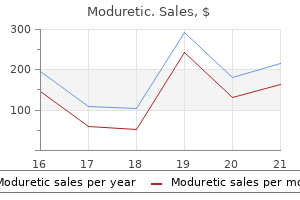
Moduretic dosages: 50 mg, 50 mg
Moduretic packs: 60 pills, 90 pills, 120 pills, 180 pills, 270 pills, 360 pills

50 mg moduretic fast delivery
For example arrhythmia reference guide moduretic 50 mg buy on line, humans lack constitutively organized lymphoid tissues within the nasal passages but typically have diffuse lymphoid tissues (likely ectopic lymphoid aggregates) [174] arteria omerale moduretic 50 mg free shipping. However, immunization or infection of the nasal passages typically elicits as much IgG as IgA [208]. These responses are clearly biased by the sort of adjuvant concerned, as immunization with cholera toxin usually results in IgA responses [205,209], whereas proteincontaining microparticles primarily elicit IgG responses [210]. Bronchus-Associated Lymphoid Tissue the decrease respiratory tract contains the trachea, bronchi, bronchioles, and alveoli, which are constantly exposed to inhaled antigens and pathogens, together with frequent respiratory viruses such as influenza virus, respiratory syncytial virus, and rhinovirus. Therefore the decrease respiratory tract has to be protected by strong immunological mechanisms. However, the lung can additionally be the primary site of gas exchange, which is most efficient when the distance between the respiratory epithelium of the alveoli and the vascular endothelium of the capillaries is minimized. As a end result, the delicate constructions of the decrease lung are susceptible to harm by inflammatory responses, implying that immune responses in the lung must be appropriately tempered to provide protection towards pathogens without inflicting undue irritation and injury. Given the exposure of the lung to inhaled antigens and pathogens, one may expect that the lower respiratory tract can be full of mucosal lymphoid tissues along the bronchi and bronchioles. These completely different constructions are undoubtedly distinct at a useful stage; nonetheless, the underlying reasons why several varieties of buildings are shaped stay unclear. Nevertheless, all the inflammatory pathways eventually converge on the differentiation and upkeep of stromal cells by way of lymphotoxin and the expression of homeostatic chemokines. Furthermore, antigen-specific plasmablasts accumulate on the border between the B cell follicle and the T cell area [265], suggesting that they have been generated locally. In half, this success may be attributed to an accelerated B cell and antibody response [234,273,275]. Given the location of antigen-specific germinal heart B cells and plasmablasts, this sooner B cell response could additionally be merely as a result of proximity to antigen. Alternatively, the native differentiation of T cells may be biased towards Tfh cells quite than effector cells. These diseases are associated with persistent inflammation and continual or repeated publicity to antigens. As a end result, vaccines that focus on specific mucosal websites or immunemodulating therapies which are directed toward explicit organs must account for these variations in order to be effective. Evolution of adaptive immunity: implications of a third lymphocyte lineage in lampreys. Dependence of antibody somatic diversification on gut-associated lymphoid tissue in rabbits. African lungfish reveal the evolutionary origins of organized mucosal lymphoid tissue in vertebrates. Fibroblastic reticular cells in lymph nodes regulate the homeostasis of naive T cells. Phenotypic and morphological properties of germinal center dark zone Cxcl12-expressing reticular cells. Follicular dendritic cells: origin, phenotype, and performance in well being and disease. Multi-platform next-generation sequencing of the home turkey (Meleagris gallopavo): genome assembly and evaluation. Appearance and growth of lymphoid cells in the hen (Gallus gallus) caecal tonsil. Fate mapping reveals origin and dynamics of lymph node follicular dendritic cells. B-cell follicle development remodels the conduit system and permits soluble antigen supply to follicular dendritic cells. Lymphotoxin alpha/beta and tumor necrosis issue are required for stromal cell expression of homing chemokines in B and T cell areas of the spleen. Endothelial cell-specific lymphotoxin-beta receptor signaling is crucial for lymph node and excessive endothelial venule formation. Follicular dendritic cells, conduits, lymphatic vessels, and excessive endothelial venules in tertiary lymphoid organs: parallels with lymph node stroma. High endothelial venules and different blood vessels: crucial regulators of lymphoid organ growth and function. Tumour necrosis factor alpha blockade impairs dendritic cell survival and performance in rheumatoid arthritis. Tumor necrosis factor-alpha promotes survival and phenotypic maturation of poly(I:C)-treated dendritic cells but impairs their Th1 and Th17 polarizing capability. Lymphotoxinalpha-dependent spleen microenvironment helps the era of memory B cells and is required for his or her subsequent antigen-induced activation. Regionalized growth and maintenance of the intestinal adaptive immune panorama. Evidence for regional specialization and extrathymic T cell maturation within the human gut epithelium. Natural aryl hydrocarbon receptor ligands management organogenesis of intestinal lymphoid follicles. Identification of a number of isolated lymphoid follicles on the antimesenteric wall of the mouse small gut. Innate lymphoid cells integrate stromal and immunological indicators to enhance antibody production by splenic marginal zone B cells. Requirement for lymphoid tissueinducer cells in isolated follicle formation and T cellindependent immunoglobulin A era within the intestine. Isolated lymphoid follicles are dynamic reservoirs for the induction of intestinal IgA. Cryptopatches and isolated lymphoid follicles: dynamic lymphoid tissues dispensable for the era of intraepithelial lymphocytes. Dendritic cells within the immune systemhistory, lineages, tissues, tolerance, and immunity. Generation of gut-homing T cells and their localization to the small intestinal mucosa. Intestinal dendritic cells specialize to activate reworking growth factor-beta and induce Foxp3 1 regulatory T cells via integrin alphavbeta8. Johansson-Lindbom B, Svensson M, Pabst O, Palmqvist C, Marquez G, Forster R, et al. B cell homeostasis and follicle confines are governed by fibroblastic reticular cells. New strategy for m-cell-specific molecules screening by comprehensive transcriptome analysis. Uptake via glycoprotein 2 of FimH(1) micro organism by M cells initiates mucosal immune response.
Generic moduretic 50 mg free shipping
Dendritic cell modulation by mast cells controls the Th1/Th2 stability in responding T cells arterial dissection generic moduretic 50 mg line. Systemic mast cell degranulation will increase mortality throughout polymicrobial septic peritonitis in mice blood pressure 9050 moduretic 50 mg online. Salmonella typhimurium impedes innate immunity with a mast-cell-suppressing protein tyrosine phosphatase, SptP. Molecular mechanism of mast cell mediated innate defense in opposition to endothelin and snake venom sarafotoxin. Peptido-leukotrienes are potent agonists of von Willebrand issue secretion and P-selectin floor expression in human umbilical vein endothelial cells. Staphylococcus delta-toxin induces allergic pores and skin disease by activating mast cells. Mast cells play an necessary function in Chlamydia pneumoniae lung an infection by facilitating immune cell recruitment into the airway. Contributions of mast cells and vasoactive merchandise, leukotrienes and chymase, to dengue virus-induced vascular leakage. Development and cytokine production are tightly regulated by sequential transcription factor expression and/or exposure to the indicated stimuli. This process of lymphogenesis requires lymphotoxin-/ in addition to intercellular adhesion molecule/vascular cell adhesion molecule dependent recruitment [37]. The impression of the microbiota can also be seen at the transcriptional and epigenetic ranges. Vitamin A deficiency occurring during chronic malnutrition attempts to restrict this impairment of mucosal immunity throughout dietary deficiency. This response permits the host to maintain barrier immunity to helminth an infection in the face of malnutrition. Additional research are wanted to outline epigenetic and post-translational adjustments that will additionally contribute to this functional regulation. Specialized epithelial cells similar to tuft cells and enteric neurons also stimulate barrier immunity and tissue repair features. Collectively, these responses defend the mucosal barrier from invasive Gram-negative bacterial infections. Apparent redundancy in these mobile responses could reflect quantitative or temporal variations in exposure. This tissue restore perform plays an essential function in restoring immune competence following an infection or damage. This inflammatory loop might assist broad cross-reactive adaptive immunity generated through the major infection [121]. This cross-regulation affects IgA-dependent immunity and shapes the intestine microbiome [46]. Recent discoveries outlined here present significant new perception into their crucial roles in mucosal immunity, inflammation, metabolic homeostasis, and tissue restore. Innate lymphoid cells within the initiation, regulation and determination of inflammation. Nfil3 is crucial for growth of innate lymphoid cells and host safety in opposition to intestinal pathogens. The spectrum and regulatory panorama of intestinal innate lymphoid cells are formed by the microbiome. Transcriptional applications define molecular characteristics of innate lymphoid cell classes and subsets. Mature natural killer cell and lymphoid tissue-inducing cell growth requires Id2-mediated suppression of E protein exercise. Innate lymphoid cells as regulators of immunity, inflammation and tissue homeostasis. Innate lymphoid cells: important regulators of allergic irritation and tissue repair in the lung. Intestinal epithelial tuft cells initiate kind 2 mucosal immunity to helminth parasites. Tuft cells, taste-chemosensory cells, orchestrate parasite type 2 immunity in the gut. Notch2-dependent classical dendritic cells orchestrate intestinal immunity to attaching-andeffacing bacterial pathogens. Lipoxin A4 regulates pure killer cell and kind 2 innate lymphoid cell activation in bronchial asthma. Glial-cell-derived neuroregulators management kind three innate lymphoid cells and intestine defence. The neuropeptide neuromedin U stimulates innate lymphoid cells and type 2 irritation. Innate lymphoid cells promote lung-tissue homeostasis after an infection with influenza virus. Intestinal commensal bacteria mediate lung mucosal immunity and promote resistance of new child mice to infection. Adaptation of innate lymphoid cells to a micronutrient deficiency promotes type 2 barrier immunity. Arginase 1 is an innate lymphoid-cell-intrinsic metabolic checkpoint controlling kind 2 irritation. Maternal retinoids control kind 3 innate lymphoid cells and set the offspring immunity. Interleukin-22 mediates early host defense towards attaching and effacing bacterial pathogens. Innate manufacturing of T(H)2 cytokines by adipose tissue-associated c-Kit(1)Sca-1(1) lymphoid cells. Restoration of lymphoid organ integrity via the interaction of lymphoid tissueinducer cells with stroma of the T cell zone. Interleukin-22 protects intestinal stem cells from immune-mediated tissue harm and regulates sensitivity to graft versus host illness. Activated innate lymphoid cells are associated with a decreased susceptibility to graft-versus-host disease. Innate lymphoid cells mediate influenza-induced airway hyper-reactivity independently of adaptive immunity. Interleukin-22 induces interleukin18 expression from epithelial cells throughout intestinal an infection. Acute gastrointestinal an infection induces long-lived microbiota-specific T cell responses. Innate lymphoid cells maintain colon cancer via manufacturing of interleukin-22 in a mouse model. Innate and adaptive lymphocytes sequentially form the gut microbiota and lipid metabolism.
50 mg moduretic order fast delivery
The absence of a cell wall; some fetal arrhythmia 33 weeks moduretic 50 mg purchase without a prescription, however arteria interossea communis cheap 50 mg moduretic fast delivery, possess a versatile layer, a pellicle, or a inflexible shell of inorganic supplies exterior of the cell membrane 2. The ability to transfer by locomotor organelles or by a gliding mechanism during their complete life cycle or a part of it three. Heterotrophic nutrition whereby the free-living forms ingest particulates such as bacteria, yeast, and algae, while the parasitic types derive nutrients from the body fluids of their hosts four. Primarily asexual means of replica, though sexual modes occur in some groups Protozoan taxonomy is being continually up to date as new know-how enables classification primarily based on molecular characteristics. For our dialogue of protozoans, we follow a extra conventional taxonomic scheme, dividing them into 4 teams based on means of locomotion. Sarcodina: Motility outcomes from the streaming of ectoplasm, producing protoplasmic projections referred to as pseudopods (false feet). Prototypic amoebas include the free-living Amoeba proteus and the parasite Entamoeba histolytica. Mastigophora: One or extra whiplike, skinny structures referred to as flagella effects locomotion. Free-living members embody the genera Cercomonas, Heteronema, and Euglena, that are photosynthetic protists which may be categorized as flagellated algae. The parasitic types include Trichomonas vaginalis, Giardia intestinalis (formerly referred to as Giardia lamblia), and the Trypanosoma species. Ciliophora: Short, hairlike projections known as cilia, whose synchronous beating propels the organisms, perform locomotion. The characteristic example of free-living members of this group is Paramecium caudatum, and the parasitic example is Balantidium coli. The most significant members belong to the genus Plasmodium, the malarial parasites of animals and humans. During the initial bodily examination, the affected person mentions that he has been having the pain and bowel points for about two weeks with no lessening in severity. The hiker says that four weeks in the past, he went on a backpacking trip into the mountains to acquire fresh spring water from the supply. Unable to locate the spring source for a stream, he determined to collect some water from a clean stream and transport it house. He drank the water daily, and to be positive that no minerals were eliminated, he selected not to purify or sterilize the water before consuming. Two weeks after returning from the journey, he began to experience some stomach discomfort that progressed to extreme ache and the free stools. Reagent Methyl cellulose Equipment Microscope Glass slides Coverslips Pasteur pipettes Principle There are more than 20,000 recognized species of free-living protozoa. Obtain a drop of pond water from the bottom of the tradition and place it in the heart of a clean slide. Add a drop of methyl cellulose to the tradition to decelerate the movement of the protozoa. This organism causes amoebic dysentery and has been recognized to lead to extreme liver harm. After the drop of culture spreads alongside the inner facet of the sting of the coverslip, gently lower the coverslip onto the slide. Examine your slide preparation under scanning, low-power, and high-power aims with diminished mild, and observe for the different protozoa current. Contractile vacuole: Large, clear round construction that regulates inner water strain 1. Chloroplast: Organelles containing chlorophyll; present in photosynthetic forms only 5. Nucleus: One present Pseudopod Ectoplasm Contractile vacuole Endoplasm Food vacuole Nucleus Amoeba Mastigophora Flagellum Mouth Eye spot Chloroplast Pellicle Nucleus Euglena Ciliophora Cercomonas Heteronema 1. Micronucleus: A small nucleus that capabilities in conjugation, a mode of sexual replica Cilia Pellicle Food vacuole Oral groove Micronucleus Macronucleus Contractile vacuole Paramecium Stentor Vorticella 1. In the area provided, draw a representative sketch of several of the observed protozoa in stagnant pond water, indicate the magnifications used, and label their structural elements. Identify each organism in accordance with its class based mostly on its mode of locomotion and its genus. Magnification: Organelles of locomotion: Class: Genus: Magnification: Organelles of locomotion: Class: Genus: Experiment 33: Lab Report 227 2. Draw consultant sketches, point out magnification, and label the structural elements. Amoeba Magnification: Organelles of locomotion: Class: Genus: Paramecium Euglena Magnification: Organelles of locomotion: Class: Genus: Stentor 228 Experiment 33: Lab Report Review Questions 1. What are the distinguishing characteristics of the free-living members of Sarcodina, Mastigophora, and Ciliophora Principle Unlike the life cycles of the free-living forms, the life cycles of parasitic protozoa range greatly in complexity. Knowing the various developmental levels in these life cycles is important in the prognosis, medical management, and use of chemotherapy to deal with parasitic infections. The following parasites have the simplest or most direct life cycles not requiring an intermediate host: 1. Entamoeba histolytica: a pseudopodian parasite of the class Sarcodina that causes amebic dysentery. Infective, resistant cysts are released from the lumen of the gut via the feces and are deposited in water, in soil, or on vegetation. Upon ingestion, the mature quadrinucleated cyst wall disintegrates and the nuclei divide, producing eight active trophozoites (metabolically active cells) that transfer to the colon, where they set up infection. Balantidium coli: the ciliated parasitic protozoan displays a life cycle similar to that of Entamoeba histolytica besides that no multiplication happens throughout the cyst. This organism resides primarily within the lumen and submucosa of the big gut. Giardia intestinalis: the intestinal mastigophoric flagellate displays a life cycle corresponding to those of the above parasites. Diagnosis is made by discovering cysts within the shaped stool and both cysts and trophozoites in the diarrhetic stool. The mastigophoric hemoflagellate answerable for numerous forms of African sleeping sickness has a extra advanced life cycle. The Trypanosoma will must have two hosts to full its cyclic improvement: a vertebrate and an invertebrate, blood-sucking insect host. Humans are the definitive hosts harboring the sexually mature forms; the tsetse fly (Glossina) and the reduviid bug are the invertebrate hosts during which the developmental varieties occur. Protozoa demonstrating the greatest degree of cyclic complexity are discovered in the class Sporozoa. They are composed of completely obligate parasitic forms, similar to members of the genus Plasmodium, and are answerable for malaria in each people and animals. The life cycle requires two hosts, a human being and the female Anopheles mosquito. It is important to notice that in this life cycle, the mosquito-and not the human-is the definitive host harboring the sexually mature parasite. These parasites cross quickly from the blood into the liver, where they infect the parenchymal cells.
Cheap moduretic 50 mg without prescription
Distinct defensin profiles in Neisseria gonorrhoeae and Chlamydia trachomatis urethritis reveal novel epithelial cell-neutrophil interactions prehypertension 134 cheap moduretic 50 mg on-line. The blood-testis and blood-epididymis barriers are extra than simply their tight junctions blood pressure zanidip buy moduretic 50 mg without prescription. Phenotypic and useful heterogeneity of the testicular macrophage inhabitants: a new regulatory mannequin. Rat resident testicular macrophages have an alternatively activated phenotype and constitutively produce interleukin-10 in vitro. Yolk-sac-derived macrophages regulate fetal testis vascularization and morphogenesis. Chlamydia trachomatis an infection: incidence, well being costs and prospects for vaccine growth. A recombinant Chlamydia trachomatis major outer membrane protein binds to heparan sulfate receptors on epithelial cells. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America 1996;93(20):11143�8. Mobilization of F-actin and clathrin throughout redistribution of Chlamydia trachomatis to an intracellular site in eucaryotic cells. Lipid metabolism in Chlamydia trachomatis-infected cells: directed trafficking of Golgi-derived sphingolipids to the chlamydial inclusion. Genome sequence of an obligate intracellular pathogen of humans: Chlamydia trachomatis. Chlamydia persistence: a survival technique to evade antimicrobial effects in-vitro and in-vivo. Prevalence of Chlamydia trachomatis genital an infection among persons aged 14-39 years- United States, 2007-2012. Chlamydia trachomatis serovars causing urogenital infections in girls in Melbourne, Australia. Genotyping of urogenital Chlamydia trachomatis in Regional New South Wales, Australia. Chlamydia trachomatis serovar distribution and Neisseria gonorrhoeae coinfection in male patients with urethritis in Greece. Characterization of Chlamydia trachomatis omp1 genotypes among sexually transmitted disease patients in Sweden. Analysis of Chlamydia trachomatis serovar distribution modifications within the Netherlands (1986�2002). Estimation of the chance of tubal issue infertility related to genital chlamydial infection in girls: a statistical modelling study. The position of the immune response in Chlamydia trachomatis infection of the male genital tract: a double-edged sword. Secretion of proinflammatory cytokines by epithelial cells in response to Chlamydia infection suggests a central function for epithelial cells in chlamydial pathogenesis. Chemokine expression patterns differ inside anatomically distinct areas of the genital tract during Chlamydia trachomatis infection. A link between neutrophils and persistent disease manifestations of Chlamydia muridarum urogenital an infection of mice. A function for matrix metalloproteinase9 in pathogenesis of urogenital Chlamydia muridarum an infection in mice. Chlamydia trachomatis enhances the expression of matrix metalloproteinases in an in vitro model of the human fallopian tube an infection. Interleukin-1 is the initiator of Fallopian tube destruction during Chlamydia trachomatis infection. Repeated Chlamydia trachomatis an infection of Macaca nemestrina fallopian tubes produces a Th1-like cytokine response associated with fibrosis and scarring. Characterization of lymphocyte response within the feminine genital tract during ascending Chlamydial genital infection within the guinea pig mannequin. A cohort research of 1,844 girls with laparoscopically verified disease and 657 control ladies with regular laparoscopic outcomes. Protective immunity to chlamydial genital an infection: evidence from animal research. The natural course of Chlamydia trachomatis an infection in asymptomatic Colombian women: a 5-year follow-up examine. Recurrent genitourinary chlamydial infections in sexually energetic feminine adolescents. Spontaneous resolution of genital Chlamydia trachomatis an infection in women and protection from reinfection. Role of cell-mediated immunity within the decision of secondary chlamydial genital infection in guinea pigs contaminated with the agent of guinea pig inclusion conjunctivitis. Comparable genital tract infection, pathology, and immunity in rhesus macaques inoculated with wild-type or plasmid-deficient Chlamydia trachomatis serovar D. The potential for vaccine in opposition to infection of the genital tract with Chlamydia trachomatis. Proceedings of the thirteenth worldwide symposium on human chlamydial infections. The molecular mechanism of T-cell control of Chlamydia in mice: role of nitric oxide. Resolution of chlamydial genital infection in B-cell-deficient mice and immunity to reinfection. Chlamydia trachomatis genital tract infection of antibody-deficient gene knockout mice. A mucosal vaccine towards Chlamydia trachomatis generates two waves of protecting memory T cells. Endometrial histopathology in sufferers with culture-proved upper genital tract infection and laparoscopically recognized acute salpingitis. Vaccination with the Chlamydia trachomatis main outer membrane protein can elicit an immune response as protecting as that resulting from inoculation with live micro organism. Transcutaneous immunization with mixed cholera toxin and CpG adjuvant protects in opposition to Chlamydia muridarum genital tract infection. Comparison of intranasal and transcutaneous immunization for induction of protecting immunity in opposition to Chlamydia muridarum respiratory tract infection. In silico identification and in vivo evaluation of a novel T-cell antigen from Chlamydia, NrdB. Novel Chlamydia muridarum T cell antigens induce protective immunity against lung and genital tract infection in murine fashions. Approach to discover T- and B-cell antigens of intracellular pathogens applied to the design of Chlamydia trachomatis vaccines. High-throughput proteomic screening identifies Chlamydia trachomatis antigens which would possibly be able to eliciting T cell and antibody responses that provide safety against vaginal challenge. Comparative safety of vaccine adjuvants: a summary of current proof and future wants. Recombinant fowlpox virus vector-based vaccines: expression kinetics, dissemination and safety profile following intranasal supply. Induction of cross-serovar protection towards genital chlamydial infection by a targeted multisubunit vaccination approach.
50 mg moduretic buy visa
The impact of mucoadhesive excipient on the nasal retention time of and the antibody responses induced by an intranasal influenza vaccine blood pressure chart to record moduretic 50 mg cheap with mastercard. Comparison of the clearance of radiolabelled nose drops and nasal spray as mucosally delivered vaccine blood pressure chart tracker best moduretic 50 mg. Evaluation of interleukin 1 as a mucosal adjuvant in immunization with Streptococcus sobrinus cells by tonsillar utility in rabbits. A comparability of nontoxin vaccine adjuvants for their ability to enhance the immunogenicity of nasally-administered anthrax recombinant protective antigen. Lipidbased systems as a promising approach for enhancing the bioavailability of poorly water-soluble medicine. Intranasal immunization of ferrets with industrial trivalent influenza vaccines formulated in a nanoemulsion-based adjuvant. Structure and performance evaluation of an antibody recognizing all influenza A subtypes. Polymyxins as novel and protected mucosal adjuvants to induce humoral immune responses in mice. Gangliosides inhibit bee venom melittin cytotoxicity however not phospholipase A2-induced degranulation in mast cells. Adjuvant action of melittin following intranasal immunisation with tetanus and diphtheria toxoids. Polyethylenimine: a versatile, multifunctional non-viral vector for nucleic acid delivery. Polymeric penetration enhancers promote humoral immune responses to mucosal vaccines. H9N2 influenza entire inactivated virus mixed with polyethyleneimine strongly enhances mucosal and systemic immunity after intranasal immunization in mice. Pre-clinical evaluation of a novel nanoemulsion-based hepatitis B mucosal vaccine. Mucosal immunization with a novel nanoemulsion-based recombinant anthrax protecting antigen vaccine protects in opposition to Bacillus anthracis spore challenge. Converging roles of caspases in inflammasome activation, cell dying and innate immunity. G protein activation: a receptor-independent mode of motion for cationic amphiphilic neuropeptides and venom peptides. Compound 48/80 acts as a potent mucosal adjuvant for vaccination against Streptococcus pneumoniae infection in younger mice. Cytotoxicity of polycations: relationship of molecular weight and the hydrolytic theory of the mechanism of toxicity. Molecular hurdles in polyfectin design and mechanistic background to polycation induced cytotoxicity. Comparison of histamine release induced by artificial polycations with that by compound 48/80 from rat mast cells. A CpG-containing oligodeoxynucleotide adjuvant for acellular pertussis vaccine improves the protecting response in opposition to Bordetella pertussis. Investigation of peanut oral immunotherapy with CpG/peanut nanoparticles in a murine mannequin of peanut allergy. Toll-like receptor ligand-based vaccine adjuvants require intact MyD88 signaling in antigen-presenting cells for germinal heart formation and antibody manufacturing. Evaluation of the intramuscular administration of Cervarix vaccine on fertility; preand post-natal improvement in rats. Monophosphoryl lipid A enhances mucosal and systemic immunity to vaccine antigens following intranasal administration. An intranasal vaccine concentrating on both the Bacillus anthracis toxin and bacterium offers protection against aerosol spore challenge in rabbits. A single immunization with a dry powder anthrax vaccine protects rabbits towards deadly aerosol challenge. Lipopolysaccharideenhanced, toll-like receptor 4-dependent T helper cell sort 2 responses to inhaled antigen. A giant majority of poisons and toxin derivatives used to modulate immune responses to vaccines are of microbial origin. CyaA invades a wide range of cell varieties through a mechanism involving receptor-independent binding to the cell floor. In vivo studies in mice have revealed that Stx-2 is up to four hundred times more toxic than Stx-1 [28,29]. The ribotoxic stress response induced by Stx in contaminated cells consists of proinflammatory and proapoptotic responses [30,31]. Ingestion of ricin causes severe nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, and hemorrhage, and its inhalation leads to cough and fever. The biochemical construction of native toxins and practical traits of the binding B subunits and the catalytic A subunits. Toxin derivatives are generated by genetic modification of the catalytic A subunit or coupling (genetic or chemical) of both the A or the B subunit with antigen(s) or molecule(s) focusing on a specific receptor on host cells. Derivatives of Other Toxin Adjuvant Several approaches have been developed during the last three decades to benefit from adenylate cyclase for useful regulation of immune responses. Intranasal immunization with the mutant Cya enhanced serum IgG and IgA antibody responses to the coadministered antigen. Interestingly, the adjuvant activity of the mutant Cya for antibody and T cell responses was superior to that of the native toxin [79]. Furthermore, mutant Cya induced IgA responses in mucosal secretion and, when coadministered with B. Delivery Systems for Toxin-Based Adjuvant Toxin derivatives often display adjuvant activity and promote the specified mucosal B and T cell responses after nasal immunization. To circumvent these limitations, toxin derivatives have been produced or incorporated in vaccine vectors for oral immunization. The development of "edible" vaccines has been a significant advance within the field of vaccinology. Since tolerance is the pure response to ingested antigens, toxin-based adjuvants were included into plant vaccines. Methods for mass manufacturing of MucoRice are being developed to exploit the multiple benefits of this platform, including the extended stability (years) at room temperature, formulation with out purification of vaccines, and ease of vaccine administration [87]. Effective safety against mucosal pathogens requires prophylactic B and T cell responses that may be achieved by mucosal vaccines. Myeloid cell subsets contribute to many indicators that support IgA manufacturing and mucosal homing of effector B and T cells. These toxins also induce manufacturing of innate cytokines that may facilitate differentiation of Th1, Th2, Th17, and Treg cells. Recent studies have provided new clues concerning the relative contribution of myeloid cell signals to the ability of toxin-based adjuvants to promote mucosal immunity. Depletion of neutrophils earlier than sublingual immunization with EdTx allowed the development of antigen-specific serum and mucosal IgA responses, additional confirming that circulating neutrophils recruited in mucosal inductive websites prevented the induction of IgA responses however not IgG responses [75].
Syndromes
- X-linked recessive
- Hoarseness that does not get better in 1 - 2 weeks
- Stomach pain
- Lung collapse (atelectasis)
- Excision: Cutting out the skin cancer and stitching the skin together
- Temple
- Bone infection (osteomyelitis)
- Hematoma (blood accumulating under the skin)
Buy moduretic 50 mg line
Suffice it say that immunization of moms could provide a novel technique to prevent allergies in their offspring blood pressure chart during stress test buy moduretic 50 mg with visa. Furthermore blood pressure chart age nhs 50 mg moduretic discount overnight delivery, villous M cells may be induced by infection with pathogenic bacteria [64] or stimulation with bacterial toxin, similar to cholera toxin [65]. Summary and Future Perspectives In abstract, antigen uptake throughout the absorptive epithelium is often managed by multiple mechanisms, together with the presence of an in depth mucus layer and tight junctions that form between epithelial cells, largely operate to restrict systemic antigen exposure, and shield towards microbial invasion. For this purpose, efforts to develop new oral vaccine formulations have largely targeted on antigen or attenuated pathogen supply to gut-associated lymphoid tissues. Regardless of those limitations, both soluble and microbial antigens in addition to microbes are selectively and actively sampled throughout the huge epithelial surfaces not associated with organized lymphoid tissues beneath steady-state situations by the mechanisms described on this chapter and sure play a role in immunity to some present vaccines in addition to providing new alternatives for future vaccine development. In particular, FcRn concentrating on has been demonstrated to be a viable strategy for vaccine delivery (see Refs. Whether this technique will work for orally administered vaccines has not yet been proven; nevertheless, as was mentioned above, antigens have been delivered throughout intestinal and lung epithelial cells following oral or nasal administration of immune complexes, leading to mucosal and systemic immune responses. An extra problem might be to focus these responses towards effective immunity and away from the induction of tolerance. Goblet cells are capable of transporting both soluble antigens and pathogens corresponding to S. Shown are the assorted mechanisms which have been described along with the antigens and microbes that access the pathways which are mentioned in the text, as properly as components that have been proven to influence their regulation. In this regard, it could theoretically be potential to engineer nonpathogenic microbes and even soluble proteins with bacterial ligands from these pathogens to improve goblet cell focusing on. The antigens and bacteria proven within the determine are a few of those which have been studied experimentally and mentioned on this chapter. The mucus and mucins of the goblet cells and enterocytes provide the first protection line of the gastrointestinal tract and interact with the immune system. M cell-dependent antigen uptake on follicle-associated epithelium for mucosal immune surveillance. Histo-blood group carbohydrates as facilitators for infection by Helicobacter pylori. Listeria adhesion protein induces intestinal epithelial barrier dysfunction for bacterial translocation. Mechanisms of intestinal epithelial barrier dysfunction by adherent-invasive Escherichia coli. Mechanism of horseradish peroxidase uptake and transport in adult and neonatal rat intestine. The uptake of soluble and particulate antigens by epithelial cells in the mouse small intestine. Antibiotics promote irritation through the translocation of native commensal colonic micro organism. Microbial antigen encounter throughout a preweaning interval is important for tolerance to gut micro organism. Antibiotics promote the sampling of luminal antigens and bacteria through colonic goblet cell associated antigen passages. Regulation of the polymeric immunoglobulin receptor and IgA transport: new advances in environmental elements that stimulate pIgR expression and its function in mucosal immunity. Hormonal management of intestinal Fc receptor gene expression and immunoglobulin transport in suckling rats. Neonatal Fc receptor for IgG regulates mucosal immune responses to luminal micro organism. Human neonatal Fc receptor mediates transport of IgG into luminal secretions for delivery of antigens to mucosal dendritic cells. Rapid fucosylation of intestinal epithelium sustains host-commensal symbiosis in sickness. Antimicrobial peptides and the enteric mucus layer act in concert to defend the intestinal mucosa. Quantitative approaches to delineate paracellular diffusion in cultured epithelial cell monolayers. Multiple sides of intestinal permeability and epithelial dealing with of dietary antigens. Breast milk immune complexes are potent inducers of oral tolerance in neonates and prevent asthma improvement. The transfer of maternal antigenspecific IgG regulates the development of allergic airway irritation early in life in an FcRndependent method. Maternal IgG immune complexes induce meals allergen-specific tolerance in offspring. Utilization of Fc receptors as a mucosal vaccine technique in opposition to an intracellular bacterium, Francisella tularensis. The neonatal FcR-mediated presentation of immune-complexed antigen is associated with endosomal and phagosomal pH and antigen stability in macrophages and dendritic cells. Increased number of intestinal villous M cells in levamisole -pretreated weaned pigs experimentally infected with F4ac(1) enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli strain. Microbe sampling by mucosal dendritic cells is a discrete, MyD88-independent step in DeltainvG S. Oral tolerance originates in the intestinal immune system and depends on antigen carriage by dendritic cells. Oral MucoRice expressing double-mutant cholera toxin A and B subunits induces toxin-specific neutralising immunity. A discrete subpopulation of dendritic cells transports apoptotic intestinal epithelial cells to T cell areas of mesenteric lymph nodes. Receptor-mediated immunoglobulin G transport across mucosal obstacles in grownup life: useful expression of FcRn within the mammalian lung. The adaptive immune system, which is capable of responding to specific antigenic challenges, is represented by T cells and B cells with their terminal differentiation into antibody-secreting cells and the selective transport of antibodies into the mucosal fluids. Antibodies in human and other vertebrate external secretions are represented by immunoglobulins (Ig) of assorted isotypes. In humans, IgA is the dominant isotype in all exterior secretions excluding those of the genitourinary tract, in which IgG represents the dominant isotype [1]. The ranges of Ig, regardless of their isotype, are generally much decrease in particular person secretions than in sera. In people, the every day production of IgA exceeds the mixed manufacturing of Ig of all isotypes [2,3]. Serum IgA levels are decrease than these of IgG due to a considerably shorter half-life within the circulation (4�6 days for IgA vs 21 days for IgG) and the excessive degree of local IgA manufacturing in mucosal tissue with an effective receptor-mediated transepithelial transport into external secretions [4,5]. Furthermore, the great variability in measured ranges of Igs in external secretions is decided by the methods of assortment; assays used for measurement; hormonal standing, especially for secretions of the female genital tract; local inflammation; and presence of proteolytic enzymes of endogenous or exogenous origin, which can degrade secretory Igs [1]. The construction, distribution of IgA subclasses, spectrum of antigen specificities, cellular origins, and different maturation patterns of IgA in the systemic versus mucosal compartments convincingly reveal their mutual independence [2] and must be thought of in vaccination methods aimed at the selective induction of desired humoral responses.
Buy 50 mg moduretic visa
Early enteral feeding might blunt the hypermetabolic response and reduce intestinal permeability blood pressure medication that doesn't cause dizziness moduretic 50 mg discount fast delivery, thus preserving the intestinal barrier and doubtlessly affecting enterogenic infections prehypertension home remedies moduretic 50 mg discount with visa. Because infections are the commonest explanation for mortality after surviving the early postburn interval, efforts are required to mitigate extreme death charges by way of sufficient preventive measures and enhanced vigilance for infections and acceptable therapy. The administration of burn patients requires a multidisciplinary approach, together with infectious disease physicians. Chapter 314 Burns Key References the entire reference listing is on the market online at Expert Consult. Age-dependent differences in survival after extreme burns: a unicentric evaluation of 1,674 patients and 179 autopsies over 15 years. Pneumonia in patients with extreme burns: a classification based on the idea of the provider state. The time-related modifications of antimicrobial resistance patterns and predominant bacterial profiles of burn wounds and body flora of burned sufferers. Herpes simplex activation prolongs recovery from severe burn harm and will increase bacterial infection danger. Metabolic implications of extreme burn accidents and their management: a scientific evaluation of the literature. Local and distant burn injury alter immuno-inflammatory gene expression in skeletal muscle. Nosocomial tracheobronchitis in mechanically ventilated patients: incidence, aetiology and outcome. Comparison of floor swab cultures and quantitative tissue biopsy cultures to predict sepsis in burn sufferers: a prospective research. Comparative analysis of surface swab and quantitative full-thickness wound biopsy tradition in burn patients. Comparison of wound culture and bronchial lavage in the severely burned child: implications for antimicrobial remedy. Relationship between bacterial counts obtained by burn wound biopsy culture and floor alginate swab tradition, with clinical consequence following burn surgery and change of dressings. Pharmacokinetics of systemically administered antibiotics in sufferers with thermal harm. Serum vancomycin levels ensuing from steady or intermittent infusion in critically ill burn patients with or without continuous renal replacement therapy. Pharmacokinetics of ceftazidime and cefepime in burn patients: the importance of age and creatinine clearance. Catheter infection risk related to the distance between insertion site and burned space. Effects of early enteral feeding on the prevention of enterogenic an infection in severely burned sufferers. A comparison study between early enteral nutrition and parenteral nutrition in severe burn patients. A randomized potential trial of hyperbaric oxygen in a referral burn heart population. Mortality and morbidity amongst elderly people with burns- evaluation of information on admission. Base deficit and alveolar-arterial gradient throughout resuscitation contribute independently however modestly to the prediction of mortality after burn damage. Development and validation of an age-risk score for mortality predication after thermal injury. An evaluation of threat components for mortality after burn trauma and the identification of gender-dependent differences in outcomes. The risk components and time course of sepsis and organ dysfunction after burn trauma. The threat of pneumonia in thermally injured sufferers requiring ventilatory support. Epidemiology and outcomes of bloodstream infections in 177 extreme burn sufferers from an industrial disaster: a multicentre retrospective research. National Healthcare Safety Network report, data abstract for 2013, Device-associated Module. Aerobic bacterial isolates from burn wound infections and their antibiograms-a five-year study. Epidemiology of bloodstream infections in burn-injured patients: a review of the national burn repository. The analysis of nosocomial infection throughout 1-year-period in the burn unit of a coaching hospital in Istanbul, Turkey. Emergence of resistance in Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Acinetobacter species after using antimicrobials for burned patients. Colonization of burns and the period of hospital stay of severely burned patients. Gram adverse wound infection in hospitalised grownup burn patients�systematic evaluate and meta-analysis. Fungal wound infection (not colonization) is independently related to mortality in burn patients. Correlation of culture with histopathology in fungal burn wound colonization and infection. Incidence of systemic fungal infection and associated mortality following extreme burns. Severity of burn damage and sepsis determines the cytokine responses of bone marrow progenitor-derived macrophages. Long-term dynamic profiling of inflammatory mediators in double-hit burn and sepsis animal models. Innate lymphocyte subsets and their immunoregulatory roles in burn injury and sepsis. Toll-like receptor 2 and four ligation leads to complicated altered cytokine profiles early and late after burn harm. Increased Toll-like receptor four expression on T cells could also be a mechanism for enhanced T cell response late after burn injury. Alterations of acute phase response and cytokine production in sufferers following extreme burn harm. Extended hypermetabolic response of the liver in severely burned pediatric patients. Novel predictors of sepsis outperform the American Burn Association sepsis standards in the burn intensive care unit affected person. Use of procalcitonin for the detection of sepsis within the critically unwell burn affected person: a systematic evaluation of the literature. Sepsis within the burn patient: a special drawback than sepsis within the basic population.
Order 50 mg moduretic amex
Comparison of various routes of vaccination for eliciting antibody responses in the human stomach hypertension 32 years old order 50 mg moduretic mastercard. Lack of prophylactic efficacy of an enteric-coated bovine hyperimmune milk product towards enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli challenge administered during a standard meal pulse pressure femoral artery order moduretic 50 mg free shipping. Randomized control trials using a pill formulation of hyperimmune bovine colostrum to forestall diarrhea caused by enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli in volunteers. Evolutionary and functional relationships of colonization issue antigen I and other class 5 adhesive fimbriae of enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli. Evolution of the chaperone/ � usher meeting pathway: fimbrial classification goes greek. Cholera toxin structure, gene regulation and pathophysiological and immunological features. Essential construction for full enterotoxigenic activity of heat-stable enterotoxin produced by enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli. Molecular structure of the toxin domain of heat-stable enterotoxin produced by a pathogenic pressure of Escherichia coli. A putative binding website for a binding protein on rat intestinal epithelial cell membranes. Development of an enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli vaccine based mostly on the heat-stable toxin. Occurrence, distribution, and associations of O and H serogroups, colonization issue antigens, and [28] [29] [30] [31] [32] [33] [34] [35] [36] [37] V. Induction of long term mucosal immunological memory in people by an oral inactivated multivalent enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli vaccine. Safety and immunogenicity of a single oral dose of recombinant double mutant heat-labile toxin derived from [48] [49] [50] [51] [52] [53] [54] [55] [56] [57] [58] enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli. Role in proinflammatory response of YghJ, a secreted metalloprotease from neonatal septicemic Escherichia coli. Identification of a two-partner secretion locus of enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli. Enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli elicits immune responses to a number of surface proteins. EatA, an immunogenic protecting antigen of enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli, degrades intestinal mucin. Evaluation of the immune response following a short oral vaccination schedule with hepatitis B antigen encapsulated into alginate-coated chitosan nanoparticles. Oral immunization with urease and Escherichia coli heat-labile enterotoxin is safe and immunogenic in Helicobacter pylori�infected adults. Current progress in creating subunit vaccines in opposition to enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli-associated diarrhea. Towards rational design of a toxoid vaccine in opposition to the heat-stable toxin of Escherichia coli. Genetic fusion of a non-toxic heat-stable enterotoxin-related decapeptide antigen to cholera toxin B-subunit. Characterization of immunological cross-reactivity between enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli heat-stable toxin and human guanylin and uroguanylin. Design and characterization of a chimeric multiepitope construct containing CfaB, heat-stable toxoid, CssA, [69] [70] [71] [72] [73] [74] [75] [76] [77] [78] V. Safety and immunogenicity of oral inactivated whole-cell Helicobacter pylori vaccine with adjuvant among volunteers with or with out subclinical infection. Intestinal immune responses to an inactivated oral enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli vaccine and related immunoglobulin A responses in blood. Reduced doses of oral killed enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli plus cholera toxin B subunit vaccine is safe and immunogenic in Bangladeshi infants 6�17 months of age: dosing studies in several age teams. Randomised, doubleblind, safety and efficacy of a killed oral vaccine for enterotoxigenic E. Analysis of strategies to efficiently vaccinate infants in growing countries in opposition to enterotoxigenic E. Human experimental problem with enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli elicits immune responses to canonical and novel antigens related to vaccine development. SslE elicits practical antibodies that impair in vitro mucinase exercise and in vivo colonization by each intestinal and extraintestinal Escherichia coli strains. Most colonized people develop marginal inflammation, remaining largely asymptomatic [10]. Barry Marshall and Robert Warren had been awarded the Nobel Prize in Physiology and Medicine in 2005 for the invention of this association [11]. Indeed, a quantity of vaccine trials have efficiently compensated for this deficit by inducing substantial H. In this text, we review latest findings that provide an astounding clarification for the failure of past vaccination makes an attempt. We also illuminate eventualities via which future approaches might lead to higher results, also bearing in mind the possible dangers of vaccination. Pathogenic bacteria depend on a large repertoire of instruments to suppress immune activation [18]. Besides the exhibition of structural features, similar to antigenic mimicry of self-epitopes, they pursue direct interference with immune activation pathways. The result of such failure might, for example, involve an ineffective technology of pathogen-specific immune cells, an unfavorable stability of effector versus regulatory cells, and a failure in generating particular antibodies. However, by making use of appropriate vaccination protocols, the deficiency of immune activation might be overcome [19], thus in precept mounting robust safety lines. In fact, profitable rational vaccine design strategies have been developed against numerous pathogens through assembling efficacious antigen cocktails in combination with highly potent adjuvants [20]. In this fashion, applicable branches of the immune system could be activated, directing immunity toward desired organ sites [21]. Despite great success in preventing varied pathogenic infections [22], surprisingly, this strategy seems to fail for H. A mixture of two antibiotics is normally given together with a proton pump inhibitor [23]. Further problems related to antibiotic remedy are linked to low patient compliance, the incidence of reinfections, and the uncertainty about whether or not treatment is indicated for asymptomatic patients [25]. In this gentle, a vaccine, whether prophylactic or therapeutic, would clearly be extremely desirable. It would theoretically remedy the problems associated with current antibiotic treatment and constitute a milestone for the prevention of peptic ulcer and gastric cancer. Much effort has subsequently been invested in developing vaccines in preclinical and medical settings, but up to now, none of them have provided greater than scarce safety [15,25�27]. Even in mouse research, vaccination approaches have principally achieved solely partial reduction of pathogen colonization rather than sterile immunity [28�31]. Thus, failure to obtain sterile immunity may increase the danger of associated gastric cancer [32�34]. Moreover, boosting T helper responses may diminish the immuneregulatory results related to H.

Moduretic 50 mg buy without prescription
Stated simply heart attack 5 hour energy moduretic 50 mg discount on line, the plantmade protein business is usually restricted to applied sciences that require in depth protein purification through the manufacturing course of pulse pressure product 50 mg moduretic buy free shipping. However, if one examines the present advances in using meals crops as bioreactors, there are heaps of benefits over tobacco and plant cell cultures. Further, the worry of contamination seen in the Prodigene era [74] is presently not a well-founded argument. For instance, utilizing transgenic soybean seeds to manufacture therapeutic proteins [12,36] differs from remodeling value-added traits into soy vegetation [72,73]. One vital distinction is the goal of expressing high ranges of a specific recombinant therapeutic protein. Production of kilogram amounts of recombinant protein within safe greenhouses is theoretically possible [36] and currently sensible (unpublished results). Further, one benefit of transgenic seed expression is the benefit of such containment. Equipment to scale back seeds to powder at a commercial scale are common, and such a processing step can simply be performed in the progress facility following seed harvest. Specifically, there was a concern about probably mounting an immune response towards normal plant proteins current in a plant-derived vaccine formulation [26,27]. Conversely, it was instructed that a vaccine given inside the context of other normal plant proteins may end in tolerance to the vaccine, since tolerance is the default response to most plant proteins [26,27]. Mechanisms required for instantly breaking tolerance to regular plant proteins after a lifetime of publicity or mechanisms required for immediately inducing tolerance to a foreign vaccine candidate are troublesome to imagine. Previous Phase I scientific trials showed proof of immune responses in opposition to the particular vaccine candidate, not tolerance [14,34]. Further, when transgenic foodstuffs or formulations were given, no detectable antibody responses against normal plant proteins have been detected, and these administrations have been properly tolerated [14,34]. While extra clinical trial information would be helpful, it seems that evidently the plain statement would be the right one: A consumable formulation created from an edible transgenic plant expressing a vaccine is prone to cause few adverse effects. Another argument in opposition to formulating food-crop-made therapeutics is the notion that regulatory companies would by no means approve such complex protein mixtures for human therapies [26]. Examples of medical trials using edible vaccines produced from food crops have been reviewed [14,34], and the candidate vaccines in each of these medical trials required regulatory approval previous to use. When formulations made instantly from seed crops are considered, soybeans once more can be utilized to illustrate regulatory approval and security. A seedbased formulation containing a focus of the Bowman-Birk protease inhibitor was produced within the early Nineteen Nineties to be used in human clinical trials [75]. This focus was simple to produce and contained a precise dose of the inhibitor together with other normal soybean proteins. While formulating edible formulations from meals crops for oral remedy is intuitively engaging, purification of recombinant proteins from transgenic food crops may also be performed if a mucosal delivery methodology. This often ends in manufacturing, purification, and finishing amenities being housed in the identical structure or in very close proximity [80]. It is possible to stably transform plant traces that target expression of a selected recombinant protein to the seed. Once seeds have been harvested, a easy grinding of these transgenic seeds to nongerminable powder permits delivery to geographically distant services for prolonged storage [81]. We have saved powder from transgenic soybeans in dry conditions at room temperature for times approaching one decade with minimal or no detectable degradation of particular recombinant proteins (unpublished data). When wanted, aliquots of transgenic powder may be removed for formulating soy-based therapies or for purification of the recombinant protein from soy. Theoretically, seeds may be harvested in one geographic location, powders sent to storage amenities elsewhere, and finishing of the product completed at some future date. The ability to segregate the manufacturing course of geographically and over an extended time period is unique to such plantmade protein expression platforms when compared to current processes [80] (Chapter 20: PlantBased Mucosal Vaccine Delivery Systems). Specifically, the efficacy of mucosal immunotherapy depends upon the delivery of an antigenic formulation that may both stimulate a vaccine response or induce tolerance, as required, with acceptable opposed effects to the host. This could be a difficult task, as some immunotherapies require supply methods to transverse mucosal obstacles or require adjuvants to increase the specified response. Targeting of antigens to explicit mucosal cell varieties can also be required to improve bioavailability and therefore efficacy. As beforehand reviewed [82], these challenges can be significant ones and are considerations for all mucosal immunotherapies, together with plant-based ones. As we discussed in this chapter, there are some important differences in comparability to present recombinant protein expression systems. For instance, plant-based expression platforms start the manufacturing process with no animal pathogens or animal toxins. In addition to these safety considerations, each platform utilizing plant-made proteins has its personal advantages. For example, transient expression of influenza vaccine candidates in tobacco has proven speed and adaptability in its manufacturing processes [17]. Disadvantages embody the comparatively high leaf biomass required for initial processing and a steady manufacturing course of, for the rationale that protein must be purified. Nonseed meals crop transformations may also be formulated into consumables [16] but can have relatively low protein to biomass. Finally, plant cell culture techniques [46] have demonstrated the pace of transformation and manufacturing. This diversity of benefits over conventional recombinant protein expression platforms requires some thought in contemplating which plant-based system might be probably the most advantageous for any explicit mucosal immunotherapy utility. Each of those plant-based applied sciences also has its personal historical past of mental property rights, which have to be thought-about [83�88]. The forthcoming business successes of plantbased immunotherapeutics ought to provide extra incentives for follow-on merchandise, in addition to the evolution of products for modulating mucosal immune responses. A crucial review of the concept of transgenic plants: insights into pharmaceutical biotechnology and molecular farming. Regulatory approval and a first-in-human section I clinical trial of a monoclonal antibody produced in transgenic tobacco vegetation. Soybean seeds: a sensible host for the manufacturing of useful subunit vaccines. Expression and immunogenicity of an Escherichia coli K99 fimbriae subunit antigen in soybean. Plant-based vaccines for animals and humans: recent advances in know-how and scientific trials. Vaccination via chloroplast genetics: reasonably priced protein medication for the prevention and treatment of inherited or infectious human illnesses. Taliglucerase alfa: an enzyme alternative therapy utilizing plant cell expression expertise.
Quality 50 mg moduretic
Fertility management is far less effective than deadly baiting for controlling foxes blood pressure 9860 moduretic 50 mg buy discount online. The impact of lively immunization in opposition to inhibin on gonadotropin secretions and follicular dynamics during the estrous cycle in cows heart attack upper back pain 50 mg moduretic purchase free shipping. Efficacy for a brand new stay attenuated Salmonella Enteritidis vaccine candidate to cut back inner egg contamination. Immunization of cattle with a mixture of purified intimin-531, EspA and Tir considerably reduces shedding of Escherichia coli O157:H7 following oral challenge. The efforts to combat malaria are challenged by the complexity of Plasmodium parasite life cycle, which supplies rise to distinct developmental stages that specific variable antigens, in addition to different survival strategies of the parasite, including antigenic polymorphism, antigenic diversion, epitope masking, and host immunosuppression [5]. Malaria an infection begins with the injection of Plasmodium parasites in the form of sporozoites from the Anopheles mosquito salivary gland into the skin of the human host. Some of the sporozoites travel to the liver via the bloodstream to infect the liver hepatocytes. After exiting the cycle of liver-stage infection, the parasites are released into the bloodstream in the type of merozoites to start the pathologic blood-stage infection. The merozoites rapidly invade the erythrocytes and differentiate into ring, trophozoite, and schizont stages by digesting the host hemoglobin for nutrient to grow and multiply. The erythrocytic life cycle of human Plasmodium parasites is 48�72 hours, relying on the species. The parasites continue to differentiate in the mosquito midgut to produce sporozoites to repeat their life cycle once more. It has recently been getting consideration that Plasmodium parasite presence in numerous organs should be considered in a tissue-specific context [12]. This article will evaluation the current proof that Plasmodium parasites could have an ability to modify the intestine surroundings and vice versa. We may even talk about potential mucosal vaccination strategies in opposition to malaria in the gentle of recent proof. Impaired intestinal function with elevated permeability in gastric and intestinal mucosa and intestinal damage have been seen in people with P. The current mouse research utilizing a severe Plasmodium berghei cerebral malaria mannequin has shown that the shortening of the villi, bleeding within the small gut, and sequestration of pink blood cells to blood vessels are obvious and could be inflicting dysbiosis [18]. Malaria and invasive intestinal pathogens similar to Salmonella [19�24] or helminthes [25,26] are incessantly copresent in malaria-endemic regions, increasing the illness severity [27,28]. It has been shown that a rise in gut mastocytosis throughout malaria an infection may cause increases in ileal and plasma histamine levels and/or cytokine alterations such as interleukin 10, which may be immediately associated with increased gut permeability to invasive bacterial infections [24,27,28]. The release of toxic heme due to malaria-induced hemolysis may cause release of immature neutrophils into circulation that lack reactive oxygen species exercise [21,29], although neutrophils are initially totally competent against systemic infection with Plasmodium [30]. Growing evidence indicates the important effects of a "healthy" intestine microbiota towards a number of ailments, including malaria [31�33] (Chapter 9: Influence of Commensal Microbiota and Metabolite for Mucosal Immunit). A significant affiliation between the microbiota composition earlier than the malaria season and the risk of P. Microbiota of individuals with a low risk of malaria contained a significantly larger proportion of Bifidobacterium, Streptococcus, Escherichia, and Lactobacillales [33], suggesting the useful effects of those microbes in the intestine towards malaria. The following mouse study additional supported the hypothesis of the position of microbiota on malaria susceptibility by using genetically related mice from completely different distributors with different intestine microbiomes [32]. Hence it was concluded that the gut microbiome influences the parasite burden and severity of a number of mouse Plasmodium infections. To immediately evaluate the function of Lactobacillus and Bifidobacterium in resistance to extreme malaria, the malariasusceptible mice had been treated with laboratorycultured yogurt supplemented with these probiotics, and a decreasing effect on parasitemia was discovered [32]. Parasite sequestration, inflammation, and resultant bleeding due to malaria infection may trigger main adjustments in the gut microbiota composition. For example, the increase in intestine mastocytosis throughout malaria an infection could cause enhance in ileal and plasma histamine ranges and/or cytokine alterations. In addition, the discharge of poisonous heme as a end result of malaria-induced hemolysis may cause immature neutrophil release into circulation, inflicting exhausted immature neutrophils deficient in killing invasive Salmonella. These changes might result in dysbiosis and promote the invasion of different intestinal pathogens. On the opposite hand, intestine microbiota could contribute to malaria susceptibility, directly or not directly. The particular antibodies to some intestine pathobionts and/or their metabolites might cross-react with sporozoites and subsequently impair transmission of the parasite from mosquitoes to mammalian host. It is feasible that the alteration of gut microbiota composition may be controlling the microbial metabolite productions, thus immediately or not directly influencing host immunity. Therefore these possible microbial metabolites have to be further investigated in response to malaria infection. In addition, the low-risk population in Malawi had a substantial proportion of Escherichia in the stool that may be contributing to the safety, though the expression of -gal was not examined in that study [33]. Mucosal vaccines have several advantages, such as the capability of inducing protecting immunity domestically and systemically with decrease value (less purity is needed, owing to mucosal administration), needle-free delivery, and thus easy mass immunization benefits, particularly during pandemics [41]. Moreover, mucosal immunizations have a possible to induce good immunogenicity, owing to being able to goal larger surface areas with higher vascularity and simple accessibility to lymphoid tissues. Developing vaccines in opposition to malaria has been a fantastic problem, and a systemic subunit protein vaccination strategies has mainly been used [42�44]. The strain-specificity and the polymorphisms of antigens, the short length of antibodies, and lack of good adjuvants to improve immunogenicity are a quantity of drawbacks of the present strategy of malaria vaccine growth. Therefore a quantity of strategies, including mucosal immunizations, have been tried, though with questions as to whether or not this type of immunization is more likely to be beneficial in opposition to a parasite with a systemic life in erythrocytes, not invading mucosa in any respect. Later studies have improved the manufacturing of Plasmodium antigens in vegetation [52�56], bacterial outer membrane vesicles [57], or wheat-germ free system [58] to be used for mucosal vaccination towards malaria. Another method was the intranasal or oral immunization with live attenuated Salmonella expressing Plasmodium antigens [59�61], which confirmed promising leads to mice (Table 49. The key question with mucosal immunization towards a quantity of pathogens, together with malaria, is why and the way the mucosal vaccination is profitable. These amassed data present a brand new platform for the development of suitable antigens as nicely as adjuvant formulations concentrating on mucosal surfaces [62,63]. The chapter has also summarized malaria vaccine trials to date which have used mucosal route of immunization. However, it should be saved in thoughts that many pathogens, together with bacteria, viruses, and parasites, are found in resourcelimited settings with no clean water and malnutrition the place the mucosal surfaces are more uncovered to dangerous pathogens and will have more disruption of mucosal limitations [64]. Acknowledgments We thank Malaria Immunology Lab members for his or her useful inputs. Quantitative assessment of multiorgan sequestration of parasites in deadly pediatric cerebral malaria. Reduced hepatic blood move and intestinal malabsorption in extreme falciparum malaria. Increased gastrointestinal permeability in patients with Plasmodium falciparum malaria. Malaria impairs resistance to Salmonella through hemeand heme oxygenase�dependent dysfunctional granulocyte mobilization.