Floxin dosages: 400 mg, 200 mg
Floxin packs: 30 pills, 60 pills, 90 pills, 120 pills, 180 pills, 270 pills, 360 pills
Cheap floxin 200 mg
Fetal sheep research demonstrate the fetus is unable to generate warmth via thermogenesis252 and reduces in sheep fetal temperature can lead to antibiotics video 400 mg floxin generic tachycardia and hypertension in utero infection definition biology purchase 400 mg floxin. In contrast, human reviews associate maternal/fetal hypothermia with fetal bradycardia. During open fetal surgical procedure, use of warmed fluid for intrauterine irrigation and monitoring of both maternal core and amniotic fluid temperatures are additionally necessary. The fetus reveals pituitary-adrenal, sympathoadrenal, 63 � Anesthesia for Fetal Surgery and Other Fetal Therapies 2061 and circulatory stress responses to noxious stimuli as early as 16 to 18 weeks gestation. Given this uncertainty and the more than 35-year historical past of secure anesthetic administration in neonates and fetuses undergoing invasive procedures,271-273 analgesia must be provided throughout fetal surgery. Opioid analgesics could be transferred to the fetus by maternal administration or direct fetal intramuscular or intravenous umbilical twine administration using ultrasound steering. For most invasive procedures inflicting noxious fetal stimulation, fetal intramuscular administration of fentanyl 10 to 20 g/kg (or different opioid in equivalent dosing) is used to provide analgesia instantly before the intervention. Some physicians administer prophylactic intramuscular atropine 20 g/kg with opioids to minimize the danger for fetal bradycardia. Maternal administration and placental switch of intravenous remifentanil provides sufficient fetal immobility during fetoscopic interventions that involve only the umbilical wire or placenta. These anesthetics readily transfer across the placenta, with fetal focus and the fetal-to-maternal (F/M) ratio relying on both the maternal inspired anesthetic concentration and the length of maternal anesthetic administration. In human studies of anesthetic levels on the time of cesarean delivery (10-minute duration of basic anesthesia), isoflurane has an F/M ratio of approximately 0. Anesthetic neurotoxicity of the developing brain is a priority for all providers administering anesthetic agents for fetal procedures. In animal models, anesthetics affect neonatal brain growth and create histologic changes, in addition to studying and memory deficits. Two prospective trials examining the impact of a short anesthetic publicity have instructed no long-term neurodevelopmental penalties. One study seemed retrospectively at using common anesthesia for cesarean section and the incidence of studying disabilities at age 5 and found no correlation. No basic anesthetic agent is thought to be superior to another, and whether or not exposure to basic anesthetics throughout gestation in comparison with the neonatal interval is more helpful or harmful is unknown. In an effort to systematically acquire current knowledge, an international registry has been established for the aim of assessing the long-term neurodevelopmental outcomes of fetal surgery patients (Clinical Trials. Administration of extra opioid, benzodiazepine, or other anesthetic agent can be utilized for maternal analgesia and anxiolysis. Use of supplemental anesthetic medicine will also decrease the likelihood of fetal movement by way of placental switch. Local anesthetic infiltration can additionally be used for fetoscopic procedures, which usually employ endoscope trocars which are solely 2 to 5 mm in diameter. Fetal immobility can be safely achieved with direct fetal intramuscular or umbilical venous administration of muscle relaxant. When basic anesthesia is employed, placental transfer of a risky anesthetic provides vital fetal anesthesia and reduces fetal movement, however supplemental opioids must also be administered if fetal analgesia is required. Weight-based unit doses of atropine (20 g/kg) and epinephrine (10 g/kg) must be instantly available in individually labeled syringes for direct fetal administration by the surgeon underneath ultrasonography guidance. These drugs require sterile transfer to the surgical subject preoperatively, meticulous labeling, and correct dosing earlier than graduation of the process. The surgeon can administer the indicated medication by quite a lot of routes (intramuscular, intravenous, or intracardiac) relying on the process and urgency of the state of affairs. If gestational development is suitable with extrauterine life, the obstetric group must be prepared to perform an emergency cesarean supply if fetal bradycardia persists despite efforts to resuscitate in utero. The anesthesiologist should be prepared to emergently present maternal common anesthesia and help with neonatal resuscitation. Unlike minimally invasive fetal procedures, open fetal surgery requires profound uterine relaxation and sometimes entails additional fetal monitoring past intermittent ultrasonography. Open surgical procedure entails extra surgical stimulation, hemodynamic perturbation, and threat for fetal compromise and requires direct administration of drugs to the fetus. Compared to minimally invasive procedures, open fetal procedures current greater threat to the mother. The anesthesiologist and other group members ought to be ready for important maternal and fetal blood loss, the need for maternal and fetal resuscitation, and potential emergent delivery. Weight-based unit doses of medications for fetal analgesia and muscle rest as previously detailed within the part on "Fetal Anesthesia, Analgesia, and Pain Perception" ought to be available for administration by the surgical team. In addition, resuscitation drugs (atropine 20 g/kg, epinephrine 10 g/kg, and crystalloid 10 mL/kg) ought to be prepared preoperatively in sterile weight-based unit doses for emergent treatment of intraoperative fetal hemodynamic compromise. For procedures with a high danger of fetal hemorrhage, acceptable blood for fetal transfusion. An epidural catheter is positioned preoperatively for administration of postoperative analgesia. Absent or reversed umbilical artery diastolic move intraoperatively could additionally be an early signal of fetal distress. After anesthetic induction and earlier than maternal skin incision, standard concentrations of anesthetics are administered to the mother. Ventilation is managed to keep eucapnia (end-tidal carbon dioxide levels of 28-32 mm Hg). Intravenous fluids administered to the mom are minimized (<2 L) to lower the chance for perioperative pulmonary edema associated with using tocolytics, similar to magnesium sulfate or administration of large doses of nitroglycerine throughout fetal surgical procedure. Typical maternal hemodynamic objectives include maintaining systolic arterial blood stress within 10% of baseline values and imply arterial pressure larger than 65 mm Hg with acceptable maternal coronary heart price. Phenylephrine administration can be utilized to treat maternal hypotension with minimal modifications within the fetal acid-base status. Administration of intravenous propofol and/or remifentanil with risky anesthetic at 1. Currently, no specific anesthetic method demonstrates significant improvement in fetal end result. In some open fetal procedures, pulse oximetry or additional direct fetal monitoring can be employed after the hysterotomy is carried out, as beforehand discussed within the section on fetal physiology and monitoring. Rarely, when uncertainty exists concerning fetal situation, umbilical cord blood gasoline measurements may be obtained. As described in the prior section on fetal anesthesia, analgesia, and pain perception, an opioid and a muscle relaxant could be administered to the fetus intramuscularly both before uterine incision with ultrasound guidance or beneath direct vision after uterine incision. Intramuscular atropine also could be administered concurrently to reduce opioid-induced fetal bradycardia. After uterine exposure and ultrasound placental mapping, a small hysterotomy is created away from the placenta. A stapling device with absorbable lactomer staples is used to extend the incision. The staples stop hemorrhage from the relaxed uterus and seal the amniotic membranes to the uterine endometrium. Vigilant remark of the surgical field, close communication with the surgeon, and careful maternal monitoring are essential to avoid occult hemorrhage. Lost amniotic fluid is changed with warmed crystalloid to bathe the uncovered fetus.
200 mg floxin cheap otc
Onset time is shortened antibiotic resistance lyme disease order floxin 400 mg mastercard, however duration of blockade is lowered as a outcome of trapping of native anesthetics inside myelin with subsequent progressive launch is decreased and since local circulation and due to this fact vascular absorption are larger in infants antibiotics quiz medical students floxin 200 mg discount on-line. The motivational-directive component is conveyed by unmyelinated C fibers ("sluggish" pain or "true" pain). Pain results in protecting reflexes similar to autonomic reactions, muscle contraction, and rigidity. However, nociceptive stimulations transmitted to the dorsal horn by C fibers elicit long-lasting responses,5,6 in all probability on account of extensive depolarization of surrounding neurons in response to the manufacturing of huge quantities of substance P. As the number of dorsal horn receptors to substance P decreases during the first 2 weeks of life, this exaggerated response of neonates to nociceptive stimulation progressively disappears. The inhibitory management pathways, which are immature at start, develop concomitantly. Painful procedures through the neonatal period modify subsequent pain responses in infancy and childhood,7 depending on the developmental stage of the toddler (fullterm vs. Noxious procedures in full-term neonates react with heightened behavioral responsiveness, whereas preterm neonates react with a dampened response. When analgesic medicine (local anesthetics or opioids) are administered earlier than painful procedures, infants show much less evidence of procedural ache and a reduction within the magnitude of long-term adjustments in pain behaviors. During the previous 2 many years, pediatric ache has received appreciable attention, and dependable age-related ache scales have been developed to evaluate each the severity of pain and the efficacy of its treatment. Delayed Ossification of Bones and Fusion of Sacral Vertebrae Bones of neonates, together with vertebrae, are mostly cartilaginous. Sharp needles can simply traverse them as a result of cartilage offers little resistance to penetration, and ossification nuclei could be severely damaged, thus compromising further bone and joint growth. Consequently, bone contact ought to be avoided as often as possible during block procedures, especially in infants. This cartilaginous structure additionally permits simple penetration of radiographs and ultrasound. Development of Curvature of the Spine At delivery, a single spinal curvature is current and the orientation of epidural needles is the same regardless of the intervertebral area. Loose Attachment of Fasciae and Fluidity of Epidural Fat Fasciae and perineurovascular sheaths are loosely hooked up to underlying constructions. This permits prolonged spread of native anesthetics, leading to high-quality nerve blockade whatever the approach but additionally, occasionally, undesirable spread to distant nerves or anatomic spaces. The epidural fat is very fluid in infants and young youngsters (up to 6-7 years of age). This fluidity combined with the unfastened attachment of the sheaths surrounding the spinal roots favors consistent leakage of local anesthetics injected throughout the epidural house; therefore comparatively giant volumes of epidural native anesthetics (up to 1. A main pharmacologic consequence of this condition is that local anesthetics can penetrate and block nerve fibers extra simply. Drug prescriptions made based on physique surface area are the same as (or in simple ratio with) grownup dosing. Delayed myelinization of nerve fibers Easier intraneural penetration of native anesthetics Onset time is shortened, and diluted local anesthetic is as efficient as more concentrated anesthetic in adults. Reduced resistance to penetration by sharp needles Danger of direct trauma and bacterial contamination of ossification nuclei compromising further bone or joint growth Persistence of sacral intervertebral spaces Cervical lordosis (3-6 months) Lumbar lordosis (8-9 months) Sacral hiatus comparatively smaller with growing age Tuffier line, which joins anterior superior iliac spinous processes, crosses the backbone at L5 or lower in infants. Increased diffusion of native anesthetic as a lot as 6-7 years of age Increased unfold alongside nerve paths with danger of penetrating distant anatomic spaces and blocking distant nerves Slower metabolism of native anesthetics (usually compensated by other enzyme pathways) Avoid use of skinny and sharp needles; use short and quick beveled ones as a substitute. Do not apply excessive pressure on needle: if resistance is felt, cease attempting to insert the needle farther. Same orientation of epidural needles is appropriate whatever the spinal stage earlier than 6 months of age; then adapt needle orientation to spinal flexures. Identification of sacral hiatus becomes more difficult after 6-8 years (increased failure price of caudal anesthesia). Excellent blockade after caudal anesthesia can be achieved up to 6-7 years of age. Larger quantity of local anesthetic is required for epidural blocks because of leakage along spinal nerve roots. Smaller quantity of local anesthetic is important to produce glorious peripheral blocks. Increased mean physique residency time and half-life, with accumulation (especially after repeat injection and continuous infusions of local anesthetic), are characteristic. Decreased Cmax happens after single injection but accumulation occurs with repeat or steady injections. Vasoconstriction reduces absorption (thus toxicity) and prolongs duration of blockade. Heavy sedation or basic anesthesia is required in most patients (especially when a "dangerous" technique is deliberate to keep away from detrimental penalties of panic attacks at a important part of the block procedure). The major consequences are (1) shorter onset time of motion, (2) more prolonged longitudinal and circumferential spread of local anesthetics, and (3) shorter duration of motion because of reduced secondary release from local binding websites. The goal of native anesthetic action is voltage-dependent sodium channels positioned within nerve fibers. Nonionized molecules can achieve penetration of solely biologic membranes, and the pace of the method depends on the quantity and thickness (increasing with age) of sheaths. Nonionized native anesthetics easily traverse the capillary wall close to the injection site. Because cardiac output and local blood circulate are two to 3 times larger in infants than in adults, systemic native anesthetic absorption is elevated accordingly and vasoactive agents corresponding to epinephrine are very effective in slowing systemic uptake. Once within the bloodstream, native anesthetics distribute to pink blood cells, which retain 20% to 30% of the entire dose, relying on the anesthetic and the hematocrit. Red cell storage usually has a minor influence on the pharmacokinetics of native anesthetics except in the following situations: In neonates: High hematocrit values (which could exceed 70%) and enlargement of erythrocytes (physiologic macrocytosis) result in constant "entrapment" of local anesthetics, thus decreasing peak plasma concentration (Cmax) values after a single injection but increasing secondary launch, thus increasing the half-life of all native anesthetics. In infants: Physiologic anemia reduces red cell storage and its protecting impact towards systemic toxicity of native anesthetics (after a single-shot injection only) when the plasma protein binding websites are saturated-that is, near poisonous blood concentrations. In children and infants, the same kinetics of absorption is reported, however the youthful the patient, the much less accentuated is the biphasic shape of the plasma focus curve. After caudal or lumbar epidural injection, Tmax is prolonged up to 2 hours in infants and Cmax is increased. After caudal injection of levobupivacaine 2 mg/kg in infants youthful than 2 years of age, the Cmax vary is 0. Their plasma focus in pulmonary veins and then in systemic arterial circulation (especially coronary and cerebral arteries) is constantly decreased. Thus pulmonary extraction represents a temporary protection in opposition to systemic toxicity. Some medicines similar to propranolol decrease pulmonary extraction in a clinically related way. After intravenous injection, volume distribution at the regular state (Vdss) is 1 to 2 L/kg for all aminoamides (Table 76. After administration at different sites, calculated distribution is increased, typically considerably, because of the "flip-flop" effect, particularly for long-lasting native anesthetics. After a single injection, the clearance of levobupivacaine increases during the first months of life, but during steady infusion (even with zero.
Cheap 200 mg floxin with visa
The new child goes by way of a transitional circulation and it takes some days for the pulmonary circulation to regulate antimicrobial medication cheap floxin 400 mg overnight delivery. Hypoxia or acidosis in the newborn can result in antimicrobial lighting 400 mg floxin discount amex vital pulmonary vasoconstriction and resultant pulmonary hypertension. This could result in proper to left shunting, exacerbating arterial hypoxia and thus resulting in a vicious cycle of worsening pulmonary hypertension, acidosis, hypoxia, and eventual cardiovascular collapse. The neonatal lung is fragile and notably vulnerable to harm from extreme tidal volumes. In contrast, careful consideration to ventilation is required to preserve practical residual capacity and avoid atelectasis. Even temporary disconnection of the airway circuit or mechanical ventilator can result in important alveolar collapse and may thus be prevented if possible. It can be increasingly acknowledged that intubated neonates ought to be transferred to and from the working room with applicable neonatal transport ventilator tools quite than simply a bag and t-piece. Recent studies have instructed that the neonatal brain could additionally be significantly susceptible to hypotension. The differentiation between aware and unconscious can also be problematic in neonates. However, what precisely constitutes a state of enough anesthesia in the neonate is unclear. Propofol and inhaled anesthetics can outcome in profound cardiovascular despair in the neonate. Anesthesiologists must be notably cautious about opioid-induced bradycardia and its penalties on cardiac output. Low concentrations of potent inhaled anesthetics can be used with opioids to present a means of controlling hemodynamic responses without significantly miserable the myocardium. Caudal and spinal anesthesia are relatively straightforward; nevertheless the secure placement of a lumbar or thoracic epidural block requires appreciable skill. Epidural local anesthetic infusions can outcome in systemic toxicity because of immature metabolism. The following must be thought-about in addition to the standard issues for the management of neonates: (1) particular positioning for tracheal intubation. The anesthesiologist should establish enough intravenous access to substitute all fluid deficits, together with loss from the defect (usually with regular saline), and ensure that cross-matched blood is on the market (especially if rotational pores and skin flaps are planned). Latex allergy precautions should be used with these children for his or her first and all subsequent anesthetics. The main anesthesia-related issues with these defects include the next: (1) extreme dehydration and potential huge fluid loss from the exposed visceral surfaces and due to partial bowel obstruction; (2) heat loss; 77 � Pediatric Anesthesia 2451 (3) raised abdominal strain with closure; and (4) excessive affiliation of these circumstances with prematurity and other congenital defects, including cardiac abnormalities (with omphalocele, 20%). These kids should have an adequate preoperative work-up that features an echocardiogram to assess both anatomy and myocardial operate. Postoperative ventilation is often required for these A sufferers because of a good stomach wall closure. Infants with omphalocele or gastroschisis require cautious administration preoperatively to decrease the probability of infection or compromise of bowel function. For all kids, sufficient fluid resuscitation must be provided and electrolyte imbalances corrected previous to surgical procedure. Invasive monitoring is often needed, significantly if the child has an related cardiac defect. The liberal use of muscle relaxants supplies optimal surgical situations for closure of the defect. Hypotension during closure might occur as a result of pressure on the liver or caval compression. Similarly raised stomach pressure throughout closure may impede adequate ventilation. Postoperative ventilation may be necessary until the abdominal wall has had time to stretch to accommodate the viscera. It should be famous that increased abdominal strain after a tight closure (abdominal compartment syndrome) might compromise hepatic and renal perform and significantly alter drug metabolism. Staged closure with a premade spring-loaded silastic silo is getting used with increasing frequency, thus minimizing repeat journeys to the operating room. A small share of youngsters with omphalocele may even have Beckwith-Wiedemann syndrome, a situation characterized by profound hypoglycemia, hyperviscosity syndrome, congenital coronary heart disease, and associated visceromegaly. Tracheoesophageal Fistula A tracheoesophageal fistula can have five or more configurations, most of which are identified after an lack of ability to swallow because of an associated esophageal atresia (the esophagus ends in a blind pouch). In these circumstances the characteristic diagnostic take a look at is an incapability to pass a suction catheter into the stomach. Neonates may have aspiration pneumonitis from a distal fistula connecting the abdomen to the trachea through the esophagus or from a proximal connection of the esophagus with the trachea. Neonates with the rarer H-type fistulae have a fistula between esophagus and trachea; however the esophagus is patent with no atresia. These children current later, usually with respiratory misery and chest infections. Any child with a tracheoesophageal fistula or esophageal atresia must be suspected of having the opposite anomalies. An echocardiogram to examine for a right-sided aortic arch and the presence of congenital heart disease must be performed earlier than anesthesia. A main aim of anesthesia is to ensure adequate ventilation regardless of the presence of the fistula. Since optimistic strain ventilation might inflate the stomach through the fistula and trigger distension of the stomach, it should be avoided until an endotracheal tube is positioned distal to the fistula and/or the fistula is occluded or ligated. The risk of stomach distension and hypoventilation is best when the fistula is large or the lung compliance is poor. The distended stomach will further compromise air flow of the lungs, exacerbating the state of affairs. Coordination with the surgeon is important to defining the optimum approach to ensure sufficient air flow until the fistula is occluded. Bronchoscopy is often performed after induction to assess the size and placement of the fistula. At bronchoscopy a Fogarty catheter or comparable system may be positioned instantly within the fistula to occlude it. The endotracheal tube is ideally placed in the trachea distal to the origin of the fistula. This may be done blindly by advancing the tube into a primary bronchus and then rigorously pulling it again till equal air entry is heard. The endotracheal tube could additionally be inadvertently placed into the fistula leading to speedy gastric distension and arterial oxygen desaturation. Urgent transcutaneous gastric decompression could also be wanted or intraabdominal clamping of the distal esophagus through an belly incision. Invasive blood stress monitoring is beneficial since intraoperative arterial desaturation or hypotension might happen with manipulation of mediastinal constructions. A preductal and postductal pulse oximeter may be helpful in diagnosing an intracardiac shunting.
Floxin 200 mg free shipping
The affected person ought to be stored covered with warmed blankets whenever possible viral load 200 mg floxin purchase visa, and the surroundings must be saved heat enough to make the affected person snug antibiotics for dogs simplicef purchase floxin 200 mg with mastercard. If hypothermia has already developed, using compelled hot air warming is strongly indicated to restore normothermia. Commercial rapid-infusion devices are of great benefit in trauma care, particularly in the presence of hemorrhagic shock. These machines supply advantages when large portions of fluid resuscitation are probably (Box sixty six. Early expertise with these gadgets demonstrated higher patient temperature and reduced acidosis on the conclusion of the initial surgical procedure,212 though speedy infusers may contribute to over infusion of fluids, inappropriately increased arterial blood strain, and contribute to rebleeding. In follow, fluid boluses are given alternately with anesthetics, with the aim of reaching a normal depth of anesthesia with out considerably rising systolic arterial blood stress till active bleeding is controlled. Trauma produces shear forces that lead to main damage to neuronal cell our bodies and axons, and to the vasculature. The pathophysiologic processes of secondary harm embody metabolic failure, oxidative stress, and a cascade of biochemical and molecular occasions leading to each delayed necrotic and apoptotic cell death. Individual medication such as free radical scavengers, antiinflammatory agents, and ion channel blockers have been efficient in animals however have had little impact or yielded disappointing ends in human trials. In patients with bilateral mounted and dilated pupils, an excellent consequence was still seen in 8% of sufferers. Extubation of the trachea could be undertaken if the patient is hemodynamically stable and appropriately responsive after the diagnostic workup. Treatment of secondary mind injury is accomplished by early correction and subsequent avoidance of hypoxia, prompt intravascular fluid resuscitation, and administration of related injuries. The timing of indicated noncranial surgical procedure in these sufferers with average harm not requiring decompressive craniectomy is very controversial as a result of early surgical procedure can improve the episodes of hypoxia and hypotension. The aim of therapy is to maintain cerebral perfusion stress 60 to 70 mm Hg by help of the circulation and management of intracranial pressure. Previously, intubation of the trachea earlier than arriving on the hospital was advocated because offering a definitive airway allowed sufficient oxygen to be delivered to the brain, benefiting the sufferers. Yet worsened neurologic outcomes have been described with attempts at prehospital tracheal intubation in adult trauma sufferers. The sine qua non is adequacy of systemic oxygenation, by no matter means this will finest be achieved. A variety of monitoring gadgets have been used to assess adequacy of cerebral oxygenation, together with jugular venous oxygen saturation, positron emission tomography, near-infrared spectroscopy, and direct brain tissue oxygenation (Pbto2) monitoring. However, these recommendations ought to be taken in context and modified in the face of unstable clinical circumstances such as an increasing mass lesion or indicators of imminent herniation. Therefore fluid resuscitation is the mainstay of remedy, adopted by vasoactive infusions as needed. The perfect fluid has not been defined, but perhaps hypertonic saline solutions are optimal. Correction of anemia from acute blood loss is the precedence; nonetheless, an optimal goal hematocrit has not been defined. Early studies demonstrated that reasonable, systemic hypothermia reduces both the rate of cerebral edema and mortality after cortical injury in laboratory animals. The beforehand described therapies ought to be continued all through the perioperative interval, together with positional therapy (when possible), aggressive hemodynamic monitoring and resuscitation, administration of osmotic brokers (with attention to sustaining euvolemia), and deep levels of analgesia and sedation. Appropriate anesthetic selections embody opioids and low concentrations of risky anesthetics. Most spinal injuries are within the decrease cervical backbone, just above the thorax, or within the upper lumbar region, just below the thorax. The vertebral column is split longitudinally into three columns: anterior, center, and posterior; accidents to any two of those three columns suggest biomechanical instability. Patients with unstable cervical spine injuries who meet standards for emergency intubation should undergo rapid sequence induction (see part above on protection of the cervical spine). However, clinically significant harm to the cervical spinal wire can happen in the absence of seen skeletal damage. Incomplete deficits could additionally be worse on one aspect than the other and may enhance quickly in the first minutes after harm. Complete deficits-representing total disruption of the spinal cord at one level-are rather more ominous, with usually little enchancment seen over time. Spine accidents above the level of T4 to T6 are accompanied by vital hypotension due to inappropriate vasodilatation, lack of cardiac inotropy, and bradycardia resulting from denervation of the cardiac accelerator fibers (neurogenic shock). The Eastern Association for the Surgery of Trauma has revealed guidelines regarding which sufferers require cervical spine radiographs, which views and studies must be obtained, and tips on how to determine the absence of serious ligamentous injury in an obtunded patient. Many establishments nonetheless require magnetic resonance imaging to rule out ligamentous harm in this affected person inhabitants. The mostly missed cervical fractures are on the C1 to C2 and C7 to T1 ranges, often the results of insufficient imaging. Early intubation of the trachea is nearly universally required for patients with cervical backbone fracture and quadriplegia. Mechanical trauma to the spinal cord is exacerbated by systemic hypoperfusion or hypoxia. Early tracheal intubation is beneficial and, if elective, often may be achieved by awake fiberoptic bronchoscopy or video laryngoscopy before hypoxia renders the patient anxious and uncooperative. All sufferers with accidents at C5 and above required intubation, and 71% of these progressed to tracheostomy. First and foremost is the need for intubation of the trachea in a affected person with a recognized damage to the cervical backbone. Oral intubation could additionally be more difficult technically but shall be of higher value if the affected person stays mechanically ventilated. Again, in comparative research of direct laryngoscopy, videolaryngoscopy, fiberoptic examination, blind nasal intubation, or cricothyrotomy in sufferers with recognized cervical cord or backbone injuries, no difference is seen in neurologic deterioration with approach used and no clear evidence exists that direct laryngoscopy worsens outcome. The essential idea is to efficiently obtain tracheal intubation whereas minimizing movement of the cervical backbone and preserving the power to assess neurologic function after positioning. Timing for surgery means that earlier decompression could enhance outcomes in some patients, particularly those with cervical accidents, though the precise timing remains controversial. Hypotension from neurogenic shock is characterized by an inappropriate bradycardia ensuing from loss of cardiac accelerator function and unopposed parasympathetic tone. However, this case may be difficult to distinguish from hypotension resulting from acute hemorrhage, and a trial of fluid administration is still indicated, subject to the end points of resuscitation listed earlier. This method is very controversial but stays a suggestion in therapy based on published pointers. Therefore the objective of fracture management in the multisystem trauma patient revolves round restoring musculoskeletal anatomy that allows for mobilization, pulmonary toilet, and adequate ache management. In the patient with isolated extremity or hip fracture with out polytrauma, the proof stays clear that early definitive fracture care improves outcomes. Within the United Kingdom, surgery within 36 hours is a quality-of-care indicator though adherence to these pointers is incomplete.
Purchase 400 mg floxin amex
Cardiovascular criteria for epidural check dosing in sevoflurane- and halothane-anesthetized children antibiotic resistance in humans floxin 200 mg buy fast delivery. Caudal epidural block: A evaluation of test dosing and recognition of systemic injection in youngsters virus x reader dmmd order floxin 400 mg without a prescription. Pupillary reflex dilation and skin temperature to assess sensory degree throughout mixed general and caudal anesthesia in kids. Continuous peripheral nerve blockade for inpatient and outpatient postoperative analgesia in youngsters. Continuous peripheral nerve block for postoperative ache control at residence: A potential feasibility study in children. Does the addition of fentanyl to bupivacaine in caudal epidural block have an impact on the plasma stage of catecholamines in children The efficacy of caudal morphine or bupivacaine mixed with general anesthesia on postoperative pain and neuroendocrine stress response in youngsters. Evaluation of caudal anaesthesia performed in conscious ex-premature infants for inguinal herniotomies. Epidural-Anesthesia through Caudal Catheters for Inguinal Herniotomies in Awake Ex-Premature Babies. Thoracic epidural catheters positioned by the caudal route in infants: the significance of radiographic affirmation. Thoracic epidural catheter placement via the caudal method in infants by utilizing electrocardiographic steering. Caudal injectate can be reliably imaged using transportable ultrasound - a preliminary examine. Caudal Anesthesia in Pediatric-Surgery - Success Rate and Adverse-Effects in 750 Consecutive Patients. A Comparison of High Volume/Low Concentration and Low Volume/High Concentration Ropivacaine in Caudal Analgesia for Pediatric Orchiopexy. Determining the accuracy of caudal needle placement in children: a comparison of the swoosh check and ultrasonography. Ultrasound Evaluation of the Sacral Area and Comparison of Sacral Interspinous and Hiatal Approach for Caudal Block in Children. Investigation of the radiological relationship between iliac crests, conus medullaris and vertebral level in kids. Thoracic epidural catheter within the administration of a kid with an anterior mediastinal mass: a case report and literature evaluate. Anesthetic administration for the minimally invasive Nuss procedure in 21 sufferers with pectus excavatum. Double epidural catheter with ropivacaine versus intravenous morphine: A comparison for postoperative analgesia after scoliosis correction surgery. Bacterial colonization and an infection rate of steady epidural catheters in children. Epidural catheter placement in neonates: Sonoanatomy and feasibility of ultrasonographic steerage in time period and preterm neonates. The Lumbosacral Epidural Block - a Modified Taylor Approach for Abdominal Urologic Surgery in Children. Age-Related-Changes in Blood-Pressure and Duration of Motor Block in Spinal-Anesthesia. Spinal anesthesia with bupivacaine decreases cerebral blood circulate in former preterm infants. Spinal anesthesia in youngsters with isobaric local anesthetics: Report on 307 sufferers under 13 years of age. Use of spinal anaesthesia in paediatric sufferers: a single centre experience with 1132 cases. Postoperative analgesia after spinal blockade in infants and kids present process cardiac surgery. Apnea after Awake Regional and General Anesthesia in Infants: the General Anesthesia Compared to Spinal Anesthesia Study-Comparing Apnea and Neurodevelopmental Outcomes, a Randomized Controlled Trial. The security and efficacy of spinal anesthesia for surgery in infants: the Vermont Infant Spinal Registry. Spinal anesthesia in 62 untimely, former-premature or young infants-technical elements and pitfalls. Postdural puncture headache and transient neurologic signs in kids after spinal anaesthesia utilizing slicing and pencil level paediatric spinal needles. The "axillary tunnel": An anatomic reappraisal of the limits and dynamics of spread during brachial plexus blockade. Acute and nonacute complications associated with interscalene block and shoulder surgical procedure - A potential study. A Randomized trial of ultrasound-guided brachial plexus anaesthesia in higher limb surgery. Ultrasound Imaging for Regional Anesthesia in Infants, Children, and Adolescents A Review of Current Literature and Its Application in the Practice of Extremity and Trunk Blocks. A New Parascalene Approach to the Brachial-Plexus in Children - Comparison with the Supraclavicular Approach. Ultrasonographic examination to get your hands on the optimum higher arm position for coracoid approach to infraclavicular brachial plexus block-a volunteer study. Assessment of topographic brachial plexus nerves variations at the axilla using ultrasonography. A comparison of traditional digital blocks and single subcutaneous palmar injection blocks on the base of the finger and a meta-analysis of the digital block trials. Continuous psoas compartment blocks after main orthopedic surgery in youngsters: A potential computed tomographic scan and scientific research. Continuous psoas compartment block for postoperative analgesia after complete hip arthroplasty: New landmarks, technical tips, and medical evaluation. Lumbar plexus in children - A sonographic examine and its relevance to pediatric regional anesthesia. Continuous posterior lumbar plexus block for acute postoperative ache management in younger children. Continuous Femoral Nerve Blockade for Analgesia in Children with Femoral Fractures. Paut O, Sallabery M, Schreiber-Deturmeny E, Remond C, Bruguerolle B, Camboulives S. Continuous fascia iliaca compartment block in kids: A prospective analysis of plasma bupivacaine concentrations, pain scores, and side effects. Incisional Continuous Fascia Iliaca Block Provides More Effective Pain Relief and Fewer Side Effects than Opioids After Pelvic Osteotomy in Children. Comparison of the Fascia Iliaca Compartment Block with the 3-in-1 Block in Children. Sciatic-Nerve Blocks in Children - Comparison of the Posterior, Anterior, and Lateral Approaches in 180 Pediatric-Patients. Continuous lateral sciatic blocks for acute postoperative pain management after major ankle and foot surgery. Continuous popliteal sciatic nerve block: An unique technique to provide postoperative analgesia after foot surgical procedure.
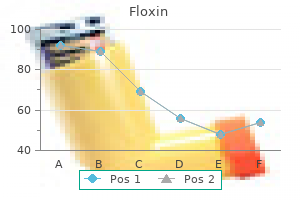
Radix Paeoniae Rubra (Peony). Floxin.
- Are there any interactions with medications?
- Are there safety concerns?
- How does Peony work?
- Dosing considerations for Peony.
- What is Peony?
- Muscle cramps, gout, osteoarthritis, breathing problems, cough, skin diseases, hemorrhoids, heart trouble, stomach upset, spasms, nerve problems, migraine headache, chronic fatigue syndrome (CFS), and other conditions.
Source: http://www.rxlist.com/script/main/art.asp?articlekey=96082
Generic 200 mg floxin amex
Comparative results of laryngeal mask airway and endotracheal tube insertion on intraocular pressure in children p11-002 antibiotic 200 mg floxin order with mastercard. Intraocular stress modifications after peribulbar injections with and without ocular compression antibiotics for streptococcus viridans uti generic floxin 200 mg otc. Risks and advantages of anticoagulant and antiplatelet medicine use earlier than cataract surgical procedure. The Cataract National Dataset digital multicentre audit of 55, 567 operations: antiplatelet and anticoagulant drugs. Hemorrhagic issues from glaucoma surgical procedure in sufferers on anticoagulation remedy or antiplatelet remedy. Risk of intraocular bleeding with novel oral anticoagulants compared with warfarin a scientific evaluation and meta-analysis. Risk of substantial intraocular bleeding with novel oral anticoagulants systematic review and meta-analysis. Ophthalmic regional blockade complication price: a single heart audit of 33,363 ophthalmic operations. Impact of anesthesia on hospital mortality and morbidities in geriatric patients following emergency hip fracture surgery. Comparison of general anesthesia and monitored anesthesia care in sufferers present process breast most cancers surgical procedure utilizing a mix of ultrasound-guided thoracic paravertebral block and native infiltration anesthesia: a retrospective study. Comparison of scientific outcomes, patient, and surgeon satisfaction following topical versus peribulbar anesthesia for phacoemulsification and intraocular lens implantation: a randomized, managed trial. Monitored anesthesia care with dexmedetomidine: a prospective, randomized, double-blind, multicenter trial. Sole use of dexmedetomidine has limited utility for conscious sedation throughout outpatient colonoscopy. Propofol versus propofol-ketamine sedation for retrobulbar nerve block: comparison of sedation high quality, intraocular strain modifications, and restoration profiles. Remifentanil versus remifentanil/midazolam for ambulatory surgery throughout monitored anesthesia care. The impact of the interaction of propofol and alfentanil on recall, lack of consciousness, and the bispectral index. The comparative amnestic results of midazolam, propofol, thiopental, and fentanyl at equisedative concentrations. Concurrent ketamine and alfentanil administration: pharmacokinetic considerations. Comparative analgesic and mental results of increasing plasma concentrations of dexmedetomidine and alfentanil in people. A novel mixture of propofol, alfentanil, and lidocaine for regional block with monitored anesthesia care in ophthalmic surgical procedure. Population pharmacokinetics of dexmedetomidine throughout long-term sedation in intensive care patients. Obesity as a threat issue sedation-related problems during propofol-mediated sedation for advanced endoscopic procedures. Evolution of modifications in upper airway collapsibility during gradual induction of anesthesia with propofol. The laryngeal masks airway for intraocular surgical procedure: effects on intraocular pressure and stress responses. Effects of propofol, etomidate, and thiopental on intraocular stress and hemodynamic responses in phacoemulsification by insertion of laryngeal mask airway. Prospective comparison of use of the laryngeal mask and endotracheal tube for ambulatory surgery. Thresholds and acute kidney and myocardial injury after noncardiac surgical procedure a retrospective cohort analysis. Perioperative stroke and associated mortality after noncardiac, nonneurologic surgery. Association between intraoperative hypotension and hypertension and 30-day postoperative mortality in noncardiac surgery. Tracheal extubation of deeply anesthetized pediatric patients: a comparability of isoflurane and sevoflurane. Tracheal extubation of deeply anesthetized pediatric patients: a comparability of desflurane and sevoflurane. Effect of propofol and sevoflurane on coughing in smokers and non-smokers awakening from common anaesthesia on the end of a cervical spine surgical procedure. Prevention of endotracheal tube-induced coughing throughout emergence from common anesthesia. The results of lidocaine spray and intracuff alkalinized lidocaine on the incidence of cough at extubation: a double-blind randomized managed trial. Influence of GlideScope assisted endotracheal intubation on intraocular strain in ophthalmic patients. The growth and validation of a threat score to predict the probability of postoperative vomiting in pediatric sufferers. Subhypnotic propofol infusion plus dexamethasone is more practical than dexamethasone alone for the prevention of vomiting in children after tonsillectomy. Preterm infants are more susceptible to issues following minor surgical procedure than are term infants. Ophthalmic pain following cataract surgical procedure: a comparison between local and common anaesthesia. Factors independently associated with increased risk of pain development after ophthalmic surgical procedure. Factors associated with postoperative ache and analgesic consumption in ophthalmic surgery: a systematic evaluation. Chronic opioid use after surgery: implications for perioperative management in the face of the opioid epidemic. Deaths from unintentional injury amongst adults aged sixty five and over: United States, 2000�2013. Local anesthesia with intravenous sedation for surgical repair of selected open globe injuries. The results of steep Trendelenburg positioning on intraocular pressure throughout robotic radical prostatectomy. Effect of dexmedetomidine premedication on the intraocular pressure changes after succinylcholine and intubation. Effects of systemic administration of dexmedetomidine on intraocular pressure and ocular perfusion strain throughout laparoscopic surgical procedure in a steep Trendelenburg place: prospective, randomized, double-blinded study. Endotracheal intubation in an awake affected person with a flexible bronchoscope is commonly used when intubation following the induction of general anesthesia could be imprudent. When the airway dysfunction is so extensive that awake endotracheal intubation is impractical, tracheostomy carried out utilizing local anesthesia (with or without judicious intravenous sedation) is normally the best option.
Syndromes
- Thin and brittle hair
- You have numbness, tingling, or weakness in your arms or legs
- Fever that does not go away
- Normal Bleeding time
- High: 160 - 189 mg/dL
- Suicide
Floxin 400 mg generic otc
Awake-caudal anesthesia has been described however normally requires substantial extra sedation antibiotics pancreatitis floxin 200 mg generic online. A caudal native anesthetic block antibiotics for acne in india cheap 400 mg floxin mastercard, ilioinguinal block, or native infiltration of local anesthetic by the surgeon can all provide adequate analgesia and obviate the necessity for opioids. Cleft Lip and Palate Cleft lip and palate are relatively common congenital malformations. Approximately one third are related to a variety of different syndromes so careful and thorough preoperative evaluation is required. Cleft lip is normally repaired at 3 to 6 months of age whereas the palate is repaired at 9 to 12 months of age. In children with large or bilateral clefts, the tongue may impinge within the cleft obstructing the airway, or the laryngoscope blade may fall into the cleft. Postoperative analgesia relies on regular acetaminophen and the considered use of opioids. This could also be asymptomatic or result in dyspnea, orthopnea, pain, cough, or superior vena cava syndrome. These youngsters frequently current for a biopsy of the lesion or different lymph node which, for correct diagnosis and applicable management, must be obtained previous to any chemotherapy or radiotherapy. The major anesthesia concern is profound cardiorespiratory collapse and dying on induction of anesthesia. The actual etiology of this collapse is unsure, however most likely pertains to increasing compression of main vessels, heart, and/or the airway. As a outcome, some pediatric anesthesiologists advocate avoiding neuromuscular blocking agents and maintaining spontaneous respiration. Echocardiography may be useful to decide if positioning may need any influence on compression of vessels and cardiac function. In severe cases, every effort ought to be made to get hold of the biopsy with out basic anesthesia in order that further administration options may be determined. Inhaled Foreign Body Inhalation of overseas our bodies is a significant supply of morbidity and mortally in younger children, occurring most incessantly in youngsters ages 1 to 2 years. The airway obstruction may be acute, inflicting significant respiratory misery and require pressing management; nonetheless, typically the diagnosis is delayed. The acute choking episode could not have been witnessed and the child might current late with signs of pneumonia. The urgency of removing is dependent upon the diploma of respiratory signs and the likely location of the obstruction. Clear, effective, and ongoing communication with the surgeon earlier than and throughout the procedure is paramount. Often anticholinergic brokers are given previous to induction to cut back secretions and steroids given to cut back airway swelling. Ideally, spontaneous air flow is maintained to cut back the risk of constructive air flow pushing the object further distally, which makes extraction extra technically challenging. Once the child is deeply anesthetized, local anesthetic must be immediately utilized to the glottis and trachea. Anesthesia may be maintained with volatile brokers by way of the bronchoscope or with a propofol infusion. Remifentanil infusion may be used to assist obtund airway reflexes but should be used judiciously to keep away from undesirable apnea. Muscle rest could also be required in some conditions but relaxants ought to by no means be given before establishing that optimistic stress air flow is secure. Tonsillectomy and Obstructive Sleep Apnea Tonsillectomy and/or adenoidectomy are a few of the more widespread surgical procedures in children. While not performed as usually as they had been up to now, the commonest indications embody recurrent an infection and airway obstruction, together with obstructive sleep apnea. Postoperative nausea and vomiting is widespread after this surgical procedure and prophylactic antiemetics must be used. Dexamethasone is often given to scale back swelling and emesis; nevertheless, dexamethasone ought to by no means be given if lymphoma is a probable reason for tonsillar hypertrophy as dexamethasone may produce lethal hyperkalemia from tumor lysis. Such infiltration should be done cautiously as injection into the main vessels beneath the tonsillar bed might result in seizures or cerebral infarction. Tonsillectomy is related to vital ache for as much as 10 days or extra postoperatively. Bleeding after tonsillectomy might happen instantly postoperatively or within the early days after discharge. Minor bleeding may be managed conservatively however active ongoing bleeding requires anesthesia for surgical management. Anesthesia for a bleeding tonsil requires consideration of: (1) acute hypovolemia associated with huge blood loss-these children must at all times be adequately resuscitated earlier than anesthesia; (2) presence of a full stomach-the youngster might have swallowed a appreciable quantity of blood; and (3) a probably difficult airway management and laryngoscopy due to energetic bleeding and airway swelling. Children scheduled for tonsillectomy/adenoidectomy frequently have a level of obstructive sleep apnea. Most youngsters, nonetheless, will have surgical procedure for obstructive signs without having had a proper polysomnogram. Thus a wide selection of different scores based on overnight oximetry, youngster factors, and degree of symptoms have been developed to assess diploma of obstruction and therefore perioperative threat. Children with comorbidities such as Down syndrome, or craniofacial abnormalities, youthful age (>3 years), or obesity must also be thought of for overnight admission and monitoring. Codeine is no longer beneficial for analgesia after tonsillectomy/adenoidectomy as there have been stories of deaths after tonsillectomy related to altered conversion of the prodrug codeine to morphine. The impact of anesthesia on the biopsy specimen additionally wants consideration: If a contracture check is planned then a "nontriggering" anesthetic is required. Some metabolic clinicians favor propofol to be prevented if a mitochondrial enzyme evaluation is planned. Muscle Biopsy Children might require muscle biopsy to help the prognosis of a myopathy or other neurodegenerative condition. There are a broad vary of myopathies that current a range of issues for anesthesia (see Chapter 35). These include existing compromised cardiac or respiratory perform, developmental delay, poor dietary status, and risks for malignant hyperthermia, rhabdomyolysis, and propofol infusion syndrome. Thorough preoperative assessment is important, including an assessment of respiratory and cardiac operate. Halogenated volatile anesthetics have been associated with rhabdomyolysis with muscular dystrophy, significantly Duchenne and Becker muscular dystrophy, younger kids, and kids with an elevated creatinine kinase. Child With Developmental Disability Children with developmental disability usually tend to require anesthesia for surgical procedure and a spread of different procedures. For example, most studies looking at premedication exclude children with developmental disability, regardless of the reality that they could want it, and profit from it more than different children. A key aspect within the perioperative care of those children is to appreciate that they represent a heterogeneous group with a variety of disabilities and varying scientific wants.
Generic 400 mg floxin fast delivery
Supplemental intravenous crystalloids for the prevention of postoperative nausea and vomiting: quantitative review antibiotics quotes floxin 400 mg buy overnight delivery. Metoclopramide within the prevention of postoperative nausea and vomiting: a quantitative systematic evaluation of randomized virus test floxin 400 mg cheap with mastercard, placebo-controlled studies. Prevention of postoperative nausea and vomiting by metoclopramide combined with dexamethasone: randomised double blind multicentre trial. Low-dose droperidol (1 mg or 15 g kg-1) for the prevention of postoperative nausea and vomiting in adults: quantitative systematic review of randomised controlled trials. Dimenhydrinate for prophylaxis of postoperative nausea and vomiting: a metaanalysis of randomized managed trials. Meclizine together with ondansetron for prevention of postoperative nausea and vomiting in a high-risk inhabitants. Perspectives on transdermal scopolamine for the remedy of postoperative nausea and vomiting. Transdermal scopolamine decreases nausea and vomiting following cesarean section in sufferers receiving epidural morphine. Scopolamine for prevention of postoperative nausea in gynecologic laparoscopy, a randomized trial. The impact of timing of ondansetron administration on its efficacy, cost-effectiveness, and cost-benefit as a prophylactic antiemetic within the ambulatory setting. Efficacy, doseresponse, and security of ondansetron in prevention of postoperative nausea and vomiting. Pharmacology, pharmacogenetics, and clinical efficacy of 5-hydroxytryptamine sort three receptor antagonists for postoperative nausea and vomiting. Is palonosetron also effective for opioidinduced and post-discharge nausea and vomiting Dexamethasone to stop postoperative nausea and vomiting: an updated metaanalysis of randomized controlled trials. The effect of timing of dexamethasone administration on its efficacy as a prophylactic antiemetic for postoperative nausea and vomiting. Neurokinin-1 receptor antagonists within the prevention of postoperative nausea and vomiting. Fosaprepitant versus ondansetron for the prevention of postoperative nausea and vomiting in sufferers who bear gynecologic belly surgery with patient-controlled epidural analgesia: a prospective, randomized, double-blind examine. The results of intravenous fosaprepitant and ondansetron within the prevention of postoperative nausea and vomiting in sufferers who underwent lower limb surgical procedure: a prospective, randomized, double-blind examine. Rolapitant for the prevention of postoperative nausea and vomiting: a prospective, double-blinded, placebo-controlled randomized trial. A potential randomized double-blind research of the impact of intravenous fluid therapy on adverse outcomes on outpatient surgical procedure. Cost evaluation of office surgical procedure clinic with comparison to hospital outpatient services for laparoscopic procedures. Comparative outcomes analysis of procedures carried out in doctor workplaces and ambulatory surgery facilities. General anesthesia in an office-based plastic surgical facility: a report on more than 23,000 consecutive office-based procedures under basic anesthesia with no vital anesthetic issues. Office-Based Anesthesia: Considerations in Setting Up and Maintaining a Safe Office Anesthesia Environment. Recovery profile, costs, and affected person satisfaction with propofol and sevoflurane for fast-track office-based anesthesia. Fast-track office-based anesthesia: a comparison of propofol versus desflurane with antiemetic prophylaxis in spontaneously respiratory sufferers. Statement on affected person security rules for office-based surgical procedure utilizing reasonable sedation/analgesia, deep sedation/analgesia, or common anesthesia. Ability of patients to retain and recall new info in the post-anaesthetic recovery interval: a potential medical study in day surgery. A post-anesthetic discharge scoring system for home readiness after ambulatory surgical procedure. Ambulatory surgical procedure sufferers may be discharged earlier than voiding after short-acting spinal and epidural anesthesia. Pain and bleeding are the principle determinants of unscheduled contacts after outpatient tonsillectomy. Outcomes of decreased postoperative stay following outpatient pediatric tonsillectomy. Evaluation of postoperative recovery in day surgery sufferers utilizing a cell phone software: a multicentre randomized trial. Cost-effectiveness of a systematic e-assessed follow-up of postoperative restoration after day surgical procedure: a multicentre randomized trial. Call to care: the impact of 24-hour postdischarge phone follow-up within the remedy of surgical day care sufferers. American Society of Anesthesiologists Committee on Ambulatory Surgical Care and the Task Force on Office-Based Anesthesia. They seldom required involvement of an anesthesia supplier; extra generally sedation, if needed, was provided by a nurse supervised by the proceduralist. Anesthesiology support can be required as a outcome of sufferers with underlying medical circumstances and rising age are actually being supplied procedures that had been previously unavailable to them. Although some of these "minimally invasive" procedures are thought-about to be lower risk for the patient, the anesthetic issues are sometimes very advanced with important potential for physiologic modifications that require intensive administration. Fifty percent of distant location claims involved monitored anesthesia care-a reflection of the importance of close monitoring and management of patients by a skilled anesthesia provider who is in a position to transition the management to embody initiation of common anesthesia or other interventions to tackle complex medical issues. These data underscore the necessity for conscientious preparation and greater vigilance when caring for patients in these environments. The aim of anesthesia providers have to be to mitigate systemic components that contribute to the excess hazard in these environments. The intention is to promote awareness that encourages preemptive planning, and equips anesthesia suppliers with a vocabulary with which to set up effective dialogue to cultivate a collaborative practice with colleagues and to maximize the protection of patients. Given the bodily, medical, political, and financial challenges which will arise and which are usually unanticipated, the aim should be to adapt to the model new environments. We must additionally try to evolve our anesthesia follow to meet the demands of a altering affected person population. In addition, the increasing incidence of medically complex cases with sufferers needing urgent intervention, however missing periprocedural evaluation, can create challenges. This increases the time lag between a request for help and the arrival of help, each with technological and medical problems. In addition, the shortage of nearby provides might exacerbate the timely decision of widespread electrical and mechanical malfunctions or complicate the decision of a medical emergency. This scenario demands that care be taken earlier than the start of the procedure to be positive that gear is provided and dealing and that backup options (emergency provides, troublesome airway equipment) are functioning and readily available. Inadequate access to the affected person may be exacerbated if the area around the head of the patient is crowded because of constraints of the room and gear.
200 mg floxin best
However treatment for uti in guinea pigs buy 200 mg floxin amex, its clearance in neonates is approximately one third of that in adults owing to immature elimination pathways44 and a variety of other cases of respiratory despair in neonates and small infants have been reported45 antibiotics for dogs clavamox generic 200 mg floxin amex,forty six; this additive must be prevented during the first 6 months of life. A pain-free postoperative course improves the morale of the affected person, the household, and the nurses. Occasionally, unfavorable psychological effects could be observed-persistent motor (even sensory) blocks postoperatively may be horrifying to some kids (3-5 years of age especially) and their parents even though exact explanations had been given preoperatively as to the expected course of events through the postoperative period. Offering pleasant environmental situations, empathy, and extra explanations on native anesthetic pharmacology can scale back this postoperative anxiousness. Patients with facial deformities, microstomia, metabolic disorders like Hurler and Hunter syndromes and mandibular hypoplasia can be troublesome to intubate, thus making common anesthesia less safe. Also, infants with epidermolysis bullosa are extremely difficult to handle under basic anesthesia; occasionally, regional block procedures may represent an alternative with decrease morbidity. There are knowledge to show that performing regional anesthesia in youngsters can be done with them asleep safely. Occasionally, such a management approach can be thought of in children in danger for extreme complications throughout general anesthesia from certain problems, such because the following62: Intraoperative and Postoperative Analgesia and Procedural Pain Analgesia is currently the principle indication for regional blocks in children as a end result of they provide the best risk-benefit ratio for many outpatient and inpatient surgeries: orthopedic (including scoliosis surgery), thoracic, urologic, and higher and lower belly surgical procedures. Procedural pain can easily be anticipated and thus prevented largely by topical anesthesia or infiltration techniques. Virtually all techniques of regional anesthesia have been reported in this ultimate administration of ache in kids, from epidural analgesia to intrathecal infusions to celiac or brachial plexus block. Sympathetic blockade is important to protect and improve blood provide to an upper or decrease extremity in a context of severe trauma. Also, continuous epidural blockade proved to be effective in treating vascular insufficiency ensuing from Kawasaki illness, unintentional intra-arterial injection of an anesthetic drug,85 penile block with an area anesthetic containing epinephrine, and extreme frostbite. Axillary and stellate ganglion blocks have additionally successfully treated acute vascular insufficiency of the upper limb. Depending on the scientific situation of the patient and the possibility to treatment (at least temporarily) the impeding disorder, a regional block may be thought-about regardless of the existence of a contraindication. Also, some authors contemplate it acceptable to carry out a caudal block in kids with shunt gadgets under safety of antibioprophylaxis. Local pores and skin infection on the puncture web site ought to be considered before performing a peripheral nerve block, especially if a catheter is implanted. Patients at Risk for Compartment Syndrome Because pain is among the cardinal symptoms of a compartment syndrome, any ache remedy, together with regional anesthesia, is often claimed to be contraindicated because it could suppress this manifesting symptom, thus delaying the rescuing surgery. The procedure is easy and almost inexpensive, requiring only a venous cannula, an intravenous line, and a pressure gauge (as for central venous strain measurement). Regional anesthesia has been shown to improve symptoms in youngsters with sickle cell illness and decrease their ache. The prognosis have to be suspected if a clump of hairs or a dystrophic lesion of the skin is present at the lower extremity of the spinous process line or within the case of minor neurologic disorders involving pelvic nerves (minimal sphincter disorders, perineal dysesthesia). Preexisting central nervous system issues and degenerative axonal ailments have long been thought of to be contraindications, a minimum of relative, even though no data assist the speculation that a regional block could worsen their course. Inappropriate needle insertion damaging the nerve and surrounding anatomic structures 2. Injection of neurotoxic solutions (syringe mismatch, epinephrine close to a terminal artery) 4. Leakage around the puncture website, especially when a catheter has been introduced, which may trigger partial block failure and favor bacterial contamination (very rare) these local problems are easily avoidable by utilizing enough devices and making use of normal precautions (appropriate dressing and bacterial precautions). Tunneling the catheter and applying a slightly compressive dressing can reduce leakage around the catheter. Myelin, effective protection of nerve roots, is less abundant or absent in youngsters, potentially making the nerves extra delicate to native anesthetics. In animals, it has been clearly demonstrated that the sensitivity of nerve fibers to native anesthetics is inversely correlated with age. The myotoxicity of local anesthetics has been previously demonstrated in humans and animals,102 primarily through mitochondrial injury. The plasma concentration of this protein is low at delivery, and tends to enhance with the age of the child to attain values equal to these of adults on the age of 10 months. Systemic problems may be life threatening and ought to be managed in the same means as in adults. Even if poisonous occasions occur with ropivacaine, small doses of epinephrine ought to produce rapid restoration. Impaired ventricular conduction is the primary manifestation of native anesthetic toxicity. Treatment contains oxygenation, cardiac therapeutic massage, and epinephrine, which is given in small incremental boluses beginning with 1 to 2 g/kg. Although resuscitation measures have to be initiated instantly, the specific treatment of local anesthetic toxicity is rapid administration of Intralipid. Early indicators of neurologic toxicity (tinnitus, malaise, metallic taste in the mouth) are sadly masked by common anesthesia. The primary issues are heart conduction problems, cardiac arrhythmias (bradycardia or tachycardia), and atrioventricular block. In 1996, the 1-year prospective research of the FrenchLanguage Society of Pediatric Anesthesiologists evaluated 85,412 pediatric anesthetic procedures, together with 24,409 involving regional anesthesia. In 2000, the Australian Incident Monitoring Study112 included 2000 claims involving a hundred and sixty pediatric instances with a regional block procedure (83 epidurals, 42 spinals, 14 brachial plexus, four Bier blocks, three ophthalmic blocks, and 14 local infiltrations). The largest single cause of complications was circulatory problems; 24 drug errors (including 10 "mistaken drugs" and 14 "inappropriate use") were discovered. In 2007, the British National Pediatric Epidural Audit92 reported ninety six incidents in 10,633 epidural blocks carried out, as follows: Fifty-six (0. Four sufferers developed a compartment syndrome, however the condition was not masked by the epidural infusion. From November 2005 to October 2006, a large epidemiologic study recorded the characteristics and developments of regional anesthesia in kids in forty seven French hospitals. A latest 1-year potential survey of regional anesthesia evaluated issues and unwanted facet effects in 31,132 cases of regional anesthesia. Age was additionally a risk issue, as a outcome of the incidence of issues was larger earlier than 6 months of life than after (0. Fifteen circumstances of cardiotoxicity have been observed, of which 87% occurred with a central block. No everlasting neurologic deficits have been reported; however the risk of transient neurologic deficit was 2. The majority of these issues outcome from insufficient precautions at the time of the block process (drug errors) and postoperatively (pressure sores). Caudal anesthesia has been carried out in the past with virtually all kinds of needles. This is not acceptable, and only short beveled needles (Crawford needles) with a guide sealing their lumen or intravenous cannulas with an introducer needle ought to be used.