Adalat dosages: 30 mg, 20 mg
Adalat packs: 30 pills, 60 pills, 90 pills, 120 pills, 180 pills, 270 pills, 360 pills
30 mg adalat purchase amex
Appreciable proof exists that infections really confined to the bladder or urethra respond as well to single-dose or short-course (3-day) therapy as to standard remedy for 10 to 14 days arteria carotis communis adalat 30 mg cheap with amex. Reviews of short-course therapy have concluded that 3-day regimens are simpler than single-dose therapy blood pressure varies 20 mg adalat effective. One randomized trial evaluated 4 totally different 3-day drug regimens in ladies with uncomplicated acute cystitis. A 3-day regimen of trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole was simpler than a 3-day regimen of nitrofurantoin. The 3-day routine of trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole was probably the most cost-effective routine. This number of remedies is a vital breakthrough within the administration of uncomplicated cystitis and coliform urethritis, as a result of all patients had been treated formerly with the standard 10 to 14 days of therapy. A longer course of remedy for cystitis ought to be thought-about in sufferers with complicating components that lead to a decrease success price and a better danger of relapse. Symptomatic pyuria without bacteriuria in an otherwise wholesome younger individual suggests chlamydial or gonococcal urethritis. Recent pointers suggest that both a single dose of azithromycin or a 7-day course of doxycycline is efficient for chlamydial urethritis. Therapy for gonococcal urethritis includes a single dose of ceftriaxone or cefixime, or a fluoroquinolone combined with therapy for chlamydial an infection. It is widespread, however, for girls whose periurethral and vaginal epithelial cells avidly support attachment of coliform bacteria to have recurrent episodes of cystitis in the absence of acknowledged structural abnormalities of the urinary tract. In these ladies, a single dose of an antimicrobial after sexual activity or thrice weekly at bedtime has been shown to considerably scale back the frequency of episodes of cystitis from a median of 3 per patient-year to 0. Multiple antimicrobial brokers have demonstrated efficacy in prophylaxis and self-administered therapy. Some of those regimens embody nitrofurantoin, one hundred mg; trimethoprim, one hundred mg; trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole, forty mg/200 mg; and cephalexin, 250 mg. Although antimicrobial prophylaxis is efficient and normally safely tolerated for months to years, single-dose remedy for acute cystitis makes prophylaxis costlier and probably more hazardous for most patients due to alterations in fecal and vaginal bacterial flora. Indeed, self-administration of a single-dose regimen on the onset of symptoms has proved to be as price efficient as prophylaxis. Encouraging women to practice regular and complete emptying of the bladder could help prevent recurrent cystitis. Moreover, several theoretic preventive measures relate to using another contraceptive methodology: to use a properly fitted diaphragm, to void frequently when carrying a diaphragm, and to limit diaphragm use to the really helpful 6 to eight hours after intercourse. Cranberry juice (300 mL/day) was effective in reducing asymptomatic bacteriuria with pyuria in postmenopausal ladies. Pillicides are small synthetic molecules that intervene with pilus meeting, thereby blocking bacterial adhesion and subsequent reservoir formation. Mannoside, a soluble receptor analogue, is also an antiadhesive that binds to FimH. FimH allows bacteria to bind to and invade host bladder cells and mannoside prevents FimH from interacting with host receptors. Mannosides have proven nice promise as a remedy, both prophylactically and for established infections. These brokers additionally act synergistically with antibiotics to scale back micro organism 148 Chapter 7 the Patient with Urinary Tract Infection titers throughout the urinary tract of contaminated mice. Vaccination approaches have also been explored however to date, none have been proven to protect towards cystitis. The prevalence of flank ache, costovertebral angle tenderness, chills, fever, and nausea and vomiting with or with out dysuria suggests acute bacterial pyelonephritis. In this scientific setting, blood cultures and quantitative cultures of urine must be obtained. Whether ambulatory patients should be admitted to the hospital for treatment depends in part on a subjective evaluation of toxicity, likely compliance with remedy, and the home scenario. When the evaluation is doubtful, the affected person should be treated in the hospital, at least until a transparent response to therapy has occurred. This policy additionally applies to sufferers with recognized underlying uropathies as a end result of issues are extra widespread in these sufferers. Recommendations for remedy of uncomplicated pyelonephritis are outlined in Table 7-4. Fluoroquinolone or trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole is the drug of selection for initial remedy of pyelonephritis in outpatients. Patients who require admission to the hospital ought to be treated initially with a third-generation cephalosporin or a fluoroquinolone (intramuscular or intravenous), or gentamicin or tobramycin (1. If gram-positive cocci are seen in the urine, intravenous ampicillin (l g every 4 hours) ought to be given in addition to the aminoglycoside, to cover the chance of enterococcal infection whereas the outcomes of urine and blood cultures and antimicrobial susceptibility tests are pending. If no issues ensue and the affected person becomes afebrile, the remaining days of a 10- to 14-day course may be accomplished with oral remedy. However, persistent fever, persistent bacteriuria in forty eight to seventy two hours, or continuous signs of toxicity beyond three days of remedy suggest the necessity for an analysis to exclude obstruction, metastatic focus, or the formation of a perinephric abscess. The urinary tract is a common source of sepsis and bacteremic shock in patients with underlying uropathies. As with different patients in septic shock, intravenous fluids have to be given to preserve adequate arterial perfusion, which usually leads to a urinary output in extra of fifty mL/hour. Failure to reply to seemingly applicable therapy suggests the chance of undrained pus. Chronic bacterial pyelonephritis is certainly one of the most refractory problems in medical medication; relapse rates are as high as 90%. Trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole has been used in being pregnant, but it has not been permitted by the U. Fluoroquinolones obtainable for intravenous administration are listed in Table 7-3. Attempting eradication in such situations leads solely to the emergence of extra resistant strains of micro organism or fungi; consequently, the physician have to be resigned to treating symptomatic episodes of an infection and suppressing bacteriuria in selected patients. Urine cultures to detect a potential change in antimicrobial susceptibility of the infecting microorganism are important. Some sufferers with relapsing bacteriuria after 2 weeks of remedy reply to 6 weeks of antimicrobial therapy. To scale back the colony counts of their urine, patients chosen for suppressive therapy ought to have 2 to three days of specific high-dose antimicrobial therapy, to which their infecting micro organism are prone. The most popular agent for long-term suppression is methenamine mandelate, 1 g four occasions daily in adults. Alternatively, the dosage of methenamine mandelate alone may be elevated to 8 g or even 12 g/day. The dosage must be adjusted to the minimum amount required to maintain the urine freed from bacteria.
Evodia lepta (Evodia). Adalat.
- What is Evodia?
- Are there any interactions with medications?
- Dosing considerations for Evodia.
- How does Evodia work?
- Are there safety concerns?
Source: http://www.rxlist.com/script/main/art.asp?articlekey=97103
Generic adalat 30 mg on-line
Generalized lentiginosis in two children missing systemic associations: case report and evaluation of the literature prehypertension coffee adalat 30 mg purchase on line. Q-switched alexandrite laser therapy of facial and labial lentigines related to Peutz�Jeghers syndrome pulse pressure stroke volume adalat 20 mg buy amex. Q-switched ruby laser therapy of mucocutaneous melanosis associated with Peutz�Jeghers syndrome. Treatment of facial lentigines in Peutz�Jeghers syndrome with an intense pulsed gentle supply. Generalized intestinal polyposis and melanin spots of the oral mucosa, lips and digits. Peutz� Jeghers syndrome in kids: Report of two cases and evaluate of the literature. Peutz� Jeghers syndrome is brought on by mutations in a novel serine threonine kinase. Ruvalcaba�Myhre�Smith syndrome: a case with probable autosomal-dominant inheritance and extra manifestations. A new lipid storage myopathy observed in people with the Ruvalcaba�Myhre� Smith syndrome. Correlation of skeletal muscle biopsy with phenotype in the familial macrocephaly syndromes. Identification of a locus for dyschromatosis symmetrica hereditaria at chromosome 1q11�1q21. Congenital dyschromia with erythrocyte, platelet, and tryptophan metabolism abnormalities. Birthmarks and transient skin lesions in newborns and their relationship to maternal factors: a preliminary report from northern Italy. Congenital nevomelanocytic nevi: proportionate area growth throughout infancy and early childhood. Ageand site-specific variation within the dermoscopic patterns of congenital melanocytic nevi: an aid to accurate classification and evaluation of melanocytic nevi. Large congenital melanocytic nevi might replicate paradominant inheritance implying allelic loss. Cutaneous melanoma risk and phenotypic modifications in large congenital nevi: a follow-up research of forty six patients. Large or a quantity of congenital melanocytic nevi: prevalence of cutaneous melanoma in 1008 persons. The association between giant congenital melanocytic naevi and cutaneous melanoma: preliminary findings from an Internet-based registry of 379 sufferers. Giant congenital melanocytic nevi: the significance of neurocutaneous melanosis in neurologically asymptomatic children. Clinical characteristics and danger of melanoma improvement from large congenital melanocytic naevi in Korea: a nationwide retrospective research. A prospective examine of congenital melanocytic naevi: progress report and evaluation after 6 years. Great Ormond Street Hospital for Children Registry for congenital melanocytic naevi: prospective examine 1988�2007. Risk of malignant transformation of congenital melanocytic nevi: a retrospective nationwide examine from the Netherlands. Giant congenital melanocytic nevus with a large ulceration at birth: a 5-year follow-up. Neonatal large congenital nevi with proliferative nodules: a clinicopathologic examine and literature review of neonatal melanoma. Genetic adjustments in neoplasms arising in congenital melanocytic nevi: differences between nodular proliferations and melanomas. Molecular diagnosis of a benign proliferative nodule growing in a congenital melanocytic nevus in a 3-month-old toddler. Histologic persistence of a congenital melanocytic nevus of the scalp despite scientific involution. Very late metastasis (27 years) of cutaneous malignant melanoma arising in a halo big congenital nevus. Phacomatosis pigmentokeratotica related to hemihypertrophy and a rhabdomyosarcoma of the stomach wall. Number of satellite tv for pc nevi as a correlate for neurocutaneous melanocytosis in patients with massive congenital melanocytic nevi. Asymptomatic neurocutaneous melanocytosis in patients with massive congenital melanocytic nevi: a examine of instances from an Internet-based registry. Large or multiple congenital melanocytic nevi: occurrence of neurocutaneous melanocytosis in 1008 individuals. Giant congenital melanocytic nevi: Brain magnetic resonance findings in neurologically asymptomatic children. Neurocutaneous melanosis and the Dandy�Walker complicated: an unusual however not so insignificant association. Neurocutaneous melanosis in affiliation with Dandy�Walker malformation: case report and literature review. Large congenital melanocytic nevi presenting with lissencephaly with an absent corpus callosum. Iatrogenic effects of general anesthesia in children: concerns in treating massive congenital nevocytic nevi. Management of congenital nevi at a dermatologic surgical paediatric outpatient clinic: penalties of an audit survey 1990�1997. Pigmented plexiform neurofibroma: Distinction from a big congenital melanocytic nevus. Frequency of congenital nevi, nevi spili and caf�-au-lait spots and their relation to nevus count and skin complexion in 939 kids. Two distinct types of speckled lentiginous nevi characterized by macular versus papular speckles. Congenital melanocytic nevi and nevus spilus tend to follow the lines of Blaschko: an examination of 200 cases. Paradominant inheritance of twin recognizing: phacomatosis pigmentovascularis as a further possible example. Speckled lentiginous nevus syndrome: delineation of a brand new distinct neurocutaneous phenotype. Clinical review of 247 case data of Spitz nevus (epithelioid cell and/or spindle cell nevus). Multiple agminate Spitz naevi: evaluate of the literature and report of a case with distinctive immunohistological features. Multiple agminated juvenile melanoma: a case with a sunburn historical past, and a evaluate.
Cheap adalat 30 mg
Local venous thromboses can result in arrhythmia cure buy 30 mg adalat mastercard the formation of phleboliths hypertension with chronic kidney disease buy adalat 30 mg on-line, which can be tender when palpated and are seen on radiographs as spherical calcifications. During childhood, they typically acquire a deeper blue hue and thicken, and become tender when palpated. They are composed of ill-defined venous channels with irregularly attenuated partitions, focally lacking smooth muscle cells, permeating the skin and adnexal structures. Can be related to hydrocele, enlarged leg veins and recurrent cellulitis Pubertal onset, most typical kind of primary lymphedema. Pain is a standard complaint either as a result of phlebolith formation or usually in bigger extremity lesions. A variety of radiologic classification schema have been proposed and will predict response to therapy, with smaller and more localized lesions being more amenable to sclerotherapy. Sinus pericranii represents a direct communication between superficial veins and intracranial venous sinuses through a bony defect. Course Venous malformations are inclined to enlarge and turn into more symptomatic with time. Their medical course and problems rely upon anatomic location, with differing problems within the craniofacial area, trunk, and limbs. Extensive retropharyngeal involvement can end result in obstructive sleep apnea, occasionally even in younger kids. However, the deeper component might stay undiagnosed until it becomes symptomatic. Swelling, functional impairment, and limited joint motion happen when the kid turns into older and more active, particularly if playing sports. Sclerotherapy includes the introduction of an endothelial-cell cidal sclerosant into the vascular areas of the malformation. Complications of sclerotherapy embrace tissue necrosis, nerve palsies, hemoglobinuria and oliguria. A mixture of sclerotherapy followed by surgical debulking is often utilized in large or advanced instances. In craniofacial lesions, remedy is aimed toward stopping distortion of facial anatomy, limiting bone deformity, open bite or shift of the dental midline, lip growth, and displacement of the lip commissures. Treatment with low-dose aspirin is often a helpful adjunct to conservative therapy in some instances. Several forms of lymphedema are recognized, including familial congenital lymphedema, Nonne�Milroy syndrome, Meige illness, and Hennekam syndrome, summarized in Table 22. This may counsel that a genetic trigger is in all probability going associated to somatic mutations, which, if occurring within the germline, would be incompatible with life. Intraoral involvement additionally causes drainage of serosanguineous lymphatic fluid, aggressive caries, and loss of teeth. Involvement of the mandible with ensuing overgrowth is current in about 40% of those sufferers. Fluid aspiration and analysis could additionally be helpful as a end result of numerous neonatal growths, together with some malignant tumors, can current with massive cyst-like swellings. Treatment Lymphatic malformations are benign and treatment is often directed at managing complications or trying to restore anatomy. Conservative measures include statement, prophylactic antibiotics when an infection is a concern, and in the case of main lymphedema, compression. Sclerotherapy has emerged Pathogenesis Arteriovenous malformations arise as a end result of errors in vascular growth, which happen throughout embryogenesis. Complications embody disfigurement, pain, bony erosion, hemorrhage, and even death. Angiography is typically carried out to help in diagnosis or in preparation for embolization or resection. In extra advanced malformations, where there are issues or useful compromise, embolization is normally the first-line therapy. In the previous, many of these problems have been named eponymously, which generally results in confusion within the analysis of those rare entities. Classification based mostly on the vessel kind predominant within the malformation may be a greater approach to distinguish them. Many of the mixed vascular malformations are related to overgrowth of the affected areas of the physique Table 22. Syndromes related to vascular malformations the syndromes described below are associated with varied vascular anomalies. We have elected to group them primarily based on essentially the most distinguished or characteristic cutaneous vascular anomaly as this is often the primary presenting signal of the dysfunction. Most of these malformations are evident at birth or turn into obvious in infancy or early childhood. The danger increases to 25% with both bilateral V1 or concurrent V1, V2, and V3 involvement. Consequences of intracranial vascular anomalies include seizures, headaches (including migraines), spastic hemiparesis, visible field defects, cognitive impairment and behavioral issues including consideration deficit dysfunction. Typical neuroimaging adjustments embrace visualization of the pial vascular malformation, cerebral atrophy, and calcifications of the leptomeninges, the abnormal cortex and the underlying white matter. It is associated with persistent nevus simplex or capillary malformation of the midforehead. Other findings include overgrowth of tissues and organs, macroglossia, and stomach wall defects, usually omphalocele. Inheritance may be via autosomal dominant, contiguous gene duplication or genomic imprinting. An alternate classification uses descriptive terminology to spotlight the cutaneous features Table 22. The pigmentary anomalies include blue-gray macules/patches (dermal melanocytosis), nevus spilus and epidermal nevi that are darkly pigmented. Mutations within the glomulin gene have been identified in affected hypoperfusion with decreased glucose utilization after the onset of seizures. Although controversial, some pediatric neurologists believe that prophylactic anti-seizure medicines or low dose aspirin regimens are worth contemplating for at-risk infants. Other options embody seizures, developmental delay, hydrocephalus, and joint laxity. The related capillary stain is mostly located on the central face (philtrum and glabella) but can be seen on any space of the physique. They are bluish to purple, cobblestoned in appearance and infrequently painful on palpation. This type of enchondromatosis is associated with spindle cell hemangioma, begins in childhood and worsens with maturity.
Adalat 20 mg purchase on line
Meningoceles are cephaloceles in which solely the meninges and cerebrospinal fluid herniate via a calvarial defect blood pressure ranges discount 30 mg adalat with amex. Large encephaloceles and meningoceles pose no diagnostic downside and are often simply recognized prenatally or at delivery hypertension classification cheap adalat 30 mg mastercard. Smaller or atretic encephaloceles and meningoceles could also be mistaken for cutaneous lesions such as hematomas, hemangiomas, aplasia cutis, dermoid cysts, or inclusion cysts. These varied classifications had been derived from the amount and type of neural tissue present, as nicely as the degree of connection to the central nervous system. Therefore, all congenital exophytic scalp nodules must be evaluated thoroughly, as 20�37% of congenital, nontraumatic scalp nodules connect to the underlying central nervous system. They are normally midline, though they may also be discovered Cutaneous signs of neural tube dysraphism the skin and the nervous system share a standard ectodermal origin. Separation of the neural and cutaneous ectoderm happens early in gestation, at the identical time the neural tube is fusing. This shared embryologic origin explains the simultaneous occurrence of congenital malformations of the skin and neural tube dysraphism, which is an incomplete closure or faulty fusion. Open neural tube defects are often large and recognized in utero or at start; nonetheless, closed or occult neural tube defects often current solely with congenital abnormalities of the skin overlying the defect. It is important to recognize these cutaneous markers and display with the suitable radiologic imaging strategies. A common data of embryology and formation and closure of the neural tube is beneficial in identifying which cutaneous markers are extremely indicative of underlying defects. Small cephaloceles are clinically heterogeneous; their appearance dictated by the kind and amount of cutaneous ectoderm overlying the lesion. They could also be lined with regular pores and skin, or have a blue, translucent, or glistening floor. There is often a disruption of the surrounding and overlying regular hair sample. They are soft, compressible, round nodules that increase in measurement when the child cries or with a Valsalva maneuver. The affiliation of a congenital scalp mass with other cutaneous abnormalities makes the analysis of cranial dysraphism extremely suspicious. All congenital midline scalp nodules carry a major risk of intracranial connection and may have radiologic imaging studies performed before surgical removal to forestall issues similar to meningitis. Differential analysis and management Included in the differential diagnoses of congenital scalp nodules are pilomatrixoma, epidermoid cyst, lipoma, osteoma, eosinophilic granuloma, hemangioma, sinus pericranii, dermoid cyst, leptomeningeal cyst, and cephalohematoma. Immediate neurosurgical referral is required for surgical elimination and reconstruction. The cysts could occur within the fusion lines of the facial processes or alongside the neural axis. They symbolize defective growth and should include each epidermal and dermal components. They can happen anyplace on the face, scalp, or spinal axis however are most incessantly seen overlying the anterior fontanelle, on the junction of the sagittal and coronal sutures on the scalp, on the upper lateral region of the brow inside or close to the eyebrow, and within the submental region. Dermoid cysts often adhere to the underlying periosteum and should really feel like abnormalities of the bone. Dermal sinuses are 1�5 mm tracts that usually join a dermoid cyst to the pores and skin surface. They may turn into clinically obvious when they turn into infected and drain purulent materials. If the sinus and/or cyst communicates immediately with the central nervous system, the affected person is at risk for meningitis. Staphylococcus aureus meningitis must be thought-about secondary to a dermal sinus until proved in any other case, and a thorough search for a cutaneous fistula should be carried out, which may necessitate shaving the scalp hair. Extracutaneous findings Midline or nasal dermoid cysts are of the greatest concern because 25% have an intracranial connection. If the dermoid cyst connects to the central nervous system, cerebrospinal fluid may drain from the sinus. As with nasal gliomas, the patient might have the appearance of hypertelorism if the cyst has widened the nasal bones. Nasal dermoids should all the time be excised, as a result of over time, they enlarge and harm the nasal bones. Lateral brow dermoids seem deceptively superficial, but most are actually situated beneath muscle, in order that both elimination should be by way of an endoscopic strategy or the surgeon should be ready to dissect via the muscle to remove the cyst. Dermoids cysts are normally found in the subcutaneous tissue and are lined by stratified squamous epithelium, typically containing hair follicles, sebaceous glands, and sweat glands. Radiologic imaging is a really sensitive screening method and should be undertaken prior to surgical intervention. However, small or occult malformations coated with skin may have subtle indicators and be asymptomatic. Early prognosis is crucial, as it may stop irreversible neurologic damage brought on by tethering of the spinal cord. A diagnosis of occult spinal dysraphism is often suspected solely on the premise of overlying cutaneous findings, particularly within the new child. Most are found on or near the midline in the lumbosacral region; nonetheless, related markers in the cervical or thoracic regions can also be indicative of an underlying malformation. The literature suggests that certain pores and skin lesions are more indicative than others of underlying malformation. Other studies have documented an even larger incidence of cutaneous malformations (71�100%). Unfortunately, no prospective studies have been carried out to determine what share of children with cutaneous anomalies overlying the spinal axis has occult dysraphism. Congenital cutaneous anomalies of the lumbosacral region must be evaluated within the context of a full historical past and bodily examination, significantly in the older child. The historical past should embody questions on additional congenital malformations, family history of neural tube defects, weak point or pain within the lower extremities, abnormal gait, scoliosis, difficulties with rest room coaching or incontinence, recurrent urinary tract infections, and recurrent meningitis. Examination of the rectum and genitalia can be indicated, as there are often associated congenital abnormalities of the urogenital system. Examination of the lower extremities is important in older kids as a end result of they might have trophic adjustments secondary to nerve damage. The texture of the hair can range but is incessantly described as silky (faun tail nevus). Prominent hypertrichosis is usually associated with different cutaneous stigmata of spinal dysraphism and is 102 9 Developmental Abnormalities extremely indicative of a spinal defect. However, hypertrichosis within the lumbosacral area can be a standard discovering, especially in sure ethnic or racial teams, and it might be troublesome to decide whether or not or not further analysis is indicated. Referral to a neurologist or neurosurgeon for a extra full neurologic examination may be a prudent measure in these instances. Unlike acquired lipomas, they could be poorly circumscribed and really feel more like an area of elevated subcutaneous fat than a discrete lesion. The lipoma may lie within the dermis or the spinal canal, and often penetrates from the dermis by way of a vertebral defect into the intraspinal space (lipomyelomeningocele).
30 mg adalat trusted
Exogenous sources of phosphorus include oral phosphorus-containing laxatives pulse pressure 49 buy adalat 20 mg with amex, phosphate-containing enemas blood pressure low heart rate high adalat 20 mg generic, high-dose liposomal amphotericin, and solvent detergent�treated contemporary frozen plasma. Tumor lysis syndrome most commonly is seen with therapy of quickly growing malignancies corresponding to leukemias and lymphomas. It can occur after therapy of strong tumors corresponding to small cell lung carcinoma, breast cancer, and neuroblastoma. Risk factors for tumor lysis syndrome in patients with stable tumors embrace pretreatment renal impairment, an increased lactate dehydrogenase degree, and hyperuricemia. Increased lactate dehydrogenase levels and hyperuricemia are indicators of a big tumor burden. They can happen in hypoparathyroidism; in acromegaly, on account of direct stimulation of insulin-like development factor on phosphate transport; with bisphosphonates, by way of a direct effect on renal phosphate reabsorption; and in tumoral calcinosis. Tumoral calcinosis is an autosomal recessive dysfunction associated with hyperphosphatemia and soft tissue calcium deposition brought on by mutations in three genes. Many of the signs and symptoms of an acute rise in serum phosphorus concentration are secondary to concomitant hypocalcemia (mechanism mentioned earlier- web page 93). Hyperphosphatemia can even cause hypocalcemia by decreasing 1-hydroxylase exercise and calcitriol formation. Clinically unexplained, persistent hyperphosphatemia ought to raise the suspicion of pseudohyperphosphatemia, the most common cause of which is paraproteinemia. No constant relationship of immunoglobulin one hundred Chapter 5 the Patient with Disorders of Serum Calcium and Phosphorus sort or subclass has been recognized. This is a method-dependent artifact, and paraprotein interference could additionally be a basic problem in spectrophotometric assays. Treatment of hyperphosphatemia is aimed at decreasing intestinal phosphate absorption. This is achieved by way of the use of oral phosphate-binding drugs similar to calcium carbonate, calcium acetate, sevelamer carbonate, lanthanum carbonate, and aluminum hydroxide. Aluminum hydroxide may be used within the brief time period, but continual use in sufferers with kidney illness ought to be prevented due to the potential for aluminum toxicity. The non-calcium containing binders sevelamer and lanthanum carbonate are high in value. Lanthanum carbonate is frequently associated with nausea and gastrointestinal upset. Hypophosphatemia might result from redistribution of phosphorus from the extracellular to the intracellular area, a lower in intestinal phosphate absorption, a lower in renal phosphate reabsorption, or extrarenal losses from the gastrointestinal tract or by way of dialysis. Respiratory alkalosis causes a rise in intracellular pH that stimulates phosphofructokinase, the rate-limiting step in glycolysis. This leads to extreme hypophosphatemia with serum phosphorus concentrations of less than 0. Intracellular shifts are additionally seen with the therapy of diabetic ketoacidosis and in "hungry bone syndrome," which happens after parathyroidectomy for secondary and tertiary hyperparathyroidism. In "hungry bone syndrome," serum calcium and phosphorus focus fall dramatically within the postoperative period, though clinically, hypocalcemia is extra of a administration problem than hypophosphatemia. Decreased dietary consumption is an unusual explanation for hypophosphatemia as a end result of oral intake nearly at all times exceeds gastrointestinal losses, and the kidney is able to reclaiming nearly all of the filtered load of phosphate. In basic, decreased intake should be combined with increased gastrointestinal losses. Increased urinary phosphate excretion occurs in primary hyperparathyroidism, secondary hyperparathyroidism because of defects in vitamin D metabolism, Fanconi syndrome, osmotic diuresis, acetazolamide use, Chapter 5 the Patient with Disorders of Serum Calcium and Phosphorus 101 Table 5-6. It is characterized by hypophosphatemia, phosphaturia, decreased 102 Chapter 5 the Patient with Disorders of Serum Calcium and Phosphorus calcitriol focus, normal calcidiol concentration, and clinical and histologic evidence of osteomalacia. A considerable delay may happen between the presentation of the syndrome and discovery of the tumor. When fibrous dysplasia of bone is associated with precocious puberty and caf� au lait spots, this triad is named the McCune�Albright syndrome. Hereditary hypophosphatemic rickets with hypercalciuria is inherited as an autosomal recessive disorder manifested by increased renal phosphate excretion, hypophosphatemia, and rickets. The impact of tertiary hyperparathyroidism normally resolves after the first yr of transplantation, however might persist in some circumstances. Fanconi syndrome is related to glycosuria, aminoaciduria, bicarbonaturia, and phosphaturia. Inherited ailments embrace Lowe syndrome, Wilson illness, cystinosis, and hereditary fructose intolerance. Tenofovir, cidofovir, adefovir, valproic acid, ranitidine, ifosfamide, and tetracyclines have been implicated. Phosphorus is absorbed within the small bowel so high-output ileostomies or cutaneous small bowel fistulas are inclined to lead to hypophosphatemia extra incessantly than colostomies or diarrhea. Treatment with oral phosphate is tough as a result of it could exacerbate the diarrhea requiring admission for intravenous phosphate substitute. Typically phosphorus is elevated in dialysis patients as a end result of dialysate removing is proscribed and oral phosphorus intake is commonly excessive. When oral consumption is poor, phosphorus elimination through dialysis can lead to hypophosphatemia. This is particularly true when continuous dialysis modalities are used within the therapy of acute kidney damage the place removal is enhanced and oral intake is reduced. Decreases in serum phosphorus concentration can develop a quantity of days after a major thermal harm associated to phosphorus losses in the exudate. In vitro hypophosphatemia causes a leftward shift in the oxygen dissociation curve. Neuromuscular symptoms include paresthesias, tremor, muscle weak spot, and altered mental standing; extreme hypophosphatemia increases pink cell fragility, which may result in hemolysis, and decreases chemotaxis, phagocytosis, and bacterial killing by white cells, with an elevated susceptibility to infection because the potential result. Correction of severe hypophosphatemia 104 Chapter 5 the Patient with Disorders of Serum Calcium and Phosphorus has been reported to increase myocardial contractility by as much as 20%. Phosphate repletion should be undertaken with extreme caution in the rare patient with renal dysfunction; the safest mode of therapy is oral, and hypophosphatemia usually could be corrected with 1,000 mg/day of phosphate. Intravenous alternative carries the danger of hypocalcemia and hyperphosphatemia and is only warranted in patients with severe symptomatic hypophosphatemia. Serum concentrations of phosphorus, calcium, magnesium, potassium, and urine output should be carefully monitored during intravenous alternative. Contents 250 mg phosphate, 12 mEq sodium, 2 mEq potassium per pill 149 mg phosphate, 6 mEq sodium per mL 250 mg phosphate, 14 mEq potassium per capsule 114 mg phosphate, three. K-phos Chapter 5 the Patient with Disorders of Serum Calcium and Phosphorus one hundred and five concentration has increased to more than 1 mg/dL, the affected person must be switched to an oral preparation. Hypophosphatemia: an evidence-based method to its clinical consequences and management. It is estimated that, by the age of 70 years, as many as 20% of all white men and 7% of all white girls will undergo from kidney stone disease. In the United States, calcium-containing stones make up approximately 90% of all stones; they comprise calcium oxalate alone, calcium phosphate alone, or a combination of each. A kidney stone can form solely when urine is supersaturated with respect to a stone-forming salt. Interestingly, urine in many wholesome subjects is usually supersaturated with respect to calcium oxalate, calcium phosphate, or uric acid and crystalluria was described in as many as 15% to 20% of healthy subjects.
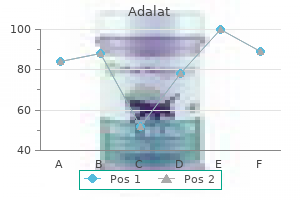
Adalat 30 mg purchase otc
Extraureteral Pelvic or stomach malignancy Retroperitoneal fibrosis Accidental ureteral ligation or trauma during pelvic surgery c young squage heart attack discount adalat 30 mg fast delivery. Bladder neck/urethral obstruction (lower urinary tract obstruction) Prostatic hypertrophy Prostatic and bladder carcinoma Autonomic neuropathy or anticholinergic brokers inflicting urinary retention Urethral stricture Bladder stones Fungal an infection arrhythmia while pregnant 20 mg adalat mastercard. Large- and medium-sized vessels Renal artery thrombosis or embolism Operative arterial cross-clamping Bilateral renal vein thrombosis Polyarteritis nodosa 210 Chapter 10 the Patient with Acute Kidney Injury b. Glomerular illnesses are sometimes categorized primarily based on urine findings as either nephrotic or nephritic. Nephrotic glomerular issues are characterized by massive proteinuria (greater than 3 g in 24 hours) and minimal hematuria. Nephritic glomerular disorders (glomerulonephritis) are characterised by hematuria and proteinuria (typically 1 to 2 g in 24 hours). Diseases with Granular Immune Complex Deposition Acute postinfectious glomerulonephritis Lupus nephritis Infective endocarditis Immunoglobulin (Ig) A glomerulonephritis Henoch�Sch�nlein purpura Membranoproliferative glomerulonephritis Cryoglobulinemia iii. Most of the renal biopsies are, nevertheless, late and due to this fact may miss early tubular necrosis. Renal Ischemia Shock Hemorrhage Trauma Gram-negative sepsis Pancreatitis Hypotension from any trigger 212 Chapter 10 the Patient with Acute Kidney Injury b. Nephrotoxic Drugs Aminoglycoside antibiotics Amphotericin B Pentamidine Foscarnet Acyclovir Indinavir Antineoplastic agents. A complete history and thorough bodily examination suggest the prognosis in most sufferers. The following historical past is suggestive of prerenal azotemia from true quantity depletion or hypovolemia: thirst, decreased fluid consumption, fever, nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, burns, peritonitis, and pancreatitis. Features suggesting liver illness and cirrhosis embody a historical past of alcohol abuse or hepatitis. A full documentation of medicines (prescribed and over-the-counter) is important in the analysis of prerenal azotemia. Physical findings that recommend a discount in intravascular volume embrace the following: Absence of axillary sweat A current discount in physique weight Orthostatic hypotension. Defined as a fall in systolic blood strain of more than 20 mmHg or an increase in pulse fee of greater than 10 beats/minute after standing Tachycardia Dry mucous membranes "Tenting" of higher thorax pores and skin when pinched between the fingers Jugular venous pressure not seen when supine b. The urine dipstick should be normal with negative protein, heme, leukocyte esterase, and nitrate. In the presence of medical circumstances with increased renal vasoconstrictor activity. The loss of renal function is mostly reversible when the dosage of the drug is lowered. Animal and human data counsel that concurrent administration of calcium channel blockers might protect against calcineurin inhibitor toxicity. Diuretic-induced sodium depletion and underlying persistent renal insufficiency are different main predisposing elements. Symptoms that suggest urinary tract obstruction are anuria or intermittent anuria and polyuria, prostatic symptoms (urinary frequency and urgency, dysuria, straining upon urination), pelvic malignancy or earlier radiotherapy, and recurrent renal stones. Patients may complain of ache over a distended bladder; severe ache (renal colic) may be present if obstruction is due to renal calculi. Patients with diabetes mellitus, sickle cell anemia, analgesic nephropathy, and benign prostatic hypertrophy are predisposed to papillary necrosis that causes obstruction. Careful belly examination could uncover a distended, tender bladder or bilaterally hydronephrotic kidneys. As discussed under, ultrasound is the modality of choice to consider for obstruction; however, if the obstruction is relieved by catheterization, then the diagnostic utility of ultrasound is lost. Furthermore, catheter placement could considerably alter the diagnostic utility of urinalysis [i. The patient must be requested to try and void, and urine output after catheterization should be recorded. The urine dipstick must be regular with adverse protein, heme, leukocyte esterase, and nitrite. A secondary an infection could also be current because of urine stasis; on this setting, the dipstick could additionally be positive for leukocyte esterase, nitrite, heme, and hint protein. Prostatitis and a few circumstances of benign prostatic hypertrophy may also be related to hematuria. Renal ultrasonography is sufficient to diagnose urinary obstruction in most sufferers. Renal ultrasonography is the radiologic test of option to evaluate for obstruction, characterized by dilatation of the urinary tract (hydronephrosis). The absence of hydronephrosis virtually excludes necessary urinary tract obstruction; hydronephrosis could also be absent, nevertheless, within the following settings: early obstruction (before the urinary tract has been capable of dilate) and obstruction as a outcome of the encasement of the urinary system by retroperitoneal fibrosis or tumor. If the functional significance of hydronephrosis is unsure, a furosemide isotope renogram can consider the functional significance of the obstruction. Isotope renography is carried out by the intravenous injection of a radionucleotide and furosemide. Furosemide increases urinary circulate and usually causes a rapid washout of the radionucleotide. Poor renal perform limits the usefulness of this check because the diuretic response could also be blunted, thereby making interpretation of the test difficult. Renal artery thrombosis or embolism, or bilateral renal vein thrombosis might present with flank pain. Predisposing problems similar to membranous nephropathy or antiphospholipid antibody syndrome may be present. Doppler ultrasonography may be used to assess renal blood flow and to consider for renal vein thrombosis. Intrinsic renal illness because of small vessel illness is caused by either atheroembolic illness or thrombotic microangiopathy. Atheroembolic illness is attributable to the detachment of atheromatous plaques from the intimal floor of huge vessels. These plaques travel distally and occlude small arteries or massive arterioles of the kidney. Showers of cholesterol crystals or microemboli from the floor of ulcerated plaques may happen, traveling distally to occlude small arterioles throughout the body. The presentation and clinical findings of atheroembolic disease can be confused with those of polyarteritis nodosa, allergic vasculitis, subacute bacterial endocarditis, or left atrial myxoma. However, milder types of kidney injury with some restoration of perform have been described. Skin manifestations of ldl cholesterol emboli include discrete peripheral necrotic areas, blue toe syndrome, and livedo reticularis. Laboratory investigation could reveal an increased erythrocyte sedimentation price, eosinophilia, and hypocomplementemia (C3 is lowered whereas C4 stays normal). Thrombotic microangiopathies are characterized by a microangiopathic hemolytic anemia, thrombocytopenia, and variable renal and neurologic manifestations. These disorders start with endothelial harm followed by secondary platelet thrombi formation in renal arterioles; renal cortical necrosis might result from the arterial lesions.
Syndromes
- 2 slices of whole-grain bread
- Echocardiogram - ultrasound examination of the heart
- Lack of sex drive (in women)
- Lecithin, gelatins, corn starch, waxes, gums, and propylene glycol in food stabilizers and emulsifiers
- Gallbladder removal
- Disturbance of the acid balance of the blood (leads to multi-organ failure)
- Use simple phrases to avoid misunderstandings.
- Delayed sexual maturity
- Androgenic and anabolic steroids
- Make sure your child understands the exact body part involved, and that the procedure will be done only on that area.
Adalat 20 mg on-line
Allopurinol should solely be used when stones recur despite fluid and alkali administration blood pressure chart during pregnancy adalat 20 mg line, or if uric acid excretion is above 1 prehypertension pediatrics adalat 20 mg buy on line,000 mg/day. When allopurinol is administered for enormous uric acid overproduction, sufficient hydration have to be maintained to keep away from the precipitation of xanthine crystals. Open surgical elimination was formerly the remedy of selection for staghorn struvite-carbonate calculi. More lately, the combination of percutaneous nephrolithotomy and extracorporeal shock wave lithotripsy has decreased morbidity considerably and is now the therapy modality of selection. Total stone elimination stays a problem, because of the inability to take away small, bacteria-containing particles that act as nidi for additional crystal development. After full elimination, continual culture-specific antimicrobial brokers are indicated as prophylaxis against recurrent infection. Stone progress in most sufferers with residual fragments progresses despite antibiotic treatment. It may be slowed by reducing the bacterial population, however treatment with antibiotics alone is distant. Urease inhibitors, similar to acetohydroxamic acid, reduce urinary saturation of struvite-carbonate and prevent stone progress and should, once in a while, cause dissolution of present stones. These brokers, nonetheless, are related to quite a lot of extreme complications together with hemolytic anemia, thrombophlebitis, and nonspecific neurologic signs. A urine output of a minimum of 4 L/day is commonly required to cut back recurrent stone formation in patients with extreme cystinuria. Urine could be periodically examined for cystine crystals to assess adequacy of fluid intake. Caution should be exercised in deciphering urinary cystine concentrations in treated patients. In addition, many cystine assays make use of steps that disrupt cysteine�thiol bonds releasing cysteine sure to therapeutic agents, mentioned further in the following textual content, corresponding to d-penicillamine or -mercaptopropionylglycine (tiopronin). The launched cysteine can dimerize and form cystine, overestimating the quantity of free cystine within the urine. These therapeutic brokers can even intrude with cystine assays as a result of they contain an active thiol group. Cystine excretion is related to sodium intake and a few advocate salt restriction to cut back 124 Chapter 6 the Patient with Kidney Stones urinary cystine excretion. In addition, methionine is a substrate for cystine manufacturing and fish, red meat, poultry, and dairy merchandise are rich sources of methionine. If these measures are ineffective, then either d-penicillamine or tiopronin can be tried. These compounds are thiols that bind preferentially to cysteine, forming compounds that are more soluble than cysteine�cysteine dimers (cystine). Zinc dietary supplements can normally stop the anosmia and lack of style that usually occurs with d-penicillamine. Captopril though initially reported to be of profit has extra recently fallen out of favor. Potential pharmacologic therapies for cystinuria and for calcium stones related to hyperuricosuria. Thiazides diuretics in the therapy of nephrolithiasis: are we using them in an evidence-based trend Bacterial infections of the urinary tract are the most typical explanation for each community-acquired and nosocomial infections for patients admitted to hospitals within the United States. Some definitions are needed as a result of an infection of the urinary tract may end result from microbial invasion of any of the tissues extending from the urethral orifice to the renal cortex. Although the an infection and resultant symptoms may be localized at one site, the presence of micro organism in the urine (bacteriuria) locations the entire urinary system in danger for invasion by micro organism. Infections confined to the bladder (cystitis), the urethra (urethritis), and the prostate (prostatitis) generally trigger dysuria, frequency, and urgency. Pyelonephritis is the nonspecific irritation of the renal parenchyma; acute bacterial pyelonephritis is a scientific syndrome characterised by chills and fever, flank ache, and constitutional symptoms caused by the bacterial invasion of the kidney. Relapse is a return of infection as a end result of the same a hundred twenty five 126 Chapter 7 the Patient with Urinary Tract Infection microorganism, is often drug resistant, and should require further urologic evaluation, longer remedy programs, and potential surgical intervention. Finally, asymptomatic bacteriuria is a vital clue to the presence of parenchymal infection somewhere in the urinary tract; however, the importance of the infection and the necessity for therapy rely upon the age, sex, and underlying situation of the affected person. For the clinician, another essential distinction is made between uncomplicated and sophisticated infections. An uncomplicated an infection is an episode of cystourethritis following bacterial colonization of the urethral and bladder mucosae within the absence of higher tract illness. This type of an infection is taken into account uncomplicated as a end result of sequelae are rare and exclusively because of the morbidity associated with reinfections in a subset of women. Young girls constitute a subset of sufferers with pyelonephritis (acute uncomplicated pyelonephritis) who often reply well to remedy and may have a low incidence of sequelae. In contrast, complicated infections include these involving parenchyma (pyelonephritis or prostatitis) and regularly occur in the setting of obstructive uropathy or after instrumentation. Episodes may be refractory to therapy, usually resulting in relapses, and infrequently leading to significant sequelae similar to sepsis, metastatic abscesses, and, not often, acute renal failure. Several authors have proposed a medical classification for the working towards clinician. Studies on pathogenesis have elucidated specific interactions between the host and microbes that are causally related to bacteriuria. Frequency distribution of symptomatic urinary tract infections and prevalence of asymptomatic bacteriuria by age and intercourse (male, shaded area; female, line). The subsequent bacterial colonization of uroepithelial cells is the biological phenomenon that units the stage for persistent bacteriuria. The colonization of the periurethra typically precedes the onset of bladder bacteriuria. P-fimbriated strains of Escherichia coli adhere to uroepithelial cells, during which glycolipids perform as receptors in ladies who secrete blood group antigens. Opposing colonization are a number of host factors, most notably acid pH, regular vaginal flora, and type-specific cervicovaginal antibodies. After periurethral colonization, uropathogens acquire access to the bladder by way of the urethra, to the kidneys by way of the ureters, and to the prostate through the ejaculatory ducts. The urethra and ureterovesical junction are mechanical limitations that stop ascension. In the bladder, organisms multiply, colonize the bladder mucosa, and invade the mucosal surface. Although urine adequately supports the expansion of most uropathogens, the bladder has several mechanisms that forestall bacteriuria: (a) a mucopolysaccharide (urine slime) layer covers the bladder 128 Chapter 7 the Patient with Urinary Tract Infection epithelium and prevents colonization; (b) Tamm�Horsfall protein, which is a component of uromucoid, adheres to P fimbriae and prevents colonization; and (c) urine move and bladder contraction serve to stop stasis and colonization. Bladder bacteriuria units the stage for subsequent migration to the kidneys, where organisms similar to P-fimbriated E. Other host factors that forestall a renal infection are a excessive urine osmolality, high ammonium concentration, phagocytes, and elevated urine move rate.
30 mg adalat for sale
They are generally utilized in recipients with characteristics associated with poor dialysis survival similar to superior age or diabetes zolpidem arrhythmia order 20 mg adalat with mastercard. Predictors of Outcome Recipient elements arrhythmia gerd adalat 20 mg purchase with visa, donor factors, and donor/recipient compatibility all affect long-term graft survival. Race and ethnicity could have an result on graft survival for both donors and recipients, with nonblack donor kidneys and nonblack, non-Hispanic recipients of grafts having the longest graft survival. Kidneys from residing associated or unrelated donors survive longer on common than deceased donor kidneys, as do kidneys from younger compared with older donors. Immunology A fundamental evaluation of the mechanisms of immune recognition and response to an allograft is useful to higher understand the affected person who has undergone kidney transplantation as properly as the pharmacologic brokers used to forestall allograft rejection. Although advances in immunosuppression have narrowed benefits for well-matched transplants, a two-haplotype equivalent transplant from a family member or a zero-antigen mismatched deceased donor transplant confers a graft survival benefit in contrast with transplants with lesser degrees of matching. T cells T cells are processed within the thymus and are central to cellular immunity and allograft recognition and rejection. These properties make them a standard goal of medicine designed to prevent rejection. They then initiate an immune response to overseas peptides by secreting cytokines essential in B-cell proliferation and activation and cytotoxic T-cell activation. Although signal 1 alone will cause anergy, the addition of signal 2, also called costimulation, will lead to an immune response. B Cells B cells develop at a quantity of sites of the body, including the liver, spleen, and lymph nodes. Antibody-mediated cellular cytotoxicity happens via complement fixation and subsequent cell lysis. Pharmacotherapy In the 1960s and Seventies the primary transplant immunosuppressive brokers consisted of steroids and azathioprine. Since that time the number of available 268 Chapter thirteen the Patient with a Kidney Transplant immunosuppressive brokers has increased tremendously. Agents can be utilized for desensitization therapy previous to transplant, induction therapy at the time of transplant, upkeep therapy to forestall rejection of the allograft, or the remedy of acute rejection. There is a large degree of overlap between indications, and many brokers are used "off-label. These preparations neutralize lymphocytes by a number of antibody-mediated mechanisms, with a sustained effect on proliferation, and are more practical than basiliximab in stopping acute rejection. Toxicities are associated to immunosuppression, heterogeneity of preparations, allergic or anaphylactoid responses to nonhuman preparations, and cytopenias. Furthermore, a change in sort and timing of rejection may be seen, together with monocyte-induced and humoral rejections occurring past the early posttransplant months. Dosing is adjusted based on trough or peak blood ranges and varies relying on immunosuppressive regimen (see Section V. Chapter 13 the Patient with a Kidney Transplant 271 hypertriglyceridemia, hypercholesterolemia, cytopenias, pneumonitis, delayed wound therapeutic, lymphoceles, diarrhea, and proteinuria, as nicely as potentiation of calcineurin inhibitor toxicity. As with calcineurin inhibitors, dosing is adjusted in accordance with trough or peak blood levels and varies depending on immunosuppressive routine (see Section V. Azathioprine supplies less selective lymphocyte inhibition and may be related to cytopenias and neoplasias. Corticosteroids are used during induction, as maintenance therapy, and for the treatment of acute rejection. Their effectiveness is sophisticated by quite lots of well-known side effects, including hypertension, glucose intolerance, weight achieve, cataracts, poor wound healing, osteoporosis, and osteonecrosis. Although corticosteroid withdrawal and avoidance have been explored (see Section V. Corticosteroids and antithymoctye globulin (described in the earlier sections) are used in cell-mediated (T-cell) rejection. Bortezomib is a proteasome inhibitor that reduces 272 Chapter thirteen the Patient with a Kidney Transplant numbers of antibody-secreting plasma cells. Eculizumab is a monoclonal antibody that inhibits terminal C5 complement activation, thereby limiting antibody-mediated cell toxicity, and is approved for treatment of atypical hemolytic uremic syndrome. These agents, while often very effective, are all considered off-label for the indication of kidney transplant rejection, and dosing has not been standardized. In general, interactions may result from changes in absorption, metabolism, excretion, or via additive or synergistic toxicity with brokers which have similar unwanted aspect effects. Agents that may decrease the absorption of immunosuppressive agents embody antacids, cholestyramine, and meals, whereas promotility agents can enhance absorption. Metabolism of tacrolimus and cyclosporine happens via cytochrome P-450-3A4; therefore, brokers that have an effect on this system can alter calcineurin inhibitor ranges or altered metabolism of the interacting agent, leading to toxicity or inadequate ranges. Examples embrace calcium channel blockers, azole antifungals, macrolide antibiotics, and grapefruit juice, which can improve calcineurin inhibitor levels, and anticonvulsants and rifampin, which might lower levels. Allopurinol could cause extreme myelosuppression when used with azathioprine and must be avoided. Cross-Matching and Desensitization Cross-matching between the recipient and donor is often performed instantly prior to transplantation in order to reduce the chance of hyperacute and acute antibody-mediated rejection. If a cross-match assay is optimistic, a choice is made to either cancel the procedure or proceed with some form of desensitization relying on the perceived rejection danger, transplant middle experience, and out there resources. Transplantation throughout a positive cross-match usually will increase the danger of rejection and graft loss even with desensitization, but likely improves patient outcomes in contrast with remaining on dialysis. Induction With few exceptions, kidney transplant recipients will receive a brief course of high-dose steroids at the time of transplantation, adopted by a taper to the initial maintenance dose. Either for perceived elevated threat of rejection or by local protocol, antibody remedy could additionally be given throughout induction. Donor Nephrectomy Living donor kidneys may be recovered in either an open or laparoscopic method, each with its personal benefits and drawbacks. The left kidney is most often chosen because of its longer renal vein and accessibility. Laparoscopic donation rates have increased due to technical advancement and donor preferences. In basic, laparoscopic donation has advantages of a shorter hospital stay, quicker return to work, and fewer pain, but can come with higher prices, longer operative time, and a studying curve to lower charges of morbidity to equal that of open nephrectomy. Deceased donor kidneys are removed together with a patch of aorta and inferior vena cava as part of a multiorgan recovery. The organs are then separated and saved in hypothermic preservation resolution till implantation. Transplant Surgery the transplanted kidney is positioned in either the right or left iliac fossa. The renal vein and artery are both linked by way of an end-to-side anastomosis, the donor vein normally being linked to the external iliac vein and the donor artery to the external iliac artery. The ureter is implanted into the bladder, and the bladder mucosa is pulled over the ureter to create a tunnel which prevents reflux and urine leak. A ureteral stent is commonly placed at the time of surgical procedure to ensure patency and stop urine leak.
Buy adalat 30 mg overnight delivery
These cell traces may be because of blood pressure 7850 cheap adalat 30 mg visa X-inactivation pulse pressure in athletes trusted adalat 20 mg, as is regular in all human females, or to postzygotic somatic mutation. Cutaneous findings Hypopigmented whorls and streaks are distributed along the strains of Blaschko. They tend to be steady, though there are reported cases in which the pigmentary changes become more or less pronounced over time. The presence of mosaicism can generally be documented by the karyotyping of lymphocytes from peripheral blood or by genomic analysis of both concerned and uninvolved pores and skin. In 1901, Blaschko characterised the distribution of segmental and linear skin abnormalities by analyzing patients with linear lesions and formulating a patterned composite diagram. He described these patterns as V-shaped or fountain-like over the spine, S-shaped or whorled on the anterior and lateral aspects of the trunk, and linear over the extremities (see Chapter 3). Nearly all of the defects are detectable by a radical bodily examination and common follow-up. Etiology and pathogenesis Embryonic somatic mutations are the likely pathogenesis, with distribution and sample of lesions decided by the type of progenitor cell affected and the timing of mutation during embryogenesis. Treatment and care Cosmetic cover-up merchandise can be used to conceal the hypopigmented areas but are often not wanted. The use of sunscreens can prevent or reduce the accentuation of pigmentary differences. They are usually present at birth or turn out to be evident shortly thereafter, and stay secure in dimension and shape. Some lesions might appear in the course of the first 3 years of life,117�119 with the trunk being essentially the most commonly affected web site. Neurologic abnormalities similar to seizures and psychological retardation have been reported,121 in addition to ipsilateral hypertrophy of the extremities. Differential analysis Other entities with which nevus depigmentosus is sometimes confused embody nevus anemicus, segmental vitiligo, hypopigmented lesions of tuberous sclerosis, and hypomelanosis of Ito. The distinction between nevus depigmentosus and hypomelanosis of Ito may be synthetic, as many sufferers with segmental hypopigmented macules even have linear pigmentary anomalies, much like those seen in hypomelanosis of Ito, and underlying mosaicism is the frequent factor. Genetic analysis could additionally be thought-about Localized hypopigmented problems 379 in all sufferers with segmental or linear pigmentary abnormalities, and people with extracutaneous abnormalities to examine cytogenic anomalies. Mutations causing an intermediate severity phenotype have largely been located at the transmembrane region, and the mildest phenotypes are those who occur in the amino terminal extracellular ligand-binding area. Vitiligo is acquired later in life, tends to progress, and has a different distribution. Waardenburg syndrome is the major entity in the differential prognosis of piebaldism, and the affected person should be examined for proof of facial dysmorphism, heterochromia of the irides, and congenital sensorineural listening to loss. Treatment and care Photoprotection of the depigmented patches is important, beginning early in life to defend the amelanotic areas from burning with sun exposure and to avoid skin cancers afterward. Cosmetic camouflage or the use of a pigmenting tanning product such as dihydroxyacetone to camouflage the depigmented lesions are helpful, although short-term. A white forelock, which consists of a tuft of white hair over the midfrontal scalp is present in 80�90% of patients and is associated with depigmentation of the underlying scalp. The presence of islands of normally pigmented and hyperpigmented macules within the depigmented patches is typical and aids in the medical diagnosis. Recently, the use of noncultured epidermal cellular grafting131 and melanocyte transplant strategies using noncultured melanocytes (minigrafting)157 has been shown to be helpful with high repigmentation rates. It is caused by the absence of melanocytes in the skin, hair, eyes, and stria vascularis of the cochlea, and is assessed as a dysfunction of neural crest development. Cutaneous and extracutaneous findings Affected individuals have a depigmented patch, usually V-shaped, on the central brow in association with a white forelock. Depigmented patches with irregular borders containing hyperpigmented macules, resembling piebaldism, in addition to hyperpigmented macules on regular skin, have been described. The neural crest offers rise not solely to melanocytes but in addition to the bony and cartilaginous structures of the central face, accounting for the dysmorphic options associated with Waardenburg syndrome. It is crucial for the survival and maintenance of pluripotency of migrating neural crest progenitors. The pigmentary disturbances are very similar in each Waardenburg syndrome and piebaldism, but auditory and facial developmental anomalies are absent in piebaldism. The use of multichannel cochlear implants in Waardenburg syndrome children with profound deafness was discovered to be helpful for the development and enchancment of speech perception and production. They have a partial rather than complete lack of pigmentation, and perifollicular pigmentation could also be observed in some of them. A fibrous plaque may be seen on the forehead or scalp, is often current from delivery or early infancy, and has an identical histologic seem to an angiofibroma. Examination of the mouth can reveal gingival fibromas and small dental enamel pits. Single or multiple renal cysts are inclined to appear earlier than the angiomyolipomas, and the mix of the 2 is attribute of tuberous sclerosis complicated. Hemorrhage is the commonest complication of angiomyolipomas, causing hematuria and ache. Renal failure outcomes from obstructive uropathy, or when cysts or tumors exchange much of the traditional renal parenchyma. Pulmonary adjustments are uncommon, seldom trigger signs, are 5 instances extra common in females, and have a tendency to turn out to be clinically manifest in the second decade. Neurologic lesions end result from impaired mobile interplay, resulting in disrupted neuronal migration alongside radial glial fibers and abnormal proliferation of glial elements. The extra nodular lesions may be handled with shave excision and electrodesiccation or with carbon dioxide laser, but slowly recur. Rapamycin has antineoplastic results which may be mediated by lowering the production of vascular endothelial growth issue and it corrects aberrant signaling pathways concerned in cell development and apoptosis. However, regrowth might happen with renal angiomyolipomas after stopping oral rapamycin therapy. Extracutaneous findings Nevus anemicus may be seen in close association with port wine stains. Donor dominance was demonstrated by grafting lesional pores and skin from nevus anemicus to regular skin, which retained its pale look, emphasizing that nevus anemicus is because of elevated sensitivity of the blood vessels to catecholamines rather than to increased sympathetic stimulation. These maneuvers help to distinguish nevus anemicus from vitiligo, nevus depigmentosus, tuberous sclerosis macules, tinea versicolor, and leprosy. A useful method that gives an indication of the prognosis and therapy is to categorize vitiligo into non-segmental and segmental types. It progresses rapidly however tends to be confined inside the affected segment and stays stable thereafter. Children with non-segmental disease usually have a tendency to have extra extensive involvement, extra frequent progression of illness and thyroid abnormalities on laboratory investigations than youngsters with segmental illness. Localized hypopigmented disorders 385 reported in children with non-segmental vitiligo. As the frequency of occurrence of these autoimmune diseases is low, thyroid perform tests, full blood depend and fasting blood glucose could be performed selectively, for example, in a child who fails to thrive.
30 mg adalat overnight delivery
Phosphate either could also be launched from the intracellular area arteriovascular malformation adalat 20 mg order online, as is the case in tumor lysis syndrome or rhabdomyolysis arrhythmia course 30 mg adalat with amex, or could be ingested and absorbed, as in vitamin D intoxication. However, urine of recurrent stone formers was noted to comprise crystals in first morning voided specimens far more frequently than that of stone formers without subsequent recurrence, suggesting that recurrence might rely upon the diploma and severity of crystalluria. Normal urine accommodates quite lots of inorganic and organic substances that act as crystallization inhibitors. Once a crystal forms, it was once thought that it must both grow to enough measurement to occlude the tubular lumen or anchor itself to the urinary epithelium, which in flip supplies a surface upon which it can grow. The typical transit time of a crystal via the nephron is on the order of three minutes, and that is too quick a period for it to nucleate, grow, and occlude the tubular lumen. However, studies by Evan and Coe have shed further mild on how stones type within the kidney. In patients with idiopathic hypercalciuria, the initial website of crystal formation was within the basement membrane of the thin limb of the loop of Henle. The stone core was made up of calcium phosphate alternating with layers of matrix. The crystal deposit then migrates towards the renal pelvis the place it acts as a base upon which a plaque forms, which is then bathed in urine supersaturated with stone-forming constituents upon which calcium oxalate is deposited. Why calcium phosphate precipitates at the basolateral surface of the thin limb of the loop of Henle is unclear. Further research by Worcester and Coe found a postprandial lower in proximal tubular calcium reabsorption in these sufferers. In patients with one kind of calcium phosphate stone (brushite), mineral is deposited on the luminal membrane of dilated internal medullary collecting duct cells and grows out into the renal pelvis. The dilated internal medullary collecting ducts are surrounded by areas of interstitial fibrosis. A kidney stone mostly presents with extreme flank ache, sudden in onset, and is usually related to nausea and vomiting. The radiation of the ache may present some clue as to where in the urinary tract the stone is lodged. Stones within the ureteropelvic junction cause flank pain which will radiate to the groin, whereas these lodged within the narrowest portion of the ureter, the place it enters the bladder, are associated with indicators of bladder irritation (dysuria, frequency, and urgency). Struvite-carbonate stones are, every so often, by the way discovered on abdominal radiograph. A careful abdominal examination and, in girls, a pelvic examination are essential to rule out other potential causes of stomach ache. Laboratory analysis ought to embrace an entire blood cell rely, serum chemistries, and urinalysis. The white blood cell rely could also be mildly elevated but is usually less than 15,000/mm3. A white blood cell count higher than 15,000/mm3 is suggestive of another intra-abdominal cause or an associated infection behind an obstructing calculus. Microscopic hematuria is noticed in roughly 90% of patients with renal colic. Once the diagnosis is suspected based on the historical past, bodily examination, and preliminary laboratory studies, establishing a definitive diagnosis is the focus of the following stage of the evaluation. A flat radiographic plate of the abdomen is commonly obtained and is capable of identifying radiopaque stones (calcium oxalate, calcium phosphate, struvite-carbonate, and cystine) that are 2 mm in dimension. It will miss radiolucent stones, the most common of that are composed of uric acid, and stones that overlie the bony pelvis. For these causes, an stomach flat plate is most dear in ruling out different intra-abdominal processes. An ultrasonographic examination of the genitourinary tract usually identifies stones within the renal pelvis; nevertheless, many of the stones are lodged within the ureter, and the ultrasonographic examination typically misses these. Structural or anatomic abnormalities which may be current within the urinary tract and renal or ureteral complications can be acknowledged. After the analysis is established, subsequent management is decided by (a) the presence or absence of associated pyelonephritis; (b) whether parenteral narcotics are required for pain management; and (c) the probability of spontaneous stone passage. Obstructing calculi may be managed with statement alone if pain could be controlled with oral analgesics and spontaneous passage is likely. Extracorporeal shock wave lithotripsy or ureteroscopic lithotripsy might need to be employed for stones lodged in the upper ureter. The chance of spontaneous passage is decided by stone size and location within the ureter Table 6-1). Small stones in the distal ureter will likely pass, whereas large stones within the upper ureter will probably require urologic session and intervention. Calcium-containing stones make up 90% of all stones and are generally composed of a mix of calcium oxalate and calcium phosphate. In mixed stones, calcium oxalate usually predominates, and pure calcium oxalate Chapter 6 the Patient with Kidney Stones 109 Table 6-1. Likelihood of Spontaneous Passage Likelihood of Spontaneous Passage (%) Size >6 mm 4�6 mm <4 mm Location Upper ureter, >6 mm Upper ureter, <4 mm Lower ureter, <4 mm 1 eighty one 93 25 60 ninety stones are extra frequent than pure calcium phosphate stones. The main danger factors for the formation of calciumcontaining stones embrace hypercalciuria, hypocitraturia, hyperuricosuria, hyperoxaluria, low urine volume, and medullary sponge kidney. Hypercalciuria is often defined as urinary calcium excretion larger than 250 mg/24 hours in ladies and higher than 300 mg/24 hours in males. Hypercalciuria is current in approximately two-thirds of patients with calcium-containing stones and will outcome from an elevated filtered load, decreased proximal reabsorption, or decreased distal reabsorption. Three potential pathophysiologic mechanisms are postulated: increased intestinal calcium absorption; decreased renal calcium or phosphorus reabsorption; and enhanced bone demineralization. On the premise of a fast-and-calcium-load research, some authors advocate subdividing idiopathic hypercalciuria into one hundred ten Chapter 6 the Patient with Kidney Stones Table 6-2. Patients with absorptive hypercalciuria have exaggerated intestinal calcium reabsorption, which could be reduced in some by dietary calcium restriction. Some authors have expressed concern over the potential long-term effects of dietary calcium restriction. Patients with idiopathic hypercalciuria often have reduced bone mass and are in unfavorable calcium stability, which can be further exacerbated by a low-calcium diet. In addition, a reciprocal relationship exists between free calcium and free oxalate in the intestinal lumen. If oral calcium intake is decreased, oxalate stays free within the intestinal lumen and its absorption increases. Citrate combines with calcium within the tubular lumen to form a nondissociable however soluble complex. Another important cause of hypocitraturia is hypokalemia, which will increase expression of the sodium-citrate cotransporter present within the proximal tubular luminal membrane. It is defined as uric acid excretion greater than 800 mg/day in men and larger than 750 mg/day in women.