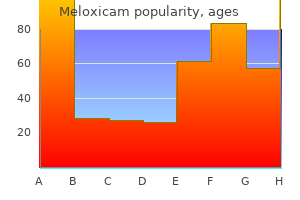
Meloxicam dosages: 15 mg, 7.5 mg
Meloxicam packs: 60 pills, 90 pills, 120 pills, 180 pills, 270 pills, 360 pills, 240 pills
15 mg meloxicam effective
Each alveolus is dependent upon the position and elasticity of the neighboring alveolar walls to keep normal shape and volume arthritis medication once a week generic meloxicam 7.5 mg fast delivery. If adjacent alveoli collapse rheumatoid arthritis and disability order meloxicam 7.5 mg visa, an alveolus both tends to overexpand and deform or collapse. In surfactant-deficient states, the more regular alveoli tend to overexpand as different regional alveoli collapse, producing a nonhomogeneously inflated lung. Surfactant therapy improves uniformity of inflation, minimizes small airway dilation, and promotes alveolar inflation. Surfactant treatment also resulted in more normal lung morphometry in preterm lambs receiving steady mechanical air flow 24 hours after supply. This surfactant impact on uniformity of lung growth will be the mechanism that decreases lung damage. These effects occur to variable levels, probably relying on components related to the disease process in each infant, the type of ventilatory administration, and the surfactant used to treat the infant. Consistent with this fast improve in lung compliance, Miedema and colleagues30 used electrical impedance tomography to measure 61% will increase in lung fuel volumes of infants handled with surfactant and high-frequency oscillation. Kelly and associates32 found no improvement in dynamic compliance after therapy of infants with surfactant, whereas static compliance decreased because of lung volume recruitment. However, when the ventilator pressures have been lowered, consistent enhancements in both static and dynamic compliance occurred. Another variable within the compliance response is the type of surfactant used for treatment. A artificial surfactant with out surfactant proteins may not enhance compliance within the first few hours after therapy. In distinction, treatment with animal-source surfactants can result in rapid improvements in compliance. These completely different responses between artificial surfactants and surfactant from animal lungs had been noted in preterm animal models33 and in medical follow. New surfactants might want to be examined for effects on lung mechanics as they turn out to be available. Surfactant treatments also will affect the time constants for lung inflation and deflation. With mechanical air flow, inspiratory instances and peak pressures are used empirically to adjust tidal volumes. The combination of surfactant remedy and a ventilatory fashion that promotes air trapping could mask surfactant treatment results. The fast enchancment in oxygenation results from the acute enhance in lung quantity and increases within the surface area for fuel change with surfactant instillation. The pressures were decreased till oxygenation decreased, and an optimum imply airway strain was then determined. J Clin Invest sixty seven:370, 1981, by copyright permission of the American Society for ClinicalInvestigation. Meanairwaypressures then have been decreased until the % oxygen increased, defining thelungasclosed. Surfactantdecreasedthe opening pressure, the closed pressure, and the optimal pressure. Surfactant therapy improved lung function and significantly decreased pneumothorax and other air leaks. Unfortunately, remedy has not persistently decreased the frequency of patent ductus arteriosus or extreme intraventricular hemorrhage. Large decreases in intraventricular hemorrhage in affiliation with surfactant therapy were reported in particular person trials,51 suggesting that different aspects of neonatal care could additionally be interacting with surfactant remedy to influence the incidence of intraventricular hemorrhage. One examine found a decrease in retinopathy of prematurity in the infants treated with surfactant. It is important to remember that the extra mature infants included in placebo-controlled trials of surfactant had been cared for in an era with completely different ventilatory assist strategies and minimal use of antenatal steroids. However, supply room treatment should be given by a person experienced in neonatal resuscitation. In practice, the benefits of avoiding mechanical ventilation for some infants could put different infants susceptible to complications that end result from delays in surfactant remedy. Various approaches to give surfactant without intubation and air flow are being actively investigated. In distinction, delivery room remedy was considered to be optimum provided that given earlier than the infant breathed or received positive-pressure ventilation. Kendig and coworkers58 demonstrated that surfactant remedy throughout the first quarter-hour after start was equal and maybe preferable to therapies earlier than the toddler was allowed to breathe. Waiting for the disease to progress to set up the diagnosis more firmly earlier than therapy will minimize the efficacy of the remedy and increase complications. These methods require the toddler to be spontaneously respiration, however the laryngoscopy procedure is considered by some practitioners as requiring ache drugs, whereas others will deal with with surfactant without ache drugs. The completely different management strategies depend on procedural expertise, expertise, and multiple features of the subsequent care, which can confound clear solutions to when and how infants are finest handled with surfactant. European and American Academy of Pediatric tips for surfactant remedies have been published lately. For infants >26 weeks, an inexpensive oxygen want for surfactant therapy should be >40%. The acute physiologic results are related to the handling of the infant and the acute effects of the quantity of surfactant within the lungs. Manipulation of the pinnacle, neck, and endotracheal tube could cause vagal responses resulting in bradycardia and cyanosis. Of extra concern are the reports of transient modifications in blood pressure, cerebral blood flow velocities, and electrocortical despair after surfactant remedies. The only extreme complication persistently associated with surfactant therapy is pulmonary hemorrhage. A patent ductus arteriosus with a left-to-right shunt resulting in elevated pulmonary vascular pressures was linked to pulmonary hemorrhage in several trials. Although this affiliation has not been recognized in other trials, increased pulmonary vascular pressures leading to stress failure of alveolar capillaries is the likely clarification for the pulmonary hemorrhage. Hemorrhage can occur in the smallest infants a selection of hours after surfactant remedy has improved lung operate. Surfactant treatment after pulmonary hemorrhage can improve subsequent lung function. In one trial, second and third doses given 12 and 24 hours after an preliminary remedy decreased the frequency of pneumothorax from 18% with a single dose to 9% with three doses of surfactant (p <. These infants may have other diseases, similar to pneumonia, pulmonary hypoplasia, or congenital heart illness. It is cheap to re-treat with surfactant if the initial response to therapy was poor and other causes of respiratory failure have been excluded. In scientific practice, re-treatment must be individualized and considered for infants with sufficient residual lung illness to put them at risk of problems similar to pneumothorax.
15 mg meloxicam order overnight delivery
In addition to megalencephaly rheumatoid arthritis lifestyle meloxicam 15 mg order without prescription, macrocephaly can be triggered hydrocephalus arthritis symptoms neck upper back meloxicam 7.5 mg buy discount on-line, ventriculomegaly, enlarged extraaxial spaces, and thickened cranium bones. Neurologic findings are usually minor, and parental head measurement can also be usually above the 90th percentile. Macrencephaly may be associated with generalized disorders of progress, similar to Beckwith-Wiedemann syndrome, Sotos syndrome, Marshall-Smith syndrome, Simpson-Golabi-Behmel syndrome, and Weaver syndrome. Several neurocutaneous problems are associated with evidence of extreme cellular proliferation within the central nervous system, typically with overt macrencephaly and proof of extreme proliferation of mesodermal constructions. Loss of the neurofibromatosis protein neurofibromin leads to elevated mitogenic signaling, inflicting the proliferative abnormalities attribute of the dysfunction. Leukodystrophies, problems of the white matter, with macrocephaly as a distinguished function include Canavan illness, Alexander illness, and megalencephalic leukoencephalopathy with subcortical cysts. Recent proof has recognized the function of somatic mutations, a postzygotic event, in mind malformations and may explain the overlap seen between syndromic causes of hemimegalencephaly and megalencephaly. Before the neural tube even closes, specialised neurons known as predecessor cells, distinctive to humans, arrive on the pial floor of the forebrain, invading it tangentially to type the preplate. They have long horizontal processes and will act as a scaffold for axonal navigation. The preplate then begins to subcompartmentalize with the looks of reelin-expressing Cajal-Retzius cells. These transient bipolar cells come up from radial migration from the local ventricular zone, as well as by tangential migration from extra distant extracortical sites. Reelin terminates additional migration, and these cells therefore mark the pial restrict of neuronal migration, the upper boundary of the protocortex, the cortical plate. Between the ventricular proliferative zones and the postmigratory neurons in the direction of the pial floor is a heterogeneous compartment, the intermediate zone. This accommodates radially and tangentially migrating cells, in addition to extrinsic axons. Eventually, the invasion of corticocortical fibers and myelination transforms the intermediate zone into the white matter. Between the cortical plate and the intermediate zone is a distinct neuronal compartment, the subplate, which accommodates heterogeneous cell populations. Note the cortical tubers (arrows) and subependymal large cell astrocytoma (asterisk). The prolonged existence of this transient fetal zone into the third trimester and early postnatal life has profound implications for perturbations of sensory input related to untimely start or an aberrant neonatal experience such as asphyxia or publicity to drugs. As they migrate along radial glia, many neurons within the cerebral wall extend processes that are quickly recognizable as axons. The formation and upkeep of axonal and dendritic arbors are largely under the control of environmental cues. The tip of each course of consists of a specialized motile structure, a growth cone, which resembles the pinnacle of a membership, with microspikes (filopodia) extending in all directions. Living progress cones, when considered in a microscope, are continuously shifting by local extension and retraction. When in touch with an appropriate substrate, they crawl forward and leave behind the elongating axon. Two of essentially the most lively promoters of growth cone migration, laminin and fibronectin, have been shown to be expressed transiently as elements of the extracellular matrix in cortical regions which have significantly active axon progress. Responsiveness to laminin may be developmentally regulated and enhanced by activation of integrins. Administration of exogenous laminin favors neuronal migration and neurite development, whereas inhibition or neutralization of laminin leads to inhibition of neurite outgrowth. Proteoglycans similar to chondroitin sulfate, which are macromolecules composed of core polypeptide and glycosaminoglycan chains, can modulate neurite outgrowth along with laminin. Matrix metalloproteinases, proteases that degrade extracellular matrix molecules, are thought to be involved in stabilization of laminin and cell-matrix interactions. Extracellular matrix proteins, corresponding to collagen, have additionally been shown in cell culture to suppress apoptosis, or programmed cell dying, and thus to provide a more nurturing substrate for neuronal survival and differentiation. As development cones advance, their filopodia prolong and appear to explore the local environment to find the trail most favorable for continued axon progress. Growth-associated protein 43 is a major development cone protein whose phosphorylation in response to extracellular steering cues can secondarily regulate microtubule conduct. Mice missing growth-associated protein 43 fail to kind the anterior commissure, hippocampal commissure, and corpus callosum. A growing physique of evidence indicates that axon guidance is directed by the integrated and summed influence of both attractant and repulsive cues. These cues may be expressed in gradients, and they finally result in the institution of axon projection maps as discovered in the projection from the retina to the midbrain tectum. In reality, a household of axon-repulsive molecules, ligands of the Eph household of receptor tyrosine kinases, has been recognized as the probable positional labels for the retinotectal projection. Additional signaling pathways regulating migration include Notch signaling via the downstream brain lipid-binding protein. Magnetic resonance imaging is essentially the most useful initial investigation when a migrational dysfunction is suspected with the hallmark discovering of gyral abnormalities and occasionally abnormalities of the corpus callosum. Cobblestone complex problems, of which Walker-Warburg syndrome is one, are characterized by clustered, whorled arrays of neurons separated by glia and large heterotopic formations of neurons, often migrating into the pia, giving a characteristic "cobblestone" appearance. Pachygyria is demonstrated by thickened easy gyri that are underdeveloped and is a continuum of lissencephaly. The recognized causes of these kind of lissencephalies are listed in Table 131-3 together with salient clinical features and diagnostic indicators. Other heterotopias are seen within the subcortical white matter and may be small rests of cells or extra generally bands. The causes of polymicrogyria include extrinsic factors, such as in utero cytomegalovirus infection or vascular insults, and intrinsic components, corresponding to single-gene mutations, copy-number variants, and metabolic situations. The cleft is lined by polymicrogyria and may be unilateral or bilateral, normally within the frontal or perirolandic area. The edges of the pial surface may be opposed ("closed lip") or more commonly extensively separated ("open lip"). As stated above, the diverse processes resulting in polymicrogyria and schizencephaly recommend many alternative mechanisms but to be elucidated. Focal cortical dysplasias characterize abnormalities of each proliferation and group. Focal cortical dysplasias with balloon cells, large dysplastic multipotent cells, are a disorder of proliferation rather than migration. Focal cortical dysplasias without balloon cells are problems of cortical group.
Diseases
- Hypoplastic thumbs hydranencephaly
- Hypogonadism hypogonadotropic due to mutations in GR hormone
- Porphyria, acute intermittent
- Egg hypersensitivity
- Adenine phosphoribosyltransferase deficiency
- Overfolded helix
- Erythrokeratodermia variabilis, Mendes da Costa type
- Craniodigital syndrome mental retardation
- MPS III-D
7.5 mg meloxicam amex
Apneic episodes in the neonate are categorized according to arthritis pain quotes 7.5 mg meloxicam sale the absence or presence of breathing efforts in the course of the interval of no airflow arthritis in the back causes order meloxicam 7.5 mg without prescription. Breath-holding apneas are those by which move stops in the middle of expiration, and the remaining expiration happens just earlier than respiratory begins again. We have lately described a model new method of classifying apneas based on a magnified cardiac-induced pulse noticed on the respiratory move tracing. This technique is prepared to detect the presence and timing of airway obstructions with great precision. In preterm infants recovering from respiratory assist, with a point of residual lung illness (bronchopulmonary dysplasia), the prevalence of obstructive apneas seems to be increased, constituting up to 48% of the apneas in some research. One report has described obstruction in 80% of the pauses in preterm infants with periodic breathing. Periodic respiratory and apneas are clearly penalties of a disturbance of the respiratory control system however the precise mechanisms are unclear. Investigators on this space are inclined to believe that the adverse suggestions loop controlling respiration is affected by a quantity of components associated primarily to anatomic and physiologic immaturity. Unfortunately, we have no idea how much immaturity is needed for a given impairment in neurophysiologic traffic. Oscillation in arterial gasoline tensions, adjustments in circulation time, incoordination of the respiratory pump as a end result of a compliant chest wall, and adjustments in sleep state may all contribute to this instability of the respiratory management system. Note the regular periodicity of breathing, with both apneic and respiratory intervals keeping a constantlength. In a study performed in our laboratory we showed that (1) a chronic apnea nearly by no means occurred in the absence of previous short apneas and (2) the chance for a chronic apnea occurring elevated significantly when the previous period contained an elevated number of apneic episodes, elevated duration of the longest apneic interval, or elevated duration of the apneic time. Compared with infants who breathe repeatedly, neonates breathing periodically have decrease Po2 values and their peripheral chemoreceptors are more hyperactive as reflected by the longer apneic interval and more pronounced quick lower in air flow in response to inhalation of high-oxygen mixtures. Indeed, PaO2 of those infants sits on the steep portion of the minute ventilation versus PaO2 regression curve for human adults. This implies that small adjustments in baseline PaO2 produce giant modifications in baseline ventilation. Hypoxia could also be a contributing issue, as a outcome of inhalation of a low-oxygen mixture simply induces periodic respiratory and apnea in these infants. It is well-known that inflammatory mediators affect each peripheral and central constructions that management breathing. We imagine that the necessary thing factor responsible for this slim difference is the well-known hypoxemic standing of these infants. Xie and colleagues45 have shown in adults that the time course of the incidence of apnea after transient hyperpnea is according to a peripheral chemoreceptor mechanism. Indeed, minor alterations throughout sleep, similar to a startle or a sigh, produce apnea in these infants. The nearly steady change in baseline ventilation throughout sleep is what Haldane known as "the hunting of the respiratory centre". When chest distortion occurs, diaphragmatic work increases by about 40%, adding to the mechanical impairment. This observation is appropriate with the finding that the applying of steady negative pressure around the chest tends to abolish apnea. The peculiar response of the neonate to low focus of inhaled oxygen is of great medical significance. These findings recommend a scarcity of major differences in the activity of the peripheral chemoreceptors throughout these sleep states. The late enhance in air flow with oxygen is likely associated to cerebral vasoconstriction with growing H+ focus at the chemoreceptor web site. This response is so powerful in the new child that many have used this inflation to produce apnea after which examine the mechanical properties of the respiratory system in the course of the passive expiratory section after apnea. The paradoxical reflex of Head is often noticed in the neonate within the type of a sigh. During periodic breathing, a sigh often seems through the first or second breath after apnea. Alvarez and colleagues,132 nonetheless, have noticed that airway occlusion within the presence of hypoxia predisposes to sighs. If the share of inhaled carbon dioxide is low (<2%) throughout steady-state inhalation, the response consists primarily of an increase in tidal volume. Inhalation of low focus of oxygen produces an instantaneous enhance in air flow (1 minute), followed by a later decrease (5 minutes). Lack of tone leads to chest wall collapse throughout inspiration, and caudal displacement of the diaphragm has to be twice as lengthy to produce the identical lung volume displacement. Similarly, sleep state profoundly impacts the muscular management of higher airway resistance. On the opposite hand, the adductor muscular tissues of the larynx-the thyroarytenoid, lateral cricoarytenoid, and intraarytenoid-have a phasic expiratory activity throughout quiet sleep. Third, the discovery of fetal respiration is probably the most thrilling contribution made in this area during the past 50 years. To clarify why this episodic breathing in utero turns into continuous after start is a serious challenge of this time. Trying to understand this modification at delivery might end result in the discovery of key mediators which might be on the heart of the mechanism controlling respiratory in general. Patrick J, Campbell K, Carmichael L, et al: A definition of human fetal apnea and the distribution of apneic intervals over the past ten weeks of pregnancy. Patrick J, Campbell K, Carmichael L, et al: Patterns of human fetal respiration over the last 10 weeks of pregnancy. Rigatto H, et al: the effect of whole peripheral chemodenervation on fetal respiration and on the establishment of respiration at birth. Rigatto H, Moore M, Cates D: Fetal respiratory and habits measured by way of a double-wall Plexiglas window in sheep. Alvaro R, Weintraub Z, Alvarez J, et al: the effects of 21 or 30% O2 plus umbilical wire occlusion on fetal respiration and conduct. Alvaro R, deAlmeida V, Al-Alaiyan S, et al: A placental extract inhibits breathing induced by umbilical wire occlusion in fetal sheep. Kitterman J: Arachidonic acid metabolites and management of respiration within the fetus and newborn. Hoppenbrouwers T, Hodgman J, Arakawa K, et al: Sleep and waking states in infancy: normative research. Rigatto H: Control of respiratory in the neonate and the sudden toddler dying syndrome. Lee D, Caces R, Kwiatkowski K, et al: A developmental examine on types and frequency distribution of quick apneas (3 to 15 seconds) in term and preterm infants. Al-Matary A, Kutbi I, Qurashi M, et al: Increased peripheral chemoreceptor exercise may be crucial in destabilizing breathing in neonates.
Meloxicam 7.5 mg order without a prescription
Differences in stromal cell populations were postulated as a mechanism explaining the difference between fetal and adult hematopoietic microenvironments arthritis bumps best 7.5 mg meloxicam. Extracellular matrix components have additionally been postulated as a mechanism explaining differences between fetal and adult hematopoietic microenvironments arthritis in fingers and feet discount meloxicam 15 mg with amex. Fibronectin, collagens, and laminin are ligands for integrins, which not solely management anchorage, spreading, and migration of hematopoietic cells however are also concerned in various intracellular signaling cascades. For occasion, erythropoietic suppression induced by polycythemia entails an increase in marrow content of sulfated glycosaminoglycans. Proteoglycans and glycosaminoglycans are involved in cell adhesion to the extracellular matrix. Treatment of stroma with heparitinase lowered adhe- sion of immature marrow granulocytes to the stroma. Different proteoglycans or glycosaminoglycans might have different roles in hematopoiesis. Hemonectin and fibronectin are extracellular matrix molecules with hematopoietic functions. Hemonectin is associated with granulocytic development, whereas fibronectin is involved in erythroid growth. Mechanisms whereby the granulocytopoietic microenvironment operates, including the genes concerned and the position of oxygen, are being studied. It is assumed that neutrophils transfer via this technique approximately so as, as if in a pipeline. The initial part of the pipeline involves dedication and clonal maturation of progenitors within the marrow. The earliest neutrophilic precursors are capable of cell division and thus are referred to as the mitotic compartment, also referred to as the neutrophil proliferative pool. Neutrophils that may no longer divide are housed within the marrow for the purposes of maturation and storage as a prepared reserve of cells to be released from the marrow into the blood on demand. This stage in neutrophil improvement is termed the maturation compartment, also referred to as the neutrophil storage pool. This compartment consists of the metamyelocytes, band neutrophils, and segmented neutrophils within the marrow. Thus the fetal spleen and liver comprise granulocyte progenitors however are most likely not normally lively websites of granulocytopoiesis. Neutrophils in the former compartment are freely circulating, whereas those within the marginal compartment are temporarily adherent to endothelial cells, typically within the postcapillary venules. In normal grownup humans, the entire of these two compartments (termed the entire blood neutrophil pool) accommodates about 0. After epinephrine administration, neutrophils are rapidly launched from the marginated compartment and enter the circulating pool. No change in differential cell depend accompanies this demargination; thus the proportion of segmented neutrophils is the same within the marginated pool and the circulating neutrophil pool. The opposite movement of neutrophils, from the circulating pool to the marginated pool, happens for 1 to 2 hours after experimental intravenous administration of endotoxin. Newborn infants with strenuous crying can expertise neutrophil demargination and may double their blood neutrophil concentration within three to 5 minutes. However, research on umbilical twine blood neutrophils recommend a lower fee of spontaneous apoptosis in contrast with adult cells. It is likely that neutrophils depart the blood and enter the tissues randomly somewhat than based on their age, as is the case for erythrocytes and platelets. This principle is supported by the observation that transfused, labeled neutrophils seem within the blood and saliva simultaneously. Within minutes of the event of a neighborhood website of tissue injury or infection, adherence of neutrophils to the endothelium and their subsequent migration into the tissues can be observed. Studies on fetal sheep present that after intraamniotic publicity to endotoxin, the variety of circulating neutrophils initially decreases by four hours owing to egress into the tissues, followed by an increase over the following 6 days. After the preliminary adherence of the neutrophil to an endothelial cell, it projects pseudopodia and forces a passageway between endothelial cells. Loss of neutrophils has been observed into the urine and thru the lungs, liver, spleen, and gastrointestinal tract. Those delivered vaginally had a lot greater neutrophil counts than did those delivered operatively. Counts then decreased, achieving a steady lower worth of 1750/�L by 72 hours of life. Mouzinho and colleagues26 revised the reference ranges for blood neutrophil concentrations in very-low-birth-weight infants. Serial counts were obtained between birth and 28 days of age from sixty three infants of 29. No difference within the higher limit of normal was noticed between those very-lowbirth-weight infants and the maturer infants reported by Manroe and colleagues. Neutrophil counts higher than 14,000/�L at 12 hours and higher than 9000/�L after 48 hours outlined neutrophilia. However, the very-low-birth-weight infants had a wider range of counts, encompassing substantially lower values compared with mature infants; neutropenia was outlined as a focus less than 2000/�L at 12 hours of life and fewer than 100/�L after 48 hours. Although strategies for measuring leukoagglutinins have improved over time, the sphere of recognition of granulocyte antigens has been plagued by an inherent tendency of granulocytes to agglutinate. Neutrophil-specific antigens had been initially discovered by Lalezari and Radel30 while they have been learning neonatal neutropenia. In the original nomenclature, the letter N stood for neutrophil-specific antigen, and was followed by a capital letter designating a specific gene locus and a number designating a certain allele at that locus. A new nomenclature proposed by the Granulocyte Antigen Working Party of the International Society of Blood Transfusion attempted to tackle these anomalies. The genes coding for glycoproteins are named based on the rules of the International Workshop on Human Gene Mapping. For the naming of newly detected antigens, the utilization of acronyms is permitted till their eventual inclusion on this system. Neutrophil-specific antigens have been recognized on mature grownup neutrophils, myeloid precursors, and umbilical cord blood neutrophils. Red cell antigen teams expressed on neutrophils embody the polylactosaminyl glycolipids bearing Ii, Lex, and P methods. Neutrophil antigens inherited from fathers however not current in mothers might cause an antibody response throughout gestation. Antineutrophil antibody can cross the placenta to the fetal circulation and cause extreme neutropenia within the fetus and new child toddler. Although self-limited, alloimmune neutropenia may be related to severe infections and demise. Antineutrophil antibodies may develop as an isolated autoimmune phenomenon and may be seen even in untimely neonates. However, the prevalence of autoimmune neutropenia of infancy in solely certainly one of monozygotic twins suggests that genetics is in all probability not the solely real factor accountable.
Discount 15 mg meloxicam fast delivery
Cerebellar subarachnoid hemorrhage in the preterm toddler exhibits a lower in the glutamate transporters in Purkinje cell dendrites rheumatoid arthritis in neck meloxicam 15 mg mastercard, resulting in dog arthritis medication over the counter meloxicam 15 mg order fast delivery an increase in extracellular glutamate and excitotoxic Purkinje cell dying. In relation to the degree of periventricular white matter injury, the scale of the cerebellum and pons was discovered to be smaller in preterm infants. The feed-forward limb initiatives within the cerebellum, through the pontine nuclei, from a particular area of the cerebral cortex. These cerebral cortical regions in turn turn out to be the feed-back projection from the dentate nucleus, the cerebellar output center. Cerebellar hypoplasia of prematurity is believed to be as a outcome of impaired development of the cerebellum, versus main injury. Characterization of the patterns of cerebellar growth impairment led to an observation of a quantity of patterns of cerebellar hypoplasia, together with (1) symmetric hemispheric quantity loss with preservation of the form of the vermis; (2) symmetric hemispheric volume loss with a small, deformed vermis; and (3) normal cerebellar shape with general dimension reduction. Associated with cerebellar hypoplasia can be flattening of the anterior pons and loss of supratentorial white matter. If so, harm to the cerebellum may trigger a functional disconnection with cerebral cortex and potentially affect subsequent development of distant areas of the cerebral cortex. This phenomenon, generally identified as diaschisis, represents the loss of a operate and/or tissue in a mind area connected to , but distant from, the mind lesion. The interconnections between cerebellum and cerebral cortex are constructed over a brief interval of the time, primarily through the third trimester of gestation. Thus both cerebellar or cerebral pathology might delay or impede the institution of important neuroanatomic connections and contribute to long-term neurodevelopmental deficits. The structural volumetric cerebellar growth deficits after supratentorial injury in extremely preterm infants seem to be considerably higher and more frequent than the mild cerebellar atrophy observed only in a minority of adults. A attainable cause for this maturation-distinctive diaschisis within the small preterm toddler could relate to the section of fast cerebellar growth. Moreover, the truth that apoptosis is a extra lively course of in developing than in adult neurons means that the apoptotic stimulus might have extra profound effects on the quickly creating cerebellum of the small premature infant than on the adult cerebellum. Adverse effects of perinatal events on cerebellar growth may be smaller than the results of cerebro-cerebellar diaschisis. This interruption may lead to lack of neuronal activation from supratentorial corticopontine tracts, with subsequent impaired improvement of the cerebellum, suggesting that neuronal activation is essential for mind development. Despite the success of those medicines on infant survival and cardiorespiratory stabilization, their impact on the creating brain, and particularly the preterm cerebellum, remains a big concern for their use. The neonatal cerebellum has the highest ranges of glucocorticoid receptors within the brain,ninety six localized to the external granular layer. Despite animal fashions suggesting toxicity with each medicine, these variations have resulted in the suggestion that hydrocortisone could also be a safer alternative drug in newborns. Multiple studies have advised adverse results of postnatal dexamethasone on the preterm cerebellum. One observational study comparing eleven newborns exposed to postnatal dexamethasone with 30 untreated newborns found smaller general brain volumes at term-equivalent age, including 20% smaller cerebellar volumes. This translated to an 8% smaller volume associated with hydrocortisone and a 10% smaller quantity associated with dexamethasone. Differences within the two studies may be related to differences in glucocorticoid dosing or different administration differences. In a cohort study together with eighty infants uncovered to hydrocortisone, developmental outcomes have been discovered to be negatively affected only if the period of publicity to hydrocortisone was longer than 7 days. In a cohort research of 172 preterm newborns, of which 85% have been uncovered to antenatal betamethasone, antenatal exposure to glucocorticoids was not found to be related to cerebellar development, even after adjusting for confounders. Multiple observational research in preterm newborns have recognized these as necessary elements related to cerebellar hypoplasia. Although voltage-dependent calcium channels are involved within the mechanisms underlying morphine administration,126 their function in morphine-induced adjustments in the creating cerebellum is unclear. Thus although animal proof suggests potential effects of opioids on preterm cerebellar growth, further analysis is needed to assess its results in people. Evidence for the importance of diet and somatic development on the cerebellum may be inferred from research on intrauterine development restriction. In fetal sheep, intrauterine progress restriction has been found to be related to changes in synaptogenesis, mitochondrial formation, and growth of the Purkinje cell dendritic tree in the cerebellar cortex. However, further research is needed to perceive the specific dietary components crucial to progress of the cerebellum. In a retrospective study of 1242 preterm infants, 35 (3%) had been identified to have cerebellar hemorrhage on head ultrasound, with a mortality price of 14%. Of the survivors, those with cerebellar hemorrhage were discovered to be microcephalic in contrast with normal peers, and one other three (60% of survivors) had severe developmental delay. In a bigger group of 35 preterm infants with isolated cerebellar hemorrhagic harm, 66% were found to have neurologic abnormalities by 2. Compared with 35 age-matched controls, these infants had significantly decrease imply scores on all examined measures, including motor, expressive language, receptive language, and cognitive testing, with findings more extreme when injury was present within the cerebellar vermis. Also prevalent had been abnormalities on autism screening and internalizing behavioral problems. Socioeconomic standing, together with household stress, infant exposures, and parental schooling, have gotten more and more acknowledged elements affecting long-term consequence after brain damage or preterm delivery. There is a breadth of literature showing that socioeconomic status is associated with a variety of cognitive outcomes, including reminiscence, cognition, executive perform, and language. Smaller cerebellar hemorrhages not detectable on head ultrasound have a generally extra favorable prognosis, with no risk of mortality within the neonatal interval. These youngsters, when assessed at 5 years of age, were found to have 5-fold increased odds of abnormalities on neurologic examination, including lower-limb hypertonia and hyperreflexia. Conversely, all of these children were ambulatory and had no differences in cognitive testing in contrast with their friends. In addition, no variations had been noted in end result when comparing the situation of the hemorrhages. Aside from supratentorial mind injury, hemorrhage, and postnatal glucocorticoid publicity, we have to enhance our understanding of how other elements, such as opioid exposure, cardiorespiratory elements, vitamin, and postnatal factors, have an effect on the event of this crucial brain construction. Identifying targets for enhancing neonatal care, corresponding to pharmacologic targets to reduce the consequences of postnatal glucocorticoids on the cerebellum, might end in enhancements in motor and cognitive outcomes after preterm delivery. Wurst W, Bally-Cuif L: Neural plate patterning: upstream and downstream of the isthmic organizer. In a research of eighty three preterm newborns assessed at three months of age, smaller cerebellar diameter was found to be related to abnormal generalized actions. Smaller volumes in total brain tissue, cerebrum, frontal lobes, basal ganglia and thalami, and cerebellum were related to neurodevelopmental impairment, including cerebral palsy, listening to loss, blindness, or considerably delayed cognitive performance. Even without neurodevelopmental impairment, smaller cerebellar volumes had been associated with poorer developmental scores. In the identical examine at 14 to 15 years of age, hypoplasia of the lateral lobes was found to be associated with reduced executive, visuospatial, and language functions. Fumagalli M, Bassi L, Sirgiovanni I, et al: From germinal matrix to cerebellar haemorrhage.
7.5 mg meloxicam discount otc
Originally arthritis wrist meloxicam 15 mg with amex, the method was utilized for estimations of volume move in large fetal vessels-that is enteropathic arthritis diet 15 mg meloxicam for sale, abdominal aorta and umbilical vein. The estimation of the quantity blood move additionally requires knowledge of the insonation angle and uniform insonation of the vessel for dependable estimation of the imply velocity. Because of all these possible sources of error, this technique has not discovered broad utility. A certain revival of this methodology has occurred, and measurements of move additionally in vessels of small caliber. The diameter of the vessel needs not be known for waveform analysis, and the utmost velocity is less complicated to report than is the mean velocity. However, cardiac efficiency, blood pressure, vessel wall properties, and viscosity of blood also affect the waveform and its indices. In the cerebral vessels of hypoxic fetuses, a rise in diastolic velocity could be noticed as an expression of decreased resistance in the cerebral vascular bed and redistribution of blood flow (brain-sparing phenomenon). For clinical use, a scoring system (uterine artery score) has been designed to characterize the resistance in both uterine arteries. An inverse linear relationship has been discovered between the intensity of the contraction, measured as the intrauterine amniotic strain, and the diploma of the enddiastolic flow. The reversal was significantly more usually seen during induced contractions than throughout spontaneous contractions in a management group. By use of color flow imaging, the modifications of blood flow between myometrium and placenta could be adopted. In sufferers in whom handbook removal of the placenta was needed, the blood circulate continued into the placenta past the latent section. In fetuses with already compromised umbilical blood circulate, nevertheless, such a slight increase in placental resistance may be of pathophysiologic and clinical importance. This is in settlement with the statement that fetuses that exhibit a scarcity of end-diastolic velocity during pregnancy often have indicators of distress in labor and incessantly require operative supply. No important modifications within the umbilical artery velocity waveform were noticed through the first stage of labor. In different circumstances, the deceleration was not preceded by a measurable increase in umbilical artery resistance. Brar and colleagues46 compared the S/D ratio in a gaggle of sufferers with late decelerations with the S/D ratio in matched controls. The imply S/D ratio within the former group was significantly greater than that within the latter group. Among girls with late decelerations, a progressive enhance was also seen within the incidence of antagonistic pregnancy outcome with growing abnormality within the waveform. Patients with late decelerations and a normal umbilical S/D ratio had an incidence of antagonistic pregnancy end result just like that of controls. The discount of blood circulate was more pronounced with variable decelerations than with late decelerations, and the blood circulate change preceded the deceleration. Therefore this methodology has not discovered widespread scientific utility in laboring sufferers. Krapp and colleagues proposed Doppler examinations of ductus venosus in labor to be presumably helpful in fetuses in danger. Fendel and colleagues30 measured the imply fetal aortic velocity in labor and located a drop in the velocity throughout contractions. During contractions, a fall occurred within the diastolic velocities, suggesting a rise in cerebral vascular resistance attributable to head compression during contractions (assuming that the fetal cardiac output and blood stress remain unchanged). However, this discovering was not confirmed by Maesel and colleagues58 within the fetal center cerebral artery. The waveforms of velocities recorded from the fetal inside carotid artery and middle cerebral artery were just like those recorded earlier than labor. This has been confirmed by S�tterlin and colleagues,sixty three who measured fetal oxygen saturation simultaneously with Doppler waveforms of the fetal center cerebral artery. Ritodrine given to patients with preterm labor results in a major lower within the uterine and umbilical S/D ratio. In a research comparing the results of nifedipine and ritodrine in preterm labor, no significant impact on umbilical artery Doppler velocimetry findings was reported for both of the therapies. In addition, they found a selective enhance of left cardiac output, indicating redistribution of fetal blood move. They interpreted these findings as a physiologic normalization course of associated to the confused preterm fetus during labor. No improve within the ductal move velocity was observed when a selective cyclooxygenase 2 inhibitor (celecoxib) was used in a comparative examine by Stika and colleagues. Epidural analgesia for labor uncomplicated by hypotension is, however, not associated with any alterations in placental blood circulate as measured by placental scintigraphy. However, in girls with pregnancy-induced hypertension, epidural analgesia led to a fall in maternal blood strain and a concomitant decrease in umbilical artery S/D ratio. This change in uteroplacental circulation was preceded by an increase within the maternal femoral artery move, most likely inflicting a loss of circulating volume in the uterine circulation. Pethidine crosses the placenta rapidly, and most concentrations are present in fetal scalp blood and umbilical arterial blood between 1 and 5 hours after an intramuscular injection in the mother. The variability additionally displays the operate of the fetal central nervous system and exhibits cyclic changes associated to fetal behavioral states. The complex results of hypoxemia and growing acidemia on chemoreceptors of the fetus lead to an increase of blood stress and bradycardia. During labor, indicators of fetal heart motion can be detected both transabdominally by use of a Doppler ultrasound transducer or, after rupture of membranes, transcervically with a fetal scalp electrode. Uterine exercise is recorded either with an external tocodynamometer or with an intrauterine strain catheter. Cardiotocography is broadly used at present as the preferred methodology for monitoring fetal well being in labor. The fee of cardiac contractions is topic to autonomic central nervous influences, humoral factors, and the metabolic situation of the myocardium. The decrement in blood move throughout contractions is inversely associated to the rise in intrauterine pressure, and, on the contraction acme in late labor, the diastolic velocities in maternal uteroplacental vessels disappear. Murakami M, Kanzaki T, Utsu M, et al: Changes within the umbilical venous blood circulate of human fetus in labor. Li H, Gudmundsson S, Olofsson P: Acute improve of umbilical artery vascular circulate resistance in compromised fetuses provoked by uterine contractions. Krapp M, Denzel S, Katalinic A, et al: Normal values of fetal ductus venosus blood move waveforms in the course of the first stage of labor. R�s�nen J, Jouppila P: Does a paracervical block with bupivacaine change vascular resistance in uterine and umbilical arteries Manninen T, Aantaa R, Salonen M, et al: A comparison of the hemodynamic effects of paracervical block and epidural anesthesia for labor analgesia.
Lappa (Burdock). Meloxicam.
- Are there safety concerns?
- How does Burdock work?
- Fluid retention, fever, anorexia, stomach conditions, gout, acne, severely dry skin, and psoriasis.
- What is Burdock?
- Are there any interactions with medications?
- Dosing considerations for Burdock.
Source: http://www.rxlist.com/script/main/art.asp?articlekey=96153

Effective 7.5 mg meloxicam
Simultaneously arthritis pain ear meloxicam 15 mg on-line, each the outflow (dorsal aortae) and inflow (venous) tracts of the heart kind within the dorsal mesenchyme and join with the endocardial tubes earlier than they fuse arthritis knee early symptoms meloxicam 15 mg buy generic online. Four extra pairs of aortic arches develop over the following week from the aortic sac, an expansion of the cranial end of the truncus arteriosus, and hook up with the dorsal aortae. These arches will kind the main arteries of the top, neck, higher thorax, upper extremities, lungs, and dorsal aorta. During this era, the best and left pulmonary arteries come up from the paired, sixth aortic arches and grow towards the lung, where their distal ends anastomose with the vascular plexus growing in the mesenchyme surrounding the bronchial buds. The inflow, or venous move, to the heart is initially supplied by six vessels, three on all sides of the embryo: (1) the posterior cardinal veins draining the trunk, (2) the anterior cardinal veins, draining the top, and (3) the vitelline veins draining the yolk sac, all of which drain into the inferior side of the primitive coronary heart tube, or the best and left horns of the primitive left atrium, or sinus venosus. Oxygenated blood from the placenta is delivered to the heart by the umbilical veins. Initially, the primitive lung bud is drained by the cardinal and vitelline veins, but this connection eventually regresses. The cardinal veins differentiate into the superior vena cava, whereas the vitelline and umbilical veins turn into the inferior vena cava. Like the pulmonary arteries, these veins grow towards the lung where they anastomose with the vascular plexus creating within the mesenchyme across the bronchial buds. Failure of the ductus arteriosus and/ or foramen ovale to close at start allows this shunting to persist and may require intervention. For instance, regular development of the primary pulmonary artery and pulmonary valve is affected by cardiac anomalies that disrupt division of the truncus arteriosus into the ascending aorta and the pulmonary artery, similar to tetralogy of Fallot (ventricular septal defect, pulmonary valve stenosis, displacement of the aorta, and proper ventricular hypertrophy) or persistent truncus arteriosus (ventricular septal defect with incomplete separation of the aortic and pulmonary outflow tracts). These abnormalities create a right-to-to left shunt, bypassing the lungs and causing hypoxemia and cyanosis in the affected neonate. Aberrant pulmonary arteries may originate from the descending or ascending aorta, from the brachiocephalic or subclavian arteries, or from a persistent ductus arteriosus, inflicting compression of the trachea and/or esophagus. Accessory arteries may arise from the descending aorta in conjunction with accent pulmonary lobes or pulmonary sequestration. Agenesis of the best or left pulmonary artery could also be partial or full and impacts growth of the ipsilateral lung, which can be hypoplastic. Blood supply to the affected lung is from enlarged collateral vessels, together with the bronchial arteries, intercostal arteries, coronary arteries, and/or a patent ductus arteriosus. Often patients are asymptomatic, unless extra cardiac abnormalities, similar to a patent ductus arteriosus, coarctation, or tetralogy of Fallot, are current, creating a big left-to-right shunt. Pulmonary artery sling is a uncommon malformation in which the left pulmonary artery originates from the posterior aspect of the right pulmonary artery. In order to get to the left lung, the artery passes anteriorly to the best primary stem bronchus and then posteriorly between the trachea and esophagus, forming a partial sling across the trachea. This causes compression of the adjoining bronchus and/or trachea with air trapping and hyperinflation of the proper lung, as properly as recurrent respiratory infections. Additional vascular abnormalities that cause compression of the tracheobronchial tree and/or esophagus include double aortic arch, right aortic arch with aberrant left subclavian artery, anomalous innominate artery, circumflex aorta, and cervical aortic arch. Symptoms depend on hemodynamic adjustments which are secondary to the left-to-right shunt, to the magnitude of the shunt, and to the presence of cardiac defects. These include dyspnea, shortness of breath, fatigue, chest ache, palpitations, tachycardia, and peripheral edema. On chest x-ray, the anomalous vein resembles a curved Turkish sword or "scimitar"-that is, a crescent-shaped tubular shadow or curvilinear density, positioned over the proper decrease lobe and coursing towards the best hemidiaphragm. Commonly, the defect affects the right pulmonary vein, which drains into the inferior vena cava, and is associated with right lung hypoplasia and dextroposition of the heart. The right bronchial tree could additionally be abnormal, exhibiting a left-sided branching pattern with a reduction in lobes from three to two on the best facet. Often, an anomalous systemic blood provide, with or with out sequestered lung tissue, bronchogenic cysts, horseshoe lung, or diaphragmatic defects, may be discovered, as nicely as hypoplasia or absence of the right pulmonary artery. Associated cardiovascular defects embody hypoplastic left heart, aortic coarctation, atrial septal defects, patent ductus arteriosus, tetralogy of Fallot, and a left pulmonary artery sling. There are 4 main sorts primarily based on location of the drainage: supracardiac, cardiac, infracardiac, or mixed. Cardiac drainage is the second most common, with venous connections to the coronary sinus or the posterior wall of the proper atrium. Infrequently, this vertical vein might be part of the ductus venosus, hepatic vein or inferior vena cava. In the blended pattern, the pulmonary veins drain into more than one location, including the brachiocephalic vein, superior vena cava, azygos vein, coronary sinus, right atrium, or a vein below the diaphragm. These malformations permit blood to bypass the pulmonary capillaries, which creates an extracardiac, or intrapulmonary, right-toleft shunt, resulting in hypoxemia, dyspnea, cyanosis, clubbing, and polycythemia. Age at presentation ranges from start to the seventh or eighth decade of life, though most are diagnosed within the second or third a long time. Most circumstances of pulmonary lymphangiectasis are sporadic, with males more incessantly affected than females (>2. Pulmonary lymphangiectasis could also be inherited as a dominant, recessive, or X-linked inheritance pattern. Thereafter, lung improvement proceeds in a stereotypical pattern, involving branching morphogenesis of the tracheobronchial tree followed by outgrowth, growth, and maturation of the alveolar parenchyma, or gas-exchange areas of the lung. This course of can be divided into five chronologic levels of morphogenesis, which prolong all through gestation and into early childhood. These are the embryonic, pseudoglandular, canalicular, saccular, and alveolar periods of lung growth, terms describing the anatomic, microscopic, biochemical, and physiologic adjustments that determine regular improvement and progress of the lung. Pulmonary malformations that arise in the course of the early embryonic and pseudoglandular stages of lung growth are a heterogeneous group of closely related abnormalities associated with faulty lung bud formation, separation of the trachea from the esophagus, branching morphogenesis, and formation of the conducting airways. These lesions typically end in obstruction of the airway, leading to secondary cystic or dysplastic changes in the distal lung. Pulmonary vascular abnormalities that arise during this period of lung development additionally trigger obstructive malformations of the lung and conducting airways. Pulmonary lymphangiectasis could be divided into three primary classes: primary, secondary, and generalized. Affected infants current with respiratory misery and pleural effusions and die shortly after birth. Secondary pulmonary lymphangiectasis is associated with cardiovascular malformations, together with anomalous pulmonary venous return, atrioventricular valve defects, ostium secundum, pulmonary stenosis, ventricular septal defect, mitral atresia, hypoplastic left coronary heart, cor triatium, and atresia of the frequent pulmonary veins. Infants born prematurely through the late saccular or early alveolar stages of lung growth are subject to biochemical immaturity of the lung, resulting in surfactant deficiency, progress issues of the parenchyma, or persistent interstitial lung disease. Chromosomal and genetic analyses of patients with hereditary lung malformations have been essential for figuring out molecular mechanisms underlying irregular lung improvement. Integration of genomic research in human patients with primary investigational studies utilizing a big selection of animal fashions will proceed to be important for elucidating further developmental and molecular pathways concerned in each normal and irregular lung improvement.
Order 15 mg meloxicam with amex
Dembinski J arthritis diet generic 7.5 mg meloxicam with visa, Behrendt D arthritis medication for dogs uk meloxicam 15 mg purchase on-line, Heep A, et al: Cell-associated interleukin-8 in twine blood of time period and preterm infants. Gu Y, Kuida K, Tsutsui H, et al: Activation of interferon-gamma inducing issue mediated by interleukin-1 changing enzyme. Li Y, Li X, Zhou X, et al: Impact of sepsis on the urinary degree of interleukin-18 and cystatin C in critically unwell neonates. Dahmen H, Horsten U, Kuster A, et al: Activation of the signal transducer gp130 by interleukin-11 and interleukin-6 is mediated by related molecular interactions. Matsubara K, Baba K, Nigami H, et al: Early elevation of serum thrombopoietin ranges and subsequent thrombocytosis in healthy preterm infants. Dame C, Cremer M, Ballmaier M, et al: Concentrations of thrombopoietin and interleukin-11 in the umbilical twine blood of patients with fetal alloimmune thrombocytopenia. Aderka D: the potential organic and scientific significance of the soluble tumor necrosis issue receptors. Engelmann H, Novick D, Wallach D: Two tumor necrosis factor-binding proteins purified from human urine. Evidence for immunological crossreactivity with cell surface tumor necrosis issue receptors. Reutershan J, Ley K: Bench-to-bedside evaluation: acute respiratory distress syndrome-how neutrophils migrate into the lung. Kotiranta-Ainamo A, Rautonen J, Rautonen N: Interleukin-10 production by wire blood mononuclear cells. Schultz C, Temming P, Bucsky P, et al: Immature anti-inflammatory response in neonates. Uzuner N, Babayigit Hocaoglu A, Olmez Erge D, et al: Raised interleukin-13 ranges in cord blood will increase the chance of allergic sensitization at 5 years of age. Vestweber D: Adhesion and signaling molecules controlling the transmigration of leukocytes via endothelium. Effects on tissue-type plasminogen activator and kind 1 plasminogen activator inhibitor. Pajkrt D, van der Poll T, Levi M, et al: Interleukin-10 inhibits activation of coagulation and fibrinolysis throughout human endotoxemia. Gabay C, Kushner I: Acute-phase proteins and other systemic responses to irritation. Loyer P, Ilyin G, Abdel Razzak Z, et al: Interleukin four inhibits the production of some acute-phase proteins by human hepatocytes in primary tradition. Lu B, Wang C, Wang M, et al: Molecular mechanism and therapeutic modulation of excessive mobility group field 1 launch and motion: an updated evaluation. Torbe A, Czajka R, Kordek A, et al: Maternal serum proinflammatory cytokines in preterm labor with intact membranes: neonatal outcome and histological associations. Schmalstieg In 1891, it was discovered that immunity was transmitted by way of breast-feeding in experimental animals. Concentrations of IgG in human milk are lower than those for IgM and are much decrease than serum IgG levels. IgA dimers produced by those plasma cells principally comprise -light chains, whereas -light chains predominate in serum Igs. Thus, enteromammary and bronchomammary pathways protect the toddler in opposition to pathogens within the surroundings of the dyad (see Table 129-2). Without colostrum, calves are IgG-deficient and susceptible to intestinal infections. Lactoferrin also kills by damaging outer membranes of many gram-positive and -negative micro organism and filamentous fungi68-70 by a peptide comprised of 18 amino acid residues from the N-terminal region formed by pepsin digestion (lactoferricin). The mean concentration of lysozyme is about 70 �g/mL in colostrum,54 20 �g/mL at 1 month, and 250 �g/mL by 6 months of lactation. The concentration of prototypic long pentraxin in human umbilical cord blood is about half that of adult blood, and so the presence of this agent in human milk could compensate for a developmental delay in its manufacturing in newborns. Their concentrations in colostrum and mature milk are about 20 mg/dL and 12 mg/dL, respectively. Oligosaccharides in human milk are receptor analogues that inhibit the binding of certain enteric or respiratory bacterial pathogens and their toxins to epithelial cells. In that respect, the severity of Campylobacter or calcivirus enteritis in breast-fed infants is inversely proportional to concentrations of certain 2-linked fucosyloligosaccharides in milk. Human milk fat globules and mucin from their membranes inhibit binding of S-fimbriated E. When these apoptotic cells are phagocytized by macrophages, less inflammation is produced. Because of those intracytoplasmic bodies, the cells are tough to acknowledge by common staining methods. For instance, the decreased calcium inflow found in human milk neutrophils may be replicated by incubating blood neutrophils in human milk. Because solely small numbers of memory T cells are detected in infancy,154 maternal reminiscence T cells in milk might compensate for that developmental delay within the infant. There is proof from experimental animal research that milk lymphocytes enter neonatal tissues,145 but that has not been demonstrated in people. However, that possibility is suggested by the discovering that cellular immunity may be transferred by breast-feeding. The major antioxidants in human milk embody an ascorbatelike compound,162 uric acid,162 -tocopherol163,164 and carotene. Epidemiologic studies advised that youngsters who had been breast-fed during infancy have been at less danger for sure ailments mediated by immunologic, inflammatory, or oncogenic mechanisms, including sort 1 and a pair of diabetes mellitus,181-183 childhood leukemia and lymphoma,184-186 and ulcerative colitis and Crohn illness. For instance, breast-feeding primes the recipient to produce higher blood ranges of interferon- in response to respiratory syncytial virus infections. Thymic growth193 and function,194 T cell emigration from the thymus,195 and T cell maturation and function194 are elevated in breast-fed compared with non�breast-fed infants. Finally, all leukocytes in human milk are activated, suggesting that breast milk could each activate leukocytes and modulate their behavior to forestall injurious effects. Many features of the immune system are incompletely developed at delivery and even more so in very-lowbirth-weight infants. Human milk incorporates vital portions of many of those immune defense merchandise (Table 129-5). In each case, endogenous production is developmentally delayed, however the agent is well represented in human milk. Animal research indicate that commensal enteric bacteria initiate a complex chain of events that profoundly affect mucosal immunity. That in turn promotes the discharge of granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating issue from intestinal lymphoid cells that controls the number and performance of mucosal dendritic cells and macrophages. A related chain of events that lessens intestinal inflammation in breastfed infants appears probably. High lysozyme ranges in human milk55 are coupled with low production of the protein by tracheobronchial mucosal cells during infancy. Function of human milk immune components within the infant depends on upkeep of their structural integrity, or survival, after ingestion by the toddler. Proteins also might escape digestion because of developmental delays in manufacturing of gastric acid and pancreatic proteases,258 shielding of acid-labile components by the buffering capability of milk, antiproteases in human milk,258 inherent resistance of many defense agents in human milk to digestive processes, or compartmentalization of some protection brokers in human milk.
7.5 mg meloxicam buy mastercard
Supramaniam V arthritis pain worse after exercise meloxicam 7.5 mg buy fast delivery, Vontell R rheumatoid arthritis definition pdf 15 mg meloxicam cheap fast delivery, Srinivasan L, et al: Microglia activation in the extremely preterm human mind. Inder T, Mocatta T, Darlow B, et al: Markers of oxidative injury in the cerebrospinal fluid of a untimely toddler with meningitis and periventricular leukomalacia. Randomised trial of early tapping in neonatal posthaemorrhagic ventricular dilatation. Matsumae M, Sogabe T, Miura I, Sato O: Energy metabolism in kaolin-induced hydrocephalic rat mind. Assessed by phosphorus (31P) magnetic resonance spectroscopy and the range of lactate-dehydrogenase and its isoenzyme patterns. Suzuki F, Handa J, Maeda T: Effects of congenital hydrocephalus on serotonergic enter and barrel cytoarchitecture within the growing somatosensory cortex of rats. Alvisi C, Cerisoli M, Giulioni M, et al: Evaluation of cerebral blood move changes by transfontanelle Doppler ultrasound in childish hydrocephalus. Klebermass-Schrehof K, Rona Z, Waldhor T, et al: Can neurophysiological evaluation enhance timing of intervention in posthaemorrhagic ventricular dilatation Rowlatt U: the microscopic effects of ventricular dilatation without improve in head measurement. Casaer P, von Siebenthal K, van der Vlugt A, et al: Cytochrome aa3 and intracranial stress in new child infants: a close to infrared spectroscopy study. Shirane R, Sato S, Sato K, et al: Cerebral blood move and oxygen metabolism in infants with hydrocephalus. Klebermass-Schrehof K, Czaba C, Olischar M, et al: Impact of low-grade intraventricular hemorrhage on long-term neurodevelopmental outcome in preterm infants. Heine It is well-known that preterm birth is associated with elevated risks of mind harm and impaired brain development resulting in impairments in motor, cognitive, and behavioral operate. In latest years, it has become evident that the cerebellum is one other main target for injury and developmental impairment associated with prematurity. Such main accidents can embody cerebellar hemorrhage or ischemia, with long-term outcomes depending on the dimensions and location of the lesions. Secondary impairments in cerebellar development are extra prevalent and may be associated with a number of scientific threat factors in the early postnatal interval (Table 135-1). Functional buildings of the cerebellum structures embrace (1) the medial section, the spinocerebellum with the vermis; (2) the lateral sections, the cerebrocerebellum; and (3) essentially the most posterior section, the vestibulocerebellum (flocculonodular lobe). The spinocerebellum is concerned in course and fee of supposed actions, the cerebrocerebellum plans and modifies motor output to muscle tissue, and the vestibulocerebellum regulates steadiness, posture, and eye movements. The granule layer is packed with granule (the most plentiful neuronal cell sort in the brain), Golgi, Lugaro, and unipolar brush cells. The molecular layer accommodates the dendritic timber of the Purkinje cells, as well as the stellate and basket interneurons. The Purkinje and granule cells are the two major neuronal cell sorts in the cerebellar circuit. Underneath the cortex lies the cerebellar white matter, which additionally contains gray matter deep nuclei constructions. The cerebrospinal fluid�filled fourth ventricle is positioned between the mind stem and cerebellum. The cerebellum receives data from the motor cortex, the proprioceptors, vestibular organs, and other brain stem nuclei. All climbing fibers originate from the inferior olivary nucleus, and the mossy fibers originate from a quantity of sources. Before coming into the cerebellar cortex, climbing fibers additionally give off collaterals to the deep nuclei. Next to the input from one climbing fiber, the Purkinje cells receive enter from quite a few granule cells through the parallel fibers onto their distal dendrites. The Purkinje cells in turn innervate different parts of the cerebellar cortex, together with different Purkinje, Golgi, Lugaro, and basket cells, and project onto the deep cerebellar nuclei. Four deep nuclei reside within the cerebellar white matter and are from lateral to medial: dentate, emboliform, globose, and fastigii. The dentate nucleus belongs to and communicates solely with the lateral cerebrocerebellum. The different three deep nuclei belong to the spinocerebellum and talk with completely different regions of the cerebellum and cerebrum. Next to the vestibular nuclei, the deep cerebellar nuclei give the sole output of the cerebellum. The cerebellar primordium is formed at the border of the mid- and hindbrain and can be identified as thickenings on the lateral sites of the alar plate going through the fourth ventricle, as early as gestational week 6. Around gestational weeks eight and 9, the vermis begins to fuse, and after gestational week 12, the vermis and cerebellar hemispheres begin to grow rapidly. The formation of the white matter of the cerebellum turns into apparent between gestational weeks 32 and 37. Two germinative neuroepithelia-the ventricular zone and the rhombic lip, which turn out to be anatomically apparent round gestational day 579- generate the completely different cerebellar cell types. The Purkinje cells migrate along the fibers of the radial glial cells, previous the deep nuclei. Between gestational weeks 12 and 20, the Purkinje precursor cell inhabitants drastically reduces in number. Shortly after reaching their maturity, the Purkinje cells receive a layer of myelin round their axons. The rhombic lip offers rise to the granule cells, the pontine nuclei, the inferior olive, and the unipolar brush cells. Although human development exhibits differences, many mechanisms are highly conserved between species. Loss-of-function mutations within the genes encoding these signaling pathways and transcription elements end in irregular cerebellar development. However, data about genetic control of the technology of the different cerebellar cell sorts from the ventricular zone is restricted. As such it has become a focus of research that seek to understand the molecular mechanisms affected by developmental injuries to the cerebellum in human preterm neonates. Preterm infants have a excessive danger of developing cerebellar hemorrhage, ensuing from injury to the weak germinal matrix present within the fourth ventricle and the exterior granular layer overlaying the surface of the cerebellum. This is a extremely vascularized area of the brain, with immature vascular partitions prone to hemorrhage. Postmortem evaluation reveals that cerebellar hemorrhage is usually multifocal, bilateral, and variable in size in numerous ages of preterm infants,59 although this observation is predicated on a biased population of probably the most severely unwell infants. Pathology within the deep cerebellar nuclei, similar to dentate nuclei, as nicely as the inferior olivary, usually occurs in affiliation with cerebellar hemorrhage. In giant cerebellar hemorrhages, a reduction in contralateral cerebral quantity has been found, which might be due to impaired remote transsynaptic trophic results.
Meloxicam 15 mg buy mastercard
Kaplan M arthritis neck & back pain center 7.5 mg meloxicam discount visa, Hammerman C: Bilirubin and the genome: the hereditary basis of unconjugated neonatal hyperbilirubinemia arthritis in dogs knee symptoms meloxicam 7.5 mg cheap with visa. Kaplan M, Bromiker R, Hammerman C: Hyperbilirubinemia, hemolysis, and elevated bilirubin neurotoxicity. Valaes T: Severe neonatal jaundice associated with glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase deficiency: pathogenesis and global epidemiology. Kaplan M, Hammerman C: Glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase deficiency: a hidden danger for kernicterus. Yamada N, Yamaya M, Okinaga S, et al: Microsatellite polymorphism within the heme oxygenase-1 gene promoter is associated with susceptibility to emphysema. Kaplan M, Renbaum P, Hammerman C, et al: Heme oxygenase-1 promoter polymorphisms and neonatal jaundice. Lin R, Wang X, Wang Y, et al: Association of polymorphisms in 4 bilirubin metabolism genes with serum bilirubin in three Asian populations. Immenschuh S, Shan Y, Kroll H, et al: Marked hyperbilirubinemia related to the heme oxygenase-1 gene promoter microsatellite polymorphism in a boy with autoimmune hemolytic anemia. Kaplan M, Hammerman C: Glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase deficiency and extreme neonatal hyperbilirubinemia: a complexity of interactions between genes and environment. Olusanya B, Emokpae A, Zamora T, Slusher T: Addressing the burden of neonatal hyperbilirubinaemia in nations with significant glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase deficiency. Sgro M, Campbell D, Shah V: Incidence and causes of severe neonatal hyperbilirubinemia in Canada. Meloni T, Cutillo S, Testa U, Luzzatto L: Neonatal jaundice and severity of glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase deficiency in Sardinian babies. Kaplan M, Herschel M, Hammerman C, et al: Studies in hemolysis in glucose6-phosphate dehydrogenase-deficient African American neonates. Kaplan M, Herschel M, Hammerman C, et al: Hyperbilirubinemia amongst African American, glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase-deficient neonates. Kaplan M, Muraca M, Hammerman C, et al: Bilirubin conjugation, reflected by conjugated bilirubin fractions, in glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenasedeficient neonates: a determining factor within the pathogenesis of hyperbilirubinemia. Kaplan M, Hammerman C, Feldman R, Brisk R: Predischarge bilirubin screening in glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase-deficient neonates. Algur N, Avraham I, Hammerman C, Kaplan M: Quantitative neonatal glucose6-phosphate dehydrogenase screening: distribution, reference values, and classification by phenotype. Further enhancements of the staining process and a few observations with glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase deficiency. Zangen S, Kidron D, Gelbart T, et al: Fatal kernicterus in a woman deficient in glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase: a paradigm of synergistic heterozygosity. Luzzatto L: Glucose 6-phosphate dehydrogenase deficiency: from genotype to phenotype. Beutler E, Gelbart T: Estimating the prevalence of pyruvate kinase deficiency from the gene frequency within the general white population. Bianchi P, Zanella A: Hematologically necessary mutations: purple cell pyruvate kinase (third update). Iolascon A, Miraglia del Giudice E, Perrotta S, et al: Hereditary spherocytosis: from scientific to molecular defects. Maruo Y, Nishizawa K, Sato H, et al: Prolonged unconjugated hyperbilirubinemia related to breast milk and mutations of the bilirubin uridine diphosphate- glucuronosyltransferase gene. Lamola the pathways by which gentle reduces levels of circulating bilirubin and how this mechanism leads to the discount of attainable toxic byproducts has been the subject of intense inquiry and debate for the reason that 1960s. Over the intervening years, the mechanism of motion of phototherapy has been extensively studied, and enough proof is out there to information its use in term and late-preterm neonates. Prescription of phototherapy for neonatal hyperbilirubinemia is relatively simple and efficacious if correctly applied. Furthermore, a a lot better definition of the phototherapy "motion spectrum" has emerged, taking into account enhancements in mild sources, variables affecting efficacy (such as dosimetry and hematocrit levels), and potential undesirable results (such as heating by absorption of sunshine wavelengths which would possibly be comparatively useless therapeutically). In this articler, we evaluation the problems associated to bilirubin photochemistry, photobiology, and photomedicine to delineate our understanding of how phototherapy light (photons) should be viewed as a drug that interacts with bilirubin molecules (Table 98-1). A evaluate of selected terms related to photobiology merchandise may be found in Box 98-1. They provided the "evidence for the reduction of circulating bilirubin ranges in some cases of neonatal jaundice by exposing these infants to daylight. Eight 24-inch 40-watt blue fluorescent tubes (General Electric Corporation) at 2-inch separation have been arranged around the curve of the reflector. Although the Lancet acknowledged this as a contribution of significance to benefit publication, it obtained only limited consideration both in Europe and North America. The breakthrough scientific concepts, novel prototype gadget, and alter in medical follow, nonetheless, subsequently made their way to Italy, Brazil, and other Latin American nations. Almost all the bilirubin in blood is reversibly bound to its transport protein, albumin, in a form that can be distributed to quite lots of tissues. The regular lipid- to watersoluble conversion of unconjugated bilirubin is mediated by way of a process of conjugation occurring in the liver. Phototherapy-induced conversion of bilirubin to extra water-soluble and colorless products bypasses this hepatobiliary excretion course of. J Pediatr seventy five: 718�726, 1969; American Academy of Pediatrics Subcommittee on Hyperbilirubinemia: Management of hyperbilirubinemia in the new child infant 35 or extra weeks of gestation. Precise assessment of neurotoxicity should address a quantity of domains of sensory processing. Table 98-2 lists present and prospective biomarkers for identifying infants most in danger for neurotoxicity. The perception of sunshine as a steady power stream obscures the truth that it contains discrete packets (quanta) of energy referred to as photons. From this equation, it can be seen that a photon at 400-nm wavelength (visibly blue) incorporates approximately 25% extra energy than one at 500-nm wavelength (visibly green)-that is, for the same mild exposure measured in energy models (such as �W/cm2), there are approximately 25% extra photons at 500 than at four hundred nm. All photochemical reactions require, in odd circumstances, the absorption of single photons by particular person molecules. The absorption spectrum is a plot of the chance of light absorption as a function of the wavelength of the sunshine. The spectrum on this illustration is definitely that of bilirubin bound to albumin, which is the form of nearly all of the bilirubin in blood. Therefore the wavelength (color) of sunshine (drug) designed to work together with the molecular target (bilirubin) could be predicted by figuring out its absorption by the molecular target. Additional specificity of the wavelength vary could also be dictated by the avoidance of untoward side effects. The number of therapeutic photons absorbed by the molecular goal is analogous to the dose of a drug. The depth or irradiance (photons per unit time) of the light is analogous to the drug dose price. One means absorbed mild usually differs from molecular medication is within the deposition of heat. For a sufficiently dilute resolution of a photochemically reactive materials, the motion spectrum typically is identical to the absorption spectrum. This follows the fundamental law of photochemistry that states that light must be absorbed for a photochemical response to occur.