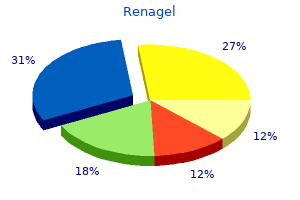
Renagel dosages: 800 mg, 400 mg
Renagel packs: 10 pills, 30 pills, 60 pills, 120 pills, 90 pills
Buy renagel 800 mg with amex
The affected person is normally an elderly gastritis diet 2013 renagel 400 mg purchase online, afebrile female gastritis symptoms wiki renagel 400 mg buy low cost, presumably with Gallstones and Benign Biliary Disease 279 a preceding historical past suggestive of chronic cholecystitis. The onset is insidious, with nausea, occasional vomiting, colicky belly pain, and a somewhat distended however flaccid stomach. A plain Xray of the stomach might present loops of distended bowel with fluid ranges and pos sibly the obstructing stone. Gas could additionally be seen within the bil iary tract and gallbladder, indicating a biliary fistula. Biliary leak age from the widespread bile duct may be treated by bile duct exploration and external bile drainage by Ttube insertion. In the absence of surgical experience, surgical lavage and drainage could possibly be adopted by endoscopic stenting (with or without sphincterotomy) or nasobiliary drainage. The intestinal obstruction must be relieved surgically with removing of the obstructing stone and closure of the bowel. The decision should be primarily based on the clini cal situation of the patient, the operative findings, and the experience of the working surgeon. Surgical mortality could additionally be 5�15%, partly associated to the process performed, and the underlying comor bidities on this broadly elderly group of sufferers [200]. Bile peritonitis Aetiology Relationships to malignant change Association between gallstones and most cancers of the gallbladder Population surveys have confirmed the wellrecognized link between gallstones and gallbladder carcinoma [203]. Association between gallstones, cholecystectomy and others cancers Patients with gallstones even have an increased risk of growing different malignancies, including bile duct, liver, pancreas, stomach, and small bowel most cancers [204�206]. The results from two of the cited studies relating to gallstones and colonic carcinoma are conflicting, one displaying an elevated threat [205] and the opposite not [206]. Postcholecystectomy from an aberrant bile duct, cystic duct stump, or bile duct injury. Usually leakage of bile from the anastomosis between the donor and recipient bile duct (see Chapter 37). Predisposing factors embody raised intraductal stress, calculous erosion, and necrosis of the duct wall second ary to vascular thrombosis [201,202]. Clinical image Bile peritonitis presents with acute onset of extreme basic ized stomach ache. Serum bilirubin rises and this is adopted by an increase in alkaline phosphatase ranges. The most up-to-date research were centered on the management of strictures Percutaneous imageguided drainage of the peritoneal fluid reveals bile, often contaminated. In sufferers present process liver transplantation, a bile duct stricture is doubtless considered one of the commonest late complica tions. These strictures could additionally be anastomotic or nonanas tomotic depending on the aetiology. Approximately 13% of sufferers undergoing cadaveric liver transplantation and 19% of those with a living donor transplant develop an anastomotic biliary stricture [210]. This might occur second ary to organ retrieval and preservation harm, or because of hepatic artery stenosis or thrombosis [211,212]. Following cadaveric transplantation, about 5% of patients develop ischaemic cholangiopathy [213] and 17% nonanastomotic strictures [214]. Symptoms and complications Patients with benign biliary strictures may be asympto matic and recognized following investigation of abnor mal liver operate tests, or as an incidental discovering on imaging. Most, however, have higher abdominal pain, jaundice, itching, cholangitis, and pyogenic abscess [216�218]. Since sufferers may be asymptomatic or have only nonspecific symptoms, a high index of suspicion is critical in these in danger. Chronic bile duct obstruc tion can result in hepatic fibrosis and secondary biliary cirrhosis [219]. Diagnosis Patients with a benign stricture normally have cholestatic liver operate tests. Although the his tory may favour a benign stricture, malignancy should always be borne in mind and, where applicable, a tissue Gallstones and Benign Biliary Disease 281 Biliary stricture Review danger factors and medical traits. Often repeat imaging after a few months is required to ensure that an underlying malignancy has not been ignored and all sufferers should undergo followup. Systematic reviews and metaanalyses have been car ried out for a number of approaches used to detect biliary malignancy. In the same examine, the addi tion of intraductal biopsy had an identical diagnostic take a look at accuracy to brush cytology [221]. Other new methods to differentiate benign from malignant biliary strictures are beneath evaluation [218,223]. Since the vast majority of tests have a low sensi tivity and high specificity, it sometimes requires repeated sampling of the stricture before cancer could be excluded. Additional tests similar to a liver biopsy could additionally be required in those that have undergone liver transplantation to rule out persistent graft rejection [217] or to diagnose unusual causes of a biliary stricture, for example, IgG4 associated illness. Treatment the treatment of benign biliary strictures relies upon upon their location and trigger. Some might be handled surgically, some endoscopically or percutaneously, and a few could have systemic medical remedy, for example, for IgG4 illness. Traditionally, surgical procedure has been the mainstay of treat ment for benign biliary strictures, in particular those because of iatrogenic bile duct injury. Bile duct accidents may be classified according to the Bismuth, Strasberg, or Stewart� Way system according to the placement and mechanism of injury [224]. Of these, the Bismuth and Strasberg classifi cations have been derived particularly to describe strictures following bile duct damage (Table 14. Recently, endoscopic methods have turn into the primary strategy for the remedy of strictures following bile duct injury [216,225] and liver transplantation [217,225]. The type of stent inserted after dilation of the benign stricture is a subject of much debate. Type 5 � Type 5 E5 Anastomotic strictures following biliary surgical procedure Choledochojejunostomy and hepaticojejunostomy could also be used to relieve obstructive jaundice because of a benign stricture. However, between 10 and 30% of sufferers with such anastomoses will develop another biliary�enteric anastomotic stricture and will want an extra process � surgical or radiological [231,232]. Of the recurrent strictures, twothirds occur within 2 years and 90% by 5 years [233]. Clinical features Restricturing of the anastomosis presents with fever, rigors, and jaundice. Cholangitis can be due to a recurrent stricture, intrahepatic stones, or ascending infection due to reflux up the bowel loop [234]. Investigations Investigations in the acute section present leucocytosis and irregular liver operate exams. If there has been prolonged partial obstruction with recurrent cholangitis, there could additionally be secondary scle rosing cholangitis.
400 mg renagel discount with mastercard
When bile flow is graphically plotted in opposition to bile salt secretion gastritis symptoms of renagel 800 mg purchase on line, bile saltindependent flow is the worth obtained when bile salt excretion is extrapolated to zero gastritis symptoms last buy renagel 400 mg without prescription. The bile saltdependent and unbiased bile circulate every con tribute about 225 mL/day and bicarbonate secretion about 150 mL/day. Bile ductules the bile ductules characterize a vast network within the liver connecting the canalicular community with the bile ducts downstream in the biliary tree. Bicarbonate makes bile extra alkaline and prevents the diffusion of the negatively charged bile salts via the membranes of bile duct epithelial cells [22]. Bicarbonate secretion is underneath the management of hormones similar to secretin and somatostatin. Gastrin, insulin, and endothelin inhibit secretin induced bicarbonaterich choleresis. Secretin additionally triggers the insertion of aqua porin 1 into the apical membrane of the cholangiocyte and this facilitates transport of water into bile. Aquaporin 4, in the basolateral membrane, subserves entry of water into the cell [23]. In a subset of kids with cystic fibrosis, this results in cholestatic liver illness [24]. Ursodeoxycholate is an efficient drug within the treatment of main biliary cholangitis (see Chapter 17). This could contribute to bile saltinduced harm of bile ducts and sur rounding stroma. Norursodeoxycholic acid is a recent drug that increases bicarbonate secretion [26]. Bile is concentrated in the gallbladder primarily by the absorption of water via water channels called aquaporins. Enterohepatic circulation Gallbladder contraction after a meal causes the release of bile salts into the gut and this helps lipase from the pancreas to digest lipids within the intestine that as 238 Chapter 13 monoand diglycerides could be absorbed. In the ileum, 95% of the entire circulating bile salt pool is reabsorbed and transported back to the liver. It could also be due to inherited transporter defects or, extra typically, illness of the bile ducts or liver. The defect or disease can happen at any stage between the basolateral (sinusoi dal) membrane of the hepatocyte and the ampulla of Vater. Morphologically, cholestasis is recognized from accumulation of biliary constituents in liver cells and bil iary passages. This depends on the completeness of the failure of bile production or the obstruction to bile circulate. The classification into hepatic and cholestatic causes of jaundice described earlier is somewhat artificial. Similarly, the genetic or acquired inability to secrete phospholipids on the hepatocanalicu lar degree causes the formation of toxic bile with bile salts in extra over phospholipids. This harm of the liver parenchyma is, to an extent, attributable to the buildup of bile salts. Experimental proof signifies that bile salts at con centrations in the 50�200 �mol/L range cause apoptosis, at ~200 �mol/L bile salts are proinflammatory, and at greater concentrations they cause necrosis and act as detergents. During extreme cholestasis, bile salts in serum attain concentrations of ~200 �mol/L. This is high enough to trigger harm to hepatocytes but the bile salt focus within the canalicular and ductular networks is in the millimolar vary, at which focus bile salts act as detergents and are extremely poisonous to the liver parenchyma. Disruption of the canalicular or ductular networks would cause severe liver toxicity. Cholestatic liver illnesses often run prolonged courses with years of mild cholestasis earlier than the development of liver cirrhosis. Adaptation of hepatocytes to elevated bile salt concentrations could underlie the chronic nature of these illnesses. This is why serum bilirubin is elevated during haemolysis regardless of the abundant capacity of the liver to conjugate and secrete bilirubin [5]. In chronic haemolysis, as in one of the inherited haemoglobinopathies, serum unconjugated bilirubin ranges may be elevated [32]. Neonatal jaundice is a form of prehepatic jaundice brought on by the mix of fast breakdown of fetal haemoglobin and immaturity of transport methods in the liver [33]. Jaundice in sickle cell anaemia and some other haemoglobin issues is caused by a mixture of elevated degradation of irregular haem and enhanced breakdown of erythrocytes in the spleen because of splenomegaly. Inherited haemoglobinopathies such as sickle cell disease, and thalassaemia and glucose6phosphate dehydrogenase deficiency are notably prevalent in Mediterranean international locations, the Middle East, subSaharan Africa, central India and areas in the New World (Caribbean, Brazil), into which international locations these traits have been launched by the slave commerce within the nineteenth century [32]. Disorders of bilirubin conjugation Gilbert syndrome Causes of isolated hyperbilirubinaemia Isolated hyperbilirubinaemia in prehepatic jaundice is caused by overproduction of bilirubin, lowered uptake of bilrubin into the liver, or decreased conjugation of biliru bin. Impaired conjugation as in Gilbert and Crigler�Najjar syndromes leads to unconjugated hyperbilirubinaemia. In hepatic and posthepatic (cholestatic) jaundice, the hepatic secretion of bilirubin is impaired and the liver enzymes are elevated; bilirubin in the circulation is mainly conjugated. This is unlucky, since a reliable check for conjugated bilirubin provides a easy check for the secretory perform of the liver. After fasting, serum bilirubin ranges in patients with Gilbert syndrome improve by about 7�10 �mol/L [39]. The mixture of a haemoglobin disorder (sickle cell anaemia, thalassaemia) and Gilbert syndrome can provide rise to extra extreme jaundice. Crigler�Najjar syndrome Crigler�Najjar syndrome is essentially the most severe bilirubin conjugation defect. In most sufferers in the Amish and Mennonite communi ties of Pennsylvania, the mutation is in exon 1; in other components of the world, the mutation may be wherever in one of the five exons [41]. Instead of differen tiating Crigler�Najjar syndrome into type 2 and kind 1, the phrases phenobarbitalresponsive and phenobarbital unresponsive Crigler�Najjar syndrome are more to the purpose. In phenobarbitalresponsive Crigler�Najjar syndrome, serum bilirubin ranges typically are between one hundred and 340 �mol/L and in phenobarbitalunresponsive Crigler�Najjar syndrome between 400 and 800 �mol/L. High levels of unconjugated bilirubin cause harm to the basal ganglia within the mind [42]. Safe bilirubin levels could be calculated from the bilirubin: albumin molar ratio and must be <0. A recommen dation from a trial report is to start phototherapy at bilirubin levels of 240�300 �mol/L and trade transfu sion at ranges of 310�380 �mol/L [42]. Exposure to light (blue facet of the visible spectrum but ultraviolet gentle must be avoided) converts unconju gated bilirubin within the capillaries of the skin to watersol uble photoproducts. In phenobarbitalunresponsive Crigler� Najjar syndrome, phototherapy is the only validated Jaundice and Cholestasis 241 type of remedy that helps to keep the serum bilirubin inside safe limits. Because of thickening of the skin and modifications in surfacebody mass ratio, phototherapy becomes much less efficient at greater age and socially unac ceptable. Eventually, people with Crigler�Najjar syndrome want a liver transplantation. However, with pro longed phototherapy, bilirubin precipitates within the liver and this will likely trigger mild liver function abnormalities, fibrosis, and (bilirubin) gallstones.
Renagel 800 mg generic free shipping
A review of 7000 biopsies [12] indicated that the transjugular approach provided samples of similar high quality to these from the percutaneous strategy gastritis root word renagel 400 mg cheap with amex. Providing four passes are performed gastritis hiv renagel 800 mg buy lowest price, biopsies are adequate to stage continual viral hepatitis [13,14]. The catheter is within the hepatic vein and the QuickCore needle is taking the liver biopsy. In continual liver disease, the blind approach yields sufficient diagnostic material 81% of the time, but this can be raised to 95% if a laparoscopic directed liver biopsy is used [16]. It is particularly useful for the analysis of focal lesions, although diagnostic accuracy may not be improved [17]. Cytological examination of the aspirate is beneficial for tumour typing [18] and this method will permit introduction of local therapies such as ethanol or acetic acid. After care Observations must be frequent (quarter hourly for 2 h, half hourly for two h, and hourly for 2 h) and analgesia ought to be prescribed [5]. During the puncture the patient may complain of a drawing feeling throughout the epigastrium. Afterwards some patients have a slight ache in the best facet for about 24 h and some complain of pain referred from the diaphragm to the best shoulder � this often indicates a capsular haematoma. Number of passes It has been demonstrated that taking a couple of core of liver at biopsy can enhance the diagnostic yield [19], but extra passes enhance the incidence of issues of percutaneous biopsy [8,20,21]. No studies have compared the newer (but extra expensive) springloaded Trucut needles. The usual indicators of issues following biopsy are extreme pain (either shoulder tip or abdominal) unrelieved by a single injection of pethidine (meperidine), hypotension, and tachycardia. The presence of all or a few of the indicators ought to prompt the physician to advocate the patient is observed in a single day and if ongoing, investigate and deal with. Bleeding could additionally be a lifethreatening event, particularly if not detected immediately, in order that prompt recognition is crucial (see later). Pleurisy and perihepatitis A friction rub brought on by fibrinous perihepatitis or pleurisy could also be heard on the next day. Malignancy, age, female sex, and variety of passes were the only predictable factors for bleeding. Bleeding might be associated to factors aside from clotting diathesis, such as the failure of mechanical compression of the needle tract by elastic tissue [23]. Bleeding from the puncture wound normally consists of a thin trickle lasting 10�60 s and the entire blood loss is Risks and issues Major and minor issues occur in as much as 6% of patients and can be fatal in 0. A sharp, white space of distinction is current throughout the parenchyma of the pseudoaneurysm. Serious haemorrhage is usually intraperitoneal but may be intrathoracic from an intercostal artery. The bleeding results from perforation of distended portal or hepatic veins or aberrant arteries. In some instances, a tear of the liver follows deep breathing in the course of the intercostal process. Perforation of the capsule with intraperitoneal haemorrhage may rarely observe transvenous biopsy, but this ought to be apparent on the time of biopsy [12]. Spontaneous cessation of bleeding can happen, but in any other case angiography adopted by transcatheter embolization is often profitable. Laparotomy is indicated if bleeding continues regardless of embolization, or when a big haematoma requires evacuation. The threshold for laparotomy may be lower in the transplant patient, in whom arterial embolization carries the chance of main bile duct injury. Intrahepatic haematomas At 2�4 h postbiopsy, intrahepatic haematomas are detected by ultrasound in only about 2% [24]. They may cause fever, rises in serum transaminases, a fall in haematocrit, and, if massive, right upper quadrant tenderness and an enlarging liver. It is marked by biliary colic with enlargement and tenderness of the liver and generally the gallbladder. Endoscopic drainage/sphincterotomy may be required to take away clotted blood from the biliary tree. The bile normally comes from the gallbladder, which may be in an unusual position, or from dilated bile ducts. Biopsy of the Liver 45 Infection Transient bacteraemia is comparatively frequent, particularly in sufferers with cholangitis. Sampling variability Liver biopsy histopathology is only a part of formulating a analysis in liver illness. Together with the other investigations, it may be an important part of the general image. Given the dangers of liver biopsy to the affected person, the knowledge out there within the biopsy must be maximized by insisting upon shut clinicopathological correlation. Some histopathological options, corresponding to cholestasis, steatosis, irritation, and fibrosis associated to chronic viral hepatitis, are often diffuse enough for reliable assessment offered that minimum standards of biopsy adequacy are acknowledged. Traditionally, a biopsy containing six portal tracts has been considered sufficient for prognosis [28]. Recently, a reproducible assessment of persistent viral hepatitis (the related studies have largely been involved with hepatitis C) has been thought-about as needing a pattern containing at least eleven full portal tracts. However, particular research are wanted to establish the adequacy of pattern size for every individual illness, and thus to set up the diploma of confidence that can be positioned on the actual sample. Puncture of different organs Puncture of organs such because the kidney or colon are a acknowledged, however fortunately uncommon, complication, and often are asymptomatic. Macronodular cirrhosis, and the increasing use of thinner needles are especially problematic. Misdiagnosis is often because of smallness of the sample, particularly failure to get hold of portal tracts, or the focal nature of the disease process, or in particular the inexperience of the interpreter. Interobserver variation is lessened by improving the adequacy of liver biopsy specimens [30]. The diagnostic yield could also be improved if three consecutive samples could be obtained by redirecting the biopsy needle through a single percutaneous entry site, but this unacceptably will increase the complication price [21]. Multiple passes are more safely performed with the transjugular route and indeed four passes present very enough specimens [13,14]. Fibrous tissue is increased beneath the capsule in operative biopsies and this will likely give a false impression of the liver as a complete. Operative biopsies may present artefactual change corresponding to patchy loss of glycogen, haemorrhage, polymorph infiltration, and even focal necrosis. These are presumably associated to the effects of trauma, circulatory changes, and hypoxia. This demonstrates: darkbrown elastic fibres; hepatitis B floor antigen in the hepatocyte cytoplasm as a uniform, finely brown materials; and copperassociated protein in lysosomes as black�brown granules in the periportal space in continual cholestasis and extra irregularly in Wilson illness. Biopsy material (at least three mm in length) could be removed from paraffin blocks and analysed retrospectively for iron and copper content material by atomic absorption spectrophotometry [32]. If iron overload is suspected, the unfixed specimen should not be placed in saline as this results in fast lack of iron.
Generic renagel 800 mg without a prescription
They have a crucial role in immune responses gastritis symptoms temperature 400 mg renagel order free shipping, recognizing and binding to particular antigens gastritis diet 7 day 400 mg renagel buy otc. There are 5 main immunoglobulin isotypes that differ in structure, target specificity, and distri bution: IgA, IgD, IgE, IgG, and IgM. The IgG and IgA isotypes may be further divided into subclasses based on additional, small differences within the amino acid heavy chain sequences: IgG1 to four, and IgA1 or 2. Predominant immunoglobulin isotypes and subclasses could present clues to the aetiology of liver disease: IgG. Generalized, polyclonal hypergammaglobinaemia happens in all forms of cirrhosis, in all probability reflecting nonspecific immune activation consequent to portosystemic shunt ing of gutderived antigens [72]. In the fed state, glycogen synthesis happens preferentially in perivenous hepato cytes; in the fasting or postabsorptive state, glucose launch by way of glycogenolysis and gluconeogenesis happens in periportal hepatocytes. Once glycogen shops are replenished, glucose could also be metabolized to fat or lac tate. Lactate is released into the systemic circulation and taken up by periportal cells as a substrate for glu coneogenesis. In fasted patients with cirrhosis, the contribution of carbohydrates to power production is reduced, whereas the contribution from fats is increased [73]. This may be attributable to impaired release of hepatic glucose or a decreased reserve of glycogen within the liver. After consuming a meal, nevertheless, cirrhotic sufferers, like management topics, make quick use of dietary carbohydrate. The enzyme is current in giant quantities in liver, coronary heart, skeletal muscle, kidneys, brain, pancreas, lungs, leucocytes, and erythrocytes. Elevated transaminases A disproportionate elevation of the transaminases sug gests hepatocellular harm. Increased serum aminotransferase Alcohol abuse Obesity Diabetes Haemochromatosis Chronic hepatitis Drug hepatotoxicity Heart failure Virus B and C markers Liver Function in Health and Disease 33 Wilson disease; pregnancyrelated liver disease; coeliac illness; thyroid disease; anorexia nervosa. The enzyme is ubiquitous however particularly abundant in proximal renal tubule, liver, pancreas (acinar cells and ductules), and intestine. Intrahepatic cholestasis could itself be classified as hepatocellular or biliary, primarily based on the principle site of injury. Haematology in liver disease Anaemia Anaemia is common in patients with liver disease. In patients with autoimmune liver disease, comorbid coeliac illness is a vital consideration. Folate and B12 deficiency might outcome from malnutrition, for instance in chronic alcoholism, or malabsorption, for instance from coeliac illness. They have diminished deformability, leading to entrapment and destruction in the spleen. This outcomes from hepatic congestion caused by right heart failure from any cause. Liver Function in Health and Disease 35 anaemia, hyperlipidaemia, unconjugated or mixed hyperbilirubinaemia, and alcoholic steatohepatitis [79]. In patients with hepatitis C, haemolysis might arise as a complication of remedy with ribavirin. Hypoplastic and aplastic anaemia Hypoplastic anaemia could result from persistent alcoholism owing to direct toxic effects of alcohol on erythrocyte precursors in the bone marrow. Thrombocytopenia Thrombocytopenia is a frequent discovering in sufferers with chronic liver illness. It may outcome from splenomegaly and splenic sequestration or decreased production of thrombopoietin. In continual alcoholism, the platelet count may be low owing to the direct toxic effects of alcohol on megakaryocytes in the bone marrow. In sufferers with liver illness and coagulopathy, it is important to think about vitamin K deficiency. Effects of ageing on the liver Liver weight, quantity, and liver blood move are lowered with age [81]. In wholesome people, the speed of hepatic regeneration is unaffected by age; in those with liver disease, regeneration slows with age. Structural adjustments within the hepatocyte embrace an increase in secondary lysosomes and residual our bodies, with a con comitant accumulation of lipofuscin. However, impaired mitochondrial enzyme exercise and defects in the respiratory chain are reported. Hepatic nitrogen clearance (conversion of amino nitrogen into urea nitrogen) is impaired with advancing age [83]. Firstpass metabolism of medication is reduced and could additionally be as a end result of lowered liver mass and hepatic blood flow rather than to alterations in the relevant enzyme systems [84]. Cholesterol saturation of bile increases with age owing to enhanced hepatic secretion of choles terol and decreased bile acid synthesis, and may account for the elevated threat of ldl cholesterol gallstones with age. Inherited disorders of bilirubin transport and conjugation: new insights into molecular mechanisms and penalties. Localization and genomic organization of a brand new hepatocellular natural anion transporting polypeptide. Alteration of the expression of adenosine triphosphatebinding cassette transporters associated with bile acid and ldl cholesterol transport in the rat liver and gut during cholestasis. Definition of a novel growth factordependent signal cascade for the suppression of bile acid biosynthesis. Characterization of bile acid transport mediated by multidrug resistance related protein 2 and bile salt export pump. Cellular 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 localization and upregulation of multidrug resistance associated protein three in hepatocytes and cholangiocytes throughout obstructive cholestasis in rat liver. Principles of hepatic natural anion transporter regulation during cholestasis, irritation and liver regeneration. Homozygous disruption of the murine mdr2 P glycoprotein gene leads to a whole absence of phospholipid from bile and to liver illness. Dietary lipid absorption, complicated lipid synthesis, and the intracellular packaging and secretion of chylomicrons. Role of lipoproteinX in the forty 41 42 43 forty four 45 46 47 48 forty nine 50 51 52 fifty three fifty four fifty five pathogenesis of cholestatic hypercholesterolemia. Uptake of lipoproteinX and its impact on 3hydroxy3 methylglutaryl coenzyme A reductase and chylomicron remnant removing in human fibroblasts, lymphocytes, and within the rat. Hyperviscosity syndrome in a hypercholesterolemic patient with primary biliary cirrhosis. Liver microsomal triglyceride switch protein is involved in hepatitis C liver steatosis. Ammonia and associated amino acids within the pathogenesis of brain edema in acute ischemic liver failure in rats. Systemic major carnitine deficiency: an overview of medical manifestations, analysis, and management.
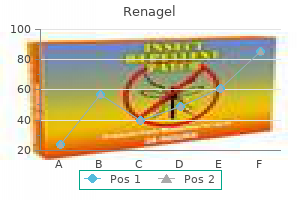
400 mg renagel cheap with visa
Lipids are insoluble in water; lipoproteins gastritis diet 02 400 mg renagel discount amex, being hydrophobic inside and hydrophilic outside gastritis diet karbo 400 mg renagel buy fast delivery, enable their transport in the plasma. Cholesterol is a constituent of cell membranes and a precursor of bile acids, vitamin D and steroid hormones. Some is obtained from intestinal absorption, reaching the liver in chylomicron remnants; most is synthesized, primarily in liver. Cholesterol syn thesis is elevated in bile duct obstruction, terminal ileal resection, biliary or intestinal lymph fistula, and with medicines. Synthesis is inhibited by bile acids, ldl cholesterol feeding, fasting, and drugs. Cholesterol in membranes and bile is current virtually completely as free cholesterol. Cholesterol esters are also found in plasma, liver, adrenal, and skin; these are both less polar and metabolically lively than free cholesterol. Free cholesterol is derived from intracellular synthesis and uptake of chylomicron remnants and lipoproteins from the circulation. Phospholipids include glycerol, one or more phos phoric acid groups, one other polar group similar to a heterogeneous base. Phospholipids are necessary constituents of cell membranes and participate in plenty of reactions. The most plentiful phospholipid in plasma and most cellular membranes is phosphatidyl choline (lecithin), which accounts for 66% of all phospholipids. Phospholipid secretion into bile is promoted by efflux of bile salts into the canalicular lumen, which induces vesiculation of the outer, canalicular membrane. Triglycerides have a spine of glycerol, with hydroxy teams esterified with fatty acids. Naturally occurring triglycerides contain quite so much of fatty acids, appearing as a store of energy and a method of vitality transport from small intestine and liver to peripheral tissues. Lipoproteins Lipoproteins, hydrophobic inside and hydrophilic out side, allow the transport of lipids in the plasma (choles terol being insoluble in water) and are essential for their circulation and metabolism. They are separated by differing density on ultracentrifugation, explaining the nomenclature. Dietary fats is absorbed from the small gut and included into chylomicrons [33,34]. Chylomicrons cross via the thoracic duct into the circulation where triglyceride is removed by lipoprotein lipases and utilized or saved in tissue. It contributes to elevated cholesterol levels, not only by advantage of its own cholesterol content, but also by rising hepatic cholesterol synthesis [39]. In cirrhosis, whole serum ldl cholesterol is often normal; low outcomes indicate malnutrition or hepatic decompensation. The aromatic amino acids and methionine are increased while the branchedchain amino acids are decreased. Amino acid metabolism Amino acids derived from the diet attain the liver by way of the portal vein, those from tissue breakdown through the hepatic artery. Specific Na+independent and Na+ dependent methods mediate transport of free amino acids across hepatocyte sinusoidal membranes [44]. Some are transaminated or deaminated to keto acids, then metabolized by quite a few pathways including the tricarboxylic acid cycle (Krebs�citric acid cycle). Patients with minimal liver dis ease additionally show modifications, significantly a discount in plasma proline, which is more probably to symbolize increased collagen manufacturing. In acute liver failure, generalized aminoaciduria involving notably cysteine and tyrosine carries a poor prognosis. Ammonia is a vital source of nitrogen for amino acid metabolism, protein synthesis and pH homeostasis. Most ammonia is generated throughout the gut, primarily by cleavage of urea to ammonia and carbonate by urease producing micro organism within the colon. In the liver, most ammonia is detoxified by the urea cycle, forming urea for renal elimination. A small quantity of ammonia is removed by glutamine synthetase, generating glutamine from ammonia and glutamate. Of observe, astrocytes additionally specific glutamine synthetase [46], protecting them from intracel lular accumulation of ammonia however leading to increased levels of glutamine when blood levels of ammonia are raised [47]. As glutamine is osmotically energetic, increased levels cause astrocyte swelling [48]. Increased blood ammonia results in greater ranges of ammonia within the brain, eventually inflicting astrocyte swelling, increased blood� mind barrier permeability, cerebral oedema, altered cerebral metabolism and neurotransmission [49]. Elevated ammonia ranges might outcome from impaired hepatic detoxing in acute liver failure, cirrhosis, or portosystemic shunting of any trigger. Other necessary causes embrace: Reye syndrome, a rare, acquired mitochondrial dysfunction characterized by quickly progressive encephalopathy and acute fatty liver [50], typically in youngsters recovering from viral infections. Features include hyperammonaemia, Liver Function in Health and Disease 29 hypoglycaemia, and coagulopathy. Inborn urea cycle disorders, rare hereditary problems ensuing from deficiencies of urea cycle enzymes [51]. Infants with extreme urea cycle problems are wholesome at start but develop progressive encephalopathy. In milder (or partial) deficiencies, hyperammonaemia and encephalopathy could additionally be triggered by sickness or stress at any age. Carnitine defi ciency leads to cytosolic accumulation of unoxidized fatty acylCoA molecules, inhibiting the urea cycle. The dysfunction has a spread of options that include hyperam monaemia and cardiomyopathy, which can be deadly in infants and kids [53]. Secondary carnitine deficiency might occur in severe malnutrition, related to a high ammonia degree and aware of carnitine substitute [54]. Increased manufacturing of ammonia, for example gut or urinary tract overgrowth of ureaseproducing bacte ria such as Proteus mirabilis [55]. Total parenteral diet, following hyperalimentation with essential amino acids. Plasma proteins Plasma proteins made by hepatocytes include albumin, 1antitrypsin, haptoglobin, caeruloplasmin, transferrin, fibrinogen, and coagulation elements (Table 2. Falls in the focus of these proteins usually reflects decreased hepatic synthesis, although adjustments in plasma volume and losses into the intestine or urine might contribute. Some liverproduced proteins are acute section reactants that increase in response to tissue damage and inflamma tion (Table 2. These include fibrinogen, haptoglobin, 1antitrypsin, C3 element of complement, ferritin, and caeruloplasmin. An acute section response could contrib ute to increased serum concentrations of these proteins, even in sufferers with hepatocellular failure. These cytokines not only stimulate production of acute part reactants but also inhibit synthesis of albumin, transferrin, and different proteins. Human serum albumin, a nonglycosylated, negatively charged protein, is essentially the most abundant plasma protein and the primary determinant of plasma colloid osmotic (oncotic) pressure [58].
400 mg renagel
Liver biopsy gastritis ulcer cheap 400 mg renagel, if performed chronic gastritis reflux esophagitis 400 mg renagel cheap visa, will present particular viral inclusions, but the presence of pores and skin lesions benefit initiation of acyclovir therapy. However, paracetamol levels are often unde tectable in the setting of unintentional circumstances if symptoms have already developed. Paracetamol protein adducts correlate with hepatotoxicity and remain detect in a position for as much as 12 days after ingestion. The detection of adducts, presently a researchonly assay, may present an important scientific tool when it becomes extra broadly out there [32]. Antinuclear antibodies, smooth muscle antibodies, antibodies to liver/kidney microsomes sort 1, and immunoglobulin ranges should be checked for potential autoimmune hepatitis; liver biopsy could help to set up the analysis and is encouraged in indeterminate case settings [26]. Serum ceruloplasmin is unhelpful in fulminant Wilson illness since levels are low in practically 50% of all forms of acute liver failure [25]. Determination that the ratio of alkaline phosphatase to bilirubin of less than 4 and aspar tate aminotransferase to alanine aminotransferase is greater than 2. Use of a guidelines may be useful to make sure that all diagnostic potentialities are entertained and remedy options considered [33]. Abdominal imaging and liver biopsy Abdominal ultrasound is used to assess for vasculature patency and mass lesions. Hepatic nodularity may be observed on imaging, reflecting regenerative nodules and confluent necrosis rather than cirrhosis [34]. Liver histology can show considerable variability of necrosis that could be prognostically deceptive though necrosis >75% of hepatocytes has been shown to have worse outcomes without liver transplant [36]. Complications and administration of acute liver failure Acute liver failure represents a syndrome precipitated by numerous causes quite than a single illness. Treatment has focused on the management of problems except for a couple of aetiologyspecific thera pies (Table 5. Once stupor develops with or with out decerebrate posturing (stage 3�4 encephalopa thy), cerebral oedema is likely. The pathogenesis of hepatic encephalopathy is multi factorial (Chapter 8) and centres on failure of the liver to take away poisonous, primarily gutderived, substances including ammonia from the circulation. Levels higher than 150�200 mmol/L have been shown to correlate closely with presence of cerebral oedema and herniation [41,42]. The onset of encephalopathy is usually sudden, may pre cede jaundice, and, in contrast to chronic liver disease, could additionally be associated with agitation, modifications in personality, delu sions, and restlessness. Management of the portosystemic encephalopathy of cirrhosis has centred on lactulose and nonabsorbable antibiotics. However, lactulose has shown no benefit in acute liver failure and should increase aspiration threat and bowel distension, which complicates transplantation. The prognosis for sufferers with stage 1 or 2 encepha lopathy (confused or drowsy) is comparatively good. Progression of encephalopathy may be trig gered by infection; nevertheless, the usage of prophylactic antibiotics remains controversial, with no agency evidence of profit [44]. The net blood sup ply to the brain depends on the stability between carotid arterial strain and intracerebral strain (cerebral perfusion pressure = imply arterial stress - intracra nial pressure). Cerebral blood circulate autoregulation (main tained blood move despite falling or rising blood pressure) is misplaced in sufferers with fulminant hepatic failure [46]. This can lead to relative intracranial hypertension because of growing cerebral blood flow and interstitial water, as properly as cerebral hypoperfusion and hypoxia because of sys temic hypotension. Clinically, raised intracerebral strain is suggested by systolic hypertension (sustained or intermittent), elevated muscle tone and myoclonus, which progress to extension and hyperpronation of the arms and extension of the legs (decerebrate posturing). If not managed by therapy, this scientific image progresses to loss of pupillary reflexes and respiratory arrest from brainstem herniation. Haematoxylin and eosin slide demonstrates centrilobular necrosis with surviving periportal hepatocytes. Trichrome stain exhibits cirrhosis with bands of fibrosis surrounding regenerative nodules. Haematoxylin and eosin slide (right) reveals extreme hepatocyte harm with ballooning degeneration, microsteatosis, and cholestasis. Victoria blue stain highlights copper pigment throughout the hepatocytes (H) and Kupffer cells (K). Cerebral oedema could also be reducing in prevalence, per haps as a end result of earlier referral to tertiary centres and emer gent transplantation [48]. General management of cerebral oedema contains limiting stimulation, elevating the head to no much less than 30 levels, and correction of acidosis and electrolytes. Additional therapies focus on decreas ing cerebral oedema by growing intravascular osmotic gradient (hypertonic saline, mannitol) [49]. Use of hyper ventilation, barbiturates, indomethacin have fallen out of favour and no survival profit has been proven with hypo thermia [50,51]. Prophylactic infusion of hypertonic saline to hold serum sodium 145�155 mmol/L in patients with severe 72 Chapter 5 encephalopathy is related to fewer episodes of intrac ranial hypertension [52]. Trials are wanted to check additional its efficacy in established intracranial hypertension. Volume overload can develop and ultra filtration may be necessary within the setting of renal impairment. Nearly 60% of intracranial hypertension circumstances reply and mannitol has been shown to enhance survival [49]. Coagulopathy the liver synthesizes practically all the coagulation components, inhibitors of coagulation and proteins involved within the fibrinolytic system (Chapter 4). The coagulopathy of fulminant hepatic failure is thus complicated and due not solely to issue deficiency, but additionally to enhanced fibrinolytic activity and decreased platelet number and performance. Overall, there appears to be less clinically significant bleeding in acute liver failure than may need been assumed from the plain derangements in prothrombin time and platelet ranges. Thromboelastography may be of worth in figuring out want for particular remedy to improve coagula tion abnormalities. Despite prolonged prothrombin time, most patients with acute liver failure have been found to have regular haemostasis as measured by thromboelas tography [53]. Coagulopathy is managed by routine intra venous or subcutaneous vitamin K initially, and barely requires additional measures. A current evaluation of adjustments over the previous 16 years in administration of acute liver failure, suggested that severity of sickness had not modified but that outcomes had improved. Fewer transplants and more sufferers survived without transplant between 2007 and 2013 than within the earlier eight years, despite a diminished use of plasma and purple blood cell replacement remedy. Indeed, much less may be extra, since there must be fewer cases of transfusionassociated lung damage if use of contemporary frozen plasma is saved to a minimum [54]. Platelet transfusions have particularly been linked to acute lung injury and must also be minimized [55]. Metabolic derangements Hypoglycaemia is present in as a lot as 40% of patients with acute liver failure. Plasma insulin ranges are excessive because of lowered hepatic uptake; gluconeogenesis is decreased within the failing liver. Blood glucose ranges less than 60 mg/dL must be handled with a continuous infusion of 10% dex trose.

Cheap renagel 400 mg line
Under reporting and poor adherence to monitoring guidelines for severe cases of isoniazid hepatotoxicity gastritis quotes 400 mg renagel cheap with visa. Deleterious influence of pyrazinamide on the end result of patients with fulminant or subfulminant liver failure during antituberculosis remedy including isoniazid gastritis symptoms heartburn buy renagel 400 mg without a prescription. Azathioprine and 6mercaptopurine induced liver harm: medical options and outcomes. Venoocclussive illness of the liver after chemotherapy of acute leukemia: report of two circumstances. Liver fibrosis in patients with psoriasis and psoriatic arthritis on longterm, excessive cumulative dose methotrexate remedy. Liver harm from tumor necrosis issue antagonists: analysis of thirtyfour instances. Druginduced liver injury due 150 151 152 153 154 a hundred and fifty five 156 157 158 159 a hundred and sixty 161 162 163 164 a hundred sixty five 166 to cancer chemotherapeutic agents. Chemotherapy, liver injury and postoperative complications in colorectal liver metastases. Hepatotoxicity of tyrosine kinase inhibitors: medical and regulatory perspectives. Risk of tyrosine kinase inhibitorsinduced hepatotoxicity in most cancers sufferers: a metaanalysis. Amiodarone hepatotoxicity: prevalence and clinicopathologic correlations amongst 104 patients. Amiodarone induced hepatic phospholipidosis: a morphological alteration unbiased of pseudoalcoholic liver illness. Verapamil hepatotoxicity: a 168 169 one hundred seventy 171 172 173 174 a hundred seventy five 176 177 178 179 one hundred eighty 181 182 183 hypersensitivity reaction. Antiliver microsomes autoantibodies and dihydralazine induced hepatitis: specificity of autoantibodies and inductive capability of the drug. Epidemiology of opposed drug reactions to carbamazepine as seen in a spontaneous reporting system. The effects of phenobarbital and diphenylhydantoin on liver perform and morphology. Hepatic injury related to diphenylhydantoin remedy: a clinicopathological study of 20 cases. Hepatotoxicity related to antiepileptic drug therapy � avoidance, identification and management. Lamotrigine: medical expertise in 200 sufferers with epilepsy and 4year followup. Hypersensitivity myocarditis and hepatitis related to imipramine and its metabolite, desipramine. Intrahepatic obstructive jaundice 185 186 187 188 189 one hundred ninety 191 192 193 194 195 196 197 198 199 200 from amitriptyline. Duloxetine hepatotoxicity: A case series from the Druginduced liver injury network. Severe liver harm due to phenelzine with distinctive hepatic deposition of extracellular material. A fatal case of bupropion (Zyban) hepatotoxicity with autoimmune features: a case report. Hypolipidaemics carcinogenicity and extrapolation of experimental results for human security assessments. Light and electron microscopy of liver in hyperlipoproteinemic sufferers underneath longterm gemfibrozil treatment. A comparison of the efficacy and toxic effects of sustained vs immediaterelease niacin in DrugInduced Liver Injury 493 hypercholesterolemic sufferers. Spectrum of statin hepatotoxicity: experience of the DrugInduced Liver Injury Network. Hepatotoxicity associated with 201 202 203 204 205 supplements containing Chinese green tea (Camellia sinensis). Side effects of anabolic androgenic steroids: pathological findings and construction activity relationships. Hepatic disease when it happens could also be fatty liver, alcoholic hepatitis, cirrhosis, or hepatocellular carcinoma. Patients with extreme alcoholic hepatitis could additionally be provided corticosteroids, however the benefit is marginal. Improvements in the supportive management of sepsis, bleeding, and hepatorenal syndrome in patients with alcoholic hepatitis have resulted in a big reduction in mortality over the last 30 years. Patients with a minimal of 3 months of abstinence who nonetheless have decompensated liver disease are unlikely to improve additional and must be thought of for liver transplantation assessment. Trials of early transplantation in highly selected patients with alcoholinduced hepatitis with a really poor prognosis have proven promise when it comes to each survival and longterm abstinence, but this approach is controversial. All sufferers with alcoholinduced liver disease require help to keep longterm abstinence. The pathogenesis of alcoholinduced liver harm is still not well worked out, however is no doubt linked, at least partly, to ethanol metabolism. It has by no means been understood, nonetheless, why some people can drink heavily for a number of years and not develop important liver injury. Linked to this, and equally unclear, is why some individuals develop liver disease whereas others could develop pancreatitis or neurological damage. Further understanding of the mechanisms should result in better therapies and preventive methods. This article focuses first on ethanol metabolism and the proposed mechanisms of liver harm. This is adopted by the frequent modes of presentation with alcohol induced liver harm and the investigations required. Finally, present greatest therapy of both alcohol dependence and the liver illness, including transplantation, is mentioned. Alcohol metabolism Absorption and distribution Alcohol is absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract by easy diffusion and peak blood alcohol concentrations are reached after 20 min. Introduction Matthew Baillie acknowledged the association of alcohol with liver cirrhosis in 1793. An essential example of this phenomenon is the increased susceptibility to the toxic effects of paracetamol (acetaminophen), the place extreme liver damage has been reported in dependent drinkers taking therapeutic doses [4]. Alcohol distribution depends on blood move, with vascular organs such because the brain rapidly equilibrating with plasma levels. Acetate may be oxidized to carbon dioxide and water, or converted by the citric acid cycle into different compounds, together with fatty acids.
400 mg renagel generic visa
Attacks on the snails are limited by value gastritis gallbladder removal renagel 800 mg purchase amex, the need for this to be repeated over lengthy periods gastritis medicine over the counter purchase 400 mg renagel otc, and the results on fish. It is often controlled by variceal banding or sclerotherapy and could also be decreased by propranolol prophylaxis (Chapter 11). In terms of surgical procedures, gastrooesophageal devascularization with splenectomy may be the procedure of choice [110] as it has a low mortality and encephalopathy rate. In the preerythrocytic (exoerythrocytic) stage, schizogony takes place within the liver without apparent effect on its operate. The hepatocyte is invaded by the sporozoite through the formation of the parasitophorous vacuole. This schizont bursts and the merozoites are discharged into the sinusoids and invade erythrocytes. In quartan or benign tertian malaria, a few merozoites return to the liver cells to provoke the exoerythrocytic or relapse cycle. The an infection of both liver cells and erythrocytes appears to be ruled by haemoxygenase1, which is upregulated throughout preliminary invasion. Absence or downregulation leads to proinflammatory cytokine release and termination of an infection [115]. Pathology the liver shows sinusoidal dilation and congestion, portal infiltration, and Kupffer cells proliferation. Hepatocyte damage is slight with nuclei of variable measurement and shape and elevated mitoses. Reaction to the malarial parasite is reticuloendothelial, with minor effects on the liver cells and no fibrosis. Occasionally, in acute malignant malaria, there could also be gentle jaundice, hepatomegaly, and tenderness over the liver. Treatment choices lie between pentavalent antimony compounds and liposomal amphotericin B [119]. Miltefosine is an orally energetic drug which seems to have efficacy approaching that of amphotericin B [120]. Kalaazar (visceral leishmaniasis) Visceral leishmaniasis is primarily a reticuloendothelial illness, involving lymph nodes, liver, spleen, and bone marrow. Mature granuloma formation appears to correlate with resolving an infection within the liver [116]. Kalaazar presents with fever, splenomegaly, a firm, tender liver, pancytopenia, anaemia, and really high serum globulins. The disease could also be selfresolving but usually runs a persistent course with out treatment. The disease has occurred in liver transplant recipients, but appears unusual, occurring at a rate of 1 in 800 in patients from an endemic area of Spain [118]. Diagnosis is often via microscopic identification of amastigotes in tissue aspirates or biopsies. Echinococcosis (hydatid disease) Hydatid disease is due to the larval or cyst stage of infection by the tapeworm, Echinococcus granulosus, which lives in canine. Scolices, contained in the cysts, adhere to the small gut of the dog and turn out to be grownup worms which attach to the intestinal wall. The infected faeces of the canine contaminate grass and farmland, and the contained ova are ingested by sheep, pigs, camels, or humans. The ova adhere to the coats of canine, so persons are infected by dealing with canine, as well as by consuming contaminated vegetables. The liberated ovum burrows via the intestinal mucosa and is carried by the portal vein to the liver, where it develops into an adult cyst. A few ova might pass by way of the liver and coronary heart, and are held up within the lungs, causing pulmonary cysts. The peripheral zone, derived from the host tissues, turns into the adventitia or ectocyst, a thick layer which may calcify. Adventitia or ectocyst (may be calcified) Scolices Brood capsule Germinal layer Laminated layer Hydatid sand which supplies rise to pedunculated nodes of multiplying cells that project into the lumen of the cyst as brood capsules. The attachment of the brood capsules to the germinal layer turns into progressively thinner till the capsule bursts, releasing the scolices into the cyst fluid. Daughter and even granddaughter cysts develop by fragmentation of the germinal layer. The illness is widespread in sheepraising nations, where canine have access to contaminated offal. These embrace South 670 Chapter 33 Australia, New Zealand, Africa, South America, southern Europe, especially Cyprus, Greece, and Spain, and the Middle and Far East. Clinical features these depend upon the site, the stage and whether or not the cyst is alive or lifeless. The only complaints may be a dull ache in the proper upper quadrant and sometimes a feeling of stomach distension. Intraperitoneal rupture is frequent and results in a quantity of cysts throughout the peritoneal cavity with intestinal obstruction and gross stomach distension. The stress in the cyst significantly exceeds that in bile and rupture into bile ducts is frequent. The cysts could adhere to the diaphragm, rupture into the lungs and end in expectoration of daughter cysts. Secondary invasion by pyogenic organisms follows rupture into biliary passages, giving the picture of a pyogenic abscess; the parasite dies. Occasionally, the entire cyst content undergoes aseptic necrosis and once more the parasite dies. This amorphous yellow particles have to be distinguished from the pus of secondary an infection. Cysts can happen in lung, kidney, spleen, mind, or bone, but mass infestation is uncommon; the liver is usually the only organ concerned. Cyst fluid accommodates a variety of overseas proteins together with proteases and cyclophilins which sensitize the host. This is seen sometimes and could additionally be associated to glomerular deposits of hydatid antigens [123,124]. Diagnosis Serological tests Hydatid fluid contains specific antigens, leakage of which sensitizes the affected person with the production of antibodies. Results could additionally be negative for all exams if the cyst has by no means leaked, if it contains no scolices, or if the parasite is dead. Imaging Radiology normally reveals a raised, poorly moving proper diaphragm and hepatomegaly. Characteristic radiological adjustments could also be seen in the lungs, spleen, kidney, or bone.