Acticin dosages: 30 gm
Acticin packs: 3 creams, 4 creams, 5 creams, 6 creams, 7 creams, 8 creams, 9 creams, 10 creams

30 gm acticin generic free shipping
Patel R: Matrix-assisted laser desorption ionization-time of flight mass spectrometry in medical microbiology skin care 360 acticin 30 gm buy discount on line. Many infections current with constellations of focal and systemic indicators and signs that in typical instances are extremely suggestive of the diagnosis acne underwear acticin 30 gm, although the illness might be attributable to any of several completely different organisms. Making a clinical analysis with subsequent laboratory confirmation is part of the artwork of drugs. This chapter presents 24 circumstances and brief discussions of the differential analysis and management of these infections. The reader is referred to earlier chapters of this guide for characterizations of the organisms; to Chapter 47 for information about diagnostic microbiology exams; and to textbooks of drugs and infectious illnesses for more complete information about the medical entities. Ophthalmoscopic examination confirmed no papilledema, indicating that there had been no long-term increase in intracranial stress. Laboratory Findings Minutes later, blood was obtained for culture and different laboratory checks, and an intravenous line was positioned. Lumbar puncture was carried out lower than 30 minutes after the patient arrived in the emergency room. She attended a day care center and had a historical past of a quantity of episodes of presumed viral infections similar to those of other kids at the heart. Rifampin prophylaxis was given to the other kids who attended the day care heart. Physical examination confirmed a well-developed and well-nourished baby of normal peak and weight who was somnolent. When her neck was passively flexed, her legs also flexed (positive Brudzinski sign, suggesting irritation of the Comment Clinical features of bacterial meningitis vary with the age of the affected person. The viruses that most commonly trigger meningitis are the enteroviruses (echoviruses and coxsackieviruses) and mumps virus. Initial therapy for bacterial meningitis in infants lower than 1 month of age should consist of parenteral remedy known to be efficient against the pathogens listed in Table 48-1 and including L monocytogenes. Ampicillin plus cefotaxime or ceftriaxone with or without gentamicin or ampicillin in combination with an aminoglycoside is beneficial. For children between the ages of 1 month and 18 years of age and for the grownup older than 50 years, the beneficial therapies are vancomycin plus a third-generation cephalosporin because of the prevalence of multidrug-resistant S pneumoniae, stories photophobia, altered mental status ranging from sleepiness to coma, and neurologic indicators ranging from abnormalities of cranial nerve perform to seizures. However, subtle signs similar to fever and lethargy are consistent with meningitis, significantly in infants. Acute meningitis is most often brought on by micro organism of some species (Table 48-1): Lancefield serogroup B streptococci (Streptococcus agalactiae) (Chapter 14) and Escherichia coli (Chapter 15) in neonates; Haemophilus influenzae (Chapter 18) in unvaccinated children between the ages of 6 months and 6 years; N meningitidis in kids and unvaccinated adolescents and young adults; and Streptococcus pneumoniae (Chapter 14) occasionally in youngsters and rising in incidence in middle-aged and elderly individuals. Listeria monocytogenes (Chapter 12) causes meningitis in immunosuppressed sufferers and normal persons. Gram-negative bacilli cause meningitis in acute head trauma and neurosurgical patients and neonates (encapsulated E coli). S pneumoniae is present in recurrent meningitis in sufferers with basilar skull fractures. Ampicillin prophylaxis during labor of ladies at excessive danger (prolonged rupture of membranes, fever, etc) or of identified carriers reduces the incidence of an infection in infants. Chapter 14 Serogroup B streptococci (S agalactiae) Escherichia coli Listeria monocytogenes Neonates Neonates; elderly; immunocompromised kids and adults Children 6 months to 5 years Infants to 5 years and young adults 15 12 Haemophilus influenzae Neisseria meningitidis Widespread use of vaccine significantly reduces the incidence of H influenzae meningitis in kids. Polysaccharide conjugate vaccines against serogroups A, C, Y, and W135 are used in epidemic areas and in association with outbreaks. Often happens with pneumonia; also with mastoiditis, sinusitis, and basilar cranium fractures. Since adults older than 50 years are additionally susceptible to L monocytogenes, the addition of ampicillin to the regimen for older kids and adults as listed earlier is really helpful. Available evidence supports administration of adjunctive dexamethasone 10�20 minutes prior to or concomitant with the primary antimicrobial dose to youngsters with H influenzae meningitis and in the grownup with pneumococcal meningitis with continuation of steroids for the primary 2�4 days of remedy. Several vaccines are at present available and are beneficial for the prevention of the more serious causes of bacterial meningitis. The H influenzae sort B conjugate vaccine and the 13-valent conjugate pneumococcal vaccine are presently a part of the routine vaccination collection for infants and younger youngsters. The 23-valent polysaccharide pneumococcal vaccine is recommended for prevention of invasive pneumococcal illness in sure high-risk groups older than 2 years. Vaccination with considered one of two available quadrivalent conjugated meningococcal vaccines is currently recommended for all healthy adolescents 11 or 12 years of age with a booster dose at age sixteen and for 2- to 55-year-old individuals at risk similar to travelers to endemic areas, asplenic sufferers and patients with complement deficiencies. For adults older than fifty five, the meningococcal polysaccharide vaccine is currently really helpful pending evaluation of the conjugate vaccine in this age group. Three weeks earlier, he had developed bifrontal complications that were relieved by analgesics. On the morning of admission, he was famous to have focal seizures with involuntary movements of the right facet of his face and arm. While in the emergency room, he had a generalized seizure that was managed by intravenous lorazepam, phenytoin, and phenobarbital. Brain abscess could be caused by a single species of bacteria, however extra typically infections are polymicrobial. Of the facultative and aerobic bacteria, the viridans streptococci (including nonhemolytic and - and -hemolytic strains, the S anginosus group, Streptococcus mitis, and so on; see Chapter 14) are most typical, occurring in one-third to one-half of patients. Staphylococcus aureus (Chapter 13) is isolated in 10�15% and, when present, is commonly the only isolate found. Peptostreptococcus is most typical, adopted by Bacteroides and Prevotella species. Fusobacterium, Actinomyces, and Eubacterium are much less common, adopted by different anaerobes. Candida species are the most prevalent fungi, but opportunistic molds similar to Aspergillus sp. The increased intracranial pressure makes the process life threatening, because herniation of the brain via the tentorium cerebelli can end result in midbrain compression. Definitive differentiation between mind abscess and tumor is completed by pathologic examination and tradition of tissue from the lesion obtained by a neurosurgical process. Surgical excision offers the preliminary remedy in addition to the analysis of mind abscess. Needle aspiration using stereotactic approach is a substitute for surgical excision. Antibiotic remedy must be parenteral and should embrace high-dose penicillin G for streptococci and heaps of anaerobes, metronidazole for anaerobes resistant to penicillin G, plus a third-generation cephalosporin for enteric gram-negative rods. Vancomycin or another Clinical Features the temperature was 37�C, the heart beat 110/min, and respirations 18/min. On physical examination, the affected person was sleepy and had a decreased attention span.
Ze Xie (Water Plantain). Acticin.
- Bladder and urinary tract diseases.
- Are there safety concerns?
- Dosing considerations for Water Plantain.
- How does Water Plantain work?
- What is Water Plantain?
Source: http://www.rxlist.com/script/main/art.asp?articlekey=96365
30 gm acticin order fast delivery
Cardiac ascites skin care jogja acticin 30 gm purchase fast delivery, peritoneal carcinomatosis acne research 30 gm acticin generic with mastercard, and "mixed" ascites ensuing from cirrhosis and a second disease account for 10�15%. Initiating event may be peripheral arterial vasodilation triggered by endotoxin and cytokines and mediated by nitric oxide. Ifascites M is still present with the above measures, that is outlined as refractory ascites. Lymph enters the node by way of the afferent vessel and leaves via an efferent vessel. Because antigen-presenting cells move through lymph nodes, they current antigen to lymphocytes residing there. Lymphocytes in a node are constantly being changed by antigen-na�ve lymphocytes from the blood. B cells populate the lymphoid follicles within the cortex; T cells populate the paracortical regions. The B cell then migrates to the medullary region, differentiates right into a plasma cell, and secretes immunoglobulin into the efferent lymph. The efferent lymph laden with antibodies and T cells particular for the inciting antigen passes by way of a quantity of nodes on its method to the thoracic duct, which drains lymph from a lot of the physique. Lymph from the top and neck and the best arm drains into the right subclavian vein. Lymphadenopathy could also be attributable to infections, immunologic illnesses, malignancies, lipid storage diseases, or different disorders of uncertain etiology. The two major mechanisms of lymphadenopathy are hyperplasia, in response to immunologic or infectious stimuli, and infiltration, by cancer cells or lipid- or glycoprotein-laden macrophages. Generalized adenopathy (three or extra anatomic regions) implies systemic infection or lymphoma. Rock-hard nodes mounted to surrounding delicate tissue are usually an indication of metastatic carcinoma. If generalized adenopathy is noted, an excisional node biopsy should be carried out for prognosis, rather than a panoply of laboratory checks. In addition, it has a well-developed reticuloendothelial system for eradicating particles and antibody-coated micro organism. Under sure circumstances, the spleen can generate hematopoietic cells in place of the marrow. Dullness from the spleen may be percussed between the ninth and eleventh ribs with the pt mendacity on the best facet. Massive enlargement, with spleen palpable >8 cm under the left costal margin, normally signifies a lymphoproliferative or myeloproliferative dysfunction. Decreases in a quantity of cell lineages may indicate hypersplenism, increased destruction. In circumstances with hypersplenism, the spleen is eliminated and the cytopenia is usually reversed. In the absence of hypersplenism, most causes of splenomegaly are recognized on the idea of signs and signs and laboratory abnormalities related to the underlying dysfunction. Splenectomy compromises the immune response to T-independent polysaccharide antigens. Newer vaccine formulations are T dependent and are simpler in splenectomized persons. Signs and symptoms of anemia are diversified, relying on the level of anemia and the time course over which it developed. In acute blood loss, hypovolemia dominates the clinical image; hypotension and decreased organ perfusion are the primary points. Symptoms associated with more persistent onset vary with the age of the pt and the adequacy of blood provide to crucial organs. Moderate anemia is associated with fatigue, lack of stamina, breathlessness, and tachycardia. If the palmar creases are lighter in color than the encircling skin with the fingers extended, Hb stage is often <80 g/L (8 g/dL). In pts with coronary artery illness, anginal episodes might appear or enhance in frequency and severity. The reticulocyte count is corrected for the Hct level and for early release of marrow reticulocytes into the circulation, which leads to a rise in the lifespan of the circulating reticulocyte past the standard 1 day. Bone marrow examination is commonly helpful within the analysis of anemia but is completed most regularly to diagnose hypoproliferative marrow states. Other laboratory tests indicated to evaluate particular forms of anemia depend upon the preliminary classification based mostly on the pathophysiology of the defect. Concern that the Hb degree may be abnormally excessive ought to be triggered at a stage of a hundred and seventy g/L (17 g/dL) in men and one hundred fifty g/L (15 g/dL) in girls. For instance, an 80-kg man ought to excrete between ~1500 and 2000 mg of creatinine in an "sufficient" collection. Manifestations of impaired renal perform embrace volume overload, hypertension, electrolyte abnormalities. When extreme, the symptom complicated of "uremia" might develop, encompassing a quantity of of the next symptoms and indicators: anorexia, dysgeusia, nausea, vomiting, lethargy, confusion, asterixis, pleuritis, pericarditis, enteritis, pruritus, sleep and taste disturbance, nitrogenous fetor. Oliguria most frequently happens in the setting of volume depletion and/or renal hypoperfusion, resulting in "prerenal azotemia" and acute renal failure (Chap. It is usually accompanied by nocturia and urinary frequency and have to be differentiated from different more common conditions associated with lower urinary tract pathology and urinary urgency or frequency. Excess fluid intake can lead to polyuria, however major polydipsia rarely ends in modifications in plasma osmolality except urinary diluting capacity is impaired. More sensitive assays can in turn be used to detect microalbuminuria, an important screening software for diabetic nephropathy. A urine albumin to creatinine ratio >30 mg/g defines the presence of microalbuminuria. Formal assessment of urinary protein excretion requires a 24-h urine protein assortment (see "Abnormalities of Renal Function, Azotemia," above). Urinary protein excretion rates between 500 mg/d and 3 g/d are nonspecific and could be seen in a variety of renal illnesses (including hypertensive nephrosclerosis, interstitial nephritis, vascular disease, and different major renal illnesses with little or no glomerular involvement). Protein excretion rates >3 g/d are termed nephrotic range proteinuria in that they may be accompanied by hypoalbuminemia, hypercholesterolemia, and edema (the nephrotic syndrome). Nephrotic syndrome may be related to quite a lot of extrarenal issues (Chap. Specific remedy for quite so much of causes of nephrotic syndrome is discussed in Chap. Hematuria Gross hematuria refers to the presence of frank blood within the urine and is extra attribute of lower urinary tract illness and/or bleeding diatheses than intrinsic renal illness (Table 46-3). Cyst rupture in polycystic kidney disease and postpharyngitic flares of IgA nephropathy are exceptions. Specificity of urinalysis may be enhanced by inspecting urine with a part contrast microscope capable of detecting dysmorphic pink cells ("acanthocytes") related to glomerular disease. Isolated pyuria is most commonly noticed in association with an an infection of the upper or lower urinary tract. Pyuria may also occur with allergic interstitial nephritis (often with a preponderance of eosinophils), transplant rejection, and noninfectious, nonallergic tubulointerstitial illnesses, together with atheroembolic renal illness.
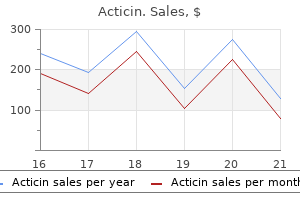
30 gm acticin purchase with visa
Properties of the Agent C pneumoniae produces spherical skin care myths buy acticin 30 gm free shipping, dense acne tretinoin cream 005 cheap acticin 30 gm amex, glycogen-negative inclusions which would possibly be sulfonamide resistant, just like C psittaci (see Table 27-1). In a clinically appropriate case, a rising antibody level or a single titer of greater than 1:64 is good proof of lively an infection. Clinical Findings Most infections with C pneumoniae are asymptomatic or related to delicate illness, but severe disease has been reported. An Immunity Untreated infections are inclined to be persistent, with persistence of the agent for a few years. The proportion of instances of community-acquired pneumonia brought on by C pneumoniae varies within the literature from 0% to 40%, but seems to be decrease in more recent sequence (<5%). Prolonged infections can happen with C pneumoniae, and asymptomatic carriage could additionally be widespread. Treatment C pneumoniae is vulnerable to the macrolides and tetracyclines and to some fluoroquinolones. Treatment with doxycycline, azithromycin, or clarithromycin, levofloxacin or moxifloxacin, seems to significantly benefit patients with C pneumoniae an infection, but there are only restricted information on the efficacy of antibiotic treatment. Reports point out that the signs may continue or recur after routine programs of remedy with erythromycin, doxycycline, or tetracycline, and these drugs must be given for 10- to 14-day courses. Culture Swab specimens of the pharynx should be put into a chlamydiae transport medium and placed at 4�C; C pneumoniae is quickly inactivated at room temperature. It grows poorly in cell culture, forming inclusions smaller than these formed by the other chlamydiae. The sensitivity of the culture is elevated by incorporation of cycloheximide into the cell culture medium to inhibit the eukaryotic cell metabolism and by centrifugation of the inoculum onto the cell layer. It is moderately troublesome to develop C pneumoniae-as evidenced by the variety of isolates described in contrast with the incidence of infection. Few younger kids have antibody, but after the age of 6�8 years, the prevalence of antibody will increase via young adulthood. Infection is each endemic and epidemic, with multiple outbreaks attributed to C pneumoniae. Lines of evidence suggesting that C pneumoniae is associated with atherosclerotic coronary artery and cerebrovascular disease encompass seroepidemiologic studies, detection of C pneumoniae in atherosclerotic tissues, cell tradition studies, animal fashions, and trials of prevention using antibiotic agents. The possible hyperlink between C pneumoniae an infection and coronary artery illness remains controversial. The take a look at is species particular and might detect IgG or IgM antibodies by utilizing the appropriate reagents. Primary infection yields IgM antibody after about 3 weeks adopted by IgG antibody at 6�8 weeks. In reinfection, the IgM response may be absent or minimal, and the IgG response occurs in 1�2 weeks. The following criteria have been instructed for the serologic prognosis of C pneumoniae an infection: a single IgM titer of 1:16 or larger, a single IgG titer of 1:512 or greater, and a fourfold rise in either the IgM or IgG titers. The time period ornithosis is applied to infection with comparable agents in all kinds of home birds (eg, pigeons, chickens, ducks, geese, turkeys) and free-living birds (eg, gulls, egrets, petrels). In people, C psittaci produces a spectrum of clinical manifestations starting from severe pneumonia and sepsis with a high mortality rate to a gentle inapparent an infection. Such checks are needed so Properties of the Agent C psittaci can be propagated in embryonated eggs, in mice and other animals, and in some cell cultures. Antibodies to the species-specific antigen are able to neutralize toxicity and infectivity. Specific serovars attribute for sure mammalian and avian species could additionally be demonstrated by immunofluorescence typing. Neutralization of infectivity of the agent by particular antibody or cross-protection of immunized animals can be used for serotyping, and the outcomes parallel these of immunofluorescence typing. Psittacosis causes a patchy irritation of the lungs by which consolidated areas are sharply demarcated. The lesions are much like those found in pneumonitis caused by some viruses and mycoplasmas. A probable case is one associated with a appropriate illness linked epidemiologically with a confirmed case or a titer of at least 1:32 in a single specimen. Although antibodies usually develop inside 10 days, the utilization of antibiotics could delay their development for 20�40 days or suppress it altogether. This could be confirmed by demonstration of particles in smears or sections of organs and by passage of the agent in mice and eggs. Clinical Findings A sudden onset of sickness taking the type of influenza or nonbacterial pneumonia in a person uncovered to birds is suggestive of psittacosis. The onset is usually sudden, but may be insidious, with malaise, fever, anorexia, sore throat, photophobia, and extreme headache. In severe cases, the indicators and signs of bronchial pneumonia seem at the finish of the primary week of the illness. The scientific picture often resembles that of influenza, nonbacterial pneumonia, or typhoid fever. The mortality rate may be as excessive as 20% in untreated instances, particularly in aged adults. Treatment Because of the issue in acquiring laboratory affirmation of C psittaci an infection, most infections are handled based only on the medical analysis. Doxycycline and tetracycline are the preferred brokers for therapy; macrolides and fluoroquinolones may be options. If essential, C psittaci can be cultured from blood or sputum or from lung tissue by culture in tissue culture cells, embryonated eggs, or mice in an appropriate biosafety level-3 laboratory. Isolation of C psittaci is confirmed by the serial transmission, its microscopic demonstration, and serologic identification. Birds typically purchase an infection as fledglings within the nest, could develop diarrheal illness or no illness, and infrequently carry the infectious agent for his or her normal lifespan. When subjected to stress (eg, malnutrition, shipping), birds might turn out to be sick and die. The agent is current in tissues (eg, the spleen) and is often excreted in feces by healthy birds. The inhalation of infected dried fowl feces is a typical technique of human an infection. Another supply of an infection is the dealing with of contaminated tissues (eg, in poultry rendering plants) and inhalation of an infected aerosol. The following are part of the management of Chlamydia psittaci and psittacosis in birds except (A) Quarantine of psittacine birds imported into the United States (B) Only allowing sale of psittacine birds hatched in the United States (C) Testing of birds for C psittaci an infection (D) Controlling the cargo of psittacine birds (E) Putting tetracycline in the feed of psittacine birds All of the following statements about perinatal Chlamydia trachomatis infections are correct except (A) Between 15% and 40% of infants born to contaminated ladies develop inclusion conjunctivitis. An adolescent lady got here to the clinic due to a brand new and unusual vaginal discharge. She had lately turn out to be sexually lively and had two new partners through the earlier month.
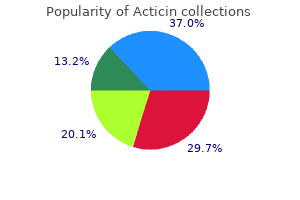
Generic acticin 30 gm mastercard
Particles obtained from varied sources are equivalent whatever the mobile origin by which the virus is grown acne under eyes acticin 30 gm cheap fast delivery. The degree of infective exercise of the preparation varies directly with the number of particles present acne at 40 30 gm acticin safe. Destruction of the physical particle by chemical or physical means is related to a loss of viral activity. Certain properties of the particles and infectivity should be proven to be identical (eg, their sedimentation behavior in the ultracentrifuge and their pH stability curves). Antisera prepared against the infectious virus should react with the attribute particle and vice versa. Direct statement of an unknown virus can be accomplished by electron microscopic examination of aggregate formation in a mixture of antisera and crude viral suspension. The particles ought to be in a position to induce the attribute disease in vivo (if such experiments are feasible). Passage of the particles in tissue culture should end result in the manufacturing of progeny with biologic and antigenic properties of the virus. Additional precautions and special containment services (Biosafety Level 4) are essential when personnel are performing analysis with high-risk brokers such as the filoviruses (see Chapter 38) and rabies virus (see Chapter 42). Icosahedral viruses are inclined to be stable, shedding little infectivity after several hours at 37�C. Viral infectivity is mostly destroyed by heating at 50�60�C for 30 minutes, though there are some notable exceptions (eg, hepatitis B virus, polyomaviruses). Viruses may be preserved by storage at subfreezing temperatures, and a few might withstand lyophilization and may thus be preserved within the dry state at 4�C or even at room temperature. Enveloped viruses are inclined to lose infectivity after extended storage even at -90�C and are notably sensitive to repeated freezing and thawing. Stabilization of Viruses by Salts Many viruses could be stabilized by salts in order to resist heat inactivation, which is necessary within the preparation of vaccines. The odd nonstabilized oral polio vaccine must be saved at freezing temperatures to protect its efficiency. However, with the addition of salts for stabilization of the virus, efficiency could be maintained for weeks at ambient temperatures even in the high temperatures of the tropics. Among the widespread hazards that might expose laboratory personnel to the danger of an infection are the following: (1) aerosols-generated by homogenization of contaminated tissues, centrifugation, ultrasonic vibration, or broken glassware; (2) ingestion- from mouth pipetting, consuming or smoking within the laboratory, or inadequate washing of hands; (3) skin penetration-from needle sticks, broken glassware, hand contamination by leaking containers, handling of contaminated tissues, or animal bites; and (4) splashes into the eye. Good biosafety practices embrace the next: (1) training in and use of aseptic methods; (2) no consuming, drinking, pH Viruses are normally steady between pH values of 5. Infectivity is probably the most radiosensitive property because replication requires expression of the entire genetic contents. Irradiated particles that are unable to replicate may still have the power to express some particular features in host cells. Vaccine manufacturing could contain using formaldehyde, -propiolactone, psoralen + ultraviolet irradiation, or detergents (subunit vaccines) to inactivate the vaccine virus. Detergents Nonionic detergents (eg, Nonidet P40 and Triton X-100) solubilize lipid constituents of viral membranes. Anionic detergents (eg, sodium dodecyl sulfate) additionally solubilize viral envelopes; as properly as, they disrupt capsids into separated polypeptides. The host cell supplies the power and artificial machinery and the low-molecular-weight precursors for the synthesis of viral proteins and nucleic acids. The viral nucleic acid carries the genetic specificity to code for all the virus-specific macromolecules in a highly organized trend. For a virus to replicate, viral proteins have to be synthesized by the host cell protein-synthesizing machinery. The distinctive characteristic of viral multiplication is that quickly after interaction with a bunch cell the infecting virion is disrupted and its measurable infectivity is lost. The eclipse period is actually considered one of intense synthetic exercise as the cell is redirected toward fulfilling the needs of the viral parasite. In some circumstances, as soon as the viral nucleic acid enters the host cell, the cellular metabolism is redirected exclusively toward the synthesis of recent virus particles and the cell is destroyed. After the synthesis of viral nucleic acid and viral proteins, the parts assemble to type new infectious virions. The yield of infectious virus per cell ranges broadly, from modest numbers to greater than 100,000 particles. The length of the virus replication cycle also varies extensively, from 6 to eight hours (picornaviruses) to more than forty hours (some herpesviruses). Productive infections happen in permissive cells and outcome in the production of infectious virus. Abortive infections fail to produce infectious progeny, both as a result of the cell may be nonpermissive and unable to support the expression of all viral genes or as a outcome of the infecting virus may be defective, missing some functional viral gene. A latent an infection may ensue, with the persistence of viral genomes, the expression of no or a couple of viral genes, and the survival of the infected cell. The sample of replication could vary for a given virus, depending on the sort of host cell contaminated. Formaldehyde Formaldehyde destroys viral infectivity by reacting with nucleic acid. Viruses with single-stranded genomes are inactivated far more readily than these with double-stranded genomes. Formaldehyde has minimal opposed results on the antigenicity of proteins and due to this fact has been used regularly in the manufacturing of inactivated viral vaccines. Photodynamic Inactivation Viruses are penetrable to a various degree by important dyes such as toluidine blue, neutral purple, and proflavine. These dyes bind to the viral nucleic acid, and the virus then turns into prone to inactivation by visible gentle. Larger concentrations of chlorine are required to destroy viruses than to kill micro organism, especially in the presence of extraneous proteins. For example, the chlorine remedy of stools enough to inactivate typhoid bacilli is insufficient to destroy poliomyelitis virus present in feces. Alcohols, similar to isopropanol and ethanol, are comparatively ineffective in opposition to certain viruses, especially picornaviruses. Common Methods of Inactivating Viruses for Various Purposes Viruses could additionally be inactivated for various causes, corresponding to to sterilize laboratory supplies and gear, disinfect surfaces or pores and skin, make drinking water safe, and produce inactivated virus vaccines. Sterilization may be achieved by steam beneath pressure, dry heat, ethylene oxide, and -irradiation. Although the primary points differ from group to group, the final outline of the replication cycles is comparable. Attachment, Penetration, and Uncoating the first step in viral an infection is attachment, interplay of a virion with a particular receptor web site on the floor of a cell. In this instance a number of steps within the replication cycle take place within the nucleus. In some cases, the virus binds protein sequences (eg, picornaviruses) and in others oligosaccharides (eg, orthomyxoviruses and paramyxoviruses). The presence or absence of receptors performs an necessary figuring out function in cell tropism and viral pathogenesis.
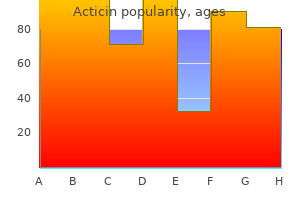
Acticin 30 gm free shipping
Cutaneous leishmaniasis: After an incubation period of days or weeks acne nyc buy acticin 30 gm fast delivery, papular lesions progress to nodules that ulcerate over weeks or months skin care guru 30 gm acticin buy amex. Mucosal leishmaniasis: this disfiguring sequela of New World cutaneous leishmaniasis results from dissemination of parasites from the skin to the naso-oropharyngeal mucosa. Diagnosis � Visceral leishmaniasis: Identification of amastigotes in smears of tissue aspirates is the gold standard for analysis. Systemic treatment is required for a number of lesions; lesions on the face, arms, or joints; and lesions of New World cutaneous leishmaniasis. Organisms disseminate via the lymphatics and the bloodstream, typically parasitizing muscles particularly closely. An estimated 8 million people are chronically contaminated, with 14,000 deaths annually. Clinical Manifestations An indurated area of erythema and swelling (the chagoma) with local lymphadenopathy develops 1 week after parasite invasion and generally precedes malaise, fever, anorexia, and edema of the face and lower extremities. Diagnosis Microscopic examination of fresh anticoagulated blood, the buffy coat, or blood smears may reveal organisms in instances of acute Chagas disease. Given the frequency of falsepositive results, a positive end result ought to be confirmed by no much less than two further assays. Clinical Manifestations A trypanosomal chancre develops ~1 week after the chew of an infected tsetse fly. Malaise, headache, arthralgias, hepatosplenomegaly, and other nonspecific manifestations can develop. Extrapyramidal signs might include choreiform movements, tremors, and fasciculations; ataxia is widespread. Increased opening stress, increased protein stage, and increased mononuclear cell counts are widespread. Treatment should be discontinued if hematuria or increasing proteinuria is found or if casts are present in the sediment. To cut back reactive encephalopathy, administer prednisolone (1 mg/kg) with every dose of melarsoprol. The primary route of transmission to humans is ingestion of tissue cysts from soil, food. Immunocompromised hosts lack elements required to control infection; the consequences are progressive focal destruction and organ failure. Generalized lymphadenopathy, fever <40�C (104�F), headache, malaise, and fatigue occur in 20�40% of pts. Clinical disease usually resolves inside a number of weeks, although lymphadenopathy could persist for several months. Pts may develop adjustments in mental status (75%), fever (10�72%), seizures (33%), headaches (56%), and focal neurologic findings (60%). The brainstem, basal ganglia, pituitary gland, and corticomedullary junction are most often involved. Blurred vision, macular involvement with loss of central vision, scotoma, photophobia, and eye pain are manifestations of an infection. On examination, yellow-white cotton-like patches with indistinct margins of hyperemia are seen. Diagnosis Culture of the parasite is tough and can be carried out solely at specialized laboratories. Radiologic studies demonstrate bilateral contrast-enhancing lesions, typically within the basal ganglia and corticomedullary junction. Personal Protection Measures Toxoplasma infection could be prevented by the avoidance of undercooked meats and oocyst-contaminated supplies. Trichinellosis Microbiology and Epidemiology Eight species of Trichinella trigger human an infection; two-T. Clinical Manifestations Most mild infections (<10 larvae per gram of muscle) are asymptomatic. Diagnosis Eosinophilia develops in >90% of pts, peaking at a stage of >50% at 2�4 weeks after an infection. Visceral and Ocular Larva Migrans Microbiology and Epidemiology Humans are incidental hosts for nematodes that cause visceral larva migrans. Infection results when humans-most typically preschool children-ingest soil contaminated by pet feces that contain infective T. Larvae penetrate the intestinal mucosa and disseminate hematogenously to all kinds of organs. Clinical Manifestations Symptomatic infections lead to fever, malaise, anorexia, weight reduction, cough, wheezing, rashes, hepatosplenomegaly, and occasional profound eosinophilia (up to 90%). Ocular disease often develops in older children or younger adults and contains an eosinophilic mass that mimics retinoblastoma, endophthalmitis, uveitis, and/or chorioretinitis. Cutaneous Larva Migrans this illness is caused by larvae of animal hookworms, often the canine and cat hookworm Ancylostoma braziliense. Larvae in contaminated soil penetrate human skin; intensely pruritic, erythematous lesions form along the tracks of larval migration and advance a number of centimeters each day. Ivermectin (a single dose of 200 g/kg) or albendazole (200 mg bid for 3 days) can relieve the signs of this self-limited infestation. Intestinal Nematode Infections Intestinal nematodes infect >1 billion individuals worldwide, mostly in areas with poor sanitation and particularly in developing international locations in the tropics or subtropics. Ascariasis Microbiology Ascariasis is brought on by Ascaris lumbricoides, the largest intestinal nematode, which reaches lengths as a lot as 40 cm. Clinical Manifestations Most infections have a low worm burden and are asymptomatic. During lung migration of the parasite (~9�12 days after egg ingestion), pts might develop a cough and substernal discomfort, sometimes with dyspnea or bloodtinged sputum, fever, and eosinophilia. Adult worms can cross within the stool or, much less commonly, by way of the mouth or nose. Hookworm Microbiology Two hookworm species, Ancylostoma duodenale and Necator americanus, cause human infections. Infectious larvae current in soil penetrate the pores and skin, attain the lungs by way of the bloodstream, invade the alveoli, ascend the airways, are swallowed, attain the small intestine, mature into adult worms, attach to the mucosa, and suck blood (0. Chronic infection causes iron deficiency and-in marginally nourished persons-progressive anemia and hypoproteinemia, weak point, and shortness of breath. Strongyloidiasis Microbiology and Epidemiology Unlike different helminths, Strongyloides stercoralis can replicate in the human host, allowing ongoing cycles of autoinfection from endogenously produced larvae. Clinical Features Uncomplicated illness is related to mild cutaneous and/or belly manifestations corresponding to recurrent urticaria, larva currens (a pathognomonic serpiginous, pruritic, erythematous eruption along the course of larval migration which will advance as much as 10 cm/h), belly ache, nausea, diarrhea, bleeding, and weight loss. Diagnosis A single stool examination detects rhabditiform larvae (~250 m long) in about one-third of uncomplicated infections. Duodenojejunal contents may be sampled if stool examinations are repeatedly unfavorable. Asymptomatic pts must be handled, given the potential for later deadly hyperinfection.
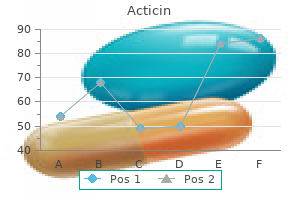
Cheap 30 gm acticin with mastercard
A 37-year-old sheep farmer from Australia presents with higher proper quadrant ache and seems slightly jaundiced skin care oils purchase acticin 30 gm. An apparently fatigued however alert 38-year-old lady has spent 6 months as a teacher in a rural Thailand village college acne care order acticin 30 gm with amex. Her chief complaints embrace frequent headaches, occasional nausea and vomiting, and periodic fever. You suspect malaria and certainly discover parasites in purple blood cells in a skinny blood smear. Given a prognosis of uncomplicated Plasmodium falciparum malaria for the patient in Question 15, which one of the following remedy regimens is suitable the place chloroquineresistance is understood Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report: Malaria Surveillance - United States, 2011, November 1, 2013/62(ss05);1�17. Mendes C, et al: Duffy negative antigen is now not a barrier to Plasmodium vivax � Molecular evidences from the African west coast (Angola and Equatorial Guinea). Laboratory procedures used within the analysis of infectious disease in people embody the next: 1. Morphologic identification of the agent in stains of specimens or sections of tissues (light and electron microscopy). Susceptibility testing of the agent by culture or nucleic acid methods, the place acceptable. Demonstration of significant antibody or cell-mediated immune responses to an infectious agent. Although physicians ought to be competent to perform a few easy, crucial microbiologic exams (perform direct wet mounts of certain specimens, make a Gram-stained smear and look at it microscopically, and streak a culture plate), the technical details of the extra involved procedures are usually left to trained microbiologists. Physicians who take care of infectious processes must know when and tips on how to take specimens, what laboratory examinations to request, and tips on how to interpret the outcomes. The techniques used to characterize infectious brokers differ tremendously relying on the scientific syndrome and the kind of agent being considered, be it virus, bacterium, fungus, or parasite. The clinician should make a tentative prognosis rather than wait until laboratory outcomes can be found. When exams are requested, the physician ought to inform the laboratory workers of the tentative diagnosis (type of an infection or infectious agent suspected). Contamination of the specimen must be averted by using only sterile gear and aseptic method. Meaningful specimens to diagnose bacterial and fungal infections should be secured earlier than antimicrobial medication are administered. If antimicrobial drugs are given before specimens are taken for microbiologic research, drug remedy may have to be stopped and repeat specimens obtained a number of days later. The sort of specimen to be examined is decided by the presenting scientific image. If signs or indicators point to involvement of one organ system, specimens are obtained from that supply. In the absence of localizing indicators or symptoms, repeated blood samples for culturing are taken first, and specimens from other websites are then thought-about in sequence, depending partially on the likelihood of involvement of a given organ system in a given patient and partly on the ease of acquiring specimens. This "feedback" info from the laboratory consists of preliminary stories of the outcomes of individual steps within the isolation and identification of the causative agent. When important pathogens are isolated earlier than treatment, follow-up laboratory examinations during and after remedy may be appropriate. A correctly collected specimen is the one most necessary step in the diagnosis of an an infection, as a end result of the outcomes of diagnostic checks for infectious illnesses depend on the choice, timing, and methodology of collection of specimens. Bacteria and fungi grow and die, are susceptible to many chemical substances, and could be found at totally different anatomic sites and in numerous body fluids and tissues in the course of the course of infectious ailments. For every sort of specimen, recommendations for optimal dealing with are given within the following paragraphs and in the later section on diagnosis by anatomic web site. Recovery of bacteria and fungi is most significant if the agent is isolated from a site normally devoid of microorganisms (a usually sterile area). Conversely, many parts of the body have normal microbiota (Chapter 10) which could be altered by endogenous or exogenous influences. Recovery of potential pathogens from the respiratory, gastrointestinal, or genitourinary tracts; from wounds; or from the pores and skin have to be considered within the context of the conventional microbiota of each specific website. Microbiologic knowledge should be correlated with scientific data to be able to arrive at a significant interpretation of the outcomes. The pattern must be representative of the infectious course of (eg, sputum, not saliva; pus from the underlying Microscopy and Stains Microscopic examination of stained or unstained specimens is a relatively simple and cheap, but much much less sensitive technique than tradition for detection of small numbers of bacteria. Specimens containing 102�103 organisms per milliliter produce development on solid media, and people containing 10 or fewer micro organism per milliliter might produce growth in liquid media. Most specimens submitted when bacterial an infection is suspected ought to be smeared on glass slides, Gram-stained, and examined microscopically. On microscopic examination, the Gram response (purple-blue indicates gram-positive organisms; pink, gram-negative) and morphology (shape: cocci, rods, fusiform, or other; see Chapter 2) of bacteria must be noted. In addition, the presence or absence of inflammatory cells and the kind of cell are necessary to observe and quantify. Reports of gram-positive cocci in chains are suggestive of, however not definitive for, streptococcal species; gram-positive cocci in clusters counsel a staphylococcal species. Kinyoun carbolfuchsin acid-fast stain (1) Formula: 4 g basic fuchsin, 8 g phenol, 20 mL 95% alcohol, a hundred mL distilled water. Calcofluor white binds to cellulose and chitin in the cell walls of fungi and fluoresces beneath long-wavelength ultraviolet gentle. Pneumocystis jirovecii cysts are recognized morphologically in silver-stained specimens. After main isolation of fungi, stains such as lactophenol cotton blue are used to distinguish fungal growth and to determine organisms by their morphology. Specimens to be examined for fungi can be examined unstained after therapy with a solution of 10% potassium hydroxide, which breaks down the tissue surrounding the fungal mycelia to allow a greater view of the hyphal types. Dark-field microscopy is used to detect Treponema pallidum in material from major or secondary syphilitic lesions or different spirochetes such as Leptospira. Culture Systems Typically, bacterial morphology has been outlined utilizing organisms grown on agar. Specimens submitted for examination for mycobacteria should be stained for acid-fast organisms. The most sensitive fluorescent stains for mycobacteria detection, such as auramine-rhodamine, ought to be used. Confirmation of a constructive fluorescent stain is usually performed using one of the nonfluorescent acid-fast stains, either Ziehl-Neelsen stain or Kinyoun stain (Table 47-1). These stains can be used as options to the fluorescent stains for mycobacteria in laboratories that lack fluorescence microscopy (see Chapter 23). Such procedures are extra particular than other staining techniques but also more cumbersome to perform. The fluorescein-labeled antibodies in frequent use are created from antisera produced by injecting animals with whole organisms or complicated antigen mixtures.
Syndromes
- Changes in birth control pills or hormone medications
- Etching cream
- Suggest alternative ways to do the same things, for example, try a hook and loop closure instead of laces for shoes.
- Weak urine stream
- Heart problems
- Have bladder stones with your enlarged prostate
Acticin 30 gm order on-line
Unless the ipsilateral breast is radiated acne 8 year old child acticin 30 gm discount with visa, up to acne 7061 buy 30 gm acticin with mastercard 50% of these pts will later develop a breast mass. First, endocrine syndromes that result may either be the presenting manifestations of the neoplasm or happen late in the course. The frequency with which ectopic hormone production is acknowledged varies with the criteria used for analysis. For most ectopic hormone syndromes, an extensive list of tumors has been reported to produce a number of hormones. Because of the rapidity of development of hormone secretion in some quickly growing tumors, diagnosis might require a high index of suspicion, and hormone ranges may be elevated out of proportion to the manifestations. However, in pts with malignancies that are identified to secrete hormones, serial measurements of circulating hormone ranges can serve as markers for completeness of tumor excision and for effectiveness of radiation remedy or chemotherapy. Likewise, tumor recurrence may be heralded by reappearance of elevated plasma hormone levels earlier than mass effects of the tumor are evident. Of most cancers pts with hypercalcemia, 80% have humoral hypercalcemia mediated by parathyroid hormone�related peptide; 20% have local osteolytic hypercalcemia mediated by cytokines such as interleukin 1 and tumor necrosis factor. Pts may have malaise, fatigue, confusion, anorexia, bone ache, polyuria, weak point, constipation, nausea, and vomiting. In the setting of hematologic malignancies, hypercalcemia could reply to glucocorticoids. Symptoms of fatigue, poor consideration span, nausea, weak spot, anorexia, and headache may be controlled by proscribing fluid intake to 500 mL/d or blocking the effects of the hormone with 600- to 1200-mg demeclocycline a day. With extreme hyponatremia (<115 meq/L) or in the setting of psychological status modifications, normal saline infusion plus furosemide could additionally be required; fee of correction ought to be <1 meq/L per hour to stop issues. Ketoconazole (400�1200 mg/d) or metyrapone (1�4 g/d) could also be used to inhibit adrenal steroid synthesis. Clinical manifestations rely upon area concerned, and syndromes may happen alone or together. Despite dramatic severity at occasions, sufferers often reply to therapy of the tumor (if found) and immunotherapy. Although efforts to decrease an infection risks have been challenged by the growing numbers of immunocompromised pts, antibioticresistant micro organism, fungal and viral superinfections, and invasive procedures and devices, the "zero-tolerance" viewpoint of consumer advocates holds that nearly all well being care�associated infections should be avoidable. Most hospitals purpose surveillance at infections related to highlevel morbidity or great expense. Results of surveillance are expressed as rates and should include a denominator indicating the number of pts uncovered to a particular threat. More than one precaution can be used for ailments which have multiple mode of transmission. Intensive schooling, "bundling" of evidence-based interventions, and use of checklists to facilitate adherence can scale back an infection rates. Table 78-1 summarizes efficient interventions to scale back the incidence of the more common nosocomial infections. The 3�7% risk of infection for every day a catheter remains in place is due to the ascent of micro organism from the periurethral area or via intraluminal contamination of the catheter. Administer prophylactic antibiotics inside 1 h before surgical procedure; discontinue inside 24 h. Prevention of Pathogen Cross-Transmission Cleanse palms with alcohol hand rub earlier than and in spite of everything contacts with pts or their environments. The prognosis is confirmed by isolation of the identical bacteria from peripheral-blood cultures and from semiquantitative or quantitative cultures of samples from the vascular catheter tip. Contact precautions might must be augmented by environmental cleansing and lively exclusion of sick employees and visitors, who usually characterize index instances. Infection-associated mortality rates amongst cancer pts have decreased on account of an evolving strategy entailing early use of empirical broad-spectrum antibiotics; empirical antifungal remedy in neutropenic pts who, after 4�7 days of antibiotic therapy, stay febrile with out constructive cultures; and use of antibiotics for afebrile neutropenic pts as broad-spectrum prophylaxis towards infections. Pts have persistent fever unresponsive to antibiotics, stomach ache, and increased alkaline phosphatase ranges. The analysis is confirmed by documentation of a thickened cecal wall by way of imaging. Treatment ought to embrace antibiotics directed against bowel flora and surgery (in the case of perforation). Pts with defects in humoral immunity are additionally in danger for an infection with encapsulated micro organism corresponding to Streptococcus pneumoniae, Haemophilus influenzae, and Neisseria meningitidis. Pts with extended neutropenia are at increased threat for a brain abscess as a result of Aspergillus, Nocardia, or Cryptococcus. A biopsy performed with direct visualization may be required for definitive prognosis. Obvious infectious web site discovered No obvious infectious site Subsequent Treat the infection with therapy the best obtainable antibiotics. Several general guidelines are helpful in the preliminary treatment of febrile neutropenic pts: (1) the agents used should replicate each the epidemiology and the antibiotic resistance sample of the hospital. The growth of fever in a pt who has obtained antibiotics impacts the choice of subsequent remedy (which ought to goal resistant organisms and organisms recognized to cause infections in pts being treated with the antibiotics already administered). Pneumocystis prophylaxis is necessary for pts with acute lymphocytic leukemia and for those receiving glucocorticoid-containing regimens. Given the consequences of underlying continual disease and chemotherapy, serologic testing of the recipient is most likely not dependable. This transient state of full immunologic incompetence and the reconstitution that follows make the host extraordinarily susceptible to infections. Aspergillus, Fusarium) are becoming extra widespread due to the increased use of prophylactic fluconazole. Severe disease is extra common amongst allogeneic transplant recipients and is usually related to graft-versus-host disease, with pneumonia as the foremost explanation for death. However, strong organ transplant recipients are immunosuppressed for longer intervals with brokers that chronically impair T-cell immunity. Pts receiving a liver transplant have a excessive incidence of fungal infections correlated with preoperative glucocorticoid use, long-term antimicrobial use, and a excessive degree of immunosuppression. Recurrent (reactivated) hepatitis B and C infections are problematic; while hepatitis B immunoglobulin administration and prophylaxis with antiviral brokers energetic in opposition to hepatitis B virus have been successful in preventing reinfection with hepatitis B virus, reinfection with hepatitis C virus happens in all pts. In stable organ transplant recipients, the standard vaccines and boosters must be given before immunosuppression. Should be Should be administered administered to splenectomized pts to splenecto- and to pts residing in mized pts and endemic areas, includto pts residing ing school students in endemic in dormitories. Seasonal Seasonal immunization immunization (A seasonal dose is beneficial and could be given as early as four months after transplantation; if given <6 months after transplantation, an extra dose is recommended. Because the ablative chemotherapy given to recipients of hematopoietic stem cell transplants eradicates immunologic reminiscence, revaccination is recommended for all such pts. Vaccination is much more efficient once immunologic reconstitution has occurred; however, because of the want to stop serious illness, pneumococcal vaccine must be administered 6�12 months after transplantation typically. Subacute endocarditis follows an indolent course, rarely causes metastatic an infection, and progresses steadily until difficult by a significant embolic event or a ruptured mycotic aneurysm. The remainder of culturenegative circumstances represent an infection by fastidious organisms, such as the nutritionally variant bacteria Granulicatella and Abiotrophia spp.

Order acticin 30 gm otc
Which of the next statements regarding antigenic drift in influenza viruses is appropriate Prevention by Hand Hygiene Although transmission of influenza virus occurs primarily by aerosol spread acne face map 30 gm acticin purchase fast delivery, hand transmission also is potentially essential skin care event ideas discount acticin 30 gm visa. Studies have shown that handwashing with soap and water or the use of alcohol-based hand rubs is very effective at reducing the amount of virus on human hands. Influenza type A is highly variable antigenically and causes most epidemics and all world pandemics. Influenza A strains are also found in aquatic birds, geese, domestic poultry, pigs, and horses. Both inactivated and live-virus vaccines exist but are regularly being rendered out of date as new antigenic variants of influenza viruses come up. Antiviral medicine exist, however resistant viruses emerge frequently, particularly to M2 ion channel inhibitors. A 32-year-old male physician developed a "flulike" syndrome with fever, sore throat, headache, and myalgia. To provide laboratory affirmation of influenza, a tradition for the virus was ordered. Which of the next would be the most effective specimen for isolating the virus liable for this an infection The principal reservoir for the antigenic shift variants of influenza virus appears to be which of the next Each of the next statements in regards to the prevention and therapy of influenza is right besides (A) the inactivated influenza vaccine contains H1N1 virus but the live, attenuated influenza vaccine incorporates H3N2 virus. Each of the following statements regarding the antigenicity of influenza A virus is right besides (A) Antigenic shifts, which symbolize major changes in antigenicity, happen occasionally and are caused by the reassortment of segments of the viral genome. Horimoto T, Kawaoka Y: Influenza: Lessons from past pandemics, warnings from current incidents. Recommendations of the Healthcare Infection Control Practices Advisory Committee and the Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices. Neumann G, Noda T, Kawaoka Y: Emergence and pandemic potential of swine-origin H1N1 influenza virus. The World Health Organization estimates that acute respiratory infections and pneumonia are accountable every year worldwide for the deaths of 4 million kids youthful than 5 years. All members of the Paramyxoviridae household initiate infection through the respiratory tract. Whereas replication of the respiratory pathogens is limited to the respiratory epithelia, measles and mumps become disseminated all through the body and produce generalized illness. Rubella virus, although categorized as a togavirus because of its chemical and bodily properties (see Chapter 29), could be thought of with the paramyxoviruses on an epidemiologic basis. Matrix (M) protein underlies the viral envelope; it has an affinity for each the N and the viral floor glycoproteins and is important in virion assembly. The activities of those surface glycoproteins assist differentiate the assorted genera of the Paramyxoviridae household (Table 40-2). Classification the Paramyxoviridae family is divided into two subfamilies and seven genera, six of which comprise human pathogens (see Table 40-2). Most of the members are monotypic (ie, they encompass a single serotype); all are antigenically secure. The genus Respirovirus contains two serotypes of human parainfluenza viruses, and the genus Rubulavirus contains two other parainfluenza viruses in addition to mumps virus. Sendai virus of mice, which was the primary parainfluenza virus isolated and is now recognized as a common infection in mouse colonies, is a subtype of human kind 1 virus. Newcastle disease virus, the prototype avian parainfluenza virus of genus Avulavirus, can additionally be associated to the human viruses. Although the viruses can be distinguished antigenically utilizing well-defined reagents, hyperimmunization stimulates cross-reactive antibodies that react with all four 579 Structure and Composition the morphology of Paramyxoviridae is pleomorphic, with particles one hundred fifty nm or extra in diameter, sometimes ranging as much as seven-hundred nm. The envelope of paramyxoviruses appears to be fragile, making virus particles labile to storage circumstances and vulnerable to distortion in electron micrographs. Such heterotypic antibody responses, which embody antibodies directed against both internal and surface proteins of the virus, are commonly observed in older folks. This phenomenon makes it difficult to determine by serodiagnosis the more than likely infecting type. These viruses are antigenically associated to one another however not to members of the opposite genera. The Henipavirus genus contains zoonotic paramyxoviruses which are able to infect and trigger illness in people. Hendra and Nipah viruses, each indigenous to fruit bats, are members of the genus. Human metapneumoviruses are respiratory pathogens of humans classified in the genus Metapneumovirus. The infecting virus particle fuses with the plasma membrane and releases the viral nucleocapsid into the cytoplasm. Dotted lines point out transport of newly synthesized viral proteins to plasma membrane. The F1 protein undergoes complex refolding in the course of the means of viral and mobile membrane fusion. Fusion by F1 occurs on the impartial pH of the extracellular environment, permitting release of the viral nucleocapsid directly into the cell. Transcriptional regulatory sequences at gene boundaries signal transcriptional start and termination. The place of a gene relative to the 3 end of the genome correlates with transcription efficiency. The viral polymerase protein complicated (P and L proteins) can additionally be answerable for viral genome replication. For successful synthesis of a positive-strand antigenome intermediate template, the polymerase complex should disregard the termination alerts interspersed at gene boundaries. The nonsegmented genome of paramyxoviruses negates the potential for gene section reshuffling (ie, genetic reassortment) so necessary to the pure historical past of influenza viruses. One attainable rationalization is that nearly all the amino acids within the major constructions of paramyxovirus glycoproteins may be involved in structural or functional roles, leaving little alternative for substitutions that would not markedly diminish the viability of the virus. If acceptable host cell proteases are current, F0 proteins within the plasma membrane will be activated by cleavage. Inclusions are believed to reflect sites of viral synthesis and have been discovered to include recognizable nucleocapsids and viral proteins. They are major pathogens of severe respiratory tract illness in infants and young youngsters. Pathogenesis and Pathology Parainfluenza virus replication in the immunocompetent host seems to be restricted to respiratory epithelia. The infection could contain solely the nose and throat, leading to a "frequent cold" syndrome. However, infection could additionally be extra extensive and, especially with types 1 and a pair of, could contain the larynx and upper trachea, resulting in croup (laryngotracheobronchitis).
Purchase 30 gm acticin overnight delivery
Cattle acne x out acticin 30 gm discount visa, sheep acne breakout acticin 30 gm purchase without prescription, and goats are liable for most circumstances of human infection; many different animals can serve as vectors of transmission or as reservoirs of illness. It is reactivated in being pregnant and is found at excessive concentrations within the placenta. At parturition, the organism is dispersed as an aerosol, and infection usually follows inhalation. Clinical Manifestations the specific presentation of acute Q fever differs geographically. The vegetations differ from those in bacterial endocarditis of other etiologies and manifest as endothelium-covered nodules on the valve. The mixture of rifampin (300 mg once daily) plus doxycycline (100 mg bid) or ciprofloxacin (750 mg bid) has been used with success. Genome sequence knowledge from many different Mycoplasma species have helped outline the minimal set of genes needed for cellular life. Lacking a cell wall and bounded solely by a plasma membrane, mycoplasmas colonize mucosal surfaces of the respiratory and urogenital tracts. Infection causes upper respiratory tract illness ~20 times more frequently than pneumonia. Epidemiology � Legionella is present in contemporary water and human-constructed water sources. Outbreaks have been traced to consuming water systems and infrequently to cooling towers. Diagnosis the use of Legionella testing-especially the Legionella urinary antigen test-is beneficial for all pts with community-acquired pneumonia. Among immunocompetent hosts, mortality can method 31% without therapy but ranges from 0 to 11% with acceptable and well timed remedy. Seropositivity is first detected at school age and then increases by ~10% per decade. Transmission happens through contact with ocular discharge from infected pts, which is typically transferred by flies. In the hyperendemic areas of northern and sub-Saharan Africa, the Middle East, and parts of Asia, the prevalence of trachoma is ~100% by the third 12 months of life. Diagnosis Clinical prognosis of trachoma is predicated on the presence of two of the following signs: lymphoid follicles on the higher tarsal conjunctiva, typical conjunctival scarring, vascular pannus, or limbal follicles. Treatment of sexual partners is needed to prevent ocular reinfection and chlamydial genital disease. Clinical Manifestations Psittacosis in humans can vary in severity from asymptomatic or mild infections to acute primary atypical pneumonia (which could be deadly in 10% of untreated cases) to severe continual pneumonia. The incubation interval for main an infection with both virus is 1�26 days (median, 6�8 days). Pain, itching, dysuria, vaginal and urethral discharge, and tender inguinal lymphadenopathy are the predominant local symptoms. In common, these isolates are also immune to valacyclovir and famciclovir, which have comparable mechanisms of motion. The virus replicates and causes viremia, which is mirrored by the diffuse and scattered skin lesions in varicella; it then establishes latency in the dorsal root ganglia and may reactivate via unknown mechanisms at a later time. In bone marrow and renal transplant recipients, oral valacyclovir (2 g/d) can be effective in reducing cytomegalovirus an infection. First episodes: Oral acyclovir (200 mg five instances per day or 400 mg tid), valacyclovir (1 g bid), or famciclovir (250 mg bid) for 7�14 days is effective. Symptomatic recurrent genital herpes: Short-course (1- to 3-days) regimens are most well-liked due to low value, likelihood of adherence, and convenience. Oral acyclovir (800 mg tid for 2 days), valacyclovir (500 mg bid for three days), or famciclovir (750 or 1000 mg bid for 1 day, a 1500-mg single dose, or 500 mg stat followed by 250 mg q12h for three days) successfully shortens lesion length. Other options embody oral acyclovir (200 mg five instances per day), valacyclovir (500 mg bid), and famciclovir (125 mg bid for 5 days). Suppression of recurrent genital herpes: Oral acyclovir (400�800 mg bid) or valacyclovir (500 mg daily) is given. Pts with greater than nine episodes per yr should take oral valacyclovir (1 g daily or 500 mg bid) or famciclovir (250 mg bid or 500 mg bid). First episode: Oral acyclovir is given (200 mg five times per day or four hundred mg tid); an oral acyclovir suspension can be utilized (600 mg/m2 qid). Recurrent episodes: If initiated on the onset of the prodrome, single-dose or 1-day therapy successfully reduces ache and speeds therapeutic. Regimens include oral famciclovir (a 1500-mg single dose or 750 mg bid for 1 day) or valacyclovir (a 2-g single dose or 2 g bid for 1 day). Herpetic whitlow: Oral acyclovir (200 mg) is given 5 occasions every day (alternative: four hundred mg tid) for 7�10 days. Herpetic eye infections: In acute keratitis, topical trifluorothymidine, vidarabine, idoxuridine, acyclovir, penciclovir, and interferon are all beneficial. Continued suppression with oral acyclovir suspension should be given for 3�4 months. In some pts with milder types of immunosuppression, oral remedy with valacyclovir or famciclovir is effective. The optimal duration of therapy and the usefulness of its continuation to suppress lesions are unclear. Some pts might profit from cutaneous software of trifluorothymidine or 5% cidofovir gel. The skin lesions are small, with an erythematous base of 5�10 mm, and appear in successive crops over 2�4 days. Severity varies from person to individual, however older pts are inclined to have extra severe illness. In contrast, immunocompromised pts have quite a few slower-healing lesions (often with a hemorrhagic base) and usually have a tendency to develop visceral problems that, if not handled, are deadly in 15% of circumstances. Pts are infectious for 48 h earlier than onset of rash and stay infectious till all vesicles have crusted. Historically, kids 5�9 years old accounted for half of all circumstances; vaccination has dramatically changed the epidemiology of infection and has caused a big decrease within the annualized incidence of chickenpox. The onset comes 3�5 days into sickness, with tachypnea, cough, dyspnea, fever, cyanosis, pleuritic chest pain, and hemoptysis. Cutaneous dissemination happens in 40% of these pts and increases the chance for different problems (pneumonitis, meningoencephalitis, hepatitis). Prednisone (given together with antiviral therapy at 60 mg/d for the primary week of zoster and then at a dose tapered by 50% weekly over the next 2 weeks) can speed up quality-of-life enhancements, including a return to ordinary activity; prednisone therapy is indicated just for healthy aged individuals with reasonable or severe ache at presentation. Irrespective of serologic standing, pts >50 years old ought to receive a vaccine with 18 times the viral content of varicella vaccine; zoster vaccine reduces the incidence of zoster and postherpetic neuralgia. In many areas, the vast majority of adults are seropositive, as are ~50% of adults in the United States and Canada. The primary antagonistic occasions include electrolyte disturbances and renal dysfunction.
Acticin 30 gm order overnight delivery
Immunity against the floor projection antigen might be most essential for defense skin care 777 acticin 30 gm discount with amex. Resistance to reinfection may final several years acne 2nd trimester 30 gm acticin purchase, but reinfections with comparable strains are frequent. Enteric coronaviruses may be detected by examination of stool samples by electron microscopy. Super spreaders have been described for different illnesses similar to rubella, Ebola, and tuberculosis and presumably mirror a certain constellation of host, viral, and environmental components. Subsequently, it was decided to be the cause for a number of outbreaks of respiratory illness from a quantity of international locations in the Arabian Peninsula. Infected travelers have unfold the virus in different international locations, and it remains a threat for transmission from pilgrims coming back from the annual Hajj in Mecca. The prevention or therapy of these diseases could be accomplished by (A) A subunit vaccine (B) A cold-adapted live-attenuated vaccine (C) the antiviral drug amantadine (D) Infection control measures, together with isolation and wearing of protecting gear (E) the antiviral drug acyclovir An epidemic of acute respiratory virus infections occurred among the many aged residents of a nursing residence. Influenza viruses and coronaviruses, which might cause critical respiratory disease within the elderly, are suspected. Lee N, Hui D, Wu A, et al: A main outbreak of extreme acute respiratory syndrome in Hong Kong. Reactions to Physical and Chemical Agents Rabies virus survives storage at 4�C for weeks and at -70�C for years. Rabies virus is killed quickly by exposure to ultraviolet radiation or sunlight, by heat (1 hour at 50�C), by lipid solvents (ether, zero. Rabies virus attaches to cells by way of its glycoprotein spikes; the nicotinic acetylcholine receptor could function a cellular receptor for rabies virus. Ongoing translation is required for replication, significantly of viral N and P proteins. The viral matrix protein varieties a layer on the internal side of the envelope, whereas the viral glycoprotein is on the outer layer and varieties the spikes. Structure Rabies virus is a rhabdovirus with morphologic and biochemical properties in common with vesicular stomatitis virus of cattle and a number of other animal, plant, and bug viruses (Table 42-1). The particles are surrounded by a membranous envelope with protruding spikes, 10 nm lengthy. Rabies viruses belong to the genus Lyssavirus, whereas the vesicular stomatitis-like viruses are members of the genus Vesiculovirus. The rhabdoviruses are very extensively distributed in nature, infecting vertebrates, invertebrates, and vegetation. Susceptibility varies amongst mammalian species, starting from very high (foxes, coyotes, wolves) to low (opossums); those with intermediate susceptibility embody skunks, raccoons, and bats (Table 42-2). The virus is extensively distributed in contaminated animals, especially in the nervous system, saliva, urine, lymph, milk, and blood. This fastened (or mutant) virus multiplies quickly, and the incubation period is shortened to 4�6 days. However, there are strain differences amongst viruses isolated from totally different species (raccoons, foxes, skunks, canines, bats) in numerous geographic areas. These viral strains could be distinguished by epitopes in the nucleoprotein and glycoprotein acknowledged by monoclonal antibodies as properly as by specific nucleotide sequences. There are no much less than seven antigenic variants present in terrestrial animals and bats. The G glycoprotein is a important component in rabies virus neuroinvasiveness and pathogenicity. Avirulent mutants of rabies virus have been selected utilizing certain monoclonal antibodies against the viral glycoprotein. A substitution at amino acid place 333 of the glycoprotein ends in lack of virulence, indicating some essential position for that site of the protein in illness pathogenesis. Purified spikes containing the viral glycoprotein elicit neutralizing antibody in animals. Antiserum prepared bats, where the virus has turn into peculiarly adapted to the salivary glands. Hematophagous vampire bats may transmit the virus for months without themselves ever displaying any indicators of illness. When freshly isolated in the laboratory, the strains are referred to as street virus. Such strains show lengthy and variable incubation periods (usually 21�60 days in dogs) and frequently produce intracytoplasmic inclusion bodies. A: Electron micrograph of bullet-shaped particle typical of the rhabdovirus household (100,000�). Shown here is vesicular stomatitis virus negatively stained with potassium phosphotungstate. Pathogenesis and Pathology Rabies virus multiplies in muscle or connective tissue at the site of inoculation after which enters peripheral nerves at neuromuscular junctions and spreads up the nerves to the central nervous system. It multiplies within the central nervous system and progressive encephalitis develops. The virus then spreads by way of peripheral nerves to the salivary glands and other tissues. Other organs the place rabies virus has been found include pancreas, kidney, coronary heart, retina, and cornea. There is a better assault price and shorter incubation period in persons bitten on the face or head; the lowest mortality happens in these bitten on the legs. Rabies virus produces a specific eosinophilic cytoplasmic inclusion, the Negri physique, in infected nerve cells. The significance of Negri bodies in rabies analysis has been lessened by the development of the extra delicate fluorescent antibody and reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction diagnostic checks. The incubation interval in people is often 1�3 months however may be as brief as 1 week or more than a 12 months. The scientific spectrum can be divided into three phases: a short prodromal phase, an acute neurologic section, and coma. The prodrome, lasting 2�10 days, may show any of the following nonspecific symptoms: malaise, anorexia, headache, photophobia, nausea and vomiting, sore throat, and fever. During the acute neurologic section, which lasts 2�7 days, patients show indicators of nervous system dysfunction similar to nervousness, apprehension, hallucinations, and weird conduct. They are sharply demarcated, kind of spherical, and 2�10 m in diameter, and so they have a particular internal construction with basophilic granules in an eosinophilic matrix. Reverse transcription-polymerase chain response testing can be used to amplify elements of a rabies virus genome from fastened or unfixed mind tissue or saliva. Sequencing of amplified products can permit identification of the infecting virus strain.