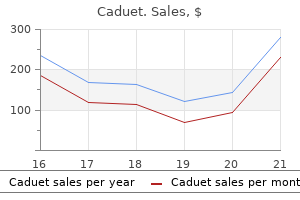
Caduet dosages: 5 mg
Caduet packs: 30 pills, 60 pills, 90 pills

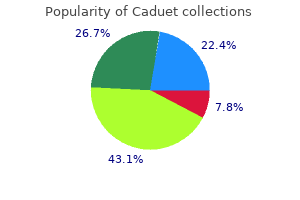
Generic caduet 5mg with mastercard
Next-generation sequencing103 strategies are even more sensitive and potentially simpler to standardize cholesterol vegetables caduet 5mg free shipping. More recently high cholesterol fat foods 5 mg caduet generic otc, there has been appreciable curiosity in pharmacogenomics as a device to clarify variability of patient response to therapy. Polymorphisms within the thiopurine methlytransferase gene significantly affect the toxicity of thiopurines, and testing for these can be used to modify dosing in sufferers with leukemia. Differential Diagnosis the differential diagnosis usually consists of a variety of hematopoietic tumors that will possess blastlike morphology, in addition to a small number of undifferentiated or primitive non-hematopoietic tumors (Table 42-2). Operationally, identification of T-cell antigen expression is required for the prognosis of T-cell lymphoblastic tumors. Pulmonary and cardiac function may also be compromised by the presence of pleural or pericardial effusions. Moreover, distinguishing T-cell lesions from B-cell lesions by morphology alone is inconceivable. Typically, T-cell lymphoblasts are inclined to have more cytologic heterogeneity and extra nuclear convolutions than B lymphoblasts; however, no phenotypic, molecular, or clinical differences have been correlated with convoluted morphology. Precursor T-cell malignancies can specific markers associated with T-cell differentiation and maturation in nearly any mixture, although an understanding of phenotypic adjustments related to regular T-cell maturation is useful in understanding malignant phenotypes. TdT continues to be expressed all through cortical thymic improvement and is lost because the thymocytes enter the medullary section of maturation. Because precursor T-cell tumors resemble their normal thymic counterparts, data of the conventional patterns of Etiology Although specific genetic disturbances are involved in T-lymphoblastic lesions, the underlying etiologic elements are unknown. In patients with mediastinal involvement, the mass is commonly quite giant, leading to compromise of regional anatomic structures. A, Bone marrow aspirate shows a predominant inhabitants of heterogeneous blasts with a range of sizes. An important level is that virtually all precursor T-cell tumors have aberrant patterns of antigen expression that distinguish them from normal thymocytes. Many of these same transcription components may additionally be dysregulated by mechanisms other than translocation. Further, overexpression of explicit oncogenes correlated with outlined phases of normal thymopoiesis may predict clinical consequence. The relationship of a few of these molecular lesions to immunophenotype and stage of T-cell maturation is proven in Table 42-1. As noted earlier, these precursor cells possess unique antigen-expression patterns that clearly distinguish them from extra mature extrathymic T cells. In part, this is as a outcome of of the shortage of clear-cut prognostic significance of those lesions, and the reality that routine diagnostic strategies solely establish a couple of such cases. Because local recurrence can also be a serious indication of treatment failure, inclusion of mediastinal radiotherapy may play a task in stopping relapse, significantly in adult patients. The function of newer diagnostic modalities such as positron emission tomography scanning may play a role in threat stratification. If a mediastinal mass is shipped for flow cytometry, failure to acknowledge the traditional pattern in maturation of thymocytes within the thymoma is particularly likely to lead to misdiagnosis. However, with acceptable intensive remedy, these malignancies could also be curable, significantly within the pediatric inhabitants. Greater understanding of the biology of lymphoblastic tumors will undoubtedly result in more tailored remedy, in phrases of both risk stratification and the event of focused therapeutic brokers. However, due to the reproducible nature of antigen acquisition in regular precursors, virtually all neoplastic populations may be reliably distinguished from normal precursors by multiparametric flow cytometry. Inclusion of different lymphoid markers and TdT could additionally be helpful in distinguishing between these options. Developmental hierarchy of immunoglobulin gene rearrangements in human leukemic pre-B-cells. Immunoglobulin gene rearrangement and cell surface antigen expression in acute lymphocytic leukemias of T cell and B cell precursor origins. Patterns of leukemia inci, dence in the United States by subtype and demographic characteristics, 1997-2002. Precursor B-cell lymphoblastic lymphoma: a predominantly extranodal tumor with low propensity for leukemic involvement. A study of 9 circumstances missing blood and bone marrow involvement and evaluation of the literature. Backtracking leukemia to start: identification of clonotypic gene fusion sequences in neonatal blood spots. Immunophenotypes and karyotypes of leukemic cells in children with Down syndrome and acute lymphoblastic leukemia. A genomewide affiliation examine of susceptibility to acute lymphoblastic leukemia in adolescents and young adults. Laboratory correlates and prognostic significance of granular acute lymphoblastic leukemia in children. Acute lymphoblastic, leukemia with chromosomal 5;14 translocation and hypereosinophilia: case report and literature evaluate. The t(5;14) chromosomal translocation in a case of acute lymphocytic leukemia joins the interleukin-3 gene to the immunoglobulin heavy chain gene. Acute lymphocytic leukemia with, eosinophilia: two case reports and a literature evaluation. Follicular lymphoma transformed to "double-hit" B lymphoblastic lymphoma presenting within the peritoneal fluid. Prognostic significance of fluorescence intensity of surface marker expression in childhood B-precursor acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Clinical significance of myeloid antigen expression in grownup acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Expression of myeloid antigens by blast cells in acute lymphoblastic leukemia of adults. The reliability and specificity of c-kit for the prognosis of acute myeloid leukemias and undifferentiated leukemias. Acute lymphoblastic leukemia with Burkitt-like morphologic features and excessive myeloperoxidase exercise. Transitional preB-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia of childhood is associated with favorable prognostic scientific features 47. Immunoglobulingene rearrangements as distinctive clonal markers in human lymphoid neoplasms. Prognostic significance of chromosome number in 136 untreated kids with acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Clinical relevance of lymphoblast organic features in children with acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Trisomy of leukemic cell chromosomes four and 10 identifies children with B-progenitor cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia with a really low risk of therapy failure: a Pediatric Oncology Group research. Prognostic impression of trisomies of chromosomes 10, 17, and 5 among children with acute lymphoblastic leukemia and excessive hyperdiploidy (>50 chromosomes).
5mg caduet cheap free shipping
Rare large lymphocytes with vesicular nuclei and visual nucleoli in addition to plasmacytoid cells with or with out Dutcher our bodies could also be admixed among the many small neoplastic lymphocytes cholesterol levels mayo clinic cheap 5 mg caduet free shipping. This sample of infiltration is troublesome to respect on hematoxylin and eosin�stained section but may be highlighted by immunostaining for B-cell markers cholesterol test for particle size generic 5mg caduet otc. A, the infiltrate blends in with the conventional hematopoietic components and is troublesome to determine on the hematoxylin and eosin�stained section. Most of the lymphoma cells are small, with barely irregular nuclei; a reactive germinal center is present within the neoplastic infiltrate. The paratrabecular lymphoid infiltrates "hug" the bone and conform to its contour. Focal random or interstitial infiltration is comparatively common; paratrabecular infiltration occurs less regularly, and diffuse infiltration is uncommon. Large lymphocytes with distinguished nucleoli (centroblasts) may be current but often are fewer in number. The lymphoma cells in the bone marrow aspirate smears are sometimes small to medium in dimension with deep nuclear clefts; similar cells are occasionally identified within the peripheral blood smear but are often few in quantity. In this bone marrow core biopsy, the focal infiltrate accommodates a neoplastic follicle. In addition, a discordant histologic subtype of lymphoma between the bone marrow and the extramedullary website happens. The lymphoma cells are barely bigger than regular lymphocytes and have barely dispersed chromatin and deeply cleaved nuclei. Diffuse massive B-cell lymphoma with discordant morphology between lymph node and bone marrow. A, the bone marrow core biopsy incorporates a number of paratrabecular lymphoid aggregates composed of small lymphocytes. B, the lymphoma cells are small to medium sized, with condensed chromatin and spherical to irregular nuclei. A, the infiltrate in the bone marrow core biopsy shows a diffuse infiltrative pattern and incorporates medium to giant cells with dispersed chromatin and a quantity of visible nucleoli. B, A lymphoma cell with cleaved nucleus, barely dispersed chromatin, and scant cytoplasm is current within the peripheral blood. B, this case exhibits an absolute lymphocytosis (134 � 109/L) composed of variably sized lymphoma cells. C, the lymphoma cells in this case are medium to massive and have an ample amount of cytoplasm, condensed chromatin, and a distinguished central nucleolus resembling prolymphocytic leukemia. A, the infiltrate is paratrabecular and consists of small to medium-sized lymphocytes with irregular nuclei. A, Lymphoma cells within the bone marrow core biopsy are massive, with irregular nuclei and vesicular chromatin; many have distinct nucleoli. B, the lymphoma cells within the bone marrow aspirate comprise cytoplasmic vacuoles on this case. Diffuse giant B-cell lymphoma, T-cell/histiocyte-rich subtype, involving the bone marrow. A, the infiltrate has poorly defined borders and contains many small lymphocytes, histiocytes, and scattered massive, irregular lymphocytes. On cytologic evaluation, the tumor cells might present plasmablastic, immunoblastic, or anaplastic look. Concurrent blood involvement is widespread, ranging from occasional lymphoma cells to overt lymphocytosis; however, a pure leukemic presentation is rare. A, the lymphoma cells are present throughout the sinusoids and could be missed in hematoxylin and eosin�stained part. A, Bone marrow core biopsy contains a diffuse infiltration of medium-sized lymphocytes with several small seen nucleoli and scant to average quantities of cytoplasm. B, Bone marrow aspirate accommodates lymphoma cells with basophilic cytoplasm and a quantity of cytoplasmic vacuoles. B-Lymphoblastic Leukemia/Lymphoma B-lymphoblastic leukemia/lymphoma is a neoplasm of precursor B cells. The blasts are sometimes uniformly small to medium in measurement, with nice chromatin, scant and sometimes vacuolated cytoplasm, indistinct nucleoli, and frequent mitoses. Other options, corresponding to immunophenotype and genetic characteristics, are briefly mentioned; more particulars can be found within the other specific illness chapters on this e-book. T-Lymphoblastic Leukemia/Lymphoma Overall, T-lymphoblastic leukemia/lymphoma extra commonly has a lymphomatous presentation compared with B-lymphoblastic leukemia/lymphoma. It may also happen exterior the nasal cavity, commonly within the skin, nasopharynx, or testis. Bone marrow core biopsy demonstrates diffuse infiltration of neoplastic cells, replacing virtually the entire bone marrow. A, the tumor cells are difficult to recognize in hematoxylin and eosin�stained bone marrow core biopsy. A, the lymphoma cells in the blood smears resemble blasts; a number of the lymphoma cells present erythrophagocytosis. B, Lymphoma cells in the bone marrow aspirate smears show similar morphology to these in the peripheral blood smears. C, the bone marrow core biopsy exhibits intrasinusoidal infiltration of lymphoma cells that increase the sinusoid (arrows). The blasticappearing lymphoma cells and the interstitial infiltration increase with the disease progression. The B-cell lymphomas, similar to intravascular giant B-cell lymphoma and splenic marginal zone lymphoma, can be easily excluded by constructive staining for B-cell markers. The latter is characterized by a brief, linear array of small lymphocytes throughout the sinusoids (inset). However, these leukemia/lymphomas hardly ever present outstanding intrasinusoidal infiltration in the bone marrow. Mycosis Fungoides and S�zary Syndrome Mycosis fungoides is the most typical primary cutaneous T-cell lymphoma that typically remains localized for years. S�zary syndrome is a uncommon disorder characterized by diffuse erythroderma, lymphadenopathy, and circulating lymphoma cells (S�zary cells). A, the bone marrow core biopsy exhibits focal lymphoid infiltrates with distinguished rimming of the adipocytes, similar to the sample within the subcutaneous website. Cutaneous T-cell lymphoma (S�zary syndrome) involving the bone marrow and peripheral blood. A, the bone marrow core biopsy shows focal lymphomatous infiltrate in loose stroma, with poorly demarcated borders. C, Lymphoma cells in the peripheral blood differ in measurement however are bigger than regular lymphocytes and have convoluted, "cerebriform" nuclei, less condensed chromatin, and vague nucleoli. The neoplastic lymphocytes could also be small or giant with variable quantities of cytoplasm. Neoplastic cells with clear cytoplasm sometimes seen within the extranodal websites are normally not widespread in the bone marrow biopsy. In some instances, the prominent plasmacytosis may obscure the neoplastic infiltrates.
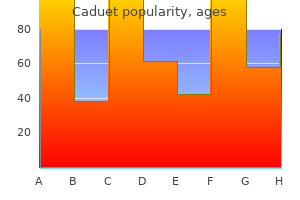
Caduet 5mg purchase
These cells are optimistic for vimentin cholesterol explained caduet 5mg purchase on line, smooth muscle actin cholesterol numbers ratio calculator 5 mg caduet cheap with amex, desmin, and keratin 8 and 18. Follicles and germinal facilities are found within the malpighian corpuscles, and T cells and interdigitating cells are discovered in the adjacent periarteriolar lymphoid sheath. The pink pulp also accommodates antigen-presenting cells; lymphocytes, significantly a subset of gamma-delta T lymphocytes; and plasma cells. Similar to the lymph nodes, the T-cell and B-cell compartments are recruited and maintained by specific chemokines. These cells predominantly surround the follicles but are almost absent from the surface of the T-cell regions. Instead, the human marginal zone is surrounded by a perifollicular area with more broadly separated fibers and capillaries sheathed by ample macrophages which are positive for sialoadhesin. A great amount of the splenic blood passes by way of this area, the place the flow seems to be retarded. This anatomic relationship between an open blood area and the marginal zone seems to facilitate direct contact between blood-borne antigens and B cells. The cells have cytoplasmic stress fibers that regulate the passage of blood cells. A, At low magnification, the white pulp contains a reactive follicle with a germinal heart (left) and a T-cell zone (right); both are surrounded by a pale-staining marginal zone. C, Splenic follicle incorporates a germinal heart, a marginal zone, and a palestaining marginal zone composed of medium-sized cells with abundant pale cytoplasm. E, T-cell zone has an look just like that of nodal paracortex, with interdigitating dendritic cells present in a background of small lymphocytes. G, Periodic acid�Schiff stain highlights the basement membrane of the sinuses, which are fenestrated, permitting nucleated purple blood cells to be trapped in the cords. B, Adenoid exhibiting a reactive follicle with pale-staining marginal-zone cells extending towards a crypt. The only distinction right here is the expanded marginal zone, which tends to reach the superficial epithelium. The interfollicular areas are occupied by T cells and interdigitating dendritic cells. The mucosal lamina propria incorporates mature plasma cells and macrophages and occasional B lymphocytes and T lymphocytes. These plasma cells secrete primarily dimeric IgA, but small populations producing IgM, IgG, and IgE are also present. The dimeric IgA and pentameric IgM are secreted into the intestinal lumen certain to the secretory element, a glycoprotein produced by the enterocytes. Intraepithelial lymphocytes are observed between the epithelial cells and are composed of a heterogeneous population of T cells. These cells are also found extra dispersed in different components of the gastrointestinal tract and different mucosal websites, notably within the epithelium over lymphoid follicles. The basic structure of mesenteric lymph nodes is much like that of different lymph nodes, however the marginal zone surrounding the follicles is usually expanded and visual. The group of the immune system in mucosal sites is orchestrated by the coordinated action of several adhesion molecules, chemokines, and their respective receptors. Foreign antigen�independent differentiation happens within the main lymphoid organs-bursa equivalent (bone marrow) and thymus-without publicity to overseas antigen. Na�ve B cells and T cells carry surface molecules that are receptors for antigens (the T-cell antigen receptor and surface immunoglobulin). On exposure to antigens that fit their surface receptors, na�ve lymphocytes remodel into massive, proliferating blast cells (immunoblasts for progenitor cells of immune effector cells, or centroblasts for blast cells of the germinal center). These blasts give rise to progeny that are able to direct activity against the inciting antigen: antigen-specific effector cells. Differentiation of Cells of the Adaptive Immune Response B cells and most T cells described earlier symbolize mediators of the adaptive immune system, which may recognize a nearly unlimited variety of antigens using specific receptors generated by the somatic recombination of the receptor genes. Memory cells are also generated, which assist respond quicker throughout subsequent contact with the antigen. B-Cell Differentiation Antigen-Independent B-Cell Differentiation Precursor B Cells Precursor B cells develop from hematopoietic stem cells and differentiate within the bone marrow before they migrate to the peripheral lymphoid tissues as na�ve mature B lymphocytes. The earliest phases lack floor immunoglobulin and are known as progenitor B cells (pro-B cells). In the subsequent steps, the precursor B cells (pre�B cells) acquire cytoplasmic mu heavy chain and later specific surface mu heavy chain with a surrogate light chain composed of two linked small peptides consisting of a variable area (Vpre-B) and a constant region (5). When light-chain rearrangement is complete, a whole surface IgM molecule is expressed (immature B cell). These antigens could activate the B cells instantly or could also be introduced by antigen-presenting cells. When na�ve B cells encounter antigen, they remodel into proliferating blast cells; a number of the daughter cells mature into short-lived plasma cells, producing the IgM antibody of the first immune response, however no memory cells are generated. Studies of the T-cell�independent immune response in the spleen have proven that na�ve B cells from the marginal zone are activated and rapidly rework into plasmablasts that localize in the sinuses. T-Cell�Dependent Germinal-Center Reaction Later in the primary response (within three to 7 days of antigen problem in experimental animals) and in secondary responses, the T-cell�dependent germinal-center response occurs. Each germinal center is fashioned from three to 10 na�ve B cells and in the end contains approximately 10,000 to 15,000 B cells; thus, more than 10 generations are required to kind a germinal heart. This process contains four major steps: proliferation, induction of immunoglobulin somatic hypermutation and sophistication switch, choice, and differentiation. Interactions between different transcription components within the germinal-center formation and B-cell differentiation. The antigen-stimulated B blasts differentiate into centroblasts, which seem at about 4 days and accumulate on the darkish zone of the germinal heart. This high proliferation is associated with the inactivation of cell cycle inhibitors and the expression of cell cycle activators. The proliferation program of germinal-center cells differs from that of proliferative cells in different tissues. The effect of this proapoptotic default program is to facilitate the survival of solely those cells that might be rescued by the era of extremely selected receptors to the precise antigen present in the germinal center. Centroblasts bear somatic hypermutation of the immunoglobulin V region genes, which alters the antigen affinity of the antibody produced by the cell. Somatic hypermutation leads to marked intraclonal variety of antibody-combining sites in a inhabitants of cells derived from only some precursors. Studies of single centroblasts picked from the dark zone of germinal centers counsel that within the early stages, a germinal heart could contain about 5 to 10 clones of centroblasts, which present solely a moderate amount of immunoglobulin V area gene mutation; later, the number of clones diminishes to as few as three, and the diploma of somatic mutation increases. Centroblasts mature to non-proliferating centrocytes, which accumulate within the opposite pole of the germinal center-the light zone. Cells within the light zone also undergo heavy-chain class change, which modifications the IgM fixed region to IgG, IgA, or, less commonly, IgE. The centrocytes are able to process the antigen and current it to T cells within the mild zone of the germinal heart.
Caduet 5mg discount overnight delivery
Silastic prostheses-a forgotten reason for lymphadenopathy in rheumatoid arthritis does cholesterol ratio 2.3 mean caduet 5mg purchase on-line. Silicone lymphadenopathy in a protracted distance runner: complication of a silastic prosthesis cholesterol ratio in human body order 5mg caduet. Primary prognosis of, whipple illness manifesting as lymphadenopathy: use of polymerase chain response for detection of Tropheryma whippelii. Whipple illness a century after the preliminary description: elevated recognition of surprising shows, autoimmune comorbidities, and remedy effects. Diagnosis of Whipple disease by immunohistochemical evaluation: a delicate and particular technique for the detection of Tropheryma whipplei (the Whipple bacillus) in paraffin-embedded tissue. Morphologic findings in lymph nodes after occlusion of their efferent lymphatic vessels and veins. Diagnostic analysis of patients with suspected haemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis. Subcutaneous panniculitis-like T-cell lymphoma: an elusive case presenting as lipomembranous panniculitis and a review of 72 circumstances within the literature. Haemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis in affiliation with granular lymphocyte proliferative problems in early childhood: characteristic bone marrow morphology. Langerhans cell histiocytosis of lymph nodes: a morphological assessment of 43 biopsies. Definitive, prognosis with the use of monoclonal antibody O10 on routinely paraffin-embedded samples. Autoimmune disease-associated lymphadenopathy with histological appearance of T-zone dysplasia with hyperplastic follicles. Paracortical alteration in lymphadenopathic and tumor-draining lymph nodes: histologic examine. An in situ immunohistochemical evaluation of primary, secondary, and tertiary T-nodules. Histologic evaluation of lymph nodes in mycosis fungoides/Sezary syndrome (cutaneous T-cell lymphoma): scientific correlations and 177. Histopathologic staging at preliminary prognosis of mycosis fungoides and the Sezary syndrome. Analysis of T-cell receptor gene rearrangement in lymph nodes of sufferers with mycosis fungoides. Diagnostic and prognostic significance of clonal T-cell receptor beta gene rearrangements in lymph nodes of patients with mycosis fungoides. Structural similarities between hematoidin crystals and asteroid our bodies: proof of lipid composition. Asteroid bodies: products of unusual microtubule dynamics in monocyte-derived big cells. T-cell subsets in sarcoidosis: an immunocytochemical investigation of blood, bronchoalveolar lavage fluid, and prescalenic lymph nodes from eight sufferers. Atypical mycobacterial cervicofacial lymphadenitis in kids: a disease as old as mankind, yet a persistent problem. Nontuberculous mycobacterial adenitis of the top and neck in kids: expertise from a tertiary care pediatric middle. An improved technique for the speciesspecific assessment of mycobacteria in routinely formalin-fixed and paraffin-embedded tissues. Cultural and morphologic findings in cervical and mediastinal lymph nodes at necropsy, with reference to fungi. Histopathology of human lymph node tularemia attributable to Francisella tularensis var palaearctica. Demonstration of Chlamydia trachomatis in inguinal lymphadenitis of lymphogranuloma venereum: a lightweight microscopy, electron microscopy and polymerase chain reaction examine. IgG4-related sclerosing illness: a important appraisal of an evolving clinicopathologic entity. Association between IgG4-related illness and progressively reworked germinal centers of lymph nodes. Epstein-Barr virus-infected cells in IgG4-related lymphadenopathy with comparability with extranodal IgG4-related illness. Involvement of regional lymph nodes and distinction from angiolymphoid hyperplasia with eosinophilia. Observations in regards to the, pathogenesis of epithelioid hemangioma (angiolymphoid hyperplasia). Infrequent detection of Toxoplasma gondii genome in toxoplasmic lymphadenitis: a polymerase chain response research. Lupus lymphadenitis: report of a case with immunohistologic studies on frozen sections. Lymphadenitis displaying focal reticulum cell hyperplasia with nuclear debris and phagocytes. Kikuchi illness in systemic lupus erythematosus: clinical features and literature evaluate. Inflammatory pseudotumor of lymph nodes: clinicopathologic and immunohistological study of eleven Japanese circumstances. Hypocellular anaplastic giant cell lymphoma mimicking inflammatory lesions of lymph nodes. Immunocytochemical identification of Rochalimaea henselae in bacillary (epithelioid) angiomatosis, parenchymal bacillary peliosis, and persistent fever with bacteremia. The spectrum of morphologic changes simulating lymphoma in lymph nodes and tonsils. Lymphadenopathy as a end result of infectious mononucleosis: its confusion with malignant lymphoma. Epstein-barr virus infection of monocytoid B-cell proliferates: an early function of major viral infection Epstein-Barr virus latent membrane protein expression by Hodgkin and Reed-Sternberg-like 204. Cytomegalovirus as a attainable reason for a illness resembling infectious mononucleosis. Concurrent herpes simplex viral lymphadenitis and persistent lymphocytic leukemia/small lymphocytic lymphoma, mimicking large-cell (Richter) transformation. Localized herpes simplex lymphadenitis: report of three instances and evaluate of the literature. Lymphadenopathy induced by anticonvulsant medicine and mimicking clinically pathologically malignant lymphomas. All lymphopoietic and hematopoietic cells are finally derived from pluripotent hematopoietic stem cells-slowly cycling cells with a capability for self-renewal.
Caduet 5mg buy generic on line
Most authors settle for that this condition is a variant of mycosis fungoides rather than an inflammatory disease cholesterol in eggs compared to meat 5 mg caduet cheap amex. Pagetoid reticulosis was initially described by Woringer and Kolopp in two kids; subsequent reviews have highlighted that it occurs in younger sufferers than is common for mycosis fungoides cholesterol levels vary day to day caduet 5 mg mastercard. It additionally differs from conventional mycosis fungoides by its failure to disseminate in most cases because it normally presents as a solitary plaque. Many sufferers obtain sturdy remissions by local therapeutic means, similar to excision of lesions or radiation remedy. Another entity that shares the moniker pagetoid reticulosis is the Ketron-Goodman variant of mycosis fungoides, with striking epidermotropism and disseminated lesions. A, Syringotropic mycosis fungoides features dense infiltrates of lymphocytes across the eccrine secretory coils. B, There may be hyperplasia of the epithelial and myoepithelial cells, much like that in epimyoepithelial islands. Woringer-Kolopp disease, or pagetoid reticulosis, presents as verrucous plaques on acral pores and skin. Histopathologic findings in pagetoid reticulosis include verrucous epidermal hyperplasia with infiltration of the epidermis, similar to or much more pronounced than that seen in typical mycosis fungoides. In the initial description of granulomatous mycosis fungoides, the authors noted that their affected person had survived longer than expected. Fourteen years later, their patient was still alive and had had granulomatous mycosis fungoides for nearly 3 decades. A reanalysis of the data appears to be prudent earlier than firm conclusions are reached in regards to the prognosis of this variant. Granulomatous Slack Skin Granulomatous slack skin is a peculiar situation in which the cells of an epidermotropic T-cell lymphoma entice histiocytes, which in turn digest elastic tissue and result in the formation of large saclike pores and skin folds. The disease impacts youthful sufferers than is usual for mycosis fungoides, with most cases beginning in young maturity. The most striking histopathologic function of granulomatous slack skin is involvement of the dermis and subcutaneous lobules by tuberculoid granulomas-clusters of histiocytes and large cells surrounded and infiltrated by small lymphocytes. Only when one examines the epidermis and papillary dermis is it evident that granulomatous slack skin is related to mycosis fungoides. Indeed, the changes in the superficial a half of the biopsy specimen may be equivalent to those of mycosis fungoides. Granulomatous slack pores and skin usually presents with pendulous masses within the axilla and groin. Gene rearrangement research have shown clonality in nearly all instances examined to date. Although S�zary syndrome was formerly thought of to be a leukemic counterpart of mycosis fungoides,eighty three more recent studies have demonstrated different molecular phenotypes in these two circumstances. Whereas light microscopic evaluation of peripheral blood was used prior to now to assess for the presence of S�zary cells within the peripheral blood, studies have since demonstrated limitations to this method. In particular, a small cell variant of the S�zary cell was described that might not have been detected on a peripheral smear. Granulomatous slack skin normally shows a dense, diffuse infiltrate of small lymphocytes all through the dermis (A), with infiltration of the dermis much like that seen in mycosis fungoides and large histiocytic big cells that exhibit elastophagocytosis (B). Recognition of these cells is now not important for the prognosis for the reason that introduction of clonality research and flow cytometry. The time period erythroderma is usually overused by clinicians; it should check with confluent erythema, not simply widespread erythematous lesions. Chromosomal abnormalities could be recognized in S�zary syndrome, however nobody abnormality is present in a preponderance of circumstances. The histopathologic findings in S�zary syndrome typically fall in need of being diagnostic. In reality, one study confirmed that diagnostic findings of S�zary syndrome are current in only 60% of instances. As such, if S�zary syndrome is a severe clinical consideration, analysis of the peripheral blood for the presence of a clone or an irregular immunophenotype as assessed by flow cytometry should be carried out, as discussed earlier than. If these exams present findings that meet the standards for diagnosis, the patient must be categorised as having S�zary syndrome with nondiagnostic skin biopsies. Erythroderma is a medical sign during which the complete skin becomes purple and sometimes scaly. In erythroderma because of lymphoma, the pores and skin can turn into doughy as properly in some circumstances however not in all. There are many other causes of erythroderma in addition to S�zary syndrome, however its presence in a middle-aged or older affected person ought to evoke a differential prognosis that includes lymphoma. Hyperkeratosis of the palms and soles leads to red, scaly, and sometimes fissured skin. Differential Diagnosis Because of the numerous inflammatory situations that cause erythroderma and because of the shortage of diagnostic adjustments in the biopsy specimens of many sufferers with S�zary syndrome, one must method the differential analysis of erythroderma with nice caution. The most common causes of erythroderma include psoriasis, pityriasis rubra pilaris, generalized allergic contact dermatitis, and drug eruptions. In basic, the histopathologic options of erythrodermic presentations of inflammatory skin diseases are these of the underlying condition. The findings in erythrodermic psoriasis resemble these of early patches of psoriasis rather than well-developed plaques. The rete ridges are slightly elongated; keratinocytes have pale cytoplasm; and dilated, tortuous vessels are distinguished in edematous dermal papillae and may even seem to touch the undersurface of the dermis. Pityriasis rubra pilaris shares many features with psoriasis, but it presents with diffuse orange-red pores and skin. The palms and soles of affected sufferers are often thickened by cornified material that has been likened to carnauba wax. Biopsy specimens of pityriasis rubra pilaris often show slight psoriasiform epidermal hyperplasia, an dermis with a gently undulating surface, and lamellar hyperkeratosis containing scattered parakeratotic nuclei. Histopathologic Features Diagnostic biopsy specimens of S�zary syndrome show equivalent features to definitive biopsy specimens of late patch- or plaque-stage mycosis fungoides. Nonetheless, performing pores and skin biopsies as a way to diagnose S�zary syndrome can be a irritating train because spongiosis may be the predominant finding Chapter 39 � Mycosis Fungoides and S�zary Syndrome 729 Erythrodermic allergic contact dermatitis represents a generalized response to a contactant. There could additionally be extra of an inclination for the inflammatory cells in the papillary dermis to have a bandlike sample than in standard allergic contact dermatitis. These embody the findings of spongiotic dermatitis, interface dermatitis, and, hardly ever, psoriasiform dermatitis. Histopathologic features of early (patch) lesions of mycosis fungoides: a morphologic study on 745 biopsy specimens from 427 patients. Light-microscopic evaluation of a hundred patients with patch/plaque-stage mycosis fungoides. Transformation of mycosis fungoides/S�zary syndrome: scientific characteristics and prognosis. Long-term end result of 525 patients with mycosis fungoides and S�zary syndrome: clinical prognostic factors and threat for disease progression.
Syndromes
- Infection in the joint
- Autoimmune disorders such as bullous pemphigoid or pemphigus
- Certain medicines
- Ear infections
- H2 blockers, like Pepcid AC, Tagamet, and Zantac, reduce stomach acid production.
- Vomiting blood
- Hold the view they are not good socially, not as good as other people, or unappealing
- Slight blurring of vision due to excess oil in tears -- usually cleared by blinking
- You will probably have general anesthesia. This will make you unconscious and unable to feel pain. Or, you may have epidural or spinal anesthesia instead. The doctor will inject your spine with medicine to make you numb from your waist down.
- Vasoactive intestinal peptide (VIP) level in the blood
5 mg caduet order mastercard
In such circumstances cholesterol meter cheap caduet 5mg line, the report ought to indicate what additional materials or research are required for a conclusion to be reached dietary portfolio of cholesterol-lowering foods order caduet 5mg mastercard. In the absence of any of the three major clonal mutations, a search for other myeloid neoplasm�associated mutations. Polycythemia vera and essential thrombocythemia: 2015 update on diagnosis, riskstratification and management. Primary myelofibrosis: 2014 replace on prognosis, risk-stratification, and management. Clonality in persistent myeloproliferative disorders outlined by X-chromosome linked probes: demonstration of heterogeneity in lineage involvement. Chronic myelogenous leukemia and exposure to ionizing radiation-a retrospective research of 443 sufferers. Increased risks of polycythemia vera, essential thrombocythemia, and myelofibrosis among 24,577 first-degree relatives of 11,039 sufferers with myeloproliferative neoplasms in Sweden. Agnogenic myeloid metaplasia: a clonal proliferation of hematopoietic stem cells with secondary myelofibrosis. Bone marrow fibrosis in myeloproliferative neoplasms�associated myelofibrosis: deconstructing a fantasy Endogenous erythroid colony formation by peripheral blood mononuclear cells from patients with myelofibrosis and polycythemia vera. A new constant chromosomal abnormality in continual myelogenous leukaemia identified by quinacrine fluorescence and Giemsa staining [Letter]. A mobile oncogene is translocated to the Philadelphia chromosome in persistent myelocytic leukaemia. Philadelphia chromosomal breakpoints are clustered within a restricted area, bcr, on chromosome 22. Induction of continual myelogenous leukemia in mice by the P210bcr/ abl gene of the Philadelphia chromosome. Effects of a selective inhibitor of the Abl tyrosine kinase on the expansion of Bcr-Abl constructive cells. Rabaptin-5 is a novel fusion partner to platelet-derived progress factor beta receptor in continual myelomonocytic leukemia. A primer on genomic and epigenomic alterations within the myeloproliferative neoplasms. Regional variations in age at diagnosis and overall survival amongst patients with chronic myeloid leukemia from low and center earnings international locations. Evidence from a leukaemia mannequin for upkeep of vascular endothelium by bone-marrow-derived endothelial cells. Estimations of the increasing prevalence and plateau prevalence of chronic myeloid leukemia within the era of tyrosine kinase inhibitor therapy. Update on current monitoring recommendations in continual myeloid leukemia: practical factors for scientific practice. Clinical and biological, options at prognosis in forty children with chronic myeloid leukemia. Clinical features at diagnosis in 430 sufferers with persistent myeloid leukaemia seen at a referral centre over a 16-year period. The continual myeloid leukaemias: pointers for distinguishing persistent granulocytic, atypical continual myeloid, and continual myelomonocytic leukaemia. Extreme thrombocy, tosis in continual myeloid leukemia in the period of tyrosine kinase inhibitors. Diagnostic significance of detecting dysgranulopoiesis in persistent myeloid leukemia. Bone marrow histopathology in the diagnosis of continual myeloproliferative disorders: a forgotten pearl. The relevance of reticulin stain�measured fibrosis at analysis in persistent myelogenous leukemia. Transformation of chronic myelogenous leukemia: scientific, morphologic, and cytogenetic options. Translocation of c-ab1 oncogene correlates with the presence of a Philadelphia chromosome in persistent myelocytic leukaemia. Gene expression changes related to progression and response in continual myeloid leukemia. Potential mechanisms of illness progression and management of advanced-phase chronic myeloid leukemia. Causes of resistance and treatment decisions of second- and thirdline therapy in chronic myelogenous leukemia sufferers. Predicting, early blast transformation in chronic-phase continual myeloid leukemia: is immunophenotyping the lacking hyperlink Sudden onset of the blastic phase of continual myelogenous leukemia: patterns and implications. The immunophenotype of blast transformation of persistent myelogenous leukemia: a excessive frequency of blended lineage phenotype in "lymphoid" blasts and a comparability of morphologic, immunophenotypic, and molecular findings. Immunophenotype and ultrastructural research in blast crisis of chronic myeloid leukemia. Phenotype of blasts in persistent myeloid leukemia in blastic phase- analysis of bone marrow trephine biopsies and correlation with cytogenetics. Characterisation of blast cells during blastic section of persistent myeloid leukaemia by immunophenotyping-experience in 60 sufferers. Blast part in chronic myelogenous leukemia is skewed towards uncommon blast varieties in sufferers handled with tyrosine kinase inhibitors: a comparative study of 67 cases. Coexistence of inversion 16 and the Philadelphia chromosome in acute and chronic myeloid leukemias: report of six circumstances and review of literature. Five-year, follow-up of sufferers receiving imatinib for persistent myeloid leukemia. Eosinophilic myeloid issues: new classification and novel therapeutic methods. Pathogenesis and classification of eosinophil issues: a review of current developments within the field. Bedside to bench in juvenile myelomonocytic leukemia: insights into leukemogenesis from a uncommon pediatric leukemia. Chronic neutrophilic leukaemia and plasma cell�related neutrophilic leukaemoid reactions. Chronic neutrophilic leukaemia: 14 new cases of an uncommon myeloproliferative disease. Chronic neutrophilic leukemia 2014: replace on prognosis, molecular genetics, and administration. Hematological and iron-related analytes-reference data for persons aged 1 yr and over: United States, 198894. Blast transformation and fibrotic development in polycythemia vera and essential thrombocythemia: a literature evaluation of incidence and risk elements.
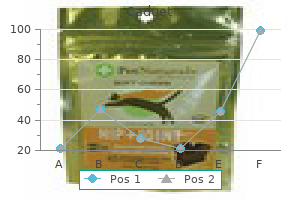
Order caduet 5 mg with visa
As mentioned earlier cholesterol and food labels generic 5 mg caduet amex, the thymus is incessantly concerned in mediastinal disease cholesterol ratio 3.8 best 5 mg caduet, which is sort of all the time of the nodular sclerosis subtype. Major variations in antigen expression in multiple biopsy websites or recurrences from the identical affected person are rare, especially with using heat-induced antigen retrieval. However, the digital lack of a B-cell gene-expression profile underlines that the sum of genetic alterations of a neoplastic cell quite than its origin shapes its phenotype and clinical conduct. The pure history of the disease is characterised by gradual but relentless tumor development with extensive organ involvement, and in the past, many patients succumbed to infectious problems. In the last a long time, a vast variety of medical options and biomarkers related to medical outcome have been described. However, immunohistochemical stains often make the neoplastic character of the background inhabitants in these cases readily obvious. It presents with cumbersome mediastinal disease and is characterized by a diffuse proliferation of medium-sized to massive blasts usually with clear cytoplasm, generally resembling lacunar cells. Many instances present a dense meshwork of collagen fibers rather than concentric fibrosis. These two parts could also be identified sequentially at different times, suggesting phenotypic plasticity of the neoplastic clone. Both entities normally show a predominance of B cells within the background population and contain follicular dendritic cell networks. Infectious mononucleosis typically shows florid interfollicular hyperplasia, with no less than partial preservation of the lymph node architecture. Morphologically, the range of cell sizes and the marked cytoplasmic basophilia of many blasts are indicators of a reactive dysfunction. This disorder, which appears to be extra widespread in Asian countries, is believed to be the end result of a deteriorated immune system brought on by the getting older course of. However, one should concentrate on the potential pitfalls of a restricted antibody panel. Loss of the B-lineage-specific gene expression program in Hodgkin and Reed-Sternberg cells of Hodgkin lymphoma. Shades of gray between large B-cell lymphomas and Hodgkin lymphomas: differential diagnosis and biological implications. A revised EuropeanAmerican classification of lymphoid neoplasms: a proposal from the international lymphoma research group. From Hodgkin disease to Hodgkin lymphoma: biologic insights and therapeutic potential. Epstein-Barr, virus latent membrane protein expression in Hodgkin and Reed-Sternberg cells. Contribution of the Epstein Barr virus to the molecular pathogenesis of Hodgkin lymphoma. Analyzing major Hodgkin and Reed-Sternberg cells to seize the molecular and cellular pathogenesis of classical Hodgkin lymphoma. Analysis of, Epstein-Barr virus gene polymorphisms in normal donors and in virus-associated tumors from totally different geographic locations. European Task Force on Lymphoma project on lymphocyte predominance Hodgkin illness: histologic and immunohistologic evaluation of submitted cases reveals 2 types of Hodgkin illness with a nodular development pattern and abundant lymphocytes. Infectious mononucleosis, childhood social environment, and threat of Hodgkin lymphoma. Clinically unsuspected Hodgkin disease presenting initially within the bone marrow of patients infected with the human immunodeficiency virus. Clinical and histoimmunophenotypic findings and affiliation with Epstein-Barr virus in 16 instances. Identification of Hodgkin and Sternberg-Reed cells as a unique cell type derived from a newly-detected small-cell population. Hodgkin and Sternberg-Reed cells contain antigens particular to late cells of granulopoiesis. Expression patterns of transcription factors in progressively transformed germinal facilities and Hodgkin lymphoma. Hodgkin lymphoma: pathology, pathogenesis, and a plethora of potential prognostic predictors. A paraffin-section immunohistochemical examine utilizing the heat-induced epitope retrieval method. The nature of the lymphocytes surrounding Reed- Sternberg cells in nodular lymphocyte predomi- 181. Hodgkin illness: Hodgkin and Reed-Sternberg cells picked from histological sections present clonal immunoglobulin gene rearrangements and seem to be derived from B cells at various phases of growth. Hodgkin and Reed-Sternberg cells symbolize an expansion of a single clone originating from a germinal middle B-cell with useful immunoglobulin gene rearrangements however faulty immunoglobulin transcription. Defective octamerdependent transcription is answerable for silenced immunoglobulin transcription in Reed-Sternberg cells. Peripheral T-cell lymphoma with Reed-Sternberglike cells of B-cell phenotype and genotype related to Epstein-Barr virus an infection. Classical Hodgkin lymphoma is characterized by recurrent copy number features of the short arm of chromosome 2. Gene expression profiling of microdissected Hodgkin Reed-Sternberg cells correlates with therapy consequence in classical Hodgkin lymphoma. Epigenetic, processes play a serious role in B-cell-specific gene silencing in classical Hodgkin lymphoma. Activated Notch1 signaling promotes tumor cell proliferation and survival in Hodgkin and anaplastic large cell lymphoma. Biologic features of Hodgkin lymphoma and the development of biologic prognostic factors in Hodgkin lymphoma: tumor and microenvironment. Immunosuppressive regulatory T cells are abundant in the reactive lymphocytes of Hodgkin lymphoma. Galectin-1 mediated suppression of Epstein-Barr virus specific T-cell immunity in traditional Hodgkin lymphoma. Mediastinal diffuse giant cell lymphoma with sclerosis: a clinicopathologic analysis of 60 circumstances. Gray zone lymphoma: chromosomal aberrations with immunophenotypic and medical correlations. Primary mediastinal large B-cell lymphoma: a clinicopathologic examine of 141 instances compared with 916 nonmediastinal massive 272. World Health Organization Classification of Neoplastic Diseases of the Hematopoietic and Lymphoid Tissues: report of the Clinical Advisory Committee Meeting Airlie House, Virginia, November 1997. Follicular peripheral T-cell lymphoma expands the spectrum of classical Hodgkin lymphoma mimics. Post-transplant lymphoproliferative issues: a morphologic, phenotypic and genotypic spectrum of illness. Epstein-Barr virus latent membrane protein expression by Hodgkin and Reed-Sternberg-like cells in acute infectious mononucleosis.
Caduet 5mg purchase with visa
The primary differential diagnoses are listed in Table 23-6 (see additionally the Pearls and Pitfalls field at the finish of this chapter) food cholesterol chart uk order caduet 5 mg without prescription. Similarities embody incidence in young sufferers cholesterol usmle cheap caduet 5mg on line, predominant anterior mediastinal location, large tumor cells, and sclerosis. Thymic carcinoma and neuroendocrine tumor might enter into the differential diagnosis in small biopsy samples. The neurologic signs are often bizarre, owing to the presence of a quantity of sites of infarct ensuing from vascular occlusion. Patients may have a number of of the 4 neurologic syndromes: multifocal cerebrovascular events, spinal wire and roots lesions, subacute encephalopathy, and peripheral or cranial neuropathy. They normally lack lymphadenopathy, mass lesions, neurologic abnormalities, or skin lesions. A, the non-cohesive lymphoma cells are confined inside medium-sized blood vessels. B, Lymphoma cells distend the capillaries of the glomeruli and the renal parenchyma. The lymphoma cells may be entrapped within organized fibrin thrombi, and there could also be superimposed florid endothelial hyperplasia. Palisading of tumor cells alongside the luminal side of the blood vessel ends in an angiosarcoma-like appearance. A, In the prostate, plugging of the blood vessels by tumor cells leads to a sample reminiscent of islands of carcinoma. B, this island resembles high-grade carcinoma because of the apparently cohesive development and the presence of glandlike areas. The surrounding mind parenchyma shows rarefaction as a outcome of ischemia from the vascular occlusion. Mediastinal germ-cell tumor and T-lymphoblastic lymphoma are extra considerations in young male sufferers. The histologic features and immunoprofile must be considered to make the distinction. The blasts normally have fantastic chromatin, and cytoplasmic granules may be present in the myeloid type. Blasts in acute myeloid leukemia usually specific myeloperoxidase but not pan�B-cell or pan�T-cell markers, whereas those in acute lymphoblastic leukemia specific terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase (TdT) with pan�B-cell or pan�Tcell markers. In sufferers with carcinomatosis, clusters of carcinoma cells may be lodged in the small lymphovascular channels. A revised European-American classification of lymphoid neoplasms: a proposal from the International Lymphoma Study Group [see comments]. Malignant lymphoma in southern Taiwan in accordance with the revised EuropeanAmerican classification of lymphoid neoplasms. B-cell lineage confers a positive end result among kids and adolescents with large-cell lymphoma: a Pediatric Oncology Group research. Large cell non-Hodgkin lymphoma of childhood: Analysis of seventy eight consecutive patients enrolled in 2 thirteen. Epstein-Barr viruspositive B-cell lymphoproliferative problems arising in immunodeficient patients beforehand treated with fludarabine for low-grade B-cell neoplasms. B-cell lymphoma after angioimmunoblastic lymphadenopathy: a case with oligoclonal gene rearrangements associated with Epstein-Barr virus. Oyama T, Ichimura K, Suzuki R, Suzumiya J, Ohshima K, Yatabe Y, Yokoi T, Kojima M, Kamiya Y, Taji H, Kagami Y, Ogura M, Saito H, Morishima Y, Nakamura S. Metallic implant-associated lymphoma: a definite subgroup of huge B-cell lymphoma related to pyothoraxassociated lymphoma Primary juxtaarticular delicate tissue lymphoma arising in the neighborhood of inflamed joints in sufferers with rheumatoid arthritis. Correlation of morphologic, immunophenotypic, and molecular genetic findings in 12 instances. Diffuse histiocytic lymphoma with sclerosis: a clinicopathologic entity incessantly inflicting superior venacaval obstruction. Kojima M, Nakamura S, Motoori T, Kurabayashi Y, Hosomura Y, Itoh H, Yoshida K, Suzuki R, Seto M, Koshikawa T, Suchi T, Joshita T. Centroblastic and centroblastic-centrocytic lymphomas associated with outstanding epithelioid granulomatous response with out plasma cell differentiation: a clinicopathologic examine of 12 circumstances [see comments]. Cutaneous spindle-cell B-cell lymphoma: a morphologic variant of cutaneous large B-cell lymphoma. Transformation of monocytoid B-cell lymphoma to massive cell lymphoma associated with crystal-storing histiocytes. Comparison of anaplastic giant cell Ki-1 lymphomas and microvillous lymphomas in their immunologic and ultrastructural features. Harada S, Suzuki R, Uehira K, Yatabe Y, Kagami Y, Ogura M, Suzuki H, Oyama A, Kodera Y, Ueda R, Morishima Y, Nakamura S, Seto M. Molecular and immunological dissection of diffuse giant B cell lymphoma: Chapter 23 � Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma 445. Immunophenotypic and genotypic markers of follicular center cell neoplasia in diffuse giant B-cell lymphomas. Germinal heart phenotype and bcl-2 expression mixed with the International Prognostic Index improves affected person danger stratification in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. The t(14;18) defines a unique subset of diffuse massive B-cell lymphoma with a germinal middle B-cell gene expression profile. Onizuka T, Moriyama M, Yamochi T, Kuroda T, Kazama A, Kanazawa N, Sato K, Kato T, Ota H, Mori S. Falini B, Fizzotti M, Pucciarini A, Bigerna B, Marafioti T, Gambacorta M, Pacini R, Alunni C, Natali-Tanci L, Ugolini B, Sebastiani C, Cattoretti G, Pileri S, DallaFavera R, Stein H. Valera A, Lopez-Guillermo A, Cardesa-Salzmann T, Climent F Gonzalez-Barca E, Mercadal S, Espinosa I, 445. Bellas C, Garcia D, Vicente Y, Kilany L, Abraira V, Navarro B, Provencio M, Martin P. Immunohistochemical and molecular traits with prognostic significance in diffuse giant B-cell lymphoma. Clinical significance of bcl2 and p53 protein expression in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma: a population-based research. Different bcl-2 protein expression in high-grade B-cell lymphomas derived from lymph node or mucosa-associated lymphoid tissue. Yamaguchi M, Seto M, Okamoto M, Ichinohasama R, Nakamura N, Yoshino T, Suzumiya J, Murase T, Miura I, Akasaka T, Tamaru J, Suzuki R, Kagami Y, Hirano M, Morishima Y, Ueda R, Shiku H, Nakamura S. Nakamura N, Kuze T, Hashimoto Y, Hara Y, Hoshi S, Sasaki Y, Shirakawa A, Sato M, Abe M.
5 mg caduet generic
Prediction of survival in diffuse giant B-cell lymphoma based mostly on the expression of 2 genes reflecting tumor and microenvironment cholesterol test validity purchase 5 mg caduet mastercard. A redox signature score identifies diffuse giant B-cell lymphoma sufferers with a poor prognosis cholesterol value in eggs caduet 5 mg buy otc. Vitolo U, Gaidano G, Botto B, Volpe G, Audisio E, Bertini M, Calvi R, Freilone R, Novero D, Orsucci L, Pastore C, Capello D, Parvis G, Sacco C, Zagonel V, Carbone A, Mazza U, Palestro G, Saglio G, Resegotti L. Rearrangements of bcl-6, bcl-2, c-myc and 6q deletion in B-diffuse large-cell lymphoma: medical relevance in 71 sufferers. Vitolo U, Botto B, Capello D, Vivenza D, Zagonel V, Gloghini A, Novero D, Parvis G, Calvi R, Ariatti C, Milan I, Bertini M, Boccomini C, Freilone R, Pregno P, Orsucci L, Palestro G, Saglio G, Carbone A, Gallo E, Gaidano G. Akasaka T, Akasaka H, Ueda C, Yonetani N, Maesako Y, Shimizu A, Yamabe H, Fukuhara S, Uchiyama T, Ohno H. Ichikawa A, Kinoshita T, Watanabe T, Kato H, Nagai H, Tsushita K, Saito H, Hotta T. A study of five phenotypically unusual cases verified by polymerase chain reaction. Bernard M, Gressin R, Lefrere F Drenou B, Branger B, Caulet-Maugendre S, Tass P, Brousse N, Valensi F, Milpied N, Voilat L, Sadoun A, Ghandour C, Hunault M, Leloup R, Mannone L, Hermine O, Lamy T. The cytomorphological spectrum of mantle cell lymphoma is reflected by distinct organic features. Large-cell variants of mantle cell lymphoma: cytologic traits and p53 anomalies could predict poor consequence. Morphology, immunophenotype, and distribution of latently and/or productively Epstein-Barr virus-infected cells in acute infectious mononucleosis: implications for the interindividual an infection route of Epstein-Barr virus. A study of 30 instances, supporting its histologic heterogeneity and lack of scientific Chapter 23 � Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma445. T-cell/histiocyte-rich large B-cell lymphoma: a definite clinicopathologic entity. T-cell/histiocyte-rich large B-cell lymphoma: a heterogeneous entity with derivation from germinal heart B cells. Interleukin-4 could contribute to the ample T-cell response and paucity of neoplastic B cells in T-cell-rich B-cell lymphomas. Nodular lymphocyte-predominant Hodgkin lymphoma with nodules resembling T-cell/histiocyterich B-cell lymphoma: differential prognosis between nodular lymphocyte-predominant Hodgkin lymphoma and T-cell/histiocyte-rich B-cell lymphoma. Nodular lymphocyte predominant hodgkin lymphoma and T cell/histiocyte rich large B cell lymphoma�endpoints of a spectrum of 1 illness Histiocyte-rich, T-cell-rich B-cell lymphoma: a definite diffuse large B-cell lymphoma subtype displaying characteristic morphologic and immunophenotypic features. Micronodular T-cell/histiocyte-rich large B-cell lymphoma of the spleen: histology, immunophenotype, and differential analysis. Molecular analysis reveals somatically mutated and unmutated clonal and oligoclonal B cells in T-cell-rich B-cell lymphoma. Molecular analysis of single B cells from T-cell-rich B-cell lymphoma reveals the derivation of the tumor cells from mutating germinal middle B cells and exemplifies means by which immunoglobulin genes are modified in germinal heart B cells. Franke S, Wlodarska I, Maes B, Vandenberghe P, Achten R, Hagemeijer A, De Wolf-Peeters C. Array comparative genomic hybridization reveals similarities between nodular lymphocyte predominant Hodgkin lymphoma and T cell/histiocyte wealthy massive B cell lymphoma. Van Loo P, Tousseyn T, Vanhentenrijk V, Dierickx D, Malecka A, Vanden Bempt I, Verhoef G, Delabie J, Marynen P, Matthys P, De Wolf-Peeters C. T-cell/ histiocyte-rich large B-cell lymphoma shows transcriptional options suggestive of a tolerogenic host immune response. Epstein-Barr virus, related hemophagocytic syndrome in a T-cell rich B-cell lymphoma. Bouabdallah R, Mounier N, Guettier C, Molina T, Ribrag V, Thieblemont C, Sonet A, Delmer A, Belhadj K, Gaulard P, Gisselbrecht C, Xerri L. T-cell/histiocyte-rich massive B-cell lymphomas and classical diffuse massive B-cell lymphomas have similar end result after chemotherapy: a matched-control evaluation. T cell/histiocyte-rich giant B-cell lymphoma: an replace on its biology and classification. Primary cutaneous T-cell-rich B-cell lymphoma: clinically distinct from its nodal counterpart Large B-cell lymphoma with T-cell-rich background and nodules lacking follicular dendritic cell meshworks: description of an insufficiently acknowledged variant. Epstein-Barr virus-associated B-cell lymphoproliferative disorders in angloimmunoblastic T-cell lymphoma and peripheral T-cell lymphoma, unspecified. Frequent detection of Epstein-Barr virus-infected B cells in peripheral T-cell lymphomas. Mediastinal large-B-cell lymphoma with sclerosis: a medical examine of 21 patients. Primary mediastinal B-cell lymphoma with sclerosis: an aggressive tumor with distinctive scientific and pathologic options. Large cell lymphoma of the mediastinum: a B-cell tumour of probable thymic origin. Mediastinal B-cell lymphoma: a study of its histomorphologic spectrum based on 109 circumstances. Treatment outcome and prognostic factors for major mediastinal (thymic) B-cell lymphoma: a multicenter research of 106 sufferers. Identification of Primary Mediastinal Large B-cell Lymphoma at Nonmediastinal Sites by Gene Expression Profiling. A low serum beta 2-microglobulin level regardless of bulky tumor is a characteristic feature of main mediastinal (thymic) massive B-cell lymphoma: implications for serologic staging. Diffuse giant cell and undifferentiated lymphomas with outstanding mediastinal involvement. Primary large-cell, lymphoma of the thymus: a diffuse B-cell neoplasm presenting as primary mediastinal lymphoma. Mediastinal massive B-cell lymphoma: new proof in support of its distinctive identity. Moller P, Moldenhauer G, Momburg F Lammler B, Eberlein-Gonska M, Kiesel S, Dorken B. Mediastinal lymphoma of clear cell type is a tumor similar to terminal steps of B cell differentiation. Isotype, switched immunoglobulin genes with a high load of somatic hypermutation and lack of ongoing mutational activity are prevalent in mediastinal B-cell lymphoma. Downregulation of inside enhancer exercise contributes to abnormally low immunoglobulin expression within the MedB-1 mediastinal B-cell lymphoma cell line. Immunohistochemical study on normal thymus and lymphofollicular hyperplasia of the thymus. Immunophenotypic similarities of mediastinal clear-cell lymphoma and sinusoidal (monocytoid) B cells. Similar patterns of genomic alterations characterize main mediastinal large-B-cell lymphoma and diffuse large-B-cell lymphoma.
Caduet 5mg line
Depending on the prevalent defect and signs cholesterol levels in beef purchase 5 mg caduet with visa, a few of the inherited problems are listed underneath a quantity of headings cholesterol levels diet purchase caduet 5 mg online. Morphologically, lymph nodes show complete effacement of the structure with a depleted look and elevated number of dendritic cells and eosinophils; they usually lack primary and secondary B follicles. The underlying genetic defect is unknown in the majority of instances, and it remains a analysis of exclusion. Incidence ranges from 1: 10,000 to 1: 50,000 (Europe/North America); women and men are equally affected. Clinically the symptoms are very heterogeneous, however two major teams could be broadly recognized based on predominant recurrent infections of the respiratory tract versus inflammatory problems with a selection of autoimmune issues (22% to 48%) including cytopenias, granulomatous illness, and increased improvement of malignancy, mainly lymphomas. From the pathology standpoint, the lungs are the major target organ with acute bacterial infections, with possible subsequent improvement of bronchiectasis and non-infectious immune-mediated adjustments with lymphocytic interstitial infiltrate, follicular bronchiolitis, and follicular hyperplasia with typically "bare" germinal facilities and paucity of plasma cells. It presents with recurrent upper and decrease respiratory tract involvement due to opportunistic infections (P. Subsequent issues involving the biliary tree and liver are often related to Cryptosporidium- and Giardia-persistent infections of the biliary system leading to sclerosing cholangitis, hepatitis, cirrhosis, and increased gastrointestinal malignancies including cholangiocarcinoma. Morphologically the lymph nodes are characterised by florid follicular hyperplasia with massive, expanded germinal facilities. A, Small lymph node with prominent paracortical hyperplasia missing secondary B follicles in the cortex. In addition, outstanding lymphoid aggregates in keeping with nodular lymphoid hyperplasia are noted. The presence of ill-defined follicular structures might have led in the past to overdiagnosed B-cell lymphomas due to the impression of a distorted structure. Immunophenotypic research as nicely as clonality studies are helpful in clarifying the analysis in such circumstances. It is noteworthy that these patients more frequently additionally had splenomegaly, granulomatous disease, and enteropathy, that are all associated with decreased overall survival. Immunoglobulin ranges have been variable (IgG), but normally excessive for IgM with low IgA; falling ranges of IgG were noticed over time in some sufferers. These observations were confirmed by in vitro studies the place the B-cell proliferation was within normal limits, however the cells have impaired immunoglobulin production (defects in class-switch recombination). Often these patients had prominent lymphadenopathy involving central and peripheral lymph nodes with compression of the airways in some patients. A, Low-power view displaying typical options with "naked" reactive germinal centers and distinguished monocytoid B-cell reaction. B, Numerous IgM-positive cells are within the parafollicular areas, and IgG-positive cells are additionally current throughout the germinal center (C). Subsequent biopsy (6 years interval) reveals related morphologic features, with giant expanded naked germinal facilities (D) surrounded by numerous IgM-positive cells (E), and very few IgGpositive cells (F), in keeping with the serum immunoglobulin ranges, simulating a hyper IgM syndrome. In some circumstances, the monocytoid B-cell response was extra in depth, elevating the potential of involvement by nodal marginal-zone lymphoma. These patients, as properly as, show outstanding nodular lymphoid hyperplasia involving the respiratory and gastrointestinal tracts with outstanding proliferation of B cells and T cells, usually with germinal-center formation with out significant colitis. David Purtilo and colleagues described it in 1975 primarily based on a study from a single generation of the Duncan household. It is a uncommon immunodeficiency with an incidence of roughly 1 to 2 per million males. In uncommon instances, aplastic anemia, vasculitis, and lymphomatoid granulomatosis have been described in these patients. It is of interest that the diagnosis was regularly delayed even in sufferers with a constructive household history; regardless, nearly all sufferers grew to become symptomatic earlier than 5 years of age. Autosomal Dominant Immune Dysregulation Syndrome with Heterozygous Germline Mutations of Cytotoxic T-Cell Antigen-4 this illness has been recently characterized. Histologically, the infiltrate was either lymphohistiocytic with scattered plasma cells or mostly lymphoplasmacytic. These problems have provided the chance to better perceive the regulatory T-cell operate both centrally and peripherally, their improvement and their maintenance of homeostasis. It has been proven that a quantity of patients have diminished and defective Tregs65; nevertheless, it stays unclear whether these adjustments take place within the thymus or in peripheral organs. A and B, Lymphohistiocytic infiltrates involving the white matter with isolated plasma cells are shown. C, A dense plasmacytic perivascular infiltrate extending into the surrounding mind parenchyma; the plasma cells are polyclonal. A progressive B-cell lymphopenia was additionally famous with a rise of autoreactive B cells. The presence of typical morphologic and immunophenotypic findings represents one of the secondary accent standards. Female carriers are asymptomatic, with extreme uncommon symptomatic cases because of deleterious mutations on the paternally derived X and nonrandom inactivation of the maternally derived X. Spontaneous chimerism because of genetic reversion, which may confer a selective advantage, has been observed in about 11% of sufferers, however the medical significance of this discovering is unclear. Clinically, sufferers current with pores and skin rash (eczema) and bleeding (80%) corresponding to petechiae and ecchymoses. In addition, only a 60% penetrance was found among family members carrying the same heterozygous gene mutation, indicating that different genetic differences or modifiers might exist. As expected, almost all symptomatic sufferers had continual adenopathy and splenomegaly. High risk for sepsis was extra pronounced in sufferers that underwent splenectomy at a younger age. Abundant S-100�positive dendritic cells are also current inside the expanded paracortex. Sequencing also has been used in the context of prenatal prognosis in at-risk couples. Laboratory findings confirm that every one arms of the immune system are affected: adaptive, humoral, and innate. Analysis of lymphocyte subsets reveals T-cell lymphopenia (lymphocyte depend >1,000/�L) with an irregular response to mitogen. T-cell defects also result in impaired antibody production by B cells, however intrinsic defects in B cells have additionally been described with hyperresponsiveness and autoantibody manufacturing. This deficit in cytotoxic exercise, at the facet of the lymphopenia and intrinsic T-cell and B-cell defects, could additionally be in the end liable for the lack to clear infectious brokers and may contribute to the development of B-cell lymphomas. Primary immunodeficiency diseases: an update on the classification from the worldwide union of immunological societies skilled committee for major immunodeficiency. Phosphoinositide, 3-kinase delta gene mutation predisposes to respiratory infection and airway harm. Also, other malignancies had been very uncommon (rare) like myeloid neoplasms, mature T cell malignancies, and carcinomas involving breast, gastric, liver, and thyroid.