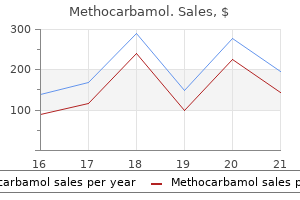
Methocarbamol dosages: 500 mg
Methocarbamol packs: 60 pills, 90 pills, 120 pills, 180 pills, 270 pills, 360 pills

Methocarbamol 500 mg safe
The security and feasibility of this method are but to be confirmed in bigger collection back spasms 22 weeks pregnant discount methocarbamol 500 mg otc. Because of its higher vulnerability to ischemia-reperfusion harm 2410 muscle relaxant generic methocarbamol 500 mg without a prescription, the pancreas is often implanted first, on the best side. Some degree of mobilization of the caecum and proper colon is normally necessary if the venous anastomosis to be onto the inferior vena cava, thus creating an essentially retroperitoneal placement of the graft. The proper common iliac artery is absolutely mobilized and Back-table surgical procedure this is a crucial a half of the operation and more advanced than the back-table process required in kidney or liver transplantation. Back-table surgical procedure for the pancreas requires a sequence of steps of paramount importance. The pancreas is a retroperitoneal organ and is retrieved with surrounding tissue, which must all be dissected and ligated/sealed in order to cut back bleeding at the time of revascularization. The duodenum and segment of proximal jejunum are dissected and shortened, to depart the graft with a section of donor intestine of 8�15 cm in size, stapled and oversewn at each end. The root of the mesentery often closed at the retrieval operation with a stapler, has to be dissected and oversewn to ensure hemostasis. Some surgeons place the venous anastomosis onto the right frequent iliac vein, during which case that is mobilized, presumably requiring division of the interior iliac vein. The portal venous anastomosis is the primary to be carried out, adopted by the arterial conduit. The kidney will later be implanted on the left iliac vessels after pancreas reperfusion and hemostasis. This has allowed further choices for the endocrine drainage of the gland, whereas bladder drained pancreases are solely really accessible to the iliac axis, enteric drained grafts may be also be drained through the portal circulation. The pancreas portal vein is most commonly anastomosed to the recipient vena cava or proper iliac vein. According to international registries, approximately 18%68 of implanted pancreases are anastomosed with portal venous drainage. Leakage of pancreatic enzymes can set off a cascade of complications: these were typically a explanation for demise in the early days of this procedure, and still remains a explanation for considerable morbidity. The outcomes of pancreatic transplantation improved significantly after 1983 when Sollinger et al. This was by far the most typical technique adopted for at least a decade: it lowered the incidence of surgical issues and allowed assessment of pancreatic function by measurement of urinary amylase ranges. However, this strategy was burdened by important long-term localized and systemic problems, together with hematuria, urinary infections, reflux pancreatitis, metabolic acidosis, and dehydration. However, this is on the value of a high incidence of those unwanted effects: conversion to enteric drainage is often required for those recipients, up to 50% within 15 years from transplantation. Leakage at the enteric anastomosis is also a supply of morbidity, as is bleeding within the immediate postoperative part. Pancreatic inflammation is fairly common within the instant postoperative period; this is as a result of of ischemia-reperfusion, possibly exacerbated by surgical manipulation of the graft. The frequent incidental finding of graft pancreatitis in patients investigated for different A. Whole pancreas allo-transplantation Complications 143 reasons suggests that the frequency of this complication is underestimated. Unlike native pancreatitis, there might or is most likely not a correlation with serum amylase and lipase ranges. Symptoms may be nonspecific and prognosis could additionally be delayed by confounding components that always occur in a daily postoperative course, corresponding to protracted ileus, abdominal distension, tenderness, elevated inflammatory markers, and generalized malaise. In case of extra extreme pancreatitis, probably with necrosis, symptoms are severe and patients deteriorate quickly due to underlying sepsis and systemic inflammatory response. The most frequent indication for graft pancreatectomy is venous thrombosis, with a reported incidence of as much as 10%�20%, with nice variations amongst transplant centers. In such circumstances, full therapeutic anticoagulation has a excessive likelihood of success. Complete thrombosis requires pressing laparotomy; thrombectomy has been carried out efficiently, however probably hardly ever, and nearly all of such instances require graft pancreatectomy. The function of pretransplant thrombophilia screening has not been proven effective in predicting the likelihood of pancreas transplant thrombosis,seventy one nonetheless, most transplant models carry out coagulation research at the time of itemizing. The adoption of anticoagulation protocols in association with close monitoring of coagulability in the first postoperative course. Acute intraoperative hypotension related to main surgical stress and large cytokine launch at reperfusion can result in generalized tissue hypoperfusion and exacerbate organ harm, particularly in sufferers with superior macrovascular disease. Equally essential is frequent monitoring of Hb levels within the early postoperative hours when the person response to systemic anticoagulation is yet to be ascertained. Postoperative bleeding is a frequent explanation for relaparotomy, a consequence of the multiple potential bleeding factors on the pancreas graft and the state of anticoagulation required to cut back the chance of early thrombus formation. These could be the outcome of perioperative bleeding, graft pancreatitis, and enteric or (occasionally) ureteric leaks. Insidious infections of vascular anastomoses, resulting in pseudoaneurysm, are a wellrecognized complication of pancreatic transplantation. This complication typically presents months and even years after removing of a failed graft, or in a patient with a functioning graft. The management of arterial pseudo-aneurysms is difficult and requires a mix of surgical and endovascular approaches. Simultaneous pancreas-kidney transplantation Medical postoperative problems Together with cardiovascular events, sepsis is probably the most frequent life-threatening medical early complication. This is mostly a manifestation of underlying intraabdominal issues, however it may also be secondary to catheterization, the presence of a ureteric stent, central venous and hemodialysis traces, and opportunistic bacterial, viral, and fungal infections. The management of postoperative an infection is a vital side of the management of pancreas transplant recipients, and it could possibly characterize a big problem. The shut engagement of infective illness specialists is crucial within the management of these sufferers and beneficial even when apparently the clinical impact is modest. Life-threatening infections can happen with little, if any, signs and evolve rapidly in heavily immunosuppressed sufferers treated. It is unclear which of the 2 grafts is more frequently implicated in discordant rejection. The absence of an accurate marker of pancreatic operate makes a diagnosis of isolated pancreas rejection problematic. Pancreatic graft biopsy is claimed by some units to be the gold commonplace: research using concurrent biopsy of each kidney and pancreas have shown a comparatively excessive proportion of discordant rejection (37%), and differing histological grades of rejection between the two organs. Various methods have been proposed to minimize the danger of undetected pancreatic rejection: a correlation between de novo donor-specific antibodies, rejection, and allograft loss has been demonstrated. As with different organs, the classification of rejection relies on histopathological findings using a nomenclature that has been agreed by the Banff group. The latest revision of the Banff classification for pancreas transplantation contains (1) acute T cell-mediated rejection, (2) antibody-mediated rejection, and (3) persistent allograft rejection/graft fibrosis. Hyperacute rejection is a direct and catastrophic immune response that results almost inevitably in graft loss. As with kidney transplantation, that is now a really uncommon event, because of pretransplant crossmatching techniques. The histopathological findings verify the presence of diffused microvascular thrombosis and the presence of coagulation fragment C4d, which is a marker of antibody deposition on the endovascular degree.
Purchase methocarbamol 500 mg without a prescription
Novel putative glycosylphosphatidylinositol-anchored micronemal antigen of Plasmodium falciparum that binds to erythrocytes muscle relaxant long term use methocarbamol 500 mg generic visa. Cytoplasmic tail motifs mediate endoplasmic reticulum localization and export of transmembrane reporters in the protozoan parasite Toxoplasma gondii spasms knee methocarbamol 500 mg without a prescription. Proteolytic processing and first construction of Plasmodium falciparum apical membrane antigen-1. Distinct mechanisms govern proteolytic shedding of a key invasion protein in apicomplexan pathogens. Trans-genera reconstitution and complementation of an adhesion complex in Toxoplasma gondii. Toxoplasma secretory proteins and their roles in parasite cell cycle and an infection Huynh, M. A conserved apicomplexan microneme protein contributes to Toxoplasma gondii invasion and virulence. Toxoplasma gondii cyclophilin 18 regulates the proliferation and migration of murine macrophages and spleen cells. Toxoplasma gondii myosin F, an important motor for centrosomes positioning and apicoplast inheritance. Effects of antiphagocytic brokers on penetration of Eimeria magna sporozoites into cultured cells. Fetuin-A, a hepatocyte-specific protein that binds Plasmodium berghei thrombospondin-related adhesive protein: a possible role in infectivity. Aldolase varieties a bridge between cell floor adhesins and the actin cytoskeleton in apicomplexan parasites. Rapid membrane disruption by a perforin-like protein facilitates parasite exit from host cells. Conservation of a gliding motility and cell invasion equipment in apicomplexan parasites. The protozoan parasite Toxoplasma gondii targets proteins to dense granules and the vacuolar area using both conserved and strange mechanisms. The glideosome: a molecular machine powering motility and host-cell invasion by Apicomplexa. Secretion by Toxoplasma gondii of an antigen that appears to turn out to be related to the parasitophorous vacuole membrane upon invasion of the host cell. Expression, purification, and biochemical characterization of a recombinant lectin of Sarcocystis muris (Apicomplexa) cyst merozoites. The position of sialyl glycan recognition in host tissue tropism of the avian parasite Eimeria tenella. Toxoplasma gondii toxolysin four is an extensively processed putative metalloproteinase secreted from micronemes. Toxoplasma secretory proteins and their roles in parasite cell cycle and an infection Lek, A. Ferlins: regulators of vesicle fusion for auditory neurotransmission, receptor trafficking and membrane restore. Characterization of Toxoplasma DegP, a rhoptry serine protease crucial for deadly infection in mice. Exocytosis of Toxoplasma gondii dense granules into the parasitophorous vacuole after host cell invasion. Characterization of the protein contents of rhoptries and dense granules of Toxoplasma gondii tachyzoites by subcellular fractionation and monoclonal antibodies. Stability and function of a putative microtubule-organizing heart within the human parasite Toxoplasma gondii. Intravacuolar community may act as a mechanical assist for Toxoplasma gondii contained in the parasitophorous vacuole. Interrelations between the parasitophorous vacuole of Toxoplasma gondii and host cell organelles. Identification, cloning, expression, and characterization of the gene for Plasmodium knowlesi surface protein containing an altered thrombospondin repeat domain. Plasmodium sporozoite invasion into insect and mammalian cells is directed by the same twin binding system. Identification of heparin as a ligand for the A-domain of Plasmodium falciparum thrombospondin-related adhesion protein. Dense granules: Are they key organelles to assist perceive the parasitophorous vacuole of all Apicomplexa parasites Apical membrane antigen 1, a serious malaria vaccine candidate, mediates the shut attachment of invasive merozoites to host purple blood cells. Host cell floor sialic acid residues are concerned on the method of penetration of Toxoplasma gondii into mammalian cells. Intracellular destiny of vacuoles containing Toxoplasma gondii is decided at the time of formation and depends on the mechanism of entry. Conditional knockdown of a novel coccidian protein results in the formation of aberrant apical organelles and abrogates mature rhoptry positioning in Toxoplasma gondii. Identification and partial characterization of a second Kazal inhibitor in Toxoplasma gondii. The loss of cytoplasmic potassium upon host cell breakdown triggers egress of Toxoplasma gondii. Toxoplasma secretory proteins and their roles in parasite cell cycle and an infection Muniz-Hernandez, S. Contribution of the residual physique in the spatial group of Toxoplasma gondii tachyzoites inside the parasitophorous vacuole. Structures of monomeric and oligomeric types of the Toxoplasma gondii perforin-like protein 1. Intramembrane cleavage of microneme proteins on the floor of the apicomplexan parasite Toxoplasma gondii. A Toxoplasma gondii rhoptry protein associated with host cell penetration has unusual cost asymmetry. Identification of novel dense-granule proteins in Toxoplasma gondii by two proximity-based biotinylation approaches. Intramembrane proteolysis of Toxoplasma apical membrane antigen 1 facilitates hostcell invasion however is dispensable for replication. Relationship between intracellular free calcium concentrations and the intracellular development of Toxoplasma gondii. Toxofilin, a novel actin-binding protein from Toxoplasma gondii, sequesters actin monomers and caps actin filaments. A lipolytic lecithin: ldl cholesterol acyltransferase secreted by Toxoplasma facilitates parasite replication and egress. Amino acid sequence of the murine Mac-1 alpha chain reveals homology with the integrin household and an extra domain related to von Willebrand factor. Novel structural and regulatory features of rhoptry secretory kinases in Toxoplasma gondii. Coupling of retrograde flow to force production during malaria parasite migration.
Buy 500 mg methocarbamol amex
Effect of insulin on the proliferation of cultured primate arterial clean muscle cells back spasms 24 weeks pregnant methocarbamol 500 mg discount overnight delivery. Insulin potentiates platelet-derived progress issue motion in vascular clean muscle cells zma muscle relaxant methocarbamol 500 mg order on-line. The potential influence of insulin and plasminogen activator inhibitor sort 1 on the formation of susceptible atherosclerotic plaques associated with type 2 diabetes. The effect of portal versus systemic venous drainage of the pancreas on the lipoprotein composition. Relationship of the metabolic syndrome and weight problems to polycystic ovary syndrome: a controlled, population-based research. Insulin receptor down-regulation and impaired antilipolytic action of insulin in diabetic sufferers after pancreas/kidney transplantation. Effect of the surgical method on long-term end result of pancreas transplantation. Combined kidney and pancreas transplants by way of decrease transverse belly incisions. The utility of retroperitoneal kidney placement in simultaneous kidney pancreas transplantation. The impression of midline versus transverse incisions on wound issues and outcome in simultaneous pancreas-kidney transplants: a retrospective evaluation. Use of the circular stapler in construction of the duodenoneocystostomy for drainage into the bladder in transplants involving the entire pancreas. Urologic complications after simultaneous pancreas-kidney transplantation: hand-sewn versus stapled duodenocystostomy. Simultaneous pancreas-kidney transplantation in the mycophenolate mofetil/ tacrolimus era: evolution from induction remedy with bladder drainage to noninduction therapy with enteric drainage. A new methodology of preparation of segmental pancreatic grafts for transplantation: trials in canines and in man. Pancreas after islet transplantation: a first report of the international pancreas transplant registry. Combined liver-pancreas transplantation in a affected person with major sclerosing cholangitis and insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus. Robotic pancreas transplantation in a type 1 diabetic affected person with morbid weight problems. Moreover, laparoscopic transplantation of solid organs is associated with additional and specific difficulties. Acquisition of the skills required to perform laparoscopic transplantation is related to a steep learning curve. Third, the intrinsic limitations of laparoscopy make minimally invasive transplantation demanding, predictably operator-dependent, and poorly reproducible on a big scale. Robotic pancreas transplantation instantly achieved during laparoscopic procedures in order that extended heat ischemia of the graft could happen. Sixth, at a distinction from nearly all different procedures, the success of solid organ transplantation is decided by a quantity of components, with the initial operation being just one of many steps required for a profitable outcome. Overall, the use of the da Vinci surgical system is believed to surpass most of the limitations of typical laparoscopy thus enhancing surgical dexterity in minimally invasive procedures. Fourth, reduction in tissue dealing with is known to be related to decrease activation of coagulation techniques. However, through the building of vascular anastomoses, the graft is exposed to progressive rewarming, while at the time of reperfusion bleeding could become a problem if huge or arising from multiple sites. Additionally, soon after reperfusion, the graft shall be uncovered to the impact of pneumoperitoneum that might lower the quality of graft perfusion. Graft rewarming/cooling the impact of graft rewarming during transplantation was studied for the kidney. The temperature of renal grafts will increase according to a logarithmic curve, on the velocity of zero. The combination of those unfavorable operative conditions could prolong anastomotic time, eventually leading to the same diploma of graft rewarming achieved without intracorporeal graft cooling. To tackle this problem, experimental cooling kidney jackets have been described for the kidney,31 but no medical experience is on the market and no gadget was specifically developed for the pancreas. First, discount in the size of surgical incision could result in reduced rates of wound complications and surgical web site infections that are as an alternative known to happen regularly in diabetic recipients. Diabetic recipients are indeed at elevated danger for lymphatic leak after transplantation doubtlessly resulting in symptomatic lymphocele. Whole pancreas allo-transplantation Introduction 171 Pneumoperitoneum is thought to decrease graft perfusion in laparoscopic procedures. However, when working beneath robotic assistance lower pneumoperitoneum pressures can be set up while maintaining optimum publicity of the surgical subject. Graft bleeding on the time of reperfusion Although robotic help permits to management quite simply even main bleeding arising from large vessels,36 alike in some other laparoscopic procedure bleeding is healthier prevented than arrested. Furthermore, ought to the graft bleed from a number of sites, even if not massively, to obtain an excellent hemostasis may become tedious and will lead to undue graft manipulation. Regarding the later problem, the dearth of haptic suggestions of present robotic techniques is a further concern that should be born in mind. As higher detailed under, meticulous graft preparation is key to minimize the chance of bleeding at the time of reperfusion. However, the whole operative staff, including the surgeon on the desk and the anesthetist, ought to be prepared to face this instance. Examples of such procedures are pyeloplasty and repair of splenic artery aneurysms. The use of the latter clamps requires the supply of versatile cannulas to allow the introduction of curved jaws. It can additionally be sensible to have the double of all types of vascular clamps that are anticipated to be needed in an easy process. Needless to say that each one the standard devices required for the open procedure ought to be ready in the operating room within the event of an urgent conversion. Malpractice litigations have been reported when robotic procedures had been suffering from complications and surgeons had been demonstrated to have received inadequate training. Recipient process the sufferers are placed supine, with the right flank slightly elevated, and secured to the operating desk utilizing wide banding. The working desk is oriented some 15� within the Trendelenburg position and tilted some 25� to the left. Using a da Vinci Si system a complete of three robotic arms are employed, whereas utilizing a Xi system also the fourth robotic is used. The fourth robotic arm could possibly be really used additionally with the Si system, although the different arm design might increase the chance of arm collision thus proportionally decreasing the benefits of having an additional operative arm. It could additionally be price to underscore that the optic port has to be positioned in front of the goal anatomy. Pneumoperitoneum is maintained at 10 mmHg throughout dissection of vessels and graft implantation and is lowered to 8 mmHg after graft reperfusion. Using a Xi system the tower of the da Vinci may be placed anywhere in the working room, provided that the overhead growth is available in a handy position. Using an Si system the tower has to be positioned opposite to the target anatomy and has therefore to stay at the right facet of the affected person.
Cheap 500 mg methocarbamol fast delivery
Glucose clamp technique- methodology for quantifying insulin-secretion and resistance muscle relaxant norflex methocarbamol 500 mg generic on-line. Isotope Tracers in Metabolic Research: Principles and Practice of Kinetic Analysis infantile spasms 2012 methocarbamol 500 mg cheap on line. Equivalence of the insulin sensitivity index in man derived by the minimal model technique and the euglycemic glucose clamp. A comparability between the minimal mannequin and the glucose clamp within the assessment of insulin sensitivity across the spectrum of glucose-tolerance. Insulin sensitivity index in type 1 diabetes and following human islet transplantation: comparability of the minimal mannequin to euglycemic clamp measures. A modified protocol for estimation of insulin sensitivity with the minimal model of glucose kinetics in patients with insulin-dependent diabetes. A modified minimal mannequin analysis of insulin sensitivity and glucose-mediated glucose disposal in insulin-dependent diabetes. Reduced glucose effectiveness associated with lowered insulin release: an artifact of the minimal-model method. Lack of glucagon response to hypoglycemia in diabetes-evidence for an intrinsic pancreatic alpha cell defect. Regulation of alpha-cell operate by the beta-cell in isolated human and rat islets deprived of glucose: the "switch-off" hypothesis. Regulation of alpha-cell operate by the beta-cell throughout hypoglycemia in Wistar rats: the "switch-off" hypothesis. Restoration of glucose counterregulation by islet transplantation in long-standing type 1 diabetes. Hierarchy of glycemic thresholds for counterregulatory hormone-secretion, symptoms, and cerebral-dysfunction. The function of intramyocellular lipids throughout hypoglycemia in patients with intensively treated type 1 diabetes. Islet cell hormonal responses to hypoglycemia after human islet transplantation for type 1 diabetes. Persistence of counter-regulatory abnormalities in insulin-dependent diabetes-mellitus after pancreas transplantation. Suppression of counterregulatory hormone response to hypoglycemia by insulin per se. Mechanism of awareness of hypoglycemia-perception of neurogenic (predominantly cholinergic) quite than neuroglycopenic signs. Reduction of blood glucose variability in type 1 diabetic patients treated by pancreatic islet transplantation. Assessment of glycemic control after islet transplantation using the continual glucose monitor in insulin-independent versus insulin-requiring kind 1 diabetes topics. Glycemic thresholds for activation of counterregulatory hormone and symptom responses in islet transplant recipients. Continuous glucose monitoring for hypoglycemia avoidance and glucose counterregulation in long-standing type 1 diabetes. Overall, the type of problems that may come up from general intraportal islet transplantation may be broadly categorized into three types: hemorrhagic, thrombotic, and steatotic. Intraportal infusion of islet cells may be achieved through percutaneous or surgical strategies. Percutaneous access is performed as a Seldinger approach with wire catheterization of portal venous branches. Thus, the danger of iatrogenic damage is lower in this setting in comparability with percutaneous transplantation carried out extra generally in allogeneic recipients. In addition, the overall greater whole islet mass sometimes infused with allogeneic transplantation can predispose to particular problems mentioned later on this chapter. Complications associated to percutaneous islet cell transplantation Among the percutaneous approaches to intraportal islet cell transplantation are the transhepatic and transjugular entry routes, both of which are often performed in an angiographic suite. Percutaneous transhepatic intraportal access is achieved by way of the best lobe of the liver by catheterization (tract represented by dashed lines). Islet cells are infused by way of a portal venous department and comply with the portal circulation (arrows). Bleeding may happen via the tract or sequester beneath the liver capsule as a hematoma. The thrombus is composed of islet cells, blood cells, clotting elements, and leukocytes. Bleeding Hemorrhage is the most common complication after islet cell transplantation, with a prevalence of 15% reported in retrospective research. Additional sources of bleeding also can come up from the liver parenchyma (resulting in intraperitoneal hemorrhage, hepatic, or subcapsular hematoma) and less generally, from intra- or extrahepatic vasculature (that could lead to a hematoma or pseudoaneurysm if arterial injury is present8�10). Although rare, other reported sources of bleeding may be from iatrogenic harm to extraperitoneal buildings close to the intercostal trajectory of percutaneous access such because the intercostal artery and the lung (hemothorax11, 12). Risk components for bleeding problems There are many potential risk factors for bleeding complications after islet cell transplantation. These embrace the usage of anticoagulation or antiplatelet therapy (preprocedural or periprocedural), portal hypertension, baseline coagulopathies, and technical aspects intrinsic to the procedure (accumulative variety of procedures patient bear and total of makes an attempt at percutaneous cannulation to establish portal access). Antiplatelet remedy and anticoagulation Antiplatelet agents similar to low-dose aspirin may be common drugs among diabetic patients and may pose risk for procedural-related bleeding. Procedure-related and medical problems in and after intraportal islet transplantation facilities. Optimal dosing of heparin depends on patient elements similar to portal venous stress, institutional protocols, and procedure-related components such because the infusion volume. Portal venous pressure Elevated portal venous stress (>10 mmHg) can exacerbate bleeding and present difficulties in hemorrhage management. The regular range for portal vein strain previous to islet cell infusion has been reported to be less than 12 mmHg and generally increases by 1�2 mmHg after infusion. Portal vein pressures greater than 20 mmHg or more than double the baseline stress current as a contraindication to islet infusion because of elevated risks of such issues. Platelet counts lower than a hundred,000 ought to be considered high danger for bleeding problems and corrected with appropriate transfusions. Technical elements of procedure Increasing number of islet cell infusions has been recognized as an independent threat factor for bleeding. Bleeding patients may show basic signs of hypovolemia together with altered psychological status, hypotension, and tachycardia. On physical examination, pallor may be evident and as well as enlarged stomach girth if intraperitoneal hemorrhage is energetic. Laboratory tests may reveal important anemia associated to acute blood loss, and coagulopathy may be current from using anticoagulants through the procedure. It is important to recognize, nonetheless, that sufferers with longstanding T1D could not manifest scientific indicators of hypovolemic shock because of impaired compensatory mechanisms from autonomic neuropathy. Preventative measures towards bleeding problems In addition to optimizing anticoagulation parameters to reduce the risk of bleeding throughout percutaneous islet cell transplantation, embolization of the parenchymal tract with metallic coils or hemostatic agents has been confirmed to decrease the incidence of procedural-related hemorrhage. In the absence of track closure, the incidence of bleeding has been reported to be as high as 30% in retrospective research. More significant bleeding leading to extreme anemia and/or hemodynamic instability could require interventions similar to cessation of postprocedural anticoagulation, blood transfusion, administration of anticoagulant-reversal agents, angiography with repeated embolizations, and/ or operative intervention if lively intraperitoneal bleeding is current.
Discount 500 mg methocarbamol with visa
Simultaneous pancreas/kidney transplantation-a comparison of enteric and bladder drainage of exocrine pancreatic secretions1 spasms during meditation 500 mg methocarbamol generic. Posttransplant an infection in enteric versus bladder-drained simultaneous pancreas-kidney transplant recipients1 muscle relaxant radiolab methocarbamol 500 mg sale. Use of recipient mesenteric vessels for revascularization of segmental pancreas grafts: technical and metabolic considerations. Systemic venous drainage of pancreas allografts as unbiased explanation for hyperinsulinemia in sort I diabetic recipients. A 30� endoscope is employed and dissection begins with mobilization of the right colon, as described within the open process. In common ligatures, that are easily performed utilizing robotic help, are most popular since as clips could turn out to be caught or trapped within the jaws of laparoscopic clamps thus complicating the flow of the process. After an intravenous bolus of 5000 units of Donor process Pancreas grafts are procured from mind dead multiorgan donors. This strategy requires that the procurement operation is carried out by an professional pancreatic surgeon. Modern vessel sealing devices can be used to minimize the time required for full pancreatic dissection, as already proven in complex pancreatic procedures. Using this system, on the end of the donor procedure, the pancreas graft is totally cleaned up, so that again desk surgical procedure is only required to create a single arterial conduit utilizing a Y-iliac donor graft. Avoiding an extended again table procedure, along with the sooner definition of graft suitability for transplantation, offers the chance to cut back the interval of cold ischemia. Whole pancreas allo-transplantation Donor procedure 173 sodium heparin, the vessels are crossclamped utilizing either laparoscopic bulldog clamps or typical bulldog clamps positioned under handbook help, through the GelPort. After releasing of bulldog clamps hemostasis is perfected as required, with out reversing the heparin in anticipation for the need of postoperative anticoagulation. For exocrine drainage, as described for the open process, we choose to use a Roux-en-Y jejunal limb. The optic port is positioned along the left pararectal line some 5 cm below the navel. Two 8-mm robotic ports are placed along the proper pararectal line some 5 cm under the costal margin and three cm above the pubis, respectively. The console is placed at the head of the patient so that the operating surgeon can stay in direct visible contact with both the anesthesia staff and the surgeons on the table. Surgical assistants, scrub nurse, instrument desk, and back-table are all positioned to the left of the patient making this part of the working room "clear. At the top of the process, the pneumoperitoneum is reestablished, the operative subject is inspected and two drains are placed alongside the graft. A midline incision (7 cm) was made alongside the midline above the camera port and sealed utilizing a GelPort. The exocrine drainage was created into the urinary bladder utilizing a round stapler. This patient was reported to have achieved insulin independence and having remained insulin unbiased at 1 yr after transplantation. Similarly, the widespread limb of the Y donor graft is anastomosed end-to-side to the best frequent iliac artery. A Roux-en-Y limb is used and transferred to the site of graft transplantation via the mesentery of the right colon. Although based mostly on just three circumstances no sound conclusion could be drawn, using robotic help A. Further expertise with kidney transplantation, as properly with different complicated stomach procedures requiring intracorporeal vascular reconstructions, confirmed that robotic help surpasses many of the limitations encountered using pure laparoscopic techniques. A comparative analysis of the protection, efficacy, and cost of islet versus pancreas transplantation in nonuremic patients with sort 1 diabetes. Preoperative glycosylated hemoglobin and postoperative glucose together predict major issues after stomach surgical procedure. Perioperative cardiac morbidity in kidney transplant recipients: incidence and risk factors. Identifying the need for and content material of a sophisticated laparoscopic expertise curriculum: results of a national survey. Minimally invasive surgery: nationwide trends in adoption and future directions for hospital strategy. First robotic-assisted dual kidney transplant: surgical approach and report of a case with 24-month follow-up. Current perspectives on laparoscopic robot-assisted pancreas and pancreas-kidney transplantation. Robotic pancreas transplantation in a sort 1 diabetic patient with morbid weight problems: a case report. Symptomatic lymphoceles after kidney transplantation-multivariate evaluation of danger components and consequence after laparoscopic fenestration. Intrapyloric injection of botulinum toxin a for the remedy of persistent gastroparesis following profitable pancreas transplantation. Effective surface cooling of the kidney throughout vascular anastomosis decreases the chance of delayed kidney perform after transplantation. Evaluation of the ischemic protection efficacy of a laparoscopic renal cooling gadget using renal transplantation viability evaluation standards in a porcine mannequin. Influence of pneumoperitoneum strain on surgical subject during robotic and laparoscopic surgical procedure: a comparative examine. Medicolegal evaluation of legal responsibility dangers for gynecologists stemming from lack of coaching in robot-assisted surgery. A laboratory training and analysis approach for robotic assisted ex vivo kidney transplantation. Another essential discovering of the experiment was the later rejection of the liver when compared to liver transplantation alone. In 1967, when once more the pioneer Richard Lillehei, tried the primary intestinal transplant in a human, parenteral diet was not yet out there, and immunosuppression drugs were very primitive. It was not until the late 1970s, with the primary human transplant trials using cyclosporine, that solid organ transplantation revitalized with larger survival charges. Pancreas transplantation within the setting of multivisceral transplantation performed the primary successful multivisceral transplant in a 3-year-old child. Historically hampered by its preliminary outcomes, intestinal, and multivisceral transplantation has advanced from an experimental subject to a regular therapeutic possibility. Indications and types of grafts the pancreas organ as part of multivisceral or multiorgan transplantation has always approached with warning because of graft pancreatitis, rejection or technical issues. Moreover, to keep away from that it at all times better to embody the pancreaticoduodenal complicated as a half of multivisceral transplant. The debate regarding maintaining the native pancreaticoduodenal complex whereas transplanting multivisceral allografts has aroused. Removal of the native wholesome pancreas and spleen to get replaced with visceral donor graft may have some considerations.
Methocarbamol 500 mg discount on-line
Interferongamma suppresses the growth of Toxoplasma gondii in human fibroblasts through hunger for tryptophan spasms 5 month old baby methocarbamol 500 mg buy cheap. Toxoplasma gondii salvages sphingolipids from the host Golgi through the rerouting of selected Rab vesicles to the parasitophorous vacuole muscle relaxants best methocarbamol 500 mg. Toxoplasma co-opts host gene expression by injection of a polymorphic kinase homologue. Alarmin S100A11 initiates a chemokine response to the human pathogen Toxoplasma gondii. Murine gamma interferon fails to inhibit Toxoplasma gondii development in murine fibroblasts. Innate recognition of Toxoplasma gondii in humans entails a mechanism distinct from that utilized by rodents. Human lymphokine-activated killer cells are cytotoxic towards cells contaminated with Toxoplasma gondii. Externally triggered egress is the main fate of Toxoplasma gondii during acute an infection. Interferon-induced guanylate-binding proteins: guardians of host defense in health and disease. Necrotizing toxoplasmic encephalitis in a toddler with the X-linked hyper-IgM syndrome. Toxoplasma gondii-infected natural killer cells display a hypermotility phenotype in vivo. Host cell autophagy is induced by Toxoplasma gondii and contributes to parasite growth. Failure to trigger the oxidative metabolic burst by regular macrophages: attainable mechanism for survival of intracellular pathogens. Inherent oxidative stress in the Lewis rat is associated with resistance to toxoplasmosis. Autophagosome-independent essential operate for the autophagy protein Atg5 in cellular immunity to intracellular pathogens, Cell Host Microbe, four. Proper balance of the adaptive immune response is the vital thing for the survival of both parasite and host, since inadequate immune responses (as in immunocompromised or fetal hosts) result in uncontrolled parasite replication and extreme disease, whereas extreme immune responses result in immune-mediated pathology. In contrast to innate immunity (Chapter 25 "Innate immunity to Toxoplasma gondii") which is relatively nonspecific and speedy, adaptive immunity is very particular for a particular pathogen, and it develops over a interval of days or even weeks. This article summarizes our current understanding of how the adaptive immune system acknowledges and responds to T. The chapter begins with a quick overview of the mammalian adaptive immune system, emphasizing these components that are most relevant in the setting of T. The dialogue then progresses offering a extra detailed description of the adaptive immune response to T. Cell varieties are proven in gray, and immune protecting "effector" mechanisms are indicated in purple. B cells contribute to protection by producing antibodies that bind particularly to the parasite. T cells are an alternate thymus-derived T cell inhabitants whose function during T. After mature T cells exit the thymus, they flow into between secondary lymphoid organs Toxoplasma Gondii 26. They purchase effector features, corresponding to the power to produce cytokines or kill goal cells. This is pivotal in situations of an infection when exacerbated responses may be deleterious for the host and trigger immune pathology. Following initial activation, one additional end result of T cell differentiation is the formation of memory T cell populations, which both recirculate from secondary lymphoid organs to tissues or reside within tissues without recirculating. Adaptive immunity proteins which are taken up by way of phagocytosis or endocytosis (termed the exogenous pathway). T cells can secrete lots of the same cytokines as T cells, but they seem to play a more modest role throughout T. Also like T cells, B cells initially exist in a quiescent or "naive" � form and require activation by antigen encounter to set off clonal expansion and differentiation into antibody secreting cells. Activated B cells secrete antibody into extracellular spaces in tissues and mucosal sites. Antibodies can then bind directly to pathogens, marking them for destruction by other components of the immune system. It is now well established that inverse situations exist and that they play main features in controlling T cell responses. Notably, however, in sure contexts, different cell varieties, for example, mind endothelial cells and liver sinusoid endothelial cells, are additionally endowed with the ability to carry out cross-presentation. In all nucleated cells, cytosolic antigens are degraded by cytosolic proteases, including the proteasome, into shorter polypeptides. Source antigens in the cytoplasm are fragmented into smaller polypeptides by the proteasome, with the help of other proteases and chaperones. The precise nature of the supply antigens continues to be debated, but it appears clear that both end-of-life proteins as properly as newly synthesized, presumably defective, merchandise are related antigenic sources (Anton and Yewdell, 2014; Rock et al. Two major situations of cross-presentation have been described: the "cytosolic" and the "vacuolar" pathways. The most common situation is the "cytosolic" pathway, also recognized as phagosome-tocytosol pathway. This pathway entails uptake of antigens into intracellular organelles, adopted by their translocation into the cytosol. Efficient cross-presentation requires limited antigen degradation inside the phagosome before cytosol export. In the much less frequently noticed "vacuolar" pathway, particulate antigens taken up during phagocytosis or endocytosis are degraded throughout the endocytic compartment itself. The topology of membrane insertion also plays a critical function since inverting the orientation of the epitope. It is believed to permit retrotranslocation of luminal antigens to the host cytosol. Finally, similar to what has been suggested for phagosomal antigens (Blander, 2018; NairGupta et al. Remarkably, numerous options differ regarding the processing mechanisms of membrane-bound antigens. Indeed, displacing the C-terminal epitope reduces its immunogenicity, and inserting a subdominant epitope to the C-terminal position ameliorates the response (Feliu et al. P62 could bind to and goal vacuolar antigens to the proteasome though the character of the ubiquitinated targets remains unclear (Jensen, 2016; Lee et al. In cell types corresponding to human glioblastoma cells, primary rat astrocytes, microglia (Luder et al.
Methocarbamol 500 mg free shipping
Toxoplasma secretory proteins and their roles in parasite cell cycle and an infection Carruthers muscle relaxant lactation order methocarbamol 500 mg online, V muscle relaxant yellow pill with m on it methocarbamol 500 mg otc. Molecular characterization of a 23-kilodalton major antigen secreted by Toxoplasma gondii. Similarities between the first buildings of two distinct major surface proteins of Toxoplasma gondii. Milieu-induced, selective aggregation of regulated secretory proteins in the transGolgi community. Toxoplasma gondii: characterization and localization of antigens secreted from tachyzoites. A glycosylphosphatidylinositol-anchored carbonic anhydrase-related protein of Toxoplasma gondii is important for rhoptry biogenesis and virulence. In silico identification of specialized secretory-organelle proteins in apicomplexan parasites and in vivo validation in Toxoplasma gondii. Regions of an Eimeria tenella antigen contain sequences which are conserved in circumsporozoite proteins from Plasmodium spp. A member of the ferlin calcium sensor household is crucial for Toxoplasma gondii rhoptry secretion. The most polymorphic residue on Plasmodium falciparum apical membrane antigen 1 determines binding of an invasion-inhibitory antibody. An inhibitory antibody blocks interactions between components of the malarial invasion equipment. Host however not parasite ldl cholesterol controls Toxoplasma cell entry by modulating organelle discharge. Intracellular trafficking of dense granule proteins in Toxoplasma gondii and experimental evidences for a regulated exocytosis. Immunolocalization of an osteopontin-like protein in dense granules of Toxoplasma gondii tachyzoites and its affiliation with the parasitophorous vacuole. Toxofilin upregulates the host cortical actin cytoskeleton dynamics, facilitating Toxoplasma invasion. Apicomplexan rhomboids have a possible role in microneme protein cleavage during host cell invasion. Toxoplasma secretory proteins and their roles in parasite cell cycle and an infection Dunn, J. A novel adaptor protein orchestrates receptor patterning and cytoskeletal polarity in T-cell contacts. The expression and distribution of dense granule proteins in the enteric (Coccidian) forms of Toxoplasma gondii in the small gut of the cat. Members of a novel protein family containing microneme adhesive repeat domains act as sialic acid-binding lectins throughout host cell invasion by apicomplexan parasites. Proteomic analysis of fractionated Toxoplasma oocysts reveals clues to their environmental resistance. Transcriptomic analysis of Toxoplasma development reveals many novel functions and constructions particular to sporozoites and oocysts. Erythrocyte invasion by Babesia bovis merozoites is inhibited by polyclonal antisera directed in opposition to peptides derived from a homologue of Plasmodium falciparum apical membrane antigen 1. Toxoplasma gondii makes use of uncommon sorting mechanisms to ship transmembrane proteins into the host-cell vacuole. Toxoplasma gondii targets a protein phosphatase 2C to the nuclei of contaminated host cells. Independent roles of apical membrane antigen 1 and rhoptry neck proteins during host cell invasion by Apicomplexa. Toxoplasma secretory proteins and their roles in parasite cell cycle and an infection Gold, D. Host cell entry by Apicomplexa parasites requires actin polymerization within the host cell. Efficient invasion by Toxoplasma depends on the subversion of host protein networks. Structural foundation of Toxoplasma gondii perforin-like protein 1 membrane interaction and activity throughout egress. Heparin- and sulfatide-binding peptides from the sort I repeats of human thrombospondin promote melanoma cell adhesion. Complete major structure and useful characterization of the sixth element of the human complement system. Molecular dissection of novel trafficking and processing of the Toxoplasma gondii rhoptry metalloprotease toxolysin-1. Electron tomography of Plasmodium falciparum merozoites reveals core cellular occasions that underpin erythrocyte invasion. Dense granule trafficking in Toxoplasma gondii requires a novel class 27 myosin and actin filaments. Toxoplasma gondii homologue of Plasmodium apical membrane antigen 1 is concerned in invasion of host cells. A hosttargeting signal in virulence proteins reveals a secretome in malarial infection. The cathepsin B of Toxoplasma gondii, toxopain-1, is crucial for parasite invasion and rhoptry protein processing. Cathepsin Cs are key for the intracellular survival of the protozoan parasite, Toxoplasma gondii. Toxoplasma secretory proteins and their roles in parasite cell cycle and infection Reese, M. Identification and characterization of an escorter for two secretory adhesins in Toxoplasma gondii. Identification of rhoptry trafficking determinants and proof for a novel sorting mechanism in the malaria parasite Plasmodium falciparum. Interaction between Plasmodium falciparum apical membrane antigen 1 and the rhoptry neck protein complex defines a key step in the erythrocyte invasion strategy of malaria parasites. Superresolution dissection of coordinated occasions during malaria parasite invasion of the human erythrocyte. A highly conserved amino-acid sequence in thrombospondin, properdin and in proteins from sporozoites and blood phases of a human malaria parasite. Functional dissection of Toxoplasma gondii perforin-like protein 1 reveals a twin area mode of membrane binding for cytolysis and parasite egress. Acidification prompts Toxoplasma gondii motility and egress by enhancing protein secretion and cytolytic activity. Localization of a Toxoplasma gondii rhoptry protein by immunoelectron microscopy during and after host cell penetration. A novel galectin-like domain from Toxoplasma gondii micronemal protein 1 assists the folding, meeting, and transport of a cell adhesion complex. Microneme protein 5 regulates the exercise of Toxoplasma subtilisin 1 by mimicking a subtilisin prodomain.
Cheap 500 mg methocarbamol amex
Immunostains for insulin and glucagon reveal decreased staining for insulin in comparison to muscle relaxant nerve stimulator 500 mg methocarbamol generic with mastercard regular controls muscle relaxant adverse effects methocarbamol 500 mg purchase with visa. Amyloid deposition in the pancreatic islets indicates dysfunction corresponding to that seen in kind 2 diabetes resulting in islet exhaustion. Other (nonrejection) histological diagnoses Graft thrombosis Thrombosis in large- and medium-size vessels is common in pancreatectomies carried out at any time posttransplantation. Pathological evaluation of whole pancreas transplants thrombosis and parenchymal necrosis. Atherosclerotic modifications and atheromatous emboli may lead to nonimmune graft thrombosis. Needle biopsies obtained from the grafted pancreas during abdominal exploration for drainage and debridement of peripancreatic infections present blended inflammation (lymphocytes, eosinophils, neutrophils, and less numerous plasma cells) within the septa with an related fibroblastic reaction. The histological analysis reveals neutrophilic and macrophage-rich inflammation related to edema and tissue due to enzymatic necrosis of fats and parenchyma. Frequently ultrasound research are carried out displaying no, or limited move within the pancreas. Pathological evaluation of complete pancreas transplants anastomosis and acute inflammation. The adjoining peritoneal surfaces typically present acute fibrinous or purulent serositis. These lesions embrace a variety of histological presentations from benign hyperplastic, to overtly malignant. Histological analysis is important, and likewise contributes to an accurate etiological willpower of graft dysfunction in quite so much of other scientific settings. These could also be narrowed by the point posttransplantation and type of graft dysfunction. A record of various clinicopathological settings is introduced in Table 2, highlighting situations that require pathological evaluation for an correct prognosis. Pancreas allograft biopsy: security of percutaneous biopsy-results of a giant experience. Isolated pancreas rejection in mixed kidney-pancreas transplantation: outcomes of percutaneous pancreas biopsy. Role of surveillance biopsies in monitoring recipients of pancreas alone transplants. Use of ultrasound and cystoscopically guided pancreatic allograft biopsies and transabdominal renal allograft biopsies: safety and efficacy in kidney-pancreas transplant recipients. Retrospective evaluation of the position of pancreatic biopsy (open and transcystoscopic technique) in the administration of solitary pancreas transplants. Diagnostic utility and correlation of duodenal and pancreas biopsy tissue in pancreaticoduodenal transplants with emphasis on therapeutic use. Histologic diagnosis of rejection by using cystoscopically directed needle biopsy specimens from dysfunctional pancreatoduodenal allografts with exocrine drainage into the bladder. Specific humoral rejection of a pancreas allograft in a recipient of pancreas after kidney transplantation. Banff schema for grading liver allograft rejection: a global consensus doc. Studies on the survival of simultaneous canine renal and segmental pancreatic allografts. Differential response of kidney and pancreas rejection to cyclosporine immunosuppression. Surveillance pancreas biopsies in solitary pancreas transplantation: a shot in the dead of night. Antibody monitoring in pancreas transplantation: when should we do protocol biopsies Rejection with duodenal rupture after solitary pancreas transplantation: an unusual reason for extreme hematuria. Allograft duodenal cuff biopsy as surrogate in analysis of pancreatic transplant rejection-a multicenter knowledge effort. Enteroscopic biopsies within the management of pancreas transplants: a proof of concept examine for a novel monitoring tool. Outcomes in pancreas transplantation with exocrine drainage via a duodenoduodenostomy versus duodenojejunostomy. Distinctive morphological features of antibody-mediated and T-cell-mediated acute rejection in pancreas allograft biopsies. Distinct histologic patterns of acute, extended, and chronic rejection in vascularized rat pancreas allografts. Histological options of acute pancreatic allograft rejection after pancreaticoduodenal transplantation within the rat. Distribution of alpha and beta cells in pancreas allograft biopsies: correlation with rejection and different pathologic processes. Pancreas allograft biopsies in the administration of pancreas transplant recipients: histopathologic evaluation and clinical correlations. Effectiveness of immunosuppressive therapy for recurrent or refractory pancreas allograft rejection: correlation with histologic grade. Epstein-Barr virus-related posttransplantation lymphoproliferative dysfunction involving pancreas allografts: histological differential analysis from acute allograft rejection. Posttransplant lymphoproliferative disorder in a kidney-pancreas transplanted recipient: simultaneous development of clonal lymphoid B-cell proliferation of host and donor origin. Rapid incidence of lymphoproliferative disease after pancreas-kidney transplantation performed throughout acute main Epstein-Barr virus an infection. Epstein-Barr virus-associated posttransplant lymphoproliferative disorder of donor origin after simultaneous pancreas-kidney transplantation limited to pancreas allograft: a case report. Pancreas allograft biopsies with positive c4d staining and anti-donor antibodies associated to worse outcome for sufferers. Outcomes of pancreas transplant recipients with de novo donor particular antibodies. Antibody-mediated rejection of the kidney after simultaneous pancreas-kidney transplantation. Cluster evaluation of lesions in nonselected kidney transplant biopsies: microcirculation modifications, tubulointerstitial inflammation and scarring. Influence of rejection episodes on the connection between exocrine and endocrine perform in bladder-drained pancreas transplants. Islet cell injury associated with tacrolimus and cyclosporine: morphological options in pancreas allograft biopsies and medical correlation. Ischemia as a end result of vascular rejection causes islet loss after pancreas transplantation.