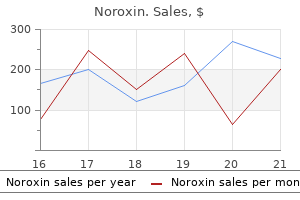
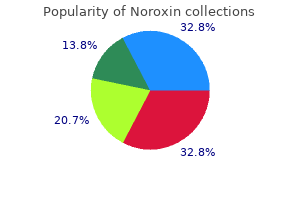
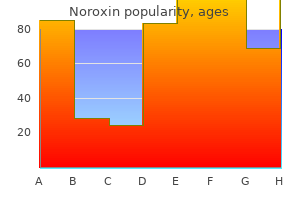
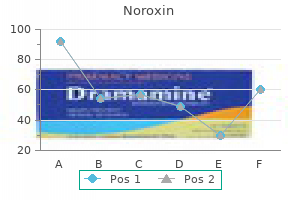
Noroxin dosages: 400 mg
Noroxin packs: 60 pills, 90 pills, 120 pills, 180 pills, 270 pills, 360 pills

Noroxin 400 mg generic with visa
This could allow for preservation of the immunologic and hematologic perform of the spleen antibiotic medication list 400 mg noroxin buy with mastercard. In the 2011 retrospective follow-up research at Massachusetts General Hospital of 158 patients who obtained the Warshaw process between 1986 and 2009 antimicrobial kitchen countertops noroxin 400 mg buy cheap on-line, just one. Diagram of key ideas in spleen-preserving distal pancreatectomy (Warshaw procedure). Top, the pancreas is mobilized by incising the retroperitoneum alongside the left inferior margin and opening the avascular airplane behind it. Dissection is carried to the left, previous the tip of the pancreas to isolate the splenic vascular pedicle. Bottom, the splenic artery and vein may be ligated and divided individually (as shown) or collectively, then physique and tail of pancreas eliminated. To enhance affected person restoration, distal pancreatectomy may be performed laparoscopically. A recent meta-analysis examined 18 research that included 1814 sufferers with pancreatic tumors amenable to resection by way of distal pancreatectomy. Forty-three % of patients underwent laparoscopic resection, and the remaining have been approached with laparotomy. The laparoscopic group had a shorter size of keep, much less blood loss, and fewer postoperative complications. Encouragingly, there was no distinction in margin positivity, postoperative pancreatic fistula improvement, or mortality, though there did seem to be a development toward fewer lymph nodes being sampled with the laparoscopic approach (Venkat et al, 2012). Some surgeons have begun performing robotic distal pancreatectomy, and although they anecdotally report good outcomes, inadequate proof has been gathered to support the routine use of this modality in oncologic cases (Cirocchi et al, 2013). One argument towards resection is that the affected person is unlikely to get hold of a healing (R0) resection and thus bears the chance of a large operation with out the reward of improved survival. Vascular invasion or encasement on preoperative imaging ought to therefore not be considered as contraindicating resection. B, Enucleation of a pancreatic neuroendocrine tumor positioned on the superior facet of the neck of the pancreas. The tumor (circle) is generally detached at this level and rolled inferiorly over the pancreas. In a retrospective analysis of the Surveillance Epidemiology and End Results database, Hill and colleagues (2009) demonstrated that total survival of pancreatic neuroendocrine tumor patients could be improved if surgical resection of the first tumor can be performed. Patients in whom surgical procedure was beneficial, but not carried out (including palliative procedures), had median survival on par with sufferers in whom surgery was not provided. Much debate exists as to the way to treat these tumors surgically, as biochemical remedy is rare and recurrence is frequent. Endocrine Tumors Chapter 65 Pancreatic neuroendocrine tumors: classification, clinical picture, analysis, and remedy 1005 gastrinomas (Sugg et al, 1993). Patients had been adopted for a median of 32 months (range, four to 110 months), and none that had undergone resection developed metastatic disease (Libutti et al, 2000). The gold-standard cytoreductive approach is formal segmental resection (Mayo et al, 2010; Norton et al, 2003; Sarmiento et al, 2003), though wedge resection, enucleation, and ablation (radiofrequency or microwave ablation, hepatic artery embolization) (see Chapter 30) are also useful methods and have the benefits of preserving a maximal amount of regular liver parenchyma, with lower complication rates. Ablative methods are greatest used for small metastases (<5 cm) and can be utilized to deal with many lesions in a single setting (Elias et al, 2009; Eriksson et al, 2008; Zappa et al, 2012). Because most patients with liver metastases have giant, multiple tumors, hepatic artery embolic therapy is often probably the most rational method. The objective must be to enhance high quality of life and extend survival (Kuo et al, 2014; Vinik et al, 2010). The hypoglycemia seen with insulinomas could be handled with diazoxide (200 to 600 mg/day). Nearly 50% of patients taking the drug will expertise unwanted effects, which embrace fluid retention, nausea, hirsuitism, palpitations, and anorexia (Baudin et al, 2013; Oberg, 2010). In 2012, Bartsch and colleagues analyzed 48 instances of sporadic gastrinoma with N1 disease. These patients had their main tumor resected (via a variety of procedures) and a scientific lymphadenectomy performed, which included clearance of the peripancreatic and pancreaticoduodenal lymph nodes, the lymph nodes within the hepatoduodenal ligament along the hepatic artery, and the lymph nodes in between the aorta and inferior vena cava. To be classified as a proper lymphadenectomy, greater than 10 lymph nodes had been required to have been pathologically assessed. In this set of sufferers, a proper lymphadenectomy resulted in a considerably larger postoperative biologic remedy fee (fasting gastrin <125 pg/mL and unfavorable secretin stimulation test) and a development towards improved disease-free survival (Bartsch et al, 2012). In a set of patients with sporadic gastrinomas who had been treated by enucleation only versus a more intensive pancreatic procedure and formal lymphadenectomy, a big enchancment in time-to-recurrence was seen in those who had lymphadenectomy (Giovinazzo et al, 2013). A retrospective research in 2013 demonstrated partial response in 7% of patients, secure disease in 58%, and progressive disease in 35%. There were no complete responses, and solely two of three partial responses continued beyond 12 months of remedy (Jann et al, 2013). Only one research has reported a whole response on this routine, however many sufferers have achieved partial responses, and the minority in each examine progressed. The median duration of response is roughly 1 year in most research, which is an improvement over most of the previous chemotherapy regimens (Fine et al, 2013; Peixoto et al, 2014; Saif et al, 2013; Strosberg et al, 2011a). Response charges vary from 42% to 67%, and median survival hovers simply at more than 1 yr (Mitry et al, 1999; Moertel et al, 1991). In this examine, 64% of sufferers demonstrated some tumor shrinkage whereas on the drug, compared with 21% who were treated with the placebo. Most adverse events had been grade 1 or 2 and included stomatitis, rash, diarrhea, fatigue, and higher respiratory infections (Yao et al, 2011). Although these results are mediocre, the medical benefit fee for this routine was 92%, which is best than many other drug mixtures (Bajetta et al, 2014). The enhancements seen within the remedy group have been so nice that the trial was stopped early and all patients receiving the placebo have been offered sunitinib (Raymond et al, 2011). An asymptomatic patient with a low tumor burden could be followed every 3 to 12 months with biomarkers and imaging. Onset of latest signs or evidence of illness development ought to prompt extra frequent follow-up. Endocrine Tumors Chapter sixty five Pancreatic neuroendocrine tumors: classification, scientific picture, analysis, and therapy1006. Anlauf M, et al: Sporadic versus hereditary gastrinomas of the duodenum and pancreas: distinct clinico-pathological and epidemiological features, World J Gastroenterol 12:5440�5446, 2006. Asayama M, et al: Everolimus dramatically improves glycemic control in unresectable metastatic insulinoma: a case report, Jpn J Clin Oncol forty four:186�190, 2014. Baudin E, et al: Malignant insulinoma: recommendations for characterisation and therapy, Ann Endocrinol (Paris) seventy four:523�533, 2013. Bernstein J, et al: Performance of endoscopic ultrasound-guided fine needle aspiration in diagnosing pancreatic neuroendocrine tumors, Cytojournal 10:10, 2013. Bertani E, et al: Resection of the primary pancreatic neuroendocrine tumor in patients with unresectable liver metastases: potential indications for a multimodal method, Surgery 155:607�614, 2014. Bertolino P, et al: Genetic ablation of the tumor suppressor menin causes lethality at mid-gestation with defects in a number of organs, Mech Dev one hundred twenty:549�560, 2003. Bhate K, et al: Functional assessment in the multimodality imaging of pancreatic neuroendocrine tumours, Minerva Endocrinol 35:17�25, 2010.
400 mg noroxin cheap with mastercard
Guglielmi A antimicrobial journal pdf 400 mg noroxin best, et al: Intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma: prognostic components after surgical resection bacteria types of bacteria noroxin 400 mg overnight delivery, World J Surg 33(6):1247�1254, 2009. Guichard C, et al: Integrated analysis of somatic mutations and focal copy-number modifications identifies key genes and pathways in hepatocellular carcinoma, Nat Genet 44(6):694�698, 2012. Handra-Luca A, et al: Multiple mixed adenoma-focal nodular hyperplasia of the liver associated with spontaneous intrahepatic portosystemic shunt: a model new type of vascular malformation associated with the multiple focal nodular hyperplasia syndrome Hirota N, et al: Resistance to iron accumulation and presence of hepatitis B surface antigen in preneoplastic and neoplastic lesions in human hemochromatotic livers, Hepatogastroenterology 29:49�51, 1982. Clinicopathologic research and evaluate of the literature, Cancer 65(7):1583� 1590, 1990. Hoshida Y, et al: Gene expression in fastened tissues and consequence in hepatocellular carcinoma, N Engl J Med 359:1995�2004, 2008. Hytiroglou P, et al: Hepatic precancerous lesions and small hepatocellular carcinoma, Gastroenterol Clin North Am 36:867�887, 2007. International Consensus Group for Hepatocellular Neoplasia: Pathologic analysis of early hepatocellular carcinoma: a report of the International Consensus Group for Hepatocellular Neoplasia, Hepatology 49(2):658�664, 2009. International Working Party: Terminology of nodular hepatocellular lesions, Hepatology 22(3):983�993, 1995. Iwai M, et al: Cholestatic liver disease in a 20-yr-old lady with histiocytosis X, Am J Gastroenterol 83(2):164�168, 1988. Jia D, et al: Exome sequencing of hepatoblastoma reveals novel mutations and most cancers genes in the Wnt pathway and ubiquitin ligase complicated, Hepatology 60(5):1686�1696, 2014. Clinicopathologic and immunohistochemical research of 14 post-mortem instances, Cancer 59(2):310�316, 1987. Report of an enormous tumor studied by light and electron microscopy, Cancer 52(9):1662�1665, 1983. A scientific and pathologic analysis of 57 hepatectomy circumstances, Cancer 51:542�548, 1983. Klastkin G: Adenocarcinomas of the hepatic duct at its bifurcation inside the porta hepatitis. An uncommon tumor with distinctive scientific and pathological options, Am J Med 38:241�256, 1965. Kloppel G, et al: Precancerous lesions of the biliary tree, Best Pract Res Clin Gastroenterol 27(2):285�297, 2013. Kobayashi M, et al: Dysplastic nodules incessantly become hepatocellular carcinoma in sufferers with chronic viral hepatitis and cirrhosis, Cancer 106:636�647, 2006. Kobayashi M, et al: Incidence of primary cholangiocellular carcinoma of the liver in japanese sufferers with hepatitis C virus-related cirrhosis, Cancer 88(11):2471�2477, 2000. Kojiro M: Focus on dysplastic nodules and early hepatocellular carcinoma: an Eastern viewpoint, Liver Transpl 10:3�8, 2004. Pathomorphologic examine of 29 autopsy circumstances, Arch Pathol Lab Med 109(9):853�857, 1985. Kojiro M, Roskams T: Early hepatocellular carcinoma and dysplastic nodules, Semin Liver Dis 25:133�142, 2005. Kojiro M, et al: Hepatocellular carcinoma with sarcomatous change: a particular reference to the connection with anticancer therapy, Cancer Chemother Pharmacol 23(Suppl):4�8, 1989. Komori K, et al: Mesothelial cyst of the liver in a neonate, Pediatr Surg Int 24(4):463�465, 2008. Komuta M, et al: Clinicopathological study on cholangiolocellular carcinoma suggesting hepatic progenitor cell origin, Hepatology 47(5):1544�1556, 2008. Kondo F: Benign nodular hepatocellular lesions brought on by abnormal hepatic circulation: etiological analysis and introduction of a new concept, J Gastroenterol Hepatol sixteen:1319�1328, 2001. Kondo F, et al: Histological features and clinical course of large regenerative nodules: evaluation of their precancerous potentiality, Hepatology 12(1698171):592�598, 1990. Kondo F, et al: Nodular lesions associated with abnormal liver circulation, Intervirology forty seven:277�287, 2004. Kottke-Marchant K, et al: Localized fibrous tumor (localized fibrous mesothelioma) of the liver, Cancer 64(5):1096�1102, 1989. Kuma S, et al: Leiomyosarcoma originating from the superior mesenteric vein: a case report and review of the literature, Ann Vasc Surg 22(3):453�455, 2008. Kuwano H, et al: Hepatocellular carcinoma with osteoclast-like big cells, Cancer 54(6331629):837�842, 1984. Clinical and pathologic examine of sixteen circumstances with emphasis on immunohistochemical options, Am J Surg Pathol 15(1):1�16, 1991. Lee J-S, et al: Classification and prediction of survival in hepatocellular carcinoma by gene expression profiling, Hepatology 40:667�676, 2004. Lepreux S, et al: Expression of fibrillin-1 in focal nodular hyperplasia of the liver: a job in microcirculation adaptability, Comp Hepatol 3(Suppl 1):S57, 2004. Leung C, et al: Characteristics of hepatocellular carcinoma in cirrhotic and non-cirrhotic non-alcoholic fatty liver illness, World J Gastroenterol 21(4):1189�1196, 2015. Libbrecht L, et al: Preneoplastic lesions in human hepatocarcinogenesis, Liver Int 25:16�27, 2005. Spectrum of morphologic modifications and scientific findings, Mayo Clin Proc 50(5):255� 263, 1975. Maeda T, et al: Combined hepatocellular and cholangiocarcinoma: proposed criteria according to cytokeratin expression and analysis of clinicopathologic options, Hum Pathol 26(9):956�964, 1995. Maggioni M, et al: Molecular modifications in hepatocellular dysplastic nodules on microdissected liver biopsies, Hepatology 32:942�946, 2000. Marijon H, et al: Epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition and acquired resistance to sunitinib in a affected person with hepatocellular carcinoma, J Hepatol 54(5):1073�1078, 2011. Mehrabi A, et al: Primary malignant hepatic epithelioid hemangioendothelioma: a complete evaluation of the literature with emphasis on the surgical therapy, Cancer 107(9):2108�2121, 2006. Mercadier M, et al: Papillomatosis of the intrahepatic bile ducts, World J Surg eight:30�35, 1984. Mion F, et al: Adult cirrhotic liver explants: precancerous lesions and undetected small hepatocellular carcinomas, Gastroenterology 111(6):1587�1592, 1996. Miura K, Shirasawa H: Primary carcinoid tumor of the liver, Am J Clin Pathol 89(4):561�564, 1988. Moon C, et al: Lower incidence of hepatocellular carcinoma and cirrhosis in hepatitis C sufferers with sustained virological response by pegylated interferon and ribavirin, Dig Dis Sci 60(2):573�581, 2015. Nakanuma Y, et al: Incidental solitary hepatocellular carcinomas smaller than 1 cm in size discovered at autopsy: a morphologic research, Hepatology 6:631�635, 1986. Nakanuma Y, et al: Pathology of peripheral intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma as regards to tumorigenesis, Hepatol Res 38(4):325�334, 2008. Nakashima T, Kojiro M: Pathologic traits of hepatocellular carcinoma, Semin Liver Dis 6:259�266, 1986. Nathan H, et al: Predictors of survival after resection of early hepatocellular carcinoma, Ann Surg 249:799�805, 2009.
Order 400 mg noroxin with mastercard
Generally bacteria helicobacter pylori sintomas generic 400 mg noroxin amex, the circulate within the portal branches may even turn out to be hepatofugal toward the shunt bacteria yogurt lab 400 mg noroxin discount, even if good hepatopetal flow was present earlier than shunt creation. If aspiration is finished while passing the needle across the liver parenchyma, entry right into a cyst is recognized by aspiration of clear fluid; the needle can then be redirected across the cyst. Bureau C, et al: Patency of stents coated with polytetrafluoroethylene in sufferers handled by transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunts: long-term outcomes of a randomized multicentre examine, Liver Int 27(6):742�747, 2007. Cabrera J, et al: Transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt versus sclerotherapy in the elective treatment of variceal hemorrhage, Gastroenterology 110(3):832�839, 1996. A randomized, controlled trial [see comments], Ann Intern Med 126(11):858�865, 1997. Chalasani N, et al: Determinants of mortality in sufferers with superior cirrhosis after transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunting, Gastroenterology 118(1):138�144, 2000. Chen L, et al: Outcomes of transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt through the left branch vs. Corbett C, et al: A case-control examine of transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic stent shunts for sufferers admitted to intensive care following variceal bleeding, Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol 25(3):344�351, 2013. De Magistris L, et al: Transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt and laparoscopic colorectal resection: the ideal minimally-invasive management for the therapy of colorectal cancer in extreme cirrhotic sufferers. Dhanasekaran R, et al: Transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt for symptomatic refractory hepatic hydrothorax in patients with cirrhosis, Am J Gastroenterol 105(3):635�641, 2010. Farsad K, et al: Transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt creation using intravascular ultrasound steerage, J Vasc Interv Radiol 23(12):1594�1602, 2012. Garcia-Tsao G, Bosch J: Management of varices and variceal hemorrhage in cirrhosis, N Engl J Med 362(9):823�832, 2010. Garcia-Villarreal L, et al: Transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt versus endoscopic sclerotherapy for the prevention of variceal rebleeding after recent variceal hemorrhage, Hepatology 29(1):27�32, 1999. Gil A, et al: the position of transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt prior to abdominal tumoral surgical procedure in cirrhotic patients with portal hypertension, Eur J Surg Oncol 30(1):46�52, 2004. Gines P, et al: Transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunting versus paracentesis plus albumin for refractory ascites in cirrhosis, Gastroenterology 123(6):1839�1847, 2002. Hamel B, et al: Prognostic elements in sufferers with refractory ascites treated by transjugular intrahepatic porto-systemic shunt: from the liver to the kidney, Dig Liver Dis 46(11):1001�1007, 2014. Han G, et al: Transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt for portal vein thrombosis with symptomatic portal hypertension in liver cirrhosis, J Hepatol 54(1):78�88, 2011. Jalan R, et al: A randomized trial evaluating transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic stent-shunt with variceal band ligation in the prevention of rebleeding from esophageal varices, Hepatology 26(5):1115� 1122, 1997. Kochar N, et al: Bleeding ectopic varices in cirrhosis: the function of transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic stent shunts, Aliment Pharmacol Ther 28(3):294�303, 2008. Lebrec D, et al: Transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunts: comparability with paracentesis in sufferers with cirrhosis and refractory ascites: a randomized trial. French Group of Clinicians and a Group of Biologists, J Hepatol 25(2):135�144, 1996. Lodato F, et al: Transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt placement for refractory ascites: a single-centre experience, Scand J Gastroenterol 47(12):1494�1500, 2012. Mahadeva S, et al: Cost-effectiveness of N-butyl-2-cyanoacrylate (histoacryl) glue injections versus transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt within the management of acute gastric variceal bleeding, Am J Gastroenterol 98(12):2688�2693, 2003. Merli M, et al: Transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt versus endoscopic sclerotherapy for the prevention of variceal bleeding in cirrhosis: a randomized multicenter trial. Mizrahi M, et al: Endotipsitis-persistent an infection of transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt: pathogenesis, scientific features and management, Liver Int 30(2):175�183, 2010. Parvinian A, et al: Older patient age might predict early mortality after transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt creation in people at intermediate danger, J Vasc Interv Radiol 24(7):941�946, 2013. Parvinian A, et al: Transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt for the therapy of medically refractory ascites, Diagn Interv Radiol 20(1):58�64, 2014. Peter P, et al: Hepatic encephalopathy after transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt in patients with recurrent variceal hemorrhage, Gastroenterol Res Pract 2013:398172, 2013. Qi X, et al: Transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt for portal cavernoma with symptomatic portal hypertension in non-cirrhotic sufferers, Dig Dis Sci 57(4):1072�1082, 2012. Qi X, et al: Timing of transjugular intrahepatic portosystmic for BuddChiari syndrome: nonetheless an open concern, Liver Int 34(8):1288�1289, 2014. Riggio O, et al: Clinical efficacy of transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt created with coated stents with completely different diameters: outcomes of a randomized managed trial, J Hepatol 53(2):267�272, 2010. Rossle M, et al: Randomised trial of transjugular-intrahepaticportosystemic shunt versus endoscopy plus propranolol for prevention of variceal rebleeding, Lancet 349(9058):1043�1049, 1997. Rossle M, et al: A comparability of paracentesis and transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunting in patients with ascites [see comments], N Engl J Med 342(23):1701�1707, 2000. Salerno F, et al: Transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt for refractory ascites: a meta-analysis of particular person patient data, Gastroenterology 133(3):825�834, 2007. A randomized, controlled trial [see comments], Ann Intern Med 126(11):849�857, 1997. Sauer P, et al: Transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic stent shunt versus sclerotherapy plus propranolol for variceal rebleeding, Gastroenterology 113(5):1623�1631, 1997. Taki Y, et al: Predictive components for enchancment of ascites after transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt in sufferers with refractory ascites, Hepatol Res 44(8):871�877, 2014. Tripathi D, et al: Good scientific outcomes following transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic stent-shunts in Budd-Chiari syndrome, Aliment Pharmacol Ther 39(8):864�872, 2014. Tripathi D, Jalan R: Transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic stentshunt within the management of gastric and ectopic varices, Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol 18(11):1155�1160, 2006. Tsauo J, et al: Three-dimensional path planning software-assisted transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt: a technical modification, Cardiovasc Intervent Radiol 38(3):742�746, 2015. Hepatic Cirrhosis, Portal Hypertension, and Hepatic Failure Chapter 87 Transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunting: indications and technique1247. Vidal V, et al: Usefulness of transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt in the management of bleeding ectopic varices in cirrhotic sufferers, Cardiovasc Intervent Radiol 29(2):216�219, 2006. Wils A, et al: Transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt in patients with persistent portal vein occlusion and cavernous transformation, J Clin Gastroenterol 43(10):982�984, 2009. Wu X, et al: Clinical consequence utilizing the fluency stent graft for transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt in sufferers with portal hypertension, Am Surg 79(3):305�312, 2013. Xue H, et al: Transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt vs endoscopic therapy in stopping variceal rebleeding, World J Gastroenterol 18(48):7341�7347, 2012. Yang Z, et al: Patency and clinical outcomes of transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt with polytetrafluoroethylene-covered stents versus naked stents: a meta-analysis, J Gastroenterol Hepatol 25(11): 1718�1725, 2010. Zhang F, et al: Different scoring techniques in predicting survival in Chinese sufferers with liver cirrhosis present process transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt, Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol 26(8):853� 860, 2014. Orloff Among the etiologies of portal hypertension, these caused by postsinusoidal obstruction are seen sometimes by most clinicians. Nonetheless, these illness processes represent complex scientific challenges and require a radical information of the obtainable diagnostic and therapy modalities. The latter situation can be referred to as sinusoidal obstruction syndrome and is most often seen after myeloablation with chemotherapy or radiation therapy earlier than hematopoetic stem cell transplant. For sufferers in whom these measures fail, liver transplantation remains a viable possibility, with wonderful outcomes despite recurrent illness in some reports. Many centers have adopted a stepwise strategy to treatment that has converted this once uniformly fatal process to a well-controlled, manageable condition.
400 mg noroxin purchase otc
In adults antibiotics libido discount noroxin 400 mg fast delivery, hemangiomas are often found in patients at a imply age of fifty years antibiotics and pregnancy cheap noroxin 400 mg with visa, equally in the left and proper lobes of the liver. The overwhelming majority of hemangiomas are lower than 5 cm in diameter and are not often pediculated. Some of these tumors have estrogen receptors, and accelerated development has been observed with excessive estrogen states, corresponding to these related to puberty, pregnancy, oral contraceptive use, and androgen therapy (see Chapter 89). Macroscopic examination demonstrates well-delineated, red-blue, flat lesions that will partially collapse on sectioning. Small hemangiomas may become entirely fibrous, showing as "a solitary fibrous nodule. Portal venous section helical computed tomography and centripetal distinction enhancement. In this setting, giant lesions present considerably greater growth over time (Hasan et al, 2014). Pain related to an uncomplicated hemangioma is most probably as a result of related issues such as gallbladder illness, liver cysts, gastroduodenal ulcers, or a hiatal hernia (Farges et al 1995). Large hemangiomas can be asymptomatic or might manifest as an stomach mass (Erdogan et al, 2007). Microscopic view of hemangioma exhibiting cavernous vascular areas lined by flattened endothelium underlying fibrous septa of assorted widths. Benign and Premalignant Tumors Chapter 90A Benign liver lesions 1301 adjacent constructions with resulting signs. Jaundice due to compression of bile ducts by hemangioma has been noticed however remains exceptional (Losanoff & Millis, 2008). Liver biologic checks, including alkaline phosphatase and -glutamyl transferase are regular. Normal laboratory tests associated with a big hepatic tumor with mild symptoms might be of assist in the analysis of hemangioma. Complications are principally observed in massive hemangiomas and could be divided into (1) alterations of internal structure, such as with inflammation; (2) coagulation abnormalities, which might lead to systemic disorders corresponding to hemorrhage, rupture, and subsequent hemoperitoneum; and (3) compression of adjacent structures. Inflammatory processes complicating large hemangiomas are not often observed, but their prevalence is probably underestimated. In this case, first described by Bornman and colleagues (Bornman et al, 1987; Takayasu et al, 1990), irritation might occur as a consequence of the thrombosis of a part of the hemangioma. Signs and symptoms of this process embrace low-grade fever, weight loss, abdominal pain, accelerated erythrocyte sedimentation rate, anemia, thrombocytosis, and increased fibrinogen stage, which distinction with in any other case normal white blood cell rely and liver perform tests. Clinical and laboratory abnormalities disappear after surgical excision of the hemangioma (Bornman et al, 1987; Pateron et al 1991; Pol et al, 1998). Kasabach-Merritt syndrome is an distinctive complication of hepatic hemangioma in adults (Hall, 2001) (see Chapter 89). This coagulopathy, which consists of intravascular coagulation, clotting, and fibrinolysis within the hemangioma, could progress to secondary increased systemic fibrinolysis and thrombocytopenia (Concejero et al, 2009). Spontaneous rupture of a hemangioma is phenomenal, and less than 50 indeniable circumstances have been reported to date (Corigliano et al, 2003; Jr et al, 2010). This rare complication could occur in association with the Kasabach-Merritt syndrome and is associated with a short-term mortality rate of 35% (Jr et al, 2010). Imaging Hemangiomas are highly characteristic on imaging and are subsequently recognized precisely within the overwhelming majority of the circumstances. Among these criteria, the presence of peripheral puddles at arterial part has a sensitivity of 67%, a specificity of 99%, and a constructive predictive worth of 86% for the analysis of hemangioma (Nino-Murcia et al, 2000). Hemangiomas could be a quantity of in 10% of circumstances, and in exceptional instances, the presence of innumerable hemangiomas is called hemangiomatosis (Ishak & Rabin, 1975; Keegan et al, 2001). The two most typical imaging atypias are present in large hemangiomas and in quickly filling hemangiomas. Giant hemangiomas, that are defined as exceeding 6 to 12 cm in diameter, are sometimes heterogeneous with marked central areas similar to thrombosis, in depth hyalinization, and fibrosis (Coumbaras et al, 2002; Danet et al, 2003). However, the everyday early, peripheral, globular enhancement is usually noticed in addition to sturdy hyperintensity on T2-weighted photographs on the periphery. Their analysis is based on robust hyperintensity on T2-weighted photographs, the parallelism enhancement with arterial constructions, and the persistent enhancement on delayed-phase imaging. To observe, these rapidly filling hemangiomas could induce arterial�portal venous shunts (Kim et al, 2001). Ultrasound (A) exhibits a hypoechoic liver lesion with posterior acoustic enhancement. Contrast-enhanced ultrasound (B and C) demonstrates peripheral puddling, adopted by complete and delayed enhancement. In these situations, biopsy of hemangiomas could also be performed with out vital risk of hemorrhage (Caldironi et al, 1998; Heilo & Stenwig, 1997) and allows an general accuracy of 96% (Caldironi et al, 1998). However, as in other tumors, it is strongly recommended to interpose a layer of normal hepatic parenchyma between the capsule and the margin of the hemangioma. The affected person must be reassured about the uncommon incidence of growth and the extraordinarily low risk of complications. Indications for treatment include extreme signs, problems, and inability to exclude malignancy (Duxbury & Garden, 2010;Yoon et al, 2003). Symptoms are more regularly encountered with large hemangiomas (Erdogan et al, 2007). Surgical resection stays the definitive therapy, however other less effective options embrace hepatic artery ligation and radiation therapy. Arterial embolization, which can be thought-about for momentary management of hemorrhage has limited success and is occasionally associated with morbidity (Reading et al, 1988). Arterial ligation may be thought of throughout surgical procedure to enable handbook decompression of enormous hemangioma to facilitate their manipulation and enucleation (Yoon et al, 2003). When indicated, the one remedy to be considered is resection (Erdogan et al, 2007; Herman et al, 2005), and it should be carried out in specialised units, the place a wide range of techniques (enucleation or resection) and approaches (laparotomy or laparoscopy) can be used (see Chapter 103B). The choice between enucleation and resection requires consideration of the scale and anatomic location of the lesion. Hemangiomas situated within the peripheral liver space are preferably treated by enucleation, whereas tumors deeply positioned are more safely resected with a formal anatomic liver resection (Fu et al, 2009; Gedaly et al, 1999; Kuo et al, 1994). In the overwhelming majority of cases, patients present symptom reduction after resection of a symptomatic hemangioma (Erdogan et al, 2007). In the absence of enchancment, surgical complications ought to be ruled out, and the preliminary accountability of the lesion ought to be reconsidered as the cause of signs. Liver transplantation has also been used efficiently in distinctive situations to deal with symptomatic patients with technically unresectable sophisticated giant hemangiomas or hemangiomatosis with cardiopulmonary problems (Browers et al, 1997; Ercolani et al, 2010; Ferraz et al, 2004; Keegan et al, 2001; Tapetes et al, 1995) (see Chapter 112). However, most cohort and medical research found no influence of oral contraceptives (Kapp & Curtis, 2009; Mathieu et al, 2000) and being pregnant (Cobey & Salem, 2004; Rifai et al, 2013; Weimann et al, 1998) on tumor growth (see Chapter 89). The heterogeneous distribution of glutamine synthase is attributable to -catenin activation without -catenin�activating mutations, in accordance with polyclonal origin, and could possibly be the results of abnormal arterial blood circulate (Rebouissou et al, 2008). This also doubtless explains the prevalence of those lesions in patients with vascular issues of the liver, together with Budd-Chiari syndrome (CazalsHatem et al, 2003), hereditary hemorrhagic telangiectasia (Gincul et al, 2008), congenital absence of portal flow (Kim et al, 2004), or portal thrombosis with subsequent hepatic arterialization (Bureau et al, 2004).
Noroxin 400 mg generic free shipping
Bachellier P antibiotic used for kidney infection cheap noroxin 400 mg with visa, et al: Is pancreaticoduodenectomy with mesentericoportal venous resection secure and worthwhile Basse L antibiotic 3 day dose 400 mg noroxin cheap overnight delivery, et al: Accelerated postoperative restoration programme after colonic resection improves bodily efficiency, pulmonary operate and physique composition, Br J Surg 89:446�453, 2002. Benoist S, et al: Is there a job of preservation of the spleen in distal pancreatectomy Bettschart V, et al: Presentation, therapy and end result in patients with ampullary tumours, Br J Surg 91(12):1600�1607, 2004. Capussotti L, et al: Extended lymphadenectomy and vein resection for pancreatic head most cancers: outcomes and implications for remedy, Arch Surg 138:1316�1322, 2003. Carrere N, et al: Pancreaticoduodenectomy with mesentericoportal vein resection for adenocarcinoma of the pancreatic head, World J Surg 30:1526�1535, 2006. Fong Y, et al: Long-term survival is superior after resection for cancer in high-volume centers, Ann Surg 242(4):540�544, 2005. Friess H, et al: Randomised managed multicentre study of the prevention of issues by octreotide for patients present process surgery for persistent pancreatitis, Br J Surg 82:1270�1273, 1995. Gress F, et al: Endoscopic ultrasonography-guided fine-needle aspiration biopsy of suspected pancreatic cancer, Ann Intern Med 134:459�464, 2001. Gudjonsson B: Carcinoma of the pancreas: crucial evaluation of costs, results of resections, and the need for standardized reporting, J Am Coll Surg 181:483�503, 1995. Gurleyik E, et al: Perfusion and useful anatomy of the splenic remnant supplied by brief gastric vessels, Am J Surg 179:490�493, 2000. Hartwig W, et al: Multivisceral resection for pancreatic malignancies: riskanalysis and long-term end result, Ann Surg 250(1):81�87, 2009. Henne-Bruns D, et al: Ductal adenocarcinoma of the pancreas head: survival after regional versus extended lymphadenectomy, Hepatogastroenterology forty five:855�866, 1998. Horstmann O, et al: Pylorus preservation has no influence on delayed gastric emptying after pancreatic head resection, Pancreas 28:69�74, 2004. Iacono C, et al: Is there a place for central pancreatectomy in pancreatic surgery Imamura M, et al: A randomized multicenter trial comparing resection and radiochemotherapy for resectable regionally invasive pancreatic most cancers, Surgery 136:1003�1011, 2004. Ishikawa O: What constitutes curative pancreatectomy for adenocarcinoma of the pancreas Japan Pancreas Society: General guidelines for the examine on pancreatic most cancers, ed four, Tokyo, 1993, Kanehara. Klauss M, et al: A new invasion rating for determining the resectability of pancreatic carcinomas with contrast-enhanced multidetector computed tomography, Pancreatology 8(2):204�210, 2008. LaFemina J, et al: Hepatic arterial nodal metastases in pancreatic cancer: is this the node of significance Leach S, et al: Survival following pancreaticoduodenectomy with resection of the superior mesenteric-portal vein confluence for adenocarcinoma of the pancreatic head, Br J Surg 85:611�617, 1998. Li-Ling J, Irving M: Somatostatin and octreotide in the prevention of postoperative pancreatic complications and the treatment of enterocutaneous pancreatic fistulas: a systematic evaluate of randomized controlled trials, Br J Surg 88:190�199, 2001. Menges M, et al: the double duct sign in sufferers with malignant and benign pancreatic lesions, Gastrointest Endosc 52:74�77, 2000. Mismetti P, et al: Meta-analysis of low molecular weight heparin within the prevention of venous thromboembolism in general surgery, Br J Surg 88:913�930, 2001. Nagakawa T, et al: the pattern of lymph node involvement in carcinoma of the top of the pancreas: histologic study of the surgical findings in sufferers undergoing extensive nodal dissections, Int J Pancreatol thirteen:15�22, 1993. Nakao A, et al: Indications and techniques of prolonged resection for pancreatic cancer, World J Surg 30:976�982, 2006. Nimura Y, et al: Standard versus extended lymphadenectomy in pancreatoduodenectomy for pancreatic most cancers: a multicenter randomized controlled trial, Pancreatology 4:274, 2004. Pedrazzoli S, et al: Standard versus prolonged lymphadenectomy related to pancreatoduodenectomy in the surgical remedy of adenocarcinoma of the top of the pancreas: a multicentre prospective randomized study. Pedrazzoli S, et al: A surgical and pathological based mostly classification of resective treatment of pancreatic most cancers, Dig Surg 16:337�345, 1999. Popiela T, et al: Does extended lymphadenectomy improve survival of pancreatic cancer sufferers Posner S, et al: Safety and long-tem efficacy of transduodenal excision for tumours of the ampulla of Vater, Surgery 128:694�701, 2000. Riediger H, et al: Delayed gastric emptying after pylorus-preserving pancreatoduodenectomy is strongly associated to other postoperative issues, J Gastrointest Surg 7(6):758�765, 2003. Riediger H, et al: Postoperative morbidity and long-term survival after pancreaticoduodenectomy with superior mesentericoportal vein resection, J Gastrointest Surg 10:1106�1115, 2006. Sasson A, et al: En bloc resection for domestically superior cancer of the pancreas: is it worthwhile Sch�fer M, et al: Evidence-based pancreatic head resection for pancreatic cancer and continual pancreatitis, Ann Surg 236:137�148, 2002. Sganga G: New views in antibiotic prophylaxis for intraabdominal surgery, J Hosp Infect 50(Suppl A):S17�S21, 2002. Shoup M, et al: the value of splenic preservation with distal pancreatectomy, Arch Surg 137:164�168, 2002. Siriwardana H, Siriwardena A: Systematic evaluation of end result of synchronous portal-superior mesenteric vein resection during pancreatectomy for most cancers, Br J Surg 93:662�673, 2006. Stojadinovic A, et al: An evidence-based method to the surgical administration of resectable pancreatic adenocarcinoma, J Am Coll Surg 196:954�964, 2003. Sugiyama M, Atomi Y: Pylorus-preserving whole pancreatectomy for pancreatic cancer, World J Surg 24:66�71, 2000. Tran K, et al: Occlusion of the pancreatic duct versus pancreaticojejunostomy: a potential randomized trial, Ann Surg 236:422�428, 2002. Trede M, et al: Personal observations, opinions, and approaches to most cancers of the pancreas and periampullary space, Surg Clin North Am 81:595�610, 2001. Van Buren G, et al: A randomized potential multicenter trial of pancreaticoduodenectomy with and with out routine intraperitoneal draingage, Ann Surg 259(4):605�612, 2014. Wagner M, et al: Pylorus-preserving total pancreatectomy: early and late results, Dig Surg 18:188�195, 2001. Wagner M, et al: Curative resection is the only most important issue figuring out end result in sufferers with pancreatic adenocarcinoma, Br J Surg 91:586�594, 2004. Weitz J, et al: the "artery first" approach for resection of pancreatic head most cancers, J Am Coll Surg 210(2):e1�e4, 2010. Welsch T, et al: Evaluation of the International Study Group of Pancreatic Surgery definition of delayed gastric emptying after pancreatoduodenectomy in a high-volume centre, Br J Surg 97(7): 1043�1050, 2010. White R, et al: Current utility of staging laparoscopy for pancreatic and peripancreatic neoplasms, J Am Coll Surg 206(3):445�450, 2008.
Syndromes
- Abnormal tricuspid valve
- Fludrocortisone, midodrine, botox, sidenafil for autonomic dysfunction
- Threonine
- Drug manufacturers
- Smoking
- Nitrites
- Urinary frequency
- Disregard the safety of self and others
- Infection
- Long-term pressure on the elbow
Discount 400 mg noroxin with mastercard
However antibiotic resistance zone of inhibition discount 400 mg noroxin with amex, most authors prefer to carry out commonplace pancreatic resections bacteria mod noroxin 400 mg generic on line, even in instances of small pancreatic metastases (Adler et al, 2014). The benefits of standard procedures include reaching a whole lymphadenectomy and reducing native recurrence and possibly postoperative complication charges. For sufferers with multiple lesions, to perform a normal resection in addition to enucleation in an effort to keep away from complete pancreatectomy seems to be possible. However, long-term follow-up must be scheduled for the potential for native relapse in the pancreas, in addition to in different distant organs. Data for these variants are too restricted to define correct biology and natural history. Whenever other organs are involved, pancreatic resections are associated with very poor consequence with early relapse and dying (Reddy & Wolfgang, 2009; Strobel et al, 2009; Sugimoto et al, 2013). In such selected cases, the surgeon should concentrate on the poor consequence after surgical procedure, and the clinical choice must be taken only in the setting of a multidisciplinary method. Such oncologic analysis has been already assessed for liver metastases of colorectal origin (Pulitano et al, 2010; Tomlinson et al, 2007). Unfortunately, there are sparse data available on the long-term outcome after resection of pancreatic metastases (Table sixty four. In our experience, the median general survival of a cohort of resected patients was one hundred forty months (95% confidence interval, one hundred and one. From Facy et al, 2013; Konstantinidis et al, 2010; Law et al, 2003; Strobel et al, 2009; Tosoian et al, 2014; and Zerbi et al, 2008. This is notably better than the finish result obtained in the cited Italian multicenter study for the subgroup of medically handled sufferers (median general survival of 86 months). Nevertheless, the actual advantage of resection should be evaluated only within the light of the long-term results. We have discovered a really favorable 25% disease-free survival 10 years after resection, which emphasizes that only a curative resection has the flexibility to provide long-term disease-free survival. In the modern period, and as for different oncologic illness, a multidisciplinary approach involving surgeons and medical oncologists should be advocated to "tailor" the suitable remedy for the only affected person. Pan B, et al: Secondary tumors of the pancreas: a case collection, Anticancer Res 32:1449�1452, 2012. Perez Ochoa A, et al: Pancreatic metastases from ductal and lobular carcinomas of the breast, Clin Transl Oncol 9:603�605, 2007. Reddy S, et al: Pancreatic resection of isolated metastases from nonpancreatic major cancers, Ann Surg Oncol 15:3199�3206, 2008. Sperti C, et al: Metastatic tumors to the pancreas: the function of surgical procedure, World J Gastrointest Oncol 6:381�392, 2014. Strobel O, et al: Survival information justifies resection for pancreatic metastases, Ann Surg Oncol 16:3340�3349, 2009. Sugimoto M, et al: Pancreatic resection for metastatic melanoma originating from the nasal cavity: a case report and literature review, Anticancer Res 33:567�573, 2013. Yamamoto H, et al: Surgical treatment for pancreatic metastasis from soft-tissue sarcoma: report of two circumstances, Am J Clin Oncol 24:198� 200, 2001. Zerbi A, et al: Pancreatic metastasis from renal cell carcinoma: which sufferers benefit from surgical resection Akashi Y, et al: Outcome after surgical resection of isolated metastases to the pancreas, Hepatogastroenterology fifty seven:1549�1552, 2010. Balzano G, et al: Effect of hospital volume on consequence of pancreaticoduodenectomy in Italy, Br J Surg 95:357�362, 2008. Bassi C, et al: High recurrence rate after atypical resection for pancreatic metastases from renal cell carcinoma, Br J Surg 90:555�559, 2003. Bednar F, et al: Breast most cancers metastases to the pancreas, J Gastrointest Surg 17:1826�1831, 2013. Crippa S, et al: Surgical remedy of metastatic tumors to the pancreas: a single center experience and review of the literature, World J Surg 30:1536�1542, 2006. Facy O, et al: Interest of intraoperative ultrasonography throughout pancreatectomy for metastatic renal cell carcinoma, Clin Res Hepatol Gastroenterol 37:530�534, 2013. Ghavamian R, et al: Renal cell carcinoma metastatic to the pancreas: clinical and radiological features, Mayo Clin Proc 75:581�585, 2000. Jarufe N, et al: Surgical therapy of metastases to the pancreas, Surgeon three:79�83, 2005. Jingu K, et al: Surgical remedy of a solitary pancreatic metastasis from renal cell carcinoma: report of a case, Surg Today 28:91�94, 1998. Minni F, et al: Pancreatic metastases: observations of three circumstances and evaluate of the literature, Pancreatology four:509�520, 2004. Molino C, et al: Pancreatic solitary and synchronous metastasis from breast most cancers: a case report and systematic review of controversies in analysis and treatment, World J Surg Oncol 12:2, 2014. Mourra N, et al: Isolated metastatic tumors to the pancreas: Hopital St-Antoine expertise, Pancreas 39:577�580, 2010. These tumors are classified as functional, if they trigger a selected hormonal syndrome, or nonfunctional. Homozygous deletion of the gene is lethal in mouse embryos (Bertolino et al, 2003, J. The most commonly mutated genes in this group of tumors are the tumor suppressors p53 (95%) and Rb (74%) (Yachida et al, 2012, J. Most sufferers are recognized between the ages of 60 to eighty years (Fraenkel et al, 2012). It is the most broadly used grading system and the tactic utilized by most surgical pathology laboratories. Grade is set either by the mitotic index or Ki-67 index (Bosman et al, 2010). Ki-67 labeling tags neoplastic cells with an antibody after which reports the percentage of cells that stain positively (Jamali et al, 2008) (Table sixty five. In addition to grade and the presence of distant metastases, age at diagnosis can even help stratify sufferers into prognostic categories, as an older age at prognosis correlates with impaired survival (<55 years, 67. Endocrine Tumors Chapter 65 Pancreatic neuroendocrine tumors: classification, clinical image, prognosis, and therapy 999 of tumors. The surgical management of those tumors is advanced and mentioned in higher detail later (see Chapters 66 and 67). The prognosis may be confirmed by drawing plasma glucose, insulin, C-peptide, and proinsulin levels during a 72-hour quick. Malignant insulinomas are inclined to produce larger ranges of insulin and proinsulin and thus more extreme signs because of the reality that their metastases also secrete these hormones. To carry out this take a look at, the right and left hepatic veins are catheterized by way of a femoral puncture.
Noroxin 400 mg with amex
Hirooka M antibiotics korean buy noroxin 400 mg visa, Kimura C: Membranous obstruction of the hepatic portion of the inferior vena cava bacterial 16s sequencing purchase 400 mg noroxin overnight delivery, Arch Surg 100:656�663, 1970. Hirschberg B, et al: Flow cytometric evaluation of autonomous development of erythroid precursors in liquid tradition detects occult polycythemia vera within the Budd-Chiari syndrome, J Hepatol 32:574�578, 2000. Hoekstra J, et al: Vascular liver disease: prognosis, therapy and prognosis of Budd-Chiari syndrome, Neth J Med 66:334�339, 2008. Hoekstra J, et al: Paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria in Budd-Chiari syndrome: findings from a cohort study, J Hepatol fifty one:696�706, 2009. Hosoki T, et al: Hepatic venous outflow obstruction: evaluation with pulsed Doppler sonography, Radiology 170:733�737, 1989. Huguet C, et al: Interposition mesocaval shunt for continual primary occlusion of the hepatic veins, Surg Gynecol Obstet 148:691�698, 1979. Inafuku H, et al: A three-decade expertise of radical endvenectomy with pericardial patch graft for correction of Budd-Chiari syndrome, J Vasc Surg 50:590�593, 2009. Iwahashi K: Surgical correction of the inferior vena cava obstruction with Budd-Chiari syndrome, Arch Jpn Chir 50:559�570, 1981. Iwatsuki S, et al: Liver transplantation in the remedy of bleeding esophageal varices, Surgery 104:697�705, 1988. Kage M, et al: Histopathology of membranous obstruction of the inferior vena cava in the Budd-Chiari syndrome, Gastroenterology 102:2081�2090, 1992. Kimura C, et al: Membranous obstruction of the hepatic portion of the inferior vena cava: medical examine of 9 instances, Surgery 72:551�559, 1972. Knoop M, et al: Liver transplantation for Budd-Chiara syndrome, Transplant Proc 26:3577�3578, 1994a. Knoop M, et al: Treatment of the Budd-Chiari syndrome with orthotopic liver transplantation and long-term anticoagulation, Clin Transplant eight:67�72, 1994b. Koja K, et al: Radical open end venectomy with autologous pericardial patch graft for correction of Budd-Chiari syndrome, Cardiovasc Surg four:500�504, 1996. Koster T, et al: Venous thrombosis as a end result of poor anticoagulant response to activated protein C: Leiden Thrombophilia Study, Lancet 342:1503�1506, 1993. Kreel L, et al: Vascular radiology within the Budd-Chiari syndrome, Br J Radiol 40:755�759, 1967. Kuniyoshi Y, et al: Improvement in esophageal varices and liver histology postoperatively in Budd-Chiari syndrome, Ann Thorac Surg sixty five:1711�1714, 1998. Langer B, et al: Clinical spectrum of the Budd-Chiari syndrome and its surgical administration, Am J Surg 129:137�145, 1975. Li T, et al: Feasibility and midterm outcomes of percutaneous transhepatic balloon angioplasty for symptomatic Budd-Chiari syndrome secondary to hepatic venous obstruction, J Vasc Surg 50:1079�1084, 2009. Mazzaferro V, et al: Liver transplantation in sufferers with previous portasystemic shunt, Am J Surg a hundred and sixty:111�115, 1990. McCarthy P, et al: the Budd-Chiari syndrome: medical and surgical administration of 30 patients, Arch Surg a hundred and twenty:657�662, 1985. Mentha G, et al: Liver transplantation for Budd-Chiari syndrome: a European study on 248 patients from 51 centers, J Hepatol forty four:520� 528, 2006. Michl P, et al: Successful remedy of continual Budd-Chiari syndrome with transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt, J Hepatol 32: 516�520, 1999. Millener P, et al: Color Doppler imaging findings in sufferers with Budd-Chiari syndrome: correlation with venographic findings, Am J Roentgenol 161(2):307�312, 1993. Minegaux F, et al: Comparison of transjugular and surgical portosystemic shunts on the result of liver transplantation, Arch Surg 129:1018�1024, 1994. Mor E, et al: Defibrotide for the therapy of veno-occlusive disease after liver transplantation, Transplantation seventy two:1237�1240, 2001. Ohashi K, et al: the Japanese multicenter open randomized trial of ursodeoxycholic acid prophylaxis for hepatic veno-occlusive illness after stem cell transplantation, Am J Hematol 64:32�38, 2000. Okamoto E, et al: Simultaneous radical surgical therapy for membranous obstruction of the inferior vena cava and the coincident hepatocellular carcinoma: the primary profitable case, Jpn J Surg thirteen: 135�140, 1983. Okuda H, et al: Epidemiological and medical options of Budd-Chiari syndrome in Japan, J Hepatol 22:1�9, 1995. Okuda K: Inferior vena cava thrombosis at its hepatic portion (obliterative hepatocavopathy), Semin Liver Dis 22:15�26, 2002. Ono J, et al: Membranous obstruction of the inferior vena cava, Ann Surg 197:454�458, 1983. In Fischer J, Bland K, editors: Mastery of surgical procedure, ed 6, Philadelphia, 2010, Lippincott Williams & Wilkins. In Clavien P-A, et al, editors: Atlas of upper gastrointestinal and HepatoPancreatico-Biliary surgery, Berlin-Heidelberg, 2007, Springer-Verlag, pp 687�702. Panis Y, et al: Portosystemic shunt in Budd-Chiari syndrome: longterm survival and factors affecting shunt patency in 25 sufferers in Western nations, Surgery 115:276�281, 1994. Pasic M, et al: Transcaval liver resection with hepatoatrial anastomosis for therapy of patients with the Budd-Chiari syndrome: late results, J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg 106:275�282, 1993. Pelletier S, et al: Antiphospholipid syndrome as the second explanation for non-tumorous Budd-Chiari syndrome, J Hepatol 21:76�80, 1994. Pezzuoli G, et al: Portacaval shunt in the treatment of major BuddChiari syndrome, Surgery ninety eight:319�323, 1985. Plessier A, et al: Aiming at minimal invasiveness as a therapeutic strategy for Budd-Chiari syndrome, Hepatology 44:1308�1316, 2006. Prandi D, et al: Side-to-side portacaval shunt in the remedy of BuddChiari syndrome, Gastroenterology 68:137�141, 1975. Qureshi A, et al: Defibrotide in the prevention and therapy of venoocclusive illness in autologous and allogeneic stem cell transplantation in kids, Pediatr Blood Cancer 50:831�832, 2008. Reichart B, et al: Surgical remedy for congenital occlusion of the inferior vena cava in its diaphragmatic portion, Thorac Cardiovasc Surg 29:180�182, 1981. Ringe B, et al: Which is one of the best surgical procedure for Budd-Chiari syndrome: venous decompression of liver transplantation Rogopoulos G, et al: Transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt for Budd-Chiari syndrome after failure of surgical shunting, Arch Surg a hundred thirty:227�228, 1995. R�ssle M, et al: the Budd-Chiari syndrome: end result after therapy with the transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt, Surgery a hundred thirty five:394�403, 2004. Ruutu T, et al: Ursodeoxycholic acid for the prevention of hepatic complications in allogeneic stem cell transplantation, Blood one hundred: 1977�1983, 2002. Salat C, et al: Plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 confirms the analysis of hepatic veno-occlusive disease in sufferers with hyperbilirubinemia after bone marrow transplantation, Blood 89:2184�2188, 1997a. Salat C, et al: Laboratory markers of veno-occlusive disease in the midst of bone marrow and subsequent liver transplantation, Bone Marrow Transplant 19:487�490, 1997b. Sato M, et al: Percutaneous transluminal angioplasty in segmental obstruction of the hepatic inferior vena cava: long-term results, Cardiovasc Intervent Radiol 13:189�192, 1990. Sawada S, et al: Budd-Chiari syndrome treated by interventional radiology including percutaneous transluminal angioplasty and selfexpandable metallic stent placement. Schramek A, et al: New observations within the medical spectrum of the Budd-Chiari syndrome, Ann Surg 180:368�372, 1974.
Discount 400 mg noroxin overnight delivery
Liver Cancer Study Group of Japan: Primary liver cancer in Japan: clinicopathologic features and outcomes of surgical remedy antibiotics make period late 400 mg noroxin sale, Ann Surg 211:277�287 antibiotics gut microbiome noroxin 400 mg quality, 1990. Liver Cancer Study Group of Japan: General rules for the scientific and pathological research of primary liver cancer, ed 2, Tokyo, 2003, Kanehara. Lumachi F, et al: Measurement of serum carcinoembryonic antigen, carbohydrate antigen 19-9, cytokeratin-19 fragment and matrix metalloproteinase-7 for detecting cholangiocarcinoma: a preliminary case-control study, Anticancer Res 34:6663�6667, 2014. Luo X, et al: Survival outcomes and prognostic components of surgical remedy for all probably resectable intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma: a large single-center cohort examine, J Gastrointest Surg 18:562� 572, 2014. MacDonald O, Crane C: Palliative and postoperative radiotherapy for biliary tract most cancers, Surg Oncol Clin N Am eleven:941�954, 2002. Manfredi R, et al: Magnetic resonance imaging of cholangiocarcinoma, Semin Liver Dis 24:155�164, 2004. Marcos L, et al: Update on hepatobiliary flukes: fascioliasis, opisthorchiasis and clinorchiasis, Curr Opin Infect Dis 21:523�530, 2008. Marumoto M, et al: Systemic gemcitabine combined with hepatic arterial infusion chemotherapy with cisplatin, 5-fluorouracil and isovorin within the therapy of advanced intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma: a pilot research, Hepatogastroenterology 61:162�167, 2014. Morris-Stiff G, et al: Cholangiocarcinoma complicating major sclerosing cholangitis: a 24 yr experience, Dig Surg 25:126�132, 2008. Mouli S, et al: Yttrium-90 radioembolization for intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma: safety, response, and survival evaluation, J Vasc Interv Radiol 24:1227�1234, 2013. Nakagawa T, et al: Number of lymph node metastases is a significant prognostic consider intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma, World J Surg 29:728�733, 2005. Nakajima T, et al: A histopathologic research of 102 instances of intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma, Hum Pathol 19:112�134, 1988. Nakanuma Y, et al: Are hepatolithiasis and cholangiocarcinoma aetiologically associated A morphological examine of 12 cases of hepatolithiasis related to cholangiocarcinoma, Virchows Arch A Pathol Anat Histopathol 406:45�58, 1985. Nakayama T, et al: Pathological affirmation of para-aortic lymph nodes standing as a potential criterion for the number of intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma patients for radical resection with regional lymph node illness, World J Surg 38:1763�1768, 2014. Nathan H, et al: A proposed staging system for intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma, Ann Surg Oncol sixteen:14�22, 2009. Ohashi K, et al: Clinical traits and proliferating activity of intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma, J Gastroenterol Hepatol 9:442�446, 1994. Ohlsson B, et al: Percutaneous fine-needle aspiration cytology in the analysis and management of liver tumours, Br J Surg 89:757�762, 1994. Ohtsuka T, et al: Carcinoma arising in a choledochoele, Endoscopy 33:614�619, 2001. Ohtsuka M, et al: Results of surgical remedy for intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma and clinicopathological components influencing survival, Br J Surg 89:1525�1531, 2002. Okabayashi T, et al: A new staging system for mass-forming intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma: evaluation of preoperative and postoperative variables, Cancer ninety two:2374�2383, 2001. Park J, et al: Inhibition of interleukin 6-mediated mitogen-activated protein kinase activation attenuates progress of cholangiocarcinoma cell line, Hepatology 30:1128�1133, 1999. Patel T: Increasing incidence and mortality of primary intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma in the United States, Hepatology 33:1353�1357, 2001. Patel T, Singh P: Cholangiocarcinoma: rising approaches to a challenging most cancers, Curr Opin Gastroenterol 23:317�323, 2007. Petrowsky H, et al: Impact of built-in positron emission tomography and computed tomography on staging and management of gallbladder cancer and cholangiocarcinoma, J Hepatol 45:43�50, 2006. Pichlmayr R, et al: Surgical remedy of cholangiocellular carcinoma, World J Surg 19:83�88, 1995. Rafi S, et al: Yttrium-90 radioembolization for unresectable commonplace chemorefractory intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma: survival, efficacy and security research, Cardiovasc Intervent Radiol 36:440�448, 2013. Rai R, et al: Radiofrequency ablation of recurrent cholangiocarcinoma after orthotopic liver transplantation: a case report, World J Gastroenterol 11:612�613, 2005. Ralphs S, Khan S: the function of hepatitis viruses in cholangiocarcinoma, J Viral Hepat 20:297�305, 2013. Ribero D, et al: Surgical approaches for long-term survival of patients with intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma: A multi-institutional analysis of 434 sufferers, Arch Surg 147:1107�1113, 2012. Roayaie S, et al: Aggressive surgical therapy of intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma: predictors of outcomes, J Am Coll Surg 187:365�372, 1998. Robles R, et al: Spanish expertise in liver transplantation for hilar and peripheral cholangiocarcinoma, Ann Surg 239:265�271, 2004. Saiura A, et al: Intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma: analysis of 44 consecutive circumstances together with 5 circumstances with repeat resections, Am J Surg 201:203�208, 2011. Schiffman S, et al: Molecular factors related to recurrence and survival following hepatectomy in patients with intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma: a guide to adjuvant scientific trials, J Surg Oncol 109: 98�103, 2014. Schwartz J, et al: Liver transplantation for cholangiocarcinoma, Transplantation 88:295�298, 2009. Shaib Y, et al: Rising incidence of intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma in the United States: a true increase Shaib Y, et al: Risk factors for intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma within the United States: a case control examine, Gastroenterology 128:620�626, 2005. Shindoh J, et al: Kinetic growth price after portal vein embolization predicts posthepatectomy outcomes: toward zero liver-related mortality in sufferers with colorectal liver metastases and small future liver remnant, J Am Coll Surg 216:201�209, 2013. Shirabe K, et al: Intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma: its mode of spreading and therapeutic modalities, Surgery 131(1 Pt 2):S159�S164, 2002. Sia D, et al: Integrative molecular evaluation of intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma reveals 2 courses which have completely different outcomes, Gastroenterology one hundred forty four:829�840, 2013a. Sia D, et al: Intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma: pathogenesis and rationale for molecular therapeutics, Oncogene 32:4861�4870, 2013b. Spolverato G, et al: Tumor measurement predicts vascular invasion and histologic grade amongst sufferers undergoing resection of intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma, J Gastrointest Surg 18:1284�1291, 2014. Sripa B, Pairojkul C: Cholangiocarcinoma: classes from Thailand, Curr Opin Gastroenterol 24:349�356, 2008. Sriputtha S, et al: Survival price of intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma sufferers after surgical treatment in Thailand, Asian Pac J Cancer Prev 14:1107�1110, 2013. Sudo Y, et al: Oncocytic biliary cystadenocarcinoma is a form of intraductal oncocytic papillary neoplasm of the liver, Mod Pathol 14:1304� 1309, 2001. Szendroi M, et al: Asbestos bodies in a bile duct most cancers after occupational exposure, Environ Res 30:270�280, 1983. Thomas M: Systemic and focused remedy for biliary tract tumors and first liver tumours, Surg Oncol Clin N Am 23:369�381, 2014. Torbenson M, et al: Bile duct dysplasia in the setting of continual hepatitis C and alcohol cirrhosis, Am J Surg Pathol 31:1410�1413, 2007. Uchiyama K, et al: Impact of nodal involvement on surgical outcomes in intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma: a multicentre evaluation by the Study Group for Hepatic Surgery of the Japanese Society of HepatoBiliaryPancreatic Surgery, J Hepatobiliary Pancreat Surg 18:443� 452, 2011. Valle J, et al: Cisplatin plus gemcitabine for biliary tract most cancers, N Engl J Med 362:1273�1281, 2010. Vallin M, et al: Unrecognised intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma: an evaluation of 993 adult cirrhotic liver explants, Clin Transplant 27:403� 409, 2013. Vogl T, et al: Hepatic arterial chemotherapy with gemcitabine in sufferers with unresectable cholangiocarcinomas and liver metastases of pancreatic most cancers: a medical examine on most tolerable dose and remedy efficacy, J Cancer Res Clin Oncol 132:745�755, 2006.

Buy cheap noroxin 400 mg
A mild microscopic and immunohistochemical research of 70 sufferers most common antibiotics for sinus infection noroxin 400 mg buy, Am J Surg Pathol 18(11):1078�1091 antimicrobial drugs antimicrobial agents noroxin 400 mg online, 1994. Di Tommaso L, et al: Diagnostic accuracy of clathrin heavy chain staining in a marker panel for the diagnosis of small hepatocellular carcinoma, Hepatology 53(5):1549�1557, 2011. Di Tommaso L, et al: Advanced precancerous lesions in the liver, Best Pract Res Clin Gastroenterol 27(2):269�284, 2013. Dietze O, et al: Malignant epithelioid haemangioendothelioma of the liver: a clinicopathological and histochemical examine of 12 instances, Histopathology 15(3):225�237, 1989. Doi H, et al: Primary hepatic marginal zone B cell lymphoma of mucosa-associated lymphoid tissue kind: case report and evaluate of the literature, Int J Hematol 88(4):418�423, 2008. Dokmak S, et al: A single-center surgical expertise of 122 sufferers with single and multiple hepatocellular adenomas, Gastroenterology 137(5):1698�1705, 2009. Ebata T, et al: the concept of perihilar cholangiocarcinoma is legitimate, Br J Surg 96(8):926�934, 2009. Fabre A, et al: Histologic scoring of liver biopsy in focal nodular hyperplasia with atypical presentation, Hepatology 35:414�420, 2002. Falk H, et al: Arsenic-related hepatic angiosarcoma, Am J Ind Med 2(1):43�50, 1981. Falk H, et al: Epidemiology of hepatic angiosarcoma in the United States: 1964-1974, Environ Health Perspect 41:107�113, 1981. Farges O, et al: Changing trends in malignant transformation of hepatocellular adenoma, Gut 60(1):85�89, 2011. Ferrell L, et al: Incidence and diagnostic features of macroregenerative nodules vs. Flemming P, et al: Common and epithelioid variants of hepatic angiomyolipoma exhibit clonal growth and share a distinctive immunophenotype, Hepatology 32(2):213�217, 2000. Flucke U, et al: Epithelioid Hemangioendothelioma: clinicopathologic, immunhistochemical, and molecular genetic evaluation of 39 cases, Diagn Pathol 9:131, 2014. Forner A, et al: Diagnosis of hepatic nodules 20 mm or smaller in cirrhosis: prospective validation of the noninvasive diagnostic standards for hepatocellular carcinoma, Hepatology 47:97�104, 2008. Fujimoto A, et al: Whole-genome sequencing of liver cancers identifies etiological influences on mutation patterns and recurrent mutations in chromatin regulators, Nat Genet 44(7):760�764, 2012. A clinicopathologic examine of 345 post-mortem circumstances of continual liver illness, Cancer 61:99�9105, 1988. Gandolfi L, et al: Natural historical past of hepatic haemangiomas: scientific and ultrasound examine, Gut 32(6):677�680, 1991. Ganne-Carrie N, et al: Predictive rating for the development of hepatocellular carcinoma and additional value of liver large cell dysplasia in Western sufferers with cirrhosis, Hepatology 23(5):1112�1118, 1996. Gaulard P, et al: Peripheral T-cell lymphoma presenting as predominant liver disease: a report of three circumstances, Hepatology 6(5):864�868, 1986. Gong Y, et al: Focal nodular hyperplasia coexistent with hepatoblastoma in a 36-d-old toddler, World J Gastroenterol 21(3):1028�1031, 2015. Grando-Lemaire V, et al: Hepatocellular carcinoma without cirrhosis in the West: epidemiological factors and histopathology of the nontumorous liver. Guedj N, et al: Comparative protein expression profiles of hilar and peripheral hepatic cholangiocarcinomas, J Hepatol 51(1):93�101, 2009. Nonomura A, et al: Angiomyolipoma of the liver: a collective review, J Gastroenterol 29(1):95�105, 1994. Nonomura A, et al: Multiple angiomyolipoma of the liver, J Clin Gastroenterol 20(3):248�251, 1995. Nordenstedt H, et al: the changing pattern of epidemiology in hepatocellular carcinoma, Dig Liver Dis 42(Suppl 3):S206�S214, 2010. Oh B-K, et al: Telomere shortening and telomerase reactivation in dysplastic nodules of human hepatocarcinogenesis, J Hepatol 39:786�792, 2003. Ohnishi K, et al: Prognosis of hepatocellular carcinoma smaller than 5 cm in relation to remedy: examine of a hundred patients, Hepatology 7:1285�1290, 1987. Ohtsuka M, et al: Intraductal papillary neoplasms of the bile duct, Int J Hepatol 2014:459091, 2014. Okuda K, et al: Clinicopathologic options of encapsulated hepatocellular carcinoma: a research of 26 instances, Cancer 40:1240�1245, 1977. Okuda K, et al: Hepatocellular carcinoma arising in noncirrhotic and extremely cirrhotic livers: a comparative research of histopathology and frequency of hepatitis B markers, Cancer 49:450�455, 1982. Okuda K, et al: Gross anatomic options of hepatocellular carcinoma from three disparate geographic areas. Omata M, et al: Sclerosing hepatic carcinoma: relationship to hypercalcemia, Liver 1:33�49, 1981. Pachera S, et al: Undifferentiated embryonal sarcoma of the liver: case report and literature survey, J Hepatobiliary Pancreat Surg 15(5):536� 544, 2008. Paradis V, et al: Evidence for the polyclonal nature of focal nodular hyperplasia of the liver by the examine of X-chromosome inactivation, Hepatology 26(4):891�895, 1997. Paradis V, et al: Clonal analysis of macronodules in cirrhosis, Hepatology 28:953�958, 1998. Paradis V, et al: Hepatocellular carcinomas in sufferers with metabolic syndrome often develop with out vital liver fibrosis: a pathological analysis, Hepatology 49(3):851�859, 2009. Paradis V: Histopathology of hepatocellular carcinoma, Recent Results Cancer Res 190:21�32, 2013. Patel T: Increasing incidence and mortality of major intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma in the United States, Hepatology 33(6):1353� 1357, 2001. Patel T: Cholangiocarcinoma, Nat Clin Pract Gastroenterol Hepatol 3(1):33�42, 2006. Pinyol R, et al: Molecular profiling of liver tumors: classification and medical translation for choice making, Semin Liver Dis 34(4):363� 375, 2014. Ramacciato G, et al: Prognostic analysis of the model new American Joint Committee on Cancer/International Union against Cancer staging system for hepatocellular carcinoma: analysis of 112 cirrhotic patients resected for hepatocellular carcinoma, Ann Surg Oncol 12(4):289�297, 2005. Rebouissou S, et al: Molecular pathogenesis of focal nodular hyperplasia and hepatocellular adenoma, J Hepatol 48(1):163�170, 2008. Rebouissou S, et al: Frequent in-frame somatic deletions activate gp130 in inflammatory hepatocellular tumours, Nature 457:200� 204, 2009. Roayaie S, et al: A system of classifying microvascular invasion to predict consequence after resection in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma, Gastroenterology 137(3):850�855, 2009. Roncalli M: Hepatocellular nodules in cirrhosis: give attention to diagnostic criteria on liver biopsy. Roncalli M, et al: the vascular profile of regenerative and dysplastic nodules of the cirrhotic liver: implications for diagnosis and classification, Hepatology 30:1174�1178, 1999. Roncalli M, et al: Hepatocellular dysplastic nodules, Hepatol Res 37(Suppl 2):125�134, 2007. Ronot M, Vilgrain V: Imaging of benign hepatocellular lesions: current ideas and recent updates, Clin Res Hepatol Gastroenterol 38(6):681�688, 2014.
Noroxin 400 mg cheap overnight delivery
These methods typically fail finally antibiotic over the counter noroxin 400 mg purchase with visa, and as a final resort antibiotics for acne causing depression noroxin 400 mg buy lowest price, a stoma gadget is placed across the entry web site to comprise the ascites. The end result depends on the condition of the underlying hepatic parenchyma, the degree of isolation of the biliary tree, and the technical expertise of the operator. A thorough understanding of useful biliary anatomy and the supply of high-quality C. Malignant Tumors Chapter fifty two Interventional strategies in hilar and intrahepatic biliary strictures 859 imaging are essential to optimize outcome. Although pruritus may be palliated by draining even one segment of the liver, reducing the serum bilirubin to regular or near-normal is best achieved by draining no less than 30% of the liver, assuming the underlying parenchyma is comparatively normal. Contamination of undrained elements of the biliary tree could result from drainage catheter placement, with ongoing or recurrent cholangitis becoming an issue. For this cause, major stent placement must be thought-about when 30% or extra of the liver could be drained on the preliminary procedure. Malignant Tumors Chapter fifty two Interventional strategies in hilar and intrahepatic biliary strictures 859. Green C, et al: Does stent placement across the ampulla of Vater improve the risk of subsequent cholangitis Inal M, et al: Percutaneous placement of biliary metallic stents in sufferers with malignant hilar obstruction: unilobar versus bilobar drainage, J Vasc Interv Radiol 14(11):1409�1416, 2003a. Inal M, et al: Percutaneous placement of metallic stents in malignant biliary obstruction: one-stage or two-stage procedure Inal M, et al: Percutaneous self-expandable uncovered metallic stents in malignant biliary obstruction: complications, follow-up and reintervention in 154 patients, Acta Radiol 44(2):139�146, 2003c. Kawakubo K, et al: Multicenter retrospective study of endoscopic ultrasound-guided biliary drainage for malignant biliary obstruction in Japan, J Hepatobiliary Pancreat Sci 21:328�344, 2014. Leng J, et al: Percutaneous transhepatic and endoscopic biliary drainage for malignant biliary tract obstruction: a meta-analysis, World J Surg Oncol 12:272, 2014. Maybody M, et al: Primary patency of Wallstents in malignant bile duct obstruction: single vs. Miura S, et al: Bismuth classification is associated with the requirement for a number of biliary drainage in pre-operative patients with malignant perihilar biliary stricture, Surg Endosc 29(7):1862�1870, 2015. Ogura T, et al: Novel method of endoscopic ultrasound-guided hepatogastrostomy to stop stent dysfunction, J Gastroenterol Hepatol 29:1815�1821, 2014. Ozden I, et al: Endoscopic and radiologic interventions as the leading causes of extreme cholangitis in a tertiary referral middle, Am J Surg 189(6):702�706, 2005. Rerknimitr R, et al: Result of endoscopic biliary drainage in hilar cholangiocarcinoma, J Clin Gastroenterol 38(6):518�523, 2004. Thornton R, et al: Outcomes of patients present process percutaneous biliary drainage to cut back bilirubin for administration of chemotherapy, J Vasc Interv Radiol 23:89�96, 2012. Ulrich R, et al: Outcomes of patients present process percutaneous biliary drainage to cut back bilirubin for administration of chemotherapy. New York, 2009, Memorial Sloan-Kettering Cancer Center & New York University School of Medicine. It is an exocrine gland that secretes enzymes of digestion into the duodenum; it additionally performs endocrine capabilities, producing insulin, glucagon, somatostatin, pancreatic polypeptide, and ghrelin. However, many congenital situations go undetected until adulthood, when the affected person involves medical attention with nonspecific signs or an abnormality is found incidentally. This article describes the diagnosis, investigation, and treatment of the assorted congenital pancreatic abnormalities. The pancreas develops from two buds originating from the endodermal lining of the duodenum. During the second month of improvement, the stomach rotates and the duodenum turns into C-shaped. In the majority of individuals, the principle pancreatic duct (of Wirsung) is fashioned by the complete ventral duct and the distal dorsal duct, and enters the duodenum at the major papilla. This abnormality is termed pancreas divisum and is described in additional detail later (see Chapter 1). Annular pancreas is a uncommon congenital abnormality, the embryologic foundation of which is poorly understood. A full or incomplete ring of pancreatic tissue is discovered around the second a part of the duodenum, and it could cause symptoms (also discussed later). A variety of published studies have recognized mechanisms by which the pancreas is specified from the early endoderm (Kumar & Melton, 2003). Retinoic acid and bone morphogenic peptide each seem to have important roles in defining early endodermal compartments within the embryo (Stafford & Prince, 2002; Tiso et al, 2002). The origins of the signaling mechanisms concerned within the specification of the dorsal and ventral pancreas are totally different (Stanger & Hebrok, 2013). In the dorsal pancreas, signals arising from the notochord (Kim et al, 1997) and dorsal aorta (Lammert et al, 2001) are required; within the ventral pancreas, the lateral plate mesoderm is important (Kumar et al, 2003). The specific id of these indicators has not yet been established, though the Hedgehog family of signaling molecules seems to be important (Kim & MacDonald, 2002). The distal dorsal pancreatic duct sometimes fuses with the ventral pancreatic duct to drain the complete pancreas into the duodenum by way of the major papilla (see Chapter 1). The proximal dorsal duct can persist as an accessory pancreatic duct and should drain through the minor papilla. Variations exist the place a small branch might connect the two ducts, termed incomplete pancreas divisum. Beginning rotation of frequent duct and of ventral pancreas Common hepatic duct Stomach Portal vein Hepatic diverticulm Gallbladder Common bile duct Ventral pancreas Dorsal pancreas Superior mesenteric vein Dorsal pancreas Ventral pancreas three. However, as discussed by Stern (1986), numerous anatomists have been conscious of it much sooner than this, including Regnier de Graaf, who described the finding in 1664. Congenital Disorders Chapter 53 Congenital problems of the pancreas: surgical issues 863 bias, issue within the interpretation of pancreatograms, or inability to cannulate the minor papilla. With regard to the second level, you will want to become proficient at cannulation of the minor papilla, which is considerably tougher than cannulating the main papilla (see Chapter 29). Those proposing the theory counsel that obstruction happens at the degree of the minor papilla, the caliber of which is simply too slim to drain nearly all of the pancreas. This is supported by an early study reporting an elevated strain within the dorsal duct (23. Documented pancreatitis was current in 15 sufferers, and one other eleven had recurrent episodes of ache typical of pancreatitis. This controversy is a good example of the issue in figuring out a causal relationship between two components that seem to be related. The traditional criteria utilized in evaluating such a relationship can be utilized: (1) power of affiliation, (2) consistency across studies, (3) dose-response relationship, and (4) biologic plausibility. Of these, one observer detected three cases, and a second observer discovered four instances by A.