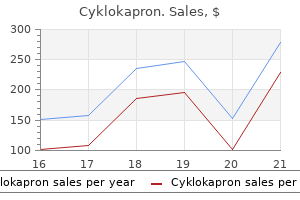
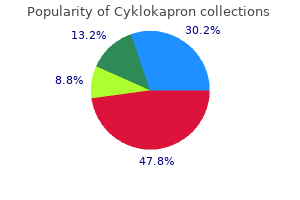
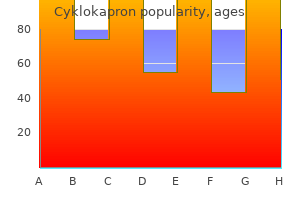
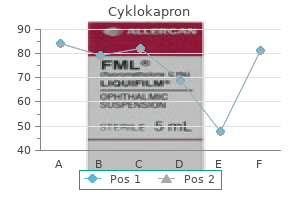
Cyklokapron dosages: 500 mg
Cyklokapron packs: 30 pills, 60 pills, 90 pills, 120 pills, 180 pills, 270 pills

Cyklokapron 500 mg line
Greater than 40% of the patients met the prognosis of systemic inflammatory response syn drome in each teams medications affected by grapefruit order 500 mg cyklokapron with amex. Treatment response (20% reduction in the measurement of the erythema) at 48�72 hours was demonstrated in 81 medications not to take after gastric bypass cyklokapron 500 mg purchase line. Overall, this examine demonstrated that the therapy response of a singledose dalbavancin reg imen was noninferior compared with the twodose routine. The number of catheters eliminated or changed was similar between therapy arms, however more antibioticimpregnated catheters had been used in the vancomycin group (56%) than in the dalbavancin group (30%). Dimerization and membrane anchors in extracellular concentrating on of vancomycin group antibiotics. In vitro exercise of oritavancin and comparator agents in opposition to staphylococci, streptococci and enterococci from scientific infections in Europe and North America, 2011�2014. Activities of dalbavancin against a worldwide collection of 81,673 gram-positive bacterial isolates. Antibacterial susceptibility of vancomycin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus strain isolated on the Hershey Medical Center. Pharmacokinetics, safety and tolerability of single dose dalbavancin in youngsters 12�17 years of age. Audiologic monitoring for potential ototoxicity in a section 1 medical trial of a new glycopeptide antibiotic. Analysis of patients with community-acquired methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus in a section 3 research of dalbavancin versus linezolid for the treatment of complicated pores and skin and delicate tissue infections. Human pharmacokinetics and rationale for once-weekly dosing of dalbavancin, a semi-synthetic glycopeptide. A randomized clinical trial of single-dose versus weekly dalbavancin for remedy of acute bacterial pores and skin and skin construction infection. Extended-duration dosing and distribution of dalbavancin into bone and articular tissue. Safety of dalbavancin within the treatment of skin and skin construction infections: a pooled evaluation of randomized, comparative research. In vitro activities of dalbavancin and nine comparator brokers against anaerobic Grampositive species and Corynebacteria. In vitro activities of dalbavancin and 12 different brokers against 329 aerobic and anaerobic Gram-positive isolates recovered from diabetic foot infections. Evaluation of dalbavancin, tigecycline, minocycline, tetracycline, teicoplanin and vancomycin towards community-associated and multidrug-resistant hospital-associated methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus. Antimicrobial spectrum and efficiency of dalbavancin examined against medical isolates from Europe and North America (2003): preliminary outcomes from a global surveillance protocol. Comprehensive update of dalbavancin activity when examined against uncommonly isolated streptococci, Corynebacterium spp. Spectrum and potency of dalbavancin tested towards 3322 Gram-positive cocci isolated in the United States Surveillance Program (2004). Activities of dalbavancin in vitro and in a rabbit model of experimental endocarditis because of Staphylococcus aureus with or without decreased susceptibility to vancomycin and teicoplanin. Tolerability, pharmacokinetics, and serum bactericidal exercise of intravenous dalbavancin in healthy volunteers. Impact of glycopeptide resistance in Staphylococcus aureus on the dalbavancin in vivo pharmacodynamic goal. In vitro activity of dalbavancin in opposition to drug-resistant Staphylococcus aureus isolates from a world surveillance program. Comparison of community and health care-associated methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus infection. Efficacy and safety of weekly dalbavancin therapy for catheter-related bloodstream infection caused by Gram-positive pathogens. Factors influencing broth microdilution antimicrobial susceptibility test outcomes for dalbavancin, a model new glycopeptide agent. In vitro exercise of dalbavancin and five comparator agents towards common and unusual Gram-positive organisms isolated from most cancers patients. Monte Carlo simulation evaluation of ceftobiprole, dalbavancin, daptomycin, tigecycline, linezolid and vancomycin pharmacodynamics towards intensive care unit�isolated methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus. Pharmacokinetics, security, and tolerability of a single 500-mg or 1000-mg intravenous dose of dalbavancin in wholesome Japanese subjects. Once-weekly dalbavancin versus standard-of-care antimicrobial regimens for remedy of skin and soft-tissue infections. Distribution of radioactivity in bone and related buildings following administration of [14C]dalbavancin to New Zealand white rabbits. Worldwide evaluation of dalbavancin activity and spectrum against over 6000 scientific isolates. Dalbavancin exercise against selected populations of antimicrobial-resistant Gram-positive pathogens. Glycopeptides in scientific development: pharmacological profile and scientific views. New lipoglycopeptides: a comparative evaluate of dalbavancin, oritavancin and telavancin. The addition of the lipophilic aspect chain classifies this agent as a lipoglycopeptide just like oritavancin (see Chapter forty six, Oritavancin) and dalbavancin (see Chapter forty seven, Dalbavancin). The accredited dosage is 10 mg/kg each 24 hours in sufferers 18 years of age or older with adjustment for renal function. The imply protein binding of telavancin is 90%, and the serum half-life is approximately 7�9 hours in sufferers with normal kidney function, which supports once-daily dosing of the compound (Shaw et al. Analogous to vancomycin, telavancin interferes with the bacterial cell wall by binding to the d-alanyl-d-alanine terminal residue of peptidoglycan, thus interfering with peptidoglycan synthesis. However, unlike different glycopeptides, telavancin additionally disrupts cell membrane barrier function by a noncovalent interaction between its lipophilic facet chain and the lipid bilayer of the bacterial cell membrane (Lunde et al. This ultimately causes the disruption of the cell membrane integrity and elevated membrane permeability. Routine susceptibility Telavancin possesses in vitro exercise towards aerobic and anaerobic Gram-positive bacteria but lacks activity against Gram-negative bacteria (Table 48. Additionally, telavancin has activity in opposition to some multidrug-resistant Gram-positive organisms (Laohavaleeson et al. In 2014, the Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute revised the methodology pointers for the susceptibility testing of telavancin. To conform with the suggestions for water-insoluble antimicrobial brokers, the use of dimethyl sulfoxide as a solvent and diluent is required for inventory resolution preparation in addition to the addition of 0. Telavancin also demonstrates activity against heterogeneous vancomycin-intermediate S. Despite this observation, telavancin has demonstrated a low potential and low frequency for selecting resistant mutations amongst S. The first mechanism of action is just like vancomycin and different glycopeptides, by which telavancin inhibits cell wall synthesis by interfering with peptidoglycan synthesis as a consequence of binding to d-alanyl-d-alanine terminal residues. Telavancin is over 10 instances more potent than vancomycin in its inhibition of peptidoglycan synthesis and transglycosylase activity. Telavancin also binds noncovalently to the cell membrane molecule and the lipophilic moiety by immediately interacting with the cell membrane (Lunde et al.
Cyklokapron 500 mg buy mastercard
Correlation of daptomycin bactericidal exercise and membrane depolarization in Staphylococcus aureus medicine quest cyklokapron 500 mg cheap on line. Pharmacokinetic/pharmacodynamic evaluation of the efficacy and security of daptomycin against Staphylococcus aureus symptoms juvenile diabetes buy cheap cyklokapron 500 mg on-line. Characterizing vancomycinresistant Enterococcus strains with varied mechanisms of daptomycin resistance developed in an in vitro pharmacokinetic/pharmacodynamic mannequin. Mode of action of the brand new antibiotic for Gram-positive pathogens daptomycin: comparability with cationic antimicrobial peptides and lipopeptides. Clinical expertise with daptomycin for the remedy of gram-positive infections in youngsters and adolescents. Efficacy of daptomycin lock therapy within the treatment of bloodstream infections related to long-term catheter. Ceftobiprole is superior to vancomycin, daptomycin, and linezolid for remedy of experimental endocarditis in rabbits brought on by methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus. Daptomycin and its immunomodulatory effect: consequences for antibiotic treatment of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus wound infections after coronary heart surgery. Soft tissue and bone penetration abilities of daptomycin in diabetic sufferers with bacterial foot infections. Evaluation of daptomycin, telavancin, teicoplanin, and vancomycin activity in the presence of albumin or serum. Short-course gentamicin together with daptomycin or vancomycin against Staphylococcus aureus in an in vitro pharmacodynamic model with simulated endocardial vegetations. Community- and well being care-associated methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus: a comparison of molecular epidemiology and antimicrobial activities of assorted brokers. In vitro actions of daptomycin, vancomycin, and penicillin against Clostridium difficile, C. Daptomycin antibiotic lock therapy in a rat mannequin of staphylococcal central venous catheter biofilm infections. Daptomycin plus trimethoprim/ sulfamethoxazole mixture remedy in post-neurosurgical meningitis brought on by linezolid-resistant Staphylococcus epidermidis. Daptomycin pharmacokinetics in critically sick patients receiving steady venovenous hemodialysis. Efficacy of daptomycin in the treatment of experimental endocarditis because of prone and multidrug-resistant enterococci. Daptomycin failure in a neutropenic leukemia affected person with Staphylococcus aureus meningitis. The security and efficacy of daptomycin versus other antibiotics for pores and skin and soft-tissue infections: a meta-analysis of randomised managed trials. Interaction of daptomycin with two recombinant thromboplastin reagents leads to falsely extended patient prothrombin time/international normalized ratio results. Multiple-dose pharmacokinetics of daptomycin during steady venovenous haemodiafiltration. Evaluation of ceftaroline, vancomycin, daptomycin, or ceftaroline plus daptomycin towards daptomycin-nonsusceptible methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus in an in vitro pharmacokinetic/pharmacodynamic model of simulated endocardial vegetations. The efficacy of daptomycin versus vancomycin for methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus bloodstream an infection in sufferers with impaired renal operate. Systematic review and meta-analysis of linezolid and daptomycin for therapy of vancomycin-resistant enterococcal bloodstream infections. Single-dose pharmacokinetics and antibacterial exercise of daptomycin, a new lipo-peptide antibiotic, in healthy volunteers. In vivo exercise of daptomycin/colistin mixture therapy in a Galleria mellonella model of Acinetobacter baumannii infection. Daptomycin susceptibility of 833 strains of Gram-positive cocci from a college hospital in Japan (2009�2011). This lipophilic aspect chain in oritavancin allows stronger anchoring of the compound to the cell membrane by way of hydrophobic interactions, thus increasing its half-life (Guskey and Tsuji, 2010) and enhancing its spectrum of activity in addition to the pace of bactericidal exercise (Zhanel et al. The structural variations between oritavancin and vancomycin (the addition of a 4-epi-vancosamine monosaccharide and a 4-chlorobiphenylmethyl substituent on the disaccharide sugar) are indicated by circles. Mechanistically, oritavancin exerts its action by interfering with bacterial cell wall synthesis and altering the cell membrane. Oritavancin inhibits transglycosylation by binding to the d-alanyl-d-alanine terminus of the peptidoglycan chain, like vancomycin. It additionally binds to depsipeptides, together with d-alanyl-d-lactate, in addition to inhibiting transpeptidation by binding to a secondary website, thus retaining activity towards vancomycin-resistant organisms (Patti et al. The addition of a hydrophobic 4-chlorobiphenylmethyl side chain also causes concentration-dependent membrane depolarization and elevated permeability in various resistant phenotypes of S. However, due to its lack of ability to cross the outer membrane, oritavancin possesses no activity against Gram-negative bacteria (Ward et al. In vitro exercise of oritavancin against Gram-positive aerobic and anaerobic bacteria. Against streptococci, oritavancin was much less potent than penicillin however more potent than vancomycin (Mendes et al. Against Gram-positive anaerobes besides Clostridium difficile, oritavancin exhibited potency similar to vancomycin but greater than metronidazole (Citron et al. The ensuing peptidoglycan precursors terminating in d-alanyl-d-lactate or d-alanyl-d-serine as an alternative of d-alanyl-dalanine ultimately prevent the antibiotics from binding and exerting their antibacterial actions. Although there are seven operons or gene clusters that have been described (vanA, vanB, vanC, vanD, vanE, vanG, and vanL) (Henson et al. VanA enterococci are immune to both vancomycin and teicoplanin, whereas VanB organisms retain susceptibility to teicoplanin (Gold, 2001). On the opposite hand, each dalbavancin and telavancin are proof against vanA-producing strains whereas retaining exercise towards vanB-producing isolates (Butler et al. The vanC gene clusters mediate the pathway, producing peptidoglycan precursors with d-alanyl-d-serine termini that lead to poor vancomycin binding and the intrinsic vancomycin resistance of E. Resistance to oritavancin was noticed in serial passage research in opposition to the isolates of S. The first mechanism of action, as for vancomycin, is through the inhibition of the transglycosylation (polymerization) step of cell wall biosynthesis (Zhanel et al. During the synthesis course of, transport of the disaccharide-pentapeptide units throughout the cell membrane occurs in the form of a posh with a lipid carrier. Vancomycin and other glycopeptides bind to the d-alanyl-d-alanine terminus of the growing peptidoglycan chain, thus sterically hindering transglycosylation. Emerging resistance and cross-resistance Resistance to glycopeptides has been properly documented in Enterococcus spp. Via the acquisition and expression of operons, the terminal d-alanine in peptidoglycan precursors is substituted with a terminal 4. Each dimer then has the flexibility to interact with two growing peptidoglycan precursors as a substitute of the single one afforded by a lone molecule. This, in flip, creates an additional binding site to the cytoplasmic membrane (Allen and Nicas, 2003). Unlike vancomycin, oritavancin additionally inhibits transpeptidation by binding to a secondary web site (Kim et al. Therefore, oritavancin exerts antimicrobial activity in opposition to vancomycin-resistant organisms with the termini d-alanyl-d-lactate by alternatively binding to the bridge.
Cyklokapron 500 mg order on line
Good scientific outcomes however high charges of opposed reactions throughout linezolid therapy for critical infections: a proposed protocol for monitoring remedy in complex patients treatment wax 500 mg cyklokapron order fast delivery. Pharmacokinetic/pharmacodynamic factors influencing emergence of resistance to linezolid in an in vitro mannequin symptoms tuberculosis 500 mg cyklokapron quality. Successful treatment and cerebrospinal fluid penetration of oral linezolid in a affected person with coagulase-negative Staphylococcus ventriculitis. Clarithromycin will increase linezolid exposure in multidrug-resistant tuberculosis patients. In vitro synergy between linezolid and clarithromycin towards Mycobacterium tuberculosis. Multicity outbreak of linezolid-resistant Staphylococcus epidermidis associated with clonal unfold of a cfr-containing pressure. Emergence of linezolid resistance in the vancomycin-resistant Enterococcus faecium multilocus sequence typing C1 epidemic lineage. Alveolar diffusion and pharmacokinetics of linezolid administered in steady infusion to critically unwell patients with ventilator-associated pneumonia. Pharmacokinetics and intrapulmonary concentrations of linezolid administered to critically ill sufferers with ventilator-associated pneumonia. Dose dependence of emergence of resistance to linezolid in Enterococcus faecalis in vivo. The emergence of linezolid resistance amongst enterococci in intestinal microbiota of handled patients is unrelated to particular person pharmacokinetic traits. Fatal lactic acidosis after extended linezolid exposure for treatment of multidrug-resistant tuberculosis. In vitro activity of linezolid in opposition to Gram-positive isolates inflicting an infection in continuous ambulatory peritoneal dialysis sufferers. Linezolid susceptibility in Helicobacter pylori, including strains with multidrug resistance. Susceptibilities of Mycobacterium marinum to gatifloxacin, gemifloxacin, levofloxacin, linezolid, moxifloxacin, telithromycin, and quinupristin-dalfopristin (Synercid) in comparison with its susceptibilities to reference macrolides and quinolones. Characterization of novel conjugative multiresistance plasmids carrying cfr from linezolid-resistant Staphylococcus epidermidis clinical isolates from Italy. Synthesis and antibacterial exercise of U-100592 and U-100766, two oxazolidinone antibacterial agents for the potential treatment of multidrug-resistant Gram-positive bacterial infections. Comparison of the effectiveness and safety of linezolid and daptomycin in vancomycin-resistant enterococcal bloodstream an infection: a nationwide cohort study of Veterans Affairs sufferers. In vitro activity of linezolid in opposition to slowly rising nontuberculous Mycobacteria. Successful remedy of disseminated Mycobacterium chelonae an infection with linezolid. Pharmacokinetics of unbound linezolid in plasma and tissue interstitium of critically sick patients after a quantity of dosing utilizing microdialysis. On the goal of a novel class of antibiotics, oxazolidinones, active in opposition to multidrug-resistant Grampositive micro organism. Single- and multipledose pharmacokinetics of linezolid and co-amoxiclav in healthy human volunteers. Experimental research of the efficacy of linezolid alone and in combinations in opposition to experimental meningitis due to Staphylococcus aureus strains with decreased susceptibility to beta-lactams and glycopeptides. Surgical web site infection by Corynebacterium macginleyi in a affected person with neurofibromatosis type 1. Comparative effectiveness of linezolid and vancomycin amongst a nationwide veterans affairs cohort with methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus pneumonia. Predictors of medical success amongst a national Veterans Affairs cohort with methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus pneumonia. Comparative effectiveness of linezolid and vancomycin amongst a national cohort of sufferers contaminated with methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus. Enterococcal isolates carrying the novel oxazolidinone resistance gene optrA from hospitals in Zhejiang, Guangdong, and Henan, China, 2010�2014. Systemic and intracerebral infections of mice with Listeria monocytogenes successfully handled with linezolid. Worrisome trend of new a quantity of mechanisms of linezolid resistance in staphylococcal clones subtle in Italy. Linezolid pharmacokinetics in patients with acute renal failure present process steady venovenous hemodiafiltration. Rhabdomyolysis in a patient treated with linezolid for extensively drug-resistant tuberculosis. In vitro number of mutants of Streptococcus pneumoniae proof against macrolides and linezolid: relationship with susceptibility to penicillin G or macrolides. Linezolid remedy of ventriculoperitoneal shunt infection with out implant elimination. In vitro susceptibility of Actinobaculum schaalii to 12 antimicrobial brokers and molecular analysis of fluoroquinolone resistance. Linezolid, levofloxacin, and vancomycin in opposition to vancomycin-tolerant and fluoroquinolone-resistant Streptococcus pneumoniae in an in vitro pharmacodynamic model. Can intermittent dosing optimize prolonged linezolid therapy of difficult multidrug-resistant tuberculosis Linezolid-resistant clinical isolates of enterococci and Staphylococcus cohnii from a multicentre examine in China: molecular epidemiology and resistance mechanisms. Efficacy of linezolid alone or in combination with vancomycin for therapy of experimental endocarditis as a outcome of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus. Linezolid-induced extreme hyperbilirubinemia in a affected person with decompensated cirrhosis. Daptomycin versus linezolid for remedy of vancomycin-resistant enterococcal bacteremia: systematic evaluation and meta-analysis. Colonization of the tip of a thoracic catheter by Enterococcus faecalis immune to vancomycin and linezolid. Methods for dilution antimicrobial susceptibility exams for bacteria that develop aerobically; Approved Standard M100-520. Hematologic safety profile of linezolid in the early periengraftment period after allogeneic stem cell transplantation. Pharmacokinetic/ pharmacodynamic evaluation of linezolid in hospitalized paediatric 1332 Linezolid patients: a step towards dose optimization via therapeutic drug monitoring and Monte Carlo simulation. Cross-linking within the living cell locates the positioning of action of oxazolidinone antibiotics. Treatment failure of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus endocarditis with linezolid.
Generic cyklokapron 500 mg without a prescription
As explained in Chapter 52 treatment 911 buy 500 mg cyklokapron amex, Gentamicin symptoms youre pregnant buy cyklokapron 500 mg lowest price, this mechanism confers high stage resistance to all aminoglycosides aside from neomycin, apramycin, and streptomycin (Doi and Arakawa, 2007). These methylases are frequently present in affiliation with betalactamases and carbapenems (Jia et al. A latest study showed an necessary increase in the resistance charges of Serratia marcescens nosocomial isolates in European hospitals, each in intensive care units (72. This biofilm can prevent the buildup of bactericidal concentrations of tobramycin at the target. The ordinary dosage for inhalation of tobramycin is 300 mg twice daily (Barker et al. However, dosages of up to 600 mg thrice a day have been utilized in some clinical research. In widespread with gentamicin, tobramycin can be admin istered to adults by intrathecal or intraventricular routes in single day by day doses of 5�10 mg. As with different aminoglycosides, tobramycin could additionally be used for lockin therapy in patients with catheterrelated infec tions caused by prone Gramnegative pathogens, with the aim of saving the catheter. It is usually given at 5 mg/ml with heparin or fibrinolytic brokers (Bookstaver et al. Subinhibitory tobramycin concentrations can suppress the production of exoenzymes by P. In addition, mucoid strains rising in the Similar to gentamicin (see Chapter 52, Gentamicin), tobra mycin is often administered as quickly as every day in a dosage of 4�7 mg/kg of body weight i. Studies in sufferers requiring nephrec tomy present that the buildup of tobramycin in kidney cortical tissue is less with oncedaily administration than with threetimesdaily dosing or continuous infusion (De Broe et al. Oncedaily dosing of tobramycin also leads to much less enzymuria of potential markers of nephrotoxicity than four. Mode of drug administration and dosage 995 do multiple daily administrations (Olsen et al. How ever, medical trials have demonstrated relatively equal effi cacy and safety of as quickly as and multipledaily dosing of tobra mycin (Munckhof et al. Finally, a systematic review of articles published between 1985 and 2014 showed similar or greater efficacy with oncedaily dosing and comparable renal toxicity (Stankowicz et al. With oncedaily tobramycin, a dose of 4�5 mg/kg of physique weight is recommended for many infections. For severe infec tions, particularly if tobramycin is used alone, a beginning dose of 7 mg/kg is recommended. Serum ranges then may be mea sured at 1 hour and 6�14 hours after the beginning of the infusion, and appropriate dosage adjustments can made for subsequent day by day doses (Barclay et al. Different nomograms have been developed to help in establishing essentially the most adequate dosing after an preliminary dose of 5�7 mg, with later doses being adjusted according to serum ranges (Stankowicz et al. Newborn infants and youngsters As with gentamicin, newborn infants and youngsters want the next dosage of tobramycin. One advice is to administer tobramycin at 2 mg/kg each 12 hours to infants aged 0�7 days and to give the identical dose every 8 hours to infants older than 7 days (McCracken and Nelson, 1983). Premature babies during their first week of life might have a lower tobramycin dosage (Arbeter et al. Another recommendation with much less frequent dosing is to use four mg/kg every 48 hours for neonates with gestational age lower than 32 weeks, every 36 hours for those with a gestational age of 32�36 weeks, and each 24 hours for those with a gesta tional age of 37 weeks or greater (de Hoog et al. A pharmacokinetic evaluation in 50 pedi atric sufferers showed that therapeutic nontoxic serum ranges had been achieved provided that a excessive whole every day dose of 300 mg/m2 (approximately 10 mg/kg each 24 hours) was given in six divided doses each 4 hours. It was really helpful that this tobramycin dosage should be given to kids and adoles cents younger than 18 years of age (Hoecker et al. However, oncedaily dosing of tobramycin at 8�9 mg/kg has been beneficial for youngsters in more modern studies (Sung et al. However, urinary excre tion of proteins and phospholipids was considerably much less with oncedaily dosing. Before oncedaily dosing turned normal practice, tobra mycin was usually administered in a dosage of 3. Optimally, the peak serum level should be 5�10 mg/l and the trough degree 1�2 mg/l (Kahlmeter, 1979; Follath et al. If the drug is run in more than once dose per day, critically sick patients should obtain a loading dose of at least 2. In one research, 26 consecutive sufferers with presumed sepsis or septic shock had initial peak serum ranges less than 5 mg/l after completion of a 20minute infusion of tobramycin in a dose of two. Therefore, it appears that the recom mended dosage schedules (1�2 mg/kg every eight hours) may be too low for patients with severe sepsis. The volume of dis tribution of the drug in these patients is probably a lot elevated (Summer et al. Other authors have found that an every12hours tobramycin routine, during which the whole day by day dose is given in two equal doses, is passable for the treatment of patients (Lilliestierna et al. There are reviews of fetal eighth cranial nerve toxicity and listening to loss after prolonged in utero exposure to kanamycin (see Chapter 51, Kanamycin). For this cause, tobramycin dosage in patients with impaired renal function ought to at all times be ruled by regu lar serum degree estimations. Nomograms developed to assist in prescription of amino glycosides in these patients can be used for tobramycin (Chan et al. Nomograms primarily based on creatinine clearance require conversion of the serum creatinine to creatinine clearance (see Chapter fifty two, Gentamicin). Tobramycin serum level esti mations are still advisable, even if the dosage is prescribed according to a nomogram. Tobramycin, like gentamicin (see Chapter fifty two, Gentamicin), is eliminated by hemodialysis; roughly 50% of an admin istered dose is eliminated throughout a 6hour dialysis session (Lockwood and Bower, 1973; Jaffe et al. In anephric patients maintained by regular hemodialysis, the usual single dose of 1. Removal of tobramycin by peritoneal dialysis is inefficient, and only about 50% of an administered dose is recovered throughout 36 hours of this process (Weinstein et al. Nevertheless, the tobramycin halflife in anephric patients of fifty three hours is lowered to 12�16 hours when these sufferers endure peritoneal dialysis, so a dosage schedule of two mg/kg of body weight every 24�36 hours is beneficial (Malacoff et al. Usually, the drug is added to produce a focus of eight mg/l in every dialysis exchange. This produces peak tobramycin serum concentrations of 6�8 mg/l; after 24 hours the serum stage is 5 mg/l, and the dialysate concentration is three. Much greater day by day dosages of 9�15 mg/kg have been recommended for these patients (Vic et al. A mean peak serum degree of 32 mg/l was attained in sufferers receiving this dose through a 20minute infusion; neither ototox icity nor nephrotoxicity was observed after 10 days of such remedy (Powell et al. A recent examine found that with 10 mg/kg, only 42% of the sufferers achieved the pharmacokinetic and pharmaco dynamic goal (Cmax of 20�30 mg/l) towards up to date isolates, and due to this fact the author proposed an preliminary dose of 12 mg/kg (Reyes et al. The most typical dosage of inhaled tobramycin in patients with cystic fibrosis is 300 mg twice day by day (Ramsey et al. For acute exacerbations, the drug is used for 2�4 weeks; nonetheless, about half of the inhaled tobramycin presently used is chronically adminis tered (Conway, 2005; Moskowitz et al. Critically ill sufferers in intensive care units can also have elevated volumes of distribution and require fre quent therapeutic drug monitoring (Buijk et al.
Cheap cyklokapron 500 mg mastercard
Oritavancin binds to isolated protoplast membranes but not intact protoplasts of Staphylococcus aureus medications definition cyklokapron 500 mg discount overnight delivery. In vitro characterization of oritavancin clearance from human blood by low-flux treatment tendonitis cheap cyklokapron 500 mg mastercard, high-flux, and steady renal substitute therapy dialyzers. Activities of antistaphylococcal antibiotics in direction of the extracellular and intraphagocytic types of Staphylococcus aureus isolates from a affected person with persistent bacteraemia and endocarditis. First case of infection with vancomycin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus in Europe. Oritavancin activity towards Staphylococcus aureus causing invasive infections in U. In vitro susceptibility of genotypically distinct and clonal Clostridium difficile strains to oritavancin. Pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of oritavancin towards Staphylococcus aureus using data from a neutropenic murine thigh-infection model. Paper introduced on the 49th Interscience Conference on Antimicrobial Agents and Chemotherapy, Washington, D. Vancomycin and oritavancin have totally different modes of motion in Enterococcus faecium. Emergence of vancomycin resistance within the genus Streptococcus: characterization of a vanB transferable determinant in Streptococcus bovis. Mechanisms of resistance and scientific relevance of resistance to beta-lactams, glycopeptides, and fluoroquinolones. Dalbavancin and oritavancin: an innovative strategy to the remedy of Gram-positive infections. Plasma and intrapulmonary concentrations of oritavancin and vancomycin in normal healthy adults. Paper presented at the14th European Congress of Clinical Microbiology and Infectious Diseases, Prague, Czech Republic. Population pharmacokinetic evaluation for a single 1200-milligram dose of oritavancin using knowledge from two pivotal part 3 clinical trials. Oritavancin inhabitants pharmacokinetics in healthy subjects and sufferers with sophisticated pores and skin and pores and skin structure infections or bacteremia. Its lipophilic aspect chain increases protein binding and thus provides the lengthy t1/2 typical of teicoplanintype derivatives. Routine susceptibility Like other glycopeptides similar to vancomycin, dalbavancin has excellent in vitro exercise in opposition to Grampositive organ isms and no activity towards Gramnegative organisms. An identical breakpoint has been set by the European Committee on Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing for Staphylococcus spp. Antimicrobial activity of dalbavancin towards Gram-positive micro organism with differing phenotypic profiles collected worldwide. Organism Staphylococcus aureus Methicillin prone Methicillin resistant Coagulase-negative staphylococci Methicillin susceptible Methicillin resistant Streptococcus pneumoniae Penicillin susceptible Penicillin nonsusceptible Viridans group streptococci Penicillin susceptible Penicillin nonsusceptible Beta-hemolytic streptococci E. Comparative antimicrobial activity of semisynthetic lipoglycopeptides and vancomycin in opposition to Gram-positive micro organism. Dalbavancin also retains its exercise in opposition to difficult staphylococci strains which are intermediate or immune to vancomycin, linezolid, and quinupristin�dalfopristin (Lefort et al. It is generally two to fourfold stronger than vancomycin in opposition to Grampositive anaerobes such as Actinomyces spp. Resistance arises via alteration of peptidoglycan precursors, such that pentapeptides normally terminating in dalaninedalanine are revised to terminate in dalanined lactate or dalaninedserine, potentially decreasing anti biotic goal affinity up to 100fold (Malabarba and Ciabatti, 2001; Courvalin, 2006; Bailey and Summers, 2008; Zhanel et al. Studies suggest that staphylococci are much less prone to develop resistance to dalbavancin than to vancomycin and teico planin. Susceptibility was reinstated after the isolates were grown on a drugfree medium for three days. The complex created between the heptapeptide backbone and the dalanyld alanine dipeptide blocks access for transglycosylases and transpeptidases, enzymes which are necessary to pursue polymerization and crosslinking. As a end result, the nascent peptidoglycan chain is halted from growing further, leaving cells weak to rupture from altering inner osmotic stress. The addition of a lipophilic aspect chain appears to afford dalbavancin more methods to enhance the interplay with dalanyldalanine peptides (Beauregard et al. Homodimers formed between glycopeptide molecules lock the binding pocket into a main position to facilitate cooperative binding (Van Bambeke, 2004; Van Bambeke et al. This singledose routine potentially removes logisti cal constraints related to delivery of the second dose, enhanc ing its ease of use (Dunne et al. For these with endstage renal disease requiring dialysis assist, concentrations from a 500mg dose had been just like these with none renal impairment. A smaller dose of 500 mg might suffice for dialysis sufferers, contemplating that hemodialysis was not an important route of elimination for dalbavancin (Marbury et al. Newborn infants and youngsters To date, there has been a single dalbavancin phase I examine in children (Bradley et al. Currently, no dalbavancin dose changes are really helpful for sufferers with gentle, moderate, or severe hepatic impair ment (Marbury et al. Pharmacokinetic parameters have been much like topics with normal hepatic perform on a 1000mg dose adopted by 500 mg 7 days later (Marbury et al. It must be utilized in pregnancy only if the profit justifies the potential danger to the fetus. In pregnant rats and rabbits, there were no treatmentrelated malformations or embryofetal toxicity at clinically related dalbavancin exposures. It is unknown whether dalbavancin or its metabolite is excreted in human milk (Durata, 2015). The efficacy and tolerability of dalbavancin were just like comparator regardless of age (Durata, 2015; Dunne et al. Total protein binding of dalbavancin is focus independent, reversible, and estimated to be 93%. Yet the small free fraction left over is able to bactericidal exercise (Cavaleri et al. The plasma concentra tiontime profile of dalbavancin initially has a steep decline in the course of the 24 to 48hour distribution part, which slopes down right into a slower terminal elimination part, extending out to 600�800 hours (Cavaleri et al. Drug distribution Dalbavancin exhibits linear, doseproportional pharmaco kinetics with a t1/2 of approximately 7 days (Leighton et al. Pharmacokinetic parameters of dalbavancin in healthy volunteers after administration of single and multiple i. A phase I ran domized doubleblind examine examined escalating dosages of dalbavancin as a single and multipledose (loading dose and maintenance dose in 10:1 ratio) regimen. Single doses (140, 350, 500, 630, 840, and 1120 mg) have been administered as quickly as, and a quantity of doses got daily for 7 days (300 and 30; 400 and forty; 600 and 60; 800 and 80; and a thousand and one hundred mg) with the loading dose administered in equal doses divided by 12 hours. The Cmax of dalbavancin was discovered to enhance in propor tion to the dose, rising from forty.
500 mg cyklokapron buy
Time kill curve evaluation of vancomycin and rifampin alone and together towards nine strains of nutritionally poor streptococci medicine bow discount 500 mg cyklokapron otc. Daptomycin tested towards 915 bloodstream isolates of viridans group streptococci (eight species) and Streptococcus bovis symptoms quad strain 500 mg cyklokapron cheap with mastercard. Guidelines for analysis, remedy, and prevention of Clostridium difficile infections. Treatment of recurrent Clostridium difficile colitis with vancomycin and Saccharomyces boulardii. Pharmacodynamic results of antibiotics and antibiotic combos on growing and nongrowing Staphylococcus epidermidis cells. Vancomycin versus cefazolin prophylaxis for cerebrospinal shunt placement in a hospital with a excessive prevalence of meticillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus. Is vancomycin-only prophylaxis for sufferers with penicillin allergy associated with increased threat of an infection after arthroplasty The position of vancomycin and metronidazole for the therapy of Clostridium difficile-associated diarrhea. Impact of vancomycin faecal concentrations on medical and microbiological outcomes in Clostridium difficile infection. Vancomycin resistance among methicillin resistant Staphylococcus aureus isolates from intensive care models of tertiary care hospitals in Hyderabad. Staphylococcus aureus infections: epidemiology, pathophysiology, medical manifestations, and management. Clinical and epidemiological significance of enterococci intrinsically immune to vancomycin (possessing the vanC genotype). Australasian Society of Infectious Diseases up to date pointers for the management of Clostridium difficile an infection in adults and children in Australia and New Zealand. Simple approach to improving vancomycin dosing in intensive care: a standardised loading dose results in earlier therapeutic levels. Rhodococcus lung abscess complicating kidney transplantation: profitable management by mixture antibiotic therapy. Evaluation of accessory gene regulator (agr) group and function within the proclivity towards vancomycin intermediate resistance in Staphylococcus aureus. Antibiotic failure in a renal transplant patient with Rhodococcus equi infection: a sign for surgical lobectomy. Prophylactic antibiotics for stopping Gram optimistic infections associated with long-term central venous catheters in oncology sufferers. Is it time to exchange vancomycin in the therapy of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus infections Effect of obesity on vancomycin pharmacokinetic parameters as determined by using a Bayesian forecasting method. A comparative assessment of vancomycin-associated nephrotoxicity within the younger versus the elderly hospitalized affected person. Implementation of a dose calculator for vancomycin to achieve target trough ranges of 15�20 microg/mL in persons undergoing hemodialysis. Antimicrobial susceptibility of non-enterococcal intrinsic glycopeptide-resistant Gram-positive organisms. Vancomycin resistance in Staphylococcus haemolyticus inflicting colonization and bloodstream an infection. Drug rash, eosinophilia, and systemic symptoms syndrome: two pediatric cases demonstrating the vary of severity in presentation-a case of vancomycin-induced drug hypersensitivity mimicking toxic shock syndrome and a milder case induced by minocycline. Staphylococcus epidermidis: an growing reason for an infection in patients with granulocytopenia. Development of recent antibiotic resistance in methicillin-resistant but not methicillinsusceptible Staphylococcus aureus. In vitro induction of resistance in coagulase adverse staphylococci to vancomycin and teicoplanin. In-vitro selection of resistance of Staphylococcus aureus to teicoplanin and vancomycin. Synergism of vancomycin-gentamicin and vancomycin-streptomycin in opposition to enterococci. Synergism between vancomycin and gentamicin or tobramycin for methicillin-susceptible and methicillinresistant Staphylococcus aureus strains. Aerosolized vancomycin for treatment of airway colonization by methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus. Diffuse desquamating rash following exposure to vancomycin-impregnated bone cement. Coagulase-negative staphylococcal bacteremia in sufferers receiving immunosuppressive remedy. Significant infections due to Bacillus species following abrasions associated with motor vehicle-related trauma. A multicenter research evaluating the present strategies for isolating Staphylococcus aureus strains with decreased susceptibility to glycopeptides. Topically utilized vancomycin powder reduces the speed of surgical web site an infection in diabetic sufferers undergoing foot and ankle surgery. Continuous versus intermittent infusion of vancomycin in severe staphylococcal infections: prospective multicenter randomized examine. Benefits of therapeutic drug monitoring of vancomycin: a scientific evaluation and meta-analysis. Vancomycin-associated drug reaction with eosinophilia and systemic symptoms syndrome. Coagulase-negative staphylococci isolated from cerebrospinal fluid shunts: significance of slime manufacturing, species identification, and shunt elimination to clinical consequence. A comparability of vancomycin and metronidazole for the treatment of Clostridium difficile-associated diarrhea, stratified by disease severity. Graft infection and bacteremia with Listeria monocytogenes in a patient receiving hemodialysis. Preferential emergence of reduced vancomycin susceptibility in well being care-associated methicillinresistant Staphylococcus aureus isolates throughout continuousinfusion vancomycin therapy in an in vitro dynamic mannequin. Vancomycin pharmacodynamics and survival in sufferers with methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus-associated septic shock. Systematic evaluation and meta-analysis of the epidemiology of vancomycin-intermediate and heterogeneous vancomycin-intermediate Staphylococcus aureus isolates. Glycopeptide minimum inhibitory concentration creep amongst meticillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus from 2006�2011 in China. Similar to vancomycin (see Chapter forty three, Vancomycin), it has a broad spectrum of activity in opposition to Gram-positive cardio and anaerobic bacteria, together with strains proof against many other antimicrobials (Parenti et al. Teicoplanin comprises six closely related main elements whose activities in opposition to particular microbial species differ. Teicoplanin binds to the cell wall and inhibits cell wall biosynthesis in vulnerable organisms by interfering with the polymerization of peptidoglycan (Somma et al.
500 mg cyklokapron generic mastercard
Using a composite finish level of "clinically effective" amongst fifty six evaluable patients symptoms nicotine withdrawal cyklokapron 500 mg buy on line, the investigators believed 47/51 sufferers (92 medications for ocd 500 mg cyklokapron purchase overnight delivery. Bacteremia There have been no clinical trials of doripenem remedy for bacteremia per se. In the analysis investigators identified 139 subjects with bacteremia in whom a therapy-related outcome could possibly be determined (doripenem, n = seventy six; comparator, n = 63). Overall the medical cure fee among bacteremic patients was just like that of comparator brokers throughout all the indications studied (Rice et al. Synergistic mixture therapy for extremely resistant micro organism A number of investigators have studied the usage of synergistic combos of doripenem with different brokers for the remedy of carbapenem-resistant Gram-negative bacilli and different organisms. The majority of studies have been in vitro or animal research, with solely a handful of clinical circumstances and case series reported. A 2013 systematic evaluation of in vitro synergy between carbapenems and polymyxins for Gram-negative bacilli identified doripenem because the carbapenem showing the highest synergy fee for the pathogens reviewed. Clinical reports of doripenem plus polymyxin combinations are infrequent, with the vast majority of reviews on this area using other carbapenems and/or not specifying the carbapenem used. These cases have been reported as part of a retrospective comparison with the mixture to colistin plus fosfomycin (n = 24). Clinical treatment was noticed in 60% (n = 15) of the sufferers utilizing the doripenem mixture. Clinical uses of the drug 739 Synergy has additionally been observed in vitro and in animal fashions when using doripenem together with another carbapenem (Bulik et al. Ertapenem is normally chosen with the rational that ertapenem binds to the energetic web site of the carbapenemase with greater affinity than doripenem, thus defending the doripenem from hydrolysis. It seems likely the finding of in vitro synergy is kind of depending on the carbapenem resistance mechanisms concerned (Poirel et al. Data on the clinical use of double-carbapenem combination remedy with doripenem are restricted. The utility of doripenem together remedy against Neisseria gonorrhoea has additionally been investigated in vitro. The research demonstrated no indication of synergy or antagonism when doripenem was combined with azithromycin, moxifloxacin, or gentamicin (Bharat et al. A small in vitro examine demonstrated synergy of doripenem combined with rifampicin for Mycobacterium abscessus and drug-resistant M. Population pharmacokinetics of doripenem in critically sick sufferers with sepsis in a Malaysian intensive care unit. Carbapenem-resistant Pseudomonas aeruginosa pneumonia with intermediate minimum inhibitory concentrations to doripenem: mixture remedy with high-dose, 4-h infusion of doripenem plus fosfomycin versus intravenous colistin plus fosfomycin. Pharmacokinetics of doripenem in contaminated patients handled inside and out of doors the intensive care unit. In vitro potency and combination testing of antimicrobial agents in opposition to Neisseria gonorrhoeae. Pharmacodynamics of the antibacterial effect of and emergence of resistance to doripenem in Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Acinetobacter baumannii in an in vitro pharmacokinetic model. Comparative in vitro antimicrobial exercise of a new carbapenem, doripenem: tentative disc diffusion criteria and quality management. Penetration of doripenem into skeletal muscle and subcutaneous adipose tissue in wholesome volunteers. Successful therapy of carbapenemase-producing pandrug-resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae bacteremia. Safety and tolerability of doripenem in hospitalized kids with difficult intra-abdominal infection, sophisticated urinary tract infections and pneumonia. Epidemiology and carbapenem resistance mechanisms of carbapenem-non-susceptible Pseudomonas aeruginosa collected during 2009�11 in 14 European and Mediterranean countries. Efficacy and security of intravenous infusion of doripenem versus imipenem in ventilator-associated pneumonia: a multicenter, randomized examine. In vitro activity of doripenem (S-4661) towards multidrug-resistant gram-negative bacilli isolated from sufferers with cystic fibrosis. The disposition, metabolism, and excretion of 14C-doripenem after a single 500-mg intravenous infusion in wholesome males. Influence of steady venovenous hemofiltration and steady venovenous hemodiafiltration on the disposition of doripenem. Open-label examine to consider the single-dose pharmacokinetics, safety, and tolerability of doripenem in infants lower than 12 weeks in chronological age. Prospective randomized comparability of imipenem monotherapy with imipenem plus netilmicin for treatment of extreme infections in nonneutropenic patients. Affinity of doripenem and comparators to penicillin-binding proteins in Escherichia coli and Pseudomonas aeruginosa. European Committee on Antimicrobial Susceptibility (2016) Clinical breakpoints-bacteria v 6. Treatment of extreme pneumonia in hospitalized sufferers: results of a multicenter, randomized, double-blind trial evaluating intravenous ciprofloxacin with imipenem cilastatin. A section I, double-blind, placebo-controlled examine to determine the protection, tolerability and pharmacokinetics of prolonged-infusion regimens of doripenem in wholesome topics. Antimicrobial exercise of doripenem tested against prevalent Gram-positive pathogens: results from a worldwide surveillance examine (2003�2007). Antimicrobial exercise of doripenem (S-4661): a worldwide surveillance report (2003). In vitro activities of doripenem and six comparator drugs in opposition to 423 aerobic and anaerobic bacterial isolates from infected diabetic foot wounds. Pharmacokinetic evaluation of doripenem in elderly patients with nosocomial pneumonia. Validation of doripenem dosing in patients with end-stage renal disease receiving hemodialysis. Absence of convulsive legal responsibility of doripenem, a new carbapenem antibiotic, as compared with beta-lactam antibiotics. Standard versus extended doripenem infusion for treatment of Gram-negative infections. Peritoneal penetration of doripenem after intravenous administration in abdominal-surgery sufferers. Synthesis and structure-activity relationships of 2-(5-substituted pyrrolidin-3-ylthio)-1 beta-methylcarbapenems. Pharmacodynamics of doripenem in critically unwell sufferers with ventilatorassociated Gram-negative bacilli pneumonia. In vitro potency of doripenem examined in opposition to a world collection of hardly ever isolated bacterial pathogens. Doripenem (S-4661), a novel carbapenem: comparative exercise in opposition to contemporary pathogens including bactericidal motion and preliminary in vitro strategies evaluations.
500 mg cyklokapron otc
The durations are for much longer with two- and three-drug combos than with the one drug (Horgen et al 400 medications 500 mg cyklokapron generic fast delivery. Excretion Like other aminoglycosides medicine 20th century cyklokapron 500 mg discount visa, amikacin is eliminated from the physique nearly completely by the kidney in an energetic unchanged type. It is excreted totally by glomerular filtration, however the price of renal clearance of creatinine is greater than that of amikacin, indicating that the drug undergoes appreciable tubular reabsorption (Kirby et al. In sufferers with regular renal function roughly 94% of an administered dose is excreted within the urine within 24 hours (Cabana and Taggart, 1973; Kirby et al. The prolonged terminal elimination section of amikacin in normal volunteers is 188 hours, which is barely longer than with gentamicin (French et al. Drug interactions Amikacin is probably the most stable of the aminoglycoside antibiotics to inactivation by numerous penicillins (Pickering and Rutherford, 1981; Riff and Thomason, 1982; Tindula et al. The elimination half-life of amikacin in sufferers with end-stage renal impairment was the same whether amikacin was administered alone (66. Pharmacokinetic parameter Bioavailability Distribution Serum protein binding Half-life Adults Normal renal operate Minimal renal function Anephric Children Neonates < 3 days old Neonates > 3 days old Cystic fibrosis Excretion Value 95%. In animals amikacin selectively produced an impairment of cochlear perform at five times the dose of gentamicin, which produces each vestibular and cochlear harm (Christensen et al. The price of entry of amikacin into the perilymph house of the internal ear is relatively gradual, however it persists there due to slow elimination (Desjardins-Giasson and Beaubien, 1984). Amikacin ototoxicity appears to be associated to the presence of the drug in the perilymph over the total time of amikacin exposure whatever the level within the perilymph (Beaubien et al. However, guinea pigs given 200 mg/kg as quickly as daily for 28 days have less ototoxicity than these given a hundred mg/kg twice day by day (Takumida et al. Hearing loss attributable to amikacin is usually not progressive as quickly as the drug is stopped (Black et al. Amikacin ototoxicity is often irreversible, although it ameliorates often (Meyer, 1981). In an analysis of the records of 1548 sufferers handled with amikacin, highfrequency hearing loss occurred in seventy one (4. In 11, a listening to loss of 15 decibels or higher occurred a minimal of at one frequency; all of these patients had acquired approximately twice as much amikacin as these without audiometric adjustments. In addition, eight of the eleven sufferers (73%) had obtained earlier aminoglycoside remedy, compared with only 34% of the 317 sufferers with out cochlear injury. Kahlmeter and Dahlager (1984) surveyed aminoglycoside-induced ototoxicity reported in medical trials revealed between 1975 and 1982, which included roughly 10,000 sufferers. As with different aminoglycosides, amikacin ototoxicity has been unusual in younger children (Faden et al. Infants treated with aminoglycosides had standard audiometric examinations performed once they reached the age of 6 weeks and again when aged 18 months. A complete of 150 infants with gestational ages of 27�42 weeks had been studied; 49 acquired netilmicin, 50 received amikacin, and the others served as controls. Bilateral sensorineural impairment was confirmed in a single toddler (2%) in each group. In a large metaanalysis of once-daily versus multiple-daily dosing in kids, of these studies that supplied auditory testing, the pooled fee of ototoxicity was 2. In studies that included scientific vestibular perform testing, no circumstances of vestibular toxicity had been recognized in over 200 patients in every group. Similarly, the pathologic adjustments and the mechanisms of renal tubular drug uptake and toxicity are additionally just like these described for gentamicin. Amikacin does bind to megalin, a large glycoprotein on the brush border of renal tubular cells (Nagai et al. This is the essential first step for the uptake of amikacin by pinocytosis into the renal tubular cell. In animals the renal uptake of amikacin is significantly lower than that of gentamicin (El Mouedden et al. Lower accumulation mixed with much less apoptosis would recommend that the incidence of nephrotoxicity can be lower with amikacin than with gentamicin. However, most trials evaluating these two drugs have proven related nephrotoxicity (Lau et al. When Kahlmeter and Dahlager (1984) analyzed aminoglycoside nephrotoxicity in roughly 10,000 sufferers reported within the literature between 1975 and 1982, the typical frequency of nephrotoxicity with amikacin (9. These adjustments had been more frequent in sufferers who had initial high serum creatinine values, were older, obtained a bigger whole dose of amikacin, or received different nephrotoxic agents, either previously or concurrently. Similar to different aminoglycosides, amikacin could additionally be more nephrotoxic in sufferers with obstructive jaundice (Desai and Tsang, 1988). The incidence of amikacin nephrotoxicity is also lower in children than in adults; the incidence in a quantity of medical trials was about 1. Amikacin nephrotoxicity appears to be dependent on the mode of administration and the length of therapy. In animals and people, amikacin has shown saturable uptake into the kidney (Guiliano et al. In people the renal cortical focus about 24 hours after dosing was lowest with a single dose and highest with steady infusion of the same amount of drug. A randomized, double-blind trial of amikacin, gentamicin, and tobramycin administered once or twice every day additionally demonstrated a significantly lower incidence of nephrotoxicity with once-daily dosing (Rybak et al. They include hypersensitivity reactions, nausea and vomiting, headache, drug fever, tremor, paresthesiae, arthralgia, eosinophilia, anemia, and mild abnormalities in liver perform exams (Gooding et al. Infections because of aerobic Gram-negative bacilli Controlled studies point out that amikacin is equally as efficient as gentamicin or tobramycin for the remedy of significant Gram-negative infections attributable to organisms prone to 7. Amikacin also has an efficacy comparable with that of tobramycin within the remedy of pulmonary infection because of prone strains for P. The drug has been in contrast with gentamicin for the treatment of adults with urinary tract infections. In two randomized studies, gentamicin was used in a dosage of 3�4 mg/kg/day, but amikacin was used in a decreased dosage of 9 mg/kg/day (Cox, 1976; Gilbert et al. Amikacin has been utilized in many uncontrolled studies to deal with varied infections brought on by gentamicinsensitive Gram-negative rods. In basic it has been about as effective as would be anticipated from a gentamicin regimen in complicated urinary tract infections, pyelonephritis, septicemia, bone and joint infections, Gram-negative bacillary pneumonias, and exacerbations of P. In a big observational examine of patients with bacteremia, aminoglycosides were much less efficient than beta-lactams in septic patients with Gram-negative bacillary infections from sites apart from the urinary tract (Leibovici et al. Aminoglycoside monotherapy was equally efficacious compared to beta-lactam antibiotics and fluoroquinolones for the treatment of urinary tract infections and pyelonephritis (Vidal et al. However, the number of clinical trials involving other websites of infection was insufficient to set up the full efficacy of aminoglycoside monotherapy.