory cells secrete hypophysiotropic hormones into specialized capillary beds of the hypothalamo-pituitary portal circulation. These hormones travel to the anterior lobe of the pituitary, the place they trigger or inhibit the release of pituitary hormones from secretory cells. Parvocellular neurosecretory cells that management the adrenal cortex decide whether or not a stimulus is stressful or not (as defined by the discharge of cortisol). Thus, cortisol is a lipophilic ("fat-loving") molecule, which dissolves simply in lipid membranes and readily crosses the blood-brain barrier. Physicians must be conscious of this feedback regulation when they prescribe prednisone, a synthetic type of cortisol. Cortisol can act immediately on hypothalamic neurons, in addition to on different neurons elsewhere in the mind. Among the symptoms of adrenal insufficiency are extreme abdominal ache and diarrhea, extraordinarily low blood pressure, and adjustments in temper and character. Addison acknowledged that one explanation for this constellation of symptoms is degeneration of the adrenal gland. Kennedy required a day by day routine of hormone alternative remedy to compensate for the loss of cortisol, a fact that was concealed during his presidency to defend his youthful and vigorous picture. The symptoms include speedy weight acquire, immune suppression, sleeplessness, memory impairment, and irritability. The physiological responses related to stress help protect the body and the brain from the risks that triggered the stress in the first place. Neuroscientists have solely begun to perceive the relationship between stress, the brain, and brain harm. Stress results in the discharge of the steroid hormone cortisol from the adrenal cortex. Cortisol travels to the mind through the bloodstream and binds to receptors within the cytoplasm of many neurons. The activated receptors journey to the cell nucleus, where they stimulate gene transcription and ultimately protein synthesis. Whatever the mechanism, presumably in the quick term cortisol makes the mind higher capable of cope with the stress-perhaps by helping it figure out a approach to keep away from it! Bruce McEwen and his colleagues at Rockefeller University, and Robert Sapolsky and his colleagues at Stanford University, have studied this query within the rat mind. They found that day by day injections of corticosterone (rat cortisol) for several weeks triggered dendrites to wither in plenty of neurons with corticosterone receptors. A related result was found when, as an alternative of every day hormone injections, the rats had been stressed daily. Baboons within the wild preserve a complex social hierarchy, and subordinate males avoid dominant males when they can. During one year when the baboon population boomed, native villagers caged many of the animals to forestall them from destroying their crops. Unable to escape the "top baboons" within the cages, many of the subordinate males subsequently died-not from wounds or malnutrition however apparently from severe and sustained stress-induced effects. They had gastric ulcers, colitis, enlarged adrenal glands, and intensive degeneration of neurons of their hippocampus. Indeed, research has clearly shown that chronic stress causes premature getting older of the mind. In humans, publicity to the horrors of combat, sexual abuse, and different forms of extreme violence can result in posttraumatic stress dysfunction, with signs of heightened anxiousness, reminiscence disturbances, and intrusive ideas. Imaging research have persistently discovered degenerative adjustments within the brains of victims, significantly within the hippocampus. Thus, we see that the discharge of hypophysiotropic hormones by cells within the secretory hypothalamus can produce widespread alterations within the physiology of each the physique and the mind (Box 15. From the Greek autonomia (roughly meaning "independence"), autonomic features are normally carried out mechanically, with out aware, voluntary control. You are faced with a traditional fight-or-flight situation, and your body reacts accordingly, even as your conscious thoughts frantically considers whether to blunder through it or beg off in humiliation. Within a couple of minutes, your sympathetic responses lower to low ranges, and the features of your parasympathetic division crank up again: Your coronary heart price slows and blood pressure drops, digestive features work more durable on breakfast, and also you stop sweating. Notice that you can be not have moved out of your chair all through this unpleasant occasion. The somatic motor system has a single operate: It innervates and commands skeletal muscle fibers. Both systems have upper motor neurons in the brain that send instructions to lower motor neurons, which actually innervate the target constructions exterior the nervous system. The sole output of the somatic motor system is the decrease motor neurons in the ventral horn of the spinal cord and the mind stem, which control skeletal muscle. The cell bodies of all autonomic lower motor neurons lie exterior the central nervous system, within cell clusters known as autonomic ganglia. Postganglionic neurons are pushed by preganglionic neurons, whose cell our bodies are within the spinal twine and brain stem. The sympathetic and parasympathetic divisions function in parallel, however they use pathways which might be fairly distinct in structure and of their neurotransmitter systems. Preganglionic axons of the sympathetic division emerge only from the center third of the spinal wire (thoracic and lumbar segments). The preganglionic neurons of the sympathetic division lie throughout the intermediolateral gray matter of the spinal wire. They ship their axons via the ventral roots to synapse on neurons in the ganglia of the sympathetic chain, which lies next to the spinal column, or within collateral ganglia found within the belly cavity. The preganglionic parasympathetic neurons, then again, sit within quite lots of mind stem nuclei and the decrease (sacral) spinal cord, and their axons travel within several cranial nerves in addition to the nerves of the sacral spinal cord. The physiological influences of the sympathetic and parasympathetic divisions typically oppose one another.

Cheap trazodone 100 mg online
Synapse Formation When the growth cone is available in contact with its goal 7 medications that cause incontinence discount 100 mg trazodone otc, a synapse is shaped medicine hunter best trazodone 100 mg. The first step seems to be the induction of a cluster of postsynaptic receptors underneath the site of nerve�muscle contact. This clustering is triggered by an interplay between proteins secreted by the growth cone and the goal membrane. The size of the "flock" of receptors is regulated by another molecule launched by the axon, referred to as neuregulin, which stimulates the receptor gene expression within the muscle cell. The interplay between axon and target happens in both instructions, and the induction of a presynaptic terminal additionally seems to contain proteins within the basal lamina. Growing axon 1 Filopodium Dendrite Synaptic vesicle 2 Presynaptic lively zone neurotransmitter release. Thus, though the ultimate maturation of synaptic construction might take a matter of weeks, rudimentary synaptic transmission seems very rapidly after contact is made. Besides mobilizing transmitter, Ca2 entry into the axon additionally triggers changes in the cytoskeleton that cause it to assume the looks of a presynaptic terminal and to adhere tightly to its postsynaptic companion. Microscopic imaging of neurons in tissue tradition reveals that filopodia are continually being shaped and retracted from neuronal dendrites seeking innervation. Synapse formation begins when such a dendritic protrusion reaches out and touches an axon that might be passing by. This interplay seems to cause a preassembled presynaptic active zone to be deposited on the web site of contact adopted by the recruitment of neurotransmitter receptors to the postsynaptic membrane. In addition, particular adhesion molecules are expressed by each presynaptic and postsynaptic membranes that serve to glue the companions collectively. A extended period of improvement follows, from earlier than delivery all the means in which through adolescence, during which these connections are refined. Contact results in the recruitment of synaptic vesicles and lively zone proteins to the presynaptic membrane. Although affected kids seem to be normal at start, signs progressively seem over the course of the first three years. Among the signs first observed by the parents of autistic children are a failure to communicate by 16 months of age, poor eye contact, an incapability to play with toys, an obsessive attachment to a toy or object, and a failure to smile. Although all people with an autism diagnosis will present these traits, the severity varies significantly from one person to the next, as does the association or "comorbidity" with other diagnosable disorders such as intellectual incapacity and seizures. Individuals at one end of the spectrum may by no means develop language and exhibit extreme cognitive impairment. At the opposite finish, people may develop as much as be socially awkward however intellectually gifted. In some circumstances, the gene mutations conferring threat for autism occur de novo, meaning that they occur sporadically both within the sperm or egg cells of the dad and mom. One risk issue for such sporadic mutations is superior parental age, particularly of fathers. The diversity of genetic etiologies partly explains why the symptoms vary so much from one individual to the subsequent. Imaging studies have proven that autistic youngsters additionally tend to have accelerated growth of the mind, both gray and white matter, after start. This discovering suggests the brains of autistic infants have too many neurons and too many axons, although changes in glia are also potential. Brain development is managed by balancing the genesis and destruction of cells, axons, and synapses and the proteins that comprise them. Neuroscientists hope that understanding how the mind usually becomes wired together will recommend therapies to appropriate the altered trajectory of mind progress in children in danger for autism. By knocking this gene out in mice and fruit flies, researchers have been in a place to determine how brains operate in a different way with this mutation. These studies have raised the tantalizing risk that the veil of autism and mental disability might be lifted in some instances with appropriate drug therapy. The growth of proper brain perform requires a cautious stability between the genesis and elimination of cells and synapses (Box 23. Cell Death Entire populations of neurons are eliminated during pathway formation by a course of generally known as programmed cell demise. Cell demise reflects competitors for trophic factors, life-sustaining substances which may be offered in limited portions by the goal cells. The enter neurons are believed to compete with each other for restricted portions of trophic elements produced by the goal neurons. Most of the receptors are neurotrophin-activated protein kinases, called trk receptors, that phosphorylate tyrosine residues on their substrate proteins (recall phosphorylation from Chapter 6). The essential discovery of cell death genes by Robert Horvitz at the Massachusetts Institute of Technology was acknowledged with the 2004 Nobel Prize. It is now understood that neurotrophins save neurons by switching off this genetic program. The expression of cell dying genes causes neurons to die by a process referred to as apoptosis, the systematic disassembly of the neuron. Apoptosis differs from necrosis, which is the accidental cell dying ensuing from damage to cells. Changes in Synaptic Capacity Each neuron can obtain on its dendrites and soma a finite variety of synapses. Throughout the nervous system, synaptic capability peaks early in development after which declines because the neurons mature. For instance, within the striate cortex of all species examined thus far, the synaptic capability of immature neurons exceeds that of grownup cells by about 50%. In different phrases, visual cortical neurons in the toddler mind obtain one-and-a-half times as many synapses as do the neurons in adults. Yale University scientists Jean-Pierre Bourgeois and Pasko Rakic performed an in depth research to tackle this question within the striate cortex of the macaque monkey. They found that synaptic capacity was remarkably fixed in the striate cortex from infancy till the time of puberty. However, in the course of the subsequent adolescent interval, synaptic capability declined sharply-by virtually 50% in simply over 2 years. A fast calculation revealed the next startling fact: the loss of synapses within the major visual cortex throughout adolescence happens at an average price of 5000 per second. Simply blocking a subset of receptors with -bungarotoxin also can stimulate synapse elimination. Silencing the exercise of the muscle fiber leads to a retention of polyneuronal innervation, while stimulation of the muscle accelerates the elimination of all but one input. The reply appears to be insufficient receptor activation in an otherwise lively muscle.
Discount trazodone 100 mg on line
At some synapses medicine 75 yellow order trazodone 100 mg on-line, the timing of pre- and postsynaptic actions potentials is a key variable medications for anxiety trazodone 100 mg buy with amex. The second kind, discovered a few years later, requires activation of G-protein coupled metabotropic glutamate receptors (mGluRs). This graph relates the change in synaptic strength to the relative timing difference. The uncommon circuitry of the cerebellar cortex instructed to David Marr on the University of Cambridge how this learning may occur. The output of the cerebellar cortex arises from massive neurons known as Purkinje cells, and these cells receive two converging inputs. Each Purkinje cell receives enter from a single climbing fiber that arises from a nucleus in the medulla known as the inferior olive. The climbing fiber synapses are very highly effective and at all times trigger the Purkinje cell to fireplace motion potentials. Parallel fibers arising from cerebellar granule cells present the second enter, and the organization could be very different. Each Purkinje cell receives weak parallel fiber synapses from as many as 100,000 different granule cells. Marr proposed that this uncommon convergence of parallel and climbing fiber inputs onto Purkinje cell dendrites serves motor studying. Masao Ito and his colleagues at the University of Tokyo tested this idea by pairing electrical stimulation of the climbing fibers with stimulation of the parallel fibers. For instance, within the nucleus accumbens, activation of postsynaptic mGluR5 stimulates the synthesis of endocannabinoids, which journey retrogradely to the presynaptic terminal and trigger a persistent melancholy of glutamate launch. Endocannabinoids in some neocortical pyramidal neurons are released in response to dendritic action potentials. We can speculate that these have evolved to optimize the contribution of synaptic plasticity to the functions of various brain circuits. The magnitude of the Purkinje cell response to stimulation of a "beam" of parallel fibers is monitored. Conditioning includes pairing parallel fiber stimulation with climbing fiber stimulation. On the other hand, when the postsynaptic neuron is strongly depolarized, the Mg2 block is displaced totally, and Ca2 floods into the postsynaptic neuron. These different types of Ca2 response selectively activate several varieties of enzymes. Instead of the kinases which may be activated by high [Ca2]i, modest and prolonged elevations in [Ca2]i activate protein phosphatases, enzymes that pluck phosphate groups off proteins. However, despite this outstanding turnover, synaptic transmission will stay stable as lengthy as one receptor is added every time one receptor is eliminated. The capacity of the postsynaptic membrane is determined by the scale of a scaffold of what has been termed slot proteins. Imagine the scaffold is like an egg carton, and the slot proteins type each of the egg cups. But as a end result of the scale of the carton is increased, there continues to be a web improve within the variety of eggs. Slices of human temporal cortex, removed during the course of surgical procedure to acquire access to deeper buildings, were maintained in vitro. It seems that plasticity at many synapses within the cerebral cortex may be ruled by similar rules and would possibly use comparable mechanisms. One method has been to insert stimulating and recording electrodes within the hippocampus and use these to monitor the state of synaptic transmission during learning. Because of the distributed nature of reminiscence, success with this approach required the utilization of a particularly strong kind of learning known as inhibitory avoidance. Animals of every kind (from flies to humans) will study to avoid the place they acquired the shock after only one trial (depending, after all, on the strength of the shock). To take a look at for the creation of a reminiscence trace, one can measure the time it takes for the rat to re-enter the darkish facet at varied time factors after the initial expertise. Tonegawa, who switched to neuroscience after winning the 1987 Nobel Prize for his analysis in immunology, acknowledged that molecules and conduct might be related by manipulating the genes of experimental animals. This method had already been tried with success in simple organisms like fruit flies (Box 25. Moreover, for the explanation that protein is missing in all cells that normally express it, pinpointing where and how a molecule contributes to studying may be difficult. For these reasons, researchers have tried to devise ways to limit their genetic manipulations to specific occasions and particular areas. It is even potential that some proteins are uniquely involved in learning and memory. Needless to say, we may gain considerable insight in regards to the molecular foundation of learning and learning problems if such hypothetical "memory molecules" might be identified. One way to determine a "memory protein" is to delete genes one by one and see if specific learning deficits outcome. This is exactly the technique that Seymour Benzer, Yadin Dudai, and their colleagues at the California Institute of Technology tried utilizing the fruit fly Drosophila melanogaster. Drosophila has long been a favourite species of geneticists, however one would possibly reasonably query to what extent a fruit fly learns. Fortunately, Drosophila can perform the identical methods that other invertebrate species like Aplysia have mastered. They demonstrate this memory after coaching by flying away when the odor is offered. The first mutant displaying a fairly particular studying deficit was described in 1976 and known as Dunce. Other memory-deficient mutants had been later described and given vegetable names, corresponding to Rutabaga and Cabbage. It turned out that each one three of those memory mutants lacked explicit enzymes in intracellular signaling pathways. In these early Drosophila studies, the mutations that were induced occurred at random, adopted by intensive screening, first to discover a studying deficit after which to decide exactly which gene was missing. More lately, however, genetic engineering strategies have made it attainable to make very particular deletions of recognized genes, not only in Drosophila but in addition in mammals. Experiments had already suggested that this enzyme is important for the induction of long-term potentiation. And, when examined within the Morris water maze, they had been discovered to have a extreme memory deficit. Thus, these mice had been memory mutants, similar to their distant cousins Dunce, Rutabaga, and Cabbage. Are we to conclude that the lacking proteins in these mutants are the elusive "memory molecules" We can only conclude, at current, that animals rising up with out these proteins are unusually poor learners. However, the research do underscore the crucial significance of specific second messenger pathways in translating a fleeting experience into a long-lasting reminiscence.